Kiyortza
United States of Kiyortza Kiyortzani Linsori Vyarikin | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
 | |
| Capital | Kittalor |
| Largest city | Kanistriy-Si'itivu |
| Official languages | Kiyortzani, Riyaki |
| Recognised regional languages | Astari |
| Ethnic groups | Lorzik-Kittauhri (41.3%) Itikov-Kanitzuri (29.4%) Riyaki (17.1%) Pashink-Djinatri (9.4%) Other (2.8%) |
| Demonym(s) | Kiyortzani |
| Government | Democratic Federal Republic |
• President | Niklau'iz Tariskiya |
• Vice President | Miranya Kitavis |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Establishment | |
• Second Treaty of Fukivapi | April 5, 1769 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,642,789 km2 (634,284 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 192,189,000 |
• Density | 117.0/km2 (303.0/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | K$7.396 t ($9.763 t) |
• Per capita | $38,125 KYI ($50,325) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | 6.477t KYI ($8.55t) |
• Per capita | 33,388 KYI ($44,072) |
| HDI (2019) | 0.911 very high |
| Currency | Kiyorsi (KYI) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +19 |
| Internet TLD | .ky |
Kiyortza, formally the United States of Kiyortza (Kiyortzani: Kiyortzani Linsori Vyarikin), is a nation comprised of 18 provinces and a capital district in Anteria, with a population of about 192 million. Kiyortza borders 5 nations, being Aleni to the northeast, Rvandonia and Vescarium to the east, Fichmanistan to the southeast, and the city of Valino to its south. The nation is located in northwestern Thuadia between the Variyor Mountains to its east and the Paisi Ocean to its west.
The name Kiyortza most likely came from Ikiy-vortis-za, which in Proto-Kiyortzani meant something along the lines of West-of-mountain-land. The name most likely originally referred to the region of Kivorsziya in what is currently south-central Kaprikosha/northern Tarisk-Virtakyo, before it widened to the general region west of the Variyor Mountain Range (Variyor meaning East Mountains) and later the entire nation upon its unification.
Kiyortzani citizens are taxed a relatively high amount, though in turn receive many social benefits and enjoy a high standard of living.
History
Kiyortza as a region is fairly diverse, and with it comes many conflicts. Despite the peace in current times, the region was quite turbulent in the past, and only with everyone coming to the table to talk did all the infighting end.
City-States Period
WIP
Piskatri Expansion
WIP
Itikov-Kapriszi Rivalry
WIP
The Siege of Skyorpavi and the Kanistriy Revolution
Kapriszi invades Skyorpȳ'i, Kanistri Revolutionaries take the chance to rebel. WIP
The Rise of the Kittauhri
The Kittauh and Kanistri join forces and takes over eastern Kittauhriya. WIP
The Nyirdkal Accords
Piskatri attacks Kittauhri, fails. Arkȳzya, Sivordjik, and Kirȳi secedes from Piskatri Union, joins Kittauhri WIP
The First Treaty of Fukivapi
The Kittauhri, Itikovi, and Kapriszi sign peace in neutral Fukivapi. All three states cede land to form the municipality of Fukūlyi under Fukivapi. WIP
Unification
The four major powers in Kiyortza, along with Fukūlyi, Rȳkiri, and various smaller states unify into Kiyortza with the original 17 provinces, with capital of Fukivapi; Zifrosi joins, and Kittalor is designated capital, making 18 provinces and a capital region; Timinse-Astariya joins and makes the modern 19 provinces. WIP
Industrialization
WIP
The Tsunami of 1930
Tsunami hits central-west Kiyortza in the spring of 1930 and takes out Ifuksiyaf, the largest city and port in the nation at the time. WIP
Contemporary Period
WIP
Geography
Kiyortza is located in the northwest corner of mainland Thuadia in the Western Hemisphere of Anteria. The nation as a whole is fairly hilly and mountainous, with hills and mountains lining many of the nation's borders and coasts. Kiyortza's location at the tip of Thuadia-Thrismari allowed for it to flourish as the epicenter of global trade prior to the construction of the canal at Cerisium, and to this day still allows it to remain fairly influential over trade.
Topology & Hydrology
Kiyortza is a mountainous country, with many mountain ranges across the nation. The main range dominating the nation would be the Variyor Range, taking up a good portion of the eastern part of the mainland. The Fukūlyi Range, an offshoot of the Variyor Range, acts as a divider between the watersheds of the Alf & Kaprisz Rivers, while the Zifrona Range seperates Zifrosi and Astariya from much of the rest of the mainland. In the north, the Piskatri-Patikyi Mountains makes up the bulk of the Kittauhriya Peninsula, and the mountains of Djinat makes for the formation of its many fjords.
The tallest peak in the nation, Sorzani Varȳ, often referred to as just Sorzani, has a height of 5,827 meters, which alongside many of the nation's other tall peaks, is located on the eastern edge of the province of Ra'ikishna, bordering the nation of Rvandonia. Sorzani is the tallest peak in northwestern Thuadia, the closest peak on Thuadia taller than it in the East.
The Itikov, Alf, and Kaprisz Rivers form the core of the nation's mainland area, and are important routes of cargo transport even to this day. Up in Kittauhriya, the Arkȳdjin and Patiklya Rivers feed into Lake Loryis, the largest freshwater lake in northwestern Thuadia, while the Kayitz River acts as an important waterway in eastern Piskatri.
Climate
Kiyortza hosts a wide range of climates, from the frigid mountains of the Variyor Range to the dry brushlands of southeastern Tarisk-Virtakyo, though in general the nation is split between the temperate oceanic zone in the north and warm-/hot-summer Mediterranean in the south. Ample rainfall is recorded across most of the nation, though due to climate change the south has been receiving less rainfall overall than in the past.
Inserted below are the weather data of six cities in distinct regions of Kiyortza
| Climate data for Kiathra, Djinat-Pashinkva. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1934- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.0 (53.6) |
11.6 (52.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.2 (64.8) |
20.6 (69.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
22.0 (71.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
28.3 (82.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
5.3 (41.5) |
6.1 (43.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.2 (52.2) |
14.3 (57.7) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
12.9 (55.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
6.4 (43.5) |
10.2 (50.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
2.6 (36.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
5.7 (42.3) |
8.5 (47.3) |
10.3 (50.5) |
13.0 (55.4) |
12.7 (54.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
5.3 (41.5) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.1 (44.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.3 (32.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
1.0 (33.8) |
2.7 (36.9) |
5.0 (41.0) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.7 (49.5) |
9.3 (48.7) |
7.2 (45.0) |
5.5 (41.9) |
2.3 (36.1) |
0.7 (33.3) |
4.3 (39.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −15.6 (3.9) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−10.2 (13.6) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
1.8 (35.2) |
1.2 (34.2) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−10.5 (13.1) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−15.6 (3.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 98.5 (3.88) |
96.1 (3.78) |
87.3 (3.44) |
65.4 (2.57) |
59.3 (2.33) |
53.2 (2.09) |
58.9 (2.32) |
80.1 (3.15) |
86.7 (3.41) |
95.3 (3.75) |
104.9 (4.13) |
114.2 (4.50) |
999.9 (39.35) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15.6 | 14.7 | 15.1 | 12.7 | 11.4 | 12.2 | 11.8 | 12.8 | 13.7 | 15.5 | 14.8 | 15.2 | 165.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 37 | 52 | 89 | 154 | 186 | 171 | 160 | 147 | 118 | 83 | 69 | 41 | 1,307 |
| Climate data for Pashkya, Djinat-Pashinkva. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1932- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.3 (59.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.5 (86.9) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.4 (92.1) |
29.9 (85.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
34.0 (93.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.9 (44.4) |
8.2 (46.8) |
10.4 (50.7) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
21.9 (71.4) |
18.8 (65.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
9.3 (48.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
13.9 (57.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.9 (64.2) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.8 (58.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.4 (50.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.3 (34.3) |
1.6 (34.9) |
3.4 (38.1) |
5.7 (42.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
13.8 (56.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.0 (44.6) |
3.4 (38.1) |
0.7 (33.3) |
6.8 (44.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.8 (0.0) |
−16.2 (2.8) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
0.6 (33.1) |
3.8 (38.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−14.4 (6.1) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−17.8 (0.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 138.5 (5.45) |
102.6 (4.04) |
113.0 (4.45) |
99.2 (3.91) |
75.2 (2.96) |
59.1 (2.33) |
53.6 (2.11) |
56.7 (2.23) |
65.8 (2.59) |
116.9 (4.60) |
170.2 (6.70) |
152.3 (6.00) |
1,203.1 (47.37) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 14.1 | 12.8 | 12.8 | 11.9 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 9.3 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 12.3 | 16.2 | 14.6 | 143.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 60 | 91 | 135 | 185 | 222 | 227 | 291 | 277 | 212 | 121 | 61 | 56 | 1,938 |
| Climate data for Kittalor, District of Kittalor. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1921- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.8 (67.6) |
24.9 (76.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
32.0 (89.6) |
35.5 (95.9) |
39.2 (102.6) |
41.0 (105.8) |
40.7 (105.3) |
36.8 (98.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
21.1 (70.0) |
41.0 (105.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
11.1 (52.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
16.5 (61.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
22.3 (72.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.4 (81.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
12.8 (55.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
17.5 (63.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
17.4 (63.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.0 (62.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.7 (47.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
2.3 (36.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
13.2 (55.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
10.5 (50.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.5 (−1.3) |
−15.9 (3.4) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
1.3 (34.3) |
4.7 (40.5) |
4.1 (39.4) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 106.8 (4.20) |
88.9 (3.50) |
81.1 (3.19) |
90.7 (3.57) |
84.2 (3.31) |
70.0 (2.76) |
52.9 (2.08) |
66.2 (2.61) |
95.7 (3.77) |
119.3 (4.70) |
140.2 (5.52) |
143.3 (5.64) |
1,139.3 (44.85) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 13.3 | 11.5 | 10.9 | 12.5 | 12.2 | 9.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 10.0 | 12.4 | 15.2 | 15.4 | 140.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 98 | 121 | 149 | 177 | 223 | 235 | 240 | 237 | 199 | 142 | 101 | 86 | 2,008 |
| Climate data for Ifuksiyaf, Ka'i Si'itivȳ'i. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1943- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.2 (72.0) |
25.2 (77.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
33.7 (92.7) |
38.8 (101.8) |
40.1 (104.2) |
39.7 (103.5) |
36.4 (97.5) |
30.4 (86.7) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
40.1 (104.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.3 (59.5) |
17.0 (62.6) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.9 (76.8) |
22.5 (72.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 9.0 (48.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
11.7 (53.1) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.3 (59.5) |
18.2 (64.8) |
19.9 (67.8) |
20.1 (68.2) |
18.4 (65.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.8 (53.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 5.3 (41.5) |
5.8 (42.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
8.6 (47.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
13.9 (57.0) |
11.4 (52.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −3.8 (25.2) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
0.0 (32.0) |
2.4 (36.3) |
5.0 (41.0) |
8.7 (47.7) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.2 (41.4) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 150.7 (5.93) |
114.4 (4.50) |
96.3 (3.79) |
109.6 (4.31) |
88.0 (3.46) |
52.6 (2.07) |
41.7 (1.64) |
46.3 (1.82) |
79.5 (3.13) |
150.8 (5.94) |
162.1 (6.38) |
167.4 (6.59) |
1,259.4 (49.56) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 14.2 | 12.5 | 12.1 | 13.9 | 11.8 | 6.7 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 8.1 | 13.2 | 13.4 | 15.0 | 131.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 116 | 134 | 177 | 193 | 230 | 272 | 291 | 284 | 213 | 155 | 111 | 100 | 2,276 |
| Climate data for Katyu, Andrauya. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1929- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 23.7 (74.7) |
29.4 (84.9) |
33.0 (91.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
41.2 (106.2) |
44.7 (112.5) |
46.8 (116.2) |
46.1 (115.0) |
45.1 (113.2) |
37.0 (98.6) |
30.6 (87.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
46.8 (116.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.5 (59.9) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
32.7 (90.9) |
36.5 (97.7) |
36.2 (97.2) |
31.6 (88.9) |
25.8 (78.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
16.1 (61.0) |
25.3 (77.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
20.3 (68.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.9 (82.2) |
24.5 (76.1) |
19.7 (67.5) |
14.4 (57.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
18.7 (65.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.3 (46.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
19.7 (67.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
17.4 (63.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
9.5 (49.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
12.0 (53.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.2 (19.0) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
11.3 (52.3) |
11.7 (53.1) |
7.1 (44.8) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 66.2 (2.61) |
54.7 (2.15) |
45.5 (1.79) |
54.9 (2.16) |
37.8 (1.49) |
12.7 (0.50) |
2.3 (0.09) |
4.9 (0.19) |
31.3 (1.23) |
75.3 (2.96) |
84.0 (3.31) |
108.3 (4.26) |
577.9 (22.74) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 7.1 | 5.9 | 5.0 | 6.8 | 4.7 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 2.8 | 6.4 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 55.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 176 | 190 | 219 | 236 | 289 | 321 | 362 | 333 | 247 | 209 | 180 | 150 | 2,912 |
| Climate data for Tarikya, Tarisk-Virtakyo. Normals 1969-2019, Extremes 1942- | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 29.9 (85.8) |
32.4 (90.3) |
38.4 (101.1) |
42.4 (108.3) |
45.0 (113.0) |
43.8 (110.8) |
38.2 (100.8) |
41.1 (106.0) |
41.5 (106.7) |
42.9 (109.2) |
36.0 (96.8) |
32.2 (90.0) |
45.0 (113.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 17.6 (63.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.0 (68.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.1 (86.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.5 (67.1) |
24.5 (76.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
13.9 (57.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.1 (71.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.8 (82.0) |
26.6 (79.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
14.7 (58.5) |
20.5 (68.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9.9 (49.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
11.8 (53.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.3 (68.5) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.0 (75.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
19.3 (66.7) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
16.7 (62.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.6) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
2.5 (36.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
10.2 (50.4) |
14.4 (57.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
15.1 (59.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
5.5 (41.9) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 144.3 (5.68) |
101.9 (4.01) |
58.3 (2.30) |
21.5 (0.85) |
3.8 (0.15) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1.2 (0.05) |
31.2 (1.23) |
79.6 (3.13) |
130.0 (5.12) |
571.9 (22.52) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15.2 | 12.7 | 10.1 | 3.9 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 5.6 | 9.1 | 11.8 | 70.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 189 | 202 | 237 | 269 | 330 | 356 | 369 | 357 | 299 | 280 | 234 | 191 | 3,313 |
Demographics
Ethnicity
Native Kiyortzani ethnicities are primarily divided between the northern Kiyashi and southern Riyaki, the former of which are usually further divided into Lorzik-Kittauhri, Itikov-Kanitzuri, and Pashink-Djinatri. WIP
Language
Most Kiyortzani speak Itikovi-Kiyortzani, more often referred as simply Kiyortzani, as their first language, while some, mostly in the southern Riyaki provinces, speak Riyaki-Kiyortzani, commonly referred to as Riyaki, as their first language. The two languages, while distinct from one another, are similar enough that most speakers of one can often deduce what a speaker of the other is saying, and some might even refer to the two as moreso dialects of Kiyortzani, though most speakers of either would beg to differ.
In the past, there were at least 5 other now extinct branches/dialects of Kiyortzani, that being:
- Lorziki - Mixed and homogenized with Itikovi in the Kittauhri Republic.
- Piskatri - Similar to Lorziki, but after the annexation of Kirȳi and Sivordjika. Remains as an accent in many parts of Kittauhriya and Djinat.
- Zifrosi - Overtook by Itikovi. Remains an accent in and around Zifrosi.
- Fukūlyi - Replaced by Itikovi in Fukūlyi and Alfahriya and Riyaki in Skyorpȳ'i. Remains as an accent in and around the said provinces.
- Rȳkirsi - Homogenized with Riyaki.
Religion
The Kiyortzani populous is primarily atheistic/agnostic, and while religious freedom is a basic right, uncalled for proselytizing is generally looked down upon in society. Rationalist religions such as Solarism are generally encouraged over other religions, while Samiism and [Riyaki Folk Religion] are the most common religions. WIP
Culture
WIP
Economy
Currency
Kiyortza uses the Kiyortzani Kiyorsi (KYI), which currently exchanges at a rough rate of about 1.32 ACU per 1 KYI. The currency was created with the Second Treaty of Fukivapi in 1769 as a uniform currency to promote trade between the regions, which all had separate currencies up until that point.
Tourism
Tourism is prevalent around the nation at various locations, with various attractions ranging from national parks to beaches to various museums. Notable regions for travel include the below:
Historical Locations
Most of Kiyortza has some sort of historical location, whether it is a location of a battle, an important strategic city, or just a city that has stood for centuries. Notable historical cities include: Kovil, Androki, Daiza, Kittalor, Visyari, Fukivapi, Rȳkiri, Kanistriy-Si'itivu, Alfahr, Skyorpavi, Djinatrȳ, Kalatri, and Tripȳda.
National Parks/Nature Reserves
National parks and nature reserves dot the more sparsely populated regions of the nation, covering a decent chunk of Djinat-Pashinkva and Ra'ikishna, while lining the Variyor and Fukūlya Mountains in various other provinces including Timinse-Astariya, Skyorpai'i, Alfahrya, Fukūlyi, and Kaprikosha.
Beaches and Resorts
The warm and dry climate of Riyashi means that it is quite popular as a tourist destination, where resorts line the coasts and various leisure vehicles on the Rȳko, Kaprisz, and Tarisko Rivers are not uncommon.
Major Cities
Many Kiyortzani cities have attrations of their own, with every city from the big three to ones with less than 100 thousand vying for attention. Cities worth a trip include Lorzik, Sivordjika, Kanistriy-Si'itivu, Kittalor-Kitaki, Patiklya, Niklaryi, Kirȳ'i, Ifuksiyaf, Ipaksi, Fukivapi, Rȳkiri, Androki, Kapriszin, and Tarikya.
Science and Technology
Most of the nation's scientific and technological development happens in Lorzik-Patiklya, Kittauhri, Ka'i Si'itivai'i, and Fukūlyi, while notable locations include the launch site near Nariki, the medium sized particle accelerator near Iyatzik, museums in various major cities by companies such as Kanistriy Tech and South Kiyortza Airlines, and various other locations of innovation
Production Industry
Mining
The nation has two main ore-abundant regions, that being the Piskatri Mountains and the Eastern Fukūlya Mountains near Skyorpavi. Various smaller deposits are scattered around the north of Kittauhriya and along a good part of the East Kiyortza Mountains.
Piskatri Mountain Deposit
The Piskatri Mountains on the west coast of Kittauhriya holds plenty of monazite, zircon, quartz, and various iron ores, the most exploited sites being near Malkir, Niklaryi, and Pashkya. The region provides vital thorium for the nation's many reactors, iron and various critical metals used in steel manufacturing, quartz-based gemstones, rare earth metals, and various lesser products like zircon and uranium.
Fukūlyi Mountain Deposit
The Fukūlyi Mountains on the center-east of Kiyortza holds many ores, good for all sorts of metals and products such as lead, zinc, barium, fluorine, and various rare metals. Other exploited resources in the area include calcite (marble), cadmium, germanium, and gallium.
Amitȳtza Deposit
The area around Amitȳtza, Ra'ikishna primarily holds copper and silver ores, along with small amounts of pitchblende and bauxite.
Farming
Farming in Kiyortza is primarily based in the Itikovi and Kaprisz River Basins, with a supplement in Eastern Kittauhri and the Zifrosi-Astariya Foothills
Manufacturing
Electronics
Government
WIP
Military
WIP
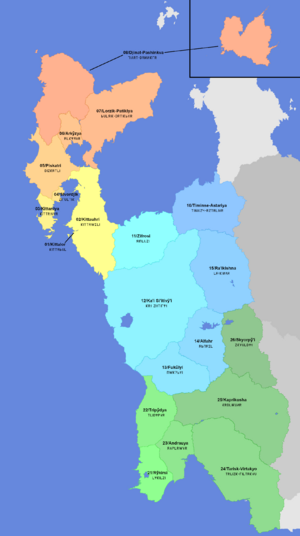
Administrative Regions
Kiyortza is comprised of 19 provinces and a capital region, with its 3 main regions acting as subdivisions between the administrative regions. The list down below is organized by area code.
| AC | Name | Capital | Area (km2) | Population | Overview |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0- | Kittauhriya | - | 482,779 | 93,406,000 | The rainy northwest of Kiyortza, hosting a good portion of the nation's population, with a economy of mostly trade, industry, and various businesses. |
| 01 | District of Kittalor | - | 261.1 | 2,609,000 | The capital city and surrounding areas, not including the port city of Kitaki. It is located on the mouth of the Kita'i River, which flows into southeastern Sivordjik Bay. |
| 02 | Kittauhri | Kiatūr | 105,719 | 21,663,000 | Named after the regional power of the same name prior to the unification of Kiyortza, which was also the namesake of the peninsula. It is located on the base of the Kittauhri Peninsula. It is one of the more densely populated provinces in the nation, with several large cities including Kitaki, Rikishyaf, Livakia, Viyarki, and Kanitzurya, while its economy is largely based off of various technology and engineering based firms, with a substantial minority of international trade and transportation. |
| 03 | Kittaniya | Kirȳ'i | 13,977 | 7,118,000 | Located on the far side of Sivordjik Bay from the Kittauhri Province, on one of the two sub-peninsulas (?) on Kittauhriya. The province's economy is primarily upheld by the fishing industry and trade via the ports of Kirȳ'i and Takitzpya. |
| 04 | Sivordjik | Sivordjika | 3,678 | 11,227,000 | The smallest and most densely populated province, located to the northeast of Kittaniya. It is the urban capital of Kiyortza, with its northern half being mostly a wide expanse of an urban cityscape, while its south is more so a intermittent mix of city and suburbia. |
| 05 | Piskatri | Daiza | 59,259 | 17,725,000 | Located to the north of Kittaniya, it is fairly mountainous, being cut in half by the south end of the Piskatri Mountains. It is mostly split between its more seafaring and trade oriented west, and more mining and production based east. |
| 06 | Arkaizya | Arkai'iz | 20,206 | 8,047,000 | Located to the north of Lake Lorzik, It is a relatively small province, with its core bordered on 3 sides by mountains and hills. The province is the industry hub of the nation, with most of its economy being propped up by exporting various manufactured goods. |
| 07 | Lorzik-Patiklya | Lorzik | 121,170 | 18,804,000 | Located on the northeastern corner of Kittauhriya, it is also mostly mountainous, with the southern panhandle hosting much of its population. It hosts Visyari, one of, if not the most important ports in the nation, which carries most of the cargo coming in from the east. The province's economy is split mostly between shipping via Visyari and the large assortment of businesses based in Lorzik and Patiklya, while Lorzikin, a decent sized international airline, contributes its share of tourism income to the province and its neighbors. |
| 08 | Djinat-Pashinkva | Djinatrȳ, Pashkya | 158,509 | 7,613,000 | The province is comprised of the northern island of Djinat and the mountainous northwest of Kittauhriya. It has two capitals, one being the city of Pashkya on the mainland, and the other being Djinatrȳ on the island of Djinat. It is the largest and the most sparsely populated province in Northwestern Kiyortza, though it has a good few few large cities. Its economy is largely based off tourism on Djinat, Shipping through Kiathra and Pashkya, and various forms of technology and software development |
| 1- | Kanitzur | - | 692,690 | 65,577,000 | The temperate central region of Kiyortza, with a economy of mostly industry, farming, and various businesses. |
| 11 | Zifrosi | Kȳ'ispa | 88,766 | 4,964,000 | Located to the east of Kittauhriya and to the south of the Astari Sea, the province sits in the Zifrosi Foothills, and is fairly isolated from the rest of the country along with Timinse-Astariya. The province is urbanized mostly alongside the coast and lower Kȳ'is River, while the rest is moreso rural. |
| 12 | Ka'i Si'itivai'i | Kanistriy-Si'itivu | 258,217 | 40,831,000 | Located in what is basically the dead center of mainland Kiyortza, it is the largest province in the nation in both size and population. The province is primarily split between the more populated west and more rural east, with most large cities mostly alongside the Itikov River or some other large body of water. Its economy is fairly diverse with various businesses located in large cities, food production and processing in more rural areas, and various forms of production and construction throughout. |
| 13 | Fukūlyi | Fukivapi | 71,691 | 9,854,000 | Located on the border between Kanitzur and Riyashi, what was once the central hub of regional trade has been long since past its peak, though not to say it's not prosperous in modern times. The province is the southernmost highly urbanized province, and its cities currently hosts an amount of software and IT firms comparable to that of Lorzik, and South Kiyortza Airlines, which is based in Fukivapi, contributes quite greatly to tourism in the area, being the largest Airline running out of Kiyortza. |
| 14 | Alfahrya | Alfahr | 62,007 | 4,803,000 | Alfahrya is located to the east of Ka'i Si'itivai'i and Fukūlyi, while the Fukūlya Mountains occupy most of its south, extending into northeastern Fukūlyi. The province's economy is mostly held up by the mines and quarries in its north and lumber industry all throughout the province. |
| 15 | Ra'ikishna | Amitȳtza | 110,688 | 2,178,000 | Located on the eastern border of Kiyortza with Rvandonia, the province is mostly rural mountains, with only a few mid-sized cities, mostly along the Itikov River. Its economy is mostly tourism based, hosting various national forests and parks, while resource extraction, farming, and woodcutting contribute as significant minorities located in the south, west, and southeast respectively. |
| 16 | Timinse-Astariya | Timinse | 101,321 | 1,547,000 | Once the Astariax City-States, Timinse-Astariya is likely the most interesting province in terms of its history. It is fairly sparsely populated and is minimally urbanized, with the largest cities holding only a few hundred-thousand people on the high end. It contains a unique mix of Kiyortzani and Astari culture alongside Rvandonian in the fringes, while both Kiyortzani and Astari are spoken widely, and to this day its Astari roots can be seen quite clearly despite it having been part of Kiyortza for over two centuries. It is located on the northeast of the Kiyortzani mainland with its capital of Timinse, the partial namesake for the province, in its northwest. The province as of currently has been sold to the Naladom of Aleni for integration into the Autonomous Province of Astariax.* |
| 2- | Riyashi | - | 568,641 | 34,757,000 | The warm and dry-ish south of Kiyortza, with a mostly farming and production based economy, whilst hosting smaller but still significant trade, tourism, and manufacturing sectors. |
| 21 | Rȳkirsi | Rykiri | 43,636 | 8,540,000 | Located in the southeast corner of the nation, Rȳkirsi is the trade and business hub of Southern Kiyortza, hosting the highest population density of all the Riyaki provinces. Besides its business aspect, the province also hosts a decently sized tourism industry thanks to its mediterranean climate and its many beaches about many peninsulas and landforms on its west coast. |
| 22 | Tripȳdya | Tripȳda | 58,735 | 4,002,000 | On the west coast of Kiyortza south of Fukūlyi, the province has a large food production and processing industry, while tourism in the south and trade via the port of Tripȳda are important contributors to the province's relative well-off position. |
| 23 | Andrauya | Androki | 44,567 | 7,134,000 | Rȳkirsi's lesser known twin, the historical core of the Kapriszi, centered on the expansive delta of the Kaprisz River. It boasts a decent throughput of trade thanks to its location on the mouth of the Kaprisz River, and its cities provide a decent source of income. |
| 24 | Tarisk-Virtakyo | Didjitaika | 178,713 | 6,224,000 | A large, expansive, mostly rural province in southeastern Kiyortza, it boasts a large farming industry, and many of the province's food exports are known as ones of quality worldwide. |
| 25 | Kaprikosha | Kapriszin | 154,964 | 5,301,000 | Located north of Tarisk-Virtakyo, the province's west host expanses of fields, the center a suburban sprawl, and the east wooded mountains. The Kaprikoshi economy mostly comprises of various production and manufacturing industries, trade with Vescarium to its east, and a small IT sector in its cities. |
| 26 | Skyorpai'i | Skyorpavi | 88,026 | 3,552,000 | Alfarhya's Riyaki twin, the province's economy is mostly comprised of resource extraction, woodcutting, and some food production/processing, while a marginal tourism industry is present in its center-east. Its terrain is similar to Ra'ikishna in the fact that it is mostly mountainous with flat regions near the edges. |
Borders
Kittauhriya
WIP
Kanitzur
WIP
Riyashi
WIP
Energy & Infrastructure
Cities & Urban Development
Information on Kiyortzani Cities are present here.
Roadways
The road system in Kiyortza is primarily divided into 3 categories: National Highways, Provincial Highways, and Local Roadways.
National Highways
National Highways uphold a national standard in road quality, generally 4-lane highways or wider, and spans the country, acting as Kiyortza's main arteries for long-distance road travel. They are numbered 1 through 14, generally with the north-south spanning highways being odd numbered and vice versa, with two short extensions off of highways 3 and 7, labeled 3A and 7A; highways 2 and 13 also happen to overlap with highways 1 and 7 respectively for significant parts of its length, while for signage the mileage of the longer highway overall takes precedent. They are usually referred to as "KN-[number]", KN standing for Kiyortza Nashakir, meaning "Kiyortza Highway".
Provincial Highways
Provincial Highways don't uphold any specific standards, being maintained by their respective province, though they are usually always the most important roads in a province, and can be anything from a two-lane road up to an arterial highway. Their numbering and signage is dependent on their respective province, and is usually referred to by their province's two-letter code and its number. (For example, Kittauhri Highway 56 is usually referred to as KT-56)
Local Roads
Local roads are ones not under any of the two previous distinctions. Depending on region there may or may not also be county roads upkept by their respective county with their own signage.
Railways
Kiyortza has a relatively well-developed modern rail system, with an extensive rail system across the nation. In the less densely populated regions of the nation, both freight and passenger trains often run on the same tracks, while in the more densely populated regions there are often separate high-speed rails with separated freight lines and stations.
Energy
A substantial portion of the power output in Kiyortza are delivered by the many thorium reactors about, with the most of the rest delivered by various renewable energy sources and uranium reactors, with only a small portion of energy generated from burning fossil fuels. The reason for this is mainly due to the fact that despite Kiyortza's abundance of many natural resources, there are fossil fuel deposits present in the general area, making finding alternatives much more lucrative. There is ongoing research and development on fusion energy as a future alternative from nuclear fission, which tends to produce highly radioactive nuclear waste.