Dzeia: Difference between revisions
m (Adding The Dze to the countries page) |
Flying Tonk (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|established_date1 = 7274 BR | |established_date1 = 7274 BR | ||
|established_event2 = Start of the Strifes | |established_event2 = Start of the Strifes | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 6429 BR | ||
|established_event3 = Founding of the 2nd Confederation | |established_event3 = Founding of the 2nd Confederation | ||
|established_date3 = 2764 BR | |established_date3 = 2764 BR | ||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The name in English is merely a translation of the Old Dze name, which translates to " | The name in English is merely a translation of the Old Dze name, which translates to "Oath/Alliance of the Dze", with the word Tśaq meaning either Alliance or Oath (added the possesive -to) and the word Dze meaning "Stargazer" and the endonym of these people in several languages and in the [[Old Liturgicals]]. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
The lands of the Dze Confederation have archaeological evidence of a cultural existance since at least 100.000 BR, belonging to the [[Leaf Lance Culture]], a Dze Paleolithic Culture that inhabited the mountainous central and northern regions of the country which seems to have mostly been located in the eastern ranges of the Great Mountains until about 70.000 BR when they began to expand alongside the hills and rocky outcrops towards the coast and the west. Characterized by their elaborate leaf shaped shrines and star-moon worship, two aspects that still carry on to this day in Dze cultures, by 50.000 BR the original culture split during the [[LNDC]] into several chalcolithic cultures later culminating in the [[Flower Stirrup Culture]], which kickstarted the Dze Bronze Age by 20.000 BR. However around 8.000 BR there is archaeological, and later written, evidence for the arrival of four distinct human groups, the [[Longplow]], [[Broadaxe]], [[Highstone]] and [[Red Arrow]] cultures; having triggered a near all out war with the first three cultures, the Dze began to coalesce into more organized societies after the Invasions, an event happening around 7.500 BR which triggered the formation of the First Confederation. The subsequent 8.000 year long conflicts culminated in the rise of the Third Confederation in the late 16th century AR and the fall of human invaders less than a decade later. | The lands of the Dze Confederation have archaeological evidence of a cultural existance since at least 100.000 BR, belonging to the [[Leaf Lance Culture]], a Dze Paleolithic Culture that inhabited the mountainous central and northern regions of the country which seems to have mostly been located in the eastern ranges of the Great Mountains until about 70.000 BR when they began to expand alongside the hills and rocky outcrops towards the coast and the west. Characterized by their elaborate leaf shaped shrines and star-moon worship, two aspects that still carry on to this day in Dze cultures, by 50.000 BR the original culture split during the [[LNDC]] into several chalcolithic cultures later culminating in the [[Flower Stirrup Culture]], which kickstarted the Dze Bronze Age by 20.000 BR. However around 8.000 BR there is archaeological, and later written, evidence for the arrival of four distinct human groups, the [[Longplow]], [[Broadaxe]], [[Highstone]] and [[Red Arrow]] cultures; having triggered a near all out war with the first three cultures, the Dze began to coalesce into more organized societies after the Invasions, an event happening around 7.500 BR which triggered the formation of the First Confederation. The subsequent 8.000 year long conflicts culminated in the rise of the Third Confederation in the late 16th century AR and the fall of human invaders less than a decade later. | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
The Mesolithic Age also defined the transition from fully nomadic to a semi-nomadic lifestyle as evidenced by the recent discovery of massive stone circles in river valleys which are thought to be temporary summer refuges, later abandoned in preference for warmer places in winter like the cliffs overlooking the High Springs on the northern edge of the Eastern Mountains. | The Mesolithic Age also defined the transition from fully nomadic to a semi-nomadic lifestyle as evidenced by the recent discovery of massive stone circles in river valleys which are thought to be temporary summer refuges, later abandoned in preference for warmer places in winter like the cliffs overlooking the High Springs on the northern edge of the Eastern Mountains. | ||
===Neolithic Age and the LNDC=== | ===Neolithic Age and the LNDC=== | ||
Around 60.000 years ago arises the first evidence for animal husbandry in the lands of the Confederation, with the previously mentioned stone circles being repurposed for keeping animals as a sort of pen. This and the continuous evolution of stone cutting techniques pinpoints to the start of a Neolithic, or Late Leaf Lance, period which ended by 50.000 BR with the Late Neolithic Dze Collapse, an event of unknown causes that led to the abandoning or destruction of the stone circles and the spreading of Dze populations westwards. A possible trigger of this event is volcanic eruptions in the Coastal Ranges, of which we have some geological evidence for, but frequent, and particularly cold, years might have caused the mass death of the game the Dze hunted or simply forced an emigration westards, the ending of these winters coinciding with the flooding of several rivers, causing the destruction of most stone circles. | Around 60.000 years ago arises the first evidence for animal husbandry in the lands of the Confederation, with the previously mentioned stone circles being repurposed for keeping animals as a sort of pen. This and the continuous evolution of stone cutting techniques pinpoints to the start of a Neolithic, or Late Leaf Lance, period which ended by 50.000 BR with the [[Late Neolithic Dze Collapse]], an event of unknown causes that led to the abandoning or destruction of the stone circles and the spreading of Dze populations westwards. A possible trigger of this event is volcanic eruptions in the Coastal Ranges, of which we have some geological evidence for, but frequent, and particularly cold, years might have caused the mass death of the game the Dze hunted or simply forced an emigration westards, the ending of these winters coinciding with the flooding of several rivers, causing the destruction of most stone circles. | ||
By the end of this period the Dze began a cultural split from the once unified nature of their species, undergoing surprisingly fast changes that prove the Dze Cultural Hibernation hypothesis, which theorizes that Dze are naturally, culturally conservative until forced by mass scale disasters to change, first evidenced by this and later quick disturbances to Dze communities inside their lands. | By the end of this period the Dze began a cultural split from the once unified nature of their species, undergoing surprisingly fast changes that prove the Dze Cultural Hibernation hypothesis, which theorizes that Dze are naturally, culturally conservative until forced by mass scale disasters to change, first evidenced by this and later quick disturbances to Dze communities inside their lands. | ||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
Human arrivals to the Dze lands begin to be documented from 8.057 BR in the Çḳunyw Stele in the far south, which tells of a meeting between Dze Chieftains and the kings of four migrating tribes of "Short Folk" as they are referred to in the carvings. The arrivals seemed to have not stirred up conflicts at first, but texts unearthed reveal that by the end of the 9th millennium BR Human-Dze conflict arose, specifically with the Longplow, Broadaxe and Highstone cultures, which led to the slow creeping of humans into the territories of iron age Dze cultures in the south and west; the Red Arrow culture seems to have settled around the north-western shores and the Western Range during those times, hinting to a more friendly interaction between them and the Dze. | Human arrivals to the Dze lands begin to be documented from 8.057 BR in the Çḳunyw Stele in the far south, which tells of a meeting between Dze Chieftains and the kings of four migrating tribes of "Short Folk" as they are referred to in the carvings. The arrivals seemed to have not stirred up conflicts at first, but texts unearthed reveal that by the end of the 9th millennium BR Human-Dze conflict arose, specifically with the Longplow, Broadaxe and Highstone cultures, which led to the slow creeping of humans into the territories of iron age Dze cultures in the south and west; the Red Arrow culture seems to have settled around the north-western shores and the Western Range during those times, hinting to a more friendly interaction between them and the Dze. | ||
Initially it seems that humans had the upper hand, driving the descendants of the Woodhut and Caveshrine cultures from the western lands | Initially it seems that humans had the upper hand, driving the descendants of the Woodhut and Caveshrine cultures from the western lands. These early defeats began to propel the Dze into more organized forms of tribal governance, around this time also arose the title of [[T'aan]] among the Dze as a word for chieftain or ruler. After some generations the Dze tribes coalesced into the [[First Dze Confederation]] under [[Tsot'aan]] [[Quƚaq]] in 7274 BR. | ||
===The First Confederation=== | ===The First Confederation=== | ||
Under the leadership of Tsot'aan Quƚaq (7274-7231 BR) the armies of the First Confederation scored several victories against the forming Human Kingdoms during a campaign known as the [[Thunderstride]] (7273-7270 BR) which culminated in the [[Battle of Bones]] in where a coalition of human kingdoms were soundly crushed by Quƚaq, the site of which was then made into a pile with all of the corpses of the defeated, which began the practice of [[Corpse Mounds]] in Dze warfare. After the Thunderstride the rest of Quƚaq's reign was spent warding off human expansion into the central meadows and eastern steppe, resorting to more defensive, guerilla style, warfare rather than military campaigns. Succeeded by his daughter, Tsot'aan Tẋeńat (7231-7182 BR), the confederation mostly kept to this policy, however during the [[Jhu'kan campaigns]] (7190-7185) they faced off against the forces of the [[Jhu'kan Empire]] in the [[Battle of Alẋḳyx]] in which the Dze managed to defeat the forces of [[Ka'sun I]], dealing his only military defeat and securing peace between the Dze and what is today known as [[The Triarchy]]. | |||
===Human Dominance=== | ===Human Dominance=== | ||
===The Strifes and the Second Confederation=== | ===The Strifes and the Second Confederation=== | ||
Revision as of 01:54, 2 January 2023
The 3rd Dze Confederation Dzetśaqto | |
|---|---|
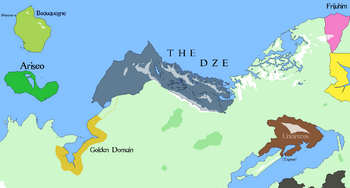 Lands and surroundings of the Dze Confederacy, 1612 AR | |
| Status | Independent state |
| Capital | Xanaaq̇ut's moving horde |
| Official languages | Old Dze |
| Ethnic groups | Dze (97.9%) Humans (2.1%) |
| Religion | Tẋeẋuq |
| Demonym(s) | Dze |
| Government | Semi-nomadic tribal confederation |
• Tsot'aan | Xanaaq̇ut |
| Establishment | |
• Founding of the 1st Confederation | 7274 BR |
• Start of the Strifes | 6429 BR |
• Founding of the 2nd Confederation | 2764 BR |
• Founding of the 3rd Confederation | 1598 AR |
• Fall of the Human Kingdoms | 1602 AR |
| Area | |
• Land Area | 695,622 km2 (268,581 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 5.31% |
| Population | |
• 1611 estimate | ~5,000,000 |
• Density | 7.19/km2 (18.6/sq mi) |
The Dze (Old Dze: Dzetśaqto ['d͡zet͡sʼaqtɔ]), officially known as The 3rd Dze Confederation, is a medium-sized nation located in north-central Pythia with no countries bordering it, however being relatively close to Axeut, Kursibar and Nishikaigan. An unknown nation in uncharted lands, it was recently unified in its totality by Tsot'aan Xanaaq̇ut, the founder of the modern confederacy.
One of the least populous countries of Sparkalia, the Dze have undergone a very recent population growth, no longer burdened by the constant conflicts against human invaders, reaching an estimated 5 million inhabitants during this century. Nontheless, it seems to be one of the oldest continuous inhabited places on the planet, having remained mostly isolated from the events that befell the surrounding lands due to it's geography and unassuming location, not being of high strategic importance.
Etymology
The name in English is merely a translation of the Old Dze name, which translates to "Oath/Alliance of the Dze", with the word Tśaq meaning either Alliance or Oath (added the possesive -to) and the word Dze meaning "Stargazer" and the endonym of these people in several languages and in the Old Liturgicals.
History
The lands of the Dze Confederation have archaeological evidence of a cultural existance since at least 100.000 BR, belonging to the Leaf Lance Culture, a Dze Paleolithic Culture that inhabited the mountainous central and northern regions of the country which seems to have mostly been located in the eastern ranges of the Great Mountains until about 70.000 BR when they began to expand alongside the hills and rocky outcrops towards the coast and the west. Characterized by their elaborate leaf shaped shrines and star-moon worship, two aspects that still carry on to this day in Dze cultures, by 50.000 BR the original culture split during the LNDC into several chalcolithic cultures later culminating in the Flower Stirrup Culture, which kickstarted the Dze Bronze Age by 20.000 BR. However around 8.000 BR there is archaeological, and later written, evidence for the arrival of four distinct human groups, the Longplow, Broadaxe, Highstone and Red Arrow cultures; having triggered a near all out war with the first three cultures, the Dze began to coalesce into more organized societies after the Invasions, an event happening around 7.500 BR which triggered the formation of the First Confederation. The subsequent 8.000 year long conflicts culminated in the rise of the Third Confederation in the late 16th century AR and the fall of human invaders less than a decade later.
Paleolithic Age
The archaeological record shows that these lands have been inhabited by an ancestor of the modern Dze, Tenacitherium anthropopsius, at around 600.000 years ago until evolving into the modern Dze, Tenacitherium terrible, around 350.000 years ago. Both a paleolithic people, it is thought that they mostly stayed around the Eastern Mountains. By around 100.000 years ago it is estimated that the first proper culture arose, the Leaf Lance Culture, named after a valley in the far east of the country; this culture's name also comes from the name given by scientists to the arrow and spear tips found, which bear a distinct leaf shape and pattern to them.
This culture spread throughout the mountains along river valleys and cliffs where they built small shrines in moon-like patterns that are still frequented to this day, some of the oldest being carbon dated to around 110.000-90.000 BR. Other distinguishing factors of this culture are an affinity towards inhabiting mountainsides rather than caves properly and their hunting method, which is depicted in some paleo-art, which puts more emphasis in Persistance Hunting in combination with either driving or calling methods as a coordinated maneuver between archers and spearmen.
Mesolithic Age
By 70.000 BR there is evidence for a slight change in the style and production of stone tools as well as the start of ceramic pottery, distinguished by their simple shapes and square painting patterns. It is also around this time when the Leaf Lance Culture, and by extention the Dze Population, began to spread into the Central Steppes and Coastal Ranges, however still mostly remaining in the east of the country as evidence by a higher abundance of pottery remains in those areas.
The Mesolithic Age also defined the transition from fully nomadic to a semi-nomadic lifestyle as evidenced by the recent discovery of massive stone circles in river valleys which are thought to be temporary summer refuges, later abandoned in preference for warmer places in winter like the cliffs overlooking the High Springs on the northern edge of the Eastern Mountains.
Neolithic Age and the LNDC
Around 60.000 years ago arises the first evidence for animal husbandry in the lands of the Confederation, with the previously mentioned stone circles being repurposed for keeping animals as a sort of pen. This and the continuous evolution of stone cutting techniques pinpoints to the start of a Neolithic, or Late Leaf Lance, period which ended by 50.000 BR with the Late Neolithic Dze Collapse, an event of unknown causes that led to the abandoning or destruction of the stone circles and the spreading of Dze populations westwards. A possible trigger of this event is volcanic eruptions in the Coastal Ranges, of which we have some geological evidence for, but frequent, and particularly cold, years might have caused the mass death of the game the Dze hunted or simply forced an emigration westards, the ending of these winters coinciding with the flooding of several rivers, causing the destruction of most stone circles.
By the end of this period the Dze began a cultural split from the once unified nature of their species, undergoing surprisingly fast changes that prove the Dze Cultural Hibernation hypothesis, which theorizes that Dze are naturally, culturally conservative until forced by mass scale disasters to change, first evidenced by this and later quick disturbances to Dze communities inside their lands.
Chalcolithic Age
After the Late Neolithic Dze Collapse, the archaeological record shows us that the range of Dze inhabitation massively expanded in all directions, specially westwards, and after population levels recovered from the collapse there arose several chalcolithic cultures, including the Moonblade, Caveshrine and Lowmound cultures, each of which began to participate in localized forms of trade, slowly expanding until what is called the "Steppe Roads" arose, which is a collection of several known trade routes that led from the westermost points of Dze inhabitation all the way to the Oriental Fjords. One evidence of this is the usage of the Dze Hieroglyphic script by the Woodhut Culture in the far west by 38.000 BR, not that far from when the script first began to be used by the Moonblade Culture.
Key developments that occured in this time also include the start of the usage of wheels and carts as depicted in rock art and evidenced in writings by the Late Moonblade period at 26.000 BR as well as the previous requirement of animal domestication, specifically of the creatures known in Standard as Dräihoufen, Krummhörn and the Gromähne, which allowed for the true start of the semi-nomadic lifestyle the Dze prefer nowadays as well as the invention of the stirrup, a localized development that seems to have occurred independently at least 4 times. By the end of the chalcolithic the Dze managed to spread to most of their currently owned lands, now also inhabiting the open prairies that define the landscape of their territories. Around 25.000 BR a second civilizsation collapse occured, evidenced by the sudden dissapearance of writing whatsoever asides for very isolated corners where the old liturgicals were still carved; this one we know was caused by volcanic activity and natural disasters that send the Dze into more than 5 milennia of darkness, a period of which we also barely have any archaeological findings.
Bronze Age
By 20.000 BR the remnants of the Moonblade Culture seem to have evolved into the Flower Stirrup Culture, denoted by the shape of the steel footing and the intricate bronze decorational patterns, which by 15.000 BR had spread the usage of Bronze alloys to all corners of Dze inhabitation. This period of renewal also saw and shed light into the evolution and further diversification of Dze Cultures that happened in the collapse, however writing seems to have been confined to the lands inhabited by the people of Flower Stirrup culture until around 15.000 BR or even later depending on the dating of tablets on the southlands. By the end of the Bronze Age around 10.000 BR the Dze civilizations and cultures had recovered from the Late Chalcolithic collapse and they had begun the usage of Iron technology in certain areas.
Arrival of Humans
Human arrivals to the Dze lands begin to be documented from 8.057 BR in the Çḳunyw Stele in the far south, which tells of a meeting between Dze Chieftains and the kings of four migrating tribes of "Short Folk" as they are referred to in the carvings. The arrivals seemed to have not stirred up conflicts at first, but texts unearthed reveal that by the end of the 9th millennium BR Human-Dze conflict arose, specifically with the Longplow, Broadaxe and Highstone cultures, which led to the slow creeping of humans into the territories of iron age Dze cultures in the south and west; the Red Arrow culture seems to have settled around the north-western shores and the Western Range during those times, hinting to a more friendly interaction between them and the Dze.
Initially it seems that humans had the upper hand, driving the descendants of the Woodhut and Caveshrine cultures from the western lands. These early defeats began to propel the Dze into more organized forms of tribal governance, around this time also arose the title of T'aan among the Dze as a word for chieftain or ruler. After some generations the Dze tribes coalesced into the First Dze Confederation under Tsot'aan Quƚaq in 7274 BR.
The First Confederation
Under the leadership of Tsot'aan Quƚaq (7274-7231 BR) the armies of the First Confederation scored several victories against the forming Human Kingdoms during a campaign known as the Thunderstride (7273-7270 BR) which culminated in the Battle of Bones in where a coalition of human kingdoms were soundly crushed by Quƚaq, the site of which was then made into a pile with all of the corpses of the defeated, which began the practice of Corpse Mounds in Dze warfare. After the Thunderstride the rest of Quƚaq's reign was spent warding off human expansion into the central meadows and eastern steppe, resorting to more defensive, guerilla style, warfare rather than military campaigns. Succeeded by his daughter, Tsot'aan Tẋeńat (7231-7182 BR), the confederation mostly kept to this policy, however during the Jhu'kan campaigns (7190-7185) they faced off against the forces of the Jhu'kan Empire in the Battle of Alẋḳyx in which the Dze managed to defeat the forces of Ka'sun I, dealing his only military defeat and securing peace between the Dze and what is today known as The Triarchy.

