Lilienburg
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Free State of Lilienburg Freistaat Lilienburg (Lilienburger Hesurian) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Brüderlichkeit Über Allem" "Fraternity Above All" | |
| Capital and largest city | Lilienburg City |
| Official languages | Lilienburger Hesurian |
| Demonym(s) | Lilienburger |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic with elements of syndicalism and direct democracy |
• High Mayor | Helena Weissmann |
• Chancellor | Hermann Thaler |
| Legislature | Stadtshaus |
| Landshaus | |
| Volkshaus | |
| Establishment | |
• Free City established | 1551 |
• Schiltach Ascendancy | 1810 |
• Edelweiss Uprising | 1893 |
• Annexation by the Cuthish Empire | 1908 |
• Free City re-established | 1917 |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,546 km2 (1,369 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2017 census | 607,183 |
• Density | 171.23/km2 (443.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $39.97 billion |
• Per capita | $65,836 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $34.73 billion |
• Per capita | $57,193 |
| Gini (2017) | 19.9 low |
| HDI (2017) | 0.907 very high |
| Currency | Lilienburger mark |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +328 |
| Internet TLD | .li |
Lilienburg, officially the Free State of Lilienburg (Lilienburger Hesurian: Freistaat Lilienburg), is a landlocked country located within Telmeria, bordering Cuthland-Waldrich to the west and south, Mascylla to the east, and Lake Sigismund to the north. The nation is the smallest in Telmeria, with an area of 3,546 square kilometers, consisting of the namesake and capital Lilienburg City, where the overwhelming majority of the nation's 607,183 residents live, and the surrounding countryside.
The city's existence is first recorded in the 11th century as a small market town and fishing village. In the 12th century, however, it became the location of a significant monastery during the 12th century and the town started to grow around the monastery. The monastery gained a reputation for scholastic work as time went on, and in 1415 the University of Lilienburg was opened by the monastic order to educate monks and civil servants, largely focusing on classics and theology. The university, being the first in Telmeria, would eventually eclipse the town's other industries and become the town's raison d'être as scholars, monks and priests flocked to the town. During the 16th century the university town would assert itself as an independent city; the city's council, consisting of property owners, nobles and university graduates, would become the sole authority over the city and it declared itself the Free City of Lilienburg. The city was headed by a High Mayor, who was often a member of one of the city's merchant families during the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries. Lilienburg, due to its strategic location and strong fortification, would be frequently contested between several historic states; it belonged to both the Cuthish Empire and Adhwin for various intervals, with the present-day country first emerging after the Cuthish Revolutionary War in 1801. Then, it was under the personal protection of Alexander I of Dulebia und guarded by an Aldian garrison. In 1841, during the Second Cutho-Mascyllary War, the Cuthish-speaking parts of Lilienburg were ceded to the Cuthish Empire, and its council government abolished in favor of a Grand Duke.
The 19th century would see the city change significantly. The House of Schiltach would come to dominate the city's government between 1810 and 1893, with the now-Grand Duke being from the House of Schiltach for the whole of that period. This was also a period in which the city industrialised and the population markedly increased to sustain this industrialisation, creating new industrial neighbourhoods of the city and drastically altering the city's social structure. However, this led to a large working-class and a growing middle-class who opposed the conservatism of the Schiltach dynasty and rallied behind the ideologies of socialism and liberalism. They were largely behind the 1896 Edelweiss Uprising, in which the House of Schiltach and the aristocracy in general were deposed in favour of a state based on popular sovereignty.
However, this new state would not last long; it was marred by divisions between socialists and liberals and a general economic decline, and after 12 years its sovereignty was abolished by the Cuthish Empire in a controversial move that would be a major contributor to the Great War in agitating Mascylla and Valimia to fortify their western frontier. However, Cuthland would lose this war and an independent Lilienburg was re-established as an Assembly of Nations Mandate in 1917. The liberal-socialist divide would continue in the new republic, yet a strong trade union movement would develop which would lead to the dominance of the socialists for much of the 20th century. Lilienburg achieved full sovereignty in 1935.
Today Lilienburg is a highly developed country with very high levels of social equality, and pursues a lenient policy of political neutrality. Its economy and political system have been of much interest to economists and political theorists, with many describing the city's economy as using a democratic socialist model based on the dominance of trade unions and co-operatives in a parliamentary democracy. The city has also been noted for its namesake university's prestige and research, and it is also considered a cultural hub in terms of music, comedy, theatre, film and cabaret. Lilienburg is one of the three founding members of the Telmerian Union, and its capital Lilienburg City hosts the High Secretariat, the Council of the TU and the Telmerian Parliamentary Assembly; it additionally is a member of the Assembly of Nations, X.
History
Early history
Independent Lilienburg
Industrialisation and Autocracy
Edelweiss Uprising and Crisis
20th century
Politics and government
Lilienburg is a unitary parliamentary representative democratic republic with elements of syndicalism and direct democracy. The city has no codified constitution, with what is termed the "Constitution of Lilienburg" being a collection of important legal documents detailing the relations of various parts of government, of which the 1551 Proclamation of the Free City and the 1893 Citizen's Declaration are the most important.
The city's legislative power is invested in the Stadtshaus, which is a bicameral body consisting of two chambers. The first of these is the Volkshaus, which consists of 72 representatives elected by the people of the city every three years using the single transferrable vote method of election. The second of these is the Landshaus, which consists of 40 members representing various trade unions, co-operative business, employers and health and education boards, as well as representatives of the civil service and the university. While the Landshaus is only able to delay legislation and cannot deny a government confidence, its verdict is rarely questioned and it has the right to reject budgets.
| Volkshaus |
|---|
|
Green Party (18) Social Labour Rally (16) Confidence and supply (4) Change (4) Opposition (34) Independents (12) Civic Unity (9) Democratic Party (7) Centre Party (3) Schiltach Independents (3) |
While officially executive power is placed in the High Mayor of Lilienburg (Oberbürgermeister) and their Cabinet, in reality executive power is exercised by the Cabinet, which is headed by a Chancellor (Kanzler). The position of Chancellor is appointed by the High Mayor and is given to the person most likely to hold the confidence of the house. Like in most parliamentary systems, the Chancellor and their Cabinet must retain the continued confidence of the Volkshaus and can be removed through a simple majority in a vote of no confidence. The position of High Mayor is elected every six years by a plurality system and expected to be non-partisan: they are expected to give up any party or trade union membership upon election. Furthermore, Lilienburg has been described by many as being a semi-direct democracy, in that while normally laws are decided by an elected legislature, in line with typical representative democracy, citizens also have a right to petition for a referendum: if an initiative to enact, repeal or amend a law gets 5,000 signatures and it is ruled compliant with the constitution by the judiciary, then it is put to a binding referendum.
Currently the High Mayor of Lilienburg is Helena Weissmann, an independent politician and former musician and the Chancellor is Hermann Thaler of the Green Party, who leads a coalition of the Greens and the Social Labour Rally.
Administrative divisions
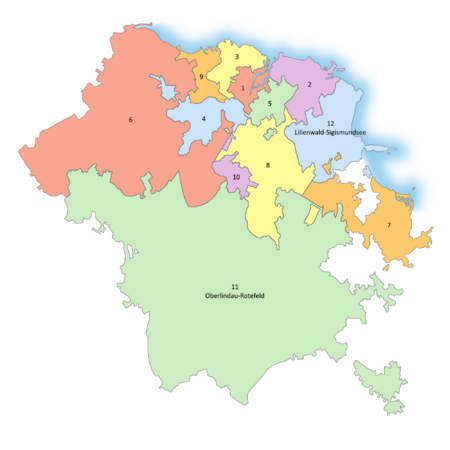
Lilienburg is divided up into twelve boroughs or districts (Bezirke), ten of which make up the city proper and are referred to as the "inner boroughs" (Innenbezirke), while the other two divide up the rest of the city state and are referred to as the "outer boroughs" (Außenbezirke). While the ten inner boroughs do not have any further divisions, the outer boroughs are divided up into several municipalities representing the various towns and villages that make up these regions.
The boroughs are governed by borough councils, which are elected yearly through single transferable vote, and a borough mayor, who is elected through instant runoff voting at the same time as the council and presides over the council. In the inner boroughs, these governments are solely responsible for managing emergency services, education, housing and welfare in their areas of jurisdiction, while in the outer boroughs these governments serve mostly to co-ordinate this between the local governments.
Military
Foreign relations
Geography
Lilienburg is the smallest country in Telmeria at only 3,546 square kilometres, being approximately 72 kilometres long and 103 kilometres wide. To the west, Lilienburg borders the Cuthish shires of Middlepoolshire and Horsebrigdeshire and to the south, it borders Waldish shires of Leechlan and Noardlan. To the north, the country borders the Mascyllary Land of Gothern, to the east X, and Lake Sigismund, the biggest freshwater lake in Telmeria to the north-east. The country is traversed by three major rives defining its western and eastern boundaries, the Meer, Erle and Wid rivers, and is generally divided into two corresponding geographical regions.
The southern half of the country makes up an area known as the Rotefeld, consisting of rolling hills, plains and sparse forests, with its highest point being outside the hamlet of Sipplingen at 192 m above lake level (405 m above sea level). The Rotefeld has a very low population density, with much of its population concentrated in small villages and hamlets geared towards farming, with only one settlement of over two thousand people, Oberlinden. The Rotefeld develops into craggy hillside with sandstone formations and dense forests in Lilienburg's east.
The northern half of the country, Sigismundsfeld, is much more populated, consisting of a flat plateau on the banks of Lake Sigismund. Lilienburg City is located centrally in this area, extending from the lake's shore towards the beginning of the Rotefeld, traversed by the Erle river originating in the Ardland hillside. The terrain rarely exceeds three metres above lake level in the entirety of Sigismundsfeld, and the extremely flat terrain extends into Cuthland-Waldrich; it is bounded by the Brunsmark massif in Mascylla to the immediate east. This extremely flat terrain on both sides of the city has made the city historically very easy to invade, and was the catalyst for the construction of its reputed fortification.
The city state has been highlighted as a world leader in environmental protection, being ranked 3rd in 2015 worldwide by the Environmental Protection Index, and the namesake city has topped the list of Telmerian cities with the cleanest air for three years running. The nation's climate has been categorised as Cfb on the Köppen climate classification, which denotes an oceanic climate. This describes the country's high levels of precipitation, warm summers, cool winters and a generally temperate climate overall.
Economy
Lilienburg maintains a developed, service-based mixed-market economy defined by heavy government intervention in industry, a skilled labour force and a high level of innovation. Lilienburg is a high-income country, with a PPP GDP per capita of $40,193, and this is relatively evenly distributed, with a Gini coefficient of 19.9, one of the lowest in the world. Lilienburg's workforce is overwhelmingly employed in the service sector, which employs 79.1% of the workforce compared to 19.1% of the workforce employed in the industrial sector and 1.8% employed in the agricultural sector, largely in Lilienburg's rural areas.
Lilienburg is known for its unique model of labour relations, based around egalitarianism and democratic socialism. As a result, the city's unions play a very strong role in the economy; 82% of the workforce are part of a trade union and unions play a large role in influencing government policy. Many workplaces are run co-operatively, with a government mandate that at least 30% of a company's board has to be elected by the workers, yet many companies have a much larger share of their board elected, and many government-owned companies have almost entirely elected boards. Furthermore, the government maintains a Tripartite Commission which negotiates wages between unions, employers and the government.
A significant portion of Lilienburg's economy surrounds the city's namesake university; the university employs around 5,000 staff and its position in the city has led to the city having a large industry based around science and technology. The Lilienburg Science Park, on the edge of the city, was opened in 1989 and hosts a large number of science and technology companies, such as Redens, a biotechnology company focused on agriculture and biodiversity, and Gutes Gefühl, a company behind experimental pharmaceuticals. Both of these companies receive significant government funds and are largely run as co-operatives. Much of the rest of the city has traditionally revolved around heavy industry, although in recent years the country has begun a process of deindustrialisation and one of the main economic issues the country has faced has been how to adequately provide new methods of sustenance to areas of the city hit by this phenomena. While the national employment rate is a low 3.2%, this rises to 5.7% in the neighbourhood of Schiltach which has traditionally been centred around steel production. The government, however, has begun initiatives to try and encourage co-operative businesses to set up in the area. Another notable industry within the city is that of shipping: the Port of Welhaven lies on one the mouth of the Wid river and is thus the access point to Lake Sigismund for nations such as Rovina and Valtriva, which have rights to the Südhafen docks as a base for transporting goods. As a result of its strategic importance, the Welhaven Port Authority is one of the state's most profitable state-owned enterprises.
Lilienburg possesses an extensive welfare state which provides free and universal education and healthcare to its citizenry, as well as 12 months paid leave for both parents, an extensive system of compensation for disability, sickness and injury, an unemployment insurance system with retraining facilities, and a very extensive network of social housing in which the state subsidises and owns a very large proportion of housing through housing co-operatives in order to ensure adequate affordable housing to all Lilienburgers; this system has resulted in Lilienburg having one of the lowest home ownership rates in the world at 37%.
Energy and environment
Lilienburg has traditionally relied on imported coal and oil for power, and still does to a large extent: 60% of the nation's electricity still comes from coal and oil power, yet the nation has invested heavily in renewable energy in recent years; the government has announced its intentions to make Lilienburg carbon-neutral by 2035 through investing in solar and wind energy, which has also given Lilienburg less dependence on other countries for electricity.
Lilienburg is heavily committed to many treaties encouraging renewable energy, reducing carbon emissions, water management and biodiversity. The country has also taken great steps to encourage recycling, through imposing charges on waste collection but opening up free recycling centres.
Transport and communications
Lilienburg possesses a well-maintained network of roads, consisting of 201 km of Autobahn that link Lilienburg City with various other towns in the country and with bordering countries and nearby cities. Despite this, most of the city itself is heavily pedestrianised and as a result the country has a rather low number of cars per capita in comparison to other developed countries. The city possesses an extensive public transport network managed by Transport für Lilienberg, a government-funded co-operative enterprise. This network consists of an underground metro system which covers much of the city with a frequent service, as well as a system of trams and buses, among other light-rail lines, above ground. The country is linked to the Mascyllary InterCity high-speed train network, and the metropolitan area is largely served by Lilienburg International Airport.
Lilienburg's telecommunications industry is dominated by the government-funded Lilienburger-Telekom, which maintains landlines and also serves as a mobile network and an internet service provider. The company has worked to provide these services at a low cost, and as a result Lilienburg has one of the highest rates of Internet users and mobile phone users. Lilienburg is often credited as being one of the leading financial technology hubs in Berea, while working as a centre and connector of all major Berean internet stock exchanges (Aniarro, Königsreh, Kingsham, Flussmund, and Toulogne).
Demographics
Ethnicity
The native people of Lilienburg are known as Lilienburgers, and are a Hesurian people like Mascyllary. In 2017, 57.3% of the population were of Lilienburger origin, which was a decrease from 2007 yet also the smallest decrease between censuses for 80 years.
The country has seen large waves of migration over the 20th and 21st centuries, especially from Cuthland-Waldrich and Rovina, with one in three residents declaring their national origin as being from one of these two countries. That immigration trend has largely been the resulf of economic turmoil in the country, with a majority of Cutho-Waldish and Rovinians in the country arriving in the 1970s due to economic stagnation. These three groups have had a large influence on the country, with signage being produced in Waldish and Rovinian across the country, as well as being taught in some schools. Many neighbourhoods across the city have been described as "Little Waldrich", "Little Rovina" or "Little Mascylla" due to the large immigrant communities resident.
Other significant minority groups include those from Mascylla, Lavaria, Valimia and Dulebia, although these groups make up very small proportions of the overall population.
Religion
Education
Education is compulsory in Lilienburg between the ages of 6 and 18, and almost entirely provided by the state, with private education and homeschooling being heavily regulated and almost nonexistent. The education system largely consists of a system of secular comprehensive schools, with students attending primary school between the ages of 6 and 14 and secondary school between the ages of 14 to 18. In part due to the small size of the country as well as social views on education, Lilienburg has one of the highest ratios of teachers to the overall population in the world.
The city is also home to one of the world's most prestigious universities, the University of Lilienburg. The university was founded in 1415 as an outgrowth of Lilienburg monastery as an ecclesiastical college for training priests, scholars and civil servants, and currently has 20,000 students enrolled in subjects spanning arts, social sciences, humanities and sciences. There are two other universities in Lilienburg: Edelweiss-Universität, which focuses more on vocational training, and the Lilienburg School of Creative Arts, which specialises in teaching art, music and drama. All three universities offer free tuition to residents of Lilienburg.
Healthcare
Lilienburg has a single-payer, tax-funded healthcare system run by Gesundheit Lilienburg, a government-owned service which consists of ten hospitals across Lilienburg, with seven general hospitals as well as a university hospital, a children's hospital and a hospital dedicated to extensive treatments, as well as a system of general practitioners offices and counselling services. The system is managed by a health board, which is elected by all the employees of Gesundheit Lilienburg and is responsible in part for the allocation of funding and resources alongside the Ministry of Health.
Lilienburgers enjoy good health as a result of this system, with an average life expectancy of 82 years and high rates of survival for conditions such as cancer. The nation's mental health facilities have enjoyed great attention in recent years, with recent governments naming the area a key priority and offering increased support for mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder.
Culture
In terms of traditional cultural achievements, Lilienburg is largely overshadowed by its neighbours and does not deviate much from their Hesurian culture, yet in modern years Lilienburg has become a pop culture centre in terms of music, folk theatre and comedy, being Erdaran Capital of Culture 2018, and it retains many of its folk traditions. The city has gained a reputation for inclusivity in recent years, and boasts a significant LGBT nightlife scene, with streets such as Leon-Abse-Strasse being known for LGBT nightlife.
The city's conflicted history and status as a university town has led to an abundance of museums in the city. The most famous of these are the Friedrich Wasserburg Museum of Art, the Volksmuseum and the Lilienburg Science and Technology Museum, all three of which are situated on an island in Lake Sigismund. Also notable is the Prehistoric Institute, which contains the largest collection of Proto-Hesurian artifacts in the world. Also culturally notable is the Wilhelm Locke Theatre, a 17th century theatre in the east of the city that has played host to many significant playwrights over the years, such as the namesake Wilhelm Locke.
Music and Cabaret

Lilienburg is known for its vibrant popular music scene. The city state has a prolific musical heritage, with its artists spanning genres such as Hesurock, synthpop, hip hop, punk rock, EDM, Neue Hesurische Welle, alternative rock, indie rock and pop. Many artists from the city are known for a DIY approach to songwriting and lyrics heavily focused on personal or sociopolitical lyrical content.
The country is also known for its cabaret scene, featuring intimate performances of singing, music, dancing and comedy, often touching on sociopolitical themes and satire. Performances often take place in environments such as a beer hall, and in modern times have evolved to take on elements of modern music, with many featuring punk rock music in a style known as dark cabaret.
Literature and philosophy
Arts
Cuisine
Lilienburger cuisine is similar to the cuisine of the rest of Telmeria, with cuisine largely consisting of meat and vegetable based dishes. Dishes such as Wurst, a type of Hesurian sausage, and Schnitzel, a breaded cutlet of meat, are popular within the country. Schnitzels in Lilienburg are often made of chicken, and a dish consisting of a chicken schnitzel sandwiched in a loaf of bread is often known as a Lilienburger in international parlance as a result.
The country has its own unique dishes as well, the most famous of which is Saumagen, consisting of a pig's stomach filled with pork, potatoes, onions and peppers. Other popular dishes include Sauerkraut, a fermented cabbage which is often served with Saumagen, and Dampfnudeln, a sweetened bread roll often served with salad. In terms of desserts, the city is best known for apple strudel, a type of pastry filled with apple and often served with ice cream. Also popular are plum cakes, dependent upon season, and Dampfnudeln served with sweet toppings.
Sports
Lilienburg's most popular sports have traditionally been lacrosse and football. Both sports have leagues within Lilienburg, in which teams representing various neighbourhoods of the city compete against each other, and the city has entered international sporting tournaments in both sports but has traditionally performed very poorly in football tournaments, rarely qualifying.
Cycling has proven very popular with the Lilienburger populace, and in the summer many take to the countryside to cycle. While many cycle as a solo sport, cycling teams for various neighbourhoods within the country exist and compete in races between each other and within their teams. Skating is also very popular within the country, especially during winter; many small lakes on the edges of the city have traditionally froze over in winter and fairs have set up around these and they are converted into ice rinks.