Gentu: Difference between revisions
Philimania (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Philimania (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Region_icon_Gentu}} | {{Region_icon_Gentu}} | ||
{{Gentu wip}} | {{Gentu wip}} | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
| allsatellites = yes | | allsatellites = yes | ||
| physical_characteristics = yes | | physical_characteristics = yes | ||
| mean_radius | | mean_radius = 6,306.9 km | ||
| equatorial_radius = {{convert|6378.1|km|mi|comma=gaps|abbr=on}} | | equatorial_radius = {{convert|6378.1|km|mi|comma=gaps|abbr=on}} | ||
| polar_radius = {{convert|6356.8|km|mi|comma=gaps|abbr=on}} | | polar_radius = {{convert|6356.8|km|mi|comma=gaps|abbr=on}} | ||
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Gentu''', also known as '''Gentǔ''', or '''Terra''', is the third {{ | '''Gentu''', also known as '''Gentǔ''', or '''Terra''', is the third {{wp|planet}} from the [[Sun (Gentu)|Sun]] and the only {{wp|astronomical object}} known to harbour life. While large amounts of water can be found throughout the [[Gentu System]], only Gentu sustains liquid surface water. About 67% of Gentu's surface is made up of the {{wp|ocean}}. The remaining 33% of Gentu's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Gentu's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving {{wp|plate tectonics|tectonic plate}}s, interacting to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes and earthquakes. | ||
Gentu | Gentu formed [[Age of Gentu|over 4.5 billion years ago]]. During the first {{wp|billion years}} of [[Gentu's history]], the ocean formed and then {{wp|Abiogenesis|life developed}} within it. the modern {{wp|Humans}} emerged 250,000 years ago and have reached a population of almost 12 billion today. Humans depend on Gentu's {{wp|biosphere}} and natural resources for their survival, but have {{wp|Human impact on the environment|increasingly impacted Gentu's environment}}. Today, humanity's impact on Gentu's climate, soils, waters and ecosystems is {{wp|sustainability|unsustainable}}, threatening people's lives and causing widespread extinction of other life. | ||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
The [[ | The [[XXX|modern XXX]] word ''Gentu'' developed from the [[old XXX]] word most often spelled Ĵĕneşės, and the [[old XXX]] phrase spelled Řėľțŭ, both words and phrases meaning ''World'' in their own languages. Where the ancient words derived from is unknown to historians currently. | ||
Historically, ''gentu'' has been | Historically, ''gentu'' has been written in lowercase. From early [[Middle XXX]], its definite sense as "the globe" was expressed as ''gentu''. By Early Modern XXX, many nouns were capitalized, and ''gentu'' was also written ''Gentu'', particularly when referenced along with other heavenly bodies. {{wp|House styles}} now vary: [[XXX spelling]] recognizes the lowercase form as the most common, with the capitalized form an acceptable variant. Another convention capitalizes "Gentu" when appearing as a name (for example, "Gentu's atmosphere") but writes it in lowercase when preceded by the (for example, "the atmosphere of gentu"). It almost always appears in lowercase in colloquial expressions such as "where on gentu are you?" | ||
== Chronology == | == Chronology == | ||
| Line 78: | Line 79: | ||
|+ Characteristics | |+ Characteristics | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="2" | [[File:FullMoon2010.jpg|center|200px|[[Full moon]] as seen from | | colspan="2" | [[File:FullMoon2010.jpg|center|200px|[[Full moon]] as seen from Earth's [[Northern Hemisphere]]]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ''' | | '''Diameter''' || {{val|3474.8|u=km|fmt=commas}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Mass''' || {{val|7.349|e=22|u=kg}} | | '''Mass''' || {{val|7.349|e=22|u=kg}} | ||
| Line 88: | Line 89: | ||
| '''Orbital period''' || {{nowrap|27{{smallsup|d}} 7{{smallsup|h}} 43.7{{smallsup|m}}}} | | '''Orbital period''' || {{nowrap|27{{smallsup|d}} 7{{smallsup|h}} 43.7{{smallsup|m}}}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Cynthia is | Cynthia is a relatively large, {{wp|Terrestrial planet|terrestrial}}, planet-like {{wp|natural satellite}}, with a diameter about one-quarter of Gentu's. It is the largest moon in the Gentu System relative to the size of its planet, although [[XXX (moon)|XXX]] is larger relative to the {{wp|dwarf planet}} [[XXX]]. The most widely accepted theory of the Cynthia's origin, the {{wp|giant-impact hypothesis}}, states that it formed from the collision of a Gentu-size protoplanet called Gaia with the early Gentu. This hypothesis explains (among other things) Cynthia's relative lack of iron and volatile elements and the fact that its composition is nearly identical to that of Earth's crust. | ||
The gravitational attraction | The gravitational attraction between Gentu and Cynthia causes {{wp|tide}}s on Gentu. The same effect on Gentu has led to its {{wp|tidal locking}}: its rotation period is the same as the time it takes to orbit Gentu. As a result, it always presents the same face to the planet. As Cynthia orbits Gentu, different parts of its face are illuminated by the Sun, leading to the {{wp|lunar phase}}s. | ||
Cynthia may have dramatically | Cynthia may have dramatically affected the development of life by moderating the planet's climate. {{wp|Paleontology|Paleontological}} evidence and computer simulations show that Gentu's axial tilt is stabilized by tidal interactions with Cynthia. Some theorists think that without this stabilization against the {{wp|torque}}s applied by the Sun and planets to Gentu's equatorial bulge, the rotational axis might be chaotically unstable, exhibiting large changes over millions of years, as is the case for XXX, though this is disputed. | ||
=== Asteroids | === Asteroids and artificial satellites === | ||
Gentu's co-orbital asteroids population consists of {{wp|quasi-satellite}}s, | Gentu's co-orbital asteroids population consists of {{wp|quasi-satellite}}s, and {{wp|Trojan (celestial body)|XXX}}. There are at least five quasi-satellites, including [[XXX]]. A XXX asteroid companion, XXX, is {{wp|Libration|librating}} around the leading {{wp|Lagrangian point|Lagrange triangular point}}, L4, in Gentu's orbit around the Sun. The tiny near-Gentu asteroid XXX makes close approaches to the Gentu-Cynthia system roughly every forty years. During these approaches, it can orbit Gentu for brief periods of time. | ||
2021, there are 5,627 operational, human-made {{wp|satellite}}s orbiting Gentu. There are also inoperative satellites, including [[Xenophus 1]], the oldest satellite currently in orbit, and over 16,000 pieces of tracked {{wp|space debris}}. Gentu's largest artificial satellite is the [[International Space Station (Gentu)|International Space Station]]. | |||
== Life on Gentu == | == Life on Gentu == | ||
| Line 104: | Line 105: | ||
[[File:Mycena interrupta.jpg|thumb|left|[[Fungus|Fungi]] are one of the kingdoms of life on Gentu.]] | [[File:Mycena interrupta.jpg|thumb|left|[[Fungus|Fungi]] are one of the kingdoms of life on Gentu.]] | ||
A planet's life forms inhabit {{wp|ecosystem}}s, whose total forms the {{wp|biosphere}}. The biosphere is divided into a number of {{wp|biome}}s, inhabited by broadly similar plants and animals. On land, biomes are separated primarily by differences in latitude, {{wp|elevation|height above sea level}} and {{wp|humidity}}. Terrestrial {{wp|tundra|biomes}} lying within the Arctic or Antarctic Circles, at {{wp|Alpine tundra|high altitudes}} or in {{wp|desert|extremely arid areas}} are relatively barren of plant and animal life; {{wp|Latitudinal gradients in species diversity|species diversity}} reaches a peak in {{wp|tropical rainforest|humid lowlands at equatorial latitudes}}. Estimates of the {{wp|number of species}} on Gentu today vary; most species have not been {{wp|Species description|described}}. Over 99% of all {{wp|species}} that ever lived on Gentu are {{wp|extinct}}. | |||
Extreme weather, such as {{wp|tropical cyclone}}s ( | Extreme weather, such as {{wp|tropical cyclone}}s (including {{wp|hurricane}}s and {{wp|typhoon}}s), occurs over most of Gentu's surface and has a large impact on life in those areas. From 1980 to 2000, these events caused an average of 11,800 human deaths per year. Many places are subject to earthquakes, {{wp|landslide}}s, {{wp|tsunami}}s, volcanic eruptions, {{wp|tornado}}es, {{wp|blizzard}}s, floods, droughts, {{wp|wildfire}}s, and other calamities and disasters. Human impact is felt in many areas due to {{wp|pollution}} of the air and water, {{wp|acid rain}}, loss of vegetation, loss of wildlife, species {{wp|extinction}}, {{wp|soil degradation}}, {{wp|soil depletion}} and {{wp|erosion}}. Human activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere which cause {{wp|global warming}}. This is driving changes such as the [[Great Retreat]], and {{wp|Sea level rise|global rise in average sea levels}}, increased risk of drought and wildfires, and migration of species to colder areas. | ||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
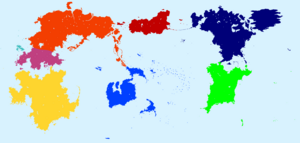
| Line 128: | Line 129: | ||
|{{legend2|#c04080|[[Oranland]]}} | |{{legend2|#c04080|[[Oranland]]}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{navbar|style=float:right;|mini=true|World map | {{navbar|style=float:right;|mini=true|World map indicating continents}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
]] | ]] | ||
Gentu is made up of eight continents, [[North Domica|North]] | Gentu is made up of eight continents, [[North Domica|North]] and [[South Domica]], [[Flonesia]], [[Trimeshia]], [[Naphtora]], [[Alabon]], [[Hesterath]], and [[Oranland]]. The largest rainforest is the [[XXX rainforest]] in [[South Domica]]. The tallest mountain is [[Mount XXX]] at the border of [[Hesterath]] and [[Oranland]] with an elevation of 9,147.09 meters. | ||
'' | ''More to be Added'' | ||
=== Countries === | === Countries === | ||
Below are | Below are listed the known countries that have formed in Gentu. | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
! style="line-height:95%; width:2em" class="unsortable" | Flag | ! style="line-height:95%; width:2em" class="unsortable" | Flag | ||
! style="line-height:95%; width:2em" class="unsortable" | CoA/Seal | ! style="line-height:95%; width:2em" class="unsortable" | CoA/Seal | ||
! Short | ! Short and formal names | ||
! Capital | ! Capital | ||
! Population | ! Population | ||
| Line 164: | Line 165: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Template:GentuInfo}} | {{Template:GentuInfo}} | ||
[[Category:Regions]] | [[Category:Regions]] | ||
[[Category:Gentu]] | [[Category:Gentu]] | ||
Revision as of 09:27, 6 April 2022
This article is a work in progress. Any information here may not be final as changes are often made to make way for improvements or expansion of lore-wise information about Gentu. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, contact User:Philimania. |
 Gentu and its moon, photo taken from the Xenophus 2 Mission in 2005. | |||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gentǔ, Terra, The World | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics | |||||||||||||
| Epoch Hodiernus | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 152100000 km (94500000 mi) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 147095000 km (91401000 mi) | ||||||||||||
| 149598023 km (92955902 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | ~0.0167086 | ||||||||||||
| 365 d (12.0 months) | |||||||||||||
Average orbital speed | 29.78 km/s (18.50 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 358.617° | |||||||||||||
| Satellites | 1 natural satellite: Cynthia 2,000+ operational artificial satellites | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||||||
Mean radius | 6,306.9 km | ||||||||||||
Equatorial radius | 6378.1 km (3963.2 mi) | ||||||||||||
Polar radius | 6356.8 km (3949.9 mi) | ||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.0033528 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference | 40075.017 km (24901.461 mi) (equatorial) 40007.86 km (24859.73 mi) (meridional) | ||||||||||||
| 510,072,000km2 (316,944,000 mi2) | |||||||||||||
| Volume | 1.08321 × 1012km3 | ||||||||||||
| Mass | 5.97237 x 1024 kg | ||||||||||||
Mean density | 5.514 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||
| 9.807 m/s2 | |||||||||||||
| 0.3307 | |||||||||||||
| 11.186 km/s (6.951 mi/s) | |||||||||||||
Sidereal rotation period | 0.99726968 d (23.934472 h) | ||||||||||||
Equatorial rotation velocity | 0.4651 km/s (0.2890 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 23.4392811° | |||||||||||||
| Albedo | 0.367 geometric 0.306 Bond | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere | |||||||||||||
Surface pressure | 101.325 kPa (at MSL) | ||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | 78.08% nitrogen (N2) (dry air) 20.95% oxygen (O2) 0.930% argon 0.039% carbon dioxide (climate-variable) | ||||||||||||
Gentu, also known as Gentǔ, or Terra, is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbour life. While large amounts of water can be found throughout the Gentu System, only Gentu sustains liquid surface water. About 67% of Gentu's surface is made up of the ocean. The remaining 33% of Gentu's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Gentu's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, interacting to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes and earthquakes.
Gentu formed over 4.5 billion years ago. During the first billion years of Gentu's history, the ocean formed and then life developed within it. the modern Humans emerged 250,000 years ago and have reached a population of almost 12 billion today. Humans depend on Gentu's biosphere and natural resources for their survival, but have increasingly impacted Gentu's environment. Today, humanity's impact on Gentu's climate, soils, waters and ecosystems is unsustainable, threatening people's lives and causing widespread extinction of other life.
Etymology
The modern XXX word Gentu developed from the old XXX word most often spelled Ĵĕneşės, and the old XXX phrase spelled Řėľțŭ, both words and phrases meaning World in their own languages. Where the ancient words derived from is unknown to historians currently.
Historically, gentu has been written in lowercase. From early Middle XXX, its definite sense as "the globe" was expressed as gentu. By Early Modern XXX, many nouns were capitalized, and gentu was also written Gentu, particularly when referenced along with other heavenly bodies. House styles now vary: XXX spelling recognizes the lowercase form as the most common, with the capitalized form an acceptable variant. Another convention capitalizes "Gentu" when appearing as a name (for example, "Gentu's atmosphere") but writes it in lowercase when preceded by the (for example, "the atmosphere of gentu"). It almost always appears in lowercase in colloquial expressions such as "where on gentu are you?"
Chronology
TBA
Gentu-Cynthia System
| Diameter | 3,474.8 km |
| Mass | 7.349×1022 kg |
| Semi-major axis | 384,400 km |
| Orbital period | 27d 7h 43.7m |
Cynthia is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Gentu's. It is the largest moon in the Gentu System relative to the size of its planet, although XXX is larger relative to the dwarf planet XXX. The most widely accepted theory of the Cynthia's origin, the giant-impact hypothesis, states that it formed from the collision of a Gentu-size protoplanet called Gaia with the early Gentu. This hypothesis explains (among other things) Cynthia's relative lack of iron and volatile elements and the fact that its composition is nearly identical to that of Earth's crust.
The gravitational attraction between Gentu and Cynthia causes tides on Gentu. The same effect on Gentu has led to its tidal locking: its rotation period is the same as the time it takes to orbit Gentu. As a result, it always presents the same face to the planet. As Cynthia orbits Gentu, different parts of its face are illuminated by the Sun, leading to the lunar phases.
Cynthia may have dramatically affected the development of life by moderating the planet's climate. Paleontological evidence and computer simulations show that Gentu's axial tilt is stabilized by tidal interactions with Cynthia. Some theorists think that without this stabilization against the torques applied by the Sun and planets to Gentu's equatorial bulge, the rotational axis might be chaotically unstable, exhibiting large changes over millions of years, as is the case for XXX, though this is disputed.
Asteroids and artificial satellites
Gentu's co-orbital asteroids population consists of quasi-satellites, and XXX. There are at least five quasi-satellites, including XXX. A XXX asteroid companion, XXX, is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in Gentu's orbit around the Sun. The tiny near-Gentu asteroid XXX makes close approaches to the Gentu-Cynthia system roughly every forty years. During these approaches, it can orbit Gentu for brief periods of time.
2021, there are 5,627 operational, human-made satellites orbiting Gentu. There are also inoperative satellites, including Xenophus 1, the oldest satellite currently in orbit, and over 16,000 pieces of tracked space debris. Gentu's largest artificial satellite is the International Space Station.
Life on Gentu

A planet's life forms inhabit ecosystems, whose total forms the biosphere. The biosphere is divided into a number of biomes, inhabited by broadly similar plants and animals. On land, biomes are separated primarily by differences in latitude, height above sea level and humidity. Terrestrial biomes lying within the Arctic or Antarctic Circles, at high altitudes or in extremely arid areas are relatively barren of plant and animal life; species diversity reaches a peak in humid lowlands at equatorial latitudes. Estimates of the number of species on Gentu today vary; most species have not been described. Over 99% of all species that ever lived on Gentu are extinct.
Extreme weather, such as tropical cyclones (including hurricanes and typhoons), occurs over most of Gentu's surface and has a large impact on life in those areas. From 1980 to 2000, these events caused an average of 11,800 human deaths per year. Many places are subject to earthquakes, landslides, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, tornadoes, blizzards, floods, droughts, wildfires, and other calamities and disasters. Human impact is felt in many areas due to pollution of the air and water, acid rain, loss of vegetation, loss of wildlife, species extinction, soil degradation, soil depletion and erosion. Human activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere which cause global warming. This is driving changes such as the Great Retreat, and global rise in average sea levels, increased risk of drought and wildfires, and migration of species to colder areas.
Geography
Gentu is made up of eight continents, North and South Domica, Flonesia, Trimeshia, Naphtora, Alabon, Hesterath, and Oranland. The largest rainforest is the XXX rainforest in South Domica. The tallest mountain is Mount XXX at the border of Hesterath and Oranland with an elevation of 9,147.09 meters.
More to be Added
Countries
Below are listed the known countries that have formed in Gentu.
| Flag | CoA/Seal | Short and formal names | Capital | Population | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|
Auralia - Auralian Commonwealth | Ironey | 19,258,000 | Parliamentary elective monarchy |
| TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA |