Bonaventura: Difference between revisions
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
===Pre-Euclean Era=== | ===Pre-Euclean Era=== | ||
[[image:TainoStoneHead.jpg|thumb|210px|left|A {{wp|Taino people|Natí}} stone head, dating back to 173 BCE, now exposed in the National History Museum, in Sermoni.]] | [[image:TainoStoneHead.jpg|thumb|210px|left|A {{wp|Taino people|Natí}} stone head, dating back to 173 BCE, now exposed in the National History Museum, in Sermoni.]] | ||
Though scarce evidence of ancient life has been found on the island of Bonaventure, it is known to historians that the Natí people are the first civilization to settle in the land. The oldest evidence of Natí presence in Bonaventure dates back to 200 BCE, and is an artifact recovered in an archeological site near the village of Padula, State of Rittona. However, the oldest inhabited settlement in Bonaventure is the city of Ixuappano, in the State of Iaitappia, dating back to between 100 BCE and 90 BCE. It is agreed upon that the Zapoyan migration down to Bonaventure, allied with fit weather for agriculture allowed the rapid settlement along the northern coast of the island. In addition to it, Marai people have also been registered to inhabit Bonaventure as early as the 2nd Century CE, in the Bassa Peninsula. | Though scarce evidence of ancient life has been found on the island of Bonaventure, it is known to historians that the {{wp|Taino people|Natí people}} are the first civilization to settle in the land. The oldest evidence of Natí presence in Bonaventure dates back to 200 BCE, and is an artifact recovered in an archeological site near the village of [[Padula (Bonaventure)]], [[State of Rittona (Bonaventure)|State of Rittona]]. However, the oldest inhabited settlement in Bonaventure is the city of [[Ixuappano]], in the [[State of Iaitappia (Bonaventure)|State of Iaitappia]], dating back to between 100 BCE and 90 BCE. It is agreed upon that the {{wp|Nahuatl people|Zapoyan}} migration down to Bonaventure, allied with fit weather for agriculture allowed the rapid settlement along the northern coast of the island. In addition to it, [[Marai people]] have also been registered to inhabit Bonaventure as early as the 2nd Century CE, in the [[Bassa Peninsula]]. | ||
The three people coexisted fairly peacefully, as a lot of economical advantages were seen to emerge out of allying with one another. The center of pre-colonial Bonaventure was the Iacattuotili Valley, the center of the island. The usage of lake Attila was vital for the commerce on the island, as it served as a passway from the southern coast onto the northern coast, connecting the Arucian islands to modern day Ardesia. By the end of the 13th century, the Omatosciacappanno Canal was built connecting the XXXX river to the XXXX river. The canal is approximately 32,6 kilometers long, and it fomented the growth of the city of Omatoyac (modern day city of La Valla), the later Zapoyan capital in Bonaventure. By the 14th century, the Zapoyans in Bonaventure decided to declare | The three people coexisted fairly peacefully, as a lot of economical advantages were seen to emerge out of allying with one another. The center of pre-colonial Bonaventure was the [[Iacattuotili Valley]], the center of the island. The usage of [[lake Attila]] was vital for the commerce on the island, as it served as a passway from the southern coast onto the northern coast, connecting the [[West Arucian Sea|Arucian islands]] to modern day [[Ardesia]]. By the end of the 13th century, the [[Bonaventure#Infrestructure|Omatosciacappanno Canal]] was built connecting the XXXX river to the XXXX river. The canal is approximately 32,6 kilometers long, and it fomented the growth of the city of [[La Valla|Omatoyac]] (modern day city of [[La Valla]]), the later Zapoyan capital in Bonaventure. By the 14th century, the Zapoyans in Bonaventure decided to declare an independent kingdom that, though not part of the mainland empire, worked as a close economical ally to the [[Ardesia#History|Zapoyan Empire]]. | ||
====The Zapoyan Empire==== | ====The Zapoyan Empire==== | ||
[[image:AztecMarket.jpeg|thumb|310px|right|A painting depicting a {{wp|Nahuatl people|Zapoyan}} market.]] | [[image:AztecMarket.jpeg|thumb|310px|right|A painting depicting a {{wp|Nahuatl people|Zapoyan}} market.]] | ||
The Zapoyan presence was permanently consolidated in Bonaventure by the beginning of the 14th century, as the Zapoyan | The Zapoyan presence was permanently consolidated in Bonaventure by the beginning of the 14th century, as the Zapoyan Kingdom of [[Bonaventure#Etymology|Chalma]] was established. Unlike most of the loose Zapoyan confederations in the mainland, Chalma remained loyal to the crown until the Etrurian colonization commenced. The island's importance position in the Arucian sea worked as a perfect gateway of commerce into the mainland, benefiting both Chalma and Tzapotla. [[King Zuma I of Chalma]] was the first crowned king of Chalma, and he promoted what came to be known as the Chalman cooperation. Basically, the Chalman cooperation promoted the adhesion of Natí and Marai people into government and economical roles, granted that they would all benefit somehow out of the commerce profits. Both Natí and Marai people were dominant in the southern coast of the island, while the Zapoyans remained strong on the northern coast. | ||
The success of the Chalman | The success of the Chalman cooperation provided the island with a long lasting peace that was brought to an end when the [[Etruria#History#Early Modern|Etrurian colonization]] attempted to decentralize the Chalman kingdom. The Etrurians sided the Natí people at first, and encoureged them to claim their independence from the Zapoyans, which led to a series of clashes between the two people. [[King Xipil II of Chalma]] also responded with violence, which led to the beginning of the [[Insular war (Bonaventure)|Insular war]], in June 1535. [[Giacomo Borghese]], Etrurian general and colonizer, assisted the Natí with weapons and military strategies, that allowed the war to end quickly by August 18th, 1536, with the complete siege of Omatoyac, and the assassnation of the Zapoyan king. The empire collapsed and it allowed the Etrurians to officially colonize the island then. Most of the Zapoyan war prisioners were {{wp|slavery|enslaved}} or imprisoned by the colonizers, while the ones who escaped hid away in the jungles and mountains of the island, organizing small independent societies known as {{wp|quilombos|''"Calpolli"''}}. | ||
===Etrurian Colonization=== | ===Etrurian Colonization=== | ||
Revision as of 07:52, 19 August 2022
Bonaventurean Federation Vespasian: Federazione Bonaventurana | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Negare e triunfare" (Estmerish: To deny and to triumph) | |
| Anthem: "Cuore dell'Aruciano" (Estmerish: Heart of the Arucian) | |
 Location of Bonaventura in the West Arucian Sea in green. | |
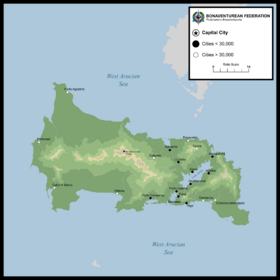 Detailed map of Bonaventure | |
| Capital and | Sermoni |
| Official languages | Vespasian |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2020) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Bonaventurean |
| Government | Federative presidential republic |
• President | Vinicio Nardiello |
• Vice President | Liberio Ceci |
• President of National Assembly | Euseo Di Marino |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation | |
| Area | |
• | 40,015.36 km2 (15,450.02 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 3,299,035 |
• Density | 82.44/km2 (213.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $50,378,555,599 |
• Per capita | $15,271 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $26,368,659,217 |
• Per capita | $7,993 |
| HDI (2020) | 0.796 high |
| Currency | Arucian shilling (ſ) (ARS) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +5 |
| ISO 3166 code | BON |
| Internet TLD | .bv |
Bonaventure (Vespasian: Bonaventura), also known as the Bonaventurean Federation (Vespasian: Federazione Bonaventurana) is a sovereign island nation located in the West Arucian sea, in between the continents of Asteria Superior and Asteria Inferior. Bonaventure has maritime borders with Ardesia to the north, Aucuria to the southeast, Eldmark to the west, and Imagua and the Assimas to the south, with whom Bonaventure has a territory dispute over the small Dunhelm Island. As of 2020, Bonaventure has a population of 3,3 million people, and a land area of 40,015.36 square kilometers, being the second biggest and second most populated of the Arucian islands. The capital and biggest city of Bonaventure is the city of Sermoni, located in the .?.?.? bay, in the southern coast of the island.
The island has been populated by the Natí people since 200 BCE and experience an increase in their population during 9th century CE. During the same time, the Zapoyan Empire landed in Bonaventure's northern coast, and quickly established the land as an important location for the seafare commerce in the Arucian Sea. While the Zapoyan influence in Bonaventure grew exponentially, many other Arucian people such as the Natí and the Marai could be found in the island, given it was the Zapoyan's main commercial point within the Arucian Sea. The island remained under the control of the Zapoyans until Assim Asteris and his expedition first harboured in Bonaventure. The Etrurian occupation of the Assimas Island also drove their attention to the Bonaventure. The first Etrurian settlement in Bonaventure was established in 1523, and the Insular War of 1536, led by Giacomo Borghese, put and end on the Zapoyan rule of the island and settled Bonaventure as the Etrurian colony of New Accadia.
New Accadia remained a colony until October 6th, 1946, when Etruria's defeat in the Solarian War put an end to their colonial empire. Eleven days following its independence, New Accadia was acquired and taken as part of the United Provinces of the Western Arucian Islands. The United Provinces remained united until the departure of Imagua and the Assimas, in 1948, and it dissoluted permanently in 1954, with the departure of Sainte-Chloé and Carucere after a constitutional crisis within the Union. New Accadia carried on the name of United Provinces for about 1 year and 3 months after its independence, when a popular referendum voted that the newly sovereign island would be named after the independence war hero, Quarto Bonaventura.
Bonaventure is a volcanic island that lays on the Arucian faultline, a divergent plate boundry between the .?.?.? and the .?.?.? plates. Such conditions have resulted in the formation of the Iacattuotili Valley, alongside the formation of Lake Attila, the biggest and deepest lake in the Arucian island. This geographic placement, however, has affected Bonaventure with many natural disasters including the 1804 Sermoni earthquake, and the 2020 Mount Micchiano eruption.
Bonaventure has the second biggest nominal GDP amongst the Arucian Nations at $26,3 billion, but the second lowest nominal GDP per capita at $7.993. The nation has experience in the service sector, with emphasis in the tourism and financial services. Bonaventure has been attractive to international investors due to its liberal economy and area size, however the 2020 Mount Micchiano eruption caused a tremendous shock to the national economy, and Bonaventure has been in an extensive economic crisis since then. Bonaventure is a member of the Community of Nations, the Organization of Asterian Nations, and co-founder of the Arucian Cooperation Organization.
Etymology
Bonaventure has gone through some name changes throughout the years prior to its current one. For instance, the first record of a name for the island was Chalma. According to linguists, the name is a reference to the Zapoyan term “Chalmecacihuatl,” which translated to the “Women from Chalmeca,” a Zapoyan deity who was worshiped by merchants as the sister of the merchant god, Yacateuctli, and also as the the goddess of “water and earth.” Following the fall of the Zapoyan Empire and the Etrurian conquest in 1536 saw the island being renamed to “New Accadia,” as a celebration to the several families natural from the Etrurian city of Accadia that arrived in the city of Sermoni in January 1538 to permanently populate the location. The colony would keep its name until October 17th, 1946, when the newley independent nation joined the United Provinces of the West Arucian Islands. The name was a reference to all of the Western Arucian islands that united to establish of the United Provinces.
The current name was a suggestion made by Ireneo Zaccaria, a former history professor in the Sermoni University, when the national government opened a contest to select three names for a referendum to change the name of the Island following the dissolution of the United Provinces in 1954. Amongst the over 100 names submitted, Bonaventura, alongside Nuova Cialma and Azzalia were the selected finalists. Ultimately, the name “Bonaventura” was the most voted and it was officially put into effect in January 1st, 1956. According to Professor Zaccaria, the reason for suggesting the name “Bonaventura” was a way to honor the image and doings of Quarto Bonaventura, a man seen by the people of the island as a war hero, a martyr, a liberator of Bonaventura during the Independence Wars, as well as the first President of Bonaventure. The Professor also explained that the name also has a linguistic meaning “land of good fortune,” as bona seems to be a variant of the Vespasian buona (good), and ventura seems to be a variant of the Vespasian fortuna (luck, good fortune). The Professor also added that the name “Bonaventura” is a reference to the Ship Bonaventura, one of the very first Etrurian expeditions to the island led by captain Benvenuto Viscuso, natural from the small Etrurian city of Paci, who’s patron saint is the catholic Saint Bonaventura. According to Zaccaria, "The history of this country is seen to be intertwined with this name, from pre-colonial times up to our modern history."
History
Pre-Euclean Era

Though scarce evidence of ancient life has been found on the island of Bonaventure, it is known to historians that the Natí people are the first civilization to settle in the land. The oldest evidence of Natí presence in Bonaventure dates back to 200 BCE, and is an artifact recovered in an archeological site near the village of Padula (Bonaventure), State of Rittona. However, the oldest inhabited settlement in Bonaventure is the city of Ixuappano, in the State of Iaitappia, dating back to between 100 BCE and 90 BCE. It is agreed upon that the Zapoyan migration down to Bonaventure, allied with fit weather for agriculture allowed the rapid settlement along the northern coast of the island. In addition to it, Marai people have also been registered to inhabit Bonaventure as early as the 2nd Century CE, in the Bassa Peninsula.
The three people coexisted fairly peacefully, as a lot of economical advantages were seen to emerge out of allying with one another. The center of pre-colonial Bonaventure was the Iacattuotili Valley, the center of the island. The usage of lake Attila was vital for the commerce on the island, as it served as a passway from the southern coast onto the northern coast, connecting the Arucian islands to modern day Ardesia. By the end of the 13th century, the Omatosciacappanno Canal was built connecting the XXXX river to the XXXX river. The canal is approximately 32,6 kilometers long, and it fomented the growth of the city of Omatoyac (modern day city of La Valla), the later Zapoyan capital in Bonaventure. By the 14th century, the Zapoyans in Bonaventure decided to declare an independent kingdom that, though not part of the mainland empire, worked as a close economical ally to the Zapoyan Empire.
The Zapoyan Empire

The Zapoyan presence was permanently consolidated in Bonaventure by the beginning of the 14th century, as the Zapoyan Kingdom of Chalma was established. Unlike most of the loose Zapoyan confederations in the mainland, Chalma remained loyal to the crown until the Etrurian colonization commenced. The island's importance position in the Arucian sea worked as a perfect gateway of commerce into the mainland, benefiting both Chalma and Tzapotla. King Zuma I of Chalma was the first crowned king of Chalma, and he promoted what came to be known as the Chalman cooperation. Basically, the Chalman cooperation promoted the adhesion of Natí and Marai people into government and economical roles, granted that they would all benefit somehow out of the commerce profits. Both Natí and Marai people were dominant in the southern coast of the island, while the Zapoyans remained strong on the northern coast.
The success of the Chalman cooperation provided the island with a long lasting peace that was brought to an end when the Etrurian colonization attempted to decentralize the Chalman kingdom. The Etrurians sided the Natí people at first, and encoureged them to claim their independence from the Zapoyans, which led to a series of clashes between the two people. King Xipil II of Chalma also responded with violence, which led to the beginning of the Insular war, in June 1535. Giacomo Borghese, Etrurian general and colonizer, assisted the Natí with weapons and military strategies, that allowed the war to end quickly by August 18th, 1536, with the complete siege of Omatoyac, and the assassnation of the Zapoyan king. The empire collapsed and it allowed the Etrurians to officially colonize the island then. Most of the Zapoyan war prisioners were enslaved or imprisoned by the colonizers, while the ones who escaped hid away in the jungles and mountains of the island, organizing small independent societies known as "Calpolli".
Etrurian Colonization
The United Provices of the Golden Isles
Independence and Modern Era
Geography
Climate
Biodiversity
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1765 | 44,883 | — |
| 1775 | 70,250 | +56.5% |
| 1800 | 155,426 | +121.2% |
| 1815 | 220,892 | +42.1% |
| 1832 | 350,051 | +58.5% |
| 1846 | 447,914 | +28.0% |
| 1860 | 583,308 | +30.2% |
| 1877 | 731,648 | +25.4% |
| 1887 | 798,565 | +9.1% |
| 1899 | 953,243 | +19.4% |
| 1910 | 1,118,012 | +17.3% |
| 1920 | 1,299,809 | +16.3% |
| 1930 | 1,543,913 | +18.8% |
| 1940 | 1,869,255 | +21.1% |
| 1950 | 2,210,703 | +18.3% |
| 1960 | 2,349,544 | +6.3% |
| 1970 | 2,712,033 | +15.4% |
| 1980 | 3,196,520 | +17.9% |
| 1990 | 3,522,037 | +10.2% |
| 2000 | 3,808,610 | +8.1% |
| 2010 | 3,725,789 | −2.2% |
| 2020 | 3,299,035 | −11.5% |
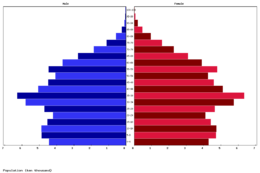
The population of Bonaventure, according to the 2020 census made by the Bonaventurean Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGS), was 3,299,035 habitants (82.4 per square kilometer), with a proportion between men and women as 0.86:1 and over 80% of the population living in the cities. The population is strongly located in the southern region (Rivermouth region), home to over 2 million people, accounting for about 62% of the country's total population. The biggest urban areas of Bonaventure, according to the estimative made by IBGS as of 2020, are the metropolitan areas of the national capital Sermoni (857,732), Fava (392,663), Appano (184,651), Porto Gamba (167,045), and Riga (163,222).
Though Bonaventure is a country of emigration tendencies, immigration has played an important part in the nation’s current demographic makeover. Waves of Vespasians, Carinthians, and Novalians in the 19th century, as well as Carinthians and Novalians again in the 20th century, are amongst the biggest Euclean descendant populations in Bonaventure. In terms of other Asterian people moving into Bonaventure, Ardesia has been a historical point of departure to Bonaventure. For instance, the Zapoyan colonies of the 9th century were the first wave of Ardesian immigration into the island, followed by another mass Ardesian immigration wave between the 1940s and the 1960s. Despite that, Bonaventure has been an emigration country, meaning that it loses more population than it gets. For instance, the current immigration rate of Bonaventure is -1.01 migrant(s) per 1,000 inhabitants. Most of this diaspora is due to better life conditions in neighboring countries, specially in Asteria Superior.
The Bonaventurean population had a significant growth throughout the 20th century, with a significant deacceleration and decrease of population in the 2000s, 2010s, and 2020s. The low birth rate alongside the growing Bonaventurean diaspora has resulted in a recurring negative population growth since the beginning of the 21st century. Nowadays, the birth rate of Bonaventure is 7.5/1,000, amongst the lowest in the world. The life expectancy is of 78,28 years; the expected years of education for Bonaventure is 13.3 years, while the mean years of education is of 11 years; the GDP PPP per capita of Bonaventure is of approximately $15.3 thousands. The Bonaventurean HDI is 0.791, considered high and ranking as the second best in the West Arucian region.
Ethnicities
The island was first inhabited by the Natí people at around the 9th century CE. The Natí people were located mostly on the southwest plains of the Bonaventurean island. The Marai people were also seen to immigrate into Bonaventure, but in less numbers than the Natí. The Marai people concentrated their settlements in the southeast in the Bassa Peninsula. The Zapoyan people, on the other hand, migrated down from Ardesia into Bonaventure, and occupied all of of the Northern coast, as well as the west coast, and the Iacattuotili Valley. The establishment of the Zapoyan Empire in Bonaventure, and the promotion of the island as a commercial hub in the region, the Native Asterians coexisted fairly peacefully.
The arrival of the Eucleans in Bonaventure during the 16th century saw the introduction of White Euclean people in the current demographic layover of Bonaventure. Mostly concentrating their settlements in the southern and eastern coast, the Eucleans were rapid to rule out the native dominion of the land. This led to many native people being killed, dying of because of new diseases, or being enslaved. The Eucleans also introduced Black Bahians into the scene, as Bonaventure became an important point of commerce during the Transvehemens slave trade.
As the Euclean and Bahian populations grew, and the Native Asterians decreased, the birth of a Mixed race (Razza mista) came to be as all three major ethnicities started to coexist and reproduce. Nowadays, the Mixed ethnicity accounts for 37.6% of Bonaventure’s population, the biggest ethnic group in the island. Additionally, the White people account for 27.4%, followed closely by Black Bahians or Bahio-Ventureans at 26.3%, and Native Asterians, most of which are of Zapoyan origins, at 6.2%. Approximately 1.4% of the population is unspecified, while 1.1% are other ethnicities, more often Southern Coians including Senrians and Shangeans.
Religion
Languages
The official language of the Bonaventurean Federation is Vespasian. All government, media, and education are performed in Vespasian. Around 99,4% of the Bonaventure population speaks Venturean Vespasian as their first language. The variation of Venturean Vespasian can be seen between regions, with accents being easily identifiable. For instance, the most widely spread accent in Bonaventure is the Metropolitan accent, spoken in the Rivermouth region. Other widely spread accents in Bonaventure include the Lake accent, spoken by the Lake States population, the Fino accent, spoken mainly in the State of Santa Fina, the Croscian accent, spoken by inhabitants of Nuova Croscia, the Southeast accent, spoken by people from Bociba, Rittona, and Trinità, and the Bassano accent, spoken by the people of Spirito Santo state.
In terms of other national languages, Souther Zapoyan is the most widespread one, with approximately 213 thousand native speakers, mostly concentrated in the Lake Valley region. The Template:WpN is still sparsely spoken by a few hundreds of people in the Southwest region, most of who live in the countryside of their respective states.
Astapasian is widely spoken in the State of Santa Fina, where about 16 thousand people speak it as their native tongue. The Astapasian language developed in the region after masses of Ardesian people migrated to the flatlands of the northwest of Bonaventure, and settled in the region. The city of San Agostino is where the most amount of Astapasian speakers live, but the city of Clemenza di Sant'antonio is considered the cultural center of the Astapasian people.
Cartesian is another language that holds a status of a regional language, being spoken mainly in the State of Nuova Croscia. The waves of Carinthian and Novalian immigrants settled in the west coast of Bonaventure and brought the language to the region. Nowadays, Cartesian is spoken by about 11 thousand people natively, almost all located in Nuova Corsica. The city of Portovest is the cultural haven of the Cartesian language, as well as where the majority of its speakers are located.
Government & Politics
Armed forces
Crime and law enforcement
International relations
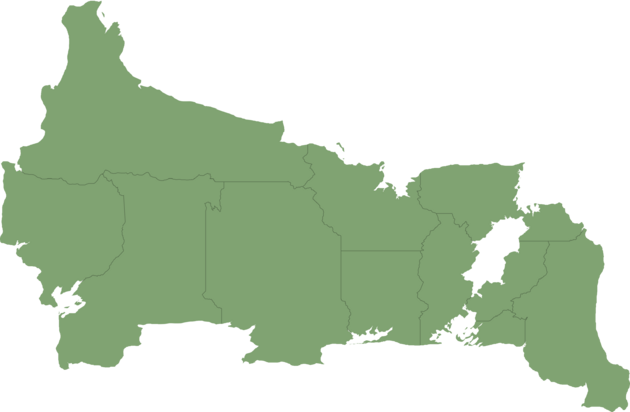
Sub-divisions
States
With the permanent dissolution of the United Provinces of the Golden Isles, and the Constitutional reform of 1956, Bonaventure became a federative republic, thus being subdivided into states as opposed to provinces. The first arrangement of the states in 1956 resulted in the creation of 15 states. In 1959, due to the increasing amount of population, political relevancy, and economic importance of the region, the Federal District was created by partitioning some municipalities belonging to the states of San Giorgio and Missioni, and assigning it under the city of Teravigo, the administrative center of the District, while the Federal Government is established in the city of Sermoni. The remaining four states were former national territories, but they were recently granted statehood due to their population passing 20,000 people; the order of admission is: Rittona in 1982, Spirito Santo in 1988, Mizzia in 1994, and Ximantuatti in 2000, becoming the 20th and the newest state in Bonaventure.
Cities and Municipalities
| Rank | State | Pop. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Sermoni  Fava |
1 | Sermoni | Federal District | 857,732 |  Appano  Porto Gamba | ||||
| 2 | Fava | Missioni | 392,663 | ||||||
| 3 | Appano | Poveromo | 184,651 | ||||||
| 4 | Porto Gamba | Santa Croce | 167,045 | ||||||
| 5 | Riga | San Giorgio | 163,222 | ||||||
| 6 | Accapucchi | Montecalvo | 132,029 | ||||||
| 7 | La Valla | Setinattia | 109,937 | ||||||
| 8 | Iecattia | Conucco | 101,838 | ||||||
| 9 | Quattecchia | San Gaetano | 90,224 | ||||||
| 10 | Sacra | Attila | 67,882 | ||||||
Economy
Tourism
Infrastucture
Education
Health
Energy
Transportation
Media and communication
Culture
Music
Television and Cinema
Sports
Celebrations and Holidays
| Date | Estmerish name | Vespasian name | Day off? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year’s Day | Capodanno | Marks the first day of the Gregorian calendar year. | |
| January 6 | Epiphany | Epifania | Celebrates the revelation of God incarnate as Jesus Christ. | |
| Feburary 10 | Nation's Day | Giorno della Nazione | Celebrates the Approval of the Constitution of 1956, that put an end to all ties between Bonaventure and the United Provinces of the Golden Isles. | |
| variable | Ash Wednesday | Mercoledì delle Ceneri | Marks the beginning of Lent. | |
| variable | Good Friday | Venerdì Santo | Commemorates the crucifixion of Jesus Soter. | |
| variable | Easter | Domenica di Pasqua | Celebrates the resurrection of Jesus Soter. | |
| May 1 | Labor Day | Festa dei lavoratori | Celebrates the international labor movement and the Bonaventurean working class. | |
| variable | Pentecost | Lunedì di Pentecoste | Celebrates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles. | |
| August 15 | Assumption | Assunzione di Maria | Celebrates the ascension of the Virgin Mary to Heaven. | |
| August 18 | All Peoples Day | Giornata di Tutti | Initially known as the Discovery Day (giorno della scoperta), or Borghese's Day (giorno di gorghese), the day celebrated the discovery of Bonaventure by the Etrurians, as well as the colonization of the island. The holiday has been recently changed to the All Peoples Day as a celebration to the pre-colonial people that already lived in the isle, alongside the Euclean settlers that later inhabited the nation and formed the Bonaventurean people as known today. | |
| October 6 | Independence Day | Giorno dell'Indipendenza | Celebration of the proclamation of independence of the Colony of New Accadia from Etruria. | |
| November 1 | All Saints' Day | Ognissanti | Commemorates all Sotirian saints, known or unknown. | |
| November 2 | All Souls' Day | Giorno della Morte | Celebration of life and the lives of the deceased. On this day, it is common to salute the souls of the gone with placing offerings (offerete), altars, candles, and flowers. | |
| December 24 | Nativity Eve | Vigilia di Natale | The day preceding Christmas. | |
| December 25 | Nativity | Natale | Celebrates the birth of Jesus Soter. | |
| December 31 | New Year's Eve | Vigilia di Capodanno (Festa di San Silvestro) | The day preceding New Year's Day. |