Produzland: Difference between revisions
Thrawsonia (talk | contribs) |
Thrawsonia (talk | contribs) |
||
| (181 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Produzland {{ref label|aaa|a}} | |conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Produzland {{ref label|aaa|a}} | ||
|common_name = | |native_name = ''O Reino de Produseía'' ([[Produese]]) | ||
|common_name = Produzland | |||
|image_flag = | |name = | ||
|image_flag = Produzland_2021-.png | |||
|alt_flag = | |alt_flag = | ||
|image_coat = | |image_coat = 2021 Produese COA.png | ||
|alt_coat = | |alt_coat = | ||
|symbol_type = Coat of Arms | |symbol_type = Coat of Arms | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
|other_symbol_type = | |other_symbol_type = | ||
|other_symbol = | |other_symbol = | ||
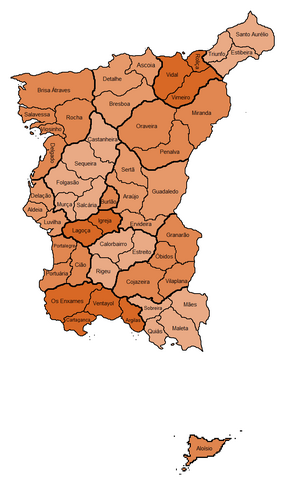
|image_map = | |image_map = New_map.png | ||
|map_width = 275px | |map_width = 275px | ||
|alt_map = | |alt_map = | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
|largest_settlement_type = city | |largest_settlement_type = city | ||
|official_languages = Produese | |official_languages = Produese | ||
|regional_languages = Produese, Cabecan, | |regional_languages = Produese, Cabecan, Rodavese | ||
|languages_type = | |languages_type = | ||
|languages = | |languages = | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
|government_type = Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy | |government_type = Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy | ||
|leader_title1 = [[Prime Minister of Produzland|Prime Minister]] | |leader_title1 = [[Prime Minister of Produzland|Prime Minister]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Riccardo Bonadeo]], [[Patron's Party (Produzland)| | |leader_name1 = [[Riccardo Bonadeo]], [[Patron's Party (Produzland)|PP]] | ||
|legislature = [[Tribunais Gerais]] | |legislature = [[Tribunais Gerais]] | ||
|upper_house = [[Senate]] | |upper_house = [[Senate]] | ||
|lower_house = [[Congress of Deputies]] | |lower_house = [[Congress of Deputies]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = Kingdom | |sovereignty_type = Kingdom | ||
|established_event1 | |established_event1 = Cavale and Galicia Split | ||
|established_date1 = March 4th, 987 | |||
|established_event2 = Unification of Cavale and Galicia | |||
| | |established_date2 = February 19th, 1140 | ||
| | |established_event3 = West Bresbon Decrees | ||
| | |established_date3 = January 15th, 1715 | ||
| | |established_event4 = Establishment of the Federal Republic of Produzland | ||
| | |established_date4 = July 16th, 1935 | ||
|established_event5 = Restoration of the Monarchy | |||
|established_date5 = February 18th, 1980 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
| Line 112: | Line 107: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Produzland''', officially, the '''Kingdom of Produzland''' (Produese: O Reino de | '''Produzland''', officially, the '''Kingdom of Produzland''' (Produese: O Reino de Produseía), is a sovereign state in [[Greater Olympus]]. Produzland is located on the western half of the [[Orthurian Peninsula]] in Southwest [[Lira]]. Produzland borders the [[Aurum Ocean]] in the west, and [[Meronnia]] in the North-East, as well as [[Parthonopia]] in the east. The Kingdom covers an area of 434,622.52 square kilometers with an oceanic and mediterranean climate. It is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with 61 million inhabitants (2019) and King [[José III]] as king since 2019. | ||
During antiquity, a group of people known as Aenians invaded the Orthurian Peninsula, the Aenians were called the "Produese" as they mixed with the local Orthurians of the the Orthurian province of Produsia. After the fall of the Orthurian Empire, the most notable nations to arise were | During antiquity, a group of people known as Aenians invaded the Orthurian Peninsula, the Aenians were called the "Produese" as they mixed with the local Orthurians of the the Orthurian province of Produsia. After the fall of the Orthurian Empire, the most notable nations to arise were Agudicia and Calmatia. West Agudicia split from Agudicia to become Cavale a few centuries later. After the division of Calmatia over the course of the middle ages Cavale conquered most of Western Orthuria and became the successor state to Produsia. After a history of imperialism and many royal dynasties, the empire fell apart over the course of the late 1800s and early 1900s. This resulted in a dictator seizing control of Produzland in 1935. The dictatorship was removed in 1980 with the monarchy being restored and Produzland in the modern day being a leading nation in Liran politics. | ||
Produzland is ones of the leading countries in seafood production | Produzland is ones of the leading countries in seafood production. luxury items, and automobiles. Manufacturing is the dominant force in the country with significant contributions from refining. The parts made in Produzland are both exported and made into finished products, though the economic goal of the nation is to export the majority of parts out of the country, while keeping/importing some parts for local manufacturing before exportation. Imports include raw materials as well as finished goods and services from other countries. The resources on hand and the priorities of Produzland influence what type of refinement and manufacturing will take place. Produzland's manufacturing specialties include trains, automobiles, luxury goods, and electrical equipment. | ||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
[[File:Merida_Roman_Theatre2.jpg|thumb|left|Orthurian Theatre in Salcária.]] | [[File:Merida_Roman_Theatre2.jpg|thumb|left|Orthurian Theatre in Salcária.]] | ||
The [[Orthurian Empire]] named their westernmost province [[Produsia]], meaning "Land of Carrots", which would evolve into Produzland in [[Lorian]]. The [[Aenians]] adopted this name from the Orthurians when they migrated to the land during antiquity. However "Produzland" throughout history was mainly used as a geographic term referring to the western half of the [[Orthurian Peninsula]]. Historians today mostly refer to the [[personal union of | The [[Orthurian Empire]] named their westernmost province [[Produsia]], meaning "Land of Carrots", which would evolve into Produzland in [[Lorian]]. The [[Aenians]] adopted this name from the Orthurians when they migrated to the land during antiquity. However "Produzland" throughout history was mainly used as a geographic term referring to the western half of the [[Orthurian Peninsula]]. Historians today mostly refer to the [[personal union of Agudicia and Cavale]] starting in the 14th century as the beginning of the country of Produzland for simplicity, as "Produzland" was really a complex entity of unions of crowns and kingdoms. The kings of the realm at the time might have even referred to themselves as the kings of the Produzlands plural to represent the several kingdoms under their rule with loose cultural connections. [[Produese]] meant more a person from western Orthuria in general rather than as a nationality. For example a [[Rodavese]] person at the time might have called themselves Produese, not insinuating that the [[Rodaves]] didn't have a national identity, but rather Produese as a superclass encompassing all the realms in western Orthuria such as the Rodaves, [[Cavale]], and [[Agudicia]]. | ||
The [[Rodavese Revolution]] of the 1640s most likely kicked off the identity that Produese was a nationality referring to Cavale and | The [[Rodavese Revolution]] of the 1640s most likely kicked off the identity that Produese was a nationality referring to Cavale and Agudicia rather than a superclass even when the Rodaves was reunited with the realm later on. Another reason is to foreign powers it was easier to refer to it as such rather than the complex and nuanced entity "Produzland" really was. | ||
Produzland didn't come as a reference to one kingdom and one kingdom only until the [[West Bresbon Decrees]] of 1715 formally united | Produzland didn't come as a reference to one kingdom and one kingdom only until the [[West Bresbon Decrees]] of 1715 formally united Agudicia and Cavale into one entity. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 140: | Line 135: | ||
[[File:Aqueduct of Segovia 01.jpg|thumb|left|Orthurian aqueduct in Lagoza.]] | [[File:Aqueduct of Segovia 01.jpg|thumb|left|Orthurian aqueduct in Lagoza.]] | ||
Under the rule of the Orthurians two main people groups rose to prominence in the west, the Aenians and Calmatians. With the fall of the Orthurian Empire over the course of the 5th century, the two people groups had set up their respective domains. Similar to the Aenians, the Calmatians were a fractured and spread people group, at some points Calmatian kingdoms would comprise territory even north of the Mazarico River, where they took the great city of Olivrium from the Orthurians. During the 6th, 7th, and 8th centuries the Aenians had unified under one country, the Kingdom of | Under the rule of the Orthurians two main people groups rose to prominence in the west, the Aenians and Calmatians. With the fall of the Orthurian Empire over the course of the 5th century, the two people groups had set up their respective domains. Similar to the Aenians, the Calmatians were a fractured and spread people group, at some points Calmatian kingdoms would comprise territory even north of the Mazarico River, where they took the great city of Olivrium from the Orthurians. During the 6th, 7th, and 8th centuries the Aenians had unified under one country, the Kingdom of Agudicia, while the Calmatians remained fractured, but began to form proper nationstates including the Kingdom of the Rodaves, the Kingdom of Selara, and the Kingdom of Cadascun, later known as Portuária, however at the time the three kingdoms all spoke a common language, Calmatian, the predecessor to modern Rodavese as the language was pushed South by the early Produese. | ||
Due to a succession crisis in | Due to a succession crisis in Agudicia in 879, the country was divided into West Agudicia and East Agudicia, the former being ruled by the bastard son of King Alfonso II of Agudicia, Ferdinand and the Galician House of Fonseca, and the latter ruled by Alfonso's legitimate son Vicente and the already Agudician ruling House of Outeiro. West Agudicia and East Agudicia both held large chunks of territory from Aenian expansion southward since the beginning of the middle ages, East Agudicia held the old united capital of Relâmpago, while West Agudicia originally made [[Aldeia]] the capital of the new country. | ||
The crown of West | The crown of West Agudicia split in 997 after the death of Ramiro II of West Agudicia, he split the country into north and south, the north known as the Kingdom of Galicia, a historical name for the region, ruled by his brother Alfonso III, the south took the name "O Reino de Cavela", or the Kingdom of Cavale ruled by Ramiro II's cousin Ferdinand III. | ||
=== Late Middle Ages (1140-1486) === | === Late Middle Ages (1140-1486) === | ||
The crowns of Cavale and Galicia unified again under King Peter I of Cavale and Galicia. This nation state would become the leader of Produese unification and the predecessor state of Produzland. During this period the country is often referred to as simply Cavale. This became an era for advancement for the region, Cavale was cemented as the dominant Produese state. | The crowns of Cavale and Galicia unified again under King Peter I of Cavale and Galicia. This nation state would become the leader of Produese unification and the predecessor state of Produzland. During this period the country is often referred to as simply Cavale. This became an era for advancement for the region, Cavale was cemented as the dominant Produese state. [[Vincent II]] wanted to guarantee this and set his eyes on the historic Orthurian city of Luville, which had been in Calmatian hands for centuries. King Vincent personally led an army to the walls of Luville. Luville had always been poorly held by the Calmatians for the last few centuries as their northernmost territory, however Cavallian monarchs had never seized the opportunity. Vincent II led an army directly to Luville while another fought their way to the banks of the Mazarico to cut off Calmatian reinforcements from the city. The city was captured and prestige grew for the united kingdom. | ||
[[File:Segovia_-_Alcázar_de_Segovia_22_2017-10-24.jpg|thumb|right|The Alcazar of Lagoza, built in the 11th century.]] | [[File:Segovia_-_Alcázar_de_Segovia_22_2017-10-24.jpg|thumb|right|The Alcazar of Lagoza, built in the 11th century.]] | ||
The Conquest of Luville firmly set Cavale as the leading power in western Orthuria, and to some is the beginning of what is known as ''[[Desiderium Meridionali]]'', "The Southern Desire", representing Cavale's desire to reach the Rosel Sea and bring all of western Orthuria under their rule. It would continue until the 16th century, and Cavale began to expand into Selará and Portuária. Portuária was captured in 1249 and Calorbairro five years later. The break-up of Calmatia in the early Middle Ages into competing kingdoms helped the long embattled northern Aeno-Orthurian kingdoms gain the initiative in southern Orthuria. The capture of the strategically central city of Araújo in 1084 marked a significant shift in the balance of power in favour of Cavale and Galicia. Following a great resurgence in the 12th century, the great Selanese strongholds in the south fell to Cavale in the 13th century—[[Rigeu]] in 1261 and [[Cojazeira]] in 1284. and Cavale gained direct access to the Rosel Sea in 1376 with the fall of the Rodavese stronghold [[Quiàs]]. | |||
In the 13th century the Kingdom of Velarre and the | In the 13th century the Kingdom of Velarre and the Agudician Duchy of Sonância had been in fierce competition over Cabeca. Velarre forming out of the Kingdom of Lurrak in the 1100s. While Sonância was Aenian as opposed to Cabecan like Velarre, they still vied for power in the region ever capturing the city of Lurrak itself, renaming it to San Aurelio after the Saint Aurelius. | ||
Due to [[Gabriel V]] of | Due to [[Gabriel V]] of Agudicia being incapable of ruling, the Cavallians took the opportunity to press their claim to eastern Galicia, which spiralled into the War of the Thymes in 1301, the war soon turned into a war of succession when the Cavallian king was killed in battle, which with the help of Philip III the Vain and the Sonâncians put Henry I, Count of Lugo on the throne of Agudicia and Cavale in 1308, leaving the two as independent kingdoms under one monarch. At this point they were practically united however. This began the de facto Kingdom of Produzland. The realm had several problems that would plague it for the coming decades, however after time the people of the country would come together and a string of competent monarchs would come to create one of the most powerful nations and empires in history. | ||
=== Early Produese Empire (1486-1550) === | === Early Produese Empire (1486-1550) === | ||
In 1486 Ferdinand | In 1486 [[Ferdinand VI]] took the Produese throne from his father, which historians claim as the beginning of the [[Produese Golden Age]], encouraging the [[Parthonopian Renaissance]] in the country with artists like [[Osório da Rosario]], [[Luca Melo]], and [[Balduíno Hernandes]]. Ferdinand VIII is also regarded as the founder of the Produese Empire, over the course of the 16th and 17th centuries, the Produese Empire expanded it's influence heavily in Nori and it's southeastern islands. The first example in 1513 explorer [[Antão do Ortigão]] became the first Liran to land on mainland Nori, despite failing to colonize mainland Nori, this opened up the gateway for Produzland to become the dominant Liran power in east Nori. Twenty years later in 1533 Ortigão and company landed on the [[Strait of Marque]] island of [[Comona]], establishing [[São Diogo]]. Years later another company landed on the mainland and established the colonies of [[Nova Agudiza]] and [[Sinais Alto e Baixo]] in modern [[Carelia]]. The trade of the empire made the monarchy immensely wealthy and the gold of the southeast flowed back to Burlon. | ||
[[File:El_nacimiento_de_Venus,_por_Sandro_Botticelli.jpg|thumb|left|Painted in Parthonopia, O Nascimento de Vênus by Luca Melo is one of the most famous artworks of the renaissance.]] | [[File:El_nacimiento_de_Venus,_por_Sandro_Botticelli.jpg|thumb|left|Painted in Parthonopia, O Nascimento de Vênus by Luca Melo is one of the most famous artworks of the renaissance.]] | ||
In 1500, the wealthy [[Republic of the Rodaves]], the last Calmatian realm remaining in west Orthuria began to collapse with wars with Parthonopia and King Ferdinand took the opportunity to seize the republic. The Rodaves had aspirations on Rodavese-speaking lands in southern Produzland, but the Rodaves couldn't afford to go to war with Produzland with their colonial bids draining the republic's treasury. Until King Ferdinand took the fight to the Rodavese, personally lead a sacking of the city of Cartaganca. After the fall of the Rodavese capital, the Rodavese forces across the country began to collapse and the Rodaves was annexed, marking an end to the half-millenia long ''Desiderium Meridionali''. Rebellion and sparse guerilla fighting in the former republic would continue until the [[Rodavese Revolution]] of 1643. | |||
Produzland allied with the neighboring nations of Parthonopia, Meronnia, and Velarre to halt Lunderfrausian advances southward, Produzland supplied troops to the famous [[Siege of Lepanto]], a victory for the southern powers. During the war, Ferdinand VI seized several islands north of the Lunderfrausian coast, using Ferdinand's claim to the islands through his wife as a casus belli. Furthering Produzland's position as the leading power in Lira. | |||
[[ | When Ferdinand VI passed in 1521, he left Produzland in the best position in Lira, however tragedy struck when his son [[Henry III]], was murdered in a jousting accident in 1539, this lead way however to second son [[Joseph the Colonizer]] to revamp the Produese Empire in east Nori with the [[Produese Gulf Company]] to promote Produzland to the richest nation in Lira, and the House of Lugo one of the richest in the world. | ||
[[File:Aleixandre_do_Orestes_(1510).jpg|thumb|Portrait of Antão do Ortigão.]] | |||
Joseph's first major feat in his reign being in 1543 when [[Jorge Adão da Coutinho]] landed in southern Kiteahu and established Fort Santa Ángela on an island he called Cavaco. Coutinho also landed in the eastern islands of modern [[Jashnagar]] a few years later, which he and his fleet gave it the name 'Jaixnágar'. | |||
=== Vincennine Produzland (1550-1700) === | === Vincennine Produzland (1550-1700) === | ||
Tensions with Meronnia were present over the last few decades, mainly as colonial rivals in south-east Nori and Cabeca, which recently was a source for tension as the Kingdom of Velarre became a vassal of Meronnia. The Lugos decided to set up several agreements with their northern neighbor including several arranged marriages and giving Produzland influence in Nori and Meronnia in Meridiq in the [[Treaty of Relâmpago]]. After Joseph I passed in 1550, he was replaced with his son Philip, and through his mother Philip also inherited the Kingdom of Meronnia in 1551 leaving him as King [[Philip I & IV]] of Produzland and Meronnia and he one of the most powerful men in history as Produzland continued their colonial reign in east Nori. | Tensions with Meronnia were present over the last few decades, mainly as colonial rivals in south-east Nori and Cabeca, which recently was a source for tension as the Kingdom of Velarre became a vassal of Meronnia. The Lugos decided to set up several agreements with their northern neighbor including several arranged marriages and giving Produzland influence in Nori and Meronnia in Meridiq in the [[Treaty of Relâmpago]]. After Joseph I passed in 1550, he was replaced with his son Philip, and through his mother Philip also inherited the Kingdom of Meronnia in 1551 leaving him as King [[Philip I and IV|Philip I & IV]] of Produzland and Meronnia and he one of the most powerful men in history as Produzland continued their colonial reign in east Nori. | ||
In 1582 when King Philip died, he split his empire in two with his son Vincent III inheriting Produzland and his daughter Ermelina I inheriting Meronnia and beginning the Meronnian branch of the House of Lugo. The two nations stayed very close allies throughout history though. | In 1582 when King Philip died, he split his empire in two with his son Vincent III inheriting Produzland and his daughter Ermelina I inheriting Meronnia and beginning the Meronnian branch of the House of Lugo. The two nations stayed very close allies throughout history though. | ||
| Line 182: | Line 177: | ||
[[File:Maixeira Palace.jpg|thumb|left|Maixeira Palace is an example of the country's prestige during the Produese Golden Age.]] | [[File:Maixeira Palace.jpg|thumb|left|Maixeira Palace is an example of the country's prestige during the Produese Golden Age.]] | ||
In 1612, rivalries with northern Lira and disputes between Lunderfrau and the Lugos over islands in the | In 1612, rivalries with northern Lira and disputes between Lunderfrau and the Lugos over islands in the [[Esketres Sea]], especially Lunderfrausian protests to the Produese inquisition in the territory spiraled into the [[20 Years War]], in which Produzland and Lugo prestige suffered a catastrophic defeat, and the Lugos lost their monopoly on Norian trade. The war became worse for Produzland when the [[Rodavese Revolution]] sprung up, as well as revolts in in Produese owned Cabeca, causing King Vincent IV to effectively lose control of the former. Unlike the previous independent Rodavese state, the Rodaves became a kingdom and crowned Louis of the [[House of Beltrão]] as King Louis I of the Kingdom of the Rodaves. At the same time Meronnia became involved in their own religious war in which Produzland was heavily involved in to continue Verroist rule in the nation. This became another defeat for the Lugos as they were deposed in Meronnia in 1684. | ||
=== | === Beltrão Produzland (1700-1818) === | ||
In early 1700 Charles I died childless, following the rules of Produese succession the crown passed to King Louis | In early 1700 Charles I died childless, following the rules of Produese succession the crown passed to King [[Louis II]] of the Rodaves of the [[House of Beltrão]]. Louis III would pass however before he could be crowned, leaving the thrones of Produzland and the Rodaves in the hands of his five year old son Prince Vícenç de Beltrà i Portell. Vícenç became [[Vincent V of Produzland|Vincent V]] of Produzland and Vincent II of the Rodaves. However the Kingdom of Parthonopia, a staunch ally of the Rodaves rejected the idea of a personal union between Produzland and the Rodaves, so Parthonopia declared war in 1701. The young king's regent was his uncle [[Carles, Duke of Argilés]] who responded quickly to the Parthonopian war. However after a couple of major naval defeats in the Rosel Sea Produzland and the Rodaves surrendered in 1709. In the [[Treaty of Piombino]], Produzland gave up the island of Aloísio to become a kingdom in a union with Parthonopia. It also ceded parts of eastern Turon and several other border regions. The border established in the treaty is the one that remains till today between the two countries. | ||
[[File:Portrait of King Joao V and the Battle of Cape Matapan.JPG|thumb|Portrait of King Vincent V.]] | [[File:Portrait of King Joao V and the Battle of Cape Matapan.JPG|thumb|Portrait of King Vincent V.]] | ||
Vincent was formally crowned in Araújo by the Archbishop of Araújo earlier that year at the age of 15. One of his earliest acts was the dissolution of the current feudal system in Produzland, removal of any regional power with the Crown of | Vincent was formally crowned in Araújo by the Archbishop of Araújo earlier that year at the age of 15. One of his earliest acts was the dissolution of the current feudal system in Produzland, removal of any regional power with the Crown of Agudicia, and formal integration of the Kingdom of the Rodaves into the larger kingdom, all included in the [[West Bresbon Decrees]] of 1715. This also de jure established the centralized Kingdom of Produzland. | ||
In 1734, at the age of 39 Vincent V began expanding the borders of Produzland into the regions he saw fit. With an alliance with Meronnia, Produzland and Meronnia invaded the financially struggling Kingdom of Velarre and deposed Louis II, who 50 years before had escaped vassalage of Meronnia in the Meronnian religious wars. Produzland drove quickly through the Cabecan lands and annexed most of the modern state of Cabeca into the kingdom | In 1734, at the age of 39 Vincent V began expanding the borders of Produzland into the regions he saw fit. With an alliance with Meronnia, Produzland and Meronnia invaded the financially struggling Kingdom of Velarre and deposed [[Louis II]], who 50 years before had escaped vassalage of Meronnia in the Meronnian religious wars. Produzland drove quickly through the Cabecan lands and annexed most of the modern state of Cabeca into the kingdom. | ||
Continuing the expansion policy Produzland invaded the Kingdom of | Continuing the expansion policy Produzland invaded the Kingdom of Aloísio in 1738, kicking off a second war with Parthonopia. However Parthonopia was unprepared and fought sloppily, leading to a massive destruction of the joint Aloísian-Parthonopian army on the island, and the destruction of the Parthonopian fleet in the Rosel. Vincent V declared his second son Philip King of Aloisio as Philip I at the age of 18, as Philip was not directly in line for the throne. After the end of the war with Aloísio and Parthonopia, King Vincent turned his eye north towards Meronnia, who over the last decade had sprung into revolution and deposed their ruling dynasty. King Vincent was determined to restore the monarchy of the country and invaded with the help of Meronnian royalists that fled to Produzland. The Produese sacked the city of [[Senone]] in 1739 and restored the monarchy of the country, a resounding victory and restored much of the lost prestige of the 17th century for Produzland. | ||
[[File:King Philip II.jpg|thumb|left||King Philip II is one of the most commemorated monarchs in Produese history for his enlightened ideas and democratic reform, represented in a statue of the king in the Praça da Vida do Sol in Luville.]] | [[File:King Philip II.jpg|thumb|left||King Philip II is one of the most commemorated monarchs in Produese history for his enlightened ideas and democratic reform, represented in a statue of the king in the Praça da Vida do Sol in Luville.]] | ||
In 1751 the king of Produzland and son of Vincent V, Vincent VI died childless. This lead to King Philip I of | In 1751 the king of Produzland and son of Vincent V, [[Vincent VI]] died childless. This lead to King Philip I of Aloísio being crowned King Philip II of Produzland as well. He fully integrated Aloísio into Produzland the next year. | ||
The reign of Philip II became an era of reform for the Produese kingdom after a rough start to the young monarch's reign. Produzland had been an absolute monarchy for all of its history, excluding the Rodavese Republic, and with the emergence of the enlightenment calls for reform grew in the country. Philip was a moderate when it came to democracy, and was open to the idea of it, he was by no means a Republican and believed in the power of his monarchy, so he implemented a system of a Parliament and an appointed Prime Minister that would govern under the supervision of the monarchy. He had a constitution drafted by appointed bureaucrats in 1771, and had a Prime Minister selected as head of government. For a country that had no previous history of democracy, Produzland had a period of stability under their popular monarch and parliament. | The reign of [[Philip II of Produzland|Philip II]] became an era of reform for the Produese kingdom after a rough start to the young monarch's reign. Produzland had been an absolute monarchy for all of its history, excluding the Rodavese Republic, and with the emergence of the enlightenment calls for reform grew in the country. Philip was a moderate when it came to democracy, and was open to the idea of it, he was by no means a Republican and believed in the power of his monarchy, so he implemented a system of a Parliament and an appointed Prime Minister that would govern under the supervision of the monarchy. He had a constitution drafted by appointed bureaucrats in 1771, and had a Prime Minister selected as head of government. For a country that had no previous history of democracy, Produzland had a period of stability under their popular monarch and parliament. | ||
[[File:La_Rendición_de_Bailén_(Casado_del_Alisal).jpg|thumb|The Surrender at | [[File:La_Rendición_de_Bailén_(Casado_del_Alisal).jpg|thumb|The Surrender at Vidal by Ricardo Lobo de Casado.]] | ||
Prince Carlos, the grandson of Philip II inherited the throne after his grandfather's death in 1801, becoming Charles II. At the end of the Meronnian Revolution near the same time, the directory of the Meronnian republic offered Produzland territory and a sphere of influence over Parthonopia if they had joined the ongoing war between Meronnia and the Parthonopian states. Despite personally not favouring the republic and Augustin Calvet, due to pressure from the parliament, Charles II had Produzland side with them in the Great Continental War. | Prince Carlos, the grandson of Philip II inherited the throne after his grandfather's death in 1801, becoming [[Charles II]]. At the end of the Meronnian Revolution near the same time, the directory of the Meronnian republic offered Produzland territory and a sphere of influence over Parthonopia if they had joined the ongoing war between Meronnia and the Parthonopian states. Despite personally not favouring the republic and [[Augustin Calvet]], due to pressure from the parliament, Charles II had Produzland side with them in the [[Great Continental War]]. | ||
Produzland and Meronnia turned victorious in the war against the coalition and several western Parthonopian territories were annexed into Produzland as well as the former Principality of Trevisa merged with lands from the Principality of Terracina into the Kingdom of Trevisa-Terracina.This alliance was turned on its head in 1813 however when Augustin invaded Produzland and deposed King Charles, as well as forcing his son to give up his right to the throne. Calvet installed his brother Francis on the Produese throne and forced Produzland to give up many of the territories won in the war against the coalition and Cabeca, being turned into sister republics of Meronnia. The Produese people engaged in fierce guerilla warfare against their Meronnian occupiers, and when Augustin was assassinated and the war turned against Meronnia, King Francis was deposed and replaced with Charles II's heir, and Produzland regained many of its lost territories, including a great sphere of influence over Parthonopia. | Produzland and Meronnia turned victorious in the war against the coalition and several western Parthonopian territories were annexed into Produzland as well as the former Principality of Trevisa merged with lands from the Principality of Terracina into the Kingdom of Trevisa-Terracina.This alliance was turned on its head in 1813 however when Augustin invaded Produzland and deposed King Charles, as well as forcing his son to give up his right to the throne. Calvet installed his brother Francis on the Produese throne and forced Produzland to give up many of the territories won in the war against the coalition and Cabeca, being turned into sister republics of Meronnia. The Produese people engaged in fierce guerilla warfare against their Meronnian occupiers, and when Augustin was assassinated and the war turned against Meronnia, King Francis was deposed and replaced with Charles II's heir, and Produzland regained many of its lost territories, including a great sphere of influence over Parthonopia. | ||
| Line 210: | Line 205: | ||
=== Late Produese Empire (1818-1925) === | === Late Produese Empire (1818-1925) === | ||
Despite ending up victorious in the Great Continental War and Carlos III with a firm grip over his realm again, the country was in ruins from the decade of war and both the king and the reinstated Prime Minister [[César | Despite ending up victorious in the Great Continental War and Carlos III with a firm grip over his realm again, the country was in ruins from the decade of war and both the king and the reinstated Prime Minister [[César Baltasar da Araújo]] knew the country was in need of reform. The country shifted away from it's traditional practices and abolished feudalism, and emancipation in the Produese Empire became a fiercely debated topic. An offshoot was the dissolution the Produese Gulf Company in 1824 which had been declining in it's prestige since the 20 Years War, and the Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition, commonly known as the Produese Inquisition, in 1832. Produzland sold the island of Comona to Carelia in 1820 and industrialization became prevalent in Produzland, including a monumental advancement with the invention of the train. Produzland became reliant on the railroad as one of the fastest countries to adopt them across the nation. While Produzland proper was rebuilding, their eastern territories in Parthonopia were revolting against their Produese occupiers, Carlos III repressed these rebellions in harsh ways which eventually turned over into the Wars of Parthonopian Independence against Produzland in 1824, with the country in no shape ready for war directly after the Great Continental War, they turned poorly for the country and Produzland lost its eastern territories, the wars left turmoil within the government and eventually came to a head with King Carlos' abdication in favour of his son Vincent VII. While Produzland was no longer the great power it once was, the mid-19th century became an era of development and general prosperity for it's people, especially with the rise of [[Vincent VIII]] and economic reform to combat poverty and the problems of the workplace. | ||
[[File:Vintage-historic-bw-photos-of-madrid-spain-1890s-01.jpg|thumb|left|Photograph taken of the center of Burlon, 1865.]] | [[File:Vintage-historic-bw-photos-of-madrid-spain-1890s-01.jpg|thumb|left|Photograph taken of the center of Burlon, 1865.]] | ||
Despite this, calls for more began from the working class, when Produzland lost the [[Cavo-Carelian War]] in 1894, demonstrations broke out in Produzland's industrial heartland in Burlon and Luville, and with the rise of nationalism, riots in | Despite this, calls for more began from the working class, when Produzland lost the [[Cavo-Carelian War]] in 1894, demonstrations broke out in Produzland's industrial heartland in Burlon and Luville, and with the rise of nationalism, riots in [[Triunfo]] broke out demanding independence for Cabeca. When the Parthonopian War of Succession arose in 1896, outrage broke out from a nation that was fiercely against war. Produzland looked like it might have to drop out of the war from a revolution, but then the elderly king Vincent VIII passed leaving the throne to his grandson [[Carlos IV]] on the throne, the charismatic yet hot-headed monarch became a symbol for the Produese army and turned the tide of the war. | ||
Once the war was won and Produzland made significant territorial gains, the king was as popular as ever, the republican Prime Minister Alexandre Coelho was voted out of power in the next election and things were looking bright for the nation that had spent the last near-decade in revolt. To coincide with the prosperity, Carlos IV ordered the construction of a monument to Produese architecture, representing the style to the world. It was built around the smaller Praça Rubescerá in Cojazeira and became an icon of Produzland when the Jubilee of the Ages was hosted in Cojazeira. | Once the war was won and Produzland made significant territorial gains, the king was as popular as ever, the republican Prime Minister Alexandre Coelho was voted out of power in the next election and things were looking bright for the nation that had spent the last near-decade in revolt. To coincide with the prosperity, Carlos IV ordered the construction of a monument to Produese architecture, representing the style to the world. It was built around the smaller Praça Rubescerá in Cojazeira and became an icon of Produzland when the Jubilee of the Ages was hosted in Cojazeira. | ||
| Line 224: | Line 219: | ||
=== Post-Olympic War and Produese Revolution (1925-1935) === | === Post-Olympic War and Produese Revolution (1925-1935) === | ||
During the Olympic War to boost moral the government under conservative Prime Minister [[Francisco Estêvão]] promised soliders things like the vote and free land. Many returning veterans were displeased to find the latter unfulfilled, however they did receive the vote. With wartime factories closed and the returning veterans unemployment skyrocketed and the economy was in shambles. Many Produes began to shift on the political spectrum, particularly with the socialist [[ | During the Olympic War to boost moral the government under conservative Prime Minister [[Francisco Estêvão]] promised soliders things like the vote and free land. Many returning veterans were displeased to find the latter unfulfilled, however they did receive the vote. With wartime factories closed and the returning veterans unemployment skyrocketed and the economy was in shambles. Many Produes began to shift on the political spectrum, particularly with the socialist [[PTSP]] lead by [[Amancio Sousa]] and the authoritarian [[União Nacional]] lead by [[Frederico Deusto]]. In 1929 Estêvão proposed a solution to the weak government the current parliamentary system had created. He decreed the winning party would automatically get 66% of the seats and a clear majority in parliament. This was supported by parliament as everyone despised the current system as nothing would get done. Carlos IV dismissed Estêvão in 1930 and replaced him with [[Filipe Góes]] who published the [[Góes Decrees]] that established a 40-hour work week and higher wages. Despite the reform internally Produzland's empire began to collapse and it lost it's remaining territories in Nori under Góes. In 1932 the country had an election and União Nacional won about 65% of the seats and Deusto became the Prime Minister, debates still exist today on how legitmate the vote was. While there was violence against Deusto's opponents, however he was wildly popular and many in the country were hoping he would fix the current problems. | ||
[[File:Antonio_Salazar-1.jpg|thumb|left|Frederico Deusto in 1940.]] | [[File:Antonio_Salazar-1.jpg|thumb|left|Frederico Deusto in 1940.]] | ||
| Line 232: | Line 227: | ||
=== Deusto Era (1935-1980) === | === Deusto Era (1935-1980) === | ||
With the Federal Republic enabling him to exercise vast political powers, Deusto's rule was conservative and nationalist in nature. Deusto promoted Verroism, but argued that the role of the Church was social, not political | With the Federal Republic enabling him to exercise vast political powers, Deusto's rule was conservative and nationalist in nature. Deusto promoted Verroism, but argued that the role of the Church was social, not political. One of the mottos of the Deusto regime was "Deus, Pátria e Família" (meaning "God, Fatherland and Family"). | ||
After the Produese Revolution, Produzland was politically and economically isolated, and was kept out of international organizations. Produzland at the time was also suffering from a sluggish economy due to Deusto intentionally keeping Produzland out of international trade with a policy called '[[Próprio Suficiência]]' (Self Sufficiency) in which Produzland sought to be entirely self-sufficient. The failing economy in the early 1950s forced the regime to implement major economic reforms that aimed at bringing in foreign investors. | |||
In the 1960s, Produzland registered an unprecedented rate of economic growth which was propelled by industrialisation, the economic reforms of the 1950s, a mass internal migration from rural areas to Burlon, Cartaganca and Cabeca and the creation of a mass tourism industry. Press censorship was also relaxed and the more repressive measures of the regime were laid back, however Produzland was still by no means a free country. | |||
=== Restoration of the Monarchy (1980-) === | === Restoration of the Monarchy (1980-) === | ||
[[File:Paolo_Monti_-_Servizio_fotografico_-_BEIC_6333091.jpg|thumb|right|Burlon in the 80's.]] | |||
By the 1970s Deusto was aging and plans around the country for his succession. With Deusto's death in March 1979, Deputy [[Alberto Saldanha Seabra]] succeeded him as President of Produzland and as was agreed with Deusto in the 1940s the positions of President and President of the Government diverged and [[Ronaldo Antunes]] took the position later that year. Antunes began working with politicians opposed to Deusto to restore democracy in Produzland and devolving the President's power. With the approval of the Produese Constitution of 1980 proposed by Antunes and the restoration of democracy, the State devolved much authority to the regions and created an internal organisation based on the states, and after fierce debate within parliament over the future of Produzland, it was finally decided on February 18th, 1980 to restore the monarchy. A relative of the former ruling [[House of Beltrão]], João de Beltrão was offered the Produese throne in February of 1980, which he accepted and became [[João II]]. The Produese 1982 Amnesty Law let people of Deusto's regime continue inside institutions without consequences. | |||
During the 1980s the democratic restoration made possible a growing open society. New cultural movements based on freedom appeared and a culture of human rights arose with [[Jorge Gonçalves Moniz]]. On May 30th, 1982, Produzland joined [[RESP]], followed by a referendum after a strong social opposition. The [[Burguês]] Party, which became the successor to the National Union Party was replaced in government by the [[Patron's Party (PP)]] in 1994 after scandals around participation of the government of Ronaldo Antunes and [[Marcelo Borges]] surrounding the [[Escândalo da Princesa]]; at that point Burguês had served almost 14 consecutive years in office. | |||
In November of 1997, the Velkanikan military seized the Produese overseas territory of [[Santa Iria]] under the pretext of halting illegal fishing boats and other vessels from evading Velkanikan law enforcement by fleeing to the island. Prime Minister [[Tomás da Rosa]] declared an exclusion zone around the island and deployed the Produese navy to the island. Heavy losses in the Rosel Sea and in the air as well as international pressure resulted in Velkanika retreating from the islands ten weeks later. | |||
On November 1st, 2018, PP leader [[Riccardo Bonadeo]] became Prime Minister after the 2018 General Election, replacing Prime Minister [[José Lérias Cascais]]. | |||
== Politics == | == Politics == | ||
| Line 241: | Line 249: | ||
[[File:Parlamento-IPPAR1.jpg|thumb|right|The Congress of Deputies.]] | [[File:Parlamento-IPPAR1.jpg|thumb|right|The Congress of Deputies.]] | ||
Produzland is a parlimentary constitutional monarchy. The Constitution grants the division or separation of powers among four bodies, the King, the Government, the parliament, and the Courts. The constitution of | Produzland is a parlimentary constitutional monarchy. The Constitution grants the division or separation of powers among four bodies, the King, the Government, the parliament, and the Courts. The constitution of 1777 also states that the capital of Produzland is always in the city of where the monarch lives, the current monarch being King [[José III]]. The current constitution of 1980 maintains most of its premises from the 1777 constitution while simultaneously compromising new elements such as the states' varying degrees of autonomy and attempts at furthering gender equality. | ||
[[File:20200321 152534.jpg|thumb|left|upright|PM Riccardo Bonadeo in 2018.]] | [[File:20200321 152534.jpg|thumb|left|upright|PM Riccardo Bonadeo in 2018.]] | ||
The Produese parliament is a bicameral system with the Senate and the Congress of Deputies. The Congress of Deputies is decided on a system proportional to the population of each state | The Produese parliament is a bicameral system with the Senate and the Congress of Deputies. The Congress of Deputies is decided on a system proportional to the population of each state adding up to a total of 305 seats, and each state with their appropriate amount of seats decides how they want to distribute their seats amongst the parties. The Senate meanwhile each province gets 4 senators giving the senate 212. Produzland has elections every 2 years. Elections are divided into two categories, [[Parliamentary Elections]] and [[General Elections]], both are essentially the same apart from in General Elections the head of the largest party elected becomes Prime Minister, whereas in Parliamentary elections they do not. This commonly results in the Prime Minister controlling a minority government. As of November 2020, Prime Minister [[Riccardo Bonadeo]] heads a minority government while [[Rodrigo Guindaste]] serves as [[Leader of the Opposition]]. | ||
Produese politics for the | Produese politics for since the resignation of Prime Minister [[Marcelo Borges]] have been dominated by two parties, the [[Produese Socialist Workers' Party (PTSP)]] (the dominant liberal party), and the Patron's Party (PP) (the dominant conservative party). Before the restoration Produzland was a single party state with [[União Nacional]] (National Union) at the lone party headed by [[Frederico Deusto]] until his death when the single party state collapsed and was replaced with the democratic multi-party system of today. | ||
=== Law and Criminal Justice=== | === Law and Criminal Justice=== | ||
| Line 258: | Line 266: | ||
=== Administrative Divisions === | === Administrative Divisions === | ||
Produzland is divided into | Produzland is divided into 16 states, states being the highest or first-order administrative division in the country. States are divided into provinces, of which there are 52 in total, and in turn, provinces are divided into municipalities. The current form was established in 1980 with the current constitution, however the system itself has existed since the early 19th century with the reforms of Prime Minister [[César Baltazar da Araújo]]. Produzland also holds several overseas territories, including [[Santa Iria]] in the eastern Rosel. | ||
Produzland is one of the most decentralized countries of western Lira, with all states possessing their own elected parliaments, governments, public administrations, budgets, and resources. Health and education systems among others are managed by the Produese states, and in addition, Cabeca and the Aloisian Islands also manage their own public finances based on foral provisions. | Produzland is one of the most decentralized countries of western Lira, with all states possessing their own elected parliaments, governments, public administrations, budgets, and resources. Health and education systems among others are managed by the Produese states, and in addition, Cabeca and the Aloisian Islands also manage their own public finances based on foral provisions. | ||
[[File: | [[File:New Provinces 13.png|thumb|right|Administrative divisions of Produzland.]] | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable uncollapsed collapsible" | {| class="wikitable sortable uncollapsed collapsible" | ||
| Line 270: | Line 278: | ||
! Area (km²) | ! Area (km²) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Agudicia | ||
| Bresbon | | Bresbon | ||
| 3,781,498 | | 3,781,498 | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
| Almúnia | |||
| Cojazeira | |||
| 5,118,344 | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Aloísio | | Aloísio | ||
| | | Capella | ||
| 1,119,439 | | 1,119,439 | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 282: | Line 295: | ||
| Burlon | | Burlon | ||
| Burlon | | Burlon | ||
| | | 5,946,071 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Cabeca | | Cabeca | ||
| | | Triunfo | ||
| | | 3,193,093 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 295: | Line 308: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Cavale-As | | Cavale-As Veigas | ||
| Araújo | | Araújo | ||
| 3,121,888 | | 3,121,888 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Esgravata | ||
| | | Oraveira | ||
| | | 1,108,130 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Galicia | ||
| | | Viosinho | ||
| | | 7,449,985 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Miragaia | ||
| Luville | | Luville | ||
| | | 5,570,908 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Portuária | | Portuária | ||
| Portuária | | Portuária | ||
| | | 5,498,566 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Rio Sujo | ||
| | | Lagoza | ||
| 2, | | 2,276,349 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Rodaves | ||
| | | Cartaganca | ||
| | | 8,419,673 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Selará | ||
| | | Calorbairro | ||
| | | 2,474,449 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Sonância | ||
| | | Vidal | ||
| 1,349,467 | | 1,349,467 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Turão | ||
| | | Maleta | ||
| | | 4,108,130 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 354: | Line 367: | ||
=== Military === | === Military === | ||
[[File:US_Navy_070223-N-3888C-005_An_AV-8B_Harrier_II_from_the_Spanish_aircraft_carrier_Principe_de_Asturias_(R_11)_hovers_in_for_a_landing_after_a_live_fire_exercise.jpg|thumb|right|An AnAV-8B Harrier II from the Produese aircraft carrier ''Principe de | {{Main|Produese Armed Forces}} | ||
[[File:US_Navy_070223-N-3888C-005_An_AV-8B_Harrier_II_from_the_Spanish_aircraft_carrier_Principe_de_Asturias_(R_11)_hovers_in_for_a_landing_after_a_live_fire_exercise.jpg|thumb|right|An AnAV-8B Harrier II from the Produese aircraft carrier ''Principe de Agudiza''.]] | |||
The armed forces of Produzland are known as the Produese Armed Forces (''Forças Armadas Produesas''). Their [[Commander-in-chief]] is the reigning [[King of Produzland]], [[José III]], following with the Prime Minister and the Minister of Defense respectively in the chain of command. The fourth in authority is the [[Chief of the Defence Staff (Produzland)|Chief of the Defense Staff]] (CEMD). The [[Defence Staff (Produzland)|Defense Staff]] (''Estado-Maior de Defesa'') is responsible for assisting the CEMD as an auxiliary staff. | |||
The armed forces | The Produese armed forces are a professional miltiary consisting of 121,900 active personnel and 4,770 reserve personnel as of 2017. The country also has the 77,000 strong [[Civil Guard]] which comes under the control of the Ministry of Defense in times of a national emergency. The Produese defense budget is 5.71 billion Rozars a 1% increase for 2015. The increase comes because of security concerns in the country. | ||
The Army ( | The [[Produese Armed Forces]] are divided into three branches: | ||
* [[Produese Army|Army (''Exército Terrestre'')]] - The Produese Army consists of 15 active brigades and 6 military regions. Modern infantry have diverse capabilities and this is reflected in the varied roles assigned to them. There are four operational roles that infantry battalions can fulfil: air assault, armoured infantry, mechanised infantry, and light role infantry. The Produese army has the latest technology at its disposal to preserve the territorial integrity of the Kingdom of Produzland. | |||
In addition | * [[Produese Navy|Navy (''Armada'')]] - Under the command of the [[Produese Admiral Chief of Naval Staff]], stationed in [[Burlon]], the Produese Navy has four area commands across the country. The current flagship of the Produese Navy is the [[amphibious assault ship]]/[[aircraft carrier]] [[Produese ship João II (L61)|''João II'']]. In addition, the fleet consists of: 2 amphibious transport docks, 11 frigates, 3 submarines, 6 mine countermeasure vessels, 23 patrol vessels and a number of auxiliary ships. The total displacement of the Produese Navy is approximately 220,000 tonnes. As of 2012, the Armada has a strength of 20,838 personnel. | ||
* [[Produese Air Force|Air Force (''Força do Ar'')]] - Produzland currently has 10 fighter squadrons, each with 18-24 airplanes. The air force also has 15 operational air bases around the country. The air force operates a wide-ranging fleet of aircraft, from fighters to transport aircraft and passenger transports to helicopters. It maintains some 450 aircraft in total, of which around 130 are fighter aircraft, including a number of Lirofighter Typhoons. The Produese Air Force is replacing older aircraft in the inventory with newer ones including the recently introduced Lirofighter Typhoon and the Airbus A400M Atlas airlifter. | |||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
| Line 374: | Line 393: | ||
=== Mountains and Rivers === | === Mountains and Rivers === | ||
Most of mainland Produzland is dominated by high [[plateaus]] and flatland. The Aloísian Islands are mainly mountainous other than the coastal regions, such as with the [[Escarré]] mountain range across the north of Aloísio. There are several major rivers in Produzland such as the [[Goute]], [[Orba]], [[Mazarico]] (Maçarico), and [[Buteira]]. Alluvial plains are found along the coast, the largest of which is that of the Orba in Galícia and [[ | Most of mainland Produzland is dominated by high [[plateaus]] and flatland. The Aloísian Islands are mainly mountainous other than the coastal regions, such as with the [[Escarré]] mountain range across the north of Aloísio. There are several major rivers in Produzland such as the [[Goute]], [[Orba]], [[Mazarico]] (Maçarico), [[Eblá]], and [[Buteira]]. Alluvial plains are found along the coast, the largest of which is that of the Orba in Galícia and [[Agudicia]]. | ||
=== Climate === | === Climate === | ||
[[File:Noriega_1.jpg|thumb|right|The coast north of the | [[File:Noriega_1.jpg|thumb|right|The coast north of the Agudician Mountains features an humid oceanic climate.]] | ||
The Marine West Coast or Oceanic Climate of Produzland has a very mild climate lacking in extreme temperatures. It typically lacks a dry season, as precipitation is consistent throughout the year. Summers are cool due to cool ocean currents, winters are mild usually very cloudy. With Summers below 22 °C (72 °F) and winters above −3 °C (27 °F). | The Marine West Coast or Oceanic Climate of Produzland has a very mild climate lacking in extreme temperatures. It typically lacks a dry season, as precipitation is consistent throughout the year. Summers are cool due to cool ocean currents, winters are mild usually very cloudy. With Summers below 22 °C (72 °F) and winters above −3 °C (27 °F). | ||
| Line 390: | Line 409: | ||
The fauna presents a wide diversity that is due in large part to the geographical position of the Orthurian peninsula between the Aurum and the Rosel at the southwest end of Lira, and the great diversity of habitats and biotopes, the result of a considerable variety of climates and well differentiated regions. | The fauna presents a wide diversity that is due in large part to the geographical position of the Orthurian peninsula between the Aurum and the Rosel at the southwest end of Lira, and the great diversity of habitats and biotopes, the result of a considerable variety of climates and well differentiated regions. | ||
Including the mainland and Aloísio, Produzland has an estimated sixty to seventy thousand species of animal. Of these, about seven hundred are vertebrates (excluding marine fish) and the remainder are invertebrates. The highest degree of endemism occurs among freshwater fish and in the mountainous areas, the coastal areas, and among the Aloísian Island fauna. About 30% of the vertebrates in Produzland are threatened | Including the mainland and Aloísio, Produzland has an estimated sixty to seventy thousand species of animal. Of these, about seven hundred are vertebrates (excluding marine fish) and the remainder are invertebrates. The highest degree of endemism occurs among freshwater fish and in the mountainous areas, the coastal areas, and among the Aloísian Island fauna. About 30% of the vertebrates in Produzland are threatened. | ||
The vegetation of Produzland is varied due to several factors including the diversity of the relief, the climate and latitude. Produzland includes different phytogeographic regions, each with its own floristic characteristics resulting largely from the interaction of climate, topography, soil type and fire, biotic factors. | The vegetation of Produzland is varied due to several factors including the diversity of the relief, the climate and latitude. Produzland includes different phytogeographic regions, each with its own floristic characteristics resulting largely from the interaction of climate, topography, soil type and fire, biotic factors. | ||
| Line 399: | Line 418: | ||
Produzland has a capitalist refining and manufacturing Economy with both lower and higher secondary sectors. Manufacturing is the dominant force in the country with significant contributions from refining. The parts made in Produzland are both exported and made into finished products, though the economic goal of the nation is to export the majority of parts out of the country, while keeping/importing some parts for local manufacturing before exportation. Imports include raw materials as well as finished goods and services from other countries. The resources on hand and the priorities of Produzland influence what type of refinement and manufacturing will take place. Produzland's manufacturing specialties include train parts, automobiles, electronics, and luxury goods. | Produzland has a capitalist refining and manufacturing Economy with both lower and higher secondary sectors. Manufacturing is the dominant force in the country with significant contributions from refining. The parts made in Produzland are both exported and made into finished products, though the economic goal of the nation is to export the majority of parts out of the country, while keeping/importing some parts for local manufacturing before exportation. Imports include raw materials as well as finished goods and services from other countries. The resources on hand and the priorities of Produzland influence what type of refinement and manufacturing will take place. Produzland's manufacturing specialties include train parts, automobiles, electronics, and luxury goods. | ||
[[File:Ferrari_F8_Tributo_Genf_2019_1Y7A5665.jpg|thumb|right|A | [[File:Ferrari_F8_Tributo_Genf_2019_1Y7A5665.jpg|thumb|right|A Bezerra F8 Leite. Produzland maintains one of the largest automotive industries in the world.]] | ||
Produzland has one of the largest automotive industries in the world with world famous luxury cars such as [[ | Produzland has one of the largest automotive industries in the world with world famous luxury cars such as [[Bezerra]], [[Venâncio]], and [[Vila Corrêa]]. By 2016, the automotive industry was generating 8.7 percent of Produzland's gross domestic product, employing about nine percent of the manufacturing industry. By 2008 the automobile industry was the 2nd most exported industry. Produzland is also a major exporter of luxury goods such as jewelry, watches, clothing, etc., [[Gárcere]], and [[Vítor Loureiro]] take center stage in the Produese luxury good industry. | ||
=== Agriculture === | === Agriculture === | ||
[[File:Vineyards_in_Piemonte,_Italy.jpg|thumb|left|Vineyards in Galicia, Produzland is one of the world's largest wine producers.]] | [[File:Vineyards_in_Piemonte,_Italy.jpg|thumb|left|Vineyards in Galicia, Produzland is one of the world's largest wine producers.]] | ||
Produzland is the largest agricultural producer in western Lira, though only about 17% of Produzland's cultivated land was irrigated, it was estimated to be the source of between 40–45% of the gross value of crop production and of 50% of the value of agricultural exports. Produzland is one of the world's largest wine producers, and one of the leading in olive oil, fruits ([[apples]], [[olives]], [[grapes]], [[oranges]], [[lemons]], [[pears]], [[apricots]], [[hazelnuts]], [[peaches]], [[cherries]], [[plums]], [[strawberries]] and [[kiwifruits]]), and vegetables (especially [[artichokes]] and [[tomatoes]]). The most famous Produese wines are probably the Galician [[Granxas]] and the | Produzland is the largest agricultural producer in western Lira, though only about 17% of Produzland's cultivated land was irrigated, it was estimated to be the source of between 40–45% of the gross value of crop production and of 50% of the value of agricultural exports. Produzland is one of the world's largest wine producers, and one of the leading in olive oil, fruits ([[apples]], [[olives]], [[grapes]], [[oranges]], [[lemons]], [[pears]], [[apricots]], [[hazelnuts]], [[peaches]], [[cherries]], [[plums]], [[strawberries]] and [[kiwifruits]]), and vegetables (especially [[artichokes]] and [[tomatoes]]). The most famous Produese wines are probably the Galician [[Granxas]] and the Agudician [[Botelho]]. Other famous wines are [[Mira de Peredo]], [[Da Vale]], [[Salgado]], [[Curbelo]], [[Arra de Viera]], and the sparkling wines [[Troncoso]] and [[Cadavid]]. | ||
The vast majority (99%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), [[grain fields]] take up 31%, [[olive tree orchards]] 8.2%, [[vineyards]] 5.4%, [[citrus orchards]] 3.8%, [[sugar beets]] 1.7%, and [[horticulture]] 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%). | The vast majority (99%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), [[grain fields]] take up 31%, [[olive tree orchards]] 8.2%, [[vineyards]] 5.4%, [[citrus orchards]] 3.8%, [[sugar beets]] 1.7%, and [[horticulture]] 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%). | ||
| Line 421: | Line 440: | ||
[[File:Cesar Baltazar Bridge.jpg|thumb|left|César Baltazar da Araújo Bridge over the Bay of Luville.]] | [[File:Cesar Baltazar Bridge.jpg|thumb|left|César Baltazar da Araújo Bridge over the Bay of Luville.]] | ||
In 2004 the transport sector in Produzland generated a turnover of about 119.4 billion Rozars, employing 935,700 persons in 153,700 enterprises. Regarding the national road network, in 2002 there were 668,721 km (415,524 mi) of serviceable roads in Produzland, including 6,487 km (4,031 mi) of motorways, state-owned but privately operated by [[Almeida | In 2004 the transport sector in Produzland generated a turnover of about 119.4 billion Rozars, employing 935,700 persons in 153,700 enterprises. Regarding the national road network, in 2002 there were 668,721 km (415,524 mi) of serviceable roads in Produzland, including 6,487 km (4,031 mi) of motorways, state-owned but privately operated by [[Almeida S.A.]]. In 2005, about 34,667,000 passenger cars (590 cars per 1,000 people) and 4,015,000 goods vehicles circulated on the national road network. | ||
The national railway network, state-owned and operated by [[Rede Ferroviária | The national railway network, state-owned and operated by [[Rede Ferroviária Produesa (RFP)]], in 2008 totalled 16,529 km (10,271 mi) of which 11,727 km (7,287 mi) is electrified, and on which 4,802 locomotives and railcars run. The main public operator of high-speed trains is [[Saraiva]], part of RFP. Produzland has 11 rail border crossings with its neighbouring countries. | ||
[[File:AVE_Tarragona-Madrid.jpg|thumb|right|High-speed AVE train, Burlon-Cartaganca line.]] | [[File:AVE_Tarragona-Madrid.jpg|thumb|right|High-speed AVE train, Burlon-Cartaganca line.]] | ||
Continental Produzland's territory is serviced by six international airports located near the cities of Portuária, Luville, Burlon and Cartaganca. Luville's geographical position makes it a stopover for many foreign airlines at several airports within the country. The government decided to build a new airport outside Burlon, to replace [[ | Continental Produzland's territory is serviced by six international airports located near the cities of Portuária, Luville, Burlon and Cartaganca. Luville's geographical position makes it a stopover for many foreign airlines at several airports within the country. The government decided to build a new airport outside Burlon, to replace [[Burlão Portela Airport]], though this plan has been suspended due to austerity measures. Currently, the most important airports are in Burlon, Portuária, [[Capella]], and Cartaganca, managed by [[Aeroportos de Produseía]]. [[Ortúria]] is the national carrier airline. | ||
The major seaports are located in Luville, Cartaganca, Maleta, Portuária, Delgado, Detalhe, and Triunfo. | |||
[[File:CartagancaPlane.jpg|thumb|left|upright|A TAP Ortúria aircraft.]] | |||
The three largest metropolitan areas have subway systems: [[Luville Metro]] and [[South Anavede Metro]] in the [[Luville Bay Metropolitan Area]], [[Burlon Metro]] in the [[Burlon-Araújo Metropolitan Area]], and [[Cartaganca Metro]] in the [[Cartaganca Metropolitan Area]], each with more than 35 km (22 mi) of lines. In Produzland, [[Laronha tram services]] have been supplied by Southwest Transport, for over a century. In Portuária, a tram network, of which only a tourist line on the shores of the inner city remains, began construction on September 12th, 1895 (a first for the Orthurian Peninsula). All major cities and towns have their own local urban transport network, as well as taxi services. | The three largest metropolitan areas have subway systems: [[Luville Metro]] and [[South Anavede Metro]] in the [[Luville Bay Metropolitan Area]], [[Burlon Metro]] in the [[Burlon-Araújo Metropolitan Area]], and [[Cartaganca Metro]] in the [[Cartaganca Metropolitan Area]], each with more than 35 km (22 mi) of lines. In Produzland, [[Laronha tram services]] have been supplied by Southwest Transport, for over a century. In Portuária, a tram network, of which only a tourist line on the shores of the inner city remains, began construction on September 12th, 1895 (a first for the Orthurian Peninsula). All major cities and towns have their own local urban transport network, as well as taxi services. | ||
| Line 446: | Line 467: | ||
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
In 2019, the population of Produzland officially reached 61 million people, as recorded by the [[Produese Bureau of Population Statistics (GPEP)]]. Produzland's population density, at 141/km², is lower than that of most Western Liran countries and its distribution across the country is very unequal. With the exception of the region surrounding the capital, Burlon, the most populated areas lie around the coast. The population of | In 2019, the population of Produzland officially reached 61 million people, as recorded by the [[Produese Bureau of Population Statistics (GPEP)]]. Produzland's population density, at 141/km², is lower than that of most Western Liran countries and its distribution across the country is very unequal. With the exception of the region surrounding the capital, Burlon, the most populated areas lie around the coast. The population of Produzland has risen 2 1/2 times since 1900, when it stood at 24.4 million, principally due to the spectacular demographic boom in the 1960s and early 1970s. | ||
=== | ===Urbanisation=== | ||
Produzland's major cities are spread out across the countries territory, with the biggest congestion being in the south and southwest. However most of the population lives in the areas between the larger cities, for example the Goute River basin between Luville and Burlon is a very densely populated area compared to most of Produzland. Another example is the western Rodaves between Portuaria | Produzland's major cities are spread out across the countries territory, with the biggest congestion being in the south and southwest. However most of the population lives in the areas between the larger cities, for example the Goute River basin between Luville and Burlon is a very densely populated area compared to most of Produzland. Another example is the western Rodaves between Portuaria and Cartaganca. | ||
{{Largest Cities in Produzland}} | {{Largest Cities in Produzland}} | ||
| Line 489: | Line 510: | ||
}} | }} | ||
Until the middle ages, Produzland was a religiously diverse nation, however holding a clear Verroin majority, then several institutions, most notably The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition, commonly known as the [[Produese Inquisition]] (Inquisição | Until the middle ages, Produzland was a religiously diverse nation, however holding a clear Verroin majority, then several institutions, most notably The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition, commonly known as the [[Produese Inquisition]] (Inquisição Produesa), were established in the late middle ages and early modern era. They were intended to maintain Verroism in their kingdoms and territories. According to modern estimates, around 150,000 were prosecuted for various offenses during the three-century duration of the Produese Inquisition, out of which between 3,000 and 5,000 were executed (~2.7% of all cases). Despite a low conviction number compared to the whole of the population, many member of minority religions fled to more tolerable nations, making Produzland a homogeneous nation religiously until the 20th century with the rise of atheism and others related groups taking prevalence as a strong minority in the country that has been steadily growing ever since. | ||
===Language=== | ===Language=== | ||
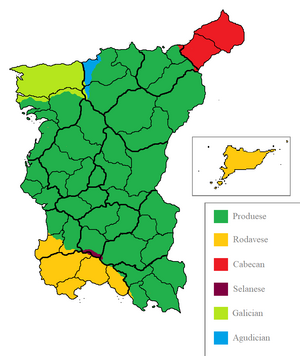
Produese, described in the constitution as Cavalian, is an Orthurian language rooted in Orthurian and Old Aenian. | Produese, described in the constitution as Cavalian, is an Orthurian language rooted in Orthurian and Old Aenian. Cavallian Produese is the official dialect of Produese as it was used by the medieval kingdom of Cavale that unified the country, however many variations of Produese are present, including the Galician and Esgravatan dialects, the former of which is sometimes classified as a separate language. States are allowed co-official languages alongside Produese, and the whole country recognized two co-official languages, Rodavese and Cabecan. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Produese Languages 1.png|thumb|left|Languages of Produzland.]] | ||
The two largest minority languages are Rodavese and Cabecan. Rodavese is, like Produese, an Orthurian language rooted in the language that dominated the Orthurian Empire, it's main derivative is [[Old Calmatian]], which at the time was spoken in most of southern Produzland until the language was pushed further south by Produese Cavallians. Rodavese is now mainly spoken in southern Portuária, the Rodaves, and the Aloísian Islands. | The two largest minority languages are Rodavese and Cabecan. Rodavese is, like Produese, an Orthurian language rooted in the language that dominated the Orthurian Empire, it's main derivative is [[Old Calmatian]], which at the time was spoken in most of southern Produzland until the language was pushed further south by Produese Cavallians. Rodavese is now mainly spoken in southern Portuária, the Rodaves, and the Aloísian Islands. | ||
Cabecan however is a language isolate that has no identifiable relatives. Despite Deustoist efforts to erase the Cabecan language, seen in the mostly Cavallian names of Cabecan cities, Cabecan speakers are still prevalent in the state and surrounding historic Cabecan lands such as [[Cabeca Alba]] in Meronnia, and western [[Cisparrania]]. A language map of the border region between Produzland, Cisparrania, and Meronnia roughly mirrors the historic borders of the Cabecan Kingdom of Velarre. | Cabecan however is a language isolate that has no identifiable relatives. Despite Deustoist efforts to erase the Cabecan language, seen in the mostly Cavallian names of Cabecan cities, Cabecan speakers are still prevalent in the state and surrounding historic Cabecan lands such as [[Cabeca Alba]] in Meronnia, and western [[Cisparrania]]. A language map of the border region between Produzland, Cisparrania, and Meronnia roughly mirrors the historic borders of the Cabecan Kingdom of Velarre. | ||
There are also several smaller recognised languages in their native states, such as [[Selanese]], a close relative of Rodavese with about 50,000 speakers, mostly in the [[Rigeu]] province. [[Galician]], a minor language in the north of Galícia and small parts of Agudicia that most consider a dialect of Produese but remains a recognised minority language. And finally [[Agudician]], a language closely related to Galician spoken only in the west of the [[Detalhe]] province. | |||
Produzland has other small minorities of speakers of [[Parthonopian]], [[Solician]], and several [[Jashnagari]] languages. | Produzland has other small minorities of speakers of [[Parthonopian]], [[Solician]], and several [[Jashnagari]] languages. | ||
As a percentage of the general population of all Produzland, Produese is | As a percentage of the general population of all Produzland, Produese as a first or second language is spoken by 99% of the population, while Rodavese by 20%, and Cabecan by 5% of all Produes. | ||
===Health=== | ===Health=== | ||
[[File:Oil-1383546_1920.jpg|thumb|right|Olive oil and vegetables are central to the Orthurian diet.]] | |||
The Produese state runs a universal public healthcare system since 1990. However, healthcare is provided to all citizens and residents by a mixed public-private system. The public part is the [[Serviço Nacional de Saúde]], which is organised under the [[Ministry of Health]] and administered on a devolved regional basis. Healthcare spending in Produzland accounted for 9.2% of the national GDP in 2012. | |||
Life expectancy in Produzland is 80 for males and 85 for females. In comparison to other Western countries, Produzland has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), as there are several health benefits of the [[Orthurian diet]]. The proportion of daily smokers was 22% in 2012, down from 24.4% in 2000 but still slightly above the world average. Smoking in public places including bars, restaurants, night clubs and offices has been restricted to specially ventilated rooms since 2005. | |||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
State education in Produzland is free and compulsory from the age of six to sixteen. The current education system is regulated by the 2006 educational law, [[LOE (Lei Orgânica da Educação)]], or Fundamental Law for the Education. In 2014, the LOE was partially modified by the newer and controversial [[LOMQE law (Lei Orgânica para a Melhoria da Qualidade Educacional)]], or Fundamental Law for the Improvement of the Education System. Since 1970 to 2014, Produzland has had seven different educational laws (LGE, LOECE, LODE, LOGSE, LOPEG, LOE and LOMQE). | |||
[[Instituição Livre de Educação]] was an educational project that developed in Produzland for the half a century of about 1876–1936 by [[André da Moura]] and [[Quirino Garcia]]. The institute was inspired by the philosophy of Krausism. Concepção Varela in feminism and [[Francés Baiget i Sitjar]] in neuroscience were in the movement. | |||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
| Line 513: | Line 546: | ||
===Art=== | ===Art=== | ||
[[File:Personificación_del_Verano.jpg|275px|thumb|right| | [[File:Personificación_del_Verano.jpg|275px|thumb|right|upright|Aníbal Inácio Monteiro, Personificação do Verão.]] | ||
Produzland has historically been a hub for flourishing artists, as one of the leading nations of the Renaissance, and cultural centers of Lira, Produese artists have been highly influential in the development of various Liran artistic movements. Due to historical, geographical and generational diversity, Produese art has known a great number of influences from the nation's Orthurian roots to its northern Gostic influences. | Produzland has historically been a hub for flourishing artists, as one of the leading nations of the Renaissance, and cultural centers of Lira, Produese artists have been highly influential in the development of various Liran artistic movements. Due to historical, geographical and generational diversity, Produese art has known a great number of influences from the nation's Orthurian roots to its northern Gostic influences. | ||
During the Renaissance and Golden Age, painters working in Produzland include [[Osório Da Rosario]], [[Luca Melo]], [[Balduíno Hernandes]], [[José de Ribeira]], and [[Maurício Simões]]. Also in the Baroque period [[Diogo Varejão]] created some of the most famous Produese portraits, such as [[O Alcance do Fim]] and [[O Dormente]] | During the Renaissance and Golden Age, painters working in Produzland include [[Osório Da Rosario]], [[Luca Melo]], [[Balduíno Hernandes]], and [[José de Ribeira]], as well as Late Renaissance painters [[Aníbal Inácio Monteiro]] and [[Maurício Simões]]. Also in the Baroque period [[Diogo Varejão]] created some of the most famous Produese portraits, such as [[O Alcance do Fim]] and [[O Dormente]]. | ||
[[Rodrigo Vila]] | [[Ricardo Lobo de Casado]] painted during a historical period that includes the [[Great Continental War]], the rise of Liberalism, and the emergence of nationalism. And during the 20th century, artists like [[Rodrigo Vila]] became influential as a well-known modern impressionist painter as well as many other important Produese painters belonging to the modernism art movement, including [[Feliciano Seixas]], | ||
[[Ângelo Azevedo]], and [[César Sapateiro]]. | [[Ângelo Azevedo]], and [[César Sapateiro]]. | ||
| Line 535: | Line 566: | ||
Traditional architecture is distinctive and include [[Vincennine]], also known as Produese late Gothic a sumptuous, composite Produese style of architectural ornamentation of the first decades of the 16th century, followed by [[Saldanine]] style of the 18th century. A 20th-century interpretation of traditional architecture, Soft Produese style, appears extensively in major cities, especially Luville. | Traditional architecture is distinctive and include [[Vincennine]], also known as Produese late Gothic a sumptuous, composite Produese style of architectural ornamentation of the first decades of the 16th century, followed by [[Saldanine]] style of the 18th century. A 20th-century interpretation of traditional architecture, Soft Produese style, appears extensively in major cities, especially Luville. | ||
The arrival of Modernism in the academic arena produced much of the architecture of the 20th century. An influential style centred in Cartaganca, known as modernisme, produced a number of important architects, of which [[Valentí Sugrañes]] is one. Produzland is currently experiencing a revolution in contemporary architecture and | The arrival of Modernism in the academic arena produced much of the architecture of the 20th century. An influential style centred in Cartaganca, known as modernisme, produced a number of important architects, of which [[Valentí Sugrañes]] is one. Produzland is currently experiencing a revolution in contemporary architecture and Produese architects like [[Menna Sadurní]], [[Vicente Guiu]], and [[Francisco Lodeiro]] as well as many others have gained worldwide renown. | ||
===Literature=== | ===Literature=== | ||
[[File:Miguel_de_Cervantes_at_the_National_Library.jpg|thumb|left|upright|Francisco de Valente is one of the most famous writers of the early modern era.]] | |||
The earliest recorded examples of vernacular [[Romance]]-based literature date from the same time and location. Until 1350, Produese troubadours spread their literary influence to most of the [[Orthurian peninsula]]. [[Luís de Magalhães]] was one of the founders of Produese dramatic traditions. Adventurer and poet [[Vasco da Cunha]] wrote the epic poem [[Os Lusíadas]] (The Lusiads). | |||
The Baroque is the most important period of Produese culture, as it corresponded with the era of Produese Empire. The famous [[Dom Calixto das Veigas]] by [[Francisco de Valente]] was written in this time. Other writers from the period are: [[Olegário Alves]], [[Francisco da Araújo]], [[Tomás Brandão]], and [[Gervásio Machado e Almeida]]. | |||
Modern Produese poetry is rooted in neoclassic and contemporary styles, as exemplified by [[Jerónimo de Gusmão]], [[Octávio Ribeiro]], and [[Ronaldo Bastos]]. Modern Produese literature is represented by authors such as [[Fernando Tavares]], [[Eduarda Correia]], [[Liana de Oliveira]], [[João Ramos]], and [[Cristiano Medeiros]]. | |||
The [[Prêmio Enéas de Guerra]] and the [[Francisco de Valente Prize]] are the two main awards nowadays in Produese literature. | |||
===Philosophy=== | ===Philosophy=== | ||
| Line 546: | Line 586: | ||
The Enlightenment in Produzland arrived later and was less strong than in other Liran countries, but during the 19th century liberal ideas arrived in Produese society. At the end of the century, socialist and libertarian ideas also flourished, with thinkers such as [[Carles Montículo i Margall]], [[Ricardo Salcária]] and [[Guilherme Pereira]]. | The Enlightenment in Produzland arrived later and was less strong than in other Liran countries, but during the 19th century liberal ideas arrived in Produese society. At the end of the century, socialist and libertarian ideas also flourished, with thinkers such as [[Carles Montículo i Margall]], [[Ricardo Salcária]] and [[Guilherme Pereira]]. | ||
In the first half of the 20th century among the most prominent philosophers were [[Maria Braga]] and [[José Outeiro e Collette]]. | In the first half of the 20th century among the most prominent philosophers were [[Maria Braga]] and [[José Outeiro e Collette]]. Contemporary philosophers include [[Fernando Velasco]] and [[Adela Delchiaro]], creator of the term aporophobia. | ||
===Music=== | |||
[[File:Belen_maya.jpg|thumb|right|upright|Flamenco is a Selanese artistic form.]] | |||
Produese music is often considered abroad to be synonymous with [[flamenco]], a West Selanese musical genre, which, contrary to popular belief, is not widespread outside southern Produzland. Various regional styles of folk music abound in [[Agudicia]], the [[Rodaves]], [[Portuária]], [[Cavale]], [[Cabeca]], [[Galícia]], [[Sonância]] and [[Miragaia]]. Pop, rock, hip hop and heavy metal are also popular. | |||
In the field of classical music, Produzland has produced a number of noted composers such as [[Eduardo de Coimbra]], [[Joaquim Botelho]], [[Teodósio Monteiro]] and singers and performers such as [[Túlio Tavares]], [[Calisto de Moniz]], [[Carlos Cerqueira]], [[Martinho Abreu]]. In Produzland there are over forty professional orchestras, including the [[Orquestra Simfònica de Cartaganca]], [[Orquestra Nacional de Produseía]] and the [[Orquestra Sinfônica de Burlão]]. Major opera houses include the [[Teatro Real]], the [[Gran Teatre del Liceu]], [[Teatro Vergé]] and the [[Grande Teatro da Rainha Lúcia]]. Thousands of music fans also travel to Produzland each year for internationally recognised summer music festivals, which often feature the top up and coming pop and techno acts. Music festivals mark Produzland as an international music presence and reflect the tastes of young people in the country. | |||
The most popular traditional musical instrument, the guitar, originated in Produzland. | |||
===Cinema=== | ===Cinema=== | ||
[[File:Cannes film festival general.jpg|thumb|right|upright|The Maleta Film Festival is one of the largest in Lira.]] | |||
Produese cinema has achieved major international success including awards for recent films such as Marinho and Costa. In the long history of Produese cinema, the great filmmaker [[Henrique Fontes]] was the first to achieve world recognition, followed by [[Evaristo Carriço Cruz]] in the 1980s. | |||
Produese cinema has also seen international success over the years with films by directors like [[Rodrigo Barreto]], [[Filipe de Furtado]], [[Felip Castany]], [[Matties Pierre]], [[Andreu Goday]], [[Ignasi Espinalt i Gari]], [[Miguel Pereira]], [[Maximiliano Brito]], and [[Camilo Silveira]]. | |||
Actresses [[Rosana Leite]] and [[Irina Cruz]] or actor [[Valentin Alvim]] are among those who have become international stars. | |||
===Fashion=== | International Film Festivals of [[Maleta]] and [[San Aurelio]] are the oldest and most famous of Produzland. | ||
===Fashion and Design=== | |||
[[File:Prada_milano.JPG|thumb|right|upright|Paladell shop in Luville.]] | |||
Produese fashion has a long tradition, and is regarded as one most important in the world. [[Luville]], [[Bresbon]] and [[Burlon]] are Produzland's main fashion capitals. Major Produese fashion labels, such as [[Gárcere]], [[Vítor Loureiro]], [[Veciana]], [[Paladell]], [[Vilarbebó]], [[Vasconcelos]], and [[Saldanha]], to name a few, are regarded as among the finest fashion houses in the world. Also, the fashion magazine [[Lia Produseía]], is considered one of the most prestigious fashion magazines in the world. | |||
Produzland is also prominent in the field of design, notably interior design, architectural design, industrial design and urban design. The country has produced some well-known furniture designers, such as [[Liana Cortes]] and [[Lluïsa Bigorra]]. Examples of classic pieces of Produzland white goods and pieces of furniture include [[Genoveva's]] washing machines and fridges, new tone sofas by [[Amorim]], and the post-modern bookcase by Lluïsa Bigorra. Today, Luville and [[Vidal]] are the nation's leaders in architectural design and industrial design. The city of Luville hosts [[Feira de Luvilha]], Lira's largest design fair. Luville also hosts major design and architecture-related events and venues, such as the [[Expo de Móveis]], and has been home to the designers [[Casimiro Carneiro]], [[Carlos Alves]], [[Antelmo Mendonça]], and [[Tomé de Sequeira]]. | |||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
| Line 564: | Line 621: | ||
Produese cuisine consists of a great variety of dishes which stem from differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by seafood available from the waters that surround the country, and reflects the country's deep Orthurian roots. Produzland's extensive history with many cultural influences has led to a unique cuisine. In particular, three main divisions are easily identified: | Produese cuisine consists of a great variety of dishes which stem from differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by seafood available from the waters that surround the country, and reflects the country's deep Orthurian roots. Produzland's extensive history with many cultural influences has led to a unique cuisine. In particular, three main divisions are easily identified: | ||
Southern Produzland – all such coastal regions, from | '''Southern Produzland''' – all such coastal regions, from Miragaia to the Rodaves – heavy use of seafood, such as [[peixe frito]] (fried fish); several cold soups like [[gazpacho]]; and many rice-based dishes like [[paella]] from [[Portuária]] and arròs negre (black rice) from the [[Rodaves]]. | ||
Inner Produzland – Cavale – hot, thick soups such as the bread and garlic-based Cavallian soup, along with substantial stews such as [[cozido burlenho]]. Food is traditionally conserved by salting, such as Produese ham, or immersed in olive oil, such as [[ | '''Inner Produzland''' – Cavale – hot, thick soups such as the bread and garlic-based Cavallian soup, along with substantial stews such as [[cozido burlenho]]. Food is traditionally conserved by salting, such as Produese ham, or immersed in olive oil, such as [[Vegano cheese]]. | ||
Northern Produzland – the whole Northern coast, including | '''Northern Produzland''' – the whole Northern coast, including Agudician, Cabecan, Sonâncian and Galícian cuisine – vegetable and fish-based stews like [[caldo gallego]] and [[marmitako]]. Also, the lightly cured lacón ham. The best known cuisine of the northern countries often rely on ocean seafood, as in the Cabecan-style cod, albacore or anchovy or the Galician octopus-based [[polbo á feira]] and shellfish dishes. | ||
===Sports=== | ===Sports=== | ||
[[File:Sergio_Perez_2011_Malaysia_FP1.jpg||thumb|right|upright|José Quintana at the 2011 Bondragonne Grand Prix]] | |||
While varieties of football have been played in Produzland as far back as Orthurian times, sport in Produzland has been dominated by football since the early 20th century. Real Burlão C.F. and FC Cartaganca are two of the most successful football clubs in the world. The country's national football team won the UEFA Liran Football Championship in 1964, 2008 and 2012 and the World Cup in 2010, and is the first team ever to win three back-to-back major international tournaments. | |||
[[File:FC Cartaganca.jpg|thumb|left|upright|FC Cartaganca is one of the most successful football clubs in the world.]] | |||
Basketball, tennis, cycling, handball, futsal, motorcycling and, lately, Formula One also can boast Produese champions with racing teams such as [[Verdadeira Bezerra]] and [[Gárcere Racing]]. Today, Produzland is a major world sports powerhouse, especially since several major sports tournaments have been hosted in Produzland, which stimulated a great deal of interest in sports in the country. The tourism industry has led to an improvement in sports infrastructure, especially for water sports, golf and skiing. In their respective regions, the traditional games of Cabecan pelota and Portuárian pilota both are popular. | |||
===Society=== | ===Society=== | ||
[[File:Día_de_la_Hispanidad_Granda_2007_(05).jpg|thumb|right|Parade for Feriado Nacional de Produseía (June 20th) in Granarón.]] | |||
Produzland remains a conservative society for the most part, aside from a few exceptions such as the Rodaves. Most Produes support traditional values, corresponding with the fact most Produes follow [[Verroism]], with varying degrees of practice. However Produzland is legally tolerant towards all human rights. The [[Produese Constitution of 1980]] "protect all Produes and all the peoples of Produzland in the exercise of human rights, their cultures and traditions, languages and institutions". Produzland provides one of the highest degrees of liberty in the world for its LGBT community. A poll in 2013 by [[GPEP]] on acceptance of homosexuality stated 88% of those surveyed responded that homosexuality should be accepted. Produzland also has one of the lowest rates of gender inequality in the world, with several laws favouring men from the [[Deusto Era]] being repealed with the restoration of the monarchy. | |||
Drug laws are one of the many things in Produzland decided by state law. For example all recreational drugs are illegal in the state of [[Burlon]], but many are legal in [[Miragaia]]. However advertising for drugs is forbidden by law, as well as drug usage under 18 nationwide. Despite anti-drug laws, drug usage is common across the nation, one study conducted in 2006 found that almost 94% of [[Produese Rozar]] bank notes in Produzland carry small traces of cocaine. | |||
Produese national pride consistently ranks high compared to most of Lira, football is a major source of pride for Produes, as the [[Produese National Football Team]] is one of the most popular in the world. The [[Feriado Nacional de Produseía]] is the only official secular holiday, it takes place on June 20th for the Coronation of [[Henrique I]] as king of the Kingdom of Cavale and the Kingdom of Agudicia, de facto uniting the Kingdom of Produzland. | |||
[[Category:Produzland]] [[Category:Greater Olympus]] | [[Category:Produzland]] [[Category:Greater Olympus]] | ||
{{Template:Greater Olympus info pages}} | {{Template:Greater Olympus info pages}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:43, 28 May 2021
Kingdom of Produzland [a] O Reino de Produseía (Produese) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Nos Sustinere." | |
| Anthem: "A Marcha Real" "A Marcha Real" | |
 Official map of the Kingdom of Produzland | |
| Capital | Burlon |
| Largest city | Burlon |
| Official languages | Produese |
| Recognised regional languages | Produese, Cabecan, Rodavese |
| Ethnic groups (2015) | Produes 89.70% Cabecans 3.612% Others 6.79% |
| Demonym(s) | Produes, Produese |
| Government | Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy |
| Riccardo Bonadeo, PP | |
| Legislature | Tribunais Gerais |
| Senate | |
| Congress of Deputies | |
| Kingdom | |
• Cavale and Galicia Split | March 4th, 987 |
• Unification of Cavale and Galicia | February 19th, 1140 |
• West Bresbon Decrees | January 15th, 1715 |
• Establishment of the Federal Republic of Produzland | July 16th, 1935 |
• Restoration of the Monarchy | February 18th, 1980 |
| Area | |
• | 434,622.52 km2 (167,808.69 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 61,432,763 (20) |
• 2019 census | 61,432,763 |
• Density | 141/km2 (365.2/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | 627,875,000,000 |
• Per capita | 10,220 |
| Gini (2011) | 34.67 medium |
| HDI (2011) | 0.781 high |
| Currency | Rozar (ROZ) |
| Date format | mmddyyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +55 |
| ISO 3166 code | PR |
| Internet TLD | .prd |
Produzland, officially, the Kingdom of Produzland (Produese: O Reino de Produseía), is a sovereign state in Greater Olympus. Produzland is located on the western half of the Orthurian Peninsula in Southwest Lira. Produzland borders the Aurum Ocean in the west, and Meronnia in the North-East, as well as Parthonopia in the east. The Kingdom covers an area of 434,622.52 square kilometers with an oceanic and mediterranean climate. It is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with 61 million inhabitants (2019) and King José III as king since 2019.
During antiquity, a group of people known as Aenians invaded the Orthurian Peninsula, the Aenians were called the "Produese" as they mixed with the local Orthurians of the the Orthurian province of Produsia. After the fall of the Orthurian Empire, the most notable nations to arise were Agudicia and Calmatia. West Agudicia split from Agudicia to become Cavale a few centuries later. After the division of Calmatia over the course of the middle ages Cavale conquered most of Western Orthuria and became the successor state to Produsia. After a history of imperialism and many royal dynasties, the empire fell apart over the course of the late 1800s and early 1900s. This resulted in a dictator seizing control of Produzland in 1935. The dictatorship was removed in 1980 with the monarchy being restored and Produzland in the modern day being a leading nation in Liran politics.
Produzland is ones of the leading countries in seafood production. luxury items, and automobiles. Manufacturing is the dominant force in the country with significant contributions from refining. The parts made in Produzland are both exported and made into finished products, though the economic goal of the nation is to export the majority of parts out of the country, while keeping/importing some parts for local manufacturing before exportation. Imports include raw materials as well as finished goods and services from other countries. The resources on hand and the priorities of Produzland influence what type of refinement and manufacturing will take place. Produzland's manufacturing specialties include trains, automobiles, luxury goods, and electrical equipment.
Etymology
The Orthurian Empire named their westernmost province Produsia, meaning "Land of Carrots", which would evolve into Produzland in Lorian. The Aenians adopted this name from the Orthurians when they migrated to the land during antiquity. However "Produzland" throughout history was mainly used as a geographic term referring to the western half of the Orthurian Peninsula. Historians today mostly refer to the personal union of Agudicia and Cavale starting in the 14th century as the beginning of the country of Produzland for simplicity, as "Produzland" was really a complex entity of unions of crowns and kingdoms. The kings of the realm at the time might have even referred to themselves as the kings of the Produzlands plural to represent the several kingdoms under their rule with loose cultural connections. Produese meant more a person from western Orthuria in general rather than as a nationality. For example a Rodavese person at the time might have called themselves Produese, not insinuating that the Rodaves didn't have a national identity, but rather Produese as a superclass encompassing all the realms in western Orthuria such as the Rodaves, Cavale, and Agudicia.
The Rodavese Revolution of the 1640s most likely kicked off the identity that Produese was a nationality referring to Cavale and Agudicia rather than a superclass even when the Rodaves was reunited with the realm later on. Another reason is to foreign powers it was easier to refer to it as such rather than the complex and nuanced entity "Produzland" really was.
Produzland didn't come as a reference to one kingdom and one kingdom only until the West Bresbon Decrees of 1715 formally united Agudicia and Cavale into one entity.
History
Early History (-490)
There is little written record of the first civilizations in modern Produzland, however archaeological evidence marks the oldest traces of human life in the region around 1.3 million years ago, living hunter-gatherer lifestyles, and making use of the main rivers of the country in the As Vega and Galicia. The region was the agricultural heartland of Orthuria until the region was brought under the rule of the Orthurian Empire. They named the province Produsia, after the abundance of carrots in the region. Produsia became an integral part of the empire until the Aenian people of northern origin were migrating throughout northwest Orthuria, they set up multiple kingdoms in the north under Aenian control. northern Produsia still had a very large Orthurian population at the time, and the breeding between the two people groups would eventually form the majority population of the region until the modern day.
Orthurian Produsia and Early Middle Ages (490-1140)
Under the rule of the Orthurians two main people groups rose to prominence in the west, the Aenians and Calmatians. With the fall of the Orthurian Empire over the course of the 5th century, the two people groups had set up their respective domains. Similar to the Aenians, the Calmatians were a fractured and spread people group, at some points Calmatian kingdoms would comprise territory even north of the Mazarico River, where they took the great city of Olivrium from the Orthurians. During the 6th, 7th, and 8th centuries the Aenians had unified under one country, the Kingdom of Agudicia, while the Calmatians remained fractured, but began to form proper nationstates including the Kingdom of the Rodaves, the Kingdom of Selara, and the Kingdom of Cadascun, later known as Portuária, however at the time the three kingdoms all spoke a common language, Calmatian, the predecessor to modern Rodavese as the language was pushed South by the early Produese.
Due to a succession crisis in Agudicia in 879, the country was divided into West Agudicia and East Agudicia, the former being ruled by the bastard son of King Alfonso II of Agudicia, Ferdinand and the Galician House of Fonseca, and the latter ruled by Alfonso's legitimate son Vicente and the already Agudician ruling House of Outeiro. West Agudicia and East Agudicia both held large chunks of territory from Aenian expansion southward since the beginning of the middle ages, East Agudicia held the old united capital of Relâmpago, while West Agudicia originally made Aldeia the capital of the new country.
The crown of West Agudicia split in 997 after the death of Ramiro II of West Agudicia, he split the country into north and south, the north known as the Kingdom of Galicia, a historical name for the region, ruled by his brother Alfonso III, the south took the name "O Reino de Cavela", or the Kingdom of Cavale ruled by Ramiro II's cousin Ferdinand III.
Late Middle Ages (1140-1486)
The crowns of Cavale and Galicia unified again under King Peter I of Cavale and Galicia. This nation state would become the leader of Produese unification and the predecessor state of Produzland. During this period the country is often referred to as simply Cavale. This became an era for advancement for the region, Cavale was cemented as the dominant Produese state. Vincent II wanted to guarantee this and set his eyes on the historic Orthurian city of Luville, which had been in Calmatian hands for centuries. King Vincent personally led an army to the walls of Luville. Luville had always been poorly held by the Calmatians for the last few centuries as their northernmost territory, however Cavallian monarchs had never seized the opportunity. Vincent II led an army directly to Luville while another fought their way to the banks of the Mazarico to cut off Calmatian reinforcements from the city. The city was captured and prestige grew for the united kingdom.
The Conquest of Luville firmly set Cavale as the leading power in western Orthuria, and to some is the beginning of what is known as Desiderium Meridionali, "The Southern Desire", representing Cavale's desire to reach the Rosel Sea and bring all of western Orthuria under their rule. It would continue until the 16th century, and Cavale began to expand into Selará and Portuária. Portuária was captured in 1249 and Calorbairro five years later. The break-up of Calmatia in the early Middle Ages into competing kingdoms helped the long embattled northern Aeno-Orthurian kingdoms gain the initiative in southern Orthuria. The capture of the strategically central city of Araújo in 1084 marked a significant shift in the balance of power in favour of Cavale and Galicia. Following a great resurgence in the 12th century, the great Selanese strongholds in the south fell to Cavale in the 13th century—Rigeu in 1261 and Cojazeira in 1284. and Cavale gained direct access to the Rosel Sea in 1376 with the fall of the Rodavese stronghold Quiàs.
In the 13th century the Kingdom of Velarre and the Agudician Duchy of Sonância had been in fierce competition over Cabeca. Velarre forming out of the Kingdom of Lurrak in the 1100s. While Sonância was Aenian as opposed to Cabecan like Velarre, they still vied for power in the region ever capturing the city of Lurrak itself, renaming it to San Aurelio after the Saint Aurelius.
Due to Gabriel V of Agudicia being incapable of ruling, the Cavallians took the opportunity to press their claim to eastern Galicia, which spiralled into the War of the Thymes in 1301, the war soon turned into a war of succession when the Cavallian king was killed in battle, which with the help of Philip III the Vain and the Sonâncians put Henry I, Count of Lugo on the throne of Agudicia and Cavale in 1308, leaving the two as independent kingdoms under one monarch. At this point they were practically united however. This began the de facto Kingdom of Produzland. The realm had several problems that would plague it for the coming decades, however after time the people of the country would come together and a string of competent monarchs would come to create one of the most powerful nations and empires in history.
Early Produese Empire (1486-1550)
In 1486 Ferdinand VI took the Produese throne from his father, which historians claim as the beginning of the Produese Golden Age, encouraging the Parthonopian Renaissance in the country with artists like Osório da Rosario, Luca Melo, and Balduíno Hernandes. Ferdinand VIII is also regarded as the founder of the Produese Empire, over the course of the 16th and 17th centuries, the Produese Empire expanded it's influence heavily in Nori and it's southeastern islands. The first example in 1513 explorer Antão do Ortigão became the first Liran to land on mainland Nori, despite failing to colonize mainland Nori, this opened up the gateway for Produzland to become the dominant Liran power in east Nori. Twenty years later in 1533 Ortigão and company landed on the Strait of Marque island of Comona, establishing São Diogo. Years later another company landed on the mainland and established the colonies of Nova Agudiza and Sinais Alto e Baixo in modern Carelia. The trade of the empire made the monarchy immensely wealthy and the gold of the southeast flowed back to Burlon.
In 1500, the wealthy Republic of the Rodaves, the last Calmatian realm remaining in west Orthuria began to collapse with wars with Parthonopia and King Ferdinand took the opportunity to seize the republic. The Rodaves had aspirations on Rodavese-speaking lands in southern Produzland, but the Rodaves couldn't afford to go to war with Produzland with their colonial bids draining the republic's treasury. Until King Ferdinand took the fight to the Rodavese, personally lead a sacking of the city of Cartaganca. After the fall of the Rodavese capital, the Rodavese forces across the country began to collapse and the Rodaves was annexed, marking an end to the half-millenia long Desiderium Meridionali. Rebellion and sparse guerilla fighting in the former republic would continue until the Rodavese Revolution of 1643.
Produzland allied with the neighboring nations of Parthonopia, Meronnia, and Velarre to halt Lunderfrausian advances southward, Produzland supplied troops to the famous Siege of Lepanto, a victory for the southern powers. During the war, Ferdinand VI seized several islands north of the Lunderfrausian coast, using Ferdinand's claim to the islands through his wife as a casus belli. Furthering Produzland's position as the leading power in Lira.
When Ferdinand VI passed in 1521, he left Produzland in the best position in Lira, however tragedy struck when his son Henry III, was murdered in a jousting accident in 1539, this lead way however to second son Joseph the Colonizer to revamp the Produese Empire in east Nori with the Produese Gulf Company to promote Produzland to the richest nation in Lira, and the House of Lugo one of the richest in the world.
Joseph's first major feat in his reign being in 1543 when Jorge Adão da Coutinho landed in southern Kiteahu and established Fort Santa Ángela on an island he called Cavaco. Coutinho also landed in the eastern islands of modern Jashnagar a few years later, which he and his fleet gave it the name 'Jaixnágar'.
Vincennine Produzland (1550-1700)
Tensions with Meronnia were present over the last few decades, mainly as colonial rivals in south-east Nori and Cabeca, which recently was a source for tension as the Kingdom of Velarre became a vassal of Meronnia. The Lugos decided to set up several agreements with their northern neighbor including several arranged marriages and giving Produzland influence in Nori and Meronnia in Meridiq in the Treaty of Relâmpago. After Joseph I passed in 1550, he was replaced with his son Philip, and through his mother Philip also inherited the Kingdom of Meronnia in 1551 leaving him as King Philip I & IV of Produzland and Meronnia and he one of the most powerful men in history as Produzland continued their colonial reign in east Nori.
In 1582 when King Philip died, he split his empire in two with his son Vincent III inheriting Produzland and his daughter Ermelina I inheriting Meronnia and beginning the Meronnian branch of the House of Lugo. The two nations stayed very close allies throughout history though.
In 1612, rivalries with northern Lira and disputes between Lunderfrau and the Lugos over islands in the Esketres Sea, especially Lunderfrausian protests to the Produese inquisition in the territory spiraled into the 20 Years War, in which Produzland and Lugo prestige suffered a catastrophic defeat, and the Lugos lost their monopoly on Norian trade. The war became worse for Produzland when the Rodavese Revolution sprung up, as well as revolts in in Produese owned Cabeca, causing King Vincent IV to effectively lose control of the former. Unlike the previous independent Rodavese state, the Rodaves became a kingdom and crowned Louis of the House of Beltrão as King Louis I of the Kingdom of the Rodaves. At the same time Meronnia became involved in their own religious war in which Produzland was heavily involved in to continue Verroist rule in the nation. This became another defeat for the Lugos as they were deposed in Meronnia in 1684.
Beltrão Produzland (1700-1818)
In early 1700 Charles I died childless, following the rules of Produese succession the crown passed to King Louis II of the Rodaves of the House of Beltrão. Louis III would pass however before he could be crowned, leaving the thrones of Produzland and the Rodaves in the hands of his five year old son Prince Vícenç de Beltrà i Portell. Vícenç became Vincent V of Produzland and Vincent II of the Rodaves. However the Kingdom of Parthonopia, a staunch ally of the Rodaves rejected the idea of a personal union between Produzland and the Rodaves, so Parthonopia declared war in 1701. The young king's regent was his uncle Carles, Duke of Argilés who responded quickly to the Parthonopian war. However after a couple of major naval defeats in the Rosel Sea Produzland and the Rodaves surrendered in 1709. In the Treaty of Piombino, Produzland gave up the island of Aloísio to become a kingdom in a union with Parthonopia. It also ceded parts of eastern Turon and several other border regions. The border established in the treaty is the one that remains till today between the two countries.
Vincent was formally crowned in Araújo by the Archbishop of Araújo earlier that year at the age of 15. One of his earliest acts was the dissolution of the current feudal system in Produzland, removal of any regional power with the Crown of Agudicia, and formal integration of the Kingdom of the Rodaves into the larger kingdom, all included in the West Bresbon Decrees of 1715. This also de jure established the centralized Kingdom of Produzland.
In 1734, at the age of 39 Vincent V began expanding the borders of Produzland into the regions he saw fit. With an alliance with Meronnia, Produzland and Meronnia invaded the financially struggling Kingdom of Velarre and deposed Louis II, who 50 years before had escaped vassalage of Meronnia in the Meronnian religious wars. Produzland drove quickly through the Cabecan lands and annexed most of the modern state of Cabeca into the kingdom.
Continuing the expansion policy Produzland invaded the Kingdom of Aloísio in 1738, kicking off a second war with Parthonopia. However Parthonopia was unprepared and fought sloppily, leading to a massive destruction of the joint Aloísian-Parthonopian army on the island, and the destruction of the Parthonopian fleet in the Rosel. Vincent V declared his second son Philip King of Aloisio as Philip I at the age of 18, as Philip was not directly in line for the throne. After the end of the war with Aloísio and Parthonopia, King Vincent turned his eye north towards Meronnia, who over the last decade had sprung into revolution and deposed their ruling dynasty. King Vincent was determined to restore the monarchy of the country and invaded with the help of Meronnian royalists that fled to Produzland. The Produese sacked the city of Senone in 1739 and restored the monarchy of the country, a resounding victory and restored much of the lost prestige of the 17th century for Produzland.
In 1751 the king of Produzland and son of Vincent V, Vincent VI died childless. This lead to King Philip I of Aloísio being crowned King Philip II of Produzland as well. He fully integrated Aloísio into Produzland the next year.
The reign of Philip II became an era of reform for the Produese kingdom after a rough start to the young monarch's reign. Produzland had been an absolute monarchy for all of its history, excluding the Rodavese Republic, and with the emergence of the enlightenment calls for reform grew in the country. Philip was a moderate when it came to democracy, and was open to the idea of it, he was by no means a Republican and believed in the power of his monarchy, so he implemented a system of a Parliament and an appointed Prime Minister that would govern under the supervision of the monarchy. He had a constitution drafted by appointed bureaucrats in 1771, and had a Prime Minister selected as head of government. For a country that had no previous history of democracy, Produzland had a period of stability under their popular monarch and parliament.
Prince Carlos, the grandson of Philip II inherited the throne after his grandfather's death in 1801, becoming Charles II. At the end of the Meronnian Revolution near the same time, the directory of the Meronnian republic offered Produzland territory and a sphere of influence over Parthonopia if they had joined the ongoing war between Meronnia and the Parthonopian states. Despite personally not favouring the republic and Augustin Calvet, due to pressure from the parliament, Charles II had Produzland side with them in the Great Continental War.
Produzland and Meronnia turned victorious in the war against the coalition and several western Parthonopian territories were annexed into Produzland as well as the former Principality of Trevisa merged with lands from the Principality of Terracina into the Kingdom of Trevisa-Terracina.This alliance was turned on its head in 1813 however when Augustin invaded Produzland and deposed King Charles, as well as forcing his son to give up his right to the throne. Calvet installed his brother Francis on the Produese throne and forced Produzland to give up many of the territories won in the war against the coalition and Cabeca, being turned into sister republics of Meronnia. The Produese people engaged in fierce guerilla warfare against their Meronnian occupiers, and when Augustin was assassinated and the war turned against Meronnia, King Francis was deposed and replaced with Charles II's heir, and Produzland regained many of its lost territories, including a great sphere of influence over Parthonopia.
Late Produese Empire (1818-1925)
Despite ending up victorious in the Great Continental War and Carlos III with a firm grip over his realm again, the country was in ruins from the decade of war and both the king and the reinstated Prime Minister César Baltasar da Araújo knew the country was in need of reform. The country shifted away from it's traditional practices and abolished feudalism, and emancipation in the Produese Empire became a fiercely debated topic. An offshoot was the dissolution the Produese Gulf Company in 1824 which had been declining in it's prestige since the 20 Years War, and the Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition, commonly known as the Produese Inquisition, in 1832. Produzland sold the island of Comona to Carelia in 1820 and industrialization became prevalent in Produzland, including a monumental advancement with the invention of the train. Produzland became reliant on the railroad as one of the fastest countries to adopt them across the nation. While Produzland proper was rebuilding, their eastern territories in Parthonopia were revolting against their Produese occupiers, Carlos III repressed these rebellions in harsh ways which eventually turned over into the Wars of Parthonopian Independence against Produzland in 1824, with the country in no shape ready for war directly after the Great Continental War, they turned poorly for the country and Produzland lost its eastern territories, the wars left turmoil within the government and eventually came to a head with King Carlos' abdication in favour of his son Vincent VII. While Produzland was no longer the great power it once was, the mid-19th century became an era of development and general prosperity for it's people, especially with the rise of Vincent VIII and economic reform to combat poverty and the problems of the workplace.
Despite this, calls for more began from the working class, when Produzland lost the Cavo-Carelian War in 1894, demonstrations broke out in Produzland's industrial heartland in Burlon and Luville, and with the rise of nationalism, riots in Triunfo broke out demanding independence for Cabeca. When the Parthonopian War of Succession arose in 1896, outrage broke out from a nation that was fiercely against war. Produzland looked like it might have to drop out of the war from a revolution, but then the elderly king Vincent VIII passed leaving the throne to his grandson Carlos IV on the throne, the charismatic yet hot-headed monarch became a symbol for the Produese army and turned the tide of the war.
Once the war was won and Produzland made significant territorial gains, the king was as popular as ever, the republican Prime Minister Alexandre Coelho was voted out of power in the next election and things were looking bright for the nation that had spent the last near-decade in revolt. To coincide with the prosperity, Carlos IV ordered the construction of a monument to Produese architecture, representing the style to the world. It was built around the smaller Praça Rubescerá in Cojazeira and became an icon of Produzland when the Jubilee of the Ages was hosted in Cojazeira.
The Olympic War lead to the abrupt end to Produzland's period of peace, however the situation was different from the wars of the late 19th century, patriotism ran high in the country and the population was enthusiastic when it came to the war, however public opinion changed when the war became long and drawn-out, Produzland became victorious in 1925 but many did not consider the spoils of the war as enough to compensate the tired country from the 12 years of war. Produzland secured it's influence in western Parthonopia and had a firm grip on it's colonial territory again, but politically the country was becoming unstable. The country used a proportional representative system in parliament, creating a weak government that was mostly held together by the king himself, masking it's instability.
Post-Olympic War and Produese Revolution (1925-1935)
During the Olympic War to boost moral the government under conservative Prime Minister Francisco Estêvão promised soliders things like the vote and free land. Many returning veterans were displeased to find the latter unfulfilled, however they did receive the vote. With wartime factories closed and the returning veterans unemployment skyrocketed and the economy was in shambles. Many Produes began to shift on the political spectrum, particularly with the socialist PTSP lead by Amancio Sousa and the authoritarian União Nacional lead by Frederico Deusto. In 1929 Estêvão proposed a solution to the weak government the current parliamentary system had created. He decreed the winning party would automatically get 66% of the seats and a clear majority in parliament. This was supported by parliament as everyone despised the current system as nothing would get done. Carlos IV dismissed Estêvão in 1930 and replaced him with Filipe Góes who published the Góes Decrees that established a 40-hour work week and higher wages. Despite the reform internally Produzland's empire began to collapse and it lost it's remaining territories in Nori under Góes. In 1932 the country had an election and União Nacional won about 65% of the seats and Deusto became the Prime Minister, debates still exist today on how legitmate the vote was. While there was violence against Deusto's opponents, however he was wildly popular and many in the country were hoping he would fix the current problems.
Over the next year Deusto was rapidly reforming the government, some of União Nacional's supporters wanted them to become more extreme and hostile but Deusto did not want to risk losing more support in the Congress of Deputies. In 1934 he transitioned from being the Prime Minister of Produzland to being the President of the Government. The next year he banned all opposition parties, had Amancio Sousa arrested and used censorship and a secret police to quell opposition, especially any that related to the communist movement. In September of 1935, horrified at the corporatist authoritarian government that was being created Carlos IV began attempts to clamp down on Deusto's power, who the king saw as seeing himself as above the king. Furious, Deusto pressured the king to abdicate, and when the king refused Deusto launched a military coup against the monarchy. King Carlos was deposed and exiled to Meronnia on the 1st of October, 1935 and the same day Frederico Deusto declared the Federal Republic of Produzland with himself as President.
Deusto Era (1935-1980)
With the Federal Republic enabling him to exercise vast political powers, Deusto's rule was conservative and nationalist in nature. Deusto promoted Verroism, but argued that the role of the Church was social, not political. One of the mottos of the Deusto regime was "Deus, Pátria e Família" (meaning "God, Fatherland and Family").
After the Produese Revolution, Produzland was politically and economically isolated, and was kept out of international organizations. Produzland at the time was also suffering from a sluggish economy due to Deusto intentionally keeping Produzland out of international trade with a policy called 'Próprio Suficiência' (Self Sufficiency) in which Produzland sought to be entirely self-sufficient. The failing economy in the early 1950s forced the regime to implement major economic reforms that aimed at bringing in foreign investors.
In the 1960s, Produzland registered an unprecedented rate of economic growth which was propelled by industrialisation, the economic reforms of the 1950s, a mass internal migration from rural areas to Burlon, Cartaganca and Cabeca and the creation of a mass tourism industry. Press censorship was also relaxed and the more repressive measures of the regime were laid back, however Produzland was still by no means a free country.
Restoration of the Monarchy (1980-)
By the 1970s Deusto was aging and plans around the country for his succession. With Deusto's death in March 1979, Deputy Alberto Saldanha Seabra succeeded him as President of Produzland and as was agreed with Deusto in the 1940s the positions of President and President of the Government diverged and Ronaldo Antunes took the position later that year. Antunes began working with politicians opposed to Deusto to restore democracy in Produzland and devolving the President's power. With the approval of the Produese Constitution of 1980 proposed by Antunes and the restoration of democracy, the State devolved much authority to the regions and created an internal organisation based on the states, and after fierce debate within parliament over the future of Produzland, it was finally decided on February 18th, 1980 to restore the monarchy. A relative of the former ruling House of Beltrão, João de Beltrão was offered the Produese throne in February of 1980, which he accepted and became João II. The Produese 1982 Amnesty Law let people of Deusto's regime continue inside institutions without consequences.
During the 1980s the democratic restoration made possible a growing open society. New cultural movements based on freedom appeared and a culture of human rights arose with Jorge Gonçalves Moniz. On May 30th, 1982, Produzland joined RESP, followed by a referendum after a strong social opposition. The Burguês Party, which became the successor to the National Union Party was replaced in government by the Patron's Party (PP) in 1994 after scandals around participation of the government of Ronaldo Antunes and Marcelo Borges surrounding the Escândalo da Princesa; at that point Burguês had served almost 14 consecutive years in office.
In November of 1997, the Velkanikan military seized the Produese overseas territory of Santa Iria under the pretext of halting illegal fishing boats and other vessels from evading Velkanikan law enforcement by fleeing to the island. Prime Minister Tomás da Rosa declared an exclusion zone around the island and deployed the Produese navy to the island. Heavy losses in the Rosel Sea and in the air as well as international pressure resulted in Velkanika retreating from the islands ten weeks later.
On November 1st, 2018, PP leader Riccardo Bonadeo became Prime Minister after the 2018 General Election, replacing Prime Minister José Lérias Cascais.
Politics
Government
Produzland is a parlimentary constitutional monarchy. The Constitution grants the division or separation of powers among four bodies, the King, the Government, the parliament, and the Courts. The constitution of 1777 also states that the capital of Produzland is always in the city of where the monarch lives, the current monarch being King José III. The current constitution of 1980 maintains most of its premises from the 1777 constitution while simultaneously compromising new elements such as the states' varying degrees of autonomy and attempts at furthering gender equality.
The Produese parliament is a bicameral system with the Senate and the Congress of Deputies. The Congress of Deputies is decided on a system proportional to the population of each state adding up to a total of 305 seats, and each state with their appropriate amount of seats decides how they want to distribute their seats amongst the parties. The Senate meanwhile each province gets 4 senators giving the senate 212. Produzland has elections every 2 years. Elections are divided into two categories, Parliamentary Elections and General Elections, both are essentially the same apart from in General Elections the head of the largest party elected becomes Prime Minister, whereas in Parliamentary elections they do not. This commonly results in the Prime Minister controlling a minority government. As of November 2020, Prime Minister Riccardo Bonadeo heads a minority government while Rodrigo Guindaste serves as Leader of the Opposition.
Produese politics for since the resignation of Prime Minister Marcelo Borges have been dominated by two parties, the Produese Socialist Workers' Party (PTSP) (the dominant liberal party), and the Patron's Party (PP) (the dominant conservative party). Before the restoration Produzland was a single party state with União Nacional (National Union) at the lone party headed by Frederico Deusto until his death when the single party state collapsed and was replaced with the democratic multi-party system of today.
Law and Criminal Justice
The Produese judicial system is originally based on Orthurian law modified by the Pretran code and later statutes. The Supreme Court of Produzland is the highest court in Produzland for both criminal and civil appeal cases. The Constitutional Court of Produzland (Corte Constitucional) rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and is a post–Deustoist innovation. Since their appearance in the middle of the 19th century, Produese organised crime and criminal organisations have infiltrated the social and economic life of many regions in Southern Produzland, the most notorious of which being the Rodavese Mafia, which would later expand into some foreign countries.
A 2009 report identified 610 municipalities which have a strong Mafia presence, where 13 million Produes live. The originally Portuárian Bandeira, nowadays probably the most powerful crime organization of Produzland, accounts alone for 3% of the country's GDP. However, at 0.013 per 1,000 people, Produzland has relatively low murder rate figures among developed countries.
Administrative Divisions
Produzland is divided into 16 states, states being the highest or first-order administrative division in the country. States are divided into provinces, of which there are 52 in total, and in turn, provinces are divided into municipalities. The current form was established in 1980 with the current constitution, however the system itself has existed since the early 19th century with the reforms of Prime Minister César Baltazar da Araújo. Produzland also holds several overseas territories, including Santa Iria in the eastern Rosel.
Produzland is one of the most decentralized countries of western Lira, with all states possessing their own elected parliaments, governments, public administrations, budgets, and resources. Health and education systems among others are managed by the Produese states, and in addition, Cabeca and the Aloisian Islands also manage their own public finances based on foral provisions.
| State | Capital | Population | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agudicia | Bresbon | 3,781,498 | |
| Almúnia | Cojazeira | 5,118,344 | |
| Aloísio | Capella | 1,119,439 | |
| Burlon | Burlon | 5,946,071 | |
| Cabeca | Triunfo | 3,193,093 | |
| Cavale | Sequeira | 2,546,078 | |
| Cavale-As Veigas | Araújo | 3,121,888 | |
| Esgravata | Oraveira | 1,108,130 | |
| Galicia | Viosinho | 7,449,985 | |
| Miragaia | Luville | 5,570,908 | |
| Portuária | Portuária | 5,498,566 | |
| Rio Sujo | Lagoza | 2,276,349 | |
| Rodaves | Cartaganca | 8,419,673 | |
| Selará | Calorbairro | 2,474,449 | |
| Sonância | Vidal | 1,349,467 | |
| Turão | Maleta | 4,108,130 |
Foreign Affairs
After the return of democracy following the death of Deusto in 1979, Produzland's foreign policy priorities were to break out of the diplomatic isolation of the Deusto years and expand diplomatic relations, enter the Liran Community, and define security relations with the West.
Produzland has established itself as a participant in multilateral international security activities. Produzland's RESP membership represents an important part of its foreign policy. Even on many international issues beyond Lira, Produzland prefers to co-ordinate its efforts with its RESP partners, including Meronnia, Ackesia, and Carelia through the Liran political co-operation mechanisms. Overall Produzland prefers to not involve in overseas conflicts, contrary to its very interactive partner Meronnia. In regards to Parthonopia, Produzland and Meronnia are heavily involved most of the time to keep their neighbor in line with the rest of western Lira, and both are heavily against war with the aggressive young nation.
Military
The armed forces of Produzland are known as the Produese Armed Forces (Forças Armadas Produesas). Their Commander-in-chief is the reigning King of Produzland, José III, following with the Prime Minister and the Minister of Defense respectively in the chain of command. The fourth in authority is the Chief of the Defense Staff (CEMD). The Defense Staff (Estado-Maior de Defesa) is responsible for assisting the CEMD as an auxiliary staff.
The Produese armed forces are a professional miltiary consisting of 121,900 active personnel and 4,770 reserve personnel as of 2017. The country also has the 77,000 strong Civil Guard which comes under the control of the Ministry of Defense in times of a national emergency. The Produese defense budget is 5.71 billion Rozars a 1% increase for 2015. The increase comes because of security concerns in the country.
The Produese Armed Forces are divided into three branches:
- Army (Exército Terrestre) - The Produese Army consists of 15 active brigades and 6 military regions. Modern infantry have diverse capabilities and this is reflected in the varied roles assigned to them. There are four operational roles that infantry battalions can fulfil: air assault, armoured infantry, mechanised infantry, and light role infantry. The Produese army has the latest technology at its disposal to preserve the territorial integrity of the Kingdom of Produzland.
- Navy (Armada) - Under the command of the Produese Admiral Chief of Naval Staff, stationed in Burlon, the Produese Navy has four area commands across the country. The current flagship of the Produese Navy is the amphibious assault ship/aircraft carrier João II. In addition, the fleet consists of: 2 amphibious transport docks, 11 frigates, 3 submarines, 6 mine countermeasure vessels, 23 patrol vessels and a number of auxiliary ships. The total displacement of the Produese Navy is approximately 220,000 tonnes. As of 2012, the Armada has a strength of 20,838 personnel.
- Air Force (Força do Ar) - Produzland currently has 10 fighter squadrons, each with 18-24 airplanes. The air force also has 15 operational air bases around the country. The air force operates a wide-ranging fleet of aircraft, from fighters to transport aircraft and passenger transports to helicopters. It maintains some 450 aircraft in total, of which around 130 are fighter aircraft, including a number of Lirofighter Typhoons. The Produese Air Force is replacing older aircraft in the inventory with newer ones including the recently introduced Lirofighter Typhoon and the Airbus A400M Atlas airlifter.
Geography
Produzland is located in south-west Lira, and is bordered by the Aurum Ocean in the west and the Rosel Sea in the south. At 434,622.52 (km²), Produzland is the largest country in western Lira. Mount Caballé is the highest peak in Produzland on the island of Aloísio.
In the east, Produzland is bordered by Parthonopia, a border that stretches from the Aurum Ocean to Cisparrania. In the northeast, Produzland borders Meronnia along the Aniene River in Cabeca.
Islands
Produzland also includes the Aloísian Islands, revolving around the large island where the island chain gets it's name, Aloísio. Produzland also possesses several islands off the coast of Galícia, and many uninhabited islands off the southern coast of the Rodaves, such as the Garrigós Islands, and the Bellpuig Islands.
Mountains and Rivers
Most of mainland Produzland is dominated by high plateaus and flatland. The Aloísian Islands are mainly mountainous other than the coastal regions, such as with the Escarré mountain range across the north of Aloísio. There are several major rivers in Produzland such as the Goute, Orba, Mazarico (Maçarico), Eblá, and Buteira. Alluvial plains are found along the coast, the largest of which is that of the Orba in Galícia and Agudicia.
Climate
The Marine West Coast or Oceanic Climate of Produzland has a very mild climate lacking in extreme temperatures. It typically lacks a dry season, as precipitation is consistent throughout the year. Summers are cool due to cool ocean currents, winters are mild usually very cloudy. With Summers below 22 °C (72 °F) and winters above −3 °C (27 °F).
The Mediterranean climate in the south of Produzland is characterized by dry summers and mild, moist winters. The average temperature is above 10 °C (50 °F) in their warmest months, and an average in the coldest between 18 to −3 °C (64 to 27 °F). The climate receives almost all of its precipitation during the winter, autumn and spring seasons, and may go anywhere from 4 to 6 months during the summer without having any significant precipitation.
Fauna and Flora
The fauna presents a wide diversity that is due in large part to the geographical position of the Orthurian peninsula between the Aurum and the Rosel at the southwest end of Lira, and the great diversity of habitats and biotopes, the result of a considerable variety of climates and well differentiated regions.
Including the mainland and Aloísio, Produzland has an estimated sixty to seventy thousand species of animal. Of these, about seven hundred are vertebrates (excluding marine fish) and the remainder are invertebrates. The highest degree of endemism occurs among freshwater fish and in the mountainous areas, the coastal areas, and among the Aloísian Island fauna. About 30% of the vertebrates in Produzland are threatened.
The vegetation of Produzland is varied due to several factors including the diversity of the relief, the climate and latitude. Produzland includes different phytogeographic regions, each with its own floristic characteristics resulting largely from the interaction of climate, topography, soil type and fire, biotic factors.
Economy
Produzland has a capitalist refining and manufacturing Economy with both lower and higher secondary sectors. Manufacturing is the dominant force in the country with significant contributions from refining. The parts made in Produzland are both exported and made into finished products, though the economic goal of the nation is to export the majority of parts out of the country, while keeping/importing some parts for local manufacturing before exportation. Imports include raw materials as well as finished goods and services from other countries. The resources on hand and the priorities of Produzland influence what type of refinement and manufacturing will take place. Produzland's manufacturing specialties include train parts, automobiles, electronics, and luxury goods.
Produzland has one of the largest automotive industries in the world with world famous luxury cars such as Bezerra, Venâncio, and Vila Corrêa. By 2016, the automotive industry was generating 8.7 percent of Produzland's gross domestic product, employing about nine percent of the manufacturing industry. By 2008 the automobile industry was the 2nd most exported industry. Produzland is also a major exporter of luxury goods such as jewelry, watches, clothing, etc., Gárcere, and Vítor Loureiro take center stage in the Produese luxury good industry.
Agriculture
Produzland is the largest agricultural producer in western Lira, though only about 17% of Produzland's cultivated land was irrigated, it was estimated to be the source of between 40–45% of the gross value of crop production and of 50% of the value of agricultural exports. Produzland is one of the world's largest wine producers, and one of the leading in olive oil, fruits (apples, olives, grapes, oranges, lemons, pears, apricots, hazelnuts, peaches, cherries, plums, strawberries and kiwifruits), and vegetables (especially artichokes and tomatoes). The most famous Produese wines are probably the Galician Granxas and the Agudician Botelho. Other famous wines are Mira de Peredo, Da Vale, Salgado, Curbelo, Arra de Viera, and the sparkling wines Troncoso and Cadavid.
The vast majority (99%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), grain fields take up 31%, olive tree orchards 8.2%, vineyards 5.4%, citrus orchards 3.8%, sugar beets 1.7%, and horticulture 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%).
Tourism
In 2017, Produzland was the second most visited country in the world, recording 82 million tourists which marked the fifth consecutive year of record-beating numbers. Produzland's geographic location, popular coastlines, diverse landscapes, historical legacy, vibrant culture, and excellent infrastructure has made the country's international tourist industry among the largest in the world. In the last five decades, international tourism in Produzland has grown to become the second largest in the world in terms of spending, worth approximately 40 billion Rozars or about 5% of GDP in 2006.
Cavale is the Produese leader in rural tourism linked to its environmental and architectural heritage.
Infrastructure
In 2004 the transport sector in Produzland generated a turnover of about 119.4 billion Rozars, employing 935,700 persons in 153,700 enterprises. Regarding the national road network, in 2002 there were 668,721 km (415,524 mi) of serviceable roads in Produzland, including 6,487 km (4,031 mi) of motorways, state-owned but privately operated by Almeida S.A.. In 2005, about 34,667,000 passenger cars (590 cars per 1,000 people) and 4,015,000 goods vehicles circulated on the national road network.
The national railway network, state-owned and operated by Rede Ferroviária Produesa (RFP), in 2008 totalled 16,529 km (10,271 mi) of which 11,727 km (7,287 mi) is electrified, and on which 4,802 locomotives and railcars run. The main public operator of high-speed trains is Saraiva, part of RFP. Produzland has 11 rail border crossings with its neighbouring countries.
Continental Produzland's territory is serviced by six international airports located near the cities of Portuária, Luville, Burlon and Cartaganca. Luville's geographical position makes it a stopover for many foreign airlines at several airports within the country. The government decided to build a new airport outside Burlon, to replace Burlão Portela Airport, though this plan has been suspended due to austerity measures. Currently, the most important airports are in Burlon, Portuária, Capella, and Cartaganca, managed by Aeroportos de Produseía. Ortúria is the national carrier airline.
The major seaports are located in Luville, Cartaganca, Maleta, Portuária, Delgado, Detalhe, and Triunfo.
The three largest metropolitan areas have subway systems: Luville Metro and South Anavede Metro in the Luville Bay Metropolitan Area, Burlon Metro in the Burlon-Araújo Metropolitan Area, and Cartaganca Metro in the Cartaganca Metropolitan Area, each with more than 35 km (22 mi) of lines. In Produzland, Laronha tram services have been supplied by Southwest Transport, for over a century. In Portuária, a tram network, of which only a tourist line on the shores of the inner city remains, began construction on September 12th, 1895 (a first for the Orthurian Peninsula). All major cities and towns have their own local urban transport network, as well as taxi services.
Energy
Produzland is one of the world's leading countries in the development and production of renewable energy. In 2010 Produzland became the solar power world leader when it opened a massive power station plant called Lugar da Flor, near Adigueira, Véal. Produzland is also Lira's main producer of wind energy. In 2010 its wind turbines generated 42,976 GWh, which accounted for 16.4% of all electrical energy produced in Produzland. On November 9th 2010, wind energy reached an instantaneous historic peak covering 53% of mainland electricity demand and generating an amount of energy that is equivalent to that of 14 nuclear reactors. Other renewable energies used in Produzland are hydroelectric, biomass and marine (2 power plants under construction).
Non-renewable energy sources used in Produzland are nuclear (8 operative reactors), gas, coal, and oil. Fossil fuels together generated 58% of Produzland's electricity in 2009, just below the OECD mean of 61%. Nuclear power generated another 19%, and wind and hydro about 12% each.
Science and Technology
In the 19th and 20th centuries, science in Produzland was held back by severe political instability and consequent economic underdevelopment. Despite the conditions, some important scientists and engineers emerged. The most notable were Egídio Monteiro, Víctor Branco, Jorge de Leitão, Guilherme Leite, Félix Tavares, Vasco Álvares, Cândido Batista, Enzo de Gusmão e Albuquerque, and Luís Moreno. Today, the Conselho Superior de Investigações Científicas (CSIC) is the leading public agency dedicated to scientific research in the country.
Demographics
In 2019, the population of Produzland officially reached 61 million people, as recorded by the Produese Bureau of Population Statistics (GPEP). Produzland's population density, at 141/km², is lower than that of most Western Liran countries and its distribution across the country is very unequal. With the exception of the region surrounding the capital, Burlon, the most populated areas lie around the coast. The population of Produzland has risen 2 1/2 times since 1900, when it stood at 24.4 million, principally due to the spectacular demographic boom in the 1960s and early 1970s.
Urbanisation
Produzland's major cities are spread out across the countries territory, with the biggest congestion being in the south and southwest. However most of the population lives in the areas between the larger cities, for example the Goute River basin between Luville and Burlon is a very densely populated area compared to most of Produzland. Another example is the western Rodaves between Portuaria and Cartaganca.
Largest cities or towns in Produzland
2014 Tri-annual Census Produese Bureau of Population Statistics (GPEP) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | State | Pop. | |||||||
| 1 | Burlon | Burlon | 5,946,071 | ||||||
| 2 | Cartaganca | Rodaves | 3,207,563 | ||||||
| 3 | Luville | Miragaia | 2,702,365 | ||||||
| 4 | Portuária | Portuária | 2,417,539 | ||||||
| 5 | Delgado | Galícia | 2,153,067 | ||||||
| 6 | Cojazeira | Almúnia | 1,520,207 | ||||||
| 7 | Biscegona | Cabeca | 940,121 | ||||||
| 8 | Maleta | Turão | 695,562 | ||||||
| 9 | Bresbon | Agudicia | 419,673 | ||||||
| 10 | Calorbairro | Selará | 276,349 | ||||||
Ethnicity
Most Produes originated from Orthurians mixing with northern tribes, mostly Aenians that immigrated southward into the Orthurian province of Produsia, however the term "Produese" was relatively vague throughout history, referring to anyone living within the historic Orthurian province, despite this most people would classify Produes from the Rodaves as ethnically different from northern Produese. This leaves surveys attempting to study the ethnic makeup of Produzland difficult, as normally around 80%-90% identify as nothing more than 'Produese'.
Produzland is also home to the world's largest population of Cabecans, a language and ethnic isolate between Meronnia, Cisparrania, and Produzland. There is also the Rodavese, primarily defined by their language of the same name, most prevalent in the Rodaves and Portuaria, however ethnically they are often included as Produese.
Historically there has also been trends of outside immigration to Produzland, most notably with the country's neighbors Parthonopia and Meronnia, however Produzland has never been a melting pot of outside cultures and a hotspot for immigration until very recently with the isolationist Deusto regime that lasted until the 1980s.
Religion
Religion in Produzland, 2015
Until the middle ages, Produzland was a religiously diverse nation, however holding a clear Verroin majority, then several institutions, most notably The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition, commonly known as the Produese Inquisition (Inquisição Produesa), were established in the late middle ages and early modern era. They were intended to maintain Verroism in their kingdoms and territories. According to modern estimates, around 150,000 were prosecuted for various offenses during the three-century duration of the Produese Inquisition, out of which between 3,000 and 5,000 were executed (~2.7% of all cases). Despite a low conviction number compared to the whole of the population, many member of minority religions fled to more tolerable nations, making Produzland a homogeneous nation religiously until the 20th century with the rise of atheism and others related groups taking prevalence as a strong minority in the country that has been steadily growing ever since.
Language
Produese, described in the constitution as Cavalian, is an Orthurian language rooted in Orthurian and Old Aenian. Cavallian Produese is the official dialect of Produese as it was used by the medieval kingdom of Cavale that unified the country, however many variations of Produese are present, including the Galician and Esgravatan dialects, the former of which is sometimes classified as a separate language. States are allowed co-official languages alongside Produese, and the whole country recognized two co-official languages, Rodavese and Cabecan.
The two largest minority languages are Rodavese and Cabecan. Rodavese is, like Produese, an Orthurian language rooted in the language that dominated the Orthurian Empire, it's main derivative is Old Calmatian, which at the time was spoken in most of southern Produzland until the language was pushed further south by Produese Cavallians. Rodavese is now mainly spoken in southern Portuária, the Rodaves, and the Aloísian Islands.
Cabecan however is a language isolate that has no identifiable relatives. Despite Deustoist efforts to erase the Cabecan language, seen in the mostly Cavallian names of Cabecan cities, Cabecan speakers are still prevalent in the state and surrounding historic Cabecan lands such as Cabeca Alba in Meronnia, and western Cisparrania. A language map of the border region between Produzland, Cisparrania, and Meronnia roughly mirrors the historic borders of the Cabecan Kingdom of Velarre.
There are also several smaller recognised languages in their native states, such as Selanese, a close relative of Rodavese with about 50,000 speakers, mostly in the Rigeu province. Galician, a minor language in the north of Galícia and small parts of Agudicia that most consider a dialect of Produese but remains a recognised minority language. And finally Agudician, a language closely related to Galician spoken only in the west of the Detalhe province.
Produzland has other small minorities of speakers of Parthonopian, Solician, and several Jashnagari languages.
As a percentage of the general population of all Produzland, Produese as a first or second language is spoken by 99% of the population, while Rodavese by 20%, and Cabecan by 5% of all Produes.
Health
The Produese state runs a universal public healthcare system since 1990. However, healthcare is provided to all citizens and residents by a mixed public-private system. The public part is the Serviço Nacional de Saúde, which is organised under the Ministry of Health and administered on a devolved regional basis. Healthcare spending in Produzland accounted for 9.2% of the national GDP in 2012.
Life expectancy in Produzland is 80 for males and 85 for females. In comparison to other Western countries, Produzland has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), as there are several health benefits of the Orthurian diet. The proportion of daily smokers was 22% in 2012, down from 24.4% in 2000 but still slightly above the world average. Smoking in public places including bars, restaurants, night clubs and offices has been restricted to specially ventilated rooms since 2005.
Education
State education in Produzland is free and compulsory from the age of six to sixteen. The current education system is regulated by the 2006 educational law, LOE (Lei Orgânica da Educação), or Fundamental Law for the Education. In 2014, the LOE was partially modified by the newer and controversial LOMQE law (Lei Orgânica para a Melhoria da Qualidade Educacional), or Fundamental Law for the Improvement of the Education System. Since 1970 to 2014, Produzland has had seven different educational laws (LGE, LOECE, LODE, LOGSE, LOPEG, LOE and LOMQE).
Instituição Livre de Educação was an educational project that developed in Produzland for the half a century of about 1876–1936 by André da Moura and Quirino Garcia. The institute was inspired by the philosophy of Krausism. Concepção Varela in feminism and Francés Baiget i Sitjar in neuroscience were in the movement.
Culture
Produzland is a western Liran country. Almost every aspect of Produese life is derived by its Orthurian heritage, making Produzland one of the major Orthurian countries of Lira. Produese culture is marked by strong historic ties to Verroism, which played a pivotal role in the country's formation and subsequent identity. Produese art, architecture, cuisine, and music have been shaped by the country's Mediterranean climate and geography. The centuries-long colonial era globalised Produese language and culture, with Produzland also absorbing the cultural and commercial products of its diverse empire.
Art
Produzland has historically been a hub for flourishing artists, as one of the leading nations of the Renaissance, and cultural centers of Lira, Produese artists have been highly influential in the development of various Liran artistic movements. Due to historical, geographical and generational diversity, Produese art has known a great number of influences from the nation's Orthurian roots to its northern Gostic influences.
During the Renaissance and Golden Age, painters working in Produzland include Osório Da Rosario, Luca Melo, Balduíno Hernandes, and José de Ribeira, as well as Late Renaissance painters Aníbal Inácio Monteiro and Maurício Simões. Also in the Baroque period Diogo Varejão created some of the most famous Produese portraits, such as O Alcance do Fim and O Dormente.
Ricardo Lobo de Casado painted during a historical period that includes the Great Continental War, the rise of Liberalism, and the emergence of nationalism. And during the 20th century, artists like Rodrigo Vila became influential as a well-known modern impressionist painter as well as many other important Produese painters belonging to the modernism art movement, including Feliciano Seixas, Ângelo Azevedo, and César Sapateiro.
Architecture
Produese architecture is derived mainly from Orthurianesque and Rodavese-style. Rodavese architecture takes center stage when it comes to Produese architecture, influencing regions of Produzland far outside historic Calmatian influence, and represents Produese architecture on a global scale. Even to today Rodavese architects dominate the scene in modern Produese architecture.
During the Middle Ages and Golden Age of Rodavese architecture, the northern Produese kingdoms gradually emerged and developed their own styles; developing a pre-Orthurianesque style when for a while isolated from contemporary mainstream Liran architectural influences during the earlier Middle Ages, they later integrated the Orthurianesque and Gothic streams. There was then an extraordinary flowering of the Gothic style that resulted in numerous instances being built throughout the entire territory. The Bassaganyes style, from the 12th to 17th centuries, was developed by introducing Calmatian style motifs, patterns and elements into Liran architecture. Calorbairro and Granarón being the biggest examples of the hybrid of Orthurian and Rodavese architecture.
Traditional architecture is distinctive and include Vincennine, also known as Produese late Gothic a sumptuous, composite Produese style of architectural ornamentation of the first decades of the 16th century, followed by Saldanine style of the 18th century. A 20th-century interpretation of traditional architecture, Soft Produese style, appears extensively in major cities, especially Luville.
The arrival of Modernism in the academic arena produced much of the architecture of the 20th century. An influential style centred in Cartaganca, known as modernisme, produced a number of important architects, of which Valentí Sugrañes is one. Produzland is currently experiencing a revolution in contemporary architecture and Produese architects like Menna Sadurní, Vicente Guiu, and Francisco Lodeiro as well as many others have gained worldwide renown.
Literature
The earliest recorded examples of vernacular Romance-based literature date from the same time and location. Until 1350, Produese troubadours spread their literary influence to most of the Orthurian peninsula. Luís de Magalhães was one of the founders of Produese dramatic traditions. Adventurer and poet Vasco da Cunha wrote the epic poem Os Lusíadas (The Lusiads).
The Baroque is the most important period of Produese culture, as it corresponded with the era of Produese Empire. The famous Dom Calixto das Veigas by Francisco de Valente was written in this time. Other writers from the period are: Olegário Alves, Francisco da Araújo, Tomás Brandão, and Gervásio Machado e Almeida.
Modern Produese poetry is rooted in neoclassic and contemporary styles, as exemplified by Jerónimo de Gusmão, Octávio Ribeiro, and Ronaldo Bastos. Modern Produese literature is represented by authors such as Fernando Tavares, Eduarda Correia, Liana de Oliveira, João Ramos, and Cristiano Medeiros.
The Prêmio Enéas de Guerra and the Francisco de Valente Prize are the two main awards nowadays in Produese literature.
Philosophy
Lestaca was a philosopher residing in Produsia during the time of the Orthurian Empire. During the medieval period Beoist philosophies flourished, including the works of such philosophers such as Dianote, Lagerroes and Cardonides.
Humanist Vítor da Lavoeira worked in Produzland during the Renaissance, as did Francisco Salagronho (creator of the School of Calorbairro and scholar on international law) and Bartolomé de Montanha.
The Enlightenment in Produzland arrived later and was less strong than in other Liran countries, but during the 19th century liberal ideas arrived in Produese society. At the end of the century, socialist and libertarian ideas also flourished, with thinkers such as Carles Montículo i Margall, Ricardo Salcária and Guilherme Pereira.
In the first half of the 20th century among the most prominent philosophers were Maria Braga and José Outeiro e Collette. Contemporary philosophers include Fernando Velasco and Adela Delchiaro, creator of the term aporophobia.
Music
Produese music is often considered abroad to be synonymous with flamenco, a West Selanese musical genre, which, contrary to popular belief, is not widespread outside southern Produzland. Various regional styles of folk music abound in Agudicia, the Rodaves, Portuária, Cavale, Cabeca, Galícia, Sonância and Miragaia. Pop, rock, hip hop and heavy metal are also popular.
In the field of classical music, Produzland has produced a number of noted composers such as Eduardo de Coimbra, Joaquim Botelho, Teodósio Monteiro and singers and performers such as Túlio Tavares, Calisto de Moniz, Carlos Cerqueira, Martinho Abreu. In Produzland there are over forty professional orchestras, including the Orquestra Simfònica de Cartaganca, Orquestra Nacional de Produseía and the Orquestra Sinfônica de Burlão. Major opera houses include the Teatro Real, the Gran Teatre del Liceu, Teatro Vergé and the Grande Teatro da Rainha Lúcia. Thousands of music fans also travel to Produzland each year for internationally recognised summer music festivals, which often feature the top up and coming pop and techno acts. Music festivals mark Produzland as an international music presence and reflect the tastes of young people in the country.
The most popular traditional musical instrument, the guitar, originated in Produzland.
Cinema
Produese cinema has achieved major international success including awards for recent films such as Marinho and Costa. In the long history of Produese cinema, the great filmmaker Henrique Fontes was the first to achieve world recognition, followed by Evaristo Carriço Cruz in the 1980s.
Produese cinema has also seen international success over the years with films by directors like Rodrigo Barreto, Filipe de Furtado, Felip Castany, Matties Pierre, Andreu Goday, Ignasi Espinalt i Gari, Miguel Pereira, Maximiliano Brito, and Camilo Silveira.
Actresses Rosana Leite and Irina Cruz or actor Valentin Alvim are among those who have become international stars.
International Film Festivals of Maleta and San Aurelio are the oldest and most famous of Produzland.
Fashion and Design
Produese fashion has a long tradition, and is regarded as one most important in the world. Luville, Bresbon and Burlon are Produzland's main fashion capitals. Major Produese fashion labels, such as Gárcere, Vítor Loureiro, Veciana, Paladell, Vilarbebó, Vasconcelos, and Saldanha, to name a few, are regarded as among the finest fashion houses in the world. Also, the fashion magazine Lia Produseía, is considered one of the most prestigious fashion magazines in the world.
Produzland is also prominent in the field of design, notably interior design, architectural design, industrial design and urban design. The country has produced some well-known furniture designers, such as Liana Cortes and Lluïsa Bigorra. Examples of classic pieces of Produzland white goods and pieces of furniture include Genoveva's washing machines and fridges, new tone sofas by Amorim, and the post-modern bookcase by Lluïsa Bigorra. Today, Luville and Vidal are the nation's leaders in architectural design and industrial design. The city of Luville hosts Feira de Luvilha, Lira's largest design fair. Luville also hosts major design and architecture-related events and venues, such as the Expo de Móveis, and has been home to the designers Casimiro Carneiro, Carlos Alves, Antelmo Mendonça, and Tomé de Sequeira.
Cuisine
Produese cuisine consists of a great variety of dishes which stem from differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by seafood available from the waters that surround the country, and reflects the country's deep Orthurian roots. Produzland's extensive history with many cultural influences has led to a unique cuisine. In particular, three main divisions are easily identified:
Southern Produzland – all such coastal regions, from Miragaia to the Rodaves – heavy use of seafood, such as peixe frito (fried fish); several cold soups like gazpacho; and many rice-based dishes like paella from Portuária and arròs negre (black rice) from the Rodaves.
Inner Produzland – Cavale – hot, thick soups such as the bread and garlic-based Cavallian soup, along with substantial stews such as cozido burlenho. Food is traditionally conserved by salting, such as Produese ham, or immersed in olive oil, such as Vegano cheese.
Northern Produzland – the whole Northern coast, including Agudician, Cabecan, Sonâncian and Galícian cuisine – vegetable and fish-based stews like caldo gallego and marmitako. Also, the lightly cured lacón ham. The best known cuisine of the northern countries often rely on ocean seafood, as in the Cabecan-style cod, albacore or anchovy or the Galician octopus-based polbo á feira and shellfish dishes.
Sports
While varieties of football have been played in Produzland as far back as Orthurian times, sport in Produzland has been dominated by football since the early 20th century. Real Burlão C.F. and FC Cartaganca are two of the most successful football clubs in the world. The country's national football team won the UEFA Liran Football Championship in 1964, 2008 and 2012 and the World Cup in 2010, and is the first team ever to win three back-to-back major international tournaments.
Basketball, tennis, cycling, handball, futsal, motorcycling and, lately, Formula One also can boast Produese champions with racing teams such as Verdadeira Bezerra and Gárcere Racing. Today, Produzland is a major world sports powerhouse, especially since several major sports tournaments have been hosted in Produzland, which stimulated a great deal of interest in sports in the country. The tourism industry has led to an improvement in sports infrastructure, especially for water sports, golf and skiing. In their respective regions, the traditional games of Cabecan pelota and Portuárian pilota both are popular.
Society
Produzland remains a conservative society for the most part, aside from a few exceptions such as the Rodaves. Most Produes support traditional values, corresponding with the fact most Produes follow Verroism, with varying degrees of practice. However Produzland is legally tolerant towards all human rights. The Produese Constitution of 1980 "protect all Produes and all the peoples of Produzland in the exercise of human rights, their cultures and traditions, languages and institutions". Produzland provides one of the highest degrees of liberty in the world for its LGBT community. A poll in 2013 by GPEP on acceptance of homosexuality stated 88% of those surveyed responded that homosexuality should be accepted. Produzland also has one of the lowest rates of gender inequality in the world, with several laws favouring men from the Deusto Era being repealed with the restoration of the monarchy.
Drug laws are one of the many things in Produzland decided by state law. For example all recreational drugs are illegal in the state of Burlon, but many are legal in Miragaia. However advertising for drugs is forbidden by law, as well as drug usage under 18 nationwide. Despite anti-drug laws, drug usage is common across the nation, one study conducted in 2006 found that almost 94% of Produese Rozar bank notes in Produzland carry small traces of cocaine.
Produese national pride consistently ranks high compared to most of Lira, football is a major source of pride for Produes, as the Produese National Football Team is one of the most popular in the world. The Feriado Nacional de Produseía is the only official secular holiday, it takes place on June 20th for the Coronation of Henrique I as king of the Kingdom of Cavale and the Kingdom of Agudicia, de facto uniting the Kingdom of Produzland.