Mascyllary colonial empire
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Mascyllary Empire Maskillisches Kolonialreich | |
|---|---|
| 1793–1994 | |
|
Left: Colonial standard of the Mascyllary Kingdom (1793–1923) Right: Flag of the Crowned Republic of Mascylla (1924–) | |
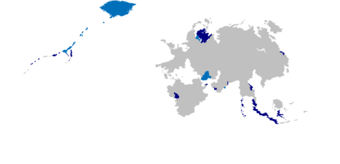 The Mascyllary colonial empire at its territorial peak 1917: Mascylla and its colonies Protectorates and mandates of Mascylla after the Treaty of Lehpold | |
| Status | Colonial empire |
| Capital | Königsreh |
| Common languages | Hesurian (official) |
| Religion | Semitarism |
| Government | Constitutional monarchy (1793–1923) Parliamentary monarchy (1924–) |
| King | |
• 1793–1827 (first) | Lukas I |
• 1976–2005 (last) | Lukas III |
| Prime Minister | |
• 1793–1835 (first) | Wilhelm von Stenreck |
• 1989–2000 (last) | Michael Meilke |
| History | |
| 18 May 1793 | |
• Independence of X | 2 October 1994 |
| Population | |
• 1800 | 21,500,000 |
• 1920 | 74,680,000 |
The Mascyllary colonial empire (Hesurian: Maskillisches Kolonialreich), also called the Maskillisches Weltreich or Mascyllary Reich, constituted the overseas colonies, territories, protectorates and later mandates under the rule of the Mascyllary Kingdom and Crowned Republic of Mascylla from 1793 onward. While attempts had been made by individual Mascyllary states in the centuries prior, and an expansive colonial empire had been established by the Kingdom of Aldia in the 17th century, a distinction is generally made between these empires and that of the Mascyllary empire, given its exceeding size and amount of political and economic effort behind it. A race for the yet unclaimed and uncontrolled territories of Caphtora and Pamira distributed by the Conference of Aniarro, and the dissolution of the First Cuthish Empire and its colonial holdings enabled Mascylla to grow into the second largest colonial empire in history and rise as a global power. At its territorial peak in 1917, the Mascyllary empire and its mandates comprised more than 74 million inhabitants and X km2 (X sq mi).
Following Mascylla's unification, the de facto successor state to the Kingdom of Aldia inherited its colonial empire in 1793, greatly bolstering international prestige and economic importance at first. Raw materials from the colonies were diverted to the metropole in exchange for manufactured items, keeping Mascylla's economic growth high while stimulating economic integrity with the colonies in order to tighten political unity within the empire. However, numerous politicians, led by Wilhelm von Stenreck, opposed Mascyllary colonialism and favored milder policies in fear of Mascyllary security and ultimately unity at risk. Imperalist elements under Lukas II emerged victorious and masterminded a rapid expansion of the Mascyllary military and colonial economy, inadvertedly coming into conflict with the Cuthish Empire.
After the recovery from the Second Cutho-Mascyllary War (1839-41), Mascylla continued to grow economically thanks to the Industrial Revolution and accompanying explosive urban growth, and seeking political allies in namely Albeinland and Lavaria. Continued expansion in overseas also covered vast trade ports, crown colonies and dependancies throughout the world; however, most of Mascylla's power is chiefly derived from its exertion of prowess not only over its colonies, but also much of the world's trade that gave it control over economies in Pamira. Furthermore, the creation of Schutzmandate ('protection mandate') in sovereign states gave it political influence and thus an extension of Mascylla's unofficial spheres of influence.
By the start of the 20th century, Cuthland and Dulebia openly competed with Mascylla's economic and colonial lead, further antagonizing and fueling the rivalry among Berea's major powers until it escalated into the Great War in 1910. Although the war turned out successful for the Armala Coalition and ultimately Mascylla, it imposed enourmous strain on the empire's political capacity and economic and military resources, despite attempts to curb its stagnation through war reparations and the confiscation of Cuthland's colonial empire as Assembly of Nations mandates under Mascyllary supervision. While it had risen even more as a global power and at its largest territorial extent, Mascylla struggled to maintain its situation as one of the world's pre-eminent powers, while an economic boom eased tensions at first. The Melasian Crisis was a turning point of the empire, since despite Mascylla and Cuthland participating in peace negotiations and a stalemate, it was forced to grant Melasia independence, helping to accelerate the decline of the empire. With Mascyllary prestige damaged and a shift in favor of decolonization by the Assembly of Nations in the 1950s, Mascylla recognized its need to disband its empire to sustainably secure its future position as a political and economic power, and opted to release its colonies voluntarily. The independence of X in 1994 and the confirmation of the AN in 1995 marked the official end of the empire. X colonial overseas territories still remain under Mascyllary sovereignty, and the empire's linguistic and cultural legacy is undisputable.
History
Rise of the empire
Exploration of Mavronesia
War with the Second Cuthish Empire
Berean power
Great War and interwar period
Melasian Crisis and aftermath
Decolonisation and decline
Governance
Colonies
| Ensign | Name of territory | Date | Status and notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jewel Coast Maskillisch-Edelsteinküste |
1846–1958 | Crown Colony, achieved independence as X in 1958. | |
| Pangakumland Maskillisch-Pang-Akumland |
1829–1890, 1890–1903 | Crown Colony, incorporated as a protectorate of Cunucaland in 1890 and as a province in 1903. | |
| Badresar Maskillisch-Badresar |
1817–1890, 1890–1903 | Crown Colony, incorporated as a protectorate of Cunucaland in 1890 and as a province in 1903. | |
| Cunucaland Maskillisch-Kunukaland |
1903–1930 | Crown Colony, reorganized into the Dominion of Cunucca in 1930. | |
| Kinh No Maskillisch-Kintou |
1866–1979 | Crown Colony, ceded to Kenlong in 1979 through plebiscite. | |
| Diajiao Maskillisch-Dientsitau |
1830–1951 | Crown Colony, ceded to X in 1951 through the Mascyllary-X Partnership Declaration. | |
| Melasian Empire (Melasia) Melasisches Reich (Maskillisch-Melasien) |
1823–1904 | Crown Colony, separate realm under Mascyllary crown rule over the Melasian feudal states and provinces of Mascyllary Melasia, reorganized into the Federated Melasian States as a Dominion in 1904. |
Dominions
| Flag | Name of territory | Date | Status and notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federated Melasian States Föderierte Melasische Staaten |
1904–1929 | Dominion with Mascyllary monarch as shared head of state, achieved independence as the Republic of Melasia in 1929. | |
| Commonwealth of Cunucca Gemeinstaat Kunukien |
1930–1966 | Dominion with Mascyllary monarch as shared head of state, negotiated unification with Cunucca in 1966. |
Protectorates
| Ensign | Name of territory | Date | Status and notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cunochuye Maskillisch-Kunotschuien (Hinterkunukien) |
1872–1904, 1943–1956 | Protectorate, incorporated as a province of the Federated Melasian States in 1904, reorganized as a Protectorate in 1943 after the Melasian Crisis, achieved independence as X in 1956. | |
| Tanjiong Maskillisch-Tanschong |
1867–1963 | Protectorate, annexed by X in 1963 through plebiscite. | |
| Western Pannaland (Bight States) Maskillisch-West-Pannaland (Buchtenstaaten) |
1839–1890, 1901–1954 | Crown Colony, incorporated as a protectorate of Cunucaland in 1890, divided from Cunucaland as a Protectorate in 1901, achieved independence as X in 1954. |
Mandates
| Ensign | Name of territory | Date | Status and notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandatory Pandalam Mandatspandalam (Maskillisch-Pandalam) |
1917–1940 | Former Cuthish colony, Mandate of the Assembly of Nations after the Treaty of Lehpold in 1917, annexed by Cunucca in 1940. | |
| Mandatory Kenlong Mandatskenlong (Mandat für das Königreich Kenlong) |
1917–1928 | Former belligerent state of the Great War, Mandate of the Assembly of Nations after the Treaty of Lehpold in 1917, achieved independence as the Kingdom of Kenlong in 1928. | |
| Mandate for the Transappiric Mandat für Transappirien (Maskillisch-Transappirien) |
1917–1935 | Former tributary of the Chaghanid Empire, Mandate of the Assembly of Nations after the Treaty of Lehpold in 1917, achieved independence as X in 1935. | |
| Mandate for Northern Alvinia Mandat für Nordalwinien (Maskillisch-Nordalwinien) |
1917–1933 | Former Cuthish colonies, Mandate of the Assembly of Nations after the Treaty of Lehpold in 1917, achieved independence as X in 1933. |

