Polyashi Sign Language
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Polyashi Sign Language (P.S.L.) | |
|---|---|
| Lingua gesticulatoria Poliacorum (L.G.P.) | |
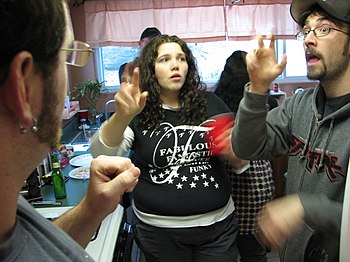 People communicating using the LGP | |
| Pronunciation | [ɛl d͡ʒiː piː] or [ɛl ɡɛː pɛː] |
| Native to | Countries influenced by the Kento-Polyashi culture |
| Region | Southern and Southwestern Thuadia |
Native speakers | L1: ~3,000,000 L2: ~2,500,000 FL: ~5,000,000 |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | lgp |
Polyashi Sign Language, usually called LGP ([ɛl d͡ʒiː piː] or [ɛl ɡɛː pɛː] in IPA) as a shortcut of "Lingua gesticulatoria Poliacorum" (which is the name in Latin), sometimes written in other scripts: ЛГП (Govoric), ⲖⲄⲠ (Protopolyash), ឯល្គេពេ (Preimeai) or ![]()
![]() File:BotoPE.png (Boto) is a sign languages used by deaf communities in southern and southwestern Thuadia, in general areas influenced by the Kento-Polyashi culture. It is a logographic language with signs for most common phonemes in local languages for possible spelling of words with no set symbol.
File:BotoPE.png (Boto) is a sign languages used by deaf communities in southern and southwestern Thuadia, in general areas influenced by the Kento-Polyashi culture. It is a logographic language with signs for most common phonemes in local languages for possible spelling of words with no set symbol.
Phoneme signs
The language has special signs for:
- Consonants: /b/, /p/, /t͡s ~ ʈ͡s/, /t͡ʃ ~ t͡ɕ ~ t͡ʂ/, /d͡z ~ ɖ͡z/, /d͡ʒ ~ d͡ʑ ~ d͡ʐ/, /ʃ ~ ɕ ~ ʂ/, /ʒ ~ ʑ ~ ʐ/, /d ~ ɖ/, /t ~ ʈ/, /tʲ~ c/, /dʲ ~ ɟ/, /h ~ ɦ/, /x ~ χ/, /z ~ zʲ/, /s ~ sʲ/, /ð ~ θ/, /ɡ ~ ɢ/, /k/, /q/, /v ~ β/, /f ~ ɸ/, /r ~ ɾ/, /ʀ ~ ɹ ~ ʁ/, /m/, /n/, /ŋ/, /nʲ ~ ɲ/, /l ~ ɫ ~ ʟ/, /ʎ ~ lʲ ~ ȴ/, /ɰ ~ w/, /j ~ ʝ/
- Vowels: /a ~ ɑ/, /ɛ ~ e/, /æ ~ ə ~ ɤ/, /ɔ ~ o/, /i ~ ɪ/, /ʊ ~ u ~ ʏ/, /ɨ ~ y/, /ø ~ œ/
Which are used for spelling untraditional words, shortcuts, and names, that do not have a classical symbol, or which are not understood by the other speaker.
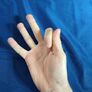
| Signs for classical phonemes and numbers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| /b/ | /p/ | /d ~ ɖ/ | /t ~ ʈ/ | /dʲ ~ ɟ/ | /tʲ ~ c/ | /ɡ ~ ɢ/ | /k/ | /q/ | /ð ~ θ/ |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| /m/ | /n/ | /nʲ ~ ɲ/ | /ŋ/ | /ʎ ~ lʲ ~ ȴ/ | /l ~ ɫ ~ ʟ/ | /ʀ ~ ɹ ~ ʁ/ | /r ~ ɾ/ | /j ~ ʝ/ | /ɰ ~ w/ |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
| /d͡z ~ ɖ͡z/ | /t͡s ~ ʈ͡s/ | /d͡ʒ ~ d͡ʑ/ | /t͡ʃ ~ t͡ɕ/ | /z ~ zʲ/ | /s ~ sʲ/ | /ʒ ~ ʑ ~ ʐ/ | /ʃ ~ ɕ ~ ʂ/ | /v ~ β/ | /f ~ ɸ/ |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
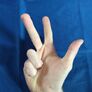
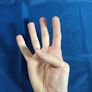
| /h ~ ɦ/ | /x ~ χ/ | /a ~ ɑ ~ ɒ/ | /ɛ ~ e/ | /æ ~ ə ~ ɤ/ | /ɔ ~ o/ | /i ~ ɪ/ | /ʊ ~ u ~ ʏ/ | /ɨ ~ y/ | /ø ~ œ/ |

|

|
|
|
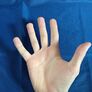
|

|

|

|
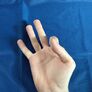
|

|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 ~ 10 |
History
The origins of the languages are unclear, but it is expected, that the language developed in perpetua as the diverging Kento-Polyashi tribes tried communicating with neighboring cultures, especially Mokhavic and Germanic in the southern Thuadia and Romance on the Canterian peninsula.
The first recorded mention of the language comes from present-day Zhousheng, where a local Proto-Bogmian Catholic priest during the times of early Kaȝin reformation complained, that a Kaȝin priest used a sign language among local Tghok populace to spread their belief onto the pagan populace rather than using a language (there was a strong belief in the Gift of Tongues at that time).
First codified form can be found in present day Kentalis from 1650, where a community of Ereskans codified a standart for communication with a local field hospital, where a lot of people were shellshocked and temporairly lost their hearing because of a loud explosion in their proximity.
The language got international codification only by the mid of 18th century after the establishment of the Empire of Three Kings, where local deaf communities in Gadorieni states, the Empire of Three Kings, western parts of Prei Meas, southern Qazhshava and Speke started coordinating in creating a sign lingua france for possible cross-border communication. Although the first codified language was incoherrent to many deaf communities, further changes allowed its development to the extend in which it exists today.
On the 1912 congress (shortly after the Great War), communities from 16 countries codified the unified language as the official sign language of their respective countries, which started to be educated on deaf schools.
