Hoy Kok: Difference between revisions
Philimania (talk | contribs) m (→Music) |
Philimania (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
=== Climate === | === Climate === | ||
Hoy Kok has a {{wp|humid subtropical climate}} (Cfa), with an average annual temperature of 15.9 °C (60.62 °F) for urban districts and 15.3–15.8 °C (59.54–60.44 °F) for suburbs. It experiences four distinct seasons. Winters are temperate to cold and damp—northwesterly winds from northern Hesterath can cause nighttime temperatures to drop below freezing. Each year, there are an average of 5.8 days with snowfall and 1.6 days with snow cover. Summers are hot and humid, and occasional downpours or freak thunderstorms can be expected. On average, 7.2 days exceed 35 °C (95 °F) annually. In summer and the beginning of autumn, the city is susceptible to {{wp|typhoons}}. | |||
The most pleasant seasons are generally spring, although changeable and often rainy, and autumn, which is usually sunny and dry. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 34% in Marto to 54% in Tebax, the city receives 1,895 hours of bright sunshine annually. | |||
{{Weather box | |||
|width = auto | |||
|location = Hoy Kok | |||
|metric first = Y | |||
|single line = Y | |||
|Jan record high C = 22.1 | |||
|Feb record high C = 27.0 | |||
|Mar record high C = 29.6 | |||
|Apr record high C = 34.3 | |||
|May record high C = 36.4 | |||
|Jun record high C = 37.5 | |||
|Jul record high C = 39.2 | |||
|Aug record high C = 39.9 | |||
|Sep record high C = 38.2 | |||
|Oct record high C = 34.0 | |||
|Nov record high C = 28.7 | |||
|Dec record high C = 23.4 | |||
|Jan high C = 8.1 | |||
|Feb high C = 10.1 | |||
|Mar high C = 13.8 | |||
|Apr high C = 19.5 | |||
|May high C = 24.8 | |||
|Jun high C = 27.8 | |||
|Jul high C = 32.2 | |||
|Aug high C = 31.5 | |||
|Sep high C = 27.9 | |||
|Oct high C = 22.9 | |||
|Nov high C = 17.3 | |||
|Dec high C = 11.1 | |||
|Jan mean C = 4.8 | |||
|Feb mean C = 6.6 | |||
|Mar mean C = 10.0 | |||
|Apr mean C = 15.3 | |||
|May mean C = 20.7 | |||
|Jun mean C = 24.4 | |||
|Jul mean C = 28.6 | |||
|Aug mean C = 28.3 | |||
|Sep mean C = 24.9 | |||
|Oct mean C = 19.7 | |||
|Nov mean C = 13.7 | |||
|Dec mean C = 7.6 | |||
|Jan low C = 2.1 | |||
|Feb low C = 3.7 | |||
|Mar low C = 6.9 | |||
|Apr low C = 11.9 | |||
|May low C = 17.3 | |||
|Jun low C = 21.7 | |||
|Jul low C = 25.8 | |||
|Aug low C = 25.8 | |||
|Sep low C = 22.4 | |||
|Oct low C = 16.8 | |||
|Nov low C = 10.6 | |||
|Dec low C = 4.7 | |||
|Jan record low C = −10.1 | |||
|Feb record low C = −7.9 | |||
|Mar record low C = −5.4 | |||
|Apr record low C = −0.5 | |||
|May record low C = 6.9 | |||
|Jun record low C = 12.3 | |||
|Jul record low C = 16.3 | |||
|Aug record low C = 18.8 | |||
|Sep record low C = 10.8 | |||
|Oct record low C = 1.7 | |||
|Nov record low C = −4.2 | |||
|Dec record low C = −8.5 | |||
|Jan precipitation mm = 74.4 | |||
|Feb precipitation mm = 59.1 | |||
|Mar precipitation mm = 93.8 | |||
|Apr precipitation mm = 74.2 | |||
|May precipitation mm = 84.5 | |||
|Jun precipitation mm = 181.8 | |||
|Jul precipitation mm = 145.7 | |||
|Aug precipitation mm = 213.7 | |||
|Sep precipitation mm = 87.1 | |||
|Oct precipitation mm = 55.6 | |||
|Nov precipitation mm = 52.3 | |||
|Dec precipitation mm = 43.9 | |||
|year precipitation mm=1166.1 | |||
|Jan sun = 114.3 | |||
|Feb sun = 119.9 | |||
|Mar sun = 128.5 | |||
|Apr sun = 148.5 | |||
|May sun = 169.8 | |||
|Jun sun = 130.9 | |||
|Jul sun = 190.8 | |||
|Aug sun = 185.7 | |||
|Sep sun = 167.5 | |||
|Oct sun = 161.4 | |||
|Nov sun = 131.1 | |||
|Dec sun = 127.4 | |||
|year sun=1775.8 | |||
|Jan humidity = 74 | |||
|Feb humidity = 73 | |||
|Mar humidity = 73 | |||
|Apr humidity = 72 | |||
|May humidity = 72 | |||
|Jun humidity = 79 | |||
|Jul humidity = 77 | |||
|Aug humidity = 78 | |||
|Sep humidity = 75 | |||
|Oct humidity = 72 | |||
|Nov humidity = 72 | |||
|Dec humidity = 71 | |||
|year humidity= 74 | |||
|precipitation colour = green | |||
|unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm | |||
|Jan precipitation days = 9.9 | |||
|Feb precipitation days = 9.2 | |||
|Mar precipitation days = 12.4 | |||
|Apr precipitation days = 11.2 | |||
|May precipitation days = 10.4 | |||
|Jun precipitation days = 12.7 | |||
|Jul precipitation days = 11.4 | |||
|Aug precipitation days = 12.3 | |||
|Sep precipitation days = 9.1 | |||
|Oct precipitation days = 6.9 | |||
|Nov precipitation days = 7.6 | |||
|Dec precipitation days = 7.7 | |||
|source 1 = [[Hoy Kok Observatory]] | |||
}} | |||
=== Architecture === | === Architecture === | ||
Revision as of 07:25, 19 May 2022
This article is a work in progress. Any information here may not be final as changes are often made to make way for improvements or expansion of lore-wise information about Gentu. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, contact User:Philimania. |
State of Hoy Kok | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motto: "Amizade, Amor, Paz" ("Friendship, Love, Peace") | |||||||
| Anthem: XXX | |||||||
 Location of Hoy Kok (Green) in Hesterath (Dark Grey) | |||||||
| Capital | Hoy Kok (city-state) | ||||||
| Largest district | Santa Sulforte | ||||||
| Official languages and national languages | Qiuese Palon | ||||||
| Ethnic groups (1997) | 65.9% Hoy Kokese 23.7% Qiuese 8.2% Palon 2.2% Others | ||||||
| Religion | 41.3% Terranity 32.8% No religion 16.7% Kaoism 6.7% Weilism 2.5% Others | ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Hoy Kokese | ||||||
| Government | Devolved gubernatorial republic | ||||||
• Governor | Ernesto Ng | ||||||
| Sofia Siu | |||||||
| Paulo Tsang | |||||||
| Legislature | National Council | ||||||
| Establishment | |||||||
| 13 Pusper 1823 | |||||||
| 20 Tebax 1953 | |||||||
| 1 Enero 1990 | |||||||
| 8 Enero 1990 | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• Total | 4,338 km2 (1,675 sq mi) (XXX) | ||||||
• Water (%) | 8.3% | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1999 estimate | |||||||
• 1998 census | |||||||
• Density | 11,325/km2 (29,331.6/sq mi) (XXX) | ||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 1995 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 1999 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| Gini (1998) | medium (XXX) | ||||||
| HDI (1996) | 0.847 very high | ||||||
| Currency | Hoy Kok Ober (HKO, HKØ) | ||||||
| Time zone | MTS-6 (Hoy Kok Time) | ||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||
| Calling code | XXX | ||||||
| Internet TLD | .hk | ||||||
| |||||||
Hoy Kok (Palon: Marcanta, Qiuese: 海角, Jyutping: Hoi2 Gok3), officially the State of Hoy Kok, is a country in Hesterath located in the northern Red River Delta by the Horapon Sea. With a population of about 49,126,800 and an area of 11,325 km2 (29,330.1 sq mi), it is the XXX populated region in Gentu.
Formerly a Palon colony, the territory of Palon Hoy Kok was ceded to Palon as a trading post by the Nanchao dynasty in 1823. The colony remained under full Palon rule until 1953 when the Treaty of Beimen granted Hoy Kok a semi-autonomous status. Hoy Kok eventually gained full independence in 1990 in a referendum making it the most recent sovereign state or country with widespread recognition as of 2000. The unique blend of Palon and Qiuese architecture in the country's historic center led to the rise of its tourism industry in 1992.
Originally a sparsely populated network of villages, Hoy Kok has become a strategic port in the Horapon Sea and a top destination for tourists. Hoy Kok's GDP per capita by purchasing power parity is ranked XXX in Gentu. It has a very high Human Development Index, as calculated by the Hoy Kok government, and the XXX-highest life expectancy in Gentu. The country is highly urbanized; four-fifth of the total land area is built on land reclaimed from the sea.
Etymology
TBA
History
Prehistorical Era and dynastic rule
The earliest known trace of human life in what is now Hoy Kok dates back to around 20,000 years ago during the Upper Vetuslithic. Discovered in 1987, archaeological works revealed stone tools from deposits that were dated using optical luminescence dating.
During the Novalithic Age, about 5,000 years ago, the region had been widely occupied by humans. Novalithic to Cuprulithic and then to Bronze Age Hoy Kok settlers were semi-coastal people. Early inhabitants are believed to be Hayosun people in the Novalithic Age and later the Qiuese people. As hinted by the archaeological works in XXX, XXX, rice cultivation had been introduced since the late Novalithic Age. Bronze Age Hoy Kok was featured with coarse pottery, hard pottery, quartz and stone jewelry, as well as small bronze implements.
The Qiu dynasty incorporated Hoy Kok into the dynasty in 267 BCE after conquering the indigenous people of the region. During the Haidao Rebellion in 199 BCE, a series of forts were built in the region. Control over these forts changed 4 times during the rebellion before the Xin government was toppled in 173 BCE and the Zhang dynasty was established. During the Juksan conquest of Wei in 618, the capital of the Wei dynasty was briefly relocated to XXX in modern day XXX before its defeat in 629 at the Battle of Zaohai. By the end of the Two Kingdoms Period in 1043, 8 large families had settled in the region and owned most of the land.
Palon colony
The earliest Oranish visitors was Neragese explorer John Leon who arrived in 1498. Neragese merchants soon established a trading post called Ezran in modern day XXX and began regular trade with southern Zhao. Military clashes between the Zhao and Neragese navies followed the expulsion of the Ezran traders in 1524. In 1823, the Nanchao dynasty ceded 118 square kilometres of land in present day XXX to the Palon Empire as a trading post in the Palonic-Nanchao agreement. The initially small population of Palon merchants rapidly became a growing city. By 1833, the Hoy Kok Council had been established to handle municipal affairs for the growing settlement. Hoy Kok was at the peak of its prosperity as a major entrepôt during the late 19th century, providing a crucial connection in exporting Nanchao silk to Oranland. Although the Palons were initially prohibited from fortifying Hoy Kok or stockpiling weapons, Fortaleza do Sabã was constructed in response to frequent Paqueon naval incursions. The Paqueon attempted to take the city in the 1843 Battle of Macau during the War of Palon Succession, but were repelled successfully by the Portuguese.
The colony was further expanded in 1868 when Paloa bought the XXX. The University of Hoy Kok was established in 1882 as the colony's first institution of higher education. Tay Mun Airport began operation in 1917, and the colony avoided any conflict during the Great War. In 1953, following a series of protests regarding the new Prime Minister of Paloa, the Treaty of Beimen was created which granted Hoy Kok a semi-autonomous status. The population of Hoy Kok boomed in the late 1950s and early 1960s as skilled Nancaho migrants and refugees fled from the Nanchao Civil War. With a rapidly increasing population, the colonial government began reforms to improve infrastructure and public services. The public-housing programme, universal healthcare programme, and Extensive UNderground Transit were all established during the 1960s and 70s decades to provide safer housing, integrity in the civil service, and more reliable transportation. By the early 1980s, Hoy Kok had established itself as a global financial centre and shipping hub.
Independence
In Disemba of 1989, a referendum known as the 1990 Hoy Kokese independence referendum was held to decide if Hoy Kok wanted full independence all continue being a semi-autonomous colony of Palon. The referendum ended on the 31st of Disemba 1989 with 26,439,204 voters voting for independence while 11,284,842 voters picked to stay as a colony. On the 1st of Enero 1990, Hoy Kok was officially granted independence and 7 days later on the 8th of Enero, its constitution would be published.
Geography
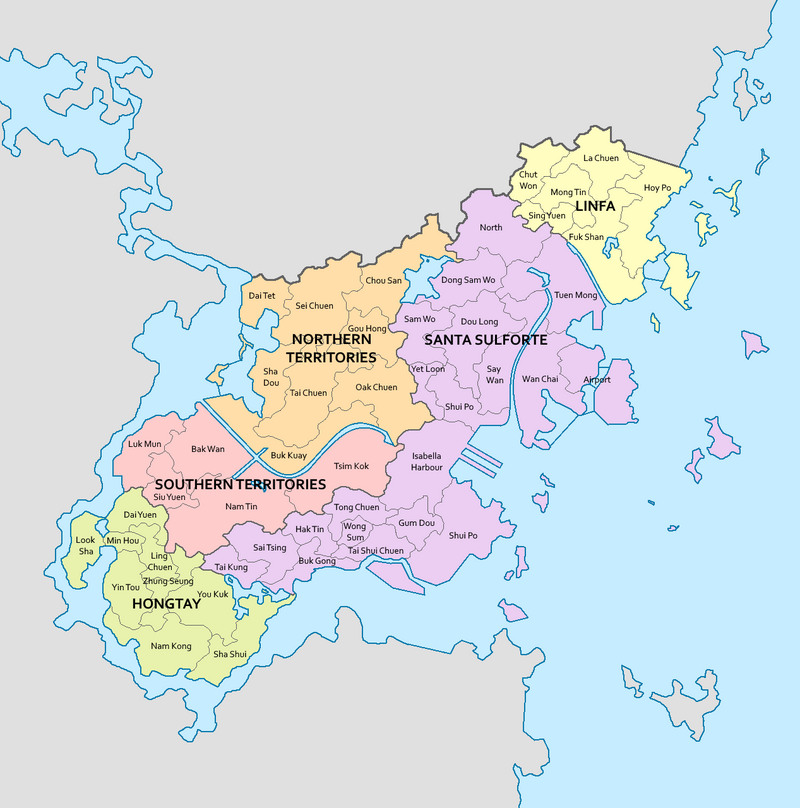
Hoy Kok is situated at the mouth of the Red River. It is surrounded on all sides by the Horapon Sea except for the west which neighbours XXX. The country's 4,338 km2 (1,675 sq mi) area comprises of the districts of Hongtay, Santa Sulforte, Southern Territories, Northern Territories, and Linfa. The tallest point is Taigo Shan which is 974.4 metres tall (3,196.85 ft). Urban development is concentrated in Santa Sulforte, Hongtay, and Linfa, with smaller settlements dotted throughout the Northern and Southern Territories. Much of Hoy Kok is built on reclaimed land; XXX km2 (XXX sq mi) is reclaimed from the sea.
Undeveloped terrain is hilly to mountainous, with very little flat land, and consists mostly of grassland, woodland, shrubland, or farmland. About 20% of the remaining land area is country parks and nature reserves. It has a diverse ecosystem; over 2,000 species of vascular plants occur in the region (500 of which are native to Hoy Kok), and thousands of insect, avian, and marine species.
Climate
Hoy Kok has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa), with an average annual temperature of 15.9 °C (60.62 °F) for urban districts and 15.3–15.8 °C (59.54–60.44 °F) for suburbs. It experiences four distinct seasons. Winters are temperate to cold and damp—northwesterly winds from northern Hesterath can cause nighttime temperatures to drop below freezing. Each year, there are an average of 5.8 days with snowfall and 1.6 days with snow cover. Summers are hot and humid, and occasional downpours or freak thunderstorms can be expected. On average, 7.2 days exceed 35 °C (95 °F) annually. In summer and the beginning of autumn, the city is susceptible to typhoons.
The most pleasant seasons are generally spring, although changeable and often rainy, and autumn, which is usually sunny and dry. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 34% in Marto to 54% in Tebax, the city receives 1,895 hours of bright sunshine annually.
| Climate data for Hoy Kok | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.1 (71.8) |
27.0 (80.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
37.5 (99.5) |
39.2 (102.6) |
39.9 (103.8) |
38.2 (100.8) |
34.0 (93.2) |
28.7 (83.7) |
23.4 (74.1) |
39.9 (103.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) |
10.1 (50.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
19.5 (67.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
27.8 (82.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.5 (88.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
20.6 (69.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.8 (40.6) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.0 (50.0) |
15.3 (59.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.9 (76.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
7.6 (45.7) |
17.1 (62.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
3.7 (38.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.8 (78.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
10.6 (51.1) |
4.7 (40.5) |
14.1 (57.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −10.1 (13.8) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
6.9 (44.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
16.3 (61.3) |
18.8 (65.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 74.4 (2.93) |
59.1 (2.33) |
93.8 (3.69) |
74.2 (2.92) |
84.5 (3.33) |
181.8 (7.16) |
145.7 (5.74) |
213.7 (8.41) |
87.1 (3.43) |
55.6 (2.19) |
52.3 (2.06) |
43.9 (1.73) |
1,166.1 (45.91) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 9.9 | 9.2 | 12.4 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 12.7 | 11.4 | 12.3 | 9.1 | 6.9 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 120.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 73 | 73 | 72 | 72 | 79 | 77 | 78 | 75 | 72 | 72 | 71 | 74 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 114.3 | 119.9 | 128.5 | 148.5 | 169.8 | 130.9 | 190.8 | 185.7 | 167.5 | 161.4 | 131.1 | 127.4 | 1,775.8 |
| Source: Hoy Kok Observatory | |||||||||||||
Architecture
TBA
Government
TBA
Administrative divisions
Hoy Kok is divided into 5 districts, each represented by a District Council. The 5 districts are divided into 48 villages. Each village have a seat in their respective district councils. They advise the government on local issues such as public facility provisioning, community programme maintenance, cultural promotion, and environmental policy.
| Current map of Hoy Kok |
|---|
Demographics
TBA
Economy
TBA
Infrastructure
Transport
TBA
Healthcare
TBA
Education
TBA
Culture
Cuisine
TBA
Sports and recreation
TBA
Media
TBA
Cinema
TBA
Music
TBA