Elbgau Confederation: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
|image_p1 = <!-- Use: [[File:Sin escudo.svg|20px|Image missing]] --> | |image_p1 = <!-- Use: [[File:Sin escudo.svg|20px|Image missing]] --> | ||
|p2 = Kingdom of Shwesia | |p2 = Kingdom of Shwesia | ||
|flag_p2 = | |flag_p2 = Flagge_Königreich_Württemberg.svg | ||
|p3 = | |p3 = Kingdom of Welsbach | ||
|flag_p3 = | |flag_p3 = Flag_of_North_Rhine-Westphalia.svg | ||
|p4 = Grand Duchy of Langquaid | |p4 = Grand Duchy of Langquaid | ||
|flag_p4 = | |flag_p4 = Flag of the Grand Duchy of Langquaid.png | ||
|p5 = Duchy of | |p5 = Duchy of Amretz-Teufurt and Mühlingshausen | ||
|flag_p5 = | |flag_p5 = | ||
|p6 = Duchy of | |p6 = Duchy of Merzenich | ||
|flag_p6 = | |flag_p6 = | ||
|p7 = | |p7 = Duchy of Eustria | ||
|p8 = | |p8 = Duchy of Konreid | ||
|p9 = Principality of Gärlburg | |p9 = Principality of Gärlburg-Altenberg | ||
|p10 = | |p10 = Free City of Flussmund | ||
|p11 = Free City of Pereuth | |p11 = Free City of Estmar | ||
| | |p12 = Free City of Pereuth | ||
|p13 = Free City of Dockfurt | |||
|s1 = Mascyllary Kingdom | |s1 = Mascyllary Kingdom | ||
|flag_s1 = MascyllaFlagIII.png | |flag_s1 = MascyllaFlagIII.png | ||
| Line 74: | Line 75: | ||
|s16 = | |s16 = | ||
|image_flag = Elbgau Confederacy flag.png | |image_flag = Elbgau Confederacy flag.png | ||
|flag_alt = Merchant | |flag_alt = Merchant flag (1791–1793) | ||
|image_flag2 = <!-- Second flag --> | |image_flag2 = <!-- Second flag --> | ||
|flag_alt2 = <!-- Alt text for second flag --> | |flag_alt2 = <!-- Alt text for second flag --> | ||
|flag = Merchant | |flag = Merchant flag (1791–1793) | ||
|flag2 = <!-- Link target under flag2 image. Default: Flag of {{{common_name}}} --> | |flag2 = <!-- Link target under flag2 image. Default: Flag of {{{common_name}}} --> | ||
|flag_type = Merchant | |flag_type = Merchant flag (1791–1793) | ||
|flag2_type = <!-- Displayed text for link under flag2. Default "Flag" --> | |flag2_type = <!-- Displayed text for link under flag2. Default "Flag" --> | ||
|image_coat = Emblem of the Elbgau Confederation.png | |image_coat = Emblem of the Elbgau Confederation.png | ||
| Line 156: | Line 157: | ||
|footnotes = <!-- Accepts wikilinks --> | |footnotes = <!-- Accepts wikilinks --> | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Template:History of Mascylla}} | |||
The '''Elbgau Confederation''' ({{wp|German laguage|Hesurian}}: ''Elbgaubund''), also referred to as the '''Elbgau Confederacy''' or '''North Mascyllary Confederation''' ({{wp|German language|Hesurian}}: ''Nordmaskillischer Bund'') was a [[Mascylla|Mascyllary]] {{wp|Federal state|federal}} idiosyncratic {{wp|association}} of initially 11 {{wp|sovereign state|sovereign states}} from its establishment by the Congress of Rehnern on 20 December 1785 until its dissolution by the Treaty of Langquaid on 18 May 1793. Although in essence a {{wp|confederacy}} of states of equal stance, it was militarly, politically and economically dominated by the [[Kingdom of Aldia]], the confederation's largest and most powerful member state. | The '''Elbgau Confederation''' ({{wp|German laguage|Hesurian}}: ''Elbgaubund'', <small>pronounced:</small> {{wp|Help:IPA/Standard German|[ˈɛlpgaʊ̯bʊnt]}}), also referred to as the '''Elbgau Confederacy''' or '''North Mascyllary Confederation''' ({{wp|German language|Hesurian}}: ''Nordmaskillischer Bund'') was a [[Mascylla|Mascyllary]] {{wp|Federal state|federal}} idiosyncratic {{wp|association}} of initially 11 {{wp|sovereign state|sovereign states}} from its establishment by the Congress of Rehnern on 20 December 1785 until its dissolution by the Treaty of Langquaid on 18 May 1793. Although in essence a {{wp|confederacy}} of states of equal stance, it was militarly, politically and economically dominated by the [[Kingdom of Aldia]], the confederation's largest and most powerful member state. | ||
Following its creation, the confederation became a vehicle for states, most notably Aldia itself, to bring about the Mascyllary unification which was ultimately reached by the outcome of the [[War of the Five Kings]]; and by the dissolution of the confederation in light of its succeeding [[Mascyllary Kingdom]], again under Aldian supervision and control, as a unified {{wp|nation state}}. While attempts had been made by Adwhin to establish a counterweight to the confederation with the remaining neutral Mascyllary states, efforts proved fruitless and led to a dramatic rise in tensions between Aldia and Adwhin. Furthermore, the rapid decline of the [[First Cuthish Empire]] destabilized the delicate {{wp|balance of powers}} of Mascylla. | Following its creation, the confederation became a vehicle for states, most notably Aldia itself, to bring about the Mascyllary unification which was ultimately reached by the outcome of the [[War of the Five Kings]]; and by the dissolution of the confederation in light of its succeeding [[Mascyllary Kingdom]], again under Aldian supervision and control, as a unified {{wp|nation state}}. While attempts had been made by Adwhin to establish a counterweight to the confederation with the remaining neutral Mascyllary states, efforts proved fruitless and led to a dramatic rise in tensions between Aldia and Adwhin. Furthermore, the rapid decline of the [[First Cuthish Empire]] destabilized the delicate {{wp|balance of powers}} of Mascylla. | ||
Due to Aldia's significance in the confederation [[Monarchy of Mascylla#List|King Albert William I]]'s successor [[Monarchy of Mascylla#List|Lucas I]] was awarded the position of {{wp|head of state}} as President of the ''Bundespräsidium'', ''{{wp|de facto}}'' exercising full control over the confederation; federal law could only be enabled by the approval of the Federal Senate (''Bundessenat'') composed of elected or appointed envoys of the member states. With the onset of the [[Cuthish Revolution]] in 1789, the Elbgau Confederation gradually repurposed itself from an opportunistic alliance of sovereign states into an increasingly {{wp|nationalism|nationalistic}} project; Lucas I of Aldia spearheaded this development, recognizing its potential to amplify Aldian power in an united Mascylla on the grounds of Mascyllary patriotism and nationalism (''Maskenfrage''). However, he disapproved of the introduction of {{wp|Enlightenment|Enlightened}} {{wp|liberalism|liberalist}} and other revolutionary ideas. | |||
Today, most historians consider the Elbgau Confederation to be a mere puppet or instrument of Aldia, ineffective and indecisive in enforcing its own political views in favor of an Aldian vision of Mascyllary unification. However, it is seen as a major milestone of Mascyllary unification both politically, but also economically (via the North Mascyllary Customs Union (''Nordmaskillischer Zollverein'') in the 1760s) and to a broader extent, socially, embodying a symbol of unity among its member states. It was also among the first proto {{wp|democracy|democracies}} in Mascyllary history and many of its institutional features are still reflected in the [[Politics of Mascylla|Crowned Republic's political system]] today. | Today, most historians consider the Elbgau Confederation to be a mere puppet or instrument of Aldia, ineffective and indecisive in enforcing its own political views in favor of an Aldian vision of Mascyllary unification. However, it is seen as a major milestone of Mascyllary unification both politically, but also economically (via the North Mascyllary Customs Union (''Nordmaskillischer Zollverein'') in the 1760s) and to a broader extent, socially, embodying a symbol of unity among its member states. It was also among the first proto {{wp|democracy|democracies}} in Mascyllary history and many of its institutional features are still reflected in the [[Politics of Mascylla|Crowned Republic's political system]] today. | ||
[[Category:Mascylla]][[Category:History of Mascylla]] | ==History== | ||
===Background=== | |||
===Establishment=== | |||
===Cuthish Revolution and impact=== | |||
===Romanticism and nationalism, ''Maskenfrage''=== | |||
===Mascyllary unification and dissolution=== | |||
==Political makeup and military== | |||
==Population and economy== | |||
==Legacy== | |||
[[Category:Mascylla]][[Category:History of Mascylla]][[Category:History of Aurorum]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:46, 16 January 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Elbgau Confederation Elbgaubund | |
|---|---|
| 1785–1793 | |
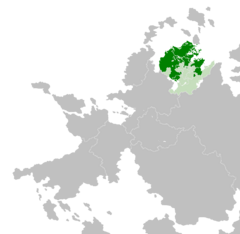 The Elbgau Confederation upon its establishment in 1785: member states in green, remaining Mascyllary states in light green | |
 | |
| Capital | Langquaid (1785–87) Augusthal (1787–1793) |
| Common languages | Hesurian · Cuthish · Waldish · Temarian · Valimian · Cuthish · Falian |
| Religion | Semitarism |
| Government | Federal association of Mascyllary sovereign states |
| President of the Präsidialmacht | |
• 1785–1793 | Lucas I |
| Legislature | Federal Senate (Bundessenat) |
| Historical era | 1785–1793 |
| 20 December 1785 | |
• Constitution adopted | 8 January 1786 |
| 1789–1793 | |
• Treaty of Langquaid | 18 May 1793 |
| Population | |
• 1790 | 22,830,150 |
| Currency | Mascyllary Unionsthaler (1785–1790) Mascyllary Karning (1790–1793) |
| Today part of | |
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Mascylla |
 |
|
|
The Elbgau Confederation (Hesurian: Elbgaubund, pronounced: [ˈɛlpgaʊ̯bʊnt]), also referred to as the Elbgau Confederacy or North Mascyllary Confederation (Hesurian: Nordmaskillischer Bund) was a Mascyllary federal idiosyncratic association of initially 11 sovereign states from its establishment by the Congress of Rehnern on 20 December 1785 until its dissolution by the Treaty of Langquaid on 18 May 1793. Although in essence a confederacy of states of equal stance, it was militarly, politically and economically dominated by the Kingdom of Aldia, the confederation's largest and most powerful member state.
Following its creation, the confederation became a vehicle for states, most notably Aldia itself, to bring about the Mascyllary unification which was ultimately reached by the outcome of the War of the Five Kings; and by the dissolution of the confederation in light of its succeeding Mascyllary Kingdom, again under Aldian supervision and control, as a unified nation state. While attempts had been made by Adwhin to establish a counterweight to the confederation with the remaining neutral Mascyllary states, efforts proved fruitless and led to a dramatic rise in tensions between Aldia and Adwhin. Furthermore, the rapid decline of the First Cuthish Empire destabilized the delicate balance of powers of Mascylla.
Due to Aldia's significance in the confederation King Albert William I's successor Lucas I was awarded the position of head of state as President of the Bundespräsidium, de facto exercising full control over the confederation; federal law could only be enabled by the approval of the Federal Senate (Bundessenat) composed of elected or appointed envoys of the member states. With the onset of the Cuthish Revolution in 1789, the Elbgau Confederation gradually repurposed itself from an opportunistic alliance of sovereign states into an increasingly nationalistic project; Lucas I of Aldia spearheaded this development, recognizing its potential to amplify Aldian power in an united Mascylla on the grounds of Mascyllary patriotism and nationalism (Maskenfrage). However, he disapproved of the introduction of Enlightened liberalist and other revolutionary ideas.
Today, most historians consider the Elbgau Confederation to be a mere puppet or instrument of Aldia, ineffective and indecisive in enforcing its own political views in favor of an Aldian vision of Mascyllary unification. However, it is seen as a major milestone of Mascyllary unification both politically, but also economically (via the North Mascyllary Customs Union (Nordmaskillischer Zollverein) in the 1760s) and to a broader extent, socially, embodying a symbol of unity among its member states. It was also among the first proto democracies in Mascyllary history and many of its institutional features are still reflected in the Crowned Republic's political system today.

