Cuthland: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
|coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | |coordinates = <!-- Coordinates for capital, using {{tl|coord}} --> | ||
|largest_city = [[Kingsham]] | |largest_city = [[Kingsham]] | ||
|largest_settlement_type = | |largest_settlement_type = largest city | ||
|largest_settlement = <!--Name of largest settlement--> | |largest_settlement = <!--Name of largest settlement--> | ||
|official_languages = {{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}} | |official_languages = {{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}} | ||
|national_languages = <!--Country/territory-wide languages recognised but not necessarily in country/territory-wide law, etc--> | |national_languages = <!--Country/territory-wide languages recognised but not necessarily in country/territory-wide law, etc--> | ||
|regional_languages = | |regional_languages = | ||
|languages_type = | |languages_type = <!--Use to specify a further type of language, if not official, national or regional--> | ||
|languages = | |languages = | ||
|languages_sub = <!--Is this further type of language a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | |languages_sub = <!--Is this further type of language a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|languages2 = <!--Languages of this second further type--> | |languages2 = <!--Languages of this second further type--> | ||
|languages2_sub = <!--Is the second alternative type of languages a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | |languages2_sub = <!--Is the second alternative type of languages a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | ||
|ethnic_groups = | |ethnic_groups = 81.5% {{wp|Anglo-Saxons|Cuthish}}<br />15.8% {{wp|West Frisians|Waldish}}<br />1.3% {{wp|Saterland Frisians|Widdalian}}<br />1.4% Other | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | |ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | ||
|ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | |ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
|religion_year = 2020 | |religion_year = 2020 | ||
|religion_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with religion data)--> | |religion_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with religion data)--> | ||
|demonym = | |demonym = Cuthish | ||
|government_type = | |government_type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|executive monarchy}} under an {{wp|Authoritarianism|authoritarian government}} | ||
|leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of Cuthland|Monarch]] | |leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of Cuthland|Monarch]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Edwin IV]] | |leader_name1 = [[Edwin IV]] | ||
|leader_title2 = [[ | |leader_title2 = [[Foresitter of Cuthland|Foresitter]] | ||
|leader_name2 = [[Clifford Goodwin]] | |leader_name2 = [[Clifford Goodwin]] | ||
|legislature = [[Wittenmoot]] | |legislature = [[Wittenmoot]] | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
|Gini_year = 2020 | |Gini_year = 2020 | ||
|HDI_year = 2020 | |HDI_year = 2020 | ||
|HDI = | |HDI = 0.887 | ||
|HDI_change = increase | |HDI_change = increase | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Cuthland''' ({{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}}: ''Cuþland''), officially the '''Kingdom of Cuthland''' ({{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}}: ''Cingdom of Cuþland'') is a {{wp|Sovereign state|sovereign state}} located on the [[Telmerian Peninsula]] in northern [[Berea]]. It lies between the [[White Sea]] to the north, [[Lake Sigismund]] to the east, and the [[Dentrian Mountains]] to the west. The nation shares borders with [[Mascylla]], [[Lilienburg]], [[ | '''Cuthland''' ({{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}}: ''Cuþland''), officially the '''Kingdom of Cuthland''' ({{wp|Anglish|Cuthish}}: ''Cingdom of Cuþland'') is a {{wp|Sovereign state|sovereign state}} located on the [[Telmerian Peninsula]] in northern [[Berea]]. It lies between the [[White Sea]] to the north, [[Lake Sigismund]] to the east, and the [[Dentrian Mountains]] to the west. The nation shares borders with [[Mascylla]], [[Temaria]], [[Lilienburg]], [[Rovina]], and [[Norden]]. Cuthland's capital and largest city is [[Kingsham]], with other major cities including [[Whitford]], [[Alderport]], [[Fenmouth]], [[Newbridge]], and [[Wealdbury-upon-Cyne]]. With a population of approximately 44.8 million and spanning an area of approximately 326,882 square kilometers, Cuthland is the Xth most populous and Xth largest state in [[Aurorum]]. | ||
Cuthland is governed as a {{wp|Unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|Constitutional monarchy| | Cuthland is governed as a {{wp|Unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|executive monarchy}}. [[Monarchy of Cuthland|King]] [[Edwin IV]] serves as {{wp|Head of state|head of state}}, while [[Foresitter of Cuthland|Foresitter]] [[Clifford Goodwin]] serves as {{wp|Head of government|head of government}}. Although constitutionally limited, the monarchy maintains substantial {{wp|Reserve power|reserve powers}} and an unusually strong degree of {{wp|soft power|soft power}} compared to most other modern monarchies, giving the crown considerable influence over domestic governance and leading many international observers to label the nation as a {{wp|Hybrid regime|hybrid regime}}. | ||
{{wp|Germanic peoples|Telmerian}} settlement in modern day Cuthland dates back to classical antiquity. These early tribes began to coalesce into various pretty kingdoms and duchies at the dawn of the {{wp|Early Middle Ages}}, leading to the Cuthland's dominance by [[Four Kingdoms]] from the 6th century onward while Waldrich unified under the [[Kingdom of Waldrich]]. During the 11th century, [[Edmund the Great]] of the [[Kingdom of Meerland]] [[Unification of Cuthland|unified]] the Cuthish states for the first time under the [[Kingdom of Cuthland]]. Cuthland remained geopolitical rivals with Waldrich for the next four centuries, culminating with the [[Cuthish conquest of Waldrich]] during the 15th century and the [[Proclamation of the Cuthish Empire|establishment]] of the [[First Cuthish Empire]] as the most powerful state in Telmeria. Cuthland continued to expand throughout the early modern period, conquering parts of [[X]], western [[Mascylla]], and the northern [[Dentrian Peninsula]] while establishing one of the world's first colonial empires in [[Alvinia]] and northern and eastern [[Pamira]]. During the mid-18th century, Cuthland's dominance in Telmeria began to falter due to increasing ethnic tensions within the empire and the rising prominence of [[Dulebia]] and the [[Mascylla]]ry states. The death of Emperor [[Edmund VII]] without an heir in 1715 led to the [[War of the Cuthish Succession]], which ended with Dulebia and the Mascyllary states [[First Partition of Cuthland|partitioning]] parts of the Empire. A [[Second Partition of Cuthland|second partition]] ceded additional territories to Mascylla in 1778 following the [[First Cutho-Mascyllary War]], including significant parts of the Cuthish colonial empire. | {{wp|Germanic peoples|Telmerian}} settlement in modern day Cuthland dates back to classical antiquity. These early tribes began to coalesce into various pretty kingdoms and duchies at the dawn of the {{wp|Early Middle Ages}}, leading to the Cuthland's dominance by [[Four Kingdoms]] from the 6th century onward while Waldrich unified under the [[Kingdom of Waldrich]]. During the 11th century, [[Edmund the Great]] of the [[Kingdom of Meerland]] [[Unification of Cuthland|unified]] the Cuthish states for the first time under the [[Kingdom of Cuthland]]. Cuthland remained geopolitical rivals with Waldrich for the next four centuries, culminating with the [[Cuthish conquest of Waldrich]] during the 15th century and the [[Proclamation of the Cuthish Empire|establishment]] of the [[First Cuthish Empire]] as the most powerful state in Telmeria. Cuthland continued to expand throughout the early modern period, conquering parts of [[X]], western [[Mascylla]], and the northern [[Dentrian Peninsula]] while establishing one of the world's first colonial empires in [[Alvinia]] and northern and eastern [[Pamira]]. During the mid-18th century, Cuthland's dominance in Telmeria began to falter due to increasing ethnic tensions within the empire and the rising prominence of [[Dulebia]] and the [[Mascylla]]ry states. The death of Emperor [[Edmund VII]] without an heir in 1715 led to the [[War of the Cuthish Succession]], which ended with Dulebia and the Mascyllary states [[First Partition of Cuthland|partitioning]] parts of the Empire. A [[Second Partition of Cuthland|second partition]] ceded additional territories to Mascylla in 1778 following the [[First Cutho-Mascyllary War]], including significant parts of the Cuthish colonial empire. | ||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
===Second Cuthish Empire and Great War=== | ===Second Cuthish Empire and Great War=== | ||
The Alhstead Revolution resulted in the establishment of a new form of governance known as a [[ | The Alhstead Revolution resulted in the establishment of a new form of governance known as a [[Limited monarchy|limited monarchy]]. Instead of turning powers over to democratically elected officials, as in a conventional {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|constitutional monarchy}}, the [[Cuthish Constitution of 1830]] created legal bounds within which the sovereign could exercise his power. The Constitution codified many of the enlightened absolutist practices normalized by Algar III, creating a bill of rights for the people and formally stripping the nobility and clergy of special privileges. The [[High Court]], the highest judicial body in Cuthland, was granted the power of {{wp|Judicial review|judicial review}} over the monarch's actions in order to maintain {{wp|Constitutionality|constitutionality}}. The 1832 Constitution also expanded the power of the Wittenmoot, requiring the approval of both houses in order for the monarch to amend the constitution or appoint new judges to the High Court. | ||
During his rule, Edwin III launched a series of military campaigns to reassert revanchist claims on former Cuthish territories that had been lost during the partitions. These campaigns, known as the [[Alhstead Wars]], began with the [[Second Cutho-Waldish War]] in 1832, which ended in the reannexation of Waldrich after a brief two month conflict. The decisive victory sparked a wave of nationalism across Cuthland, emboldening Edwin III to continue his aggressive foreign policy against [[X Peninsula War|Dulebia]] in 1834. The war was largely successful, with the [[Treaty of Ulich]] ceding most of the X Peninsula that had been seized in the fourth partition, with the exception of [[Erjarvia]], back to Cuthland. The victory over Dulebia allowed Edwin III to begin expanding east, [[Second Cutho-Mascyllary War|invading]] Mascylla in 1838. The subsequent [[Treaty of Alderport]], signed in 1841, restored eastern Cuthland to its pre-partition borders and returned most of Cuthland's former colonial possessions in Alvinia and Valimia. | During his rule, Edwin III launched a series of military campaigns to reassert revanchist claims on former Cuthish territories that had been lost during the partitions. These campaigns, known as the [[Alhstead Wars]], began with the [[Second Cutho-Waldish War]] in 1832, which ended in the reannexation of Waldrich after a brief two month conflict. The decisive victory sparked a wave of nationalism across Cuthland, emboldening Edwin III to continue his aggressive foreign policy against [[X Peninsula War|Dulebia]] in 1834. The war was largely successful, with the [[Treaty of Ulich]] ceding most of the X Peninsula that had been seized in the fourth partition, with the exception of [[Erjarvia]], back to Cuthland. The victory over Dulebia allowed Edwin III to begin expanding east, [[Second Cutho-Mascyllary War|invading]] Mascylla in 1838. The subsequent [[Treaty of Alderport]], signed in 1841, restored eastern Cuthland to its pre-partition borders and returned most of Cuthland's former colonial possessions in Alvinia and Valimia. | ||
| Line 238: | Line 238: | ||
===Biodiversity=== | ===Biodiversity=== | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
===Government=== | ===Government=== | ||
===Political parties and elections=== | ===Political parties and elections=== | ||
===Administrative divisions=== | ===Administrative divisions=== | ||
===Foreign relations=== | ===Foreign relations=== | ||
| Line 293: | Line 249: | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
===Largest cities=== | ===Largest cities=== | ||
===Ethnic groups=== | ===Ethnic groups=== | ||
===Language=== | ===Language=== | ||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
| Line 338: | Line 269: | ||
The sports landscape of Cuthland is dominated by the nation's affinity to {{wp|Ice hockey|ice hockey}}, which was developed in northern Cuthland during the 19th century and is widely considered to be the nation's {{wp|National sport|national sport}}. A 2012 poll held by the Sportswriters Association of Cuthland found that ice hockey was the preferred sport of 45% of the population, making it the most popular sport in the country. The [[Ice Hockey Association of Cuthland]] (IHAC), founded in 1890, serves as the sport's highest governing body and the oldest such ice hockey organization in the world. The IHAC operates the [[Cuthish ice hockey league system]], which organizes every internationally sanctioned division of professional ice hockey in Cuthland under a system of {{wp|Promotion and relegation|promotion and relegation}}. The [[National Division]], the highest division of ice hockey in the country, is the most widely viewed and attended sports league in Cuthland and the Xth most valuable in the world. Internationally, the [[Cuthish men's national ice hockey team]] has won the [[International Ice Hockey Championships]] (IIHC) nine times and taken home five gold medals at the [[Auroran Games]], most recently in 2018. | The sports landscape of Cuthland is dominated by the nation's affinity to {{wp|Ice hockey|ice hockey}}, which was developed in northern Cuthland during the 19th century and is widely considered to be the nation's {{wp|National sport|national sport}}. A 2012 poll held by the Sportswriters Association of Cuthland found that ice hockey was the preferred sport of 45% of the population, making it the most popular sport in the country. The [[Ice Hockey Association of Cuthland]] (IHAC), founded in 1890, serves as the sport's highest governing body and the oldest such ice hockey organization in the world. The IHAC operates the [[Cuthish ice hockey league system]], which organizes every internationally sanctioned division of professional ice hockey in Cuthland under a system of {{wp|Promotion and relegation|promotion and relegation}}. The [[National Division]], the highest division of ice hockey in the country, is the most widely viewed and attended sports league in Cuthland and the Xth most valuable in the world. Internationally, the [[Cuthish men's national ice hockey team]] has won the [[International Ice Hockey Championships]] (IIHC) nine times and taken home five gold medals at the [[Auroran Games]], most recently in 2018. | ||
Other popular team sports in Cuthland include {{wp|Association football|association football}}, {{wp|Rugby football|rugby}}, and {{wp|Cricket|cricket}}. Football is significantly more popular in Waldrich | Other popular team sports in Cuthland include {{wp|Association football|association football}}, {{wp|Rugby football|rugby}}, and {{wp|Cricket|cricket}}. Football is significantly more popular in Waldrich and other parts of southern Cuthland, and two of the nation's Waldish-based clubs, [[FC Grienfjild]] and [[Meerboarg Sport]], are among the top clubs in the world. The [[Cuthish men's national football team]] has also seen periodic success internationally, most notably winning the [[1974 Auroran Cup]]. Rugby and cricket, by contrast, are predominately Cuthish sports, seeing their greatest popularity among the upper classes in major cities such as Kingsham, Alderport, and Whitford. Rugby is particularly popular in communities along the coast of [[Lake Sigismund]], in some areas surpassing ice hockey in popularity. [[Alderport Rugby]] is the most successful rugby club in the nation, having won the [[RFC First Division]], the highest level of professional rugby competition in Cuthland, seventeen times. Cricket has declined significantly in prominence in recent years, and is now the fourth most popular team sport in the nation despite once rivaling ice hockey in popularity. Nevertheless, Cuthland remains a major hub for the sport, with the [[Cuthish men's national cricket team]] winning the [[World ODI Cricket Championships]] twice in [[1987 World ODI Cricket Championships|1987]] and [[2003 World ODI Cricket Championships|2003]]. | ||
In {{wp|Individual sport|individual sports}}, {{wp|Golf|golf}} maintains the strongest following nationwide. The [[Royal Ashbury Golf Club]], built in 1790, is among the oldest golf courses in the world, and is the site of the prestigious [[Ashbury Classic]] golf tournament. Other notable golf courses in Cuthland include the [[Prestford Manor Golf Club]], [[Hatchbury Golf Club]], and the [[Royal South Bexford Golf Club]]. {{wp|Tennis}}, {{wp|Skiing|skiing}}, {{wp|Squash (sport)|squash}}, {{wp|Swimming (sport)|swimming}}, {{wp|Fencing|fencing}}, and {{wp|Martial arts|martial arts}} are also popular individual sports in Cuthland. | In {{wp|Individual sport|individual sports}}, {{wp|Golf|golf}} maintains the strongest following nationwide. The [[Royal Ashbury Golf Club]], built in 1790, is among the oldest golf courses in the world, and is the site of the prestigious [[Ashbury Classic]] golf tournament. Other notable golf courses in Cuthland include the [[Prestford Manor Golf Club]], [[Hatchbury Golf Club]], and the [[Royal South Bexford Golf Club]]. {{wp|Tennis}}, {{wp|Skiing|skiing}}, {{wp|Squash (sport)|squash}}, {{wp|Swimming (sport)|swimming}}, {{wp|Fencing|fencing}}, and {{wp|Martial arts|martial arts}} are also popular individual sports in Cuthland. | ||
| Line 347: | Line 278: | ||
[[Category:Countries of Aurorum]] | [[Category:Countries of Aurorum]] | ||
[[Category:Cuthland | [[Category:Cuthland]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:50, 31 December 2022
Kingdom of Cuthland Cingdom of Cuþland (Cuthish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "God, Cing, and Rice" (Cuthish) "God, King, and Country" | |
| Anthem: "Loofsong of Hallow Wybert"(Cuthish) "Hymn of Saint Wybert" | |
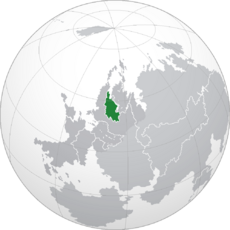 Location of Cuthland (green) in Berea (green and dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Kingsham |
| Official languages | Cuthish |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | 81.5% Cuthish 15.8% Waldish 1.3% Widdalian 1.4% Other |
| Religion (2020) | 88.5% Semitarism 3.4% Unaffiliated 8.1% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Cuthish |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary executive monarchy under an authoritarian government |
• Monarch | Edwin IV |
| Clifford Goodwin | |
| Legislature | Wittenmoot |
| House of Lords | |
| House of Burghers | |
| Establishment | |
| 21 February 1085 | |
• Proclamation of the First Cuthish Empire | 11 January 1444 |
• Establishment of the First Cuthish Republic | 6 October 1797 |
• Establishment of the Second Cuthish Empire | 19 June 1830 |
| 30 March 1969 | |
| 2 September 1969 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 326,882 km2 (126,210 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 2.2% |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 44,793,500 |
• Density | 137/km2 (354.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2020) | Error: Invalid HDI value |
| Currency | Pund (CUP) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +39 |
| ISO 3166 code | CU |
| Internet TLD | .cu |
Cuthland (Cuthish: Cuþland), officially the Kingdom of Cuthland (Cuthish: Cingdom of Cuþland) is a sovereign state located on the Telmerian Peninsula in northern Berea. It lies between the White Sea to the north, Lake Sigismund to the east, and the Dentrian Mountains to the west. The nation shares borders with Mascylla, Temaria, Lilienburg, Rovina, and Norden. Cuthland's capital and largest city is Kingsham, with other major cities including Whitford, Alderport, Fenmouth, Newbridge, and Wealdbury-upon-Cyne. With a population of approximately 44.8 million and spanning an area of approximately 326,882 square kilometers, Cuthland is the Xth most populous and Xth largest state in Aurorum.
Cuthland is governed as a unitary parliamentary executive monarchy. King Edwin IV serves as head of state, while Foresitter Clifford Goodwin serves as head of government. Although constitutionally limited, the monarchy maintains substantial reserve powers and an unusually strong degree of soft power compared to most other modern monarchies, giving the crown considerable influence over domestic governance and leading many international observers to label the nation as a hybrid regime.
Telmerian settlement in modern day Cuthland dates back to classical antiquity. These early tribes began to coalesce into various pretty kingdoms and duchies at the dawn of the Early Middle Ages, leading to the Cuthland's dominance by Four Kingdoms from the 6th century onward while Waldrich unified under the Kingdom of Waldrich. During the 11th century, Edmund the Great of the Kingdom of Meerland unified the Cuthish states for the first time under the Kingdom of Cuthland. Cuthland remained geopolitical rivals with Waldrich for the next four centuries, culminating with the Cuthish conquest of Waldrich during the 15th century and the establishment of the First Cuthish Empire as the most powerful state in Telmeria. Cuthland continued to expand throughout the early modern period, conquering parts of X, western Mascylla, and the northern Dentrian Peninsula while establishing one of the world's first colonial empires in Alvinia and northern and eastern Pamira. During the mid-18th century, Cuthland's dominance in Telmeria began to falter due to increasing ethnic tensions within the empire and the rising prominence of Dulebia and the Mascyllary states. The death of Emperor Edmund VII without an heir in 1715 led to the War of the Cuthish Succession, which ended with Dulebia and the Mascyllary states partitioning parts of the Empire. A second partition ceded additional territories to Mascylla in 1778 following the First Cutho-Mascyllary War, including significant parts of the Cuthish colonial empire.
The popularity of the monarchy declined significantly following the second partition, leading to the Cuthish Revolution and establishment of the First Cuthish Republic. Foreign intervention led to the Cuthish Revolutionary War, which briefly restored the monarchy and led to the end of the Cuthish Empire following its third partition. The nation was plagued by instability for the next 30 years, cycling through numerous republican and monarchist governments and reaching a territorial nadir following a fourth and final partition in 1825. Cuthland finally stabilized under the Alhstead monarchy in 1830, which established the highly nationalist and revanchist Second Cuthish Empire. The Alhsteads recovered many of the territories lost during the partitions through the Alhstead Wars, which allowed Cuthland to reassert itself as a great power by the mid-19th century. Cuthland expanded its colonial empire in Caphtora during the second half of the 19th century, challenging the global dominance of Mascylla. Tensions between Cuthland and Mascylla and their respective power blocs led to the outbreak of the Great War in the 1910s, ending with the cession of most Cuthish territories gained during the Alhstead Wars and the loss of Cuthland's colonial empire.
The Cuthish Revolution of 1916 overthrew the Cuthish monarchy and established the Second Cuthish Republic, which was soon embroiled in a three-war civil war between nationalist, republican, and communist factions. The war ended in a nationalist victory in 1919, resulting in the establishment of the authoritarian Cuthish State under President Wilfred Newbury. Cuthland assisted Melasian revolutionaries against Mascyllan colonial forces during the Melasian Crisis, ultimately leading to a brief military conflict that reestablished Cuthland as a global power and marked the beginning of the Great Game. Cuthland and its allies, collectively known as the Mageiros League, remained the primary challengers to the geopolitical dominance of the Mascyllary-led Berean Defense Treaty Association until the Recession of 1967, which severely weakened the Mageiros powers and led to rioting and unrest across Cuthland. The unrest led President Newbury to resign and appoint Edward II, the exiled King of Cuthland, as his successor, restoring the Cuthish monarchy. The Cuthish Constitution of 1969 created a constitutional monarchy that brought democratic governance to Cuthland for the first time since the end of the civil war. However, the nation's democratic institutions were quickly plagued by corruption and the soft influence wielded by the monarchy, and by the end of the 1970s the nation had returned to de facto authoritarianism. Nevertheless, a series of economic reforms throughout the 1970s and 80s known as the Miracle of Cuthland opened up the nation to foreign investment, established a comprehensive welfare state, and transformed its economy into one of the most developed and diverse in the world. Following the collapse of communism in Aurorum during the late 1980s and early 1990s, Cuthland once again emerged as the primary non-democratic global power.
Modern day Cuthland boasts a developed mixed economy, which is Aurorum's Xth largest by total nominal GDP. The nation maintains a comprehensive social safety net and ranks highly in measures of education, life expectancy, and health. It is one of Aurorum's major military powers, maintaining the Xth largest nuclear arsenal and Xth largest number of active military personnel. The nation is a member of the Mageiros League and Assembly of Nations, serving as a founding member of the former. Due to its substantial economic, diplomatic, and military strength, Cuthland is widely considered to be a great power in the international system.
Etymology
"Cuthland" is derived from the Cuthish Cuþland, meaning "land of the Cuths". The Cuths were a Telmerian tribe who settled in modern day Cuthland during classical antiquity, and are the ancestors of the modern day Cuthish people. The word Cuþ itself means "known" or "famous", so the name "Cuthland" can be literally translated as "land of the famous" or "land of the known".
History
Prehistory
- Cavemen blah blah blah
Antiquity
- Celtic until arrival of Cuths and Walds during late antiquity
- Coalesce into various petty duchies and kingdoms
Middle Ages
- Four Kingdoms between 6th and 11th centuries: the Kingdom of Waldrich and the Cuthish kingdoms of North Cuthia, Meerland, and Fledland
- Viking age, constant attacks from the Dentrian Peninsula
- Edmund the Great of the Kingdom of Meerland unifies the Cuthish states for the first time under the Kingdom of Cuthland in the 11th century
First Cuthish Empire
Revolution and instability
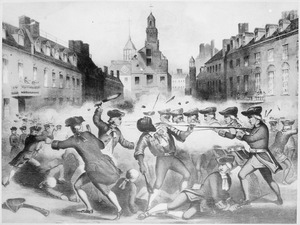
The second partition had left the Cuthish Empire a state of economic and social disarray. Cenhelm I died in 1780, leaving the throne to his son, Edmund IX. Edmund IX attempted to pay off the debts that had been incurred over decades of war and economic malaise by levying a highly regressive tax regime from which the nobility and clergy, who collectively represented the first estate in feudal Cuthland, were exempt. This enraged the second estate of burghers, who bore the brunt of Edmund IX's new taxes, and led to an increasing acceptance of liberal and republican ideals associated with the Enlightenment among the lower and middle classes. These ideals were most notably promoted by the Council of Reason, a society led by enlightenment thinkers such as Alfred Harwood and Dunstan Millard that published various articles and pamphlets between 1790 and 1795. The publication of Just Governance and the Rights of Man in 1795 proved particularly controversial for its denouncement of the Cuthish monarchy, and led Edmund IX to order the arrests and executions of both Harwood and Millard for treason. The executions led to a rapid deterioration in relations between the estates, culminating on 10 October when a group of demonstrators protesting the executions were fired upon by soldiers of the Royal Guard in front of Gledworth Palace in Kingsham. The soldiers killed 14 demonstrators in what became known as the Gledworth Massacre, leading to waves of riots and unrest across the nation and signaling the start of the Cuthish Revolution.
The Gledworth Massacre caused outrage in the House of Burghers, an advisory body to the Cuthish monarch which represented the second estate in the Wittenmoot. In March 1796, members of the House of Burghers established the Popular Committee with the intent of organizing revolutionary activities in Cuthland. The Popular Committee issued the Declaration of Rights and Liberties on 19 May, which condemned feudalism and absolute monarchism in Cuthland as infringements on the natural rights of man. The Declaration was accompanied by the Petition of the Burghers, which asked Edmund IX to abolish feudalism and the privileges of the first estate and to provide for representative government based around the Enlightenment concept of popular sovereignty. The King attempted to quash the nascent revolution by sending soldiers to arrest the members of the Committee on 3 June, leading to a violent confrontation known as Bloody Monday when the soldiers clashed with peasant militias that had been raised to defend the Committee against royal interference. News of Bloody Monday led Cuthish soldiers assigned to the garrison at Leihstead-on-Fen to mutiny, occupying the city for 10 days until a contingent from Edgton was dispatched to restore order.
Fearing that the mutiny in Leihstead would spread, Edmund IX's advisors recommended that he accept the Popular Committee's demands in order to avoid a military coup d'état. After months of negotiations, Edmund IX signed the Cuthish Constitution on 17 September 1796, officially abolishing feudalism in Cuthland and reorganizing the Wittenmoot as a legislative body. However, the monarch retained substantial powers, including the ability to veto legislation and appoint government ministers. These powers enraged the more radical members of the revolutionary movement, who had advocated for the monarchy to be abolished completely in favor of a republic. The schism between the republicans and constitutional monarchists became increasingly evident at the first meeting of the Wittenmoot, when radical leader Harold Blace famously denounced the body before storming out of the House of Burghers with 162 other republican members.
Tensions came to a head on 26 August 1797, when Edmund IX dismissed five republican ministers appointed by the Wittenmoot. Outraged by what they viewed as an undemocratic exercise of royal power, republican revolutionaries led by Blace staged an uprising in September that ended with Edmund IX's arrest. Edmund IX was subsequently tried for treason and famously executed along with his family in front of Gledworth Palace on 10 September. The republicans subsequently abolished the Wittenmoot and replaced it with the newly established Popular Council, which declared the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of the First Cuthish Republic on 6 October, with Blace as the new government's first President. The republicans subsequently rounded up and executed suspected counterrevolutionaries in the Republican Terror, killing over 30,000 royalists, constitutional monarchists, moderate liberals, and remaining members of the nobility over the next three years.

Edmund IX's brother, Algar III, met with X of Dulebia and X of Mascylla during the winter of 1797-8 in order to organize a coalition to intervene in the revolution and restore the Cuthish monarchy. Algar III offered significant territorial concessions as compensation for their assistance, granting the two nations many border territories and colonial possessions that would bring Cuthland to a historic territorial nadir and effectively end the Cuthish colonial empire. The negotiations produced the Ulich Agreement in February 1798, which led to the outbreak of the Cuthish Revolutionary War in the spring of 1798 when the Dulebian and Mascyllary armies launched a two-pronged invasion of the Cuthish Republic. Fighting spread to the Cuthish colonies during the summer, beginning with the Mascyllary invasion of X in June and spreading to Alvinia and eastern Pamira during the fall. Initial gains made by coalition forces in continental Cuthland stalled following a decisive Cuthish victory at the Battle of Crestwick in December, giving way to a Cuthish counter-offensive in the spring of 1799 that pushed coalition forces past the antebellum borders and resulted in the sack of several major Mascyllary and Dulebian cities in August and September. However, the tide turned with X's entrance to the war the next spring at the request of Algar III and the coalition powers, securing a decisive victory at the Battle of Edgton in May 1800 that allowed coalition forces to advance on Kingsham. The increasingly dire situation for the Cuthish revolutionary forces, coupled with rising public disenchantment with the authoritarianism of the Republican Terror, contributed to a strengthening reactionary movement in Cuthland that opposed the republic and advocated for the return of the monarchy. Internal instability led to a military coup d'état by royalist sympathizers on 30 June that overthrew the republic and invited Algar III to return to Kingsham, ending the war and restoring the Cuthish monarchy.

As a consequence of the war, Algar III became the first Cuthish monarch since 1444 not to hold the title of Emperor. The new Kingdom of Cuthland was reduced to a rump state in the nation's third partition since 1715, which ceded significant territories to the victorious coalition powers in keeping with Ulich Agreement. The Treaty of Swithtun granted independence to Waldrich and allowed Mascylla to annex X, while Dulebia took control of X and X. X, which was not a part of the original Ulich Agreement, was nevertheless ceded the territory of X separately in the Treaty of Bloomford. In addition, the remnants of the Cuthish colonial empire were divided among Dulebia and Mascylla, with Dulebia taking control of Cuthish colonies in eastern Pamira while Mascylla was granted the remaining Cuthish possessions in Alvinia and northern Pamira.
While the failure of the Cuthish Revolution was widely seen in Cuthland as a repudiation of republicanism as a form of government, the liberal ideals of the Enlightenment had left a permanent impact on Cuthish society. As such, Algar III attempted to rule as an enlightened absolutist, taking advantage of the centralized state apparatus established during the revolutionary period to modernize the country. He implemented economic reforms that brought the industrial revolution to Cuthland, devoted public funds to the arts and sciences, and became one of the first world leaders to abolish capital punishment. Algar III also sustained many of the social conventions brought about by the revolution, upholding civil liberties and maintaining a merit-based system in public service. His highly popular rule restored the image of the monarchy in the eyes of the Cuthish public and ushered in a brief era of stability known as The Interlude.
Algar III's death in 1817 left his son, Edmund X, as the successor to the Cuthish throne. In contrast to his father, Edmund X's rule was highly conservative, keeping many staunchly royalist members of the nobility in his closest group of advisors. Consequently, Edmund X stripped back many of the reforms made during his father's rule, controversially reinstating capital punishment for certain crimes committed against members of the clergy and nobility. These revisions of the post-revolution social order were seen as highly regressive, once more turning public opinion against the monarchy. In April 1822, riots broke out in Newbridge after a mob stormed a jailhouse in order to free two brothers who had been sentenced to death for burning a noble's field. Edmund X sent imperial troops to Newbridge to quell the unrest, resulting in a confrontation with rioters that resulted in nearly 60 fatalities and marked the start of the April Revolution. The growing unrest quickly spread to Kingsham, leading Edmund X to abdicate his throne on 29 April and flee to Ochoccola.

The Revolution resulted in the creation of the Second Cuthish Republic as the Wittenmoot announced the abolition of the monarchy for the second time in three decades. However, the Second Republic quickly fell into instability. The Dulebian Empire invaded Cuthland during the fall, sparking a three year long war which ended in a fourth and final partition in 1825 and ceded the X Peninsula to Dulebia. The war left the fledgling republic in heavy debt, which was exacerbated by the inability of the national government to raise its own taxes. Instead, the 1823 Constitution had made the national government dependent on the shires for financial support, leaving it severely underfunded and unable to pay off its war debts. The financial crisis particularly enraged elements of the military, many of whom had still not received pay after years of war. The crisis culminated in January 1828, when a group of disenchanted soldiers led by General Ecgfriþ Garfield staged a rebellion and seized Feirford Arsenal. The national government found itself unable to raise an army to suppress the rebellion as unpaid soldiers nationwide began to mutiny, allowing Garfield and his army to march into Kingsham unopposed.
Garfield subsequently suspended the Constitution and declared himself President, establishing a military junta that temporarily stabilized the Republic. However, the failures of the Second Republic had created a strong reactionary current in Cuthish politics as support quickly grew for a restoration of the monarchy. By the end of 1829, the monarchist movement had split into two camps between the supporters of the conservative Haltboruhs and those of the Alhsteads, a more liberal cadet branch of the House of Haltboruh. Fearing a return of absolutism under a Haltboruh monarch, the Alhsteadists staged a popular uprising in June 1830 and crowned Edwin III as Emperor of a restored Cuthish Empire.
Second Cuthish Empire and Great War
The Alhstead Revolution resulted in the establishment of a new form of governance known as a limited monarchy. Instead of turning powers over to democratically elected officials, as in a conventional constitutional monarchy, the Cuthish Constitution of 1830 created legal bounds within which the sovereign could exercise his power. The Constitution codified many of the enlightened absolutist practices normalized by Algar III, creating a bill of rights for the people and formally stripping the nobility and clergy of special privileges. The High Court, the highest judicial body in Cuthland, was granted the power of judicial review over the monarch's actions in order to maintain constitutionality. The 1832 Constitution also expanded the power of the Wittenmoot, requiring the approval of both houses in order for the monarch to amend the constitution or appoint new judges to the High Court.
During his rule, Edwin III launched a series of military campaigns to reassert revanchist claims on former Cuthish territories that had been lost during the partitions. These campaigns, known as the Alhstead Wars, began with the Second Cutho-Waldish War in 1832, which ended in the reannexation of Waldrich after a brief two month conflict. The decisive victory sparked a wave of nationalism across Cuthland, emboldening Edwin III to continue his aggressive foreign policy against Dulebia in 1834. The war was largely successful, with the Treaty of Ulich ceding most of the X Peninsula that had been seized in the fourth partition, with the exception of Erjarvia, back to Cuthland. The victory over Dulebia allowed Edwin III to begin expanding east, invading Mascylla in 1838. The subsequent Treaty of Alderport, signed in 1841, restored eastern Cuthland to its pre-partition borders and returned most of Cuthland's former colonial possessions in Alvinia and Valimia.
The Alhstead Wars successfully reestablished the Cuthish Empire as a great power in Berea, rivaling the established powers of Mascylla and Lavaria that had dominated Berean geopolitics since the late 18th century. Tensions continued to rise throughout the second half of the 19th century, as Cuthland expanded its colonial empire in Caphtora and challenged Lavo-Mascyllary colonial dominance. Furthermore, Cuthland sought rapprochement with Dulebia during the 1870s under the reign of Godric IX, leading to the codification of the Cutho-Dulebian Alliance in 1877. The rise of Cuthland and Dulebia as world powers prompted a reorganization of Berean geopolitics, with two primary power blocs emerging by the dawn of the 20th century. Cuthland, Dulebia, and Ertyheria established the X in 1880, while Lavaria, Mascylla, and Falland established the X in as a counter-balance in 1884.
- Tensions with Mascyllary bloc lead to Great War
- Things are going pretty well until they aren't, complete devastation
Civil War and Melasian Crisis
- Proceed to lose all of your territories gained in the Alhstead Wars via the Treaty of Lehpold, because Cuthland can't have nice things
- Cuthish Revolution of 1916, RIP monarchy press F
- Cuthish Republic?
- LOLNOPE three way civil war
- Nationalists win and establish authoritarian Cuthish State under Wilfred Newbury
- Commie Walds don't like it and the Waldish insurgency begins
- Walds persecuted during 1920s and 30s
- Melasians rebel against Mascyllary rule, Newbury takes the opportunity to challenge Mascylla and reassert territorial claims on western Mascylla
- Cuthland wins and forms Mageiros League with Melasia and longtime ally Eryheria
Contemporary history
- Tensions with Mascylla, arms race, Cuthland gets the bomb
- Recession of 1967 ruins the fun and leads to the 1968-9 Cuthish unrest
- Newbury resigns and appoints Edward II as his successor, restoring the monarchy
- Edward II establishes constitional monarchy, yay democracy
- Lol you really thought I'd let Cuthland have nice things? Fuck no, massive corruption and excessive soft influence from the monarchy turns Cuthland into a hybrid regime by the end of the 70s
- But economic reforms stabilize the economy and establish a welfare state, Cuthland finally enters the first world
- Tech sector explodes during the 80s, Cuthish Japan lol
- Can into space?
- Communism falls in the 90s, Cuthland and the Mageiros League reemerge as the predominant opposition to the BDTA
- Cuthland and Mascylla = Russia/China and the US
Geography
Climate
Environment
Biodiversity
Politics
Government
Political parties and elections
Administrative divisions
Foreign relations
Military
Economy
Science and technology
Infrastructure
Tourism
Demographics
Largest cities
Ethnic groups
Language
Religion
Education
Health
Culture
Art
Architecture
Literature
Philosophy
Music
Cinema
Media
Cuisine
Sports

The sports landscape of Cuthland is dominated by the nation's affinity to ice hockey, which was developed in northern Cuthland during the 19th century and is widely considered to be the nation's national sport. A 2012 poll held by the Sportswriters Association of Cuthland found that ice hockey was the preferred sport of 45% of the population, making it the most popular sport in the country. The Ice Hockey Association of Cuthland (IHAC), founded in 1890, serves as the sport's highest governing body and the oldest such ice hockey organization in the world. The IHAC operates the Cuthish ice hockey league system, which organizes every internationally sanctioned division of professional ice hockey in Cuthland under a system of promotion and relegation. The National Division, the highest division of ice hockey in the country, is the most widely viewed and attended sports league in Cuthland and the Xth most valuable in the world. Internationally, the Cuthish men's national ice hockey team has won the International Ice Hockey Championships (IIHC) nine times and taken home five gold medals at the Auroran Games, most recently in 2018.
Other popular team sports in Cuthland include association football, rugby, and cricket. Football is significantly more popular in Waldrich and other parts of southern Cuthland, and two of the nation's Waldish-based clubs, FC Grienfjild and Meerboarg Sport, are among the top clubs in the world. The Cuthish men's national football team has also seen periodic success internationally, most notably winning the 1974 Auroran Cup. Rugby and cricket, by contrast, are predominately Cuthish sports, seeing their greatest popularity among the upper classes in major cities such as Kingsham, Alderport, and Whitford. Rugby is particularly popular in communities along the coast of Lake Sigismund, in some areas surpassing ice hockey in popularity. Alderport Rugby is the most successful rugby club in the nation, having won the RFC First Division, the highest level of professional rugby competition in Cuthland, seventeen times. Cricket has declined significantly in prominence in recent years, and is now the fourth most popular team sport in the nation despite once rivaling ice hockey in popularity. Nevertheless, Cuthland remains a major hub for the sport, with the Cuthish men's national cricket team winning the World ODI Cricket Championships twice in 1987 and 2003.
In individual sports, golf maintains the strongest following nationwide. The Royal Ashbury Golf Club, built in 1790, is among the oldest golf courses in the world, and is the site of the prestigious Ashbury Classic golf tournament. Other notable golf courses in Cuthland include the Prestford Manor Golf Club, Hatchbury Golf Club, and the Royal South Bexford Golf Club. Tennis, skiing, squash, swimming, fencing, and martial arts are also popular individual sports in Cuthland.
Cuthland has historically been successful at the Auroran Games. The nation ranks third all time in medals with a total of 860, of which 223 have come at the Winter Games and 637 at the Summer Games. The nation and its predecessor states have hosted the Games five times: the 1904 and 1996 Summer Games, as well as the 1934, 1950, and 2006 Winter Games.