Garambura: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Infobox country |micronation = <!--yes if a micronation--> |conventional_long_name = Republic of Garambura |native_name = {{collapsible list |titlestyle = bac...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
|coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | |coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | ||
|largest_city = {{plainlist| | |largest_city = {{plainlist| | ||
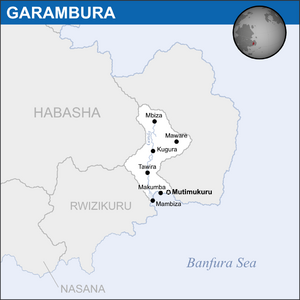
* Mambiza | * [[Mambiza]] | ||
* [[File:WMA button2b.png|17px]] [[Hytekia|8º41'N 33º39'W]]}} | * [[File:WMA button2b.png|17px]] [[Hytekia|8º41'N 33º39'W]]}} | ||
|largest_settlement_type = city | |largest_settlement_type = city | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
|established_event3 = Admitted to the [[Community of Nations|CoN]] | |established_event3 = Admitted to the [[Community of Nations|CoN]] | ||
|established_date3 = 5 March 1971 | |established_date3 = 5 March 1971 | ||
|established_event4 = Current constitution | |established_event4 = Admitted to the [[Congress of Bahian States|CBS]] | ||
| | |established_date4 = 17 November 1979 | ||
|established_event5 = Current constitution | |||
|established_date5 = 3 June 2011 | |||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | |area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | ||
| Line 155: | Line 157: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Garambura''' ({{wp|Help:IPA/English|/'gæræmbʊra:/}}), officially the '''Republic of Garambura''', is a country in eastern [[Bahia]], located on the continent of [[Coius]]. The [[River Gonda]] runs up most of the country. It borders [[Habasha]] to the north and [[Rwizikuru]] to the west. The country's capital and second-largest city is Mutimukuru, while the country's largest is Mambiza. With almost 9 million people, Garambura is one of the smallest countries in Coius and Bahia, and is also one of the poorest, with a nominal GDP per capita of only $1,884. The country has six official languages, with {{wp|Shona language|veRwizi}}, {{wp|Xhosa language|Sisulu}} and {{wp|French language|Gaullican}} being the most prevalent. | '''Garambura''' ({{wp|Help:IPA/English|/'gæræmbʊra:/}}), officially the '''Republic of Garambura''', is a country in eastern [[Bahia]], located on the continent of [[Coius]]. The [[River Gonda]] runs up most of the country. It borders [[Habasha]] to the north and [[Rwizikuru]] to the west. The country's capital and second-largest city is Mutimukuru, while the country's largest is [[Mambiza]]. With almost 9 million people, Garambura is one of the smallest countries in Coius and Bahia, and is also one of the poorest, with a nominal GDP per capita of only $1,884. The country has six official languages, with {{wp|Shona language|veRwizi}}, {{wp|Xhosa language|Sisulu}} and {{wp|French language|Gaullican}} being the most prevalent. | ||
Since the 11th century, Garambura was historically under the subjugation of the vast veRwizi Empire, who hailed from modern-day Rwizikuru. First colonial contact came when the [[Gaullica|Gaullicans]] established a trading outpost called Saint-Germain (modern-day [[Mambiza]]) in 1656. The Gaullicans eventually worked their way inland through colonial conquest and by 1840 the entirety of Garambura was part of the Gaullican Terre-Noire colony. Mambiza served as a major stopover for Gaullican merchants on their way to [[Xiaodong]] and [[Jindao]], and so the city grew quickly under colonial rule. When Raphael Duclerque's national functionalists took power in Gaullica in 1919, cultural repression began spiking on the island as previous colonial ministers were replaced with national functionalists. Many natives were conscripted into the Gaullican army and fought heavily on the Bahian front of the war. When Gaullica lost the war, Garambura was transferred to [[Estmere]] as East Riziland, a subdivision of the larger Riziland. | Since the 11th century, Garambura was historically under the subjugation of the vast veRwizi Empire, who hailed from modern-day Rwizikuru. First colonial contact came when the [[Gaullica|Gaullicans]] established a trading outpost called Saint-Germain (modern-day [[Mambiza]]) in 1656. The Gaullicans eventually worked their way inland through colonial conquest and by 1840 the entirety of Garambura was part of the Gaullican Terre-Noire colony. Mambiza served as a major stopover for Gaullican merchants on their way to [[Xiaodong]] and [[Jindao]], and so the city grew quickly under colonial rule. When Raphael Duclerque's national functionalists took power in Gaullica in 1919, cultural repression began spiking on the island as previous colonial ministers were replaced with national functionalists. Many natives were conscripted into the Gaullican army and fought heavily on the Bahian front of the war. When Gaullica lost the war, Garambura was transferred to [[Estmere]] as East Riziland, a subdivision of the larger Riziland. | ||
Revision as of 21:31, 19 October 2019
Republic of Garambura | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Kumakomo nekudzoka" ("To the mountains and back") | |
| Anthem: "Vanhu veGarambura, simuka" (Estmerish: People of Garambura, arise") | |
 Garambura (dark blue) located within Coius (light blue). | |
 | |
| Capital |
|
| Largest city | |
| Official languages | 6 languages: |
| Ethnic groups (2014) |
|
| Religion (2014) | |
| Demonym(s) | Garamburan |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
• President | Muzukuru Chiyangwa |
• Vice President | Zivai Mushohwe |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Congress | |
| Imbayaka | |
| Independence from Rwizikuru | |
• Declared | 16 February 1969 |
• Republic | 30 April 1969 |
• Admitted to the CoN | 5 March 1971 |
• Admitted to the CBS | 17 November 1979 |
• Current constitution | 3 June 2011 |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 8,635,881 |
• 2014 census | 8,401,266 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $29.9 billion |
• Per capita | $3,462 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $16.27 billion |
• Per capita | $1,884 |
| Gini (2014) | high |
| HDI (2014) | low |
| Currency | Garamburan Shilling (GSH) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +181 |
| ISO 3166 code | GAR |
| Internet TLD | .gb |
Garambura (/'gæræmbʊra:/), officially the Republic of Garambura, is a country in eastern Bahia, located on the continent of Coius. The River Gonda runs up most of the country. It borders Habasha to the north and Rwizikuru to the west. The country's capital and second-largest city is Mutimukuru, while the country's largest is Mambiza. With almost 9 million people, Garambura is one of the smallest countries in Coius and Bahia, and is also one of the poorest, with a nominal GDP per capita of only $1,884. The country has six official languages, with veRwizi, Sisulu and Gaullican being the most prevalent.
Since the 11th century, Garambura was historically under the subjugation of the vast veRwizi Empire, who hailed from modern-day Rwizikuru. First colonial contact came when the Gaullicans established a trading outpost called Saint-Germain (modern-day Mambiza) in 1656. The Gaullicans eventually worked their way inland through colonial conquest and by 1840 the entirety of Garambura was part of the Gaullican Terre-Noire colony. Mambiza served as a major stopover for Gaullican merchants on their way to Xiaodong and Jindao, and so the city grew quickly under colonial rule. When Raphael Duclerque's national functionalists took power in Gaullica in 1919, cultural repression began spiking on the island as previous colonial ministers were replaced with national functionalists. Many natives were conscripted into the Gaullican army and fought heavily on the Bahian front of the war. When Gaullica lost the war, Garambura was transferred to Estmere as East Riziland, a subdivision of the larger Riziland.
Garambura got its independence from Estmere under the Rwizikuru Republic, but growing authoritarianism and the declaration of Izibongo Ngonidzashe that he would become an absolute monarch spearheaded calls for Garamburan independence. The Garamburan National Front formed in 1968 under Kuziva Midzi as a guerrilla paramilitary, and Garambura unilaterally declared its independence on February 16, 1969, whilst Rwizikuru was fighting Nasana over the region of Yekumavirira. The war was swift as the guerrillas won a major battle at the Battle of Mambiza on April 18, forcing the Rwizikurans to retreat. Surrounded on both sides, Izibongo met with Midzi on April 30, 1969, in Port Fitzhubert, and agreed to fully recognise Garamburan independence. Izibongo referred to the Garamburans as "traitors" and relations with Rwizikuru did not recover until Kupakwashe Ngonidzashe came to power in 1979.
In the modern day, Garambura is a member of the ICD, CoN, the ITO and GIFA. Despite the country's fractured past, it scores well on democracy and freedom indexes.
History
veRwizi Empire
The empire's rule was generally quite lax and the area did not suffer any real direct oppression. Under the golden age of the veRwizi Empire, around the 1400s, pan-Bahian trade flourished and the coastal cities of Garambura attracted merchants and tradesmen for their attractive deltas and natural harbours. The start of major trade in the area caused a massive divide between the veRwizi people of the coast, now wealthy and living lives more akin to middle-class veRwizi in Rwizikuru, and the Sisulu and Njinji peoples inland, who felt neglected by the empire's rule. They revolted in 1636, losing the revolt itself but contributing as a whole to the collapse of the empire in the 1650s, after which a Sisulu-Njinji tribal confederacy invaded the veRwizi portions of Garambura, suing them for land in the north and isolating them to the direct coast.

