Rajyaghar: Difference between revisions
m (→Demographics) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (51 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Region icon Kylaris}} [[Category:Rajyaghar]] [[Category:Kylaris]] [[Category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | |||
|conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Rajyaghar | [[Category: Rajyaghar]] | ||
|native_name = | {{Region icon Kylaris}} | ||
|common_name = | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Rajyaghar | |||
|image_flag = | |native_name = {{lang|Guj|રાજ્યઘર રાજ્ય}} | ||
|common_name = Rajyaghar | |||
|image_flag = RajyagharFlag.png | |||
|image_coat = | |image_coat = Charsidhan.png | ||
|symbol_type = National Emblem | |||
|symbol_type = | |national_motto = ''Rājā nī Jaya<br><small>Hail to the King''</small> | ||
|national_motto = | |national_anthem = ''[[Kramākramānē]]<br><small>Step by Step''</small><br>[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ecMGhaq-7Hs|200px]] | ||
|image_map = RajyagharMap.png | |||
|national_anthem = | |map_caption = Location of Rajyaghar in [[Coius]] | ||
|image_map2 = | |||
|map_caption2 = | |||
|capital = [[Kinadica]] | |||
|image_map = | |largest_city = [[Kinadica]] | ||
|official_languages = {{wp|Gujarati language|Himavantan}} | |||
|map_caption = | |regional_languages = {{wp|Hindi Language|Matrabashi}}, {{wp|Marathi Language|Bhasdila}}, {{wp|Bihari Language|!Bihari}}, {{wp|Telugu Language|Tamisari}} | ||
|image_map2 = | |ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | ||
| {{nowrap| 39% {{wp|Gujarati People|Himavanti}}}} | |||
|map_caption2 = | | 25% {{wp|Rajasthani People|Matrabashi}} | ||
|capital = | | 11% {{wp|Marathi People|Bhasdilian}} | ||
| 10% {{wp|Bihari people|!Bihari}} | |||
|largest_city = | | 4% {{wp|Telugu People|Tamisari}} | ||
| 4% {{wp|Odia People|!Odia}} | |||
| 7% Other | |||
|official_languages = {{wp| | }} | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2021 | |||
|regional_languages = {{wp| | |||
|ethnic_groups = | |||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |||
|ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | |ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | ||
|religion = | |religion = [[Ashankism]] <small>(majority, unofficial)</small> | ||
|demonym = Rajyani | |||
|government_type = {{wp|Federal Monarchy|Federal, Parliamentary,<br>Constitutional Monarchy}} | |||
|demonym = | |leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of Rajyaghar|Maharaja]] | ||
|government_type = | |leader_name1 = [[Krishan VII]] | ||
|leader_title1 = | |leader_title2 = [[Premier of Rajyaghar|Premier]] | ||
|leader_name1 = | |leader_name2 = [[Madhava Thakur]] | ||
|leader_title2 = | |legislature = [[Shahee Sansad]] | ||
|leader_name2 = | |upper_house = [[Shahee Sansad#Council of Representatives|Council of States]] | ||
|lower_house = [[Shahee Sansad#House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] | |||
|sovereignty_type = [[History of Rajyaghar]] | |||
|legislature = | |||
|upper_house = | |||
|lower_house = | |||
|sovereignty_type = | |||
|sovereignty_note = | |sovereignty_note = | ||
|established_event1 = Fall of the [[Rajana Dynasty]] | |established_event1 = Fall of the [[Rajana Dynasty]] | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = 815 CE | ||
|established_event2 = Creation of [[Satria Etruriana]] | |established_event2 = Creation of [[Satria Etruriana]] | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 1847 CE | ||
|established_event3 = Independence from [[Etruria]] | |established_event3 = Independence from [[Etruria]] | ||
|established_date3 = | |established_date3 = 1946 CE | ||
|established_event4 = [[Niralan Secession]] | |||
|established_date4 = 19XX CE | |||
|established_event5 = Saṅghīya Constitution | |||
|established_date5 = 19XX CE | |||
|established_event13 = <!--(up to 13 distinct events may be included)--> | |established_event13 = <!--(up to 13 distinct events may be included)--> | ||
|established_date13 = | |established_date13 = | ||
|area_km2 = 1,254,462 | |||
|area_km2 = | |area_sq_mi = 484,350 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |percent_water = 0.4 | ||
| | |population_estimate = | ||
| | |population_estimate_year = | ||
| | |population_census = 112,215,631 | ||
| | |population_census_year = 2020 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |||
| | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |GDP_PPP = | ||
|population_density_sq_mi | |GDP_PPP_year = 2020 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = $10,214 | |||
|GDP_PPP = | |GDP_nominal = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2020 | |||
|GDP_PPP_year = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $14,255 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |Gini = 42 | ||
|Gini_change = | |||
|GDP_nominal = | |Gini_year = 2021 | ||
|HDI_year = 2021 | |||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |HDI = 0.697 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $14,255 | |HDI_change = increase | ||
|currency = Rajyani Rupee (₹) | |||
|Gini = | |currency_code = RR | ||
| | |utc_offset = -2 | ||
|date_format = dd/mm/yyyy ({{wp|Common Era|CE}}) | |||
|Gini_year = | |drives_on = {{wp|right- and left-hand traffic|left}} | ||
|HDI_year = | |cctld = [[.ra]] | ||
|HDI = | |calling_code = +52 | ||
|HDI_change = | |||
|currency = | |||
|currency_code = | |||
|utc_offset = | |||
|date_format = | |||
|cctld = | |||
|calling_code = | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Rajyaghar''' ''({{wp|Gujarati language|Himavantan}}: રાજ્યઘર)'', officially the '''Kingdom of Rajyaghar''' ''(Himavantan: રાજ્યઘર રાજ્ય)'', is a [[Satria|Satrian nation]] in [[Coius]]. The sixth most populous country in the [[Kylaris|world]], the Kingdom of Rajyaghar is a federal monarchy that is subdivided into Union States and Federal Territories. Rajyaghar shares land borders with [[Ghamistan]] to the north, [[Padaratha]] to the south and [[Nirala]] to the south-east. To the west, Rajyaghar is bounded by the [[Aechelion Sea]] and the island nation of [[Venikara]]. The capital and largest city in Rajyaghar is [[Kinadica]] within the Capital Federal Territory. | |||
Since the {{wp|secession|Niralan Secession}}, the Kingdom of Rajyaghar has consisted of 11 Union States and 2 Federal Territories and the Autonomous Province of Nivasasthan. Rajyaghar covers 1,254,462 square kilometres (484,350 sq mi) with an estimated 2021 population of over 110 million people. Moving from the coast inland, Rajyaghar's geography is highly diverse ranging from the western lowlying coastal regions to the tropical forests that lie before the Pavitra Mountain range which separates western Rajyaghar from the eastern plateau. | |||
Rajyaghar is a fast-growing economy with a rapidly expanding information and technology sector which has moved the economy from being focused on agriculture to an increasingly diverse economy. With these changes, the country has seen a booming middle class which has transformed Rajyaghar into a | Rajyaghar is a fast-growing economy with a rapidly expanding information and technology sector which has moved the economy from being focused on agriculture to an increasingly diverse economy. With these changes, the country has seen a booming middle class which has transformed Rajyaghar into a consumer society. In the last two decades, there have been major government initiatives which have focused on literacy which have increased the literacy rate from 17% to 79% in 2020. This has also resulted in more people moving from the rural areas to the urban cities and towns which has resulted in large metropolitan areas such as the Kakeki metropolitan area. In order to prevent the development of slums that began to emerge across Coius during the 20th Century, the early Central Union Governments introduced basic {{wp|welfare state|welfare programmes}} and initiated public housing schemes. | ||
A {{wp| | A {{wp|Secular state|secular}}, {{wp|federation|federal}}, {{wp|constitutional monarchy}} since independence in 1946, Rajyaghar has been governed via a democratic parliamentary system. A developed country with a strong parliamentary democracy since the {{wp|constitution|Saṅghīya Constitution}}, the Kingdom is centred upon its conservative but libertarian principles with it being one of the first in Coius do legalise women's suffragae in 1960 and legalising same-sex marriage in 1990. Society itself is highly diverse due to its large multi-ethnolonguistic demographics. Although constitutionally a secular state, the Ashankic faith dominates the country and its influence is highly institutionalised. | ||
Rajyaghar is a member of the Community of Nations and Council for Mutual Development and a founding member of [[Bashurat Cooperation Organization]]. The country also maintains a {{wp|special relationship}} with its southern neighbour [[Padaratha]] and linguistic and cultural ties with [[Nirala]], [[Venikara]] and [[Ghamistan]]. | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
Modern day Rajyaghar is still considered the | The etymology of the name "Rajyaghar" is derived from the {{wp|Gujarati language|Himavantan}} words of "Raja" and "Ghar" meaning King and Home respectively. Translated literally, the name means ''Home of the Kings'' and was what early [[Euclea|Euclean Imperialists]] would refer to the region during the colonial era. A similar name, "Rajyamina" was used by Satrians throughout the !medieval period to refer to the land that now makes up Rajyaghar due to the dozens of Madhyarajyas that goverened the land prior to colonisation. Modern day Rajyaghar is still considered the ''Land of Kings'' due to its federal system of government in which all of the Union States and the Autonomous Province of Nivasasthan have ceremonial Heads which are descendants of the pre-colonial Maharajas which reigned over the pre-colonial Madhyarajyas. | ||
The usual way to refer to a citizen of Rajyaghar is "Rajyani" | The usual way to refer to a citizen of Rajyaghar is "Rajyani". In the early decades following independence, the majority of Rajyanis would identify more along state identities but since the 1980s there has been a notable shift with the citizenry commonly more often identifying as Rajyanis than with state identities. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
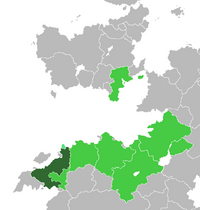
[[File:Satria Etruriana Location.png|200px|thumb|left|[[Satria Etruriana]] (dark green) amongst other [[Etruria|Etrurian colonies]] (green)]] | |||
Humans are thought to have arrived in Rajyaghar over 60,000 years ago with them being predominantly 'hunter-gatherers' which in turn has made the population of the land incredibly diverse. Settlements first began to emerge along the northern coastline and surrounding the Naratha River around 4,000 years ago, slowly evolving into the Ancient Rajyani Civilisations and then into the Naratha River Civilisation by 250 CE. Around this time was when the [[Ashankism|Ashankic faith]] began to emerge as well as a shared language and the clan system. Coalescence of communities and early political power gains around the Naratha River Basin resulted in the rise of the [[Jhanda Empire]] in the 3rd Century. The Jhanda Empire's lifespan would see the increasing status of women, development of a basic structure to society and a political framework that would last for centuries to come. The Empire would go onto conquer much of what is northern and coastal Rajyaghar until its subjugation in the 9th Century to the Sangma. | |||
| | |||
| [[ | |||
| The | |||
Throughout the Vikasan Era, the Ashankic faith would continue to dominate the region. The cultural integrity of the region was threatened numerous times during this period, ranging from the [[Irfan|irfanic sultanates]] from the north-east to the [[Togoti Khaganate]] from the east. [[Gaullica]] and [[Etruria|Etruria's]] arrival in the 19th Century would mark the end of domestic rule and the ushering in of the colonial era. In 1842, Etrurian Crown Rule began and the economy of Rajyaghar was transformed as the Madhyarajyas were united into [[Euclea|Euclean colonies]]. Over time, Etruria and Gaullica would introduce technological, educational and societal changes to Rajyaghar, some of which would be continued post-independence. By the time of the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], independence movements had begun to emerge, which was noted for its cooperative attitude which became a major factor in securing greater autonomy until the [[Solarian War]] in which the independence movement took up arms. | |||
Modern day Rajyaghar first came into being in 1946 when the [[Satria Etruriana]] and the [[Dominion of Belasaria]] became independent following the [[Coian Evacuation]]. 1947 saw the [[Gaullica|Gaullican colony]] of [[Tehandipour]] accede to the Kingdom via a referendum of the colonial population. Later that year, the Etrurian colony of [[Satria Libera]] was annexed into the Kingdom following a rapid invasion. The invasion was at the request of their Maharaja who had obtained power following a revolution against Etruria but was now facing a growing [[Council republic|Councilist]] uprising. Following the annexation, the territory was reformed into the Union State of [[Nivasasthan]]. | |||
In 19XX, a councillist uprising erupted in the Union State of Nirala. Following failed negotiations with the central government, the uprising developed into a complete rebellion sparking the [[Niralan Seccession]] (or ''War of Independence'' as it is known in Nirala). The [[Armed Forces of Rajyaghar|Rajyani military]] was in no state to fight this rebellion due to the recent Solarian War and its deployments across the rest of the country in an attempt to secure the national border. After only a few months, the rebels had secured control of the entire Union State and declared independence. The success of the rebellion placed immense pressure on the central government and with councilist movements becoming more popular in neighbouring southern Union States and growing pressure from the Community of Nations to end the conflict, the central government decided to recognise the independence of Nirala so that it could refocus the military on the remaining southern states. The failure of the central government in the Niralan Secession forced the central government to conduct a major political overhaul which dramatically shifted the balance of power from the Monarchy to the Shahee Sansad (legislature) bringing it more in line with Euclean style constitutional monarchies. Additionally, the !Bhojpuri majority Union State of Nivasasthan was given increased autonomy and given a new federal state classification as a "Princely State", effectively a Union State with increased autonomy. | |||
Rajyaghar is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, languages and beliefs and this diversity is a result of Rajyaghar's history. The history of Rajyaghar has also played a significant role in the development of its culture post-independence with aspects of modern Rajyani culture taken from different aspects of the cultures of the Kingdoms, Empires and Confederacies that came before it. | |||
=== | ===Colonial Rajyaghar=== | ||
[[File:Return visit of the Viceroy to the Maharaja of Cashmere.jpg|200px|thumb|left|A painting depicting several Maharajas signing treaties of suzerainty to Etruria]] | |||
Under Etrurian control, changes were made to the former [[Madhyarajyas]] that would remain in place even after independence. Changes included the consolidation of power into a centralised government led by the Etrurian Colonial Office. Educational, manufacturing, industrial and infrastructure reforms were undertaken. The creation of major infrastructure links, including canal systems, railways and the telegraph, increased the influence and power of the colonial regime and also allowed for the rapid movement of natural resources from Satria Etruriana to factories on the coast where the raw goods were turned to usable materials which would be transported back to Etruria. | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
The | The economic and social reforms introduced came with increased surveillance and control from the Etrurian regime which fostered resentment amongst the native populations. The transportation of natural resources out of Satria Etruriana also angered the native population which would eventually result in the [[1913 Chanak Rebellion]]. The rebellion came shortly after Etruria faced the [[Khordad Rebellion]] in [[Pardaran]] in 1912. The rebellion would highlight the invasive etrurian social and economic reforms and would also demonstrate the ruthlessness of the Etrurian regime in suppressing dissent. Although the rebellion was suppressed, it had laid the foundation for the independence struggle that would persist and grow. | ||
[[file:Lord Mountbatten addressing the Chamber of Princes.jpg|200px|thumb|right|A session of the Consular Senate]] | |||
The [[Great War]] saw the involvement of hundreds of thousands of Satria Etrurianan men under the [[Corpo di Soldati Ausiliario Satriani]]. The agreement to supply the colonial army with more troops from the native population was made by the Consular Senate, an advisory committee established by the Etrurian Colonial Empire in response to the 1913 Chanak Rebellion. The Senate had also secured guarantees that following the war a native legislature would be established for some self rule to be exercised. Following the war, a legislative assembly was established but was granted nominal powers, fueling greater resentment against Etruria. Calls for greater self rule increased following the Great War and throughout the subsequent [[Solarian War]]. Etruria’s collapse during the Solarian War and the devastation inflicted on [[Satria]] would see independence leaders turn to the [[Community of Nations]] for assurances of independence in return for Satria Etruriana’s withdrawal from the war. In 1946, Satria Etruriana surrendered in the Solarian War in return for independence being granted in October 1946. | |||
[[file: Ganga Singh c1930.jpg|150px|thumb|left|Krishan VI, 1st Maharaja of Rajyaghar]] | |||
After a century of colonial oppression, the form that an independent Rajyani government would take were questioned. Many of the independence leaders were the descendants of the former rulers of the Madhyarajyas and wanted to see their power and influence restored post-independence. Many of the rank and file members of the independence movement feared that after colonial rule, the monarchy would be a tool for establishment oppression against the common people. However, fears of [[Councilism|councilist insurgencies]] in the southern state of [[Nirala]] as well as ethnic tensions in Nivasasthan led many to fear that without a strong central government with a unifying theme, an independent Rajyaghar would quickly collapse. | |||
A {{wp|republic|republican system}} of governance brought the risk of a councilist takeover or rise of minority leadership at the presidential level if there was a charismatic, unifying minority figure and this worried the Rajyani establishment as there were already examples of these in the independence movement. A {{wp|constitutional monarchy}} was seen as a compromise between the hardliners in Sanyukt and Rathankot who wished to return to the medieval systems of governance and the socialists in the south who wished for a more democratic society. The monarchy would also rule out the possibility of an irfanic or other minority head of state which alleviated the fears of the Ashankic establishment who believed that if a minority were to become [[Premier of Rajyaghar|Premier]], their power could be tempered by the [[Shahee Sansad]] and Monarch. Throughout the independence struggle, Prince [[Krishan VI]] of Sanyukt had also been a fierce supporter of the ethnic minorities and so his appointment as the [[Monarchy of Rajyaghar|Maharaja]] was seen as a nod to those groups who feared that a monarchy would only represent ashanku interests. There were also fears that a presidential system would see complete ashankic-dominance in the politics of the country. Immediately after the Etrurian Evacuation, the Consular Senate sent a delegation to the Community of Nations petititoning for support for the new country which it obtained following guarantees of cooperation and the immediate suspension of hostilities against allied forces. | |||
===Independent Rajyaghar=== | |||
[[file: Sardar patel (cropped).jpg|150px|thumb|right|Baiju Kapadia, 1st Premier of Rajyaghar]] | |||
The end of the [[Solarian War]] saw the end of Etrurian colonial rule over Satria Etruriana and the establishment of the newly independent Kingdom of Rajyaghar. At the time of independence, Satria was consumed by destruction following the [[Great War]] and subsequent Solarian War. Despite this, Rajyaghar had significant economic opportunities. Rajyaghar was one of the largest producers of iron, and the industrial infrastructure built by [[Etruria]] was designed for efficient production, refinement and exportation of Rajyani natural resources. The resources also gave the Rajyani government the resources it would need to recover following the Solarian and Great Wars as well as invest in further industrial development and infrastructure. During these early years, the Central Union Government nationalised many industries in order to ensure control over the rebuilding process and rapidly bolster the national defence system. | |||
Despite the unity that was brought about following independence, natioanlist groups in Nivasasthan and Pinjar as well as councilst insurgents in Nirala led to increased tensions throughout the Kingdom leading to political instability in the south. It was also known that external organisations and hostile nations were funding councilist groups in Nirala and Nivasasthan in an attempt to undermine the [[Central Union Government]]. | |||
Under the leadership of Premier [[Baiju Pahir Kapadia]] and his centrist People’s Party, the government placed a large emphasis on state planning with the military, education and investment receiving the largest amount of funding. These plans helped revive the economy following the wars of the early 20th Century and protect Rajyani sovereignty and integrity. However, the councilst uprisings in the Union State of Nirala continued to grow and in 19XX erupted into a total rebellion resulting in the [[Niralan Secession]]. | |||
The | The immediate aftermath of the Niralan Seccession saw the split of the People’s Party under Kapadia into the centrist [[Liberal Party]] and left-leaning [[Cooperative Party]]. Under Kapadia’s successor, [[Anand Mahanti]], the cooperative party introduced major political reforms which shifted power from the Monarch and Ashankinc priests to the central govenrment and Shahee Sansad. Mahanti also established the national health service, codified the national educational curriculum and raised taxes in order to pay for social programmes. Slowing economic growth, increased councilst threats and growing ethnic tensions in Nivasasthan saw Mahanti’s cooperative party lose the 1955 election to the Liberals under [[Onkar Jariwala]]. Jariwala’s liberals would reverse the tax code of the CP and much of their socialist economic reforms. Jariwala would also grant increased autonomy to Nivasasthan resulting in it becoming an Autonomous Province within the Kingdom. During the late 50s, the government would also crack down on the councilist insurgencies in Sangam, banning the state councilist party and placing many of its members under house arrest. | ||
In the 1980s, the right-wing ashankic-nationalist RRP would rise to power. Despite a brief absence from government between 1985-88 as a result of failed agricultural reforms, the RRP under the leadership of Rajyaghar’s first female Premier, Kalyani Bajpeyi, would usher in an ‘economic renaissance’ with a reduced and simplified tax code, deregulation and privatisation. Many of the state bodies involved in raw material refinement and exportation as well as infrastructure development were sold off and privatised during this period which led to the rise of the millionaire class. Bajpeyi’s victory over the unions in the ’89 National Strike would also see the end of union dominance in rajyani politics and mark a clear shift in the general national political spectrum to the right. The RRP would lose power in the mid 1990s due to political infighting, resulting in the return of the Cooperative Party. Throughout the late 90s and early 2000s, social reform would rock Rajyani culture with continued economic growth seeing the emergency of Rajyaghar as a middle-income economy. However, in 2006, the economy would be hit by the collapse of the housing market which would see Rajyaghar enter a recession for the first time since independence. | |||
== | ==Politics and Government== | ||
[[File: Eminent film actor, Shri Amitabh Bachchan calling on the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, in New Delhi on December 20, 2014.jpg|300px|right|thumb|[[Monarchy of Rajyaghar|Maharaja]] [[Krishan VII]] and [[Premier of Rajyaghar|Premier]] [[Madhava Thakur]]]] | |||
The Kingdom of Rajyaghar is a {{wp|federal}}, {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary}}, {{wp|constitutional monarchy}}. The democratic system of governance, enshrined in the constitution, is centred on the ideals of {{wp|representative democracy}} and a strong {{wp|federal government}}. The [[Monarchy of Rajyaghar|Monarch]] of Rajyaghar, Maharaja [[Krishan VII]] since 1984, is the Head of State. The [[Premier of Rajyaghar|Premier]], currently [[Madhava Thakur]], is the Head of Government, appointed by the Monarch to lead the {{wp|executive government}} called the [[Central Union Government]] which itself is administered by the Premier led [[Cabinet of Rajyaghar|Ashta Pradhan]]. The Premier must be a member of, and maintain the confidence of, the national legislature; the Shahee Sansad. | |||
The | The [[Shahee Sansad]] is a {{wp|bicameralism|bicameral legislature}} comprising a [[Shahee Sansad#Council of States|Rajya Sabha]] (Council of States) and a [[Shahee Sansad#House of Representatives|Lokh Sabha]] (House of Representatives). The Council of States is made up of appointed individuals termed 'Councillors'. The House of Representatives is made up of Congressmen/women of which 400 are {{wp|Single-member district|single member constituent representatives}} and 100 are elected via the {{wp|party-list proportional representation}} method. A [[Consular Senate]] also exists which is comprised of the Rajakumars (Princes) of the Union States. The body is an {{wp|advisory opinion|advisory body}} to the Monarch and wields significant influence over the Council of State, independent advisory bodies and other government institutions. | ||
===Government=== | |||
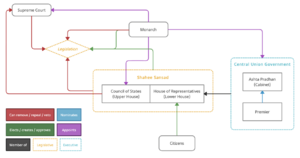
[[File: Political_system_of_Rajyaghar.png|300px|right|thumb|Political system of Rajyaghar]] | |||
Rajyaghar is a {{wp|federation|federation}} with a {{wp|parliamentary system}} in which the Monarch ''"serves to protect Rajyani culture, democracy and sovereignty"'' and from which all federal authority is derived. The federal relationship of the country is defined as the ''"Loyalty and Fielty of the Union States to the Crown and the Defence and Safeguard of the Union States by the Crown."'' Since independence, the autonomy of the Union States has slowly been eroded at the expense of the Central Union Government resulting a 'quasi-federal' system. | |||
The {{wp|executive government|federal government}} of the Kingdom is the [[Central Union Government]] which is comprised of Ministers of State. The most senior ministers of state (Secretaries of State) lead government departments and serve in the [[Cabinet of Rajyaghar|Ashta Pradhan]] (Cabinet). Ministers of State are nominated by the [[Premier of Rajyaghar]], to the Monarch, from the membership of the [[House of Representatives (Rajyaghar)|House of Representatives]], thus ensuring their accountability to the legislature. Like Ministers of State, the Premier is required to be a member of the House of Representatives. In accordance with the constitution, the Premier must maintain the confidence of the House. Therefore, the Monarch appoints the leader of the largest party or coalition in the House to serve as Premier. Constitutionally, the Premier is required to nominate Ministers of State to the Monarch but a seperate clause outlines that the Secretaries of State for Foreign Affairs and Defence are appointed by the Monarch on the advice of the Premier. The subtle difference in wording has allowed the Maharaja to intervene on the appointment of these two Ministers. | |||
[[ | |||
===Legislature=== | |||
{{Sidebar | |||
| name = Shahee Sansad | |||
| outertitle = [[Shahee Sansad|House of Representatives]] | |||
| topimage = | |||
| pretitle = | |||
| title = | |||
| image = [[File:20thShaheeSansad.svg|180px]] | |||
| headingstyle = | |||
| contentstyle = | |||
= | | heading1 = HM Government | ||
| content1 = {{legend|#FFA500|[[Rajyani Rashtriya Party]]: 229}} {{legend|#005DFF|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Udāramātāvāḍī]]: 68}} | |||
<br> | |||
| heading2 = HM Official Opposition | |||
| content2 = {{legend|#BF0505|[[Cooperative Party]]: 150}} {{legend|pink|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Sabraj Party]]: 12}} {{legend|purple|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Khisako Party]]: 8}} {{legend|lime|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Prakrati Party]]: 7}} | |||
<br> | |||
| heading3 = Other Opposition Parties | |||
| content3 = {{legend|#006D11|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Irfanic Coalition]]: 20}} {{legend|#D800DC|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|Tarkhana National Party]]: 4}} {{legend|yellow|[[List of political parties in Rajyaghar|PLU]]: 2}} | |||
= | |||
{{ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
The | The [[Shahee Sansad]] is the federal legislature of the Kingdom of Rajyaghar. It is a {{wp|bicameralism|bicameral legislature}} comprised of an upper chamber, the Council of States, and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. The Shahee Sansad can make federal law, pass resolutions of war, approve treaties, has the {{wp|power of the purse}} and {{wp|impeachment}}, through which it can remove Ministers of State, Judicial Officers and other members of the federal government. | ||
=== | =====House of Representatives===== | ||
The Lokh Sabha (House of Representatives) is comprised of 500 members called ''Congressmen/women''. The presiding officer of the House is the Speaker who is elected from amongst its members. The Speaker is required to be independent and must resign their party membership when they come to power. 400 of the Congressmen/women are elected from {{wp|Single-member district|single member constituencies}} via a {{wp|first-past-the-post voting}} system. The remaining 100 Congressmen/women are elected via the {{wp|party-list proportional representation}} method. Due to this system, there are multiple political parties in the Shahee Sansad. Since the 1960s, the two largest parties have been the [[Rajyani Rashtriya Party]] and [[Cooperative Party]]. Additional smaller parties include Udāramātāvāḍī (Liberal Party), Tarkhana National Party and Irfanic Coalition. Due to the advent of multiple minor political parties, coalitions have formed and organised the left and right of the political spectrum with the [[National Progressive Alliance]] dominating the left and being led by the CP, and the RRP leading the right-wing coalition; [[United Conservative Coalition]]. | |||
The Lokh Sabha is tasked with the formation of the Central Union Government due to the Premier and members of the Ashta Pradhan all being members of the chamber. Despite being a bicameral legislature, all Acts of Legislation must originate from the Lokh Sabha. Additional duties of the Lokh Sabha include creating the budget (done by the Government and passed by the Lokh Sabha), putting forward resolutions for war and keeping the CUG to account. The chamber also has the right to demand the resignation of the Government if it passes a {{wp|vote of no confidence}} against it. | |||
== | =====Council of State===== | ||
The Rajya Sabha (Council of States) is comprised of 250 members called ''Councillors'' who are all required to be non-partisan. The presiding officer of the Council is the Crown Prince, however, day to day duties are performed by the Adyaksh (Chairman) who is elected from amongst the Councillors. All councillors are appointed by the Monarch but are done so on different grounds: | |||
* 112 Councillors are appointed due to their status as leaders of the 112 registered clans | |||
* 100 Councillors are appointed on the advice of the Independent Royal Appointments Committee | |||
* 30 Councillors are appointed from ranks of the [[Armed forces of Rajyaghar|military]] | |||
* 8 Councillors are religious appointees | |||
The Council of State is tasked with amending, passing or rejecting legislation originating from the Lokh Sabha. The Council is also tasked with the approval of treaties, passing resolutions of war recieved from the House, approving nominees put forward by the Government and approving the budget created by the House. The Council of State can also hold the government to account via a motion of concern which, if passed, would trigger a joint session of the Shahee Sansad in which a vote of confidence will be held. The Council of State cannot hold a vote of confidence alone, unlike the House. | |||
In most cases, if the House and Council disagree on legilsation, it will undergo legislative ''ping-pong'' two times before both chambers meet in a joint session in which the House will have the advantage due to its larger size. However, in the case of the budget, the Council of State may veto a budget if they disapprove of the spending allocated to foreign and military affairs. | |||
===Judiciary=== | |||
The | The Kingdom of Rajyaghar has a multi-tiered independent judiciary consisting of the ''Federal Supreme Court'', headed by the Nyayadhyaksh (Chief Justice), Union State High Courts, a large number of Crown Courts and an even larger number of Clan (Civil) and Magistrate (Criminal) Courts. Justices of the Supreme Court and State High Courts are appointed by the Monarch on the advice of the {{wp|Bar Association}}, whilst Crown and Magistrate Court judges are appointed by Union State Princes, on the advice of the IJAC, and Clan Court judges are appointed by Clan leaders. | ||
{{ | |||
| | |||
Justices of the Supreme Court are nominated to the Maharaja by the Premier on the advice of the {{wp|Bar Association}}. The Nyayadhyaksh is nominated by the Premier from amongst the Supreme Court to the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). Justices of the State High Courts are nominated by First Ministers, on the advice of their Bar Associations, to their respective Rajakumars. Crown Court and Magistrate Court justices are appointed by First Ministers at their discretion. Clan Court judges are appointed by their respective Clan leaders however, these rulings can more frequently be appealed to the higher Crown Courts. | |||
===Administrative Divisions=== | ===Administrative Divisions=== | ||
{{Main|2 = Administrative divisions of Rajyaghar}} | |||
Rajyaghar is a {{wp|federation}} of 11 Union States, 2 federal territories and the Autonomous Princely State of Nivasasthan. Each state is divided into {{wp|Provinces}} which are subdivided into {{wp|Communes}}, with smaller states typically having only Communes. The administrative divisions are based on the historical [[Madhyarajyas|middle kingdoms]] of Rajyaghar with all of them retaining their royal families which serve as ceremonial representatives of the Monarch in the Union States and are granted the titles of ''"Rajakumars"''. | |||
Each Union State has a state government and legislature based off of the {{wp|Westminster System|Northabbey model}}. State Governments are led by a Mukhyamantrī (First Minister) who appoints their own state cabinet to assist in the duties of the state. Lower-level administration is further devolved from state governments to local authorities; provinces and communes. | |||
'''List of Union States of Rajyaghar''' | |||
{{div col|colwidth=10em}} | |||
| | * {{flagicon image|BhalesariaFlag.png}} [[Bhalesaria]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|ZulmatFlag.png}} [[Zulmat]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|SanyuktFlag.png}} [[Sanyukt]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|ChanakFlag.png}} [[Vikhera Pradesh]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|RathankotFlag.png}} [[Rathankot]] | ||
* {{flagicon image|BishnupurFlag.png}} [[Bishnupur]] | |||
* {{flagicon image|PinjarFlag.png}} [[Pinjar]] | |||
|Rathankot | * {{flagicon image|HarringhataFlag.png}} [[Harringhata]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|DedhaFlag.png}} [[Pavitra Pradesh]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|Flag-19.png}} [[Sangam]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|SanosraFlag.png}} [[Saumala]] | ||
| | * {{flagicon image|TarkhanaFlag.png}} [[Tarkhana]] | ||
|- | * {{flagicon image|KendraPradeshFlag.png}} [[Nivasasthan]] | ||
| | {{div col end}} | ||
|Tarkhana | |||
| | |||
==Foreign Relations== | ==Foreign Relations== | ||
===Foreign Policy=== | ===Foreign Policy=== | ||
{{Main|2 = Foreign Relations of Rajyaghar}} | |||
Rajyaghar is a member of the [[Community of Nations]], joining the organisation the same day that the Kingdom became an independent, sovereign nation. Rajyaghar is also a member of the [[International Trade Organization|ITO]] and [[Council for Mutual Development]] (COMDEV) as well as being a founding member of [[Bashurat Cooperation Organization]] (BCO). The Kingdom of enjoys warm relations with her fellow COMDEV member states; with their embassies hosted close to Government Hill in Kinadica as a sign of their diplomatic importance to the Kingdom. | |||
Rajyaghar | The foreign relations of Rajyaghar are managed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, with His Majesty's Diplomatic Corps being run by the Secretariat of Diplomatic Missions within the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Since independence, the Kingdom has sought to establish an expansive and diverse diplomatic network. During the [[Satrian Wars and Conflicts|early Satrian wars]], Rajyaghar developed a particularly close relationship with her western neighbour, [[Padaratha]]. Although typically aligned with [[Senria]] throughout the late 20th Century, the country has sought to carve its own independent foreign policy in a bid to act as a broker of foreign disputes in southern Coius. | ||
The | The nations of [[Senria]], [[Padaratha]] and [[Venikara]] are the most favourably viewed countries by the Rajyani people. | ||
===Armed Forces=== | ===Armed Forces=== | ||
{{Main|2 = Armed Forces of Rajyaghar}} | |||
[[File:Indian Army soldiers move into position while demonstrating a platoon-level ambush to U.S. Army paratroopers during Yudh Abhyas 2013.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Army personnel conducting drills]] | [[File:Indian Army soldiers move into position while demonstrating a platoon-level ambush to U.S. Army paratroopers during Yudh Abhyas 2013.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Army personnel conducting drills]] | ||
''His Majesty's Armed Forces'' is the professional military of the Kingdom of Rajyaghar and is charged with the defence of the Sovereign, the Kingdom and Rajyani interests. The armed forces consist of three branches: The [[Royal Navy (Rajyaghar)|Royal Navy]], the [[ | ''His Majesty's Armed Forces'' is the professional military of the Kingdom of Rajyaghar and is charged with the defence of the Sovereign, the Kingdom and Rajyani interests. The armed forces consist of three branches: The [[Royal Navy (Rajyaghar)|Royal Navy]], the [[Grand Army (Rajyaghar)|Grand Army]] and the [[Royal Air Force (Rajyaghar)|Royal Air Force]]. HM's Armed Forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence with the {{wp|national security council|National Security Council}} having control. Day to day management of the forces is led by the Minister of Defence with the Senapati (Chief of the Defence Staff) being the operational commander of the armed forces. The supreme commander-in-chief of the armed forces is the Rajyani Sovereign, to which all members of the armed forces swear an oath of allegiance, not to the constitution. The armed forces are an active military force, regularly conducting unilateral operations as well as participating in COMSED operations. At present, the Kingdom does not operate any overseas facilities. | ||
[[File:45153648 river class.jpg|145px|thumb|left|Sarisra Squadron at the mouth of the Naratha River]] | [[File:45153648 river class.jpg|145px|thumb|left|Sarisra Squadron at the mouth of the Naratha River]] | ||
There are numerous special branches of the military which have unique and distinct mission objectives. Within the Royal Navy, there is ''"The Aegis"'' which is a dedicated fleet tasked with defending territorial waters and projecting maritime strength in the Acheloian Sea. The Royal Navy also operates the ''"Sarisra Squadron"'' which is a dedicated group of {{wp|River-class offshore patrol vessel|river ships}} tasked with patrolling the major rivers of Rajyaghar to prevent against smuggling and other illegal activities. The | There are numerous special branches of the military which have unique and distinct mission objectives. Within the Royal Navy, there is ''"The Aegis"'' which is a dedicated fleet tasked with defending territorial waters and projecting maritime strength in the Acheloian Sea. The Royal Navy also operates the ''"Sarisra Squadron"'' which is a dedicated group of {{wp|River-class offshore patrol vessel|river ships}} tasked with patrolling the major rivers of Rajyaghar to prevent against smuggling and other illegal activities. The Grand Army maintains the ''"Marine Commando Group" (MCG)'', an elite corps within the army which is often tasked with conducting the most difficult of operations. The Royal Air Force operates the ''"Specialist Paratrooper Service" (SPS)'' which often works alongside the MCG in difficult operations. The air force alaso operates the ''"Rajyani Attack Wing" (RAW)''. In recent years, there have been debates within the Ministry of Defence and the parliamentary Committee on Defence about the possible creation of a fourth branch of the military dedicated to specialist service groups; namely the MCG, SPS and RAW. In 2019, Premier Thakur stated his support for a special branch of the armed forces at a {{wp|passing out (military)|passing out}} ceremony at Amdara Military College. | ||
The Navy is the most senior of the three branches of the military due to its role in Sanyukti history and its cultural significance. The Royal Navy is a {{wp|green-water navy|green-water navy}} due to its ability to operate within the nation's own territorial waters and in the wider Acheloian Sea. The current government has sought to further increase the range and operational abilities of the Navy and has awarded contracts for the creation of dedicated {{wp|Helicopter carrier|helicopter carriers}} to further project Rajyani military power. | The Navy is the most senior of the three branches of the military due to its role in Sanyukti history and its cultural significance. The Royal Navy is a {{wp|green-water navy|green-water navy}} due to its ability to operate within the nation's own territorial waters and in the wider Acheloian Sea. The current government has sought to further increase the range and operational abilities of the Navy and has awarded contracts for the creation of dedicated {{wp|Helicopter carrier|helicopter carriers}} to further project Rajyani military power. | ||
| Line 456: | Line 238: | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
[[File:Singapore Marina Bay 26.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Kinadica Financial Centre]] | [[File:Singapore Marina Bay 26.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Kinadica Financial Centre]] | ||
Rajyaghar is a {{wp|developing economy|developing economy}} which is generally considered to be a {{wp|middle class|middle-income}} {{wp|market economy|market economy}}. With a GDP of ₹1. | Rajyaghar is a {{wp|developing economy|developing economy}} which is generally considered to be a {{wp|middle class|middle-income}} {{wp|market economy|market economy}}. With a GDP of ₹1.6 trillion in 2019 and is one of the largest economies in Satria. In 2020, the Secretariat of National Statistics revealed that the unemployment rate was 5.8%, a reduction from 2015 where it was 6.7%. | ||
Since independence, successive governments have maintained protectionist policies in order to protect and develop domestic, internal industries such as agriculture and manufacturing. This involved government intervention to prop up major businesses and extensive regulation over certain industries. However, the return to power of the RRP in 1988 saw the RRP usher in a new era of economic liberalism which has dramatically increased economic growth and reduced unemployment in the Rajyaghar. However, some industries still retain heavy government involvement such as agriculture where the national government ensures a minimum price for basic crops to ensure the survival of small farms across the country. | Since independence, successive governments have maintained protectionist policies in order to protect and develop domestic, internal industries such as agriculture and manufacturing. This involved government intervention to prop up major businesses and extensive regulation over certain industries. However, the return to power of the RRP in 1988 saw the RRP usher in a new era of economic liberalism which has dramatically increased economic growth and reduced unemployment in the Rajyaghar. However, some industries still retain heavy government involvement such as agriculture where the national government ensures a minimum price for basic crops to ensure the survival of small farms across the country. | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
Rajyaghar is the | Rajyaghar is the seventh most populous country in the world, with a 2021 estimate of over 112 million according to the Secretariat of National Statistics, a department of the Ministry of Home Affairs. | ||
The population dramatically increased in the | The population dramatically increased shortly after independence and then once again in the 1980s during the economic renaissance. Since the 1990s, government policies have been enacted to encourage families to only have 2 children. Such policies include the limitation of child benefits to households to the first two children only. The number of families with over 2 children has steadily fallen since 2004. Rajyaghar's under 25s make up just over 50% and the over 60s make up 20% of the population. The sex ration was 9 females for 10 males in 2019 and it has been showing an upward trend in the last two decades with the female ratio increasing. | ||
Since the early 2000s, there has been a dramatic increase in urbanisation across Rajyaghar, with many analysts pointing to increased economic opportunities in urban centres and due to increased literacy and improved acceess to educational facilities across the country. In 2020, the SNS published figures which showed that literacy was now at 79% and expected to reach 85% in 2025. There are now also over 10 cities across the country which are each home to over 2 million people. | Since the early 2000s, there has been a dramatic increase in urbanisation across Rajyaghar, with many analysts pointing to increased economic opportunities in urban centres and due to increased literacy and improved acceess to educational facilities across the country. In 2020, the SNS published figures which showed that literacy was now at 79% and expected to reach 85% in 2025. There are now also over 10 cities across the country which are each home to over 2 million people. | ||
| Line 500: | Line 252: | ||
===Religion and Ethnicity=== | ===Religion and Ethnicity=== | ||
[ETHNICITY SECTION] | |||
Rajyaghar is officially a secular country but it is dominated by the [[Ashankism|Ashankic faith]] of which 67% of the population are followers. This is, in part, due to the significant role of Ashankism throughout Rajyani history with many of the Madhyarajyas being Ashankic realms which spread the faith during their conquests and expansions. Similarly, throughout its history the country has seen the arrival of many different religions such as the spread of [[Ashram]] and [[Tulyata]] during the Sangma Period, the arrival of [[irfan|irfanism]] with the [[Togoti Khaganate]] in medieval Rajyaghar, and the arrival of [[Sotirianity]] with the [[Etruria|Etrurian Colonial]] and [[Gaullica|Gaullican Empires]] in the 19th Century. | |||
===Language=== | |||
The official language of Rajyaghar is {{wp|Gujarati language|Himvastatan}}, owing to the dominance of the himvastatan speaking middle kingdoms throughout the Vikasan Era and extended history of Rajyaghar. Several regional languages or dialects are spoken throughout the country. Predominant amongst them is {{wp|Marathi language|bhasdilan}}, which is spoken in the south-west of the nation particularly in the Union State of Harringhata. {{wp|Sindhi language|!Sindhi}} and {{wp|Punjabi language|zebadi}}, two closely related but distinct languages are recognised as the “second languages” of the south-eastern Union States such as Sangam and Nivasasthan. | |||
The official language of Rajyaghar is {{wp| | |||
The ‘borders’ of the language groups throughout Rajyaghar can easily be correlated with the geographic, historical, ethnic and current administrative division boundaries. In the south- | The ‘borders’ of the language groups throughout Rajyaghar can easily be correlated with the geographic, historical, ethnic and current administrative division boundaries. In the south-west, the Union State of Harringhata is the successor to the historical Kingdom of Harringhata which spoke Bhasdilan, hence the prevalence of Bhasdilan throughout the state. Similar historical relations can be made for all of the language regions of Rajyaghar. Additionally, the Pavitra Mountain Range which runs through southern Rajyaghar acts as a language barrier between the Himvastatan states to the north of the mountain range and the various different languages to the south. | ||
{{wp|Italian language|Vespasian}} is widely spoken as a second language throughout Rajyaghar regardless of which Union State you are in and this is due to the influence and impact of the Etrurian Colonial Empire during the 19th and 20th centuries in Rajyaghar. During this colonial period, the Etrurian Colonial Empire enforced an educational curriculum which mandated the teaching of Vespasian in all schools throughout Rajyaghar and the Empire also invested in programmes to teach adults Vespasian. To this day, many pupils are still taught Vespasian in Rajyani schools. | {{wp|Italian language|Vespasian}} is widely spoken as a second language throughout Rajyaghar regardless of which Union State you are in and this is due to the influence and impact of the Etrurian Colonial Empire during the 19th and 20th centuries in Rajyaghar. During this colonial period, the Etrurian Colonial Empire enforced an educational curriculum which mandated the teaching of Vespasian in all schools throughout Rajyaghar and the Empire also invested in programmes to teach adults Vespasian. To this day, many pupils are still taught Vespasian in Rajyani schools. | ||
Since independence, a three-language formula has been administered throughout the national educational curriculum: | Since independence, a three-language formula has been administered throughout the national educational curriculum: | ||
* First language: | * First language: Himvastatan | ||
* Second language: | * Second language: Vespasian | ||
* Third language: local language i.e. | * Third language: local language i.e. Bhasdilan, Zubadi, Vijayan, etc, | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
[[File: Navratri garba at Ambaji temple.jpg|150px|right|thumb|Devkevapse Festival]] | |||
Rajyani culture spans a history of more than 5,000 years dating back to the earliest recorded history of civilisation in Rajyaghar; the Ancient Rajyani Civilisations in 2500 BC. It was during this period that the foundations of ashankic philosophy, mythology and practice were laid down, with many of these practices and beliefs still existing and playing a dominant role in rajyani society today. Whilst the country has seen an influx of euclean culture due to its colonial history, there are many aspects of rajyani culture that have remained the same throughout history. One aspect is clothing where, whilst casual euclean clothing has become more popular, items of clothing such as the {{wp|Achkan|achkan}} are still common place and the norm for male clothing, with the {{wp|sari|sari}} being the same for women. | |||
Rajyani festivals and national holidays are influenced by significant historical events, such as independence and military victories, as well as by religious festivals such as [[Diwasadak]] ''(Fesitval of Lights)'' and [[Devkevapse]] ''(Festival of the Homecoming)''. | |||
===Society=== | |||
{{multiple image | |||
|align = right | |||
|direction = | |||
|width = | |||
|caption_align = center | |||
|header_align = center | |||
|header = Clothing in Rajyaghar | |||
|image1 = Styles of Sari.jpg | |||
|width1 = 115 | |||
|caption1 =Styles of sari | |||
|image2 = A bridegroom outfit for Indian wedding.jpg | |||
|width2 = 150 | |||
|caption2 = Bridegroom attire | |||
}} | |||
Umersatham, literally meaning "with age comes respect", is a widely held and institutionalised belief in Rajyaghar that deference should be showed to elders and those in positions of power and authority due to their experience, length of service and wisdom. Umersatham is closely linked to the hierarchical nature of Rajyani society. | |||
Rajyani society is often described as hierarchical with the aristocracy and landowners at the apex, often enjoying institutional advantages particularly in education and employment opportunities. The caste system that was present during the medieval period is no longer observed and there are now several anti-discriminatory laws in place to dismantle remaining prejudices and discriminatory behaviour associated with castes. Society in Rajyaghar is dominated around the clan system. | |||
Family values are a vital part of Rajyani tradition, with it being closely associated with the clan system. Since the 1980s, family planning has been a key priority of successive governments which has led to a dramatic reduction in family sizes as nuclear families have become the norm. The influences of senior family members still play a large role in Rajyani society, with many marriages, with consent, are arranged by family elders. Marriage, legal for those 18 and over, is considered a sacred institution in all the major religions in Rajyaghar with divorce being a taboo, resulting in the divorce rate being extremely low. Unlike many other parts of the continent, the gender ratio of Rajyaghar is not skewed in part due to low female infanticide rates unlike in other parts of Coius. Women hold a significant role in society and are considered equals to males due to their historical and religious influence; with many of the Madhyarajyas female rulers dominating Rajyani history. | |||
====Clans==== | |||
In modern Rajyaghar, the historical clans of the past still have considerable influence. During the Vikasan era, when the Middle Kingdoms of Rajyaghar were being formed, clans retained their clan structures and the new Kingdoms and Empires would become collections of clans rather than merging clans together. In modern Rajyaghar, Clans have become societal groups with people of the same Clan often being from the same religious predisposition and living in the same states and cities. Most Clans have also retained their leading families which has resulted in the leaders of the Clans maintaining incredible influence within Rajyani society. As a result of this, the leaders of all of the recognised clans of Rajyaghar (112 in total) are granted seats in the Shahee Sansad to represent their members who may be spread across multiple Shahee Sansad elected constituencies. | |||
Throughout Rajyani history, numerous clans would be part of a single Kingdom and as such, no clan would exist in more than one kingdom. When Kingdoms expanded, clans would either gain or lose territory, rather than a part of the territory being part of one kingdom and another being part of another kingdom. There would also be migration of individuals into their new territories or away from lost ones. Clan Leaders would often make up advisory councils for their Kingdom's Maharaja and even in modern day Rajyaghar, Clan Leaders still form advisory councils to the successors of the Maharajas of the Middle Kingdoms; the Union State Rajakumars. | |||
===Customs=== | |||
Many customs originating from medieval and ancient Rajyaghar are still observed and hold significance in Modern-Rajyaghar. Zimankar and Santubhav are considered to be the most important and are often cited as the reasoning behind Rajyaghar’s relatively low crime rate, extensive natural protection laws and regulations, and the deference still shown to elders and those in positions of authority. | |||
[[file: Namaste to the rising sun, Hindu culture religion rites rituals sights.jpg|200px|left|thumb|Traditional Rajyani greeting]] | |||
"Zimankar", a combination of the matrabashi words for responsibility, duty and honesty, is a Rajyani idea which believes all people should acknowledge the mistakes and misdeeds that they have conducted and take responsibility and improve. "Santubhav", a combination of the matrabashi words ‘santulan’ and ‘sadbhaav’ meaning balance and harmony respectively, and it is a Rajyani principle centred around the beliefs that one should live a balanced life between work and leisure, between care for oneself and for others and that all actions should be done in harmony with society and nature. The principle of santubhav is a key part of Rajyani society with it being closely linked to Ashankism and the idea of reincarnation. | |||
In Rajyaghar, it is common practice to hold the hands at chest level together with the palms touching when greeting others. This is comparable to handshaking seen elsewhere. The practice of handshaking is uncommon in Rajyaghar with the !namaste greeting replacing it. The bow and curtsey are common practice when greeting members of the royal family and it is seen as a mark of disrespect and insult not to do so. Followers of Ashankism will also typically bow with the right hand placed over their heart before entering temples and when standing before idols of Gods. | |||
=== | ===Education=== | ||
[[file: FRI entry block.JPG|150px|right|thumb|Marola University]] | |||
Education in Rajyaghar is a federal issue with some devolved power for Union States. The national curriculum, which is implemented from Grade 1 through 12, is set by the Ministry of Education in conjunction with educational boards. Union States then supplement the curriculum, with the native language, history and culture often being reinforced in the state curriculum. Education is compulsory until Grade 12 (Age 17-18) with the vast majority of the population being educated in free state run schools. Following Grade 12, students have the opportunity to enroll in one of 120 Universities. The large resources devoted to education since the 1970s have been a key contributor to the economic development of Rajyaghar. In the 2020 census, about 79% of the population was literate, with 83% for men and 75% for women. | |||
Despite the vast government run education system, there are thousands of independent, prviate and religious schools throughout the country although their curriculum is constrained by federal regulations. | |||
{{Rajyaghar}} | {{Rajyaghar}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 28 May 2023
Template:Region icon Kylaris Template:Region icon Kylaris
Kingdom of Rajyaghar રાજ્યઘર રાજ્ય | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Rājā nī Jaya Hail to the King | |
| Anthem: Kramākramānē Step by Step | |
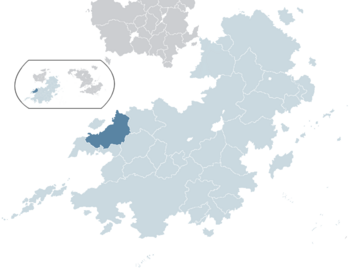 Location of Rajyaghar in Coius | |
| Capital and largest city | Kinadica |
| Official languages | Himavantan |
| Recognised regional languages | Matrabashi, Bhasdila, !Bihari, Tamisari |
| Ethnic groups (2021) |
|
| Religion | Ashankism (majority, unofficial) |
| Demonym(s) | Rajyani |
| Government | Federal, Parliamentary, Constitutional Monarchy |
• Maharaja | Krishan VII |
• Premier | Madhava Thakur |
| Legislature | Shahee Sansad |
| Council of States | |
| House of Representatives | |
| History of Rajyaghar | |
• Fall of the Rajana Dynasty | 815 CE |
• Creation of Satria Etruriana | 1847 CE |
• Independence from Etruria | 1946 CE |
| 19XX CE | |
• Saṅghīya Constitution | 19XX CE |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,254,462 km2 (484,350 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.4 |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 112,215,631 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Per capita | $10,214 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Per capita | $14,255 |
| Gini (2021) | 42 medium |
| HDI (2021) | medium |
| Currency | Rajyani Rupee (₹) (RR) |
| Time zone | UTC-2 |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +52 |
| Internet TLD | .ra |
Rajyaghar (Himavantan: રાજ્યઘર), officially the Kingdom of Rajyaghar (Himavantan: રાજ્યઘર રાજ્ય), is a Satrian nation in Coius. The sixth most populous country in the world, the Kingdom of Rajyaghar is a federal monarchy that is subdivided into Union States and Federal Territories. Rajyaghar shares land borders with Ghamistan to the north, Padaratha to the south and Nirala to the south-east. To the west, Rajyaghar is bounded by the Aechelion Sea and the island nation of Venikara. The capital and largest city in Rajyaghar is Kinadica within the Capital Federal Territory.
Since the Niralan Secession, the Kingdom of Rajyaghar has consisted of 11 Union States and 2 Federal Territories and the Autonomous Province of Nivasasthan. Rajyaghar covers 1,254,462 square kilometres (484,350 sq mi) with an estimated 2021 population of over 110 million people. Moving from the coast inland, Rajyaghar's geography is highly diverse ranging from the western lowlying coastal regions to the tropical forests that lie before the Pavitra Mountain range which separates western Rajyaghar from the eastern plateau.
Rajyaghar is a fast-growing economy with a rapidly expanding information and technology sector which has moved the economy from being focused on agriculture to an increasingly diverse economy. With these changes, the country has seen a booming middle class which has transformed Rajyaghar into a consumer society. In the last two decades, there have been major government initiatives which have focused on literacy which have increased the literacy rate from 17% to 79% in 2020. This has also resulted in more people moving from the rural areas to the urban cities and towns which has resulted in large metropolitan areas such as the Kakeki metropolitan area. In order to prevent the development of slums that began to emerge across Coius during the 20th Century, the early Central Union Governments introduced basic welfare programmes and initiated public housing schemes.
A secular, federal, constitutional monarchy since independence in 1946, Rajyaghar has been governed via a democratic parliamentary system. A developed country with a strong parliamentary democracy since the Saṅghīya Constitution, the Kingdom is centred upon its conservative but libertarian principles with it being one of the first in Coius do legalise women's suffragae in 1960 and legalising same-sex marriage in 1990. Society itself is highly diverse due to its large multi-ethnolonguistic demographics. Although constitutionally a secular state, the Ashankic faith dominates the country and its influence is highly institutionalised.
Rajyaghar is a member of the Community of Nations and Council for Mutual Development and a founding member of Bashurat Cooperation Organization. The country also maintains a special relationship with its southern neighbour Padaratha and linguistic and cultural ties with Nirala, Venikara and Ghamistan.
Etymology
The etymology of the name "Rajyaghar" is derived from the Himavantan words of "Raja" and "Ghar" meaning King and Home respectively. Translated literally, the name means Home of the Kings and was what early Euclean Imperialists would refer to the region during the colonial era. A similar name, "Rajyamina" was used by Satrians throughout the !medieval period to refer to the land that now makes up Rajyaghar due to the dozens of Madhyarajyas that goverened the land prior to colonisation. Modern day Rajyaghar is still considered the Land of Kings due to its federal system of government in which all of the Union States and the Autonomous Province of Nivasasthan have ceremonial Heads which are descendants of the pre-colonial Maharajas which reigned over the pre-colonial Madhyarajyas.
The usual way to refer to a citizen of Rajyaghar is "Rajyani". In the early decades following independence, the majority of Rajyanis would identify more along state identities but since the 1980s there has been a notable shift with the citizenry commonly more often identifying as Rajyanis than with state identities.
History
Humans are thought to have arrived in Rajyaghar over 60,000 years ago with them being predominantly 'hunter-gatherers' which in turn has made the population of the land incredibly diverse. Settlements first began to emerge along the northern coastline and surrounding the Naratha River around 4,000 years ago, slowly evolving into the Ancient Rajyani Civilisations and then into the Naratha River Civilisation by 250 CE. Around this time was when the Ashankic faith began to emerge as well as a shared language and the clan system. Coalescence of communities and early political power gains around the Naratha River Basin resulted in the rise of the Jhanda Empire in the 3rd Century. The Jhanda Empire's lifespan would see the increasing status of women, development of a basic structure to society and a political framework that would last for centuries to come. The Empire would go onto conquer much of what is northern and coastal Rajyaghar until its subjugation in the 9th Century to the Sangma.
Throughout the Vikasan Era, the Ashankic faith would continue to dominate the region. The cultural integrity of the region was threatened numerous times during this period, ranging from the irfanic sultanates from the north-east to the Togoti Khaganate from the east. Gaullica and Etruria's arrival in the 19th Century would mark the end of domestic rule and the ushering in of the colonial era. In 1842, Etrurian Crown Rule began and the economy of Rajyaghar was transformed as the Madhyarajyas were united into Euclean colonies. Over time, Etruria and Gaullica would introduce technological, educational and societal changes to Rajyaghar, some of which would be continued post-independence. By the time of the Great War, independence movements had begun to emerge, which was noted for its cooperative attitude which became a major factor in securing greater autonomy until the Solarian War in which the independence movement took up arms.
Modern day Rajyaghar first came into being in 1946 when the Satria Etruriana and the Dominion of Belasaria became independent following the Coian Evacuation. 1947 saw the Gaullican colony of Tehandipour accede to the Kingdom via a referendum of the colonial population. Later that year, the Etrurian colony of Satria Libera was annexed into the Kingdom following a rapid invasion. The invasion was at the request of their Maharaja who had obtained power following a revolution against Etruria but was now facing a growing Councilist uprising. Following the annexation, the territory was reformed into the Union State of Nivasasthan.
In 19XX, a councillist uprising erupted in the Union State of Nirala. Following failed negotiations with the central government, the uprising developed into a complete rebellion sparking the Niralan Seccession (or War of Independence as it is known in Nirala). The Rajyani military was in no state to fight this rebellion due to the recent Solarian War and its deployments across the rest of the country in an attempt to secure the national border. After only a few months, the rebels had secured control of the entire Union State and declared independence. The success of the rebellion placed immense pressure on the central government and with councilist movements becoming more popular in neighbouring southern Union States and growing pressure from the Community of Nations to end the conflict, the central government decided to recognise the independence of Nirala so that it could refocus the military on the remaining southern states. The failure of the central government in the Niralan Secession forced the central government to conduct a major political overhaul which dramatically shifted the balance of power from the Monarchy to the Shahee Sansad (legislature) bringing it more in line with Euclean style constitutional monarchies. Additionally, the !Bhojpuri majority Union State of Nivasasthan was given increased autonomy and given a new federal state classification as a "Princely State", effectively a Union State with increased autonomy.
Rajyaghar is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, languages and beliefs and this diversity is a result of Rajyaghar's history. The history of Rajyaghar has also played a significant role in the development of its culture post-independence with aspects of modern Rajyani culture taken from different aspects of the cultures of the Kingdoms, Empires and Confederacies that came before it.
Colonial Rajyaghar
Under Etrurian control, changes were made to the former Madhyarajyas that would remain in place even after independence. Changes included the consolidation of power into a centralised government led by the Etrurian Colonial Office. Educational, manufacturing, industrial and infrastructure reforms were undertaken. The creation of major infrastructure links, including canal systems, railways and the telegraph, increased the influence and power of the colonial regime and also allowed for the rapid movement of natural resources from Satria Etruriana to factories on the coast where the raw goods were turned to usable materials which would be transported back to Etruria.
The economic and social reforms introduced came with increased surveillance and control from the Etrurian regime which fostered resentment amongst the native populations. The transportation of natural resources out of Satria Etruriana also angered the native population which would eventually result in the 1913 Chanak Rebellion. The rebellion came shortly after Etruria faced the Khordad Rebellion in Pardaran in 1912. The rebellion would highlight the invasive etrurian social and economic reforms and would also demonstrate the ruthlessness of the Etrurian regime in suppressing dissent. Although the rebellion was suppressed, it had laid the foundation for the independence struggle that would persist and grow.
The Great War saw the involvement of hundreds of thousands of Satria Etrurianan men under the Corpo di Soldati Ausiliario Satriani. The agreement to supply the colonial army with more troops from the native population was made by the Consular Senate, an advisory committee established by the Etrurian Colonial Empire in response to the 1913 Chanak Rebellion. The Senate had also secured guarantees that following the war a native legislature would be established for some self rule to be exercised. Following the war, a legislative assembly was established but was granted nominal powers, fueling greater resentment against Etruria. Calls for greater self rule increased following the Great War and throughout the subsequent Solarian War. Etruria’s collapse during the Solarian War and the devastation inflicted on Satria would see independence leaders turn to the Community of Nations for assurances of independence in return for Satria Etruriana’s withdrawal from the war. In 1946, Satria Etruriana surrendered in the Solarian War in return for independence being granted in October 1946.
After a century of colonial oppression, the form that an independent Rajyani government would take were questioned. Many of the independence leaders were the descendants of the former rulers of the Madhyarajyas and wanted to see their power and influence restored post-independence. Many of the rank and file members of the independence movement feared that after colonial rule, the monarchy would be a tool for establishment oppression against the common people. However, fears of councilist insurgencies in the southern state of Nirala as well as ethnic tensions in Nivasasthan led many to fear that without a strong central government with a unifying theme, an independent Rajyaghar would quickly collapse.
A republican system of governance brought the risk of a councilist takeover or rise of minority leadership at the presidential level if there was a charismatic, unifying minority figure and this worried the Rajyani establishment as there were already examples of these in the independence movement. A constitutional monarchy was seen as a compromise between the hardliners in Sanyukt and Rathankot who wished to return to the medieval systems of governance and the socialists in the south who wished for a more democratic society. The monarchy would also rule out the possibility of an irfanic or other minority head of state which alleviated the fears of the Ashankic establishment who believed that if a minority were to become Premier, their power could be tempered by the Shahee Sansad and Monarch. Throughout the independence struggle, Prince Krishan VI of Sanyukt had also been a fierce supporter of the ethnic minorities and so his appointment as the Maharaja was seen as a nod to those groups who feared that a monarchy would only represent ashanku interests. There were also fears that a presidential system would see complete ashankic-dominance in the politics of the country. Immediately after the Etrurian Evacuation, the Consular Senate sent a delegation to the Community of Nations petititoning for support for the new country which it obtained following guarantees of cooperation and the immediate suspension of hostilities against allied forces.
Independent Rajyaghar
The end of the Solarian War saw the end of Etrurian colonial rule over Satria Etruriana and the establishment of the newly independent Kingdom of Rajyaghar. At the time of independence, Satria was consumed by destruction following the Great War and subsequent Solarian War. Despite this, Rajyaghar had significant economic opportunities. Rajyaghar was one of the largest producers of iron, and the industrial infrastructure built by Etruria was designed for efficient production, refinement and exportation of Rajyani natural resources. The resources also gave the Rajyani government the resources it would need to recover following the Solarian and Great Wars as well as invest in further industrial development and infrastructure. During these early years, the Central Union Government nationalised many industries in order to ensure control over the rebuilding process and rapidly bolster the national defence system.
Despite the unity that was brought about following independence, natioanlist groups in Nivasasthan and Pinjar as well as councilst insurgents in Nirala led to increased tensions throughout the Kingdom leading to political instability in the south. It was also known that external organisations and hostile nations were funding councilist groups in Nirala and Nivasasthan in an attempt to undermine the Central Union Government.
Under the leadership of Premier Baiju Pahir Kapadia and his centrist People’s Party, the government placed a large emphasis on state planning with the military, education and investment receiving the largest amount of funding. These plans helped revive the economy following the wars of the early 20th Century and protect Rajyani sovereignty and integrity. However, the councilst uprisings in the Union State of Nirala continued to grow and in 19XX erupted into a total rebellion resulting in the Niralan Secession.
The immediate aftermath of the Niralan Seccession saw the split of the People’s Party under Kapadia into the centrist Liberal Party and left-leaning Cooperative Party. Under Kapadia’s successor, Anand Mahanti, the cooperative party introduced major political reforms which shifted power from the Monarch and Ashankinc priests to the central govenrment and Shahee Sansad. Mahanti also established the national health service, codified the national educational curriculum and raised taxes in order to pay for social programmes. Slowing economic growth, increased councilst threats and growing ethnic tensions in Nivasasthan saw Mahanti’s cooperative party lose the 1955 election to the Liberals under Onkar Jariwala. Jariwala’s liberals would reverse the tax code of the CP and much of their socialist economic reforms. Jariwala would also grant increased autonomy to Nivasasthan resulting in it becoming an Autonomous Province within the Kingdom. During the late 50s, the government would also crack down on the councilist insurgencies in Sangam, banning the state councilist party and placing many of its members under house arrest.
In the 1980s, the right-wing ashankic-nationalist RRP would rise to power. Despite a brief absence from government between 1985-88 as a result of failed agricultural reforms, the RRP under the leadership of Rajyaghar’s first female Premier, Kalyani Bajpeyi, would usher in an ‘economic renaissance’ with a reduced and simplified tax code, deregulation and privatisation. Many of the state bodies involved in raw material refinement and exportation as well as infrastructure development were sold off and privatised during this period which led to the rise of the millionaire class. Bajpeyi’s victory over the unions in the ’89 National Strike would also see the end of union dominance in rajyani politics and mark a clear shift in the general national political spectrum to the right. The RRP would lose power in the mid 1990s due to political infighting, resulting in the return of the Cooperative Party. Throughout the late 90s and early 2000s, social reform would rock Rajyani culture with continued economic growth seeing the emergency of Rajyaghar as a middle-income economy. However, in 2006, the economy would be hit by the collapse of the housing market which would see Rajyaghar enter a recession for the first time since independence.
Politics and Government
The Kingdom of Rajyaghar is a federal, parliamentary, constitutional monarchy. The democratic system of governance, enshrined in the constitution, is centred on the ideals of representative democracy and a strong federal government. The Monarch of Rajyaghar, Maharaja Krishan VII since 1984, is the Head of State. The Premier, currently Madhava Thakur, is the Head of Government, appointed by the Monarch to lead the executive government called the Central Union Government which itself is administered by the Premier led Ashta Pradhan. The Premier must be a member of, and maintain the confidence of, the national legislature; the Shahee Sansad.
The Shahee Sansad is a bicameral legislature comprising a Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and a Lokh Sabha (House of Representatives). The Council of States is made up of appointed individuals termed 'Councillors'. The House of Representatives is made up of Congressmen/women of which 400 are single member constituent representatives and 100 are elected via the party-list proportional representation method. A Consular Senate also exists which is comprised of the Rajakumars (Princes) of the Union States. The body is an advisory body to the Monarch and wields significant influence over the Council of State, independent advisory bodies and other government institutions.
Government
Rajyaghar is a federation with a parliamentary system in which the Monarch "serves to protect Rajyani culture, democracy and sovereignty" and from which all federal authority is derived. The federal relationship of the country is defined as the "Loyalty and Fielty of the Union States to the Crown and the Defence and Safeguard of the Union States by the Crown." Since independence, the autonomy of the Union States has slowly been eroded at the expense of the Central Union Government resulting a 'quasi-federal' system.
The federal government of the Kingdom is the Central Union Government which is comprised of Ministers of State. The most senior ministers of state (Secretaries of State) lead government departments and serve in the Ashta Pradhan (Cabinet). Ministers of State are nominated by the Premier of Rajyaghar, to the Monarch, from the membership of the House of Representatives, thus ensuring their accountability to the legislature. Like Ministers of State, the Premier is required to be a member of the House of Representatives. In accordance with the constitution, the Premier must maintain the confidence of the House. Therefore, the Monarch appoints the leader of the largest party or coalition in the House to serve as Premier. Constitutionally, the Premier is required to nominate Ministers of State to the Monarch but a seperate clause outlines that the Secretaries of State for Foreign Affairs and Defence are appointed by the Monarch on the advice of the Premier. The subtle difference in wording has allowed the Maharaja to intervene on the appointment of these two Ministers.
Legislature
 |
| HM Government |
|---|
|
Udāramātāvāḍī: 68
|
| HM Official Opposition |
|
Cooperative Party: 150 Sabraj Party: 12
|
| Other Opposition Parties |
|
PLU: 2 |
The Shahee Sansad is the federal legislature of the Kingdom of Rajyaghar. It is a bicameral legislature comprised of an upper chamber, the Council of States, and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. The Shahee Sansad can make federal law, pass resolutions of war, approve treaties, has the power of the purse and impeachment, through which it can remove Ministers of State, Judicial Officers and other members of the federal government.
House of Representatives
The Lokh Sabha (House of Representatives) is comprised of 500 members called Congressmen/women. The presiding officer of the House is the Speaker who is elected from amongst its members. The Speaker is required to be independent and must resign their party membership when they come to power. 400 of the Congressmen/women are elected from single member constituencies via a first-past-the-post voting system. The remaining 100 Congressmen/women are elected via the party-list proportional representation method. Due to this system, there are multiple political parties in the Shahee Sansad. Since the 1960s, the two largest parties have been the Rajyani Rashtriya Party and Cooperative Party. Additional smaller parties include Udāramātāvāḍī (Liberal Party), Tarkhana National Party and Irfanic Coalition. Due to the advent of multiple minor political parties, coalitions have formed and organised the left and right of the political spectrum with the National Progressive Alliance dominating the left and being led by the CP, and the RRP leading the right-wing coalition; United Conservative Coalition.
The Lokh Sabha is tasked with the formation of the Central Union Government due to the Premier and members of the Ashta Pradhan all being members of the chamber. Despite being a bicameral legislature, all Acts of Legislation must originate from the Lokh Sabha. Additional duties of the Lokh Sabha include creating the budget (done by the Government and passed by the Lokh Sabha), putting forward resolutions for war and keeping the CUG to account. The chamber also has the right to demand the resignation of the Government if it passes a vote of no confidence against it.
Council of State
The Rajya Sabha (Council of States) is comprised of 250 members called Councillors who are all required to be non-partisan. The presiding officer of the Council is the Crown Prince, however, day to day duties are performed by the Adyaksh (Chairman) who is elected from amongst the Councillors. All councillors are appointed by the Monarch but are done so on different grounds:
- 112 Councillors are appointed due to their status as leaders of the 112 registered clans
- 100 Councillors are appointed on the advice of the Independent Royal Appointments Committee
- 30 Councillors are appointed from ranks of the military
- 8 Councillors are religious appointees
The Council of State is tasked with amending, passing or rejecting legislation originating from the Lokh Sabha. The Council is also tasked with the approval of treaties, passing resolutions of war recieved from the House, approving nominees put forward by the Government and approving the budget created by the House. The Council of State can also hold the government to account via a motion of concern which, if passed, would trigger a joint session of the Shahee Sansad in which a vote of confidence will be held. The Council of State cannot hold a vote of confidence alone, unlike the House.
In most cases, if the House and Council disagree on legilsation, it will undergo legislative ping-pong two times before both chambers meet in a joint session in which the House will have the advantage due to its larger size. However, in the case of the budget, the Council of State may veto a budget if they disapprove of the spending allocated to foreign and military affairs.
Judiciary
The Kingdom of Rajyaghar has a multi-tiered independent judiciary consisting of the Federal Supreme Court, headed by the Nyayadhyaksh (Chief Justice), Union State High Courts, a large number of Crown Courts and an even larger number of Clan (Civil) and Magistrate (Criminal) Courts. Justices of the Supreme Court and State High Courts are appointed by the Monarch on the advice of the Bar Association, whilst Crown and Magistrate Court judges are appointed by Union State Princes, on the advice of the IJAC, and Clan Court judges are appointed by Clan leaders.
Justices of the Supreme Court are nominated to the Maharaja by the Premier on the advice of the Bar Association. The Nyayadhyaksh is nominated by the Premier from amongst the Supreme Court to the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). Justices of the State High Courts are nominated by First Ministers, on the advice of their Bar Associations, to their respective Rajakumars. Crown Court and Magistrate Court justices are appointed by First Ministers at their discretion. Clan Court judges are appointed by their respective Clan leaders however, these rulings can more frequently be appealed to the higher Crown Courts.
Administrative Divisions
Rajyaghar is a federation of 11 Union States, 2 federal territories and the Autonomous Princely State of Nivasasthan. Each state is divided into Provinces which are subdivided into Communes, with smaller states typically having only Communes. The administrative divisions are based on the historical middle kingdoms of Rajyaghar with all of them retaining their royal families which serve as ceremonial representatives of the Monarch in the Union States and are granted the titles of "Rajakumars".
Each Union State has a state government and legislature based off of the Northabbey model. State Governments are led by a Mukhyamantrī (First Minister) who appoints their own state cabinet to assist in the duties of the state. Lower-level administration is further devolved from state governments to local authorities; provinces and communes.
List of Union States of Rajyaghar
Foreign Relations
Foreign Policy
Rajyaghar is a member of the Community of Nations, joining the organisation the same day that the Kingdom became an independent, sovereign nation. Rajyaghar is also a member of the ITO and Council for Mutual Development (COMDEV) as well as being a founding member of Bashurat Cooperation Organization (BCO). The Kingdom of enjoys warm relations with her fellow COMDEV member states; with their embassies hosted close to Government Hill in Kinadica as a sign of their diplomatic importance to the Kingdom.
The foreign relations of Rajyaghar are managed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, with His Majesty's Diplomatic Corps being run by the Secretariat of Diplomatic Missions within the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Since independence, the Kingdom has sought to establish an expansive and diverse diplomatic network. During the early Satrian wars, Rajyaghar developed a particularly close relationship with her western neighbour, Padaratha. Although typically aligned with Senria throughout the late 20th Century, the country has sought to carve its own independent foreign policy in a bid to act as a broker of foreign disputes in southern Coius.
The nations of Senria, Padaratha and Venikara are the most favourably viewed countries by the Rajyani people.
Armed Forces
His Majesty's Armed Forces is the professional military of the Kingdom of Rajyaghar and is charged with the defence of the Sovereign, the Kingdom and Rajyani interests. The armed forces consist of three branches: The Royal Navy, the Grand Army and the Royal Air Force. HM's Armed Forces are managed by the Ministry of Defence with the National Security Council having control. Day to day management of the forces is led by the Minister of Defence with the Senapati (Chief of the Defence Staff) being the operational commander of the armed forces. The supreme commander-in-chief of the armed forces is the Rajyani Sovereign, to which all members of the armed forces swear an oath of allegiance, not to the constitution. The armed forces are an active military force, regularly conducting unilateral operations as well as participating in COMSED operations. At present, the Kingdom does not operate any overseas facilities.
There are numerous special branches of the military which have unique and distinct mission objectives. Within the Royal Navy, there is "The Aegis" which is a dedicated fleet tasked with defending territorial waters and projecting maritime strength in the Acheloian Sea. The Royal Navy also operates the "Sarisra Squadron" which is a dedicated group of river ships tasked with patrolling the major rivers of Rajyaghar to prevent against smuggling and other illegal activities. The Grand Army maintains the "Marine Commando Group" (MCG), an elite corps within the army which is often tasked with conducting the most difficult of operations. The Royal Air Force operates the "Specialist Paratrooper Service" (SPS) which often works alongside the MCG in difficult operations. The air force alaso operates the "Rajyani Attack Wing" (RAW). In recent years, there have been debates within the Ministry of Defence and the parliamentary Committee on Defence about the possible creation of a fourth branch of the military dedicated to specialist service groups; namely the MCG, SPS and RAW. In 2019, Premier Thakur stated his support for a special branch of the armed forces at a passing out ceremony at Amdara Military College.
The Navy is the most senior of the three branches of the military due to its role in Sanyukti history and its cultural significance. The Royal Navy is a green-water navy due to its ability to operate within the nation's own territorial waters and in the wider Acheloian Sea. The current government has sought to further increase the range and operational abilities of the Navy and has awarded contracts for the creation of dedicated helicopter carriers to further project Rajyani military power.
Economy
Rajyaghar is a developing economy which is generally considered to be a middle-income market economy. With a GDP of ₹1.6 trillion in 2019 and is one of the largest economies in Satria. In 2020, the Secretariat of National Statistics revealed that the unemployment rate was 5.8%, a reduction from 2015 where it was 6.7%.
Since independence, successive governments have maintained protectionist policies in order to protect and develop domestic, internal industries such as agriculture and manufacturing. This involved government intervention to prop up major businesses and extensive regulation over certain industries. However, the return to power of the RRP in 1988 saw the RRP usher in a new era of economic liberalism which has dramatically increased economic growth and reduced unemployment in the Rajyaghar. However, some industries still retain heavy government involvement such as agriculture where the national government ensures a minimum price for basic crops to ensure the survival of small farms across the country.
Demographics
Rajyaghar is the seventh most populous country in the world, with a 2021 estimate of over 112 million according to the Secretariat of National Statistics, a department of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
The population dramatically increased shortly after independence and then once again in the 1980s during the economic renaissance. Since the 1990s, government policies have been enacted to encourage families to only have 2 children. Such policies include the limitation of child benefits to households to the first two children only. The number of families with over 2 children has steadily fallen since 2004. Rajyaghar's under 25s make up just over 50% and the over 60s make up 20% of the population. The sex ration was 9 females for 10 males in 2019 and it has been showing an upward trend in the last two decades with the female ratio increasing.
Since the early 2000s, there has been a dramatic increase in urbanisation across Rajyaghar, with many analysts pointing to increased economic opportunities in urban centres and due to increased literacy and improved acceess to educational facilities across the country. In 2020, the SNS published figures which showed that literacy was now at 79% and expected to reach 85% in 2025. There are now also over 10 cities across the country which are each home to over 2 million people.
Religion and Ethnicity
[ETHNICITY SECTION]
Rajyaghar is officially a secular country but it is dominated by the Ashankic faith of which 67% of the population are followers. This is, in part, due to the significant role of Ashankism throughout Rajyani history with many of the Madhyarajyas being Ashankic realms which spread the faith during their conquests and expansions. Similarly, throughout its history the country has seen the arrival of many different religions such as the spread of Ashram and Tulyata during the Sangma Period, the arrival of irfanism with the Togoti Khaganate in medieval Rajyaghar, and the arrival of Sotirianity with the Etrurian Colonial and Gaullican Empires in the 19th Century.
Language
The official language of Rajyaghar is Himvastatan, owing to the dominance of the himvastatan speaking middle kingdoms throughout the Vikasan Era and extended history of Rajyaghar. Several regional languages or dialects are spoken throughout the country. Predominant amongst them is bhasdilan, which is spoken in the south-west of the nation particularly in the Union State of Harringhata. !Sindhi and zebadi, two closely related but distinct languages are recognised as the “second languages” of the south-eastern Union States such as Sangam and Nivasasthan.
The ‘borders’ of the language groups throughout Rajyaghar can easily be correlated with the geographic, historical, ethnic and current administrative division boundaries. In the south-west, the Union State of Harringhata is the successor to the historical Kingdom of Harringhata which spoke Bhasdilan, hence the prevalence of Bhasdilan throughout the state. Similar historical relations can be made for all of the language regions of Rajyaghar. Additionally, the Pavitra Mountain Range which runs through southern Rajyaghar acts as a language barrier between the Himvastatan states to the north of the mountain range and the various different languages to the south.
Vespasian is widely spoken as a second language throughout Rajyaghar regardless of which Union State you are in and this is due to the influence and impact of the Etrurian Colonial Empire during the 19th and 20th centuries in Rajyaghar. During this colonial period, the Etrurian Colonial Empire enforced an educational curriculum which mandated the teaching of Vespasian in all schools throughout Rajyaghar and the Empire also invested in programmes to teach adults Vespasian. To this day, many pupils are still taught Vespasian in Rajyani schools.
Since independence, a three-language formula has been administered throughout the national educational curriculum:
- First language: Himvastatan
- Second language: Vespasian
- Third language: local language i.e. Bhasdilan, Zubadi, Vijayan, etc,
Culture
Rajyani culture spans a history of more than 5,000 years dating back to the earliest recorded history of civilisation in Rajyaghar; the Ancient Rajyani Civilisations in 2500 BC. It was during this period that the foundations of ashankic philosophy, mythology and practice were laid down, with many of these practices and beliefs still existing and playing a dominant role in rajyani society today. Whilst the country has seen an influx of euclean culture due to its colonial history, there are many aspects of rajyani culture that have remained the same throughout history. One aspect is clothing where, whilst casual euclean clothing has become more popular, items of clothing such as the achkan are still common place and the norm for male clothing, with the sari being the same for women.
Rajyani festivals and national holidays are influenced by significant historical events, such as independence and military victories, as well as by religious festivals such as Diwasadak (Fesitval of Lights) and Devkevapse (Festival of the Homecoming).
Society
Umersatham, literally meaning "with age comes respect", is a widely held and institutionalised belief in Rajyaghar that deference should be showed to elders and those in positions of power and authority due to their experience, length of service and wisdom. Umersatham is closely linked to the hierarchical nature of Rajyani society.
Rajyani society is often described as hierarchical with the aristocracy and landowners at the apex, often enjoying institutional advantages particularly in education and employment opportunities. The caste system that was present during the medieval period is no longer observed and there are now several anti-discriminatory laws in place to dismantle remaining prejudices and discriminatory behaviour associated with castes. Society in Rajyaghar is dominated around the clan system.
Family values are a vital part of Rajyani tradition, with it being closely associated with the clan system. Since the 1980s, family planning has been a key priority of successive governments which has led to a dramatic reduction in family sizes as nuclear families have become the norm. The influences of senior family members still play a large role in Rajyani society, with many marriages, with consent, are arranged by family elders. Marriage, legal for those 18 and over, is considered a sacred institution in all the major religions in Rajyaghar with divorce being a taboo, resulting in the divorce rate being extremely low. Unlike many other parts of the continent, the gender ratio of Rajyaghar is not skewed in part due to low female infanticide rates unlike in other parts of Coius. Women hold a significant role in society and are considered equals to males due to their historical and religious influence; with many of the Madhyarajyas female rulers dominating Rajyani history.
Clans
In modern Rajyaghar, the historical clans of the past still have considerable influence. During the Vikasan era, when the Middle Kingdoms of Rajyaghar were being formed, clans retained their clan structures and the new Kingdoms and Empires would become collections of clans rather than merging clans together. In modern Rajyaghar, Clans have become societal groups with people of the same Clan often being from the same religious predisposition and living in the same states and cities. Most Clans have also retained their leading families which has resulted in the leaders of the Clans maintaining incredible influence within Rajyani society. As a result of this, the leaders of all of the recognised clans of Rajyaghar (112 in total) are granted seats in the Shahee Sansad to represent their members who may be spread across multiple Shahee Sansad elected constituencies.
Throughout Rajyani history, numerous clans would be part of a single Kingdom and as such, no clan would exist in more than one kingdom. When Kingdoms expanded, clans would either gain or lose territory, rather than a part of the territory being part of one kingdom and another being part of another kingdom. There would also be migration of individuals into their new territories or away from lost ones. Clan Leaders would often make up advisory councils for their Kingdom's Maharaja and even in modern day Rajyaghar, Clan Leaders still form advisory councils to the successors of the Maharajas of the Middle Kingdoms; the Union State Rajakumars.
Customs
Many customs originating from medieval and ancient Rajyaghar are still observed and hold significance in Modern-Rajyaghar. Zimankar and Santubhav are considered to be the most important and are often cited as the reasoning behind Rajyaghar’s relatively low crime rate, extensive natural protection laws and regulations, and the deference still shown to elders and those in positions of authority.
"Zimankar", a combination of the matrabashi words for responsibility, duty and honesty, is a Rajyani idea which believes all people should acknowledge the mistakes and misdeeds that they have conducted and take responsibility and improve. "Santubhav", a combination of the matrabashi words ‘santulan’ and ‘sadbhaav’ meaning balance and harmony respectively, and it is a Rajyani principle centred around the beliefs that one should live a balanced life between work and leisure, between care for oneself and for others and that all actions should be done in harmony with society and nature. The principle of santubhav is a key part of Rajyani society with it being closely linked to Ashankism and the idea of reincarnation.
In Rajyaghar, it is common practice to hold the hands at chest level together with the palms touching when greeting others. This is comparable to handshaking seen elsewhere. The practice of handshaking is uncommon in Rajyaghar with the !namaste greeting replacing it. The bow and curtsey are common practice when greeting members of the royal family and it is seen as a mark of disrespect and insult not to do so. Followers of Ashankism will also typically bow with the right hand placed over their heart before entering temples and when standing before idols of Gods.
Education
Education in Rajyaghar is a federal issue with some devolved power for Union States. The national curriculum, which is implemented from Grade 1 through 12, is set by the Ministry of Education in conjunction with educational boards. Union States then supplement the curriculum, with the native language, history and culture often being reinforced in the state curriculum. Education is compulsory until Grade 12 (Age 17-18) with the vast majority of the population being educated in free state run schools. Following Grade 12, students have the opportunity to enroll in one of 120 Universities. The large resources devoted to education since the 1970s have been a key contributor to the economic development of Rajyaghar. In the 2020 census, about 79% of the population was literate, with 83% for men and 75% for women.
Despite the vast government run education system, there are thousands of independent, prviate and religious schools throughout the country although their curriculum is constrained by federal regulations.