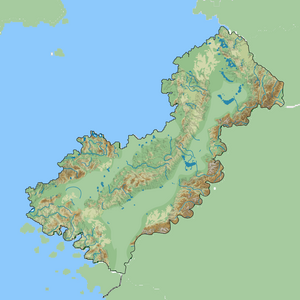
Romaia
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Romaian Empire Ρωμαϊκή Αυτοκρατορία (Greek) Romaikí Aftokratoría | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Εν τούτω νίκα" "In this sign you will conquer" | |
| Anthem: "Η Προσευχή" "the Prayer" | |
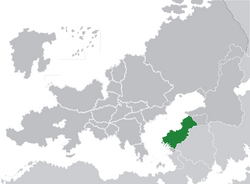 Location of Romaia (dark green) in Eulabia (grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Constantinoupoli |
| Official language and national language | Greek |
| Ethnic groups | Romaians |
| Religion (2019) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Romaian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Emperor | Ioannis IV |
| Leon Sakellarios | |
| Ieremias Mantalos | |
| Eustratios Mauros | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Formation | |
| 12 April 1805 | |
| 1 October 1868 | |
| 4 December 1967 | |
• Accession to the ETO | 25 September 2023 |
| Area | |
• Total | 576,035 km2 (222,408 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 1.05% |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | 57.602.426 (15th) |
• 2023 census | 57,602,426 |
• Density | 99.5/km2 (257.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $2.864 trillion |
• Per capita | $50,137 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $2.774 trillion (7th) |
• Per capita | $48,083 (4th) |
| Gini (2019) | 38.7 medium (5th) |
| HDI (2019) | very high (2nd) |
| Currency | Romaian Lira (£) (LIR) |
| Time zone | UTC +3 (EET) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +40 |
| ISO 3166 code | RA |
| Internet TLD | .ra .ρω |
| |
Romaia (Greek: Ρωμανία, romanized: Romania), officially the Romaian Empire (Greek: Ρωμαϊκή Αυτοκρατορία, romanized: Romaiki Aftokratoria), is a country located in the South of the Pontus in Southeastern Eulabia. The country covers a total are of 576035 km2 (222408.4 sq.mi) and shares land borders with Isfahan, Haramoun and Sanetia. With around 60 million inhabitants, Romaia is the fifth-most populous state of Eulabia. Due to its geographical location at the border between Eulabia and Hasua, Romaia has historically been home to myriad peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient peoples dispersed throughout modern Romaia, the most predominant being the Indo-European Hellenic peoples, beginning from the Bronze Age, Hellenics established settlements in the Western Romaia, while Celts and Italics inhabited Eastern Romaia.
During the Middle Ages, Romaian Kingdom endured numerous Barbarian and Islamic invasions, but by the 16th century, numerous city-states and maritime republics, mainly in the Western regions of Romaia, became prosperous through trade, commerce, and banking, laying the groundwork for modern capitalism. These mostly independent statelets served as Eulabia's main trading hubs with Eulabia and the Eastern world, often enjoying a greater degree of democracy than the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Eulabia. The Renaissance spread in Romaia bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration, and art. Centuries of foreign conquest and meddling, and the rivalry and infighting between the Romaian city-states, such as the Romaian Wars of the 17th and 18th centuries, left Romaia politically fragmented, and it was further partially conquered and divided among multiple foreign powers over the centuries.
Romaia reached its political and military zenith in the late 19th century under Constantine V, subjugating Romaian postfeudal states and Marine republics and establishing the Romaian Empire. Subsequent decades saw a period of optimism, cultural and scientific flourishing, as well as economic prosperity known as the Belle Époque. Romaia was among the Allied powers of the Great War and courageously defended and liberated it's land.
Nowadays Romaia is a unitary constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of governance in Eulabia. Romaia covers an area of 576035 km2 a largely temperate seasonal climate and the Mediterranean climate.
The area of Romaia extends from the Pontus Novus and the Illian sea to the Parthinian Mountains. It is bordered by Haramoun to the south, Isfahan to the east and Sanetia to the North.
Romaia has a very high level of human development and has one the highest life expectancy in Eulabia. It is a great power in global affairs, being one of the five permanent members of the International Security and Arbitration Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. Romaia is a permanent member is a founding and leading member of the Eulabian Community as well as a key member of the ETO. As a reflection of its extensive cultural wealth, Romaia is the most visited country in Eulabia.
Name
Romans or Rhomaioi (Ῥωμαῖοι; sg. Ῥωμαῖος Rhomaios) and Romioi (Ρωμιοί; sg. Ρωμιός Romios), is the name by which the Romaians are known since the Middle Ages. Overall, the foreign borrowed name (Romans) initially had a more political than national meaning, which went hand in hand with the universalizing ideology of Christianity and Hellenic-Roman culture that aspired to encompass all nations of the world under one true God. Various ethnicities could apply their own ethnonyms or toponyms to disambiguate citizenship from genealogy, which is why the historian Procopius prefers to call the Romaians as Hellenized Romans, while other authors use Romhellenes and Graecoromans, aiming to indicate descent and citizenship simultaneously. Nowadays it's almost impossible to determine ethnic composition of Romaians as Romaia throughout ages have been a melting pot of many different peoples.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
The earliest evidence of the presence of human ancestors in Romaia, dated to 270,000 BC, is to be found in the Samarina cave, in Illia. All three stages of the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic) are represented in Romaia.
Romaia is home to the first advanced civilizations in Eulabia, beginning with the Leukian civilization in the modern Seleukia, the Makednes civilization on the islands of the Illian Sea at around 3200 BC, the Galatian civilization in Galatia (2700–1500 BC), and then the Herminian civilization on the mainland (1600–1100 BC). The Herminians gradually absorbed the Illians, but collapsed violently around 1150 BC, along with other civilizations, during the regional event known as the Late Bronze Age collapse. This ushered in a period known as the Hellenic Dark Ages, from which written records are absent.
Iavonic colonies
The 8th century BC witnessed the emergence of Iavonic colonists onto the shores of what is now known as Romaia. Hailing from regions influenced by Ancient Iavonic culture, these settlers embarked on a journey that would result in the transplantation of their culture, dialects of the Ancient Greek language, religious practices, and traditions of independent polis to the newly established settlements in Romaia.
As the Iavonic colonists settled in their new homeland, they carried with them a rich tapestry of cultural elements rooted in their Iavonic heritage. The Ancient Greek language, as expressed in various dialects, served as a vehicle for the transmission of their intellectual, artistic, and social expressions. The Iavonic settlers, while adapting to the local environment, continued to practice their religious rites, uphold their traditions of city-state governance (polis), and foster a sense of communal identity.
In the wake of their migration, these Iavonic settlers laid the foundation for what would evolve into a distinct Romaian civilisation in the heart of Romaia. The intermingling of Iavonic culture with the local population gave rise to a unique amalgamation, as elements of Ancient Greek thought, governance structures, and artistic pursuits blended with the indigenous backdrop.
The progression of Iavonic influence and the burgeoning Romaian civilisation within Romaia inevitably intersected with the preexisting Celtic societies in the region. This interaction between the Hellenic and Celtic worlds, although characterized by periods of both cooperation and conflict, yielded a complex amalgam of cultural, linguistic, and societal exchanges.
The Iavonic colonisation of Romaia in the 8th century BC holds enduring historical significance. It marked the introduction of Ancient Greek culture, language, and governance systems to the region, laying the groundwork for the development of a robust Hellenic civilisation. The interaction with native Celtic societies contributed to the synthesis of diverse cultural elements, fostering a cultural mosaic that shaped the trajectory of Romaia's history.
Italic invasion
The first Italic tribes to step into Romaian soil were Euganoi, vorbicoi and molscoi. They settled the Northern part of the Romaian coast founding colonies. Italic culture spread across Western Romaia with increase of trade between Iavonics and Italics.
The historical narrative of Romaia is significantly enriched by the arrival of the first Italic tribes on its shores, a migratory event that introduced the Euganoi, Vorbicoi, and Molscoi to the Northern reaches of the Romaian coast. This infusion of Italic influence proved to be a watershed moment in the region's cultural and historical trajectory, as these tribes established colonies and propagated their distinct cultural ethos across Western Romaia.
Upon their arrival, the Italics displayed their pioneering spirit by establishing colonies in the Northern part of the Romaian coast. These settlements not only served as bastions of Italic culture but also served as hubs of trade, commerce, and cultural exchange. The act of colonization was a complex interplay between the preservation of ancestral traditions and the adaptation to the demands of the new environment.
These colonies served as melting pots where the traditions of the Italic tribes intertwined with the existing cultural tapestry of the region, resulting in a vibrant mosaic of ideas and practices. The establishment of these colonies marked the first tangible foothold of Italic influence in Romaia, setting the stage for a gradual proliferation of Italic culture across Western Romaia.
Middle Ages
Early Modern
The Eastern War
Unification
The Empire
Mauromatis regime
World War II
Contemporary Romaia
The modern history of Romaia begins after the Great War includes major social and economic development. The post-Great War era saw Romaia actively engaging in diplomatic initiatives and forging new international relationships. As the nation sought to solidify its place in the global arena, it participated in international organizations, trade agreements, and diplomatic treaties, thereby contributing to regional stability and cooperation. The period following the Great War was characterized by a surge in social reforms aimed at enhancing the lives of Romaia's citizens. Governments enacted policies to improve education, healthcare, and social welfare, recognizing the intrinsic value of human capital in driving societal progress. Central to the modern history of Romaia was its economic renaissance. With a vision for prosperity, the nation embraced industrialization, technological advancement, and infrastructural development. The post-war era witnessed the growth of industries, the expansion of transportation networks, and the modernization of agricultural practices. These endeavors not only bolstered the economy but also fostered employment opportunities and improved living standards for the populace.
Geography
The Romaian territory is situated in Southeastern Eulabia. Most of Romaia's land borders are roughly delineated by natural boundaries and geographic features: to the east, the Parthinian mountains and the Pontus Novus to the west. The country is encircled by seas on three sides: the Illian sea to the south, the Pontus Novus to the west. The country's total area is 576035 km2 (222408.4 sq.mi).
Romaia is situated mostly between latitudes 36° and 43° N, and longitudes TBD° W and TBD° E, on the southern edge of Eulabia, and thus lies within the northern temperate zone.
The climate of Romaia is primarily Mediterranean, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The mountainous areas of Central and Northeastern Romaia (parts of Aedonia, Galatia, Parthinia) feature an Alpine climate with heavy snowfalls. Snowfalls occur every year in the mountains and central and Eastern areas.
Politics
The constitutional history of Romaia dates back to the constitution of 1805, democratic traditions and values are deeply rooted in Romaian culture, identity and politics. The current constitution was approved by referendum on 12 November 1967, establishing a framework consisting of executive, legislative and judicial branches.
Government

|

|
| Ioannis IV Emperor |
Leon Sakellarios Prime Minister |
Romaia is a constitutional monarchy, with a hereditary monarch and a bicameral parliament (Greek: Ρωμαϊκό Κοινοβούλιο).
The legislative branch is made up of the National Assembly (Εθνοσυνέλευση), a lower house with 450 members, elected by popular vote on block lists by proportional representation to serve four-year terms, and the Senate (Σύγκλητος), an upper house with 259 seats of which 208 are directly elected by popular vote, using a limited voting method, and the other 51 appointed by the regional legislatures to also serve four-year terms.
The executive branch consists of a Council of Ministers presided over by the prime minister, who is nominated as candidate by the monarch after holding consultations with representatives from the different parliamentary groups, voted in by the members of the lower house during an investiture session and then formally appointed by the monarch.
Romaia's three major political parties are the People's Party, the Liberal Party and +Eulabia. During the 2020 general election these three parties and their coalitions won 270 out of 500 seats available in the National Assembly. The centre-right coalition, which included Leon Sakellarios' People's Party, Liberal Party, and +Eulabia, won a majority of the seats in parliament. The rest of the seats were taken by United Left, Labour Party, Libertarian Party and Zoi.
- Head of State (Emperor)
- Ioannis IV, since 14 February 2006
- Government
Main article: Government of Romaia- Prime minister (head of government) or "President of the Government" (Πρόεδρος της Κυβέρνησης): Leon Sakellarios, elected 20 September 2020.
- Deputy prime ministers (designated by the Prime Minister): TBD.
- Ministers (designated by the Prime Minister): Second government of Leon Sakellarios.
The Prime Minister, deputy prime ministers and the rest of ministers convene at the Council of Ministers.
Law and criminal justice
The law of Romaia has a plurality of sources of production. These are arranged in a hierarchical scale, under which the rule of a lower source cannot conflict with the rule of an upper source (hierarchy of sources). The Constitution of 1967 is the main source. The judiciary of Romaia is based on Roman law modified by the Napoleonic code and later statutes. The Supreme Court of Cassation is the highest court in Romaia for both criminal and civil appeal cases. The Constitutional Council rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution.
Romaia uses a civil legal system, wherein law arises primarily from written statutes; judges are not to make law, but merely to interpret it (though the amount of judicial interpretation in certain areas makes it equivalent to case law in a common law system). Basic principles of the rule of law were laid in the Napoleonic Code. In agreement with the principles of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, law should only prohibit actions detrimental to society. That is, Law should lay out prohibitions only if they are needed, and if the inconveniences caused by this restriction do not exceed the inconveniences that the prohibition is supposed to remedy.
Romaian law is divided into two principal areas: private law and public law. Private law includes, in particular, civil law. Public law includes, in particular, administrative law, constitutional law and criminal law. However, in practical terms, Romaian law comprises three principal areas of law: civil law, criminal law, and administrative law. Criminal laws can only address the future and not the past (criminal ex post facto laws are prohibited). While administrative law is often a subcategory of civil law in many countries, it is completely separated in Romaia and each body of law is headed by a specific supreme court: ordinary courts (which handle criminal and civil litigation) are headed by the Supreme Court of Cassation and administrative courts are headed by the Council of State.
To be applicable, every law must be officially published in the Official magazine of the State.
Law enforcement
The Romaian law enforcement system is complex, with multiple police forces. The national policing agencies are the Εθνική Αστυνομία (National Police), the Εθνική Χωροφυλακή (National Gendarmerie), Τελωνείο (Customs), and the Σωφρονιστική Διοίκηση (Penitentionary Administration).

The National Police is a civil police supervised by the Interior Ministry, while the National Gendarmerie is a gendarmerie supervised by the Defence Ministry; both share duties in law enforcement and the maintenance of public order. Within the Gendarmerie is a unit devoted to combating environmental crime. The Customs is responsible for combating financial crime and white-collar crime. The Penitentionary Administration is responsible for guarding the prison system. Although policing in Romaia is primarily provided on a national basis, there also exists Δημοτική Αστυνομία (municipal police).
Foreign relations
The foreign relations of the Romaian Empire are the Romaian government's external relations with the outside world. Located in Eulabia, Romaia has been considered a major Western power since its unification in 1868. Its main allies are the ETO and GDI countries and the EC states, three entities of which Romaia is a founding member. Romaia is a member and a strong supporter of a wide number of international organisations, such as the GDI and the Council of Eulabia.
Romaia is an important actor in the Pontus region and has close relations with the Greek-speaking countries in Eulabia and Hasua. Romaia is currently commanding various multinational forces and has significant troops deployed all over the world for peacekeeping missions, and for combating organized crime, illegal drug trade, human trafficking, piracy and terrorism.
Military
The Romaian Armed Forces (Ρωμαικές Ένοπλες Δυνάμεις) are the military and paramilitary forces of Romaia, the commander-in-chief is the Emperor of Romaia, Ioannis IV. The next military authorities in line are the Prime Minister and the Minister of Defence. The fourth military authority of the State is the Chief of the Defence Staff. The Defence Staff (Γενικό Επιτελείο Εθνικής Άμυνας) assists the Chief of the Defence Staff as auxiliary body. According to a 2018 study by RCG Group, the Romaian Armed Forces are the third most powerful in Eulabia after Commonwealth of Eulabia. Romaia's annual military expenditure in 2019 was NS$80 billion, or 2.9% of its GDP. There has been no national conscription since 1997. They consist of the Romaian Army (Ρωμαικός Στράτος), Romaian Navy (Πολεμικό Ναυτικό), the Romaian Air Force (Πολεμική Αεροπορία), National Gendarmerie (Εθνική Χωροφυλακή), the Airborne corps (Σώμα Αερομεταφερόμενων) and the Marine corps (Σώμα Πεζοναυτών).
Romaia has been a recognised nuclear state since 1960. The Romaian nuclear force consists of four TBD class submarines equipped with submarine-launched ballistic missiles. In addition to the submarine fleet, it is estimated that Romaia has about 60 ASMP medium-range air-to-ground missiles with nuclear warheads, of which around 50 are deployed by the Air Force using the Typhonas aircraft, while around 10 are deployed by the Navy's attack aircraft, which operate from the nuclear-powered aircraft carrier Konstantinos VI.
Romaia has major military industries with one of the largest aerospace industries in the world. Its industries have produced such equipment as the Typhonas fighter, the Konstantinos VI aircraft carrier, the TBD missile and the Heracles 2 tank among others.
The Romaian Army is the national ground defence force. Its best-known combat vehicles are the Ares fighting vehicle and Heracles 2 tank. The ground force of Romaia dates back to the Romaian Kingdom. It fought against the Isfahani Empire in the nineteenth century, during the Great War and participated in the Unification of Romaia. On 1 March 2008 it became a professional all-volunteer force when conscription was finally ended.
The navy of Romaia was created in 1805, following the proclamation of the Kingdom of Romaia, as the Βασιλικό Ναυτικό. The new navy's baptism of fire came during the TBD. During the Great War, it spent its major efforts in the Pontus, fighting the TBD Navy. It is a blue-water navy. The Maritime Gendarmerie is a subordinate of the navy.
The air force of Romaia was founded as an independent service arm on 13 September 1930. It was involved in its first military operations during the Great War. The number of aircraft in service with the Romaian Air Force varies depending on the source; the Ministry of Armed Forces gives a figure of 680 aircraft in 2014. According to 2019 data, this figure includes 350 combat aircraft, the most famous of which is Typhonas. As of 2019, the Romaian Air Force employs a total of 62,000 regular personnel.
The Airborne Corps (Greek: Σώμα Αερομεταφερόμενων, romanised: Sòma Aerometaferòmenon) are the airborne forces branch of the Romaian Armed Forces. It was formed TBD. Troops of the Romaian Airborne Corps traditionally wear maroon beret and keffiyah. The Romaian Airborne Forces utilizes a range of specialist airborne warfare vehicles . They traditionally have a larger complement of heavy weaponry than most contemporary airborne forces.
An autonomous corps of the military, the Chorofylaki is the gendarmerie and military police of Romaia, policing the military and civilian population alongside Romaia's other police forces. While the different branches of the Chorofylaki report to separate ministries for each of their individual functions, the corps reports to the Ministry of the Interior when maintaining public order and security
Administrative divisions
Romaia is constituted by 20 regions (περιφέριες), departments (νόμοι) or metropolies (μητροπολίες), and municipalities (δήμοι).
The Regions of Romaia (Greek: Περιφέριες της Ρωμανίας) are the first-level administrative divisions of the Romaian Empire, constituting its second NUTS administrative level. There are twenty regions. Under the Constitution of Romaia, each region is an autonomous entity with defined powers. Each region is divided into a number of departments.
This is a list of regions in Romaia:
| Arms | Regions | Population | % | Capital | Departments or Metropolies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apollonia | 13,101,674 | 22,7% | Constantinoupoli | 11 | |
| Aedonia | 3,360,551 | 5,8% | Nikomidia | 10 | |
| Klaudia | 6,893,274 | 11,9% | Adras | 11 | |
| Eusebia | 1,282,763 | 2,2% | Loukania | 6 | |
| Galatia | 9,333,855 | 16,2% | Nikaia | 12 | |
| Cephallonia | 992,875 | 1,7% | Ikonia | 4 | |
| Pontis | 1,940,804 | 3,7% | Poseidonia | 5 | |
| Parthinia | 1,841,703 | 3,2% | Celendria | 8 | |
| Tauria | 916,950 | 1,5% | Amos | 5 | |
| Seleukia | 2,311,124 | 4% | Salona | 7 | |
| Chalkitania | 1,459,026 | 2,5% | Lakedonia | 5 | |
| Ikaria | 1,898,761 | 3,3% | Silivria | 6 | |
| Pallania | 846,449 | 1,5% | Narona | 4 | |
| Illia | 1,843,955 | 3,2% | Sebastoupoli | 6 | |
| Kolonia | 1,511,918 | 2,6% | Korkyra | 5 | |
| Imperia | 1,799,277 | 3,1% | Platea | 5 | |
| Pelagonia | 1,540,856 | 2,7% | Tyras | 6 | |
| Philadelphia | 2,726,231 | 4,8% | Philadelphia | 6 | |
| Herminia | 1,039,682 | 1,8% | Panormo | 5 | |
| Samonitia | 960,698 | 1,7% | Sozona | 5 |
Economy
Romaia has a major advanced capitalist mixed economy, one of the largest in Eulabia and one of the most industrialised in the world, leading in imports and exports. It's a highly developed country renowned by innovative, creative and technologically advanced business with a competitive agricultural and industrial sectors (including automotive, aerospace, defence, design, fashion, food and IT industries).

Romaia is characterised by a smaller number of global multinational corporations than other economies of comparable size and many dynamic small and medium-sized enterprises, notoriously clustered in several industrial districts, which are the backbone of the Romaian industry. This has produced a manufacturing sector often focused on the export of niche market and luxury products, that if on one side is less capable to compete on the quantity, on the other side is more capable of facing the competition from Hasuan economies based on lower labour costs, with higher quality products.
The automotive industry is a significant part of the Romaian manufacturing sector, with over 100 thousand firms and almost 485,000 employed people in and a contribution of TBD% to Romaian GDP. EVORA is currently the world's tbd-largest auto maker. The country boasts a wide range of acclaimed products, from compact city cars to luxury supercars such as Pienero, Margariti, and Alea Venardi.
There are three main types of credit institutions and banks in Romaia. Commercial banks, which include three national banks, chartered banks, cooperative banks, and private banks across the country are the most common. However, savings banks organized on a provincial or regional basis in addition to investment institutions that issue bonds and provide medium- and long-term credit for public works and agriculture provide additional financial services. Midei Bank is amond the world's oldest banks in continuous operation, and the fourth-largest Romaian commercial and retail bank. The origins of modern banking can be traced to medieval and early Renaissance, to the rich cities in the west like Constantinoupoli, Adras, Nikaia. The Midei and Magdalinoi families dominated banking in renaissance Constantinoupoli, establishing branches in many other parts of Romaia. Romaian Credit is one of the largest bank in Eulabia by capitalization.
Agriculture
According to archaeological data the first agricultural settlements began in Romaia around the 2th millennium BC. Archaeologists have clearly identified the paths followed by the first Anatolian peasants who spread the Neolithic Revolution across Romaia, primarily on the Pontic and Illian coast and along Therma. Initially they arrived from Eulabia by sea, where they founded agricultural villages similar to those of the Fertile Crescent.
According to the last national agricultural census, there were 1.8 million farms in 2010. The vast majority (94%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 ha (20 acres) in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), grain fields take up 21%, olive tree orchards 18.2%, vineyards 5.4%, citrus orchards 3.8%, sugar beets 1.7%, and horticulture 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%).
Romaia is one of the leading producers of olive oil, fruits (apples, olives, grapes, oranges, lemons, pears, apricots, hazelnuts, peaches, cherries, plums, strawberries and kiwifruits), and vegetables (especially artichokes and tomatoes).
Quality goods in which Romaia specialises, particularly wines and regional cheeses such as Pergamou Livadias, are often protected under the quality assurance labels PDO. This geographical indication certificate, which is attributed by the government, is considered important in order to avoid confusion with low-quality mass-produced ersatz products.
Transport
Rail transport
Romaias's railway network, which stretches TBD kilometres (TBD mi) as of 2019,is one of the most extensive in the world. It is operated by the Romaian Rail, and high-speed trains include the TYT, which travels at 320 km/h (199 mph). Rail connections exist to all other neighbouring countries. Intra-urban connections are also well developed, with most major cities having underground or tramway services complementing bus services. Romaian Rail is the major Romaian railway infrastructure and service operator. Though Romaian Rail is a private company, the government still holds all shares and therefore Romaian Rail can still be called a state-owned company. Since its reformation under private law in 2001, Romaian Rail no longer publishes details of the tracks it owns; in addition to the Romaian Rail system there are about 280 privately or locally owned railway companies which use ESA tracks in open access.
Highways
There are approximately TBD kilometres (TBD mi) of serviceable roadway in Romaia. Romaian roads also handle substantial international traffic, connecting with cities in neighbouring countries. The Romaian motorways called (Αυτοκινητόδρομοι). The speed limit is 130 km/h. The Motorway network had a total length of about 6,870 kilometres (4,268 mi) in 2019, which ranks it among the most dense and longest systems in the world. They have their own, green-coloured signs and their own numbering system. All motorways are named by using the capital letter A, followed by a blank and a number (for example A 8).
Air transport
There are TBD airports in Romaia. Constantinos Forza Airport, located in the vicinity of Constantinoupoli, is the largest and busiest airport in the country, handling the vast majority of popular and commercial traffic and connecting Constantinoupoli with virtually all major cities across the world. Aeromaia (Αερωμάια) is the national carrier airline, although numerous private airline companies provide domestic and international travel services. There are ten major ports in Romaia, the largest of which is in Apollonia region, which also is the largest bordering the Pontus Novus.
Tourism
Romaia has been a touristic destination for years starting from Early Modern.
Factors of tourist interest in Romaia are mainly culture, cuisine, history, fashion, architecture, art, religious sites and routes, naturalistic beauties, nightlife, underwater sites and spas. Winter and summer tourism are present in many locations in the Mountains, while seaside tourism is widespread in coastal locations on the Pontus. Romaia is the leading cruise tourism destination in the Eastern Pontus.
The most visited regions of Romaia, measured by nights spent in tourist accommodation establishments, are Apollonia, Illia, Galatia, Philadelphia and Klaudia. Constantinoupoli is the TBD most visited city in Eulabia and the TBD in the world, with TBD million arrivals in 2017 while Nikaia is the TBD worldwide with TBD million tourists. In addition, Nauplia and Salona are also among the world's top 100 destinations.
Demographics
Largest cities
| Rank | City | Population | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.164.388,00 | ||
| 2 | 2.478.564,00 | ||
| 3 | 1.148.294,00 | Klaudia | |
| 4 | 678.564,00 | Ikaria | |
| 5 | Korkyra | 652.876,00 | |
| 6 | Philadelphia | 623.780,00 | |
| 7 | 615.273,00 | ||
| 8 | 592.507,00 | ||
| 9 | 543.248,00 | ||
| 10 | 542.210,00 | ||
| 11 | 417.895,00 | ||
| 12 | 381.037,00 | ||
| 13 | 378.120,00 | ||
| 14 | Ikonia | 349.019,00 | |
| 15 | 240.414,00 | ||
| 16 | Sozona | 232.457,00 | |
| 17 | Celendria | 217.675,00 | |
| 18 | Narona | 211.785,00 | |
| 19 | 198.524,00 | ||
| 20 | 178.973,00 |
Languages
The first textual evidence of the Greek language in Romaia dates back to the 10th century BC. Greek was a widely spoken lingua franca in the Pontus region, especially in its Eastern part and beyond during Classical Antiquity, and would eventually become the official parlance of the Ancient Romaian Kingdom.
During the 19th and 20th centuries there were major disputes known as the Romaian language question, on whether the official language of Romaia should be called Romaian or Greek, shoud the official language be the archaic Katharevousa, created in the end of 19th century and used as the state and scholarly language, or the Dimotiki, the form of the Greek language which evolved naturally from Koine and was the language of the people.
Romaia is today relatively homogeneous in linguistic terms, with a large majority of the native population using Greek as their first or only language. Dialect info TBD.
Twelve "historical minority languages" (TBD) are formally recognised: Italian, Herminian, Romaic and Ladin. A number of other languages are not recognised by Romaian law.
Romani is also spoken by Christian Roma in other parts of the country. Further minority languages have traditionally been spoken by regional population groups in various parts of the country. Their use has decreased radically in the course of the 20th century through assimilation with the Greek-speaking majority.
The Jewish community in Romaia traditionally spoke Yevanic (Judeo-Greek), today maintained only by a few thousand speakers. Other notable minority languages include Koptic, Italian, Georgian and Armenian.
Religion
The Romaian Constitution recognises Eastern Orthodoxy as the 'prevailing' faith of the country, while guaranteeing freedom of religious belief for all. According to the 2019 polls, an estimated 89% of Romaian citizens identify themselves as Eastern Orthodox, belonging to the Romaian Orthodox Church, which uses the Byzantine rite and the Greek language, the original language of the New Testament.
Catholics made up 4% of the total population in 2017. The Catholic community is represented by indigeneous Catholic population and has increased in size in recent years due to immigration.
Protestants, including Romaian Evangelical Church stand at about TBD. The official church, Eastern Orthodox, and the State reluctantly gave permission for Pentecostal churches to operate legally. The process of receiving permission from the Ministry of Justice to operate as a church is becoming easier.
The Paulicians in Romaia dates back centuries, when Haramounians settled in the Southern Romaia for various reasons such as war or business.
Religions with smaller numbers of followers include Islam (comprising 1% of the population), Evangelicalism, Hellenic Paganism, Zoroastrism and Hinduism.
A small number of Romaian Atheists exists, not self-identifying as religious. Religion is key part of identity for most Romaians, with 78% of Romaians in a 2015-17 survey saying that their nationality is defined by Christianity. Statistics on metaphysics and worldview, do not concern narrowly only the hyponym religion.
Religion in Romaia (2019)
Education
Romaians have a long tradition of valuing and investing in paideia (education), which was upheld as one of the highest societal values in the Hellenic world.
Compulsory education in Romaia comprises primary schools (Δημοτικό Σχολείο, Dimotikó Scholeio) and gymnasium (Γυμνάσιο). Nursery schools (Παιδικός σταθμός, Paidikós Stathmós) are popular but not compulsory. Kindergartens (Νηπιαγωγείο, Nipiagogeío) are relatively popular but not compulsory as well. Children start primary school aged six and remain there for six years. Attendance at gymnasia starts at age 12 and lasts for three years.
Post-compulsory secondary education in Romaia consists of two school types: unified upper secondary schools (Γενικό Λύκειο, Genikό Lykeiό) and technical–vocational educational schools (Τεχνικά και Επαγγελματικά Εκπαιδευτήρια, "TEE"). Post-compulsory secondary education also includes vocational training institutes (Ινστιτούτα Επαγγελματικής Κατάρτισης, "IEK") which provide a formal but unclassified level of education. As they can accept both Gymnasio (lower secondary school) and Lykeio (upper secondary school) graduates, these institutes are not classified as offering a particular level of education.
According to the Framework Law (TBD), Public higher education "Highest Educational Institutions" (Ανώτατα Εκπαιδευτικά Ιδρύματα, Anótata Ekpaideytiká Idrýmata, "ΑΕΙ") consists of two parallel sectors:the university sector (Universities, Polytechnics, Fine Arts Schools, the Open University) and the Technological sector (Technological Education Institutions (TEI) and the School of Pedagogic and Technological Education). There are also State Non-University Tertiary Institutes offering vocationally oriented courses of shorter duration (2 to 3 years) which operate under the authority of other Ministries. Students are admitted to these Institutes according to their performance at national level examinations taking place after completion of the third grade of Lykeio. Additionally, students over twenty-two years old may be admitted to the Romaian Open University through a form of lottery.
The Romaian education system also provides special kindergartens, primary, and secondary schools for people with special needs or difficulties in learning. There are also specialist gymnasia and high schools offering musical, theological, and physical education.
Eighty-three percent of Romaian adults aged 25–64 have completed upper secondary education. The average Romaian pupil scored 479 in reading literacy, maths and science in the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA).
Health
Romaia is known for its generally very good health system, and the life expectancy is about 80 for males and 85 for females and low infant mortality. In comparison to other Eulabian countries, Romaia has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), as there are several health benefits of the Mediterranean diet. The proportion of daily smokers was 34% in 2012, down from 57% in 2000 but still slightly above average in Eulabia. Smoking in public places including bars, restaurants, night clubs and offices has been restricted to specially ventilated rooms since 2008. As with any developed country, Romaia has adequate and sufficient water and food distribution, and levels of nutrition and sanitation are high.
The healthcare in Romaia is universal and is regulated by the National law on Health Insurance. There are no free state-provided health services, but private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Romaia (within three months of taking up residence or being born in the country). Health insurance covers the costs of medical treatment and hospitalisation of the insured. However, the insured person pays part of the cost of treatment. This is done (a) by means of an annual deductible (called the franchise), which ranges from LIR 400 to a maximum of LIR 3,000 for an adult as chosen by the insured person (premiums are adjusted accordingly) and by a charge of 10% of the costs over and above the excess up to a stop-loss amount of LIR 1000.
Culture
Romaia is considered one of the birthplaces of western civilization and a cultural superpower. Divided by politics and geography for centuries until its eventual unification in 1868, Romaia's culture has been shaped by a multitude of regional customs and local centres of power and patronage. Despite the political and social isolation of Romaia, it has made a substantial contribution to the cultural and historical heritage of Eulabia. The Romaian culture has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Ancient Hellenic city-states in Romaia and continuing most notably into Ancient Romaia notably influenced by the Italic culture. Other cultures and nations, such as the Ancient Celtic states, Persians, Haramounians have also left their influence on modern Romaian culture, although historians credit the Romaian Unification with revitalising Romaia and giving birth to a single, cohesive entity of its multi-faceted culture.
The arts

The Early Medieval Romaian art is mostly religious and with exceptions at certain periods is highly conventionalised, following traditional models that translate carefully controlled church theology into artistic terms. Painting in fresco, illuminated manuscripts and on wood panel and, especially in earlier periods, mosaic were the main media, and figurative sculpture very rare except for small carved ivories. Manuscript painting preserved to the end some of the classical realist tradition that was missing in larger works. The Medieval Romaian art was highly prestigious and sought-after in Western Eulabia, where it maintained a continuous influence on medieval art until near the end of the period. Romaian art became formative influences on Renaissance art. But few incoming influences affected the Romaian style. With the expansion of the Eastern Orthodox Church, Romaian forms and styles spread throughout the Orthodox world and beyond.
Romaian architecture is known for the use of domes, and pendentive architecture was invented in the Romaian Kingdom. It also often featured marble columns, coffered ceilings and sumptuous decoration, including the extensive use of mosaics with golden backgrounds. The building material used by Romaian architects was no longer marble, which was very appreciated by the Ancient Iavonians. They used mostly stone and brick, and also thin alabaster sheets for windows. Mosaics were used to cover brick walls, and any other surface where fresco wouldn't resist. Helleno-Italic temples and Romaian churches differ substantially in terms of their exterior and interior aspect. In Antiquity, the exterior was the most important part of the temple, because in the interior, where the cult statue of the deity to whom the temple was built was kept, only the priest had access. The ceremonies here held outside, and what the worshipers view was the facade of the temple, consisting of columns, with an entablature and two pediments. Meanwhile, Christian liturgies were held in the interior of the churches, the exterior usually having little to no ornamentation.

Music
Romaian vocal music extends far back into ancient times where mixed-gender choruses performed for entertainment, celebration and spiritual reasons. Instruments during that period included the double-reed aulos and the plucked string instrument, the lyre, especially the special kind called a kithara. Music played an important role in the education system during ancient times. Boys were taught music from the age of six. Later influences from the Roman Empire, Italian city-states and the Byzantine Empire also had effect on Romaian music.
While the new technique of polyphony was developing in the West, the Eastern Orthodox Church resisted any type of change. Therefore, Romaian Medieval music remained monophonic and without any form of instrumental accompaniment. As a result, and despite certain attempts by certain Romaian chanters, Medieval Romaian music was deprived of elements of which in the West encouraged an unimpeded development of art. However, this method which kept music away from polyphony, along with centuries of continuous culture, enabled monophonic music to develop to the greatest heights of perfection.
Sports
The most popular sport in Romaia is football. Romaia's top-flight club football league is named Liga A and is followed by thousands of fans around the world. Other popular team sports in Romaia include basketball, volleyball and rugby. Romaia has a long and successful tradition in individual sports as well. Bicycle racing is a familiar sport in the country.
Cuisine
The Romaian cuisine has developed through centuries of social and political changes, with roots as far back as the 2th century BC. Romaian cuisine in itself takes heavy influences, including Italic, ancient Hellenic, Jewish and Isfahani. Significant changes occurred with the discovery of the New World with the introduction of items such as potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers and maize, now central to the cuisine but not introduced in quantity until the 18th century. Romaian cuisine is noted for its regional diversity.
The Mediterranean diet forms the basis of Romaian cuisine, rich in pasta, fish, fruits and vegetables and characterised by its extreme simplicity and variety, with many dishes having only four to eight ingredients. Romaian cooks rely chiefly on the quality of the ingredients rather than on elaborate preparation. Dishes and recipes are often derivatives from local and familial tradition rather than created by chefs, so many recipes are ideally suited for home cooking. Ingredients and dishes vary widely by region.
Romaian cuisine relies heavily on traditional products; the country has a large number of traditional specialities. Cheese, cold cuts and wine are central to Romaian cuisine, and with pita, pastry and coffee (specifically espresso) form part of Romaian gastronomic culture. Some sweet desserts include melomakarona, diples and phyllo pastries.
Romaian meal structure is typical of the Mediterranean region and differs from North, Central, and Eastern Eulabian meal structure, though it still often consists of breakfast (πρόγευμα), lunch (μεσημεριανό), and supper (δείπνο). However, much less emphasis is placed on breakfast, and breakfast itself is often skipped or involves lighter meal portions than are seen in non-Mediterranean Western countries. Late-morning and mid-afternoon snacks, called μεζές, are also often included in this meal structure.
Fashion and design
Romaia is one of the leading countries in fashion design. Fashion has always been an important part of the country's cultural life and society, and Romaia are well known for their attention to dress; , or good appearance, retains its traditional importance. Romaian fashion is linked to the most generalized concept of "Made in Romaia", a merchandise brand expressing excellence of creativity and craftsmanship. Romaian luxury goods are renowned for the quality of the textiles and the elegance and refinement of their construction. Constantinoupoli acts as the center of the fashion industry and holds the name of global fashion capital. The city is home to many prime designers, including Ioannis Damalas, Valantis, Regina, and VICI.
Romaia is also prominent in the field of design, notably interior design, architectural design, industrial design and urban design. The country has produced some well-known automotive designers, such as Marco Pienero and Nikitas Margaritis. Examples of classic pieces of Romaia white goods and pieces of furniture include Favianos' washing machines and fridges. Today, Constantinoupoli and Filadelfia are the nation's leaders in architectural design and industrial design.