1881 Soravian legislative election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 500 seats to the National Congress 251 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 26,132,187 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 14,268,634 (54.6%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
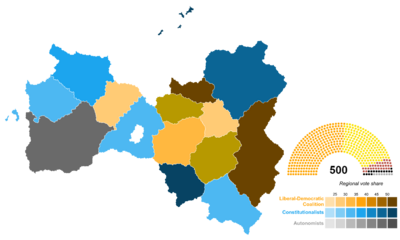 Results of the 1881 legislative election by region (party with largest vote share shown) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1881 Soravian legislative election was held between June 10 and June 18, 1881, to elect all 500 members of the Soravian National Congress. It was the last election to be held before the Congress was dissolved in 1882, and was also the first election to allocate seats using the Boeri method of proportional representation.
Turnout was around 54%, consistent with the 50–60% turnout rates seen since universal manhood suffrage was introduced in 1861. With over 14 million votes cast, it was one of the largest elections in history at the time by votes cast. Incumbent Minister-President Anton Gaweł Hlushko sought re-election for the third time under the leadership of the Liberal–Democratic Coalition. The election was notable for the large rise of Lev Rasskazov's Miscellaneous Left faction.
Hlushko won re-election, leading his coalition in 264 seats and over half of the popular vote. Liberal parties saw gains across the country, but notably in Soravia, Vedmed and Kantemosha, and coincided with the decline of independent agrarian conservatism, with Renard Borkowski leading the Miersan Agrarian Party to its worst ever result. Factions such as the Autonomists also saw a decline in the vote, mainly due to the rise of the Miscellaneous Left.
Background
The Liberal–Democratic Coalition under Hlushko entered the election as a large political force. Having secured victories in both 1871 and 1876, the LDC sought to expand on the growing popularity of liberalism among the cosmopolitan elite and Soravia's urban population. Hlushko himself was also a popular Minister-President, who was commended and lauded for his oratory skills and commitment to republican values, as well as a key parliamentary ally of Eduard Olsov. In his home country of Miersa, he was popular for his approaches to a liberalised domestic economy and the promotion of independent businesses. His main electoral bases were in the cities of Zhobrodzh, Chesvorzhno and Noviborg.
The LDC ran on policies of classical liberalism, including laissez-faire free trade policies both in Euclea and across the world. Factions within the coalition, notably the Radicals, who formed a crucial backbone of the coalition, began to espouse social liberalist policies, including means of state interventionism with regards to the state's role of a guarantor of personal liberty. Hlushko also reaffirmed his positions on anti-clericalism in the buildup to the election.
Kozirev Timochuk's Constitutionalists continued to run on a platform of general conservatism and right-wing politics, but retained their strong and influential agrarian backbone within the coalition. After the 1876 election, it was unclear whether the agrarian parties of the coalition would remain, and in 1878 the Yevdokimov letter was presented to Timochuk, calling for a more agrarian and egalitarian-focused outlook to the coalition's ideology. Timochuk ultimately conceded on some aspects, but those who weren't satisfied with the coalition left and joined Borkowski's Agrarian Party, who had been committed to independent agrarianism for years.
Trade unionism was also a large point of discussion leading up to the elections. Miscellaneous Left leader Lev Rasskazov had garnered a significantly positive public reputation with his speeches and rallies in the country's largest urban centres. As the leader of the Iron Union, Soravia's largest agglomeration of trade union representatives and workers' committees, he was a significantly influential figure among Soravia's leftist circles. In cities across the country, left-wing workers' politics was rising. In Miersa, the Congress of Miersan Trade Unions and Union of Miersan Iron and Coalworkers represented urban trade unionists and rural miners respectively. In Kantemosha, the Congress of the Kantemoshan Proletariat remained influential among its Koskunen voterbase.
The election was also the first to have its results determined by the Boeri method of proportional representation, devised and refined by Etrurian mathematician and political scientist Giovanni Boeri. Presented to the Congress and given presidential ratification in 1879, it replaced the Menshikov–Fonvizin method that had been used for prior elections. The Boeri method was criticised by smaller party officials by giving disproportionate representation to larger parties. Radzimierz Tomaszewski of the Committee of God criticised its introduction as "the death of proportionality", and accused major party officials of trying to implement "toxic bipartisanism".
Results


Analysis
By political historians, the 1881 election has been described as one of Soravia's most significant. Among its direct outcomes was a relative decline in agrarianism and ruralism, a rise in urban liberalism, the emergence of proto-socialism and the rise of trade unionism.
Slirnian political scientist Branimir Krsmanović writes of the election:
For me, the 1881 election can be called the last true exercise of democracy in Soravia. Despite the government it produced holding office for less than a year, its influence in determining both the immediate and extent futures of Soravian politics in unparalleled among the early republican period. Though unremarkable in action, it was pivotal in sentiment.
Notable results
The election produced a number of notable results. In the most industrialised parts of the country (Kantemosha, Miersa and Soravia), the left saw major gains mainly at the expense of liberal and conservative candidates. In Soravia, the Iron Union and Radicals saw gains of 8 and 3 seats respectively while the largest individual party in the congress, the Democratic–Liberal Party, lost 7 seats. In Kantemosha, both the Party for Order and Progress and Liberal Party of Kantemosha gained seats, while the agrarian parties lost votes. Unlike in other countries, the Congress of the Kantemoshan Proletariat made no gains, instead consolidating their urban working-class voting bloc in Koskunen. In Miersa, where the traditional, agrarian right-wing and the radical left-wing were the most polarised in the country, both major left-wing parties had multiple-seat gains. Agrarian, conservative and broadly Sotirian candidates lost seats, and Renard Borkowski's Agrarian Party, once regarded as a meaningful political force in Miersa, had over half of their seats taken from them during the election, even with ministerial gains from Yevdokimov rebels.
Elsewhere throughout the country, where industrialisation was lacking and the inhabitants still practising a largely rural, agrarian lifestyle, liberals consolidated large gains. In the high-population but low-industrial capacity Vedmed, the Liberal Party of Vedmed gained 4 seats to leapfrog the establishment New Metauri Congress to become the largest party in the country, taking 18 seats to the ruling Liberal–Democratic Coalition. The Congress, made up largely of estranged nobility and high-influence metauri throughout the country, was an establishment party who espoused broadly conservative and nationalist right-wing views. Their influence was highest in the rural corners, tucked away from the central government and cosmopolitan urban influence, where the metauri used a pro-tradition outlook to sway Vedmed's large rural population. In Belosoravia, the conservative Agrarian–Conservative Party made gains, the only country where conservatives made a net gain of seats. The only party to lose seats was the broadly agrarian conservative Agrarian Peasant's Party. Liberals in Belosoravia retained their five seats and both autonomist candidates, including the Szabadoki népkoalició, failed to achieve congressional representation for the second election in a row.
1882 coup
In 1882, the Radicals refused to continue to back the political agendas of Hlushko and Olsov, who had in the recent year taken a large ideological swerve to the right. The Radicals, most of whom broadly leftist in nature, threatened to fracture, and many now-independent congressmen promised their support to Rasskazov's left. Threatened by parliamentary usurpation of his agenda, Olsov and Hlushko orchestrated a parliamentary autocoup, abolishing the congress and establishing a temporary ten-men council headed by Hlushko. Rasskazov was arrested, imprisoned and hung for "inciting division and treasonous activities". His death marked the beginning of decades of left-wing repression in Soravia.
Hlushko retained his position as Minister-President, and the government was reduced to his small council that acted exclusively as a rubber stamp to Olsov's increasingly autocratic, totalitarian and dictatorial political agenda. He purged much of the inner circle that opposed his grip on power, and many prominent republicans were imprisoned in the months that followed the coup. Olsov began to enact policies that were more nationalist in nature, and his later reign was characterised by heightened militarism and clericalism. In 1883 he held a referendum, widely regarded as undemocratic and engineered, amongst the population to accept a series of changes to the legislature and presidency. The referendum passed with a majority of 91.2%, cementing Olsov's position of absolute authority within the country.






