Talahara: Difference between revisions
m (→Demographics) |
|||
| (173 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Region_icon_Ajax}} | {{Region_icon_Ajax}} | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = | |conventional_long_name = United Communes of Talahara | ||
|common_name = | |common_name = Talahara | ||
|native_name = | |native_name = ⵜⵉⵖⵉⵡⴰⵏⵉⵏ ⵢⴻⴹⵓⴽⵍⴻⵏ ⵏ ⵜⴰⵍⴰⵀⴰⵔⴰ | ||
|image_flag = | |image_flag = Black flag.svg | ||
|alt_flag = | |alt_flag = | ||
|flag_border = | |flag_border = | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|alt_flag2 = | |alt_flag2 = | ||
|flag2_border = | |flag2_border = | ||
|image_coat = | |image_coat = Lion's paw sigil.svg | ||
|alt_coat = <!--alt text for coat of arms--> | |alt_coat = <!--alt text for coat of arms--> | ||
|symbol_type = | |symbol_type = Sigil <!--emblem, seal, etc (if not a coat of arms)--> | ||
|symbol_footnote = <!--optional reference or footnote for the symbol caption--> | |symbol_footnote = <!--optional reference or footnote for the symbol caption--> | ||
|national_motto = </br>'' | |national_motto = | ||
|englishmotto = | |||
|national_anthem = [[Symbols_of_Talahara#They_shall_not_pass!|ⴰⴷⵓⵔⵣⵔⵉ!</br>''They shall not pass!'']] | |||
|royal_anthem = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | |royal_anthem = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|other_symbol_type = | |other_symbol_type = | ||
|other_symbol = | |other_symbol = | ||
|image_map = | |image_map = Talahara Location Map.png | ||
|loctext = <!--text description of location of country--> | |loctext = <!--text description of location of country--> | ||
|alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | |alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | ||
|map_caption = | |map_caption = Location of Talahara (dark green) within the [[Rubric Coast Consortium|Rubric</br>Coast Consortium]] (light green) in North Scipia | ||
|image_map2 = Aghmatia Map.png | |image_map2 = Aghmatia Map.png | ||
|alt_map2 = | |alt_map2 = | ||
|map_caption2 = Map of | |map_caption2 = Map of Talahara | ||
|capital = | |capital = [[Maktarim]] | ||
|coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | |coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | ||
| languages_type = | | languages_type = Official language</br>Regional languages | ||
| languages = {{wpl| | | languages = {{wpl|Central Atlas Tamazight|Standard Talaharan Takelat}}</br>{{wpl|Punic language|Tyrian}}, {{wpl|Latin}}, {{wpl|Hebrew}} | ||
|ethnic_groups = | |ethnic_groups = | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |ethnic_groups_year = | ||
|religion = | |religion = | ||
|demonym = | |demonym = Talaharan | ||
|government_type = {{ | |government_type = {{wp|Directorial system|Directorial}} {{wp|Council democracy|council}} {{wp|republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = | |leader_title1 = Head of state | ||
|leader_name1 = [[ | |leader_name1 = [[Executive Council (Talahara)|Executive Council]] | ||
|leader_title2 = | |leader_title2 = Legislature | ||
|leader_name2 = [[ | |leader_name2 = [[National Legislative Council (Talahara)|National Legislative Council]] | ||
| | |||
|sovereignty_type = <!--Brief description of country/territory's status ("Independence [from...]", "Autonomous province [of...]", etc)--> | |sovereignty_type = <!--Brief description of country/territory's status ("Independence [from...]", "Autonomous province [of...]", etc)--> | ||
|sovereignty_note = | |sovereignty_note = | ||
|established_event1 = | |established_event1 = First Talaharan Kingdom | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = c. 298 BCE | ||
|established_event2 = | |established_event2 = Second Talaharan Kingdom | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = March 1, 762 CE | ||
|established_event3 = | |established_event3 = Third Talaharan Kingdom | ||
|established_date3 = June 20, | |established_date3 = July 18, 1412 CE | ||
|established_event4 = [[Talaharan Civil War|United Communes of Talahara]] | |||
|established_date4 = June 20, 1838 CE | |||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | |area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = 603424 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |area_sq_mi = | ||
|area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | |area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | ||
|percent_water = | |percent_water = 0.77 | ||
|area_label = Total <!--Label under "Area" (default is "Total")--> | |area_label = Total <!--Label under "Area" (default is "Total")--> | ||
|area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | |area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | ||
|area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | |area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | ||
|population_census = 52,314,445 | |population_census = 52,314,445 | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = 2022 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 86.7 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
| Line 76: | Line 72: | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = $ | |GDP_nominal = $1.70 trillion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |GDP_nominal_year = 2022 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $ | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $32,508.37 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = | |Gini = 13.6 | ||
|Gini_change = | |Gini_change = steady | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = 2022 | ||
|HDI = . | |HDI = .878 | ||
|HDI_change = increase | |HDI_change = increase | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
|HDI_ref = | |HDI_ref = | ||
|currency = | |currency = [[Rubric_Coast_Consortium#Currency_union|Rubric (Ⲇ)]] | ||
|currency_code = | |currency_code = RCR <!--ISO 4217 code/s for currency/ies (each usually three capital letters)--> | ||
|time_zone = | |time_zone = | ||
|utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | |utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 92: | ||
|DST_note = <!--Optional note regarding DST use--> | |DST_note = <!--Optional note regarding DST use--> | ||
|antipodes = <!--Place/s exactly on the opposite side of the world to country/territory--> | |antipodes = <!--Place/s exactly on the opposite side of the world to country/territory--> | ||
|date_format = [[ | |date_format = [[Rubric_Coast_Consortium#Rubric_Standard_Calendar|Rubric standard calendar]],</br>{{abbr|yyyy|year}}-{{abbr|mm|month}}-{{abbr|dd|day}} {{abbr|AR|Asggas Ṛuḥen}}/{{wp|Common Era|CE}} | ||
|drives_on = right | |drives_on = right | ||
|cctld = . | |cctld = .ta | ||
|iso3166code = <!--Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> | |iso3166code = <!--Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> | ||
|calling_code = | |calling_code = +599 | ||
|patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | |patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | ||
|image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | |image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 107: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The ''' | The '''United Communes of Talahara''', ({{wp|Central Atlas Tamazight|Takelat}}: ⵜⵉⵖⵉⵡⴰⵏⵉⵏ ⵢⴻⴹⵓⴽⵍⴻⵏ ⵏ ⵜⴰⵍⴰⵀⴰⵔⴰ; ''Tiɣiwanin Yeḍuklen n Talahara'') referred to simply as '''Talahara''' or the '''United Communes''', is a nation in Northern Scipia on the Rubric Coast of the Periclean Sea. It is bordered by [[Tyreseia]] to the east, [[Charnea]] to the south, and [[Talakh]] and [[Yisrael]] to the west. It also shares a maritime border with [[Gran Aligonia]] to the north. Talahara’s capital and largest city is [[Maktarim]]. The name “Talahara” comes from the old Takelat “Thala N'Iheran” meaning “Font of Lions” in reference to the region’s historically large population of Rubric lions. | ||
The | |||
Talahara is a syndicalist state with a strong modern tradition of industrial democracy. In the United Communes, all industries and places of business are controlled directly by their workers who elect the directors of their businesses and associate with one another in labour unions. Government representatives are elected by a transferable vote system directly by the workers and represent their collective interests through a 3-tier nested legislative council delegation system. Political parties play an important but informal role in political organization. | |||
The major cultural groups of Talahara are the Kel Aman and the Kel Hadar; both of which are {{wpl|Amazigh peoples|Kel peoples}}. The Kel Aman are traditionally coastal dwellers while the Kel Hadar lived in the mountains and plains. Each of the two groups has similar linguistic, religious, and cultural traditions, but historically had different ways of living and different relationships with their traditions. Kel Aman and Kel Hadar clans remain important social structures for many Talaharans, though the relevance of their divide has greatly diminished since the conclusion of the [[Talaharan Civil War]] in 1838. | |||
The | |||
Talahara is a developed nation with heavy economic regulation effected by labour unions. Healthcare, education, and social services are delivered across a complex web of locally supported systems enabled by a national distribution system. Major industries include mining and mineral refining, oil extraction and refining, heavy manufacturing, construction engineering, industrial and chemical recycling, textiles, transportation, and tourism. Talahara is a member of the [[Rubric Coast Consortium]] and is a founding member of the [[Kiso Pact]]. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{main|History of Talahara}} | |||
Confirmed human habitation in present-day Talahara dates back to the ninth millennium BCE at the latest, with human activity dating back potentially as far as the 25th millennium BCE. The first records of early Talaharans were made by Aradian merchants in the second millennium BCE who traded with coastal settlements. These settlements became increasingly interconnected and culturally homogenous, gradually expanding to form coastal city-states. Human activity in the interior is less well-attested by the historical record, but settlements in the hills were the likely source of Talaharan copper. The [[Tamazgha|Confederation of Tamazɣa]] also exerted significant cultural and political influence that waxed and waned throughout the first century BCE. | |||
In the final centuries of the first millennium BCE, the Kel Aman city-states had formed a confederation, with various factions vying for influence and competing with Aradian influences and other foreigners. By the turn of the common era, the Latin Empire had expanded and created a client kingdom, later incorporated as a province of its empire that would last until 762 CE. The brief independence of Talahara would be ended in 906 CE with the occupation of Yen Caliphate which ruled until the mid-11th century. Over the course of several centuries, Talahara was subject to conflicts between the Kel Aman and Kel Hadar tribes along with its neighbouring rivals. | |||
===Modern history=== | |||
{{See also|Talaharan Civil War}} | |||
The early-modern era in Talaharan was heralded by political and economic upheaval. The death of the last ruler of the Zaraban dynasty without issues led to the creation of an assembly of the kings of each of the ruling clans and an elective monarchy. Institutional taxation, economic liberalism, and eventually industrialization followed over the subsequent centuries, turning Talahara into a centre of production in the Periclean basin. Conflicts between the rulers, the liberal industrialists, and the vast majority of workers, including slaves, led to the [[Talaharan Civil War]] in 1834. The civil war lasted four years and concluded with a socialist union of communes emerging victorious, overthrowing both the monarchy and the industrialist class. | |||
The | The United Communes of Talahara emerged as a revolutionary state but was soon joined by several others, including the Workers' Federation of Tyreseia in 1883. Talahara was faced with a number of emergent issues as it strained to develop its novel government and reordered economy, coupled with rebuilding after the war. Talahara's government and legal system were significantly developed over the 19th and early 20th centuries, with these developments characterized as a conflict for balance between anarchist and statist factions. | ||
The second half of the 20th century presented a period of relative détente as the United Communes of Talahara engaged in fewer external conflicts. However, the internal politics of the United Communes were again in turmoil as statist influence declined and pacifistic influences drew the nation away from the global stage. Despite this, in recent years Talahara has shown signs of moving arriving at another political pivot, influenced in part by geopolitical strain in its immediate neighbourhood. | |||
==Geography and climate== | |||
There is a thin band of {{wpl|Mediterranean climate|Periclean climate}} in Talahara's northern coastal region quickly giving way to {{wpl|Semi-arid climate|semi-arid climates}} and {{wpl|Desert climate|desert}} in the south. Much of Talahara is covered by the foothills and peaks of the Adras Mountains which give way in the south to the rolling dunes of the Ninva Desert. Both semi-arid and desert climates cool down with rises in elevations. | |||
=== | ===Flora and fauna=== | ||
[[File:Fennec Fox.jpg|270px|thumb|right|Fennec fox, commonly found in Talahara]] | |||
In Talahara, few mammals are capable of surviving the intense heat of the Ninva Desert. Common desert mammals include shrews, sand rats, mice, and fennec foxes. Deer are also still common along the coasts. The namesake animal of Talahara, the {{wpl|Barbary lion|Rubric lion}} is endangered and there are few endemic habitats that have not been encroached upon by human development. | |||
Migratory birds are common across the region as well. Many northern birds such as geese and ducks will winter in Talahara, while southern birds like flamingoes will fly up from central or southern Scipia in the spring. Many of the fish of the Periclean have been historically important for communities on either side of the sea. | |||
Talahara's flora varies greatly between the southern desert where very little can grow, the coastal regions where cereals and cash crops are commonly grown, and the eastern brushland. Of particular note is a species of uniquely endemic firs in the central mountains above the Ninva Desert. | |||
===Climate=== | |||
Talahara's climate is best described as exceedingly hot and dry with the exception of the coastal region which receives precipitation from the Periclean. The two other broad climate zones present in the nation include the eastern semi-arid brushland, which receives enough precipitation to support plant life; and the central mountains where the elevation leads to noticeable cooling compared to the deserts which lie in the rain shadow to the south. On average, temperatures in the desert peak around 35°C (~95°F) in mid-summer. In the winter, temperatures can fall as low as 5°C (~40°F). The daily mean temperature across the whole year is 22°C (~71°F). Along the coast temperatures are nearly identical although rainfall over the year is approximately 11× greater than in the desert (600 mm versus 54 mm of rain annually). | |||
==Government and politics== | |||
The government of the United Communes has three independent components: the [[Executive Council (Talahara)|Executive Council]], the [[National Legislative Council (Talahara)|Legislative Councils]], and the Judicial Councils. | |||
The Executive Council (''Aseqqamu n Uselway'') is a directorial body with limited jurisdiction composed of ten elected executors elected by ranked ballot. There are no qualifications to run as an executor. Each candidate must file a petition with 50,000 signatures to have their name added to the ballot. Most candidates who run have the support of a political party or salon to accumulate the necessary signatures and run a campaign. Other candidates derive their support directly from industrial unions or alliances between unions. Historically, truly independent candidates have had mixed success. | |||
At the lowest level, a Communal Legislative Council (''Aṣaḍuf n Taɣiwant'') is each chaired by ten elected representatives, each representing approximately 4,000 people. One of the ten representatives is voted as a delegate to a Regional Legislative Council (''Aṣaḍuf n Tamnaḍt''), which is made up of 25 delegates agglomerated from 25 Communal Councils. Each of these representatives thus represents approximately 40,000 people. The final level is the [[National Legislative Council (Talahara)|National Legislative Council]] (''Asaduf Aɛlayen'') which counts 50 delegates, each representing approximately 1,000,000 people. Each delegate at each level serves at the pleasure of the council below it. Additionally, general elections are held every four years. In total, there is one National Council, 50 Regional Councils, and 1,250 Communal Councils. | |||
[[File:ZarTalahara.jpg|444px|thumb|right|The ''Zar Talahara'' complex, built in 1936 and home to the {{nowrap|Executive Council}}, {{nowrap|National Legislative Council}}, and {{nowrap|National Judicial Council}}, in [[Maktarim]]]] | |||
The judicial system in Talahara operates in parallel with the legislative council system. The Communal Councils each appoint a justice to each Communal Judicial Council (''Tanzarfit n Taɣiwant'') from qualified candidates for up to 12-year terms. Candidates must have legal certification and at least five years of practice. The 25 Communal Judicial Councils then elect a Regional Judicial Council (''Tanzarfit n Tamnaḍt'') of five members from amongst themselves. Finally, the 50 Regional Judicial Councils elect a National Judicial Council (''Tanzarfit Aɛlayen'') of ten justices from amongst themselves. Legislative councils at each respective level are able to recall justices subject to a communal referendum. | |||
===Law=== | |||
The United Communes of Talahara's legal system is a hybrid {{wpl|Civil law (legal system)|civil}} and {{wpl|customary law}} system. The customary law elements in criminal and civil law are based on written and unwritten principles of traditional Talaharan clan law. The legislatures of Talahara have also instituted statutory reforms and provisions that modify the existing customary law. So long as legislation is constitutional and respects the rights and interests of the people, civil law provisions may supersede the customary law. | |||
The three-part [[National Consensus of Talahara]] is the supreme law of the country. Part I of the National Consensus provided universal human rights and freedoms for all Talaharans and foreign nationals in Talaharan jurisdiction. Part II of the National Consensus codified voting rights and property reform. Part Three established the systems of government, including the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. | |||
[[ | |||
The different levels of the Judicial Councils cover different jurisdictions in criminal and civil matters. Communal Judicial Councils adjudicate matters of familial disputes, property disputes, and minor criminal matters. Regional Judicial Councils deal with major crimes, property or personal allegations that go beyond local importance, and appeals of matters from the Communal Judicial Councils. The National Judicial Council adjudicates matters of constitutional interpretation, matters of national importance, and appeals from Regional Judicial Councils. Matters that go beyond local or are of national importance are determined by the lower Judicial Councils. For a typically local matter to pass to a Regional Judicial Council, ten of the 25 Communal Judicial Councils beneath them must vote for it to pass upward. Likewise, 20 of the 50 Regional Judicial Councils must vote for a matter to pass to the National Judicial Council. | |||
In | Law enforcement in Talahara is conducted by community policing. Each commune elects a ''šaraf'', commonly anglicized as "sheriff", for a five-year term to organize local law enforcement. A sheriff is empowered to appoint deputies for the duration of their tenure. In practice, deputies are frequently members of a local Black Guard unit, though civilian members can be drawn from different professions. In principle, deputies are encouraged to maintain part-time employment in another vocation to foster connection and integration with the community. In addition to deterring and investigating crimes, the sheriff's office is responsible for assembling cases to be presented before a justice. Talahara's trial proceedings follow an {{wpl|inquisitorial system}} and procedures assume neither party has any legal competencies. The head detective in a criminal investigation is typically appointed as the advocate of the sheriff's office. Individuals and unions defending against criminal accusations or otherwise litigating a civil matter are also entitled to legal advocacy. For inter-jurisdictional cases or particularly high-level offences, additional resources can be provided by the office of the Executor of Oversight and Public Safety, though material support at the national level is typically civilian. | ||
Sentencing and the Talaharan correctional system are heavily based on community impacts. Civil sanctions generally include restitution, either monetary or in labour time. A guilty party's labour union or other community supports are permitted to absorb costs, though repeat offenses can result in more punitive sanctions. Injunctive or prohibitory sanctions are rare for first offenses. Criminal sanctions rarely include incarceration. Instead, convicts are placed in restricted community living conditions for the period of their sentence. Severe crimes can carry more severe restrictions, education or therapy, and possible surveillance mechanisms, but the community value of continued productivity and cost savings with housing a convict in their community are held as values of the criminal justice system. | |||
The | ===Foreign relations=== | ||
Talahara maintains close diplomatic relations with its western neighbour, [[Tyreseia]]. The two syndicalist nations are economically and geopolitically intertwined through the [[Rubric Coast Consortium]]. Relations with the socialist nations of [[Ostrozava]] in Belisaria, [[Wazheganon]] in Norumbia, [[Pulau Keramat]] in Malaio, and [[Tsurushima]] in Ochran have also risen in importance over the 20th century, particularly with advents of globalization and revolutions in communication and transportation. The end of the 20th century brought renewed and closer ties with additional nations in the global left, including [[Otomarca]] and nominally [[Zacapican]]. | |||
Following the Arthuristan revolution in 1998, Talaharan and [[Arthurista]] developed significant economic and political ties. | |||
[[ | |||
Relations with Talahara's southern neighbour, [[Charnea]] have been comparatively mixed. Cultural ties to the Kel Tenere have led to a degree of political and economic support. However, the United Communes are ideologically opposed to the authoritarian government and have occasionally offered tepid protests. Despite this, Talahara maintains active economic and diplomatic relations with Charnea. Similarly, relations between Talahara and [[Talakh]] have been poor owing to the latter's monarchical government, particularly following the strife of the 1996 coup in Talakh. | |||
Relations with [[Yisrael]] to the west have been relatively poor through Talahara's modern history. The Kingdom of Yisrael's monarchical government and belligerent actions set the stage for tense relations. During the [[Talaharan Civil War]], Yisraeli forces annexed a significant portion of northwestern Talahara and incorporated it into a protectorate called Tarshish. Intermittent hostility continued through the first half of the 20th century, during which Talahara annexed the oil-rich Amara region (also known as the Timna Strip) and reannexed Tarshish. In the period following the 1951 reannexation, relations with Yisrael gradually thawed, though recent events in the [[Gran Aligonian crisis (2019-present)|Gran Aligonian crisis]] and the ensuring [[Onekawan Affair]] led to a rapid chilling of relations in the 2020s. | |||
Other monarchical and liberal nations around the world are typically subject to pragmatic approaches. The Latin-dominated sphere of the world is treated with occasional ambivalence and occasional concern, though economic relations remain open, due in part to Tyreseia's cultural relationship with [[Latium]]. [[Sante Reze]], as a major commercial centre, likewise shares relatively warm relations. Elsewhere, nations with strong monarchies, a history of poor civil or political rights, or ongoing or recent human rights abuses have been subject to diplomatic and economic sanctions. | |||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
{{Main| | {{Main|United Communes Defense Forces}} | ||
The unified armed forces of the | The unified armed forces of the United Communes of Talahara are comprised of the [[Talaharan Army Corps]], the [[Talaharan Air Corps|Air Corps]], and the [[Talaharan Navy Corps|Navy Corps]]. The land and naval forces were originally consolidated in 1838 with the addition of the aerial branch in 1920. Service is strictly voluntary and conscription has never been practiced in the modern history of the Union. Members of the armed forces are organized under a union but is under the direct governance of the Executive Council. While certain roles have educational requirements, both commissioned and non-commissioned officers are elected by their units. Certain grades require a level of seniority. Several enlisted grades are determined solely by seniority. This relaxed approach to military hierarchy has contributed to the reputation of disorganization and ill-discipline. | ||
<gallery widths="270px" heights="180px" > | |||
Desert Camo Leclerc.jpeg|{{wp|Leclerc tank|T104A2 Lion main battle tank}} | |||
MU Roundel Mirage 4000.png|[[NA48 Chainbreaker|NA107 Chainbreaker jet fighter]] | |||
Jeanne D Arc DN-ST-87-01219.JPEG|{{wp|French cruiser Jeanne d'Arc (R97)|''Mass Akli''-class helicopter cruiser}} | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
The | {{Main|List of commercial entity types of Talahara|l1=Commercial entities in Talahara}} | ||
The United Communes of Talahara has a {{wpl|Planned_economy#Decentralized_planning|distributist}} {{wpl|syndicalist}} economy facilitated by centralized distribution networking to aggregate demand and contract out supply between syndicates. In this system, cooperative and communal enterprises operate independently to extract materials, manufacture goods, or provide services, the product of which can be apportioned to a sector in need, kept as surplus, or slated for exchange or export. Outside of consumer protections, industries are subject to limited direct government regulation but interference may be undertaken if an entity is found to be operating in bad faith. Independent industrial unions are also a source of regulations, particularly in areas of health and safety. | |||
Major extractive industries include mining, petroleum, agriculture, and industrial and chemical recycling. Secondary industries include petroleum products, heavy manufacturing, textile production, and mineral refining. Major international services include construction engineering, transportation, and tourism. | |||
Talahara's economy is heavily linked with that of Tyreseia via the [[Rubric Coast Consortium]] which provides for free trade, freedom of movement, and industrial cooperation between the two constituent nations. Since 1980, the Consortium has included a currency union. Both Talahara and Tyreseia are also members of the [[Vespanian Exchange Institute|Vespanian Exchange]] through the Consortium. | |||
===Transportation=== | ===Transportation=== | ||
[[ | Talahara has an extensive light rail system linking urban areas along the Rubric Coast in addition to heavy passenger and freight rail systems that network cities to the south. Talahara's heavy rail system also networks with the [[West Scipian Railway]] which runs from Yisrael to Tyreseia. Urban areas in the north rely heavily on light rail and rapid transit systems to convey commuters. Many major cities are considered unfriendly to personal vehicles. Most settlements in the south have a greater dependence on cars or bus rapid transit. Highway systems also run parallel to major rail lines, though depending on the locale, roads may be unpaved or ill-maintained. | ||
Travel by sea or by air is also common. Maktarim has a major seaport on the Periclean and is also home to the nation's major international airport. Regional air travel supplements rail or personal vehicular transportation for rapid or convenient travel. Regional airlines also offer international flights to immediate neighbours from a number of smaller airports. | |||
===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
The petroleum industry is central to the economy of | [[File:إحدى محطات الكهرباء في السعودية.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Oil refinery in Batana]] | ||
The petroleum industry is central to the economy of Talahara, centered mostly in the province of Amara and the rich oil fields in its northwest region. The [[National Petroleum Syndicate]] is the single largest commercial entity in the country and the second largest, [[Synprosyn]], is also part of the broader petrochemical industry. Petroleum is produced in excess of the nation's energy demand which is supplemented by several large solar projects and nuclear power imported from Tyreseia. Surplus oil is sold to [[Sante Reze]] and [[Yisrael]], mostly shipped in tanks by rail or used in the production of petroleum products, including plastics. | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
Talahara has a total population of 52,314,445 as of the 2022 census. The birth rate is slightly below the replacement rate but supplemental population growth from immigration roughly offsets the deficit. The average life expectancy is rising and currently averages at 78.0 years. Talahara's population period is also stable with a slightly larger cohort of youths. The population is heavily concentrated in the north of the country, along the Rubric Coast. Over 50 million of the approximately 52.8 million inhabitants live in coastal cities. The coastal region is, in effect, a single megalopolis. However, traditional urban boundaries are reflected in the areas of Communal Council jurisdictions. | |||
{{Largest cities | {{Largest cities | ||
| name = Largest metropolitan areas of the | | name = Largest metropolitan areas of the Talahara | ||
| country = | | country = Talahara | ||
| stat_ref = Census data, | | stat_ref = Census data, 2022 | ||
| list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> | | list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> | ||
| class =info | | class =info | ||
| div_name = | | div_name = Region | ||
| div_link = | | div_link = | ||
| city_1 = | | city_1 = Maktarim | div_1 = Rubric Coast Centre | pop_1 = 8,873,785 | img_1 = Alger View Oct-2010 IMG 1039.JPG | ||
| city_2 = Takalt| div_2 = | | city_2 = Takalt | div_2 = Rubric Coast East | pop_2 = 4,884,626 | img_2 = Annaba, algeria04.jpg | ||
| city_3 = | | city_3 = Mestaɣanim | div_3 = Rubric Coast Centre | pop_3 = 4,344,527 | img_3 = Biskra Cityscape.jpg | ||
| city_4 = | | city_4 = New Rušadar | div_4 = Rubric Coast West | pop_4 = 3,497,939 | img_4 = Agadir, Morocco (5398039542) (2).jpg | ||
| city_5 = | | city_5 = Ifurša | div_5 = Rubric Coast Centre | pop_5 = 2,651,285 | ||
| city_6 = | | city_6 = Weskera | div_6 = Rubric Coast East | pop_6 = 2,391,630 | ||
| city_7 = | | city_7 = Almunaxdri | div_7 = Qeshet North | pop_7 = 1,891,631 | ||
| city_8 = | | city_8 = Kirthan | div_8 = Qeshet South | pop_8 = 1,153,101 | ||
| city_9 = | | city_9 = Zedif | div_9 = Ninva Centre | pop_9 = 966,010 | ||
| city_10 = | | city_10 = Batana | div_10 = Timna South | pop_10 = 746,862 | ||
}} | }} | ||
===Ethnicity=== | ===Ethnicity=== | ||
{{bar box | {{bar box | ||
|title = Self-identified ethnicity in | |title = Self-identified ethnicity in Talahara | ||
|titlebar=#ddd |left1=Ethnicity|right1=Percent |float=right | |titlebar=#ddd |left1=Ethnicity|right1=Percent |float=right | ||
|bars = | |bars = | ||
{{bar percent|Kel | {{bar percent|Kel Aman|DarkRed|43}} | ||
{{bar percent|Kel | {{bar percent|Kel Hadar|Red|30}} | ||
{{bar percent| | {{bar percent|Kel Tenere|Crimson|7}} | ||
{{bar percent| | {{bar percent|Kel Taram|Pink|5}} | ||
{{bar percent|Tyrian|Purple|5}} | |||
{{bar percent|Jewish|Blue|4}} | |||
{{bar percent|Other (Scipian)|LightGrey|4}} | |||
{{bar percent|Other|Grey|2}} | {{bar percent|Other|Grey|2}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
Talahara's two major cultural groups are the Kel Aman and the Kel Hadar, both of which are Kel ethnicities. The Kel Aman traditionally dwelt on the Rubric Coast and lived sedentary lives engaging in agriculture, fisheries, and commerce. Kel Aman clans grew in size and relative importance due to reliable food supply. Traditional clan structures were rigidly hierarchical based on seniority. The eldest members of the family and kinship groups directed both domestic and social affairs. The Kel Hadar traditionally came from the plains and hills of Talaharan. Significant Kel Hadar populations historically migrated to the desert in the 8th or 7th century BCE and several modern kinship groups lay claim to this lineage. Kel Hadar lifestyles and privileges included rights of way in furtherance of a pastoralist lifestyle. However, other Kel Hadar groups were sedentary, primarily developing urban areas away from the coast. For much of their history, the Kel Aman and Kel Hadar maintained distinct dialects and cultural differences. Since the 18th century, these differences have become increasingly reduced, especially following the flight of many Kel Aman individuals who were adopted by existing Kel Hadar clans. The modern Standard Talaharan Takelat language incorporates grammar and vocabulary from both dialects. Since the [[Talaharan Civil War]] in 1838, no ethnic group has special status before the law. | |||
Kel | Minor ethnic groups in Talahara include the Kel Tenere, Kel Taram, Tyrians, and Jews. The Kel Tenere make up a broad portion of the inhabitants of the Talaharan Ninva. While also a Kel ethnic group, the Kel Tenere maintain a distinct dialect, vocabulary, and religious tendencies compared to their northern kin. The Kel Taram are considered by many to be a subethnicity of the Kel Hadar native to Talakh, while other linguistics and ethnographers consider them a distinctive Kel ethnicity. The next minor ethnic group in Talahara is the Tyrians. Roughly half the Tyrian population in Talahara is made up of first- or second-generation immigrants, though longstanding communities exist in major Talaharan centres, particularly in the east. Talahara also has a significant Jewish population which is particularly concentrated in the western region of the Rubric Coast. | ||
The | ===Language=== | ||
The national language of the United Communes of Talahara is {{wpl|Central Atlas Tamazight|Standard Talaharan Takelat}}. Standard Takelat was developed in the 1840s and 1850s to bridge grammatical and vocabulary differences between Aman and Hadar languages. Standard Takelat is related to other Kel languages but is not necessarily mutually intelligible. | |||
In an 1866 constitutional amendment, Standard Takelat was codified as the language of legislative and judicial proceedings in the nation. Education in other languages remains an option for local communities, including the teaching of the Tamashek language in schools in the Talaharan Ninva. However, Standard Takelat has rapidly subsumed the use of traditional languages as of the 19th century. | |||
A plurality of Talaharans speak and read Standard Takelat as their sole language. Approximately 62% of the population has proficiency in two or more languages. Regional languages which are commonly used in business and taught in local schools include {{wp|Tamashek}}, {{wp|Punic language|Tyrian}}, {{wpl|Latin}}, and {{wp|Hebrew}}. | |||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
{{bar box | {{bar box | ||
|title = | |title = Religious expression in Talahara | ||
|titlebar=#ddd |left1=Religion|right1=Percent |float=right | |titlebar=#ddd |left1=Religion|right1=Percent |float=right | ||
|bars = | |bars = | ||
{{bar percent|[[ | {{bar percent|[[Massanism]]|Red|43}} | ||
{{bar percent|[[ | {{bar percent|[[Azdarin]]|Green|5}} | ||
{{bar percent| | {{bar percent|{{wpl|Coptic Church|Coptic Nazarism}}|Purple|3}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wpl|Judaism}}|Blue|3}} | |||
{{bar percent|{{wpl| | {{bar percent|Other|Grey|6}} | ||
{{bar percent|Other|Grey| | {{bar percent|{{wpl|Irreligion}}|DarkGrey|39}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wpl|Irreligion}}|DarkGrey| | |||
}} | }} | ||
The | [[Massanism]] was effectively a state religion in the Third Talaharan Kingdom. The modern country of Talahara is a secular nation in accordance with the universalist principles of its foundation. Following the [[Talaharan Civil War]], secularist movements gained traction in reaction to religious conservative support of the monarchist faction. Secularization was supported by a humanist reclamation of Massanism which wrapped secular philosophy and politics in the rituals and traditions of Massanism. In the present day, a plurality of Talaharans identifies as Massanist, followed by a broadly irreligious cohort including agnostic, atheist, or ambivalent Talaharans. Other minority religions are common, though state secularism affords no support for religious congregations. Religious services are typically held in homes or on public grounds. | ||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
Primary, secondary, and post-secondary education is publicly-funded in Talahara. Primary education is included with early child care in Communal Council programming, bridging age groups from infants to 13 years of age. Secondary education is also provided by commune-level institutions, but the curriculum is more intense and has more divergent streams. Between 14 and 18 years of age, students can begin apprenticing with industry unions in addition to completing required coursework. This process primes students to enter the workforce immediately upon graduation. | |||
Post-secondary educational institutions have their curriculums, mandates, and funding organized by Regional Councils. In practice, educational assets and governance duties are frequently combined between council areas to create larger, more substantial institutions. The largest post-secondary institution in Talahara is the University of West Maktarim-Mestaɣanim which offers liberal arts and STEM degree programs. General admission to universities relies on program-related standardized testing. University-bound students typically enroll in an additional year of secondary education to prepare directly for their desired programs' tests. General international students are subject to the same standardized tests but immigrants with foreign credentials are fast-tracked to have their credentials certified in the United Communes. | |||
===Healthcare=== | ===Healthcare=== | ||
Healthcare is delegated as a national responsibility under the jurisdiction of the Executor of Health. While organized at the highest level, healthcare is administered at a communal level for generalized and clinical care, long-term care, dentistry, and mental health services. Major care centres including surgery and low-intensity ancillary treatments are typically delivered at the level of a Regional Council. | |||
Healthcare funding is accumulated through an industrial risk insurance scheme. Rather than gather taxes from private citizens or via a flat tax on income or industry revenue, healthcare taxes are drawn from the gross incomes of businesses, directly proportional to the risks associated with those industries, be those acute risks of bodily harm or general occupational hazards. The purpose of the scheme is twofold. Firstly, healthcare costs are equitably distributed. Secondly, industries are encouraged to passively self-regulate and reduce occupational hazards so that their taxes are lessened. Critics of the healthcare system note that individuals are not incentivized to avoid reckless behaviours in their private lives and that communities therefore bear the costs of an individual's recklessness. | |||
===Housing=== | ===Housing=== | ||
[[File:Essaouira 210.JPG|320px|thumb|right|Traditional courtyard in a multi-family housing complex in Mestaɣanim]] | |||
Private real estate is nonexistent in the United Communes of Talahara. Housing projects are directed by communes with resources allocated by the Executor of Housing and Vital Statistics in accordance with projected population growth. Despite the local importance of housing, due to the process of redistricting communes with relative frequency, the funding process is devolved up to the top level. This allocation is statutorily set to a minimum standard of amenities which can be augmented by additional community resources. Architectural and engineering requirements are also provided to account for geographic and contextual needs. | |||
Aging residential infrastructure can be refurbished or replaced upon the application of a Communal Council should the standard of living fall beneath the statutory standard of amenities. Industrial subsidization of first-instance residential construction or refurbishment also counts as credits against taxes for public transportation. This policy promotes efficiency of movement, with workers being able to reside closer to their places of business, thereby minimizing strain to existing transportation networks. | |||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
{{See also|Community and kinship in Talahara}} | |||
Talaharan culture draws on several broader cultural sources. The first and oldest cultural source is traditional Kel Aman and Kel Hadar cultures, including the religious values and influences of Massanism. Kel culture imparts important communitarian values and broad family structures. In addition, the Takelat language laid the foundation for framing describable reality and cultural frames. The second major source is socialist universalism which builds directly with the Kel communitarian values. Socialist culture promotes industry while de-emphasizing competition. In terms of aesthetic or material culture, socialist influences appear more austere, but this is not necessarily universal. The third source is globalization and the gradual homogenization of socialization around the world. While there is no single cultural hegemon in the world, Talahara increasingly accepts cultural influences from elsewhere in Scipia, Belisaria, Norumbia and Oxidentale, and as far as East Ochran. These influences are largely on material culture but also have effects on socialization and a conflict between change and tradition. | |||
===Media=== | |||
News media and publications are ubiquitous in Talahara. By tradition, and occasionally by communal statute, local communities receive news updates and council meeting minutes every week. In addition, every labour union has its own weekly or monthly broadsheet, which typically covers industry affairs, politics, and occasionally news media and entertainment stories. ''Steelworker Today'' is one of the most-distributed daily broadsheets in the United Communes, with the Steelworkers' Union having effectively built a secondary industry in news media, political commentary, and entertainment literature. | |||
Despite the vast array of both state and independent publications, radio and television broadcasts are a regulated and unionized industry. Unlike most independent publications which are not subject to ethical standards of journalism, union journalists can be subject to sanctions for innaccurate reporting. | |||
Entertainment media in Talahara is also a major industry. Music, television, and film production is centered in the city of Mestaɣanim. Takelat-language productions are a mainstay in Talaharan homes, but Latin and Tyrian-language imports are more commonly followed by Talaharans who are fluent in those languages. | |||
Online media has been an emerging field in recent decades and remains largely unregulated. Major professional outlets, unions, and higher levels of government publish digital versions of most print materials, with some having migrated entirely to reduce paper costs. Other, smaller unions and Communal Councils have resisted the transition to the internet, opting for traditional communication standards despite creeping obsolescence. | |||
===Time=== | |||
The Talaharan calendar tracks the {{wp|solar year}}, taking influence in its modern incarnation from the {{wp|Gregorian calendar}}. The modern form of the calendar, standardized after the [[Talaharan Civil War]] in 1838, has 12 months each lasting 30 days. The additional five days (six in leap years), is an additional demi-week held at the end of the year. Each 30-day month is divided into three 10-day weeks, commonly referred to as decades. On average, the workweek covers either six or seven days per decade, typically in a staggered pattern with a two or three day weekend and a rest day interrupting the standard work schedule. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Month name !! Literal translation !! Through dates (Gregorian) <sup>†</sup> | |||
|- | |||
| Badu || Beginning [of the year] || June 21 to July 20 | |||
|- | |||
| Hama || Heat || July 21 to August 19 | |||
|- | |||
| Samayem || Dog days || August 20 to September 18 | |||
|- | |||
| Zwarunzar || First rain || September 19 to October 18 | |||
|- | |||
| Šarhert || Month of ploughing || October 19 to November 17 | |||
|- | |||
| Kasaɣul || Returning the herd || {{nowrap|November 18 to December 17}} | |||
|- | |||
| Melalen || White [nights] || December 18 to January 16 | |||
|- | |||
| Tiberkanin || Black [nights] || January 17 to February 15 | |||
|- | |||
| Imbarken || Strong winds || February 16 to March 17 | |||
|- | |||
| Aysi || ''Unknown etymology'' || March 18 to April 16 | |||
|- | |||
| Amgarunzar || Last rain || April 17 to May 16 | |||
|- | |||
| Zari || End [of the year] || May 17 to June 15 | |||
|- | |||
| Šimalas Hetafel || Demi-week festival || June 16 to June 20 | |||
|} | |||
<small>† All months except the second half of Tiberkanin and Imbarken have their through dates shifted one day forward in leap years.</small> | |||
[[File:Fez.jpg|240px|thumb|right|The ''tarbuš'' is a piece of headwear commonly associated with Talahara]] | |||
The summer solstice is the traditional Talaharan New Year. This date is standardized to June 21 (June 20 in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. The reckoning of years in Talahara is also subject to the Rubric Standard Calendar. Established in 1890 between Talahara and Tyreseia, the treaty organization saw the Rubric Standard Calendar introduced in 1891, establishing a common reckoning between both countries with 1891 as the calendar's "year 1", beginning on June 21. Dates in the calendar are noted "AR" which initializes "Rubric year" in both Takelat and Tyreseian Latin. Years prior to 1891 are noted either in negative numbers or as "BAR" or "Before Rubric years". | |||
===Arts=== | ===Arts=== | ||
[[File:Parure de femme berbère (Musée du quai Branly - Jacques Chirac, Paris) (49286249956).jpg|185px|thumb|right|Traditional Kel Hadar regalia]] | |||
The pre-eminent, traditional medium of visual art in Talahara is tapestry weaving. Talaharan tapestries are used both as floor carpeting, particularly among traditionally semi-nomadic groups, but also as adornments for walls. Matrilineal Kel Aman and Kel Hadar clans retain trace the continuity of their kinship through distinctive forms and motifs. Tapestries also tell stories through the incorporation of glyphs or sigils which are almost a distinct language on their own. The tradition of tapestry weaving is heavily related to knowledge-keeping and history. The national emblem of Talahara is a glyph or sigil representing a lion's paw. The meaning of different sigils can vary according to their context and reading tapestries correctly demands a high degree of skill and training. | |||
[[File:TapisKabyle2.jpg|130px|thumb|left|Talaharan tapestry]] | |||
The second major medium of traditional Talaharan art is silversmithing and jewelry. As with tapestry, silverwork has many regional variations and distinctions. The art of smithing was a contentious one in old Talaharan culture. Smiths were admired by common farmers, herders, and craftspeople both for their utility and for their mastery of the four elements: fire, air, water, and metal. To the political and religious elite, smiths were regarded with superstition for the same reasons, as the mystical and material power that metalworkers held could be dangerous to their rule. This led to the tradition of smiths offering gifts of silver jewelry and steel weapons to new clan rulers and their direct families. Paradoxically, this became an expectation. Smiths who did not regularly offer gifts to chiefs and priests could be subject to socio-religious sanctions. Talaharan jewelry has its own symbolic language with some overlap with tapestry weaving. Many embossments, motifs, and symbols represent purity or protection in attempts to ease the superstitions of the elite or at least put their supernatural talents to good use. Several historical examples were clearly made to mock contemporary rulers, with bracelets mocking a slave's manacles and necklaces with cursed symbols over the wearer's chest. | |||
===Sports=== | ===Sports=== | ||
{{wp|Association football}} is among the most popular and commonly played sports in Talahara, owing in part to its convenience in terms of rules and equipment. Casual pickup games are common in community parks and union leagues are ubiquitous in all regions of the country. Equestrian activities are the more traditional sports of the region, however. Racing, jumping, and horseback acrobatics are common categories of professional equestrian events. | |||
The national sport of Talahara is derived from the horseback performance of {{wp|Fantasia (performance)|''Taburida''}}. In its purest form, the event is a choreographed cavalry charge, including the firing of muzzleloading carbines, showcasing speed, balance, and eloquence. The team event follows a troupe of riders who must approach one end of the course at a walk, pivot at the end, and charge back in a synchronized formation, firing their carbines in synchronicity as well. In ideal circumstances, the horses and riders move in perfect unity and the shots from the carbines report as only a single discernable sound. Individual events typically involve a display of swordsmanship along with graceful and deliberate movement and shooting. A third, modern variation of the event has evolved as well, resembling the sport of {{wp|biathlon}}. Riders complete the course in sequence, due to the hazards of firing on horseback in a crowded group. Riders must complete a 5-lap, 30 km race, stopping each of the five laps to fire at three targets. Missing a target adds a minute to the rider's time. Muzzleloading black powder carbines are still used for the event and riders are tested on their ability to ride, ability to control their horse while shooting, their accuracy, and their speed at reloading. | |||
Talahara's mainline equestrian racing tradition has largely given way in modern times to motorsports. Open-wheel circuit racing and rallying are the two most common categories. In addition to international events, local racing and construction leagues hold minor championships. Many mechanically-minded unions offer opportunities for youths to develop racecraft and automotive knowledge from a young age, despite a comparative irrelevance of road cars compared to other nations. | |||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
Talaharan cuisine is characterized by fusions from around the Periclean. However, it maintains key endemic features. Traditionally, Talaharans consume three meals a day, two of which are served hot. Lunches may be served either hot or cold. {{wpl|Shakshouka|Šakšuka}}, {{wpl|Baghrir|baɣrir}} served with fruit preserves, and freshly grilled {{wpl|merguez|amergaz}} are common as breakfast dishes. Cold, raw vegetables, smoked meats, and cold {{wpl|Bissara|tabissart}} soups are common for lunches. Staple dishes for dinners include stews and casseroles such as {{wpl|tajine|tajin}} and {{wpl|Cholent|škina}}. {{wpl|Couscous|Kuskus}} and roasted meats are almost universal accompaniments. Endemic condiments include the tomato-based {{wpl|Matbucha|matbuɣaha}}, a spiced garlic relish called {{wpl|Chermoula|tacermult}}, and the onion-based {{wpl|Tfaya|tafaya}} sauce. Every meal can be accompanied by {{wpl|M'semen|msemmen}} flatbread which is frequently consumed on its own or with preserves for breakfast. Fruits, dates, and sweets are commonly consumed as snacks. | |||
Tea and coffee consumption in Talahara is roughly evenly divided. In addition to caffeinated black teas imported from East Scipia and Ochran, herbal teas are frequently consumed in the afternoon or evening. Mint tea, in particular, is a major cultural staple among traditional Kel Hadar groups. Domestically, alcoholic beverage consumption of wine is heavily outpaced by beer. Beer is brewed locally from local grains and botanicals. Wine and grape culture is generally regarded as a more international influence, despite the fact that they have been cultivated in the region for centuries. {{wpl|Mahia (drink)|Anunhayat}} is a local hard alcohol distilled with the sugars from dates. | |||
Talahara has a growing international cuisine based around local takes on wine, cheeses, and smoked meats like amergaz. Cheese is typically made from sheep's milk and unpasteurized, characterized by a {{wpl|Zamorano cheese|nutty flavour and hard texture}}. Cheese from cow's milk is also common and is made to be {{wpl|Oka cheese|semi-soft in texture and similarly nutty in flavour}}. Talahara's wine tradition emerged more recently in the production of Kosher sweet wines in the northern parts of the western regions. The practice was initiated by Jewish settlers in the Protectorate of Tarshish but has continued on to the present day. Other major international trends include the adoption of cuisines from the Ozeros, Belisaria, and Ochran. | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Shakshuka by Calliopejen1.jpg|Šakšuka | |||
Chorizo cortado.jpg|Sliced amergaz | |||
Bissara Moroccan split pea and fava bean soup.jpg|Tabissart with oil | |||
طاجن بيض ومطيش وكرات د اللحم.jpg|Hot tajin | |||
2008 04 23 - Laurel - Sauce.JPG|Matbuɣaha | |||
Cuscus.jpg|Kuskus | |||
Zamorano Jon Sullivan.jpg|Sheep's milk cheese | |||
The menthe.jpg|Mint tea | |||
Turkish tea2.jpg|Black tea | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:Ajax]] | [[Category:Ajax]] | ||
[[Category:Countries]] | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Talahara]] | ||
[[Category:MT]] | [[Category:MT]] | ||
[[Category:Socialist states]] | |||
[[Category:Republics]] | [[Category:Republics]] | ||
[[Category:Republics (Ajax)]] | [[Category:Republics (Ajax)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 27 November 2024
United Communes of Talahara ⵜⵉⵖⵉⵡⴰⵏⵉⵏ ⵢⴻⴹⵓⴽⵍⴻⵏ ⵏ ⵜⴰⵍⴰⵀⴰⵔⴰ | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: ⴰⴷⵓⵔⵣⵔⵉ! They shall not pass! | |
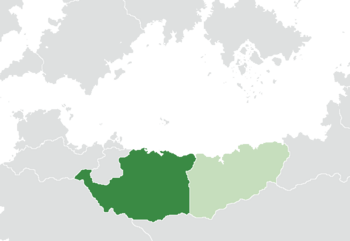 Location of Talahara (dark green) within the Rubric Coast Consortium (light green) in North Scipia | |
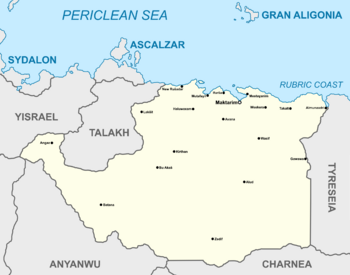 Map of Talahara | |
| Capital | Maktarim |
| Official language Regional languages | Standard Talaharan Takelat Tyrian, Latin, Hebrew |
| Demonym(s) | Talaharan |
| Government | Directorial council republic |
• Head of state | Executive Council |
• Legislature | National Legislative Council |
| Establishment | |
• First Talaharan Kingdom | c. 298 BCE |
• Second Talaharan Kingdom | March 1, 762 CE |
• Third Talaharan Kingdom | July 18, 1412 CE |
| June 20, 1838 CE | |
| Area | |
• Total | 603,424 km2 (232,983 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.77 |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 52,314,445 |
• Density | 86.7/km2 (224.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $1.70 trillion |
• Per capita | $32,508.37 |
| Gini | low |
| HDI (2022) | very high |
| Currency | Rubric (Ⲇ) (RCR) |
| Date format | Rubric standard calendar, yyyy-mm-dd AR/CE |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +599 |
| Internet TLD | .ta |
The United Communes of Talahara, (Takelat: ⵜⵉⵖⵉⵡⴰⵏⵉⵏ ⵢⴻⴹⵓⴽⵍⴻⵏ ⵏ ⵜⴰⵍⴰⵀⴰⵔⴰ; Tiɣiwanin Yeḍuklen n Talahara) referred to simply as Talahara or the United Communes, is a nation in Northern Scipia on the Rubric Coast of the Periclean Sea. It is bordered by Tyreseia to the east, Charnea to the south, and Talakh and Yisrael to the west. It also shares a maritime border with Gran Aligonia to the north. Talahara’s capital and largest city is Maktarim. The name “Talahara” comes from the old Takelat “Thala N'Iheran” meaning “Font of Lions” in reference to the region’s historically large population of Rubric lions.
Talahara is a syndicalist state with a strong modern tradition of industrial democracy. In the United Communes, all industries and places of business are controlled directly by their workers who elect the directors of their businesses and associate with one another in labour unions. Government representatives are elected by a transferable vote system directly by the workers and represent their collective interests through a 3-tier nested legislative council delegation system. Political parties play an important but informal role in political organization.
The major cultural groups of Talahara are the Kel Aman and the Kel Hadar; both of which are Kel peoples. The Kel Aman are traditionally coastal dwellers while the Kel Hadar lived in the mountains and plains. Each of the two groups has similar linguistic, religious, and cultural traditions, but historically had different ways of living and different relationships with their traditions. Kel Aman and Kel Hadar clans remain important social structures for many Talaharans, though the relevance of their divide has greatly diminished since the conclusion of the Talaharan Civil War in 1838.
Talahara is a developed nation with heavy economic regulation effected by labour unions. Healthcare, education, and social services are delivered across a complex web of locally supported systems enabled by a national distribution system. Major industries include mining and mineral refining, oil extraction and refining, heavy manufacturing, construction engineering, industrial and chemical recycling, textiles, transportation, and tourism. Talahara is a member of the Rubric Coast Consortium and is a founding member of the Kiso Pact.
History
Confirmed human habitation in present-day Talahara dates back to the ninth millennium BCE at the latest, with human activity dating back potentially as far as the 25th millennium BCE. The first records of early Talaharans were made by Aradian merchants in the second millennium BCE who traded with coastal settlements. These settlements became increasingly interconnected and culturally homogenous, gradually expanding to form coastal city-states. Human activity in the interior is less well-attested by the historical record, but settlements in the hills were the likely source of Talaharan copper. The Confederation of Tamazɣa also exerted significant cultural and political influence that waxed and waned throughout the first century BCE.
In the final centuries of the first millennium BCE, the Kel Aman city-states had formed a confederation, with various factions vying for influence and competing with Aradian influences and other foreigners. By the turn of the common era, the Latin Empire had expanded and created a client kingdom, later incorporated as a province of its empire that would last until 762 CE. The brief independence of Talahara would be ended in 906 CE with the occupation of Yen Caliphate which ruled until the mid-11th century. Over the course of several centuries, Talahara was subject to conflicts between the Kel Aman and Kel Hadar tribes along with its neighbouring rivals.
Modern history
The early-modern era in Talaharan was heralded by political and economic upheaval. The death of the last ruler of the Zaraban dynasty without issues led to the creation of an assembly of the kings of each of the ruling clans and an elective monarchy. Institutional taxation, economic liberalism, and eventually industrialization followed over the subsequent centuries, turning Talahara into a centre of production in the Periclean basin. Conflicts between the rulers, the liberal industrialists, and the vast majority of workers, including slaves, led to the Talaharan Civil War in 1834. The civil war lasted four years and concluded with a socialist union of communes emerging victorious, overthrowing both the monarchy and the industrialist class.
The United Communes of Talahara emerged as a revolutionary state but was soon joined by several others, including the Workers' Federation of Tyreseia in 1883. Talahara was faced with a number of emergent issues as it strained to develop its novel government and reordered economy, coupled with rebuilding after the war. Talahara's government and legal system were significantly developed over the 19th and early 20th centuries, with these developments characterized as a conflict for balance between anarchist and statist factions.
The second half of the 20th century presented a period of relative détente as the United Communes of Talahara engaged in fewer external conflicts. However, the internal politics of the United Communes were again in turmoil as statist influence declined and pacifistic influences drew the nation away from the global stage. Despite this, in recent years Talahara has shown signs of moving arriving at another political pivot, influenced in part by geopolitical strain in its immediate neighbourhood.
Geography and climate
There is a thin band of Periclean climate in Talahara's northern coastal region quickly giving way to semi-arid climates and desert in the south. Much of Talahara is covered by the foothills and peaks of the Adras Mountains which give way in the south to the rolling dunes of the Ninva Desert. Both semi-arid and desert climates cool down with rises in elevations.
Flora and fauna
In Talahara, few mammals are capable of surviving the intense heat of the Ninva Desert. Common desert mammals include shrews, sand rats, mice, and fennec foxes. Deer are also still common along the coasts. The namesake animal of Talahara, the Rubric lion is endangered and there are few endemic habitats that have not been encroached upon by human development.
Migratory birds are common across the region as well. Many northern birds such as geese and ducks will winter in Talahara, while southern birds like flamingoes will fly up from central or southern Scipia in the spring. Many of the fish of the Periclean have been historically important for communities on either side of the sea.
Talahara's flora varies greatly between the southern desert where very little can grow, the coastal regions where cereals and cash crops are commonly grown, and the eastern brushland. Of particular note is a species of uniquely endemic firs in the central mountains above the Ninva Desert.
Climate
Talahara's climate is best described as exceedingly hot and dry with the exception of the coastal region which receives precipitation from the Periclean. The two other broad climate zones present in the nation include the eastern semi-arid brushland, which receives enough precipitation to support plant life; and the central mountains where the elevation leads to noticeable cooling compared to the deserts which lie in the rain shadow to the south. On average, temperatures in the desert peak around 35°C (~95°F) in mid-summer. In the winter, temperatures can fall as low as 5°C (~40°F). The daily mean temperature across the whole year is 22°C (~71°F). Along the coast temperatures are nearly identical although rainfall over the year is approximately 11× greater than in the desert (600 mm versus 54 mm of rain annually).
Government and politics
The government of the United Communes has three independent components: the Executive Council, the Legislative Councils, and the Judicial Councils.
The Executive Council (Aseqqamu n Uselway) is a directorial body with limited jurisdiction composed of ten elected executors elected by ranked ballot. There are no qualifications to run as an executor. Each candidate must file a petition with 50,000 signatures to have their name added to the ballot. Most candidates who run have the support of a political party or salon to accumulate the necessary signatures and run a campaign. Other candidates derive their support directly from industrial unions or alliances between unions. Historically, truly independent candidates have had mixed success.
At the lowest level, a Communal Legislative Council (Aṣaḍuf n Taɣiwant) is each chaired by ten elected representatives, each representing approximately 4,000 people. One of the ten representatives is voted as a delegate to a Regional Legislative Council (Aṣaḍuf n Tamnaḍt), which is made up of 25 delegates agglomerated from 25 Communal Councils. Each of these representatives thus represents approximately 40,000 people. The final level is the National Legislative Council (Asaduf Aɛlayen) which counts 50 delegates, each representing approximately 1,000,000 people. Each delegate at each level serves at the pleasure of the council below it. Additionally, general elections are held every four years. In total, there is one National Council, 50 Regional Councils, and 1,250 Communal Councils.

The judicial system in Talahara operates in parallel with the legislative council system. The Communal Councils each appoint a justice to each Communal Judicial Council (Tanzarfit n Taɣiwant) from qualified candidates for up to 12-year terms. Candidates must have legal certification and at least five years of practice. The 25 Communal Judicial Councils then elect a Regional Judicial Council (Tanzarfit n Tamnaḍt) of five members from amongst themselves. Finally, the 50 Regional Judicial Councils elect a National Judicial Council (Tanzarfit Aɛlayen) of ten justices from amongst themselves. Legislative councils at each respective level are able to recall justices subject to a communal referendum.
Law
The United Communes of Talahara's legal system is a hybrid civil and customary law system. The customary law elements in criminal and civil law are based on written and unwritten principles of traditional Talaharan clan law. The legislatures of Talahara have also instituted statutory reforms and provisions that modify the existing customary law. So long as legislation is constitutional and respects the rights and interests of the people, civil law provisions may supersede the customary law.
The three-part National Consensus of Talahara is the supreme law of the country. Part I of the National Consensus provided universal human rights and freedoms for all Talaharans and foreign nationals in Talaharan jurisdiction. Part II of the National Consensus codified voting rights and property reform. Part Three established the systems of government, including the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The different levels of the Judicial Councils cover different jurisdictions in criminal and civil matters. Communal Judicial Councils adjudicate matters of familial disputes, property disputes, and minor criminal matters. Regional Judicial Councils deal with major crimes, property or personal allegations that go beyond local importance, and appeals of matters from the Communal Judicial Councils. The National Judicial Council adjudicates matters of constitutional interpretation, matters of national importance, and appeals from Regional Judicial Councils. Matters that go beyond local or are of national importance are determined by the lower Judicial Councils. For a typically local matter to pass to a Regional Judicial Council, ten of the 25 Communal Judicial Councils beneath them must vote for it to pass upward. Likewise, 20 of the 50 Regional Judicial Councils must vote for a matter to pass to the National Judicial Council.
Law enforcement in Talahara is conducted by community policing. Each commune elects a šaraf, commonly anglicized as "sheriff", for a five-year term to organize local law enforcement. A sheriff is empowered to appoint deputies for the duration of their tenure. In practice, deputies are frequently members of a local Black Guard unit, though civilian members can be drawn from different professions. In principle, deputies are encouraged to maintain part-time employment in another vocation to foster connection and integration with the community. In addition to deterring and investigating crimes, the sheriff's office is responsible for assembling cases to be presented before a justice. Talahara's trial proceedings follow an inquisitorial system and procedures assume neither party has any legal competencies. The head detective in a criminal investigation is typically appointed as the advocate of the sheriff's office. Individuals and unions defending against criminal accusations or otherwise litigating a civil matter are also entitled to legal advocacy. For inter-jurisdictional cases or particularly high-level offences, additional resources can be provided by the office of the Executor of Oversight and Public Safety, though material support at the national level is typically civilian.
Sentencing and the Talaharan correctional system are heavily based on community impacts. Civil sanctions generally include restitution, either monetary or in labour time. A guilty party's labour union or other community supports are permitted to absorb costs, though repeat offenses can result in more punitive sanctions. Injunctive or prohibitory sanctions are rare for first offenses. Criminal sanctions rarely include incarceration. Instead, convicts are placed in restricted community living conditions for the period of their sentence. Severe crimes can carry more severe restrictions, education or therapy, and possible surveillance mechanisms, but the community value of continued productivity and cost savings with housing a convict in their community are held as values of the criminal justice system.
Foreign relations
Talahara maintains close diplomatic relations with its western neighbour, Tyreseia. The two syndicalist nations are economically and geopolitically intertwined through the Rubric Coast Consortium. Relations with the socialist nations of Ostrozava in Belisaria, Wazheganon in Norumbia, Pulau Keramat in Malaio, and Tsurushima in Ochran have also risen in importance over the 20th century, particularly with advents of globalization and revolutions in communication and transportation. The end of the 20th century brought renewed and closer ties with additional nations in the global left, including Otomarca and nominally Zacapican.
Following the Arthuristan revolution in 1998, Talaharan and Arthurista developed significant economic and political ties.
Relations with Talahara's southern neighbour, Charnea have been comparatively mixed. Cultural ties to the Kel Tenere have led to a degree of political and economic support. However, the United Communes are ideologically opposed to the authoritarian government and have occasionally offered tepid protests. Despite this, Talahara maintains active economic and diplomatic relations with Charnea. Similarly, relations between Talahara and Talakh have been poor owing to the latter's monarchical government, particularly following the strife of the 1996 coup in Talakh.
Relations with Yisrael to the west have been relatively poor through Talahara's modern history. The Kingdom of Yisrael's monarchical government and belligerent actions set the stage for tense relations. During the Talaharan Civil War, Yisraeli forces annexed a significant portion of northwestern Talahara and incorporated it into a protectorate called Tarshish. Intermittent hostility continued through the first half of the 20th century, during which Talahara annexed the oil-rich Amara region (also known as the Timna Strip) and reannexed Tarshish. In the period following the 1951 reannexation, relations with Yisrael gradually thawed, though recent events in the Gran Aligonian crisis and the ensuring Onekawan Affair led to a rapid chilling of relations in the 2020s.
Other monarchical and liberal nations around the world are typically subject to pragmatic approaches. The Latin-dominated sphere of the world is treated with occasional ambivalence and occasional concern, though economic relations remain open, due in part to Tyreseia's cultural relationship with Latium. Sante Reze, as a major commercial centre, likewise shares relatively warm relations. Elsewhere, nations with strong monarchies, a history of poor civil or political rights, or ongoing or recent human rights abuses have been subject to diplomatic and economic sanctions.
Military
The unified armed forces of the United Communes of Talahara are comprised of the Talaharan Army Corps, the Air Corps, and the Navy Corps. The land and naval forces were originally consolidated in 1838 with the addition of the aerial branch in 1920. Service is strictly voluntary and conscription has never been practiced in the modern history of the Union. Members of the armed forces are organized under a union but is under the direct governance of the Executive Council. While certain roles have educational requirements, both commissioned and non-commissioned officers are elected by their units. Certain grades require a level of seniority. Several enlisted grades are determined solely by seniority. This relaxed approach to military hierarchy has contributed to the reputation of disorganization and ill-discipline.
Economy
The United Communes of Talahara has a distributist syndicalist economy facilitated by centralized distribution networking to aggregate demand and contract out supply between syndicates. In this system, cooperative and communal enterprises operate independently to extract materials, manufacture goods, or provide services, the product of which can be apportioned to a sector in need, kept as surplus, or slated for exchange or export. Outside of consumer protections, industries are subject to limited direct government regulation but interference may be undertaken if an entity is found to be operating in bad faith. Independent industrial unions are also a source of regulations, particularly in areas of health and safety.
Major extractive industries include mining, petroleum, agriculture, and industrial and chemical recycling. Secondary industries include petroleum products, heavy manufacturing, textile production, and mineral refining. Major international services include construction engineering, transportation, and tourism.
Talahara's economy is heavily linked with that of Tyreseia via the Rubric Coast Consortium which provides for free trade, freedom of movement, and industrial cooperation between the two constituent nations. Since 1980, the Consortium has included a currency union. Both Talahara and Tyreseia are also members of the Vespanian Exchange through the Consortium.
Transportation
Talahara has an extensive light rail system linking urban areas along the Rubric Coast in addition to heavy passenger and freight rail systems that network cities to the south. Talahara's heavy rail system also networks with the West Scipian Railway which runs from Yisrael to Tyreseia. Urban areas in the north rely heavily on light rail and rapid transit systems to convey commuters. Many major cities are considered unfriendly to personal vehicles. Most settlements in the south have a greater dependence on cars or bus rapid transit. Highway systems also run parallel to major rail lines, though depending on the locale, roads may be unpaved or ill-maintained.
Travel by sea or by air is also common. Maktarim has a major seaport on the Periclean and is also home to the nation's major international airport. Regional air travel supplements rail or personal vehicular transportation for rapid or convenient travel. Regional airlines also offer international flights to immediate neighbours from a number of smaller airports.
Energy
The petroleum industry is central to the economy of Talahara, centered mostly in the province of Amara and the rich oil fields in its northwest region. The National Petroleum Syndicate is the single largest commercial entity in the country and the second largest, Synprosyn, is also part of the broader petrochemical industry. Petroleum is produced in excess of the nation's energy demand which is supplemented by several large solar projects and nuclear power imported from Tyreseia. Surplus oil is sold to Sante Reze and Yisrael, mostly shipped in tanks by rail or used in the production of petroleum products, including plastics.
Demographics
Talahara has a total population of 52,314,445 as of the 2022 census. The birth rate is slightly below the replacement rate but supplemental population growth from immigration roughly offsets the deficit. The average life expectancy is rising and currently averages at 78.0 years. Talahara's population period is also stable with a slightly larger cohort of youths. The population is heavily concentrated in the north of the country, along the Rubric Coast. Over 50 million of the approximately 52.8 million inhabitants live in coastal cities. The coastal region is, in effect, a single megalopolis. However, traditional urban boundaries are reflected in the areas of Communal Council jurisdictions.
Largest cities or towns in Talahara
Census data, 2022 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Region | Pop. | |||||||
 Maktarim  Takalt |
1 | Maktarim | Rubric Coast Centre | 8,873,785 |  Mestaɣanim  New Rušadar | ||||
| 2 | Takalt | Rubric Coast East | 4,884,626 | ||||||
| 3 | Mestaɣanim | Rubric Coast Centre | 4,344,527 | ||||||
| 4 | New Rušadar | Rubric Coast West | 3,497,939 | ||||||
| 5 | Ifurša | Rubric Coast Centre | 2,651,285 | ||||||
| 6 | Weskera | Rubric Coast East | 2,391,630 | ||||||
| 7 | Almunaxdri | Qeshet North | 1,891,631 | ||||||
| 8 | Kirthan | Qeshet South | 1,153,101 | ||||||
| 9 | Zedif | Ninva Centre | 966,010 | ||||||
| 10 | Batana | Timna South | 746,862 | ||||||
Ethnicity
Talahara's two major cultural groups are the Kel Aman and the Kel Hadar, both of which are Kel ethnicities. The Kel Aman traditionally dwelt on the Rubric Coast and lived sedentary lives engaging in agriculture, fisheries, and commerce. Kel Aman clans grew in size and relative importance due to reliable food supply. Traditional clan structures were rigidly hierarchical based on seniority. The eldest members of the family and kinship groups directed both domestic and social affairs. The Kel Hadar traditionally came from the plains and hills of Talaharan. Significant Kel Hadar populations historically migrated to the desert in the 8th or 7th century BCE and several modern kinship groups lay claim to this lineage. Kel Hadar lifestyles and privileges included rights of way in furtherance of a pastoralist lifestyle. However, other Kel Hadar groups were sedentary, primarily developing urban areas away from the coast. For much of their history, the Kel Aman and Kel Hadar maintained distinct dialects and cultural differences. Since the 18th century, these differences have become increasingly reduced, especially following the flight of many Kel Aman individuals who were adopted by existing Kel Hadar clans. The modern Standard Talaharan Takelat language incorporates grammar and vocabulary from both dialects. Since the Talaharan Civil War in 1838, no ethnic group has special status before the law.
Minor ethnic groups in Talahara include the Kel Tenere, Kel Taram, Tyrians, and Jews. The Kel Tenere make up a broad portion of the inhabitants of the Talaharan Ninva. While also a Kel ethnic group, the Kel Tenere maintain a distinct dialect, vocabulary, and religious tendencies compared to their northern kin. The Kel Taram are considered by many to be a subethnicity of the Kel Hadar native to Talakh, while other linguistics and ethnographers consider them a distinctive Kel ethnicity. The next minor ethnic group in Talahara is the Tyrians. Roughly half the Tyrian population in Talahara is made up of first- or second-generation immigrants, though longstanding communities exist in major Talaharan centres, particularly in the east. Talahara also has a significant Jewish population which is particularly concentrated in the western region of the Rubric Coast.
Language
The national language of the United Communes of Talahara is Standard Talaharan Takelat. Standard Takelat was developed in the 1840s and 1850s to bridge grammatical and vocabulary differences between Aman and Hadar languages. Standard Takelat is related to other Kel languages but is not necessarily mutually intelligible.
In an 1866 constitutional amendment, Standard Takelat was codified as the language of legislative and judicial proceedings in the nation. Education in other languages remains an option for local communities, including the teaching of the Tamashek language in schools in the Talaharan Ninva. However, Standard Takelat has rapidly subsumed the use of traditional languages as of the 19th century.
A plurality of Talaharans speak and read Standard Takelat as their sole language. Approximately 62% of the population has proficiency in two or more languages. Regional languages which are commonly used in business and taught in local schools include Tamashek, Tyrian, Latin, and Hebrew.
Religion
Massanism was effectively a state religion in the Third Talaharan Kingdom. The modern country of Talahara is a secular nation in accordance with the universalist principles of its foundation. Following the Talaharan Civil War, secularist movements gained traction in reaction to religious conservative support of the monarchist faction. Secularization was supported by a humanist reclamation of Massanism which wrapped secular philosophy and politics in the rituals and traditions of Massanism. In the present day, a plurality of Talaharans identifies as Massanist, followed by a broadly irreligious cohort including agnostic, atheist, or ambivalent Talaharans. Other minority religions are common, though state secularism affords no support for religious congregations. Religious services are typically held in homes or on public grounds.
Education
Primary, secondary, and post-secondary education is publicly-funded in Talahara. Primary education is included with early child care in Communal Council programming, bridging age groups from infants to 13 years of age. Secondary education is also provided by commune-level institutions, but the curriculum is more intense and has more divergent streams. Between 14 and 18 years of age, students can begin apprenticing with industry unions in addition to completing required coursework. This process primes students to enter the workforce immediately upon graduation.
Post-secondary educational institutions have their curriculums, mandates, and funding organized by Regional Councils. In practice, educational assets and governance duties are frequently combined between council areas to create larger, more substantial institutions. The largest post-secondary institution in Talahara is the University of West Maktarim-Mestaɣanim which offers liberal arts and STEM degree programs. General admission to universities relies on program-related standardized testing. University-bound students typically enroll in an additional year of secondary education to prepare directly for their desired programs' tests. General international students are subject to the same standardized tests but immigrants with foreign credentials are fast-tracked to have their credentials certified in the United Communes.
Healthcare
Healthcare is delegated as a national responsibility under the jurisdiction of the Executor of Health. While organized at the highest level, healthcare is administered at a communal level for generalized and clinical care, long-term care, dentistry, and mental health services. Major care centres including surgery and low-intensity ancillary treatments are typically delivered at the level of a Regional Council.
Healthcare funding is accumulated through an industrial risk insurance scheme. Rather than gather taxes from private citizens or via a flat tax on income or industry revenue, healthcare taxes are drawn from the gross incomes of businesses, directly proportional to the risks associated with those industries, be those acute risks of bodily harm or general occupational hazards. The purpose of the scheme is twofold. Firstly, healthcare costs are equitably distributed. Secondly, industries are encouraged to passively self-regulate and reduce occupational hazards so that their taxes are lessened. Critics of the healthcare system note that individuals are not incentivized to avoid reckless behaviours in their private lives and that communities therefore bear the costs of an individual's recklessness.
Housing
Private real estate is nonexistent in the United Communes of Talahara. Housing projects are directed by communes with resources allocated by the Executor of Housing and Vital Statistics in accordance with projected population growth. Despite the local importance of housing, due to the process of redistricting communes with relative frequency, the funding process is devolved up to the top level. This allocation is statutorily set to a minimum standard of amenities which can be augmented by additional community resources. Architectural and engineering requirements are also provided to account for geographic and contextual needs.
Aging residential infrastructure can be refurbished or replaced upon the application of a Communal Council should the standard of living fall beneath the statutory standard of amenities. Industrial subsidization of first-instance residential construction or refurbishment also counts as credits against taxes for public transportation. This policy promotes efficiency of movement, with workers being able to reside closer to their places of business, thereby minimizing strain to existing transportation networks.
Culture
Talaharan culture draws on several broader cultural sources. The first and oldest cultural source is traditional Kel Aman and Kel Hadar cultures, including the religious values and influences of Massanism. Kel culture imparts important communitarian values and broad family structures. In addition, the Takelat language laid the foundation for framing describable reality and cultural frames. The second major source is socialist universalism which builds directly with the Kel communitarian values. Socialist culture promotes industry while de-emphasizing competition. In terms of aesthetic or material culture, socialist influences appear more austere, but this is not necessarily universal. The third source is globalization and the gradual homogenization of socialization around the world. While there is no single cultural hegemon in the world, Talahara increasingly accepts cultural influences from elsewhere in Scipia, Belisaria, Norumbia and Oxidentale, and as far as East Ochran. These influences are largely on material culture but also have effects on socialization and a conflict between change and tradition.
Media
News media and publications are ubiquitous in Talahara. By tradition, and occasionally by communal statute, local communities receive news updates and council meeting minutes every week. In addition, every labour union has its own weekly or monthly broadsheet, which typically covers industry affairs, politics, and occasionally news media and entertainment stories. Steelworker Today is one of the most-distributed daily broadsheets in the United Communes, with the Steelworkers' Union having effectively built a secondary industry in news media, political commentary, and entertainment literature.
Despite the vast array of both state and independent publications, radio and television broadcasts are a regulated and unionized industry. Unlike most independent publications which are not subject to ethical standards of journalism, union journalists can be subject to sanctions for innaccurate reporting.
Entertainment media in Talahara is also a major industry. Music, television, and film production is centered in the city of Mestaɣanim. Takelat-language productions are a mainstay in Talaharan homes, but Latin and Tyrian-language imports are more commonly followed by Talaharans who are fluent in those languages.
Online media has been an emerging field in recent decades and remains largely unregulated. Major professional outlets, unions, and higher levels of government publish digital versions of most print materials, with some having migrated entirely to reduce paper costs. Other, smaller unions and Communal Councils have resisted the transition to the internet, opting for traditional communication standards despite creeping obsolescence.
Time
The Talaharan calendar tracks the solar year, taking influence in its modern incarnation from the Gregorian calendar. The modern form of the calendar, standardized after the Talaharan Civil War in 1838, has 12 months each lasting 30 days. The additional five days (six in leap years), is an additional demi-week held at the end of the year. Each 30-day month is divided into three 10-day weeks, commonly referred to as decades. On average, the workweek covers either six or seven days per decade, typically in a staggered pattern with a two or three day weekend and a rest day interrupting the standard work schedule.
| Month name | Literal translation | Through dates (Gregorian) † |
|---|---|---|
| Badu | Beginning [of the year] | June 21 to July 20 |
| Hama | Heat | July 21 to August 19 |
| Samayem | Dog days | August 20 to September 18 |
| Zwarunzar | First rain | September 19 to October 18 |
| Šarhert | Month of ploughing | October 19 to November 17 |
| Kasaɣul | Returning the herd | November 18 to December 17 |
| Melalen | White [nights] | December 18 to January 16 |
| Tiberkanin | Black [nights] | January 17 to February 15 |
| Imbarken | Strong winds | February 16 to March 17 |
| Aysi | Unknown etymology | March 18 to April 16 |
| Amgarunzar | Last rain | April 17 to May 16 |
| Zari | End [of the year] | May 17 to June 15 |
| Šimalas Hetafel | Demi-week festival | June 16 to June 20 |
† All months except the second half of Tiberkanin and Imbarken have their through dates shifted one day forward in leap years.
The summer solstice is the traditional Talaharan New Year. This date is standardized to June 21 (June 20 in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. The reckoning of years in Talahara is also subject to the Rubric Standard Calendar. Established in 1890 between Talahara and Tyreseia, the treaty organization saw the Rubric Standard Calendar introduced in 1891, establishing a common reckoning between both countries with 1891 as the calendar's "year 1", beginning on June 21. Dates in the calendar are noted "AR" which initializes "Rubric year" in both Takelat and Tyreseian Latin. Years prior to 1891 are noted either in negative numbers or as "BAR" or "Before Rubric years".
Arts
The pre-eminent, traditional medium of visual art in Talahara is tapestry weaving. Talaharan tapestries are used both as floor carpeting, particularly among traditionally semi-nomadic groups, but also as adornments for walls. Matrilineal Kel Aman and Kel Hadar clans retain trace the continuity of their kinship through distinctive forms and motifs. Tapestries also tell stories through the incorporation of glyphs or sigils which are almost a distinct language on their own. The tradition of tapestry weaving is heavily related to knowledge-keeping and history. The national emblem of Talahara is a glyph or sigil representing a lion's paw. The meaning of different sigils can vary according to their context and reading tapestries correctly demands a high degree of skill and training.
The second major medium of traditional Talaharan art is silversmithing and jewelry. As with tapestry, silverwork has many regional variations and distinctions. The art of smithing was a contentious one in old Talaharan culture. Smiths were admired by common farmers, herders, and craftspeople both for their utility and for their mastery of the four elements: fire, air, water, and metal. To the political and religious elite, smiths were regarded with superstition for the same reasons, as the mystical and material power that metalworkers held could be dangerous to their rule. This led to the tradition of smiths offering gifts of silver jewelry and steel weapons to new clan rulers and their direct families. Paradoxically, this became an expectation. Smiths who did not regularly offer gifts to chiefs and priests could be subject to socio-religious sanctions. Talaharan jewelry has its own symbolic language with some overlap with tapestry weaving. Many embossments, motifs, and symbols represent purity or protection in attempts to ease the superstitions of the elite or at least put their supernatural talents to good use. Several historical examples were clearly made to mock contemporary rulers, with bracelets mocking a slave's manacles and necklaces with cursed symbols over the wearer's chest.
Sports
Association football is among the most popular and commonly played sports in Talahara, owing in part to its convenience in terms of rules and equipment. Casual pickup games are common in community parks and union leagues are ubiquitous in all regions of the country. Equestrian activities are the more traditional sports of the region, however. Racing, jumping, and horseback acrobatics are common categories of professional equestrian events.
The national sport of Talahara is derived from the horseback performance of Taburida. In its purest form, the event is a choreographed cavalry charge, including the firing of muzzleloading carbines, showcasing speed, balance, and eloquence. The team event follows a troupe of riders who must approach one end of the course at a walk, pivot at the end, and charge back in a synchronized formation, firing their carbines in synchronicity as well. In ideal circumstances, the horses and riders move in perfect unity and the shots from the carbines report as only a single discernable sound. Individual events typically involve a display of swordsmanship along with graceful and deliberate movement and shooting. A third, modern variation of the event has evolved as well, resembling the sport of biathlon. Riders complete the course in sequence, due to the hazards of firing on horseback in a crowded group. Riders must complete a 5-lap, 30 km race, stopping each of the five laps to fire at three targets. Missing a target adds a minute to the rider's time. Muzzleloading black powder carbines are still used for the event and riders are tested on their ability to ride, ability to control their horse while shooting, their accuracy, and their speed at reloading.
Talahara's mainline equestrian racing tradition has largely given way in modern times to motorsports. Open-wheel circuit racing and rallying are the two most common categories. In addition to international events, local racing and construction leagues hold minor championships. Many mechanically-minded unions offer opportunities for youths to develop racecraft and automotive knowledge from a young age, despite a comparative irrelevance of road cars compared to other nations.
Cuisine
Talaharan cuisine is characterized by fusions from around the Periclean. However, it maintains key endemic features. Traditionally, Talaharans consume three meals a day, two of which are served hot. Lunches may be served either hot or cold. Šakšuka, baɣrir served with fruit preserves, and freshly grilled amergaz are common as breakfast dishes. Cold, raw vegetables, smoked meats, and cold tabissart soups are common for lunches. Staple dishes for dinners include stews and casseroles such as tajin and škina. Kuskus and roasted meats are almost universal accompaniments. Endemic condiments include the tomato-based matbuɣaha, a spiced garlic relish called tacermult, and the onion-based tafaya sauce. Every meal can be accompanied by msemmen flatbread which is frequently consumed on its own or with preserves for breakfast. Fruits, dates, and sweets are commonly consumed as snacks.
Tea and coffee consumption in Talahara is roughly evenly divided. In addition to caffeinated black teas imported from East Scipia and Ochran, herbal teas are frequently consumed in the afternoon or evening. Mint tea, in particular, is a major cultural staple among traditional Kel Hadar groups. Domestically, alcoholic beverage consumption of wine is heavily outpaced by beer. Beer is brewed locally from local grains and botanicals. Wine and grape culture is generally regarded as a more international influence, despite the fact that they have been cultivated in the region for centuries. Anunhayat is a local hard alcohol distilled with the sugars from dates.
Talahara has a growing international cuisine based around local takes on wine, cheeses, and smoked meats like amergaz. Cheese is typically made from sheep's milk and unpasteurized, characterized by a nutty flavour and hard texture. Cheese from cow's milk is also common and is made to be semi-soft in texture and similarly nutty in flavour. Talahara's wine tradition emerged more recently in the production of Kosher sweet wines in the northern parts of the western regions. The practice was initiated by Jewish settlers in the Protectorate of Tarshish but has continued on to the present day. Other major international trends include the adoption of cuisines from the Ozeros, Belisaria, and Ochran.


















