Salamat: Difference between revisions
| Line 236: | Line 236: | ||
|2010 | 22729453 | |2010 | 22729453 | ||
|2014 | 24540935 | |2014 | 24540935 | ||
|2018 | | |2018 | 26493348 | ||
|2022 | 28439211 | |2022 | 28439211 | ||
|2023(Prediction)|28990931 | |2023(Prediction)|28990931 | ||
Revision as of 01:45, 18 July 2022
People's Democratic Republic of Salamat جمهورية السلامات الديمقراطية الشعبية (Arabic) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "لا اله الا الله محمد رسول الله" "There is no god but Allah and Muhammad is his messenger" | |
| Anthem: "والله زمان يا سلاحي" I swear to God it's time, my weapon | |
 Location of Salamat in Anteria. | |
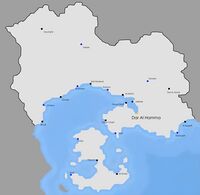 Major cities of Salamat. | |
| Capital and | Dar Al Hamma |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Ethnic groups (2018) | Arabic 85% Berber 11% Hebrew 2% Madurese 1% Other 1% |
| Religion (2016) | Sunni Islam 96% (official) Dharmaism 3% Judaism 1% |
| Demonym(s) | Salamati |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
• President | Abd-El Rahman Jarruf |
• Prime Minister | Anas Zitoune |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| National Council | |
| National Assembly of Salamat | |
| Establishment | |
• Conquest of the area by Islamic Armies | 690 CE |
• Creation of the Salimid Caliphate | 1450 CE |
• Fall of the Salimid Caliphate | 1820 CE |
• Colonization by Riamo | March 4, 1828 |
• Start of the Salamati Independence War | October 9 1964 |
• End of the Salamati Independence War | September 3 1969 |
• Coup d'Etat of Jalil Al Kharrabi | May 16 1977 |
• Start of the Salamati Civil War | April 10 1993 |
• End of the Salamati Civil War | January 29 1999 |
| Area | |
• | 137,905 km2 (53,245 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.9% |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 28,439,211 |
• Density | 206.2/km2 (534.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2014 estimate |
• Total | $320,373 billion |
• Per capita | $11,265 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2014 estimate |
• Total | $118,421 billion |
• Per capita | $4,164 |
| Gini (2010) | 28.2 low |
| HDI (2019) | high |
| Currency | Salamati Dinar (SLD) |
| Time zone | UTC-1 (SLT) |
| Antipodes | North of Lesser Velutaria |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +395 |
| ISO 3166 code | SLM |
| Internet TLD | .sl |
Salamat is a country located in North Thrismari, on the planet Anteria. It is bordered by the Anchor Lake to the south, the Khaliwi Mountains and Madura to the north and Yryel to the west.
History
Islamic Conquest and Early History
The area where Salamat is now established was pretty quiet and there were only some nomad berber tribes living there. In 685 CE, General Ghali Ibn Karim ordered his troops to explore further up north-east to the actual Anchor Lake and conquer those lands. The first soldiers arrived in ~689 CE, and started converting the local berber tribes to Islam, with little resistance from the tribes against conversion. The Anchor Island was uninhabited at that time and was conquered in 712 CE. Over time, it was starting to get inhabited by the Arabs and they eventually created the Ankur Caliphate in 770 CE, which was a vassal state of a much bigger Arabic Caliphate. The Caliphate's capital was Hayyum, on the west coast of the Anchor Island and it was home to many Arab astronomers of the 9th, 10th and 11th century.
The Ankur Caliphate was engaged in crusades against The Kakish Kingdoms in the 1210s and 1220s. in the 1st crusade , The Kysxka troops arrived on the Ankur Island in September 1218 and established the Anchur Empire which lasted for 5 years. The empire attempted to build cities, which are now popular touristic spots, in the occupied areas which were the Ankur Island and the Hani Peninsula. After those 5 years, the Ankur Caliphate along with foreign help manage to regain the Hani Peninsula and the northern part of Ankur Island. During the 2nd crusade, The Ankurids arrived on the Sugok Peninsula, occupied by the Stivir Kingdom, and now in the actual Northern Kakland and established the Kakla Caliphate in 1225. A minority of the native population converted to Islam and the Kakla Caliphate reigned until August 1228, when troops of the Kakish Kingdoms regained the area. Some Kakish persons in the area have Salamati-descent due to this crusade. The last crusade, the 3rd crusade took place in the late 1220s. The Anchor Empire tried to retake some land and besiege Hayyum in 1229. The siege failed due to bad organisation and the Ankurids replied with a big offensive all over the island, wiping the Anchor Empire from the map.
The Ankur Caliphate was annexed by the Arabic Caliphate in 1296 CE.
Salimid Caliphate
The Salimid Caliphate was established in ~1445 CE, with the first ruler being Ahmad I. The Caliphate was a marking point in the Salamati history, for creating and developing infrastructures like ports and cities, establishing trade routes and boosting the economy. The Salimid Caliphate had numerous capitals, including Dar Al Hamma (1445-1587/1802-1820), Ghafun (1587-1644), Asal (1644-1696), Douara (1696-1738) and Ankur (1738-1802). These cities benefitted from special treatment and better infrastructures than the other major cities that weren't capitals.
The Salimid Caliphate counts a total of 38 caliphs from the foundation to the collapse of the Caliphate. The most famous is Khaliq III (1495-1567/Reign from 1540-1563), who boosted the Salimid economy by opening new trade routes and developing the cotton industry, and led a great war against some Christian insurgents in 1556, which he won. This war permitted him to gain more popularity from the people, but fearing fanatism, jealousy and abandonment of Islam for a special cult dedicated to him made him step down from the throne in April 1563. He died 4 years later. Another famous caliph was Tariq I (1549-1616/Reign from 1599-1615), particularly known for his massacres and deportations, the most famous being the eradication of the Khaliwi Tribe in June-September 1605, after resisting against the authorities who tried to exploit them to farm cotton. As a result, the tribe was erased in a little less than 3 months. He also ordered the eradication of 4 other tribes who also refused to farm cotton for a total of 180,000 dead people under his reign. Tariq I lost his post of Caliph in February 1615, was judged in June of the same year and condemned to the death penalty as a result of his exactions. He was executed on January 26th 1616.
The Caliphate collapsed in 1820 CE, due to lack of trade routes, an aging infrastructure and bad life quality. The Caliphate was divided in 3 provinces after the dissolution.
Riamese Colonization
The Riamese first set foot on Salamati soil on March 4 1828 at Dar Al Hamma. A battle was engaged between the Dar Al Hamma Province and the Riamese on the 5th of March and resulted in a Riamese victory on May 20th. Most tribes were friendly with the Riamese, eventually forming an alliance and making them prevail over the rebel tribes. The rebels were led by Abd Al Fattah al Salimat, known for the battle of Ghafun (June 27th 1830-August 1st 1830), the battle of Sidi Kherridj (January 8th 1831-February 12th 1831) and the battle of Mansujah (March 10th 1831-March 25th 1831). After more than 10 years of active resistance, Abd Al Fattah Al Salimat surrenders in 1843. The resistance still went on and fought 2 more years before being destroyed. The Riamese first established the trade dependency of Salamat and reorganized the territory in 1848 and also appointed leaders of some of the friendly tribes as governors of the province. The governors had to pay taxes to the Riamese Empire in exchange of trade and land protection. There were also some cultural mixing between the Riamese and the Salamati, forming a mixed ruling class for decision-making and creating a false sentiment of respect.
The Riamese then started exploiting cotton resources in the mid-19th century, creating underpaid jobs for the locals. If the locals refused, the Riamese would slowly take their goods until they accept to farm. Due to the lack of workers, the Riamese sent Gassasinians in Salamat to farm cotton. The first Gassasinians arrived in 1878 in Hani, and the mixing between Gassasinians and Salamatis,the use of the same language and the practice of the same religion created a friendly rivalry between Gassasinians and Salamatis, and to this day, there are an estimated 110,000 Gassasinians in Salamat, mostly of Christian and Shia Muslim confession.
The poor living conditions of the Salamati was a reason for some to emigrate to Riamo in order to live decently. This emigration started in 1914 and ended in the mid-1920s. The consequences of the emigration was the creation of a Salamati intellectual class, who later advocated for the independence of Salamat. An intellectual named Anwar Al Harrani created the Salamati Star party in 1931, an independentist party who will later be involved in many revolts of the people, most notably the Jurhan Revolt on May 9 1934, where an estimated 30 000 Salamatis protested on the street with Salamati independentist flags, this pissed off the Riamese authorities who opened fire on the protesters. Some furious protesters, in response to this massacre, killed Riamese civilians. A small group of Riamese civilians were with the military and killed innocent Salamatis. Historians estimate that at least 7 500 Salamatis, 425 Riamese (civilians) and 200 soldiers were killed during this revolt and believe it was one of the reasons for an independence war.
Independence War
Al Kharrabi's regime
In the night from May 15 1977 to May 16 1977, a young marshal called Jalil Al Kharrabi, along with his friends, made a Coup d'état against the president of Salamat at this time, Majid Khummam, who was abroad. Jalil successfully seized power and at around 5:50 am on May 16 1977, he made a speech on the national radio, announcing that "the corrupt government was overthrown" and that "a new real socialist country has been created". The people didn't know about the leader's name and his face until June 1st 1977, when he made his first public speech.
However, he failed to govern the country, and all of his plans fell through in April 1981 after the assassination of Majid Muhammad in Gassasinia, who criticized Jalil Al Kharrabi and his way of governing the country. This event led to a massive embargo on Salamat for more than 11 years. The country's currency, the Salamati Dinar, suffered from inflation, the economy stagnated and regressed and youth unemployment was hitting new records, with over 60% in 1990. People revolted in November 1991 against youth unemployment and inflation, hurting the ego of the young marshal. He repressed the protests, which led to sanctions against Salamat and riots in multiple cities of Salamat.
Jalil Al Kharrabi was overthrown on February 3 1992 and was replaced by Mohammed Jandubi.
Salamati Civil War
Geography and Climate
Geographic features
Salamati geography is defined by a mountain chain in the northwestern part of the country, named the Khaliwi Mountain Chain, hills in the interior of the Hani peninsula in the south-east, a plateau spanning from the west to east of the country and some hills near Ghafun, in the southwest. Three major rivers (called "oued") flow in Salamat ; the Oued Labkheir, whose source is located in the Khaliwi mountains and flows in the western part of the country. It defines the border between the Ghafunya and Shawawiyah provinces and ends into the Anchor Lake. The Oued Harr forms near of the Oued Labkheir but flows into the northeastern part of the country and ends into the Harr Lake. Both are used for cotton farming and are drying up ; The Harr Lake's surface area in 1985 was of 3,200 km²; now it is only of 1,910 km². The third major river is the Oued Madani. It also takes its source from the Khaliwi Mountains, flows eastward along with the Oued Harr close to it, then turns southward and then westward to end in the Anchor Lake, between the cities of Al Muhni and Jadhab. It is also used for cotton farming but not as much as the Oued Harr.
The highest point of Salamat is the Chengrouh, culminating at a height of 5739 meters above sea level in the Khaliwi Mountain Chain. The lowest point is the Harraj Depression at 18 meters under sea level.
Climate
Globally, the climate is a tropical savanna climate, defined by the Koppen Climate Classification by Aw in the continental part of the country (dry winter climate) and As on the Ankur Island (dry summer climate). In the northwestern part of the country, in the Khaliwi moutain chain, the climate is a highland subhumid temperate climate (Koppen : Cwb), with dry and cool winters and milder and wetter summers. Some areas of the mountain chain even feature an alpine climate (Koppen : ETH).
Politics
Elected politicians have relatively little sway over Salamat. Instead, a group of unelected civilian and military "deciders", known as "the power", actually rule the country, even deciding who should be president. The most powerful man might have been Farouk Jamhara, the head of military intelligence, before he was brought down during the 2019 protests. In recent years, many of these generals have died, retired, or been imprisoned. Previous president Jumiyin put loyalists in key posts, notably at Salamoil, and secured constitutional amendments that made him re-electable indefinitely, until he was brought down in 2019 during protests.
The head of state is the President of Salamat, who is elected for a five-year term. The president was formerly limited to two five-year terms, but a constitutional amendment passed by the Parliament on 20 February 2007 removed this limitation. The next presidential election was planned to be in October 2023, but widespread protests erupted in October 2018 against the president's fifth reelection, which resulted in President Jumiyin announcing his resignation in May 2019. Abd-El Rahman Jarruf, an independent candidate, was elected as president after the election eventually took place on 18 May 2019. Protestors refused to recognise Jarruf as president, citing demands for comprehensive reform of the political system. Salamat has universal suffrage at 18 years of age. The President is the head of the army, the Council of Ministers and the High Security Council. He appoints the Prime Minister who is also the head of government.
The Salamati parliament is bicameral; the lower house, the National Assembly of Salamat, has 462 members who are directly elected for five-year terms, while the upper house, the National Council, has 180 members serving six-year terms, of which 136 members are chosen by local assemblies and 44 are appointed by the president. According to the constitution, no political association may be formed if it is "based on differences in religion, language, race, gender, profession, or region". In addition, political campaigns must be exempt from the aforementioned subjects.
Economy
Exportations and importations
Salamat's exportations consist mostly of natural ressources, the largest one being oil exportations (51.5% of exports), followed by cotton (12.7%), salt (8.8%), iron (7.5%), natural gas (6.8%), ivory (4.9%), rare earth metals (4.6%), anthracite (2%) and other exportations like wood, wheat and magnesite (1.3%) and importations consist of fertilizers (48.2%), automobiles (30.9%), aircraft parts (12.3%), chemicals (5.1%), electronics (1.9%) and other importations like spare parts, military equipment, plastics etc... The net exports of Salamat are positive ; the country is in a trade surplus of 215 million ACU or 40,5 billion dinara.
Economy informations
The official currency of Salamat is the Salamati Dinar, introduced in 1970. The economy is dominated by the state, a remnant of the old socialist-style development model.. In recent years, the Salamati government has halted the privatization of state-owned industries and imposed restrictions on imports and foreign involvement in its economy. These restrictions are just starting to be lifted off recently although questions about Salamat's slowly-diversifying economy remain. The GDP PPP of Salamat is of 320.373 billion ACU as of 2014 and the nominal GDP of Salamat is of 118.421 billion ACU. The nominal GDP per capita is of 4,194 ACU and the GDP PPP per capita is of 11,265 ACU. Unemployment rates are of 13.1%, the numbers being inflated by youth unemployment (25% in 2019) and women unemployment.
Transportation systems
Salamat has a dense road network in the southern part of the country, with a total of 11 193 kilometers of highway across the country , principally in the coastal areas and the Ankur Island. The network should be completed by a bridge connecting the continent to Ankur Island, and the conversion from a 3x2 to a 4x4 way highway of the West-East highway, spanning from Khutfi in the extreme west part of the country to Al Mujarrif in the east. The rail network is estimated to have a length of 1 829 kilometers in standard gauge. 391 kilometers are suited for high-speed trains, in a small part running from Hani, passing by Dar Al Hamma and ending in Douara. Projects like the Ghafun-Dar Al Hamma high speed corridor are studied.
Two cities have metro systems ; Dar Al Hamma and Ghafun. The country also has 21 airports ; 4 of them are international :
Salamat also has a bus network between numerous cities of the country, the drivers often work in agriculture to afford a bus and decide their itineraries and the fare of the travel. The average fare for bus travel between Dar Al Hamma and Jadhab (approximatively 65 kilometers) is of 1850 Salamati Dinar or approx. 9.80 ACU.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1820 | 3,931,200 | — |
| 1880 | 6,083,900 | +54.8% |
| 1912 | 7,813,410 | +28.4% |
| 1939 | 7,841,032 | +0.4% |
| 1964 | 7,921,848 | +1.0% |
| 1969 | 7,910,311 | −0.1% |
| 1974 | 8,103,297 | +2.4% |
| 1979 | 8,478,026 | +4.6% |
| 1984 | 9,234,108 | +8.9% |
| 1989 | 10,602,759 | +14.8% |
| 1994 | 13,311,287 | +25.5% |
| 1999 | 16,238,386 | +22.0% |
| 2002 | 18,439,219 | +13.6% |
| 2007 | 20,686,640 | +12.2% |
| 2010 | 22,729,453 | +9.9% |
| 2014 | 24,540,935 | +8.0% |
| 2018 | 26,493,348 | +8.0% |
| 2022 | 28,439,211 | +7.3% |
| 2023(Prediction) | 28,990,931 | +1.9% |
| Source: Salamati Bureau of Statistics | ||