Tengaria: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 232: | Line 232: | ||
After the formation of the Grand Principality, the Tengaria's culture began to become more unique, as the writings of Xenagoras once more began to gain traction and support. However, there was still a great deal of dialogue between the two, especially with the Sophist-leaning theologians of the Empire. It was not until the collapse of the Empire of Arciluco and the rise of the [[Realm of Thorns (Amathia)|Realm of Thorns]], together with the rise of the [[Empire of Tengaria]], which lead to the so called Tengarian Renaissance, which lasted from c.1350-1550. With partial influence from famous {{wp|Scholastic}} writings and learning of East Euclea caused the Emperor to establish the [[University of Lenovo]] as the first West Euclean University in 1462. During this time, the writings of Xenagoras became mainstream, and the Tengarian theologians, turning against the now heretical iconoclast theologians of Amathia, embraced Teleology. The Patriarch of Lenovo, [[St. Boris the Confessor]], famously defended the writings of Xenagoras in his tract ''On the Unity of Wisdom'', which wove together Xenagoran Philosophy with Sotrian Theology, and his work on the ''In Defense of the Images of God'', which defended the usage of Icons. During this period, Tengaria became a center for learning and {{wp|Orthodoxy|Orthodox}} [[Episemialist_Church|Episemialist]] thought in the Western portion of Euclea. In addition, Tengarian plays, in an attempt to revive and perfect the old plays of Antiquity, saw a great revival during this period, with men such as [[Gregori Rumen]] and [[Dimitri Vasilev]] writing influential tragedies and comedies. A great deal of philosophical and theological writings date to this time period, and there was an active culture of intellectual discussion in the Tengarian Empire. The old Agora school, which had fallen into decay, was revitalized. | After the formation of the Grand Principality, the Tengaria's culture began to become more unique, as the writings of Xenagoras once more began to gain traction and support. However, there was still a great deal of dialogue between the two, especially with the Sophist-leaning theologians of the Empire. It was not until the collapse of the Empire of Arciluco and the rise of the [[Realm of Thorns (Amathia)|Realm of Thorns]], together with the rise of the [[Empire of Tengaria]], which lead to the so called Tengarian Renaissance, which lasted from c.1350-1550. With partial influence from famous {{wp|Scholastic}} writings and learning of East Euclea caused the Emperor to establish the [[University of Lenovo]] as the first West Euclean University in 1462. During this time, the writings of Xenagoras became mainstream, and the Tengarian theologians, turning against the now heretical iconoclast theologians of Amathia, embraced Teleology. The Patriarch of Lenovo, [[St. Boris the Confessor]], famously defended the writings of Xenagoras in his tract ''On the Unity of Wisdom'', which wove together Xenagoran Philosophy with Sotrian Theology, and his work on the ''In Defense of the Images of God'', which defended the usage of Icons. During this period, Tengaria became a center for learning and {{wp|Orthodoxy|Orthodox}} [[Episemialist_Church|Episemialist]] thought in the Western portion of Euclea. In addition, Tengarian plays, in an attempt to revive and perfect the old plays of Antiquity, saw a great revival during this period, with men such as [[Gregori Rumen]] and [[Dimitri Vasilev]] writing influential tragedies and comedies. A great deal of philosophical and theological writings date to this time period, and there was an active culture of intellectual discussion in the Tengarian Empire. The old Agora school, which had fallen into decay, was revitalized. | ||
However, Tengaria soon began to become politically overshadowed by the nearby [[Narozalica]], and its increasing influence began to bring the Tengarian intellectual Renaissance to its end. Tengaria retained its scholarly discourse and schools of learning, but lagged behind the more modern states in terms of scientific advancement. Scholars such as [[Lawrence Lugin, 1st Marquis of Krada|Lawrence Lugin]] were know to come to Tengaria to access texts or engage in active philosophic discussions. Eventually, modern thought from Eastern Euclea began to make its way into Tengaria, but was often met with hostility by the intellectual community, but slowly modern thought began to make more progress. | {{multiple image | ||
|perrow=2 | |||
|total_width=270 | |||
|align=left | |||
|image1=Ivan Istina.jpg |width1=125 | |||
|image2=Hristo-Botev-circa-1875.jpg |width2=155 | |||
|image3=Kliment_tarnovski.jpg |width3=125 | |||
|image4=TodorIvanchov.jpg |width4=125 | |||
|footer=(From Top Left) [[Ivan Istina]] (1868{{ndash}}1928), [[Gregori Renev]] (1861{{ndash}}1931), [[Aleksandar Dilov]] (1855{{ndash}}1934) and [[Stanislav Kozlek]] (1896{{ndash}}1930), the principal authors of the Znaniya School | |||
}} | |||
However, Tengaria soon began to become politically overshadowed by the nearby [[Narozalica]], and its increasing influence began to bring the Tengarian intellectual Renaissance to its end. Tengaria retained its scholarly discourse and schools of learning, but lagged behind the more modern states in terms of scientific advancement. Scholars such as [[Lawrence Lugin, 1st Marquis of Krada|Lawrence Lugin]] were know to come to Tengaria to access texts or engage in active philosophic discussions. Eventually, modern thought from Eastern Euclea began to make its way into Tengaria, but was often met with hostility by the intellectual community, but slowly modern thought began to make more progress. With Narozalica's influence on the Empire and the formation of the Republic in 1861, Narozalic republican thought began to become prominent in intellectual circles. The focus transferred from the classics to modern Narozalic literature and Eastern Euclean scientific advancements and thought. The academic circles began trying to imitate the other places of Euclea. | |||
At the turn of the twentieth century, an Teleological resurgence began to come again with the famous Znaniya School, which was a group of scholars together at the Agora. At the head of this movement was [[Ivan Istina]], a philosopher, scientist and theologian who attempted to united Xenagoras' thought with modern advancements in science and Sotrian teachings. With him were Archbishop [[Aleksandar Dilov]], who was a prominent Theologian who published several important works the nature of grace and divine providence from Episimialist tradition, as well as other many popular tracts, . His teachings became widely popular in Tengaria at the turn of the century, although they failed to resonate with the current academics at the time. He proposed a plan for the renewal of education in Tengaria, which would later be implemented by one his pupils, [[Simeon Kovachev]]. Istina would famously die fighting during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. With the collapse of the Empire and the establishment of the Republic, civil discord undermined the philosophic and literary scene. | |||
===Music=== | ===Music=== | ||
Revision as of 02:27, 19 September 2020
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Tengaria Република Tангария Republika Tangaraiya | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Нация, ред, единство" "Natsiya, Red, Edinstvo" "Nation, Order, Unity" | |
| Anthem: "Natsionalen Pokhod" "National March" | |
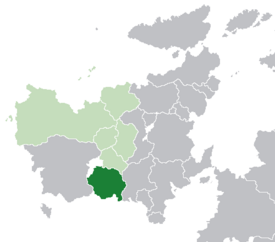 Location of Narozalica (dark green) in Euclea (light green & light grey) and in Samorspi (light green) | |
| Capital and largest city | |
| Official languages | Tengarian |
| Ethnic groups | Tengarian- 91.5% Tuathan- 3.4% Other- 5.1% |
| Religion | 93.2% Episemialist 2.8% Iconoclast 1.4% Catholic 2.6% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Tengarian |
| Government | Unitary dominant-party Presidential Republic |
| Teodora Kovacheva | |
| Boris Rumen | |
| Legislature | Grand Assembly of Tengaria |
| Senate of Tengaria | |
| National Assembly | |
| History | |
| c.1000-1350 | |
| 1350-1930 | |
• Fall of Lenovo | September 6, 1930 |
• Resistance Movement | 1930-1935 |
• Republic Established | 1935 |
| 1955-1957 | |
• Current Constitution | 15 March, 1958 |
| Area | |
• Total | 305,981 km2 (118,140 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | |
• 2014 census | 21,870,991 |
• Density | 73.08/km2 (189.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| HDI | very high |
| Currency | Lev (TL) |
| Time zone | UTC-1 |
| Date format | mm-dd-yy |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .tng |
Tengaria (Tengarian: Tангария or Tangaraiya), officially the Republic of Tengaria (Tengarian: Република Tангария or Republika Tangaraiya) is a sovereign nation situated in Western Euclea in the world of Kylaris. It is bordered by Amathia to the East, Poliania to the West, and Minilov to the North. Tengaria is located along the warm coastal plains and has a warm Temperate Climate, and shares both a border with Lake Min to the northeast and the Mazdan Sea to the south. The country's geography features fertile plains for farming, thick forests, coastal beaches and cliffs, and rolling hills. The far eastern portion of the Country is the most urbanized, and it is where the capital of Lenovo is located.
The ancient home of the Tengar tribes straddled the borders of the Solarian Empire. Soon after its fall, the tribes were conquered and Sotrianized by the Empire of Arciluco, and later became an independent Grand Principality when the Empire's authority declined. Following the collapse of the Empire to the Realm of Thorns, the Grand Prince was named Vladetel by the exiled Ecumenical Patriarch, founding the Empire of Tengaria. During the Great War, the Empire was invaded and occupied by the Amathians. A resistance movement, led by Simeon Kovachev, fought against the occupation, and successfully restored sovereignty after the war with Narozalican support. After the war a Presidential Republic was created, although it was was plagued by instability, factionalism and a rough economy, which eventually culminated in the Tengarian Civil War. After the War, Kovachev took over on a platform of National Unity and Order. Since Kovachev's reforms, Tengaria has been a Unitary Presidential Republic, well known for its strong presidential powers and centralized authority under a dominant-party system with the National Rally dominating Tengarian politics under the leadership of the Kovachev family.
Tengaria is well known for its strong patriotism and sense of national identity, highly centralized government and economy, strong agrarian infrastructure and a low crime rate; however, the country also suffers from corruption scandals and from minority tension. In addition, critics have labeled the country as "undemocratic and authoritarian", especially under the Presidency of Dimitri Kovachev, which saw strong governmental control and use of underhanded means to keep power, including the incarceration and alleged elimination of . The current President, Teodora Kovacheva, has taken measures to improve the public image and to lower abuses while maintaining the incumbent system. Tengaria has strong ties to Narozalica and has been a member of Samorspi since 1984.
Etymology
History
Early History
The earliest known records for the region was originally inhabited by a group of tribes known as the Proto-Tengars, which are a group of tribes believed to be the ancestors of the later Tengar tribes. Little is known about the Proto-Tengars outside of the artifacts they had left behind. Eventually, they came to share a common linguistic background similar to but distinct from the Marolev tribes to their west and their north, and eventually became known as the Tengars. Piraean settlers settled in the southwest region, and also the city of independent city state of Istros along the central Southern Coast. This first coastal city first exposed the Tengars to the civilization of the Piraeans, and was the largest city in the region for many years, until it eventually began to fall into decline. The Piraean language and system of writing did spread to some of the southern tribes but the did not reach most of the tribes. Eventually, the tribes formed various kingdoms, which ruled over different portions of Tengaria for different times. However, only a few kings were able to consolidate large portions of the geographic region, and so it remained disunified.
The realms of the Tengar were located at the far borders of the Solarian Empire, and engaged in warfare with the Empire. The Empire did make several incursions into the Tengar lands and even for a time controlled a slight portion of eastern marches of Tengaria. For the most part however, this border territory was often the center of many conflicts between the Solarians and the Tengars, with the Tengar tribes sometimes making advances into Solarian territory. The Solarians first called the region "Tengaria", which the region was referred to as henceforth. Several settlements and border forts in the East made by the Solarians have been discovered, but they are sparse. While the Tengarians were exposed to Solarian culture, it did not become widespread as of that time. During the late stages of the fourth century AD, the Tengars were attacking the western borders of the Empire, contributing to its collapse in 426.
Rule by the Empire of Arciluco
After the decline and fall of the Solarian Empire, the Solarian rump state of the Empire of Arciluco withstood the attacks of the Tengars, and soon began to actively conquer the region, which took several centuries. The Tengar tribes were incorporated into the Empire, brought Sotrianity, civilization and written language to the Tengarians. The complicated script used by the Amathians eventually was made into the Pavaric script, which suited the Tengarian language more naturally. The Piraean and Vulgar Solarian languages did become spread, but the Tengarians still largely spoke their own tongue. Eventually, the walled villages of the Tengarians developed into towns, and Tengaria flourished and developed under the Empire of Arciluco for several centuries. However, as Tengaria developed, its language and heritage put it at odds with the Amathian state. In addition, the Empire kept on waning in power around the turn of the first millennium; and around the turn of the century, the authority of the Empire had dwindled. The borders of Tengaria were sorely beset by other Marolev tribes, and by the tenth century, things were looking difficult.
Grand Principality
Main Article: Grand Principality of Tengaria
A Tengarian nobleman by the name of Vasil Silen was a general for the border forces of the Empire during the eleventh century. During this period Marolev invasions were particularly fierce, and Vasil managed to hold them off and win battle after battle. His victorious army threatened to proclaim him Emperor of Arciluco, and the Emperor, his authority already weakened, decided instead to establish the Grand Principality of Tengaria and name Vasil as the first Grand Prince, which would give de facto Independence to Tengaria, while still acknowledging the authority of and paying tribute to the Amathian Emperor. This arrangement proved satisfactory, and now Tengaria. Tengaria now was a regional power, although it was still part of the Empire.
Tengarian Empire
Main Article: Empire of Tengaria
The Grand Principality supported the iconodule Emperor during the Amathian Civil War which resulted in the collapse of the Empire of Arciluco and the establishment of the Realm of Thorns. The exiled iconodule Ecumenical Patriarch and the royal family fled to Tengaria. After crowning the Grand Prince as the next Emperor and marrying him to the daughter of the last impaled Emperor, the Empire of Tengaria was formed. It invaded Amathia and was able to conquer the western marches from the iconoclasts, which it lost however when the Unio Trium Nationum came into power. The Empire of Tengaria flourished culturally during this period, and it had increased contact with the Eastern Euclean civilizations as well as with the rising power of Narozalica. However, the power of the Empire began to diminish during the eighteenth century, and with the arising of the Kingdom of Amathia and the regional strength of the Narozalic Empire. The Amathians took the eastern marches of Tengaria during the early part of the nineteenth century, and thus began to fall under the sphere of influence of Narozalica.
Great War
The Empire entered into the Great War on the side of the Grand Alliance and Narozalica, in part at least to recover the eastern marches which were held by Amathia. However, the campaign against Amathia fared very poorly, and the Amathians were able to focus on the Tengarian front, making significant gains. The Tengarian army was pushed back, and by 1930, the Amathians had seized Lenovo. The government capitulated and the Royal Family fled into exile, and the Amathians declared the Empire to be over. A young but charismatic army officer, Simeon Kovachev, gathered several fragments of the Imperial Army and volunteers together in the Northern Hills, and he formed the Tengarian National Army and was proclaimed as the Head of a Provisional Imperial Government while the Emperor was in exile. The National Army was able to fight a Guerrilla War against the Amathian forces. Towards the end of the Great War, Narzolica supported the efforts of Kovachev's army in recapturing certain key positions and pushing back the Amathians from Tengarian territory. At the end of the War, Tengaria was granted the provinces it had lost to Amathia in the nineteenth century.
Republic and Civil War
Simeon Kovachev continued to function as the Head of the Imperial Government for a short duration after the war. However, at Narzolica's insistence, the royal family was not invited back to restore the Empire. Instead, a Republic was declared in 1935, although Kovachev was supposed to take charge. Kovachev, a monarchist, resigned from his position in disgust. Instead, the process of forming the new republic fell into the hands of a committee of republicans, who structured it as a Presidential Republic with a President and a National Assembly as the legislature. The Imperial Senate was transformed into the upper house, while the new National Assembly took most of the legislative power. The prominent Republicans who fashioned the new government came to be called the "Renewal Party", and their candidate, Gregori Ervo, won the first Presidential Election, in part by setting up the system to favor their election. However, the Constitution lacked many ways in which the branches could check the others, which would cause considerable issues with the division of the government later.
The primary opposition party to the Renewal Party was the Restoration Party, which was largely conservative and pro-monarchy, but lacked viable support to do much of anything. However, although the Renewal Party had majorities, soon, however, the party began fighting itself. The economically conservative republicans remained in the Renewal Party, while the moderate economic reformers split into the Reform Party and the farther-left reformers split into the Labour Party. Now none of the parties had a majority in either house, although the Renewal Party had the most seats in the Senate and Reform Party did have the most seats in the National Assembly, which remained true for the next several elections. Vasil Stoychev won the 1940 elections, but no party had a majority in the National Assembly or the Senate. As a result, legislative power faltered, but not completely. Using the people's frustration to his advantage, Vladmir Vasilov was elected as President in 1945 and 1950. However, he could not accomplish much with the legislature actively working against his policies. The Partisan fighting became worse, and the parties became solidified by their area- Labour in the Presidency, Renewal in the Senate and Reform in the National Assembly. By the 1950s, the situation was becoming increasingly worse and worse. The country was in economic shambles, the government could not accomplish anything, and soon violence began erupting on the streets. No Presidential candidate since the founding of the republic had managed to secure over 41% of the popular vote, and things were looking dire.
In the elections of 1955, Dimitri Denov, a war hero of the Great War, ran on a campaign with the Restoration Party, promising to bring stability, to end the political squabbles, and to restore the Tengarian Empire. Sick with the failure of the Republic and the other parties, Denov won the election soundly, and the Restoration Party won a majority of seats in the National Assembly. The republican parties, furious at the outcome, immediately protested the election. The incumbent members of the National Assembly barred the doors from the newly elected members. The Labour unions began to strike against the new regime. And 11 days after assuming office, President Denov was assassinated. His Deputy President, Simeon Radez, immediately assumed office and tried to resume order, but it was too late. The Senate and the National Assembly both fled Lenovo and began amassing support. On the 28th of November, a Assembly of Workers proclaimed Vasilov as President; the Senate declared Rumen Santov, and the Assembly Stoychev. Each of the factions declared that they were the legitimate government of Tengaria, and that Radez's administration was false. Many members of the military deserted during this time to one or other of the factions, although most stayed loyal to Radez under the command of Simeon Kovachev, who had remained as Commander of the Army. The Tengarian Civil War had begun.
The War would last a little under two years. Due to lack of the organized military that the Radez government possessed, the Radez government had the upper hand over the other factions. Within a few months the National Assembly, who had fled to Istros, were captured and Stoychev deposed. However, two months later, President Radev was assassinated as well. Declaring a state of National Emergency, Simeon Kovachev took over as head of the government until the crisis was over. The Senate, which had fled to the hills, proved much harder to capture, and were captured in May of 1957. The Labour Party had fought through resistance cells; however, eventually Vasilov surrendered the following November. The civil war had ended.
Simeon Kovachev's Reforms

In the wake of the Civil War, Simeon Kovachev was left in charge of the government. It was clear that the first system of the Republic was a failure. He could not restore the monarchy like he wanted, due to the international backlash that would no doubt arise, but at the same time, he realized that leaving it would only make things worse. To create a solution, he wrote a new constitution for the Republic, in which the Presidency was stronger and had more ability to prevent the issues which had happened in the early republic. The Constitution was based on a strong government to preserve order and unity, and to minimize the effects of civil strife and factionalism. In order to achieve a began a campaign known as the National Rally. The Rally was a non-partisan movement, running on a platform of establishing national stability, order, and ending partisanship. After decades of political chaos and a Civil War, the idea was massively popular. Kovachev and National Rally swept the elections under the new constitution in 1958, and he began to make reforms and to stabilize the country.
Kovachev Regime
Kovachev served as President for the rest of his life, and was succeeded by his son and his granddaughter to the Presidency.
Geography
Climate
Biodiversity
Administrative Divisions
Politics
Government
Tengaria is a Unitary Republic that uses a Presidential System of government, with heavy powers being granted to the nation's President. The First Constitution of the Republic, which was in place from 1935 until 1958, was overturned after issues with its structure of government and political division caused the rise in the Tengarian Civil War in 1955. Simeon Kovachev authored the Second Constitution after the Civil War, and it was approved by referendum and promulgated on the 15 of March, 1958. The Second Constitution of Tengaria is considered the prime legal document of the Nation, and was meant to provide a strong government to fix the problems with the nation under Kovachev's supervision. Dimitri Kovachev instituted several reforms to the Constitution in 1999.
The President is both the head of state and the head of government, and wields broad executive powers. The President is the Commander-in-Chief of the Tengarian Armed Forces, appoints the members of the Tengarian Senate, can submit or veto legislation, appoints cabinet members and justices with approval of the Senate, to determine and to implimate domestic policy and foreign policy, and has all of the ceremonial duties of a head of state. Under the original constitution, the President served for life; however, President Dimitri Kovachev reformed the limit to unlimited six-year terms as part of his constitutional reforms to bring it into more compliance with modern governments. The President is the most powerful and influential figure in the Tengarian government.
Legislative power is invested in the Grand Assembly of Tengaria, which is a bicameral legislature, consisting in the upper house, the Senate of Tengaria, and the lower house, the National Assembly of Tengaria. The Senate of Tengaria focuses on judicial oversight, presidential appointments, and cultural and ceremonial affairs of Tengaria. Senators serve for life terms or until they resign, and are appointed by the President. There are 50 seats in the Senate. The National Assembly is the house which deals more actively in legislative affairs, and can create legislation, declare war, has power of the purse, approves treaties, and other legislative affairs. There are 380 seats in the National Assembly, serve six year terms.
The government has been dominated by the Kovachev family, who have controlled the powerful Presidency for sixty years, and the political movement they lead, the National Rally, which is socially conservative and explicitly anti-partisan, has consistently dominated the legislature by huge margins. Tengaria and its constitution is considered by most Eastern Euclean sources as undemocratic and authoritatarian. Questions about the veracity of election results, combined with the promotion of the National Rally in media, literature and education, and rumors of suppression of other political movements, give it a low ranking on many international democracy listings.
Foreign Relations and International Institutions
Judiciary and Law Enforcement
Military
Army
Main Article: Tengarian National Army
Since the defeat of the Imperial Army during the Great War and the capitulation of the Empire of Tengaria in 1930 of the Great War, a young general named Simeon Kovachev withdrew the shattered remnants of the Imperial Army to the rural Visoclesian Hills, and reformed them into the Tengarian National Army.
Air Force
Demographics
Ethnic Groups
Languages
Religion
Healthcare
Education
Economy
Science and Technology
Transport
Energy
Culture
Dress
Literature and Philosophy

Tengaria has a rich tradition in both Literature and Philosophy, dating back to the ancient Piraean city state of Istros on the Southern Coast. Tengarian holds that the great philosopher Xenagoras came to Istros and founded a school of Philosophy in the late third century BC. Most historians now agree that this claim is spurious, and that it was one of Xenagoras' disciples, Xenagenes, who founded a school in the city, who is responsible for writing several works later mistakenly attributed to Xenagoras himself, namely, the Mechanics and On Indivisible Lines. Regardless, Teleological philosophy dominated the learning of the independent city state of Istros for the next few centuries through the Agora, the school which Xenagenes, even after the school of thought was largely forgotten in the Solarian Empire and Piraea itself. After the Empire of Arciluco came to dominate the region, the Tengars were exposed to the texts of the other ancient Piraean and Solarian authors, and came to follow the classical mode of the Liberal arts education which was developed in the Solarian Empire and Piraea. In addition to Teleology, Sophism and Stoicism became more widespread and became the dominant stands of philosophy, following the influence of Arciluco. The rise of Sotrianity in Tengaria also brought Sotrian Theology into the forefront, and most Theologians took a Sophist bent. In addition to the thought of antiquity being passed on, with the advent of written script, the three great Tengarian Epics, which up to that point had been passed on orally, were written down. For the next few centuries, Tengaria's philosophic and literary scene would be largely considered just as a part of the Empire of Arciluco.
After the formation of the Grand Principality, the Tengaria's culture began to become more unique, as the writings of Xenagoras once more began to gain traction and support. However, there was still a great deal of dialogue between the two, especially with the Sophist-leaning theologians of the Empire. It was not until the collapse of the Empire of Arciluco and the rise of the Realm of Thorns, together with the rise of the Empire of Tengaria, which lead to the so called Tengarian Renaissance, which lasted from c.1350-1550. With partial influence from famous Scholastic writings and learning of East Euclea caused the Emperor to establish the University of Lenovo as the first West Euclean University in 1462. During this time, the writings of Xenagoras became mainstream, and the Tengarian theologians, turning against the now heretical iconoclast theologians of Amathia, embraced Teleology. The Patriarch of Lenovo, St. Boris the Confessor, famously defended the writings of Xenagoras in his tract On the Unity of Wisdom, which wove together Xenagoran Philosophy with Sotrian Theology, and his work on the In Defense of the Images of God, which defended the usage of Icons. During this period, Tengaria became a center for learning and Orthodox Episemialist thought in the Western portion of Euclea. In addition, Tengarian plays, in an attempt to revive and perfect the old plays of Antiquity, saw a great revival during this period, with men such as Gregori Rumen and Dimitri Vasilev writing influential tragedies and comedies. A great deal of philosophical and theological writings date to this time period, and there was an active culture of intellectual discussion in the Tengarian Empire. The old Agora school, which had fallen into decay, was revitalized.
However, Tengaria soon began to become politically overshadowed by the nearby Narozalica, and its increasing influence began to bring the Tengarian intellectual Renaissance to its end. Tengaria retained its scholarly discourse and schools of learning, but lagged behind the more modern states in terms of scientific advancement. Scholars such as Lawrence Lugin were know to come to Tengaria to access texts or engage in active philosophic discussions. Eventually, modern thought from Eastern Euclea began to make its way into Tengaria, but was often met with hostility by the intellectual community, but slowly modern thought began to make more progress. With Narozalica's influence on the Empire and the formation of the Republic in 1861, Narozalic republican thought began to become prominent in intellectual circles. The focus transferred from the classics to modern Narozalic literature and Eastern Euclean scientific advancements and thought. The academic circles began trying to imitate the other places of Euclea.
At the turn of the twentieth century, an Teleological resurgence began to come again with the famous Znaniya School, which was a group of scholars together at the Agora. At the head of this movement was Ivan Istina, a philosopher, scientist and theologian who attempted to united Xenagoras' thought with modern advancements in science and Sotrian teachings. With him were Archbishop Aleksandar Dilov, who was a prominent Theologian who published several important works the nature of grace and divine providence from Episimialist tradition, as well as other many popular tracts, . His teachings became widely popular in Tengaria at the turn of the century, although they failed to resonate with the current academics at the time. He proposed a plan for the renewal of education in Tengaria, which would later be implemented by one his pupils, Simeon Kovachev. Istina would famously die fighting during the Great War. With the collapse of the Empire and the establishment of the Republic, civil discord undermined the philosophic and literary scene.





