Mambiza: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Featured Article}} | |||
{{KylarisRecognitionArticle}} | |||
{{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
| official_name = Mambiza | | official_name = Mambiza | ||
| Line 6: | Line 8: | ||
| translit_lang1_type = | | translit_lang1_type = | ||
| translit_lang1_info = | | translit_lang1_info = | ||
| image_skyline = | | image_skyline = {{multiple image | ||
| border = infobox | |||
| perrow = 1/2/1/1/1 | |||
| total_width = 280 | |||
| align = center | |||
| caption_align = center | |||
| image1 = Cape_Town_City_DSC_3621_(cropped).jpg | |||
| caption1 = [[Garambura|Mambésa Centre-Ville]] | |||
| image2 = CT_City_Hall_Before_the_Sun.jpg | |||
| caption2 = {{nowrap|[[Garambura|Hôtel de Ville de Mambésa]]}} | |||
| image3 = Cape_Coast_Castle,_Cape_Coast,_Ghana.JPG | |||
| caption3 = [[Garambura|Fort Blanc]] | |||
| image4 = View_down_Adderley_Street.jpg | |||
| caption4 = [[Garambura|Boulevard du 16 Février]] | |||
| image5 = Ciudad_del_Cabo,_Kirstenbosch_NBG_29.jpg | |||
| caption5 = [[Garambura|Jardins de Saint-Marc]] and [[Garambura|Mont Francois]] | |||
}} | |||
| imagesize = 300px | | imagesize = 300px | ||
| image_caption = | | image_caption = | ||
| image_flag = | | image_flag = | ||
| flag_size = | | flag_size = | ||
| Line 15: | Line 33: | ||
| image_shield = Coat of arms of Harare.svg | | image_shield = Coat of arms of Harare.svg | ||
| shield_size = | | shield_size = | ||
| nicknames = Iron City | | nicknames = Iron City, Jewel of Bahia | ||
| motto = "Guta relron"<br><small>("The city of iron")</small> | | motto = "Guta relron"<br><small>("The city of iron")</small><br>"Joyau de Bahia"<br><small>("Jewel of Bahia") (historical)</small> | ||
| image_map = | | image_map = | ||
| mapsize = | | mapsize = | ||
| Line 55: | Line 73: | ||
| elevation_m = 13 | | elevation_m = 13 | ||
| elevation_ft = | | elevation_ft = | ||
| population_total = | | population_total = 8,031,415 | ||
| population_as_of = | | population_as_of = 2022 | ||
| population_footnotes = | | population_footnotes = | ||
| population_density_km2 = 3089 | | population_density_km2 = 3089 | ||
| population_density_sq_mi = 8001 | | population_density_sq_mi = 8001 | ||
| population_urban = | | population_urban = | ||
| population_demonym = Mambizan | | population_demonym = Mambizan | ||
| postal_code_type = | | postal_code_type = | ||
| Line 76: | Line 94: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Mambiza''' ({{wp|Help:IPA/English|/'mæmbi:za/}}; officially ''' | '''Mambiza''' ({{wp|Help:IPA/English|/'mæmbi:za/}}; officially '''Sainte-Germaine''' until 1970) is the largest city in [[Garambura]]. The city has one of the largest designated metropolitan areas in Garambura, at 1,253.9km<sup>2</sup> (481.4mi<sup>2</sup>), with a total population of over 8 million inhabitants. Mambiza itself is a metropolitan province of Garambura, and is represented by its elected governor Rupenyu Majange. The city sits on the expansive Gonda Delta and its coastal location makes it a popular destination for global trade. | ||
The city was founded as a trading outpost in 1656 by [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] merchants, who named the city '' | The city was founded as a trading outpost in 1656 by [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] merchants, who named the city ''Sainte-Germaine'' after the [[Sotirian Catholic Church|Sotirian]] venerated figure. It served as a stopover for trade between [[Euclea]] and southern [[Coius]], namely [[Xiaodong]] and [[Senria]], and so the city's wealth grew under the Gaullicans. It was designated as the capital of [[Baséland]] when it fell under full Gaullican sovereignty in 1813, and was designated a city in 1814. Mambiza was the site of [[Charles Dumont]]'s famous ''Droits de l'homme'' speech in 1919, before he was executed in the city by national functionalists. Many of the city's inhabitants were conscripted during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. The capital was moved and the city renamed to Mambiza in 1970 after Garambura secured its independence. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
=== Merchant city ( | {{Quote box |width=25em |align=left |bgcolor=#B0C4DE |title=Historical affiliations|fontsize=90% |quote=[[File:Lower_Gonda_Company_Seal.png|22px]] [[Gaullican Lower Gonda Company]] 1656–1813<br>[[File:BLFlag.png|border|22px]] [[Baséland]] 1813–1935<br>{{flagicon|Estmere}} [[Estmere|Commonwealth of Estmere]] 1935–1946<br>{{flagicon|Rwizikuru}} [[Rwizikuru|Republic of Rwizikuru]] 1946–1964<br>{{flagicon|Rwizikuru}} [[Rwizikuru|Kingdom of Rwizikuru]] 1964–1969<br>{{flagicon|Garambura}} [[Garambura|Republic of Garambura]] 1969–present | ||
}} | |||
[[File:Cadornega.jpg|200px|left|thumb|The original charter for Sainte-Germaine issued by the Crown of Gaullica in 1655.]] | |||
=== Merchant city (1656–1813) === | |||
The location that the city of Sainte-Germaine would be settled on would be granted as a charter to the newly-created Gaullican Lower Gonda Company, founded in 1655 to subsidise colonial ventures in the region, by the Crown of Gaullica. The Gaullians settled the delta of the Gonda river sometime around October to November if 1656, with native contact being made shortly after. Early evidence suggests that the Gaullicans exhibited a native co-existence policy for the city, and thus the city had some natives as an early populace. This early contact between the natives and Gaullicans is estimated to be the likely emergence of the [[Palatara creole]], now spoken in the city. | The location that the city of Sainte-Germaine would be settled on would be granted as a charter to the newly-created Gaullican Lower Gonda Company, founded in 1655 to subsidise colonial ventures in the region, by the Crown of Gaullica. The Gaullians settled the delta of the Gonda river sometime around October to November if 1656, with native contact being made shortly after. Early evidence suggests that the Gaullicans exhibited a native co-existence policy for the city, and thus the city had some natives as an early populace. This early contact between the natives and Gaullicans is estimated to be the likely emergence of the [[Palatara creole]], now spoken in the city. | ||
Due to this city's location in a natural bay and on extremely fertile and arable land, it grew quickly and established itself as one of Gaullica's primary ports for the transportation of Bahian slaves to the Asterias at the height of the Asterian Slave Trade. The city's predominantly | Due to this city's location in a natural bay and on extremely fertile and arable land, it grew quickly and established itself as one of Gaullica's primary ports for the transportation of Bahian slaves to the Asterias at the height of the Asterian Slave Trade. The city's predominantly [[Chennois]] populace combined with the policies of [[Toubacterie]] exhibited within the city led to many of the city's Euclean residents becoming wealthy property and land-owners, with some choosing to employ natives as labourers and others choosing to expand the city's infrastructure with their plot of land, with many residential areas, including early hotels and inns, being constructed during this period. | ||
When slavery was abolished throughout the Gaullican Empire, the city's connections throughout the empire, particularly those back to Euclea and to Gaullican holdings in the Asterias, allowed it to stay as a financial hub in Bahia and retain its wealth while many other settled ports by Euclean nations dwindled as their main exports were severely neutered. The city also prospered due to its large fishing industry, an industry which many native residents of the city were employed in. As such, Sainte-Germaine became known for its exotic fish markets in the 18th century, with the exports of fish and the tourism into the city contributing to a significant chunk of its economy. This was only amplified when the Gaullican Lower Gonda Company began expanding its holdings inland and across the Garamburan coast, with Sainte-Germaine functioning as the ''de facto'' capital due to its history as the influential city on the Garamburan coast. The city's economy did take a brief hit, however, during the [[Plundering of Sainte-Germaine (1772)|Plundering of Sainte-Germaine]], where Karame [[Mabuti I]] and his forces raided and plundered the city for encroaching upon native territory in the central portions of Garambura. Its economy swiftly recovered after the 1774 [[Battle of Ingezi]] which marked the effective dominance for Gaullica throughout most of the Gonda river region. | When slavery was abolished throughout the Gaullican Empire, the city's connections throughout the empire, particularly those back to Euclea and to Gaullican holdings in the Asterias, allowed it to stay as a financial hub in Bahia and retain its wealth while many other settled ports by Euclean nations dwindled as their main exports were severely neutered. The city also prospered due to its large fishing industry, an industry which many native residents of the city were employed in. As such, Sainte-Germaine became known for its exotic fish markets in the 18th century, with the exports of fish and the tourism into the city contributing to a significant chunk of its economy. This was only amplified when the Gaullican Lower Gonda Company began expanding its holdings inland and across the Garamburan coast, with Sainte-Germaine functioning as the ''de facto'' capital due to its history as the influential city on the Garamburan coast. The city's economy did take a brief hit, however, during the [[Plundering of Sainte-Germaine (1772)|Plundering of Sainte-Germaine]], where Karame [[Mabuti I]] and his forces raided and plundered the city for encroaching upon native territory in the central portions of Garambura. Its economy swiftly recovered after the 1774 [[Battle of Ingezi]] which marked the effective dominance for Gaullica throughout most of the Gonda river region. | ||
=== Under the Gaullican Kingdom ( | === Under the Gaullican Kingdom (1813–1919) === | ||
[[File:Booker_T._Washington.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Vivien Lemaigre (second from the right) and his family outside the Sainte-Germaine Colonial Court after the 1907 ruling.]] | |||
Sainte-Germaine was essentially unanimously designated for the capital of the [[Baséland]] colony when it was officially established in 1813 after the Gaullican Lower Gonda Company was ordered to transfer its holdings to the Gaullican Empire. The colony's administrative divisions and military supplied lines were organised in a way that funneled most colonial business through either Sainte-Germaine, mainly in the populated south, and Albertsville, in the scarcer and less populated north. Sainte-Germaine benefited massively from its role in the colony, as well as many resettlement and migration programs promoted throughout Gaullica and its holdings towards Sainte-Germaine, and it quickly became one of Bahia's quickest expanding colonial cities. The influx of population led to an increased military presence within the city, with many military bases and installments constructed throughout the early-to-mid 1800s, with the last of four major bases completed in 1848. | |||
The city was, however, subject to a series of oppressive colonial ruling by the many governors that ruled the city, and by extension, the colony, throughout its existence. Whilst natives were seen as "Gaullican" by the higher-ups in Gaullica, there was still significant racial prejudice between the upper-class [[Chennois]] citizens of Sainte-Germaine and the lower-class native citizens. To preserve colonial wealth, governors would often side with the [[Chennois]] populace in the colony. Brutality heightened during the [[Sougoulie]] rebellions and in particular following the [[Sinking of the NMS Insulaire]] by [[Alphonse Amsalu]] in 1883, after which [[Yebase]] rights were curtailed, many positions revoked and their positions in the empire questioned. These policies would continue until the accession of [[Charles Dumont]] to the position of Governor of Baséland in 1906, where he would quickly introduce more native-friendly policies, including the restoring of the [[Yebase]] to many of their traditional positions. His legacy as a native-friendly ruler was solidified when he ruled in favour of the native Vivien Lemaigre in the [[Vivien Lemaigre case]] in 1907, where the accused white land-owner was forced to pay reparations to Lemaigre for violating his, and many other employed natives', labour rights. Dumont's tenure is regarded as extremely liberal compared to those he succeeded, however he was captured and arrested for treason by the national functionalists of Gaullica after they took power in the mainland, executing him in the city's harbour on October 22, 1919. | |||
=== Under the national functionalists (1919–35) === | === Under the national functionalists (1919–35) === | ||
The city took a sharp turn to repressive rule when the national functionalists completed consolidated power in Bahia in 1919, producing propaganda that mainly appealed to the white upper-class regarding the policies of Dumont and how they supposedly affected the prosperity of the colony. Despite the target audience of this propaganda, a colony-wide curfew, regardless of race, was issued in December 1919 in response to the supposed effects of Dumont's policies on the colony. The national functionalists were believers in the fact that order had to be imposed on the colonies to prevent dissident movements, with harsher rulings and slave labour being utilised, and inflicted onto both white and black residents of the city, but was notably more brutal for the native residents. More notably, during the rule of the national functionalists, the [[Adunis to Mambiza railway]] was completed in 1922, marking one of the great architectural achievements of the Gaullican Empire, and the completion of [[Grégoire Cuvillier]]'s ambitions. The railway allowed supplies and military equipment to travel between Gaullican colonies in Bahia far more easily, with supplies sometimes being shipped from [[Verlois]] to Adunis, then down the railway to Sainte-Germaine. | |||
==== Great War (1926–35) ==== | ==== Great War (1926–35) ==== | ||
[[File:Senagalese_French_soldiers_WW1.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Members of the ''2éme tirailleurs Bahiens'', based in Sainte-Germaine, in 1931.]] | |||
Sainte-Germaine was treated extremely prestigiously by the Gaullican army, and the city - along with Adunis - were considered as Gaullica's premier Bahian cities. Sainte-Germaine had some planes and naval fleets based in its ports and airbases for short amounts of time, particularly for invasions of [[Rwizikuru]] and [[Tabora]]. Around 180,000 residents of Sainte-Germaine, some 50% of which are estimated to have been native, saw some form of combat in the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], mainly in Bahia and Badawiya, and particularly against [[Estmere]] and [[Werania]] in Riziland and Tabora. Gaullica was particularly successful in the Bahian and Badawiyan fronts, owing mainly to its colonial domination of the area. Many of the residents of Sainte-Germaine fought in the ''Tirailleurs Bahiens'', colonial regiments of Bahian troops under the service of Gaullica. | |||
=== Estmerish rule (1935–46) === | === Estmerish rule (1935–46) === | ||
After the war had concluded and Gaullica had surrendered, most of its colonial possessions were transferred to the three victorious colonial powers: mainly [[Estmere]] and [[Werania]], with some going to [[Etruria]]. Estmere took control of the Baséland colony in 1935, effectively ruling it in unison with the adjacent colony of Riziland. In 1936 it was given the official colonial name of East Riziland, which was met with criticism, particularly from Sainte-Germaine, as to the future of the colony. During this time, aid was brought from Estmere to tend to wounded soldiers who were returning to their families in the city, with the city receiving ample aid due to its excessive size for a city in Bahia at the time. | |||
By the 1940s, Estmere had displayed no intent at letting Garambura choose its own path, and negotiations were being held which highly suggested that the region was going to secede as part of Rwizikuru. With many Garamburan republicans finding this unacceptable, large-scale demonstrations were held against Estmere in the city in 1944 - which to this day are still some of the largest seen in Bahia - with an estimated 250,000 protesting against inclusion within Rwizikuru for its succession, now scheduled for 1946. The government of Estmere paid little attention to the protests, however, and Sainte-Germaine, along with the rest of Garambura, was granted independence in 1946 as the Republic of Rwizikuru. | |||
=== Rwizikuran rule (1946–69) === | === Rwizikuran rule (1946–69) === | ||
Rwizikuran rule over Sainte-Germaine saw it ''de facto'' introduced as the capital of the district of [[East Riziland]]. It served as the administrative capital of the region and still attracted great amounts of wealth, quickly becoming Rwizikuru's most wealthy city. Due to the overwhelming Chennois demographic in the city, they were not subject to the same Euclean repatriation policies that had been implemented in the mainland. The city was administered fairly autonomously out of necessity rather than choice, with [[Samhuri Ngonidzashe]] unwilling to impose direct rule on the city for fear of scaring away investors in the city and destroying the city's large income. When Rwizikuru entered the [[United Bahian Republic]] in 1954, it saw more migration from UBR member nations looking to emigrate to Sainte-Germaine's comparatively affluent suburbs, diversifying the local population with sects of Sotirianity like Orthodoxy in [[Djedet]] practised by a minority in the city. It also became renowned for its cultural nightlife scene in the 1950s and 1960s, and was marketed throughout the UBR as a tourist destination. When the UBR dissolved in 1965 and [[Izibongo Ngonidzashe]] had declared himself [[Monarchy of Rwizikuru|Mambo of Rwizikuru]], Sainte-Germaine became the centre of independence discussion and internal strife within Rwizikuru, particularly after the start of the [[Mabifian-Rwizikuran War]] over the district of Yekumavirira. [[Takakunda Kuda Kani]] delivered his speech declaring Garambura unilaterally independent from Rwizikuru in 1969, and the outskirts of the city saw most of the conflict. | |||
=== Post-independence (1969–) === | === Post-independence (1969–) === | ||
[[File:Porto_de_Luanda_-_Angola_2015.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Mambiza saw rapid economic development in the 1970s and 80s.]] | |||
With Garambura now independent in April 1969 and Takakunda Kuda Kani sworn in as the first President of Garambura, economic and political transformation of the city began quickly. The city was allocated 79 seats of the [[National Assembly (Garambura)|National Assembly]], over half of the available seats, due to its large population and influential economy. The city was officially renamed to Mambiza in 1970 to popularise the city and to disavow its colonial history, with all mail addressed to Sainte-Germaine re-routed back to the sender's address. | |||
The emergence of Mambizan culture in the 1970s massively influenced culture throughout Bahia, and drew inspiration heavily from the emerging punk culture of [[Euclea]] at the same time. [[Djeli pop#Club Mambiza|Club Mambiza]], a subgrouping of [[Djeli pop]], became a popular characterisation of the city, and gained it cultural notoriety across the world. Its club scene became famous and saw the city become the most-visited destination in the whole of [[Coius]] in 1978. Coupled with economic reforms of the Takakunda administration that helped further integrate it into the regional economy, Mambiza was one of the world's fastest-growing economies throughout the 1970s and 1980s. Increased funding from [[Halland]] allowed the city's industrial sector to be bolstered, and migration from rural Garambura to the industrial outskirts of the city introduced large amounts of income inequality between the more affluent suburban [[Chennois]] populace and the native industrial workers, a divide which still exists today. The [[Métro de Mambesa]] was constructed through the 1990s and opened in 1995 to increase rapid transport links throughout the city. The metro was expanded in 2003 and again in 2009 and now covers most of the city. The city's airport, [[Mambiza–Charles Dumont International Airport]], was opened in 2001 and is the busiest in Bahia, serving most of Garambura with transport links across the world. | |||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
Mambiza's geography is mainly characterised by its coastal location, and its location on the [[Gonda]] Delta. It is a natural {{wp|entrepot}}, and has historically been a centre of trade in Bahia. It experiences a tropical climate characteristic of most of Garambura, with temperatures often ranging from 20-30 degrees Celsius, with rainfall occurring mainly in the autumn and summer months. It is located on the 8th parallel north, and is roughly adjacent to the Rwizikuran capital [[Port Fitzhubert]] on latitude. Most of Mambiza's surrounding line is flat, arable marsh and farmland, saturated largely by the Gonda. The district of Armaillé is the city's southernmost district, and sits in the west, near the Garambura-Rwizikuru border. | |||
The city has historically been divided into two sections - the West End and the East End - reflecting the ethnic divide within the city. The Chennois dominate demographics in the West End while the East End is populated mainly by the native Bahian populace. Officially, the city is divided into 47 districts - the most of any city in Bahia, presided over by an elected Mayor, currently Rupanyu Majange of the Garamburan National Party. Despite the city's 47 districts, it has 79 seats in the country's [[National Assembly (Garambura)|National Assembly]]. The terms West End and East End have fallen out of use for any official administrative purposes, but the terms are still used colloquially by the city's population. | |||
=== Climate === | === Climate === | ||
Mambiza's climate is typical of tropical Bahia, with rainfall frequent in the warmer months and temperatures usually ranging from 20 to 30 degrees throughout the entire day. Temperatures rarely drop into single digits and have never dropped below freezing in the city's climate's recorded history, which is recorded at the Mambiza Observatory on Blue Hill, in the south of the city. | |||
{{Weather box|location = Mambiza (1970–2000) | |||
|metric first = yes | |||
|single line = yes | |||
|Jan high C = 28.6 | |||
|Feb high C = 28.9 | |||
|Mar high C = 29.2 | |||
|Apr high C = 29.5 | |||
|May high C = 29.4 | |||
|Jun high C = 29.2 | |||
|Jul high C = 29.6 | |||
|Aug high C = 30.2 | |||
|Sep high C = 30.8 | |||
|Oct high C = 30.8 | |||
|Nov high C = 30.2 | |||
|Dec high C = 29.1 | |||
|year high C = 29.6 | |||
|Jan mean C = 26.1 | |||
|Feb mean C = 26.4 | |||
|Mar mean C = 26.7 | |||
|Apr mean C = 27.0 | |||
|May mean C = 26.8 | |||
|Jun mean C = 26.5 | |||
|Jul mean C = 26.6 | |||
|Aug mean C = 27.0 | |||
|Sep mean C = 27.5 | |||
|Oct mean C = 27.6 | |||
|Nov mean C = 27.2 | |||
|Dec mean C = 26.4 | |||
|year mean C = 26.8 | |||
|Jan low C = 23.6 | |||
|Feb low C = 23.9 | |||
|Mar low C = 24.2 | |||
|Apr low C = 24.4 | |||
|May low C = 24.3 | |||
|Jun low C = 23.8 | |||
|Jul low C = 23.5 | |||
|Aug low C = 23.8 | |||
|Sep low C = 24.2 | |||
|Oct low C = 24.4 | |||
|Nov low C = 24.2 | |||
|Dec low C = 23.8 | |||
|year low C = 24.0 | |||
|rain colour = green | |||
|Jan rain mm = 185.2 | |||
|Feb rain mm = 88.5 | |||
|Mar rain mm = 111.0 | |||
|Apr rain mm = 140.5 | |||
|May rain mm = 285.5 | |||
|Jun rain mm = 327.7 | |||
|Jul rain mm = 268.0 | |||
|Aug rain mm = 201.4 | |||
|Sep rain mm = 97.5 | |||
|Oct rain mm = 107.2 | |||
|Nov rain mm = 185.9 | |||
|Dec rain mm = 261.9 | |||
|year rain mm = 2260.3 | |||
|Jan rain days = 16 | |||
|Feb rain days = 10 | |||
|Mar rain days = 10 | |||
|Apr rain days = 12 | |||
|May rain days = 19 | |||
|Jun rain days = 23 | |||
|Jul rain days = 21 | |||
|Aug rain days = 15 | |||
|Sep rain days = 9 | |||
|Oct rain days = 9 | |||
|Nov rain days = 12 | |||
|Dec rain days = 18 | |||
|year rain days = 174 | |||
|unit rain days = 1.0 mm | |||
|Jan sun = 201.0 | |||
|Feb sun = 208.6 | |||
|Mar sun = 219.7 | |||
|Apr sun = 197.9 | |||
|May sun = 178.8 | |||
|Jun sun = 156.7 | |||
|Jul sun = 201.6 | |||
|Aug sun = 233.7 | |||
|Sep sun = 229.8 | |||
|Oct sun = 235.3 | |||
|Nov sun = 210.9 | |||
|Dec sun = 186.6 | |||
|year sun = 2460.6 | |||
|source 1 = Institut météorologique de Garamboure<ref name="Georgetown Wiki">IMG, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Georgetown,_Guyana#Climate, Mambiza climate data (1970-2000)], Institut météorologique de Garamboure, 17 January 2000, Retrieved 20 March 2020</ref>}} | |||
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
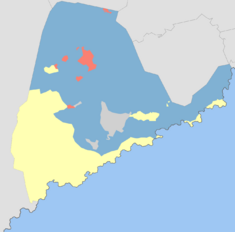
[[File:Mambiza_Language_Map.png|235px|right|thumb|Map of dominant languages in the Greater Mambiza area: | |||
{{Columns |col1= | |||
{{legend|#ffffb3|{{wp|French language|Gaullican}}}} | |||
{{legend|#fb8072|{{wp|Xhosa language|Sisulu}}}} | |||
|col2= | |||
{{legend|#80b1d3|{{wp|Shona language|veRwizi}}}} | |||
{{legend|#d0d0d0|None dominant}}}}]] | |||
Mambiza is the most populous city in Garambura, with a population of around 4.5 million in 2020, around 50% of Garambura's population of 9.3 million. Mambiza experiences extremely high population growth owing to immigration from rural Garambura and from elsewhere in Bahia, and is Bahia's fastest growing city and one of the world's fastest-growing cities. In practise, it is difficult to document Mambiza's total population due to the {{wp|shanty towns}} and {{wp|slums}} that exist in the northern and western outskirts of the city, built by rural immigrants who cannot afford to live in the city itself. | |||
The highest demographic in Mambiza is the {{wp|Shona|veRwizi}}, at 57% (4,284,281 people), followed by the [[Chennois]] at 18% (1,352,930 people), over 90% of the total Chennois population in Garambura, and the {{wp|Xhosa|Sisulu}} at 16% (1,202,605 people). The remaining 9% consist mainly of immigrants from elsewhere, as well as smaller minorities of the {{wp|Chewa people|Njinji people}} that live mainly in eastern Garambura. | |||
Linguistically, the city primarily speaks {{wp|Shona language|veRwizi}}, but {{wp|French language|Gaullican}} is also spoken by around 80% of the population as either a first or second language, and it is used as the native language of the [[Chennois]], an official administrative language, and a language of commerce and trade with the rest of the world. | |||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
The city is fairly economically developed, and has a modern {{wp|central business district}} that hosts various offices from Garamburan companies as well as international conglomerates looking to expand into the Bahian market. It also has a large and developed port capable of handing large and frequent cargo and passenger traffic, and the city is a regular stop for sea-based trade entering Garambura (almost 85% in 2009) as well as Bahia in general. Business presence as well as its importance as a global port makes Mambiza one of Bahia's richest cities. The Greater Mambiza area generates around 78% of Garambura's {{wp|gross domestic product}} as of 2015 ($65.13 billion by nominal; $121.8 billion by {{wp|purchasing power parity}}), giving it a GDP per capita of $8,665 (nominal) or $16,204 (PPP), by far the highest in Garambura. | |||
[[File:2010_Lagos_Nigeria_by_Rainer_Wozny_5342608955.jpg|right|210px|thumb|Tin-rooved houses built on the banks of the [[Gonda]] in the Pelela shanty town.]] | |||
Nearly all major institutions in Garambura are based in the city, creating work and attracting immigration from elsewhere. The city generates the highest percentage of gross domestic product of any country (excluding city-states), and the country is incredibly reliant on Mambizan business and trade for its economy. | |||
Despite the city's affluence, it suffers from widespread poverty and income inequality. Its {{wp|Gini coefficient}} was 0.52 in 2014, when the government introduced several programs aiming to tackle homelessness and poverty in the city, however the coefficient has remained stagnant since then. Poverty rates by ethnicity are 3.5% for white [[Chennois]], 10.3% for veRwizi, 10.9% for Sisulu and 22.1% for Njinji. Poverty and inequality is amplified by the presence of expanding {{wp|shanty towns}} and {{wp|slums}} in the north of the metropolitan area, which have been built up and settled by poorer rural immigrants unable to afford accommodation in the city's built-up areas. Ndirazepatswa, Pelela and Makufa are among the city's most-populated slums, and have recently begun to expand into pre-existing towns in the north such as Tsvangirayi, Mzilikazi and Ingezi. These shanty towns are often built along the [[Gonda]] to utilise its banks for small-scale farming (mainly fishing) as well as business ventures selling cheap goods along the riverbank, although more recently this has evolved into a necessity due to a lack of space in the city. | |||
[[Muzukuru Chiyangwa]] announced the government's intention to begin demolishing the slums to build proper apartment complexes and real estate, notably in Pelela and Makufa which lie fairly centrally in the metropolitan area of the city. This policy was reaffirmed by [[Sylvain Sikali]] in 2020, although no action has yet been taken due to its controversy and accusations of the government's disregard for the some 300,000 inhabitants of the city living in its shanty towns. | |||
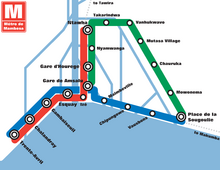
[[File:Métro de Mambesa Map.png|220px|left|thumb|Map of the Métro de Mambesa, 2016 edition]] | |||
== Transport == | == Transport == | ||
Mambiza is well-connected to itself and the rest of Garambura by road, train, tram and ferry. The A1, A2 and A4 motorways run through the city and service a large amount of car traffic to other urban centres throughout the country. In 2022, {{wp|toll roads}} will be implemented on motorways travelling in and out of the city between 5:00AM and 10:00PM, aimed to collect more revenue for the city's transport services but also to encourage the use of the city's public transport and to reduce inner-city congestion and carbon emissions. | |||
The [[Métro de Mambesa]] is the city's underground rail network, and is extremely advanced for its location. Beginning construction throughout the 1990s and opening to the public in 1995, it originally serviced the western side of the city, with its Central Line travelling from Trente-Avril to Ntawha. The Eastern Line was added in 2003 as the metro's first major expansion and connecting Gare de Amsalu to the Place de la Sougoulie in the east of the city, and the Delta Line was expanded in 2009 to connect the coastal districts of Mambiza. The service covers most of the developed areas of the city and has a daily ridership of around 1 million passengers. The city is also connected by overground train to Makumba and Mutimukuru in the east and Kugura and Tawira in the north, running along the Gonda and built off of the [[Adunis to Mambiza Railway]] built by the Gaullican Empire in the 19th and 20th centuries. | |||
Ferries run to and from Mambiza's ports to other cities in Garambura as well as locations in neighbouring [[Rwizikuru]]. The port also services {{wp|cruise ships}} whose termini include [[Dezevau]], [[Lavana]] and [[Terangau]], and is the only port in Bahia with sufficient infrastructure to do so. Many Mambizans are employed at the city's main port and smaller ports. Its airport, [[Mambiza{{ndash}}Charles Dumont International Airport]], has two runways and services a multitude of international destinations in all of the world's continents. | |||
The city also has a unique public transport city known as the SRM (''Service de la rivière Mambesa''; "Mambiza River Service"), which consists of large boats and smaller ferries travelling up the Gonda delta to a series of destinations along its banks. The SRM currently services five main routes for the five main settled rivers of the delta in the city, Trente-Avril{{ndash}}Villefavard du Ouest, Chalandray{{ndash}}Villefavard du Est, Gambeiseuil{{ndash}}Mutasa Village, Izé{{ndash}}Gare d'Hourege and Maimbeville{{ndash}}Chauruka. The SRM has a daily ridership of around 175,000, and is mainly used a tourist or sightseeing attraction, with the metro being favoured for high-speed travel. The SRM has recently had funding issues as a result of decreasing daily ridership in favour of the metro and the city's motorways. | |||
== Twin towns – Sister cities == | == Twin towns – Sister cities == | ||
* {{flagicon|Azmara}} [[Stajnensby]], [[Azmara]] (2009) | |||
* {{flagicon|Belmonte}} [[Castelonovo]], [[Belmonte]] (2001) | |||
* {{flagicon|Caldia}} [[Spálgleann]], [[Caldia]] (1993) | |||
* {{flagicon|Imagua and the Assimas}} [[Cuanstad]], [[Imagua and the Assimas]] (1999) | |||
* {{flagicon|Gaullica}} [[Verlois]], [[Gaullica]] (1978) | |||
* {{flagicon|Halland}} [[Ealaghleann]], [[Halland]] (1978) | |||
* {{flagicon|Rwizikuru}} [[Port Fitzhubert]], [[Rwizikuru]] (1945{{ndash}}1969, 1980{{ndash}}) | |||
* {{flagicon|Zorasan}} [[Zahedan]], [[Zorasan]] (2006) | |||
== References == | |||
[[Category:Garambura]] | [[Category:Cities]][[Category:Garambura]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 28 January 2024
Template:KylarisRecognitionArticle
Mambiza | |
|---|---|
City and Province | |
| Nicknames: Iron City, Jewel of Bahia | |
| Motto(s): "Guta relron" ("The city of iron") "Joyau de Bahia" ("Jewel of Bahia") (historical) | |
| Coordinates: 8º41'N 33º39'W | |
| Country | Garambura |
| Province | Mambiza |
| Founded | 1656 |
| Incorporated (city) | 1841 |
| Renamed | 1970 |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Rupenyu Majange |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,253.9 km2 (484.1 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 13 m (43 ft) |
| Population (2022) | |
| • Total | 8,031,415 |
| • Density | 3,089/km2 (8,001/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Mambizan |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (Eastern Bahian Time) |
| Area code | 85 |
| Climate | Cwb |
| Website | cityofmambiza |
| Dialling code 85 (085 in Garambura) | |
Mambiza (/'mæmbi:za/; officially Sainte-Germaine until 1970) is the largest city in Garambura. The city has one of the largest designated metropolitan areas in Garambura, at 1,253.9km2 (481.4mi2), with a total population of over 8 million inhabitants. Mambiza itself is a metropolitan province of Garambura, and is represented by its elected governor Rupenyu Majange. The city sits on the expansive Gonda Delta and its coastal location makes it a popular destination for global trade.
The city was founded as a trading outpost in 1656 by Gaullican merchants, who named the city Sainte-Germaine after the Sotirian venerated figure. It served as a stopover for trade between Euclea and southern Coius, namely Xiaodong and Senria, and so the city's wealth grew under the Gaullicans. It was designated as the capital of Baséland when it fell under full Gaullican sovereignty in 1813, and was designated a city in 1814. Mambiza was the site of Charles Dumont's famous Droits de l'homme speech in 1919, before he was executed in the city by national functionalists. Many of the city's inhabitants were conscripted during the Great War. The capital was moved and the city renamed to Mambiza in 1970 after Garambura secured its independence.
History
File:BLFlag.png Baséland 1813–1935
Template:Country data Estmere Commonwealth of Estmere 1935–1946
File:RwizikuruFlag.PNG Republic of Rwizikuru 1946–1964
File:RwizikuruFlag.PNG Kingdom of Rwizikuru 1964–1969
Merchant city (1656–1813)
The location that the city of Sainte-Germaine would be settled on would be granted as a charter to the newly-created Gaullican Lower Gonda Company, founded in 1655 to subsidise colonial ventures in the region, by the Crown of Gaullica. The Gaullians settled the delta of the Gonda river sometime around October to November if 1656, with native contact being made shortly after. Early evidence suggests that the Gaullicans exhibited a native co-existence policy for the city, and thus the city had some natives as an early populace. This early contact between the natives and Gaullicans is estimated to be the likely emergence of the Palatara creole, now spoken in the city.
Due to this city's location in a natural bay and on extremely fertile and arable land, it grew quickly and established itself as one of Gaullica's primary ports for the transportation of Bahian slaves to the Asterias at the height of the Asterian Slave Trade. The city's predominantly Chennois populace combined with the policies of Toubacterie exhibited within the city led to many of the city's Euclean residents becoming wealthy property and land-owners, with some choosing to employ natives as labourers and others choosing to expand the city's infrastructure with their plot of land, with many residential areas, including early hotels and inns, being constructed during this period.
When slavery was abolished throughout the Gaullican Empire, the city's connections throughout the empire, particularly those back to Euclea and to Gaullican holdings in the Asterias, allowed it to stay as a financial hub in Bahia and retain its wealth while many other settled ports by Euclean nations dwindled as their main exports were severely neutered. The city also prospered due to its large fishing industry, an industry which many native residents of the city were employed in. As such, Sainte-Germaine became known for its exotic fish markets in the 18th century, with the exports of fish and the tourism into the city contributing to a significant chunk of its economy. This was only amplified when the Gaullican Lower Gonda Company began expanding its holdings inland and across the Garamburan coast, with Sainte-Germaine functioning as the de facto capital due to its history as the influential city on the Garamburan coast. The city's economy did take a brief hit, however, during the Plundering of Sainte-Germaine, where Karame Mabuti I and his forces raided and plundered the city for encroaching upon native territory in the central portions of Garambura. Its economy swiftly recovered after the 1774 Battle of Ingezi which marked the effective dominance for Gaullica throughout most of the Gonda river region.
Under the Gaullican Kingdom (1813–1919)
Sainte-Germaine was essentially unanimously designated for the capital of the Baséland colony when it was officially established in 1813 after the Gaullican Lower Gonda Company was ordered to transfer its holdings to the Gaullican Empire. The colony's administrative divisions and military supplied lines were organised in a way that funneled most colonial business through either Sainte-Germaine, mainly in the populated south, and Albertsville, in the scarcer and less populated north. Sainte-Germaine benefited massively from its role in the colony, as well as many resettlement and migration programs promoted throughout Gaullica and its holdings towards Sainte-Germaine, and it quickly became one of Bahia's quickest expanding colonial cities. The influx of population led to an increased military presence within the city, with many military bases and installments constructed throughout the early-to-mid 1800s, with the last of four major bases completed in 1848.
The city was, however, subject to a series of oppressive colonial ruling by the many governors that ruled the city, and by extension, the colony, throughout its existence. Whilst natives were seen as "Gaullican" by the higher-ups in Gaullica, there was still significant racial prejudice between the upper-class Chennois citizens of Sainte-Germaine and the lower-class native citizens. To preserve colonial wealth, governors would often side with the Chennois populace in the colony. Brutality heightened during the Sougoulie rebellions and in particular following the Sinking of the NMS Insulaire by Alphonse Amsalu in 1883, after which Yebase rights were curtailed, many positions revoked and their positions in the empire questioned. These policies would continue until the accession of Charles Dumont to the position of Governor of Baséland in 1906, where he would quickly introduce more native-friendly policies, including the restoring of the Yebase to many of their traditional positions. His legacy as a native-friendly ruler was solidified when he ruled in favour of the native Vivien Lemaigre in the Vivien Lemaigre case in 1907, where the accused white land-owner was forced to pay reparations to Lemaigre for violating his, and many other employed natives', labour rights. Dumont's tenure is regarded as extremely liberal compared to those he succeeded, however he was captured and arrested for treason by the national functionalists of Gaullica after they took power in the mainland, executing him in the city's harbour on October 22, 1919.
Under the national functionalists (1919–35)
The city took a sharp turn to repressive rule when the national functionalists completed consolidated power in Bahia in 1919, producing propaganda that mainly appealed to the white upper-class regarding the policies of Dumont and how they supposedly affected the prosperity of the colony. Despite the target audience of this propaganda, a colony-wide curfew, regardless of race, was issued in December 1919 in response to the supposed effects of Dumont's policies on the colony. The national functionalists were believers in the fact that order had to be imposed on the colonies to prevent dissident movements, with harsher rulings and slave labour being utilised, and inflicted onto both white and black residents of the city, but was notably more brutal for the native residents. More notably, during the rule of the national functionalists, the Adunis to Mambiza railway was completed in 1922, marking one of the great architectural achievements of the Gaullican Empire, and the completion of Grégoire Cuvillier's ambitions. The railway allowed supplies and military equipment to travel between Gaullican colonies in Bahia far more easily, with supplies sometimes being shipped from Verlois to Adunis, then down the railway to Sainte-Germaine.
Great War (1926–35)
Sainte-Germaine was treated extremely prestigiously by the Gaullican army, and the city - along with Adunis - were considered as Gaullica's premier Bahian cities. Sainte-Germaine had some planes and naval fleets based in its ports and airbases for short amounts of time, particularly for invasions of Rwizikuru and Tabora. Around 180,000 residents of Sainte-Germaine, some 50% of which are estimated to have been native, saw some form of combat in the Great War, mainly in Bahia and Badawiya, and particularly against Estmere and Werania in Riziland and Tabora. Gaullica was particularly successful in the Bahian and Badawiyan fronts, owing mainly to its colonial domination of the area. Many of the residents of Sainte-Germaine fought in the Tirailleurs Bahiens, colonial regiments of Bahian troops under the service of Gaullica.
Estmerish rule (1935–46)
After the war had concluded and Gaullica had surrendered, most of its colonial possessions were transferred to the three victorious colonial powers: mainly Estmere and Werania, with some going to Etruria. Estmere took control of the Baséland colony in 1935, effectively ruling it in unison with the adjacent colony of Riziland. In 1936 it was given the official colonial name of East Riziland, which was met with criticism, particularly from Sainte-Germaine, as to the future of the colony. During this time, aid was brought from Estmere to tend to wounded soldiers who were returning to their families in the city, with the city receiving ample aid due to its excessive size for a city in Bahia at the time.
By the 1940s, Estmere had displayed no intent at letting Garambura choose its own path, and negotiations were being held which highly suggested that the region was going to secede as part of Rwizikuru. With many Garamburan republicans finding this unacceptable, large-scale demonstrations were held against Estmere in the city in 1944 - which to this day are still some of the largest seen in Bahia - with an estimated 250,000 protesting against inclusion within Rwizikuru for its succession, now scheduled for 1946. The government of Estmere paid little attention to the protests, however, and Sainte-Germaine, along with the rest of Garambura, was granted independence in 1946 as the Republic of Rwizikuru.
Rwizikuran rule (1946–69)
Rwizikuran rule over Sainte-Germaine saw it de facto introduced as the capital of the district of East Riziland. It served as the administrative capital of the region and still attracted great amounts of wealth, quickly becoming Rwizikuru's most wealthy city. Due to the overwhelming Chennois demographic in the city, they were not subject to the same Euclean repatriation policies that had been implemented in the mainland. The city was administered fairly autonomously out of necessity rather than choice, with Samhuri Ngonidzashe unwilling to impose direct rule on the city for fear of scaring away investors in the city and destroying the city's large income. When Rwizikuru entered the United Bahian Republic in 1954, it saw more migration from UBR member nations looking to emigrate to Sainte-Germaine's comparatively affluent suburbs, diversifying the local population with sects of Sotirianity like Orthodoxy in Djedet practised by a minority in the city. It also became renowned for its cultural nightlife scene in the 1950s and 1960s, and was marketed throughout the UBR as a tourist destination. When the UBR dissolved in 1965 and Izibongo Ngonidzashe had declared himself Mambo of Rwizikuru, Sainte-Germaine became the centre of independence discussion and internal strife within Rwizikuru, particularly after the start of the Mabifian-Rwizikuran War over the district of Yekumavirira. Takakunda Kuda Kani delivered his speech declaring Garambura unilaterally independent from Rwizikuru in 1969, and the outskirts of the city saw most of the conflict.
Post-independence (1969–)
With Garambura now independent in April 1969 and Takakunda Kuda Kani sworn in as the first President of Garambura, economic and political transformation of the city began quickly. The city was allocated 79 seats of the National Assembly, over half of the available seats, due to its large population and influential economy. The city was officially renamed to Mambiza in 1970 to popularise the city and to disavow its colonial history, with all mail addressed to Sainte-Germaine re-routed back to the sender's address.
The emergence of Mambizan culture in the 1970s massively influenced culture throughout Bahia, and drew inspiration heavily from the emerging punk culture of Euclea at the same time. Club Mambiza, a subgrouping of Djeli pop, became a popular characterisation of the city, and gained it cultural notoriety across the world. Its club scene became famous and saw the city become the most-visited destination in the whole of Coius in 1978. Coupled with economic reforms of the Takakunda administration that helped further integrate it into the regional economy, Mambiza was one of the world's fastest-growing economies throughout the 1970s and 1980s. Increased funding from Halland allowed the city's industrial sector to be bolstered, and migration from rural Garambura to the industrial outskirts of the city introduced large amounts of income inequality between the more affluent suburban Chennois populace and the native industrial workers, a divide which still exists today. The Métro de Mambesa was constructed through the 1990s and opened in 1995 to increase rapid transport links throughout the city. The metro was expanded in 2003 and again in 2009 and now covers most of the city. The city's airport, Mambiza–Charles Dumont International Airport, was opened in 2001 and is the busiest in Bahia, serving most of Garambura with transport links across the world.
Geography
Mambiza's geography is mainly characterised by its coastal location, and its location on the Gonda Delta. It is a natural entrepot, and has historically been a centre of trade in Bahia. It experiences a tropical climate characteristic of most of Garambura, with temperatures often ranging from 20-30 degrees Celsius, with rainfall occurring mainly in the autumn and summer months. It is located on the 8th parallel north, and is roughly adjacent to the Rwizikuran capital Port Fitzhubert on latitude. Most of Mambiza's surrounding line is flat, arable marsh and farmland, saturated largely by the Gonda. The district of Armaillé is the city's southernmost district, and sits in the west, near the Garambura-Rwizikuru border.
The city has historically been divided into two sections - the West End and the East End - reflecting the ethnic divide within the city. The Chennois dominate demographics in the West End while the East End is populated mainly by the native Bahian populace. Officially, the city is divided into 47 districts - the most of any city in Bahia, presided over by an elected Mayor, currently Rupanyu Majange of the Garamburan National Party. Despite the city's 47 districts, it has 79 seats in the country's National Assembly. The terms West End and East End have fallen out of use for any official administrative purposes, but the terms are still used colloquially by the city's population.
Climate
Mambiza's climate is typical of tropical Bahia, with rainfall frequent in the warmer months and temperatures usually ranging from 20 to 30 degrees throughout the entire day. Temperatures rarely drop into single digits and have never dropped below freezing in the city's climate's recorded history, which is recorded at the Mambiza Observatory on Blue Hill, in the south of the city.
| Climate data for Mambiza (1970–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28.6 (83.5) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.2 (84.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.4 (84.9) |
29.2 (84.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
29.1 (84.4) |
29.6 (85.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 23.6 (74.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 185.2 (7.29) |
88.5 (3.48) |
111.0 (4.37) |
140.5 (5.53) |
285.5 (11.24) |
327.7 (12.90) |
268.0 (10.55) |
201.4 (7.93) |
97.5 (3.84) |
107.2 (4.22) |
185.9 (7.32) |
261.9 (10.31) |
2,260.3 (88.99) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 16 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 19 | 23 | 21 | 15 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 174 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 201.0 | 208.6 | 219.7 | 197.9 | 178.8 | 156.7 | 201.6 | 233.7 | 229.8 | 235.3 | 210.9 | 186.6 | 2,460.6 |
| Source: Institut météorologique de Garamboure[1] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Mambiza is the most populous city in Garambura, with a population of around 4.5 million in 2020, around 50% of Garambura's population of 9.3 million. Mambiza experiences extremely high population growth owing to immigration from rural Garambura and from elsewhere in Bahia, and is Bahia's fastest growing city and one of the world's fastest-growing cities. In practise, it is difficult to document Mambiza's total population due to the shanty towns and slums that exist in the northern and western outskirts of the city, built by rural immigrants who cannot afford to live in the city itself.
The highest demographic in Mambiza is the veRwizi, at 57% (4,284,281 people), followed by the Chennois at 18% (1,352,930 people), over 90% of the total Chennois population in Garambura, and the Sisulu at 16% (1,202,605 people). The remaining 9% consist mainly of immigrants from elsewhere, as well as smaller minorities of the Njinji people that live mainly in eastern Garambura.
Linguistically, the city primarily speaks veRwizi, but Gaullican is also spoken by around 80% of the population as either a first or second language, and it is used as the native language of the Chennois, an official administrative language, and a language of commerce and trade with the rest of the world.
Economy
The city is fairly economically developed, and has a modern central business district that hosts various offices from Garamburan companies as well as international conglomerates looking to expand into the Bahian market. It also has a large and developed port capable of handing large and frequent cargo and passenger traffic, and the city is a regular stop for sea-based trade entering Garambura (almost 85% in 2009) as well as Bahia in general. Business presence as well as its importance as a global port makes Mambiza one of Bahia's richest cities. The Greater Mambiza area generates around 78% of Garambura's gross domestic product as of 2015 ($65.13 billion by nominal; $121.8 billion by purchasing power parity), giving it a GDP per capita of $8,665 (nominal) or $16,204 (PPP), by far the highest in Garambura.

Nearly all major institutions in Garambura are based in the city, creating work and attracting immigration from elsewhere. The city generates the highest percentage of gross domestic product of any country (excluding city-states), and the country is incredibly reliant on Mambizan business and trade for its economy.
Despite the city's affluence, it suffers from widespread poverty and income inequality. Its Gini coefficient was 0.52 in 2014, when the government introduced several programs aiming to tackle homelessness and poverty in the city, however the coefficient has remained stagnant since then. Poverty rates by ethnicity are 3.5% for white Chennois, 10.3% for veRwizi, 10.9% for Sisulu and 22.1% for Njinji. Poverty and inequality is amplified by the presence of expanding shanty towns and slums in the north of the metropolitan area, which have been built up and settled by poorer rural immigrants unable to afford accommodation in the city's built-up areas. Ndirazepatswa, Pelela and Makufa are among the city's most-populated slums, and have recently begun to expand into pre-existing towns in the north such as Tsvangirayi, Mzilikazi and Ingezi. These shanty towns are often built along the Gonda to utilise its banks for small-scale farming (mainly fishing) as well as business ventures selling cheap goods along the riverbank, although more recently this has evolved into a necessity due to a lack of space in the city.
Muzukuru Chiyangwa announced the government's intention to begin demolishing the slums to build proper apartment complexes and real estate, notably in Pelela and Makufa which lie fairly centrally in the metropolitan area of the city. This policy was reaffirmed by Sylvain Sikali in 2020, although no action has yet been taken due to its controversy and accusations of the government's disregard for the some 300,000 inhabitants of the city living in its shanty towns.
Transport
Mambiza is well-connected to itself and the rest of Garambura by road, train, tram and ferry. The A1, A2 and A4 motorways run through the city and service a large amount of car traffic to other urban centres throughout the country. In 2022, toll roads will be implemented on motorways travelling in and out of the city between 5:00AM and 10:00PM, aimed to collect more revenue for the city's transport services but also to encourage the use of the city's public transport and to reduce inner-city congestion and carbon emissions.
The Métro de Mambesa is the city's underground rail network, and is extremely advanced for its location. Beginning construction throughout the 1990s and opening to the public in 1995, it originally serviced the western side of the city, with its Central Line travelling from Trente-Avril to Ntawha. The Eastern Line was added in 2003 as the metro's first major expansion and connecting Gare de Amsalu to the Place de la Sougoulie in the east of the city, and the Delta Line was expanded in 2009 to connect the coastal districts of Mambiza. The service covers most of the developed areas of the city and has a daily ridership of around 1 million passengers. The city is also connected by overground train to Makumba and Mutimukuru in the east and Kugura and Tawira in the north, running along the Gonda and built off of the Adunis to Mambiza Railway built by the Gaullican Empire in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Ferries run to and from Mambiza's ports to other cities in Garambura as well as locations in neighbouring Rwizikuru. The port also services cruise ships whose termini include Dezevau, Lavana and Terangau, and is the only port in Bahia with sufficient infrastructure to do so. Many Mambizans are employed at the city's main port and smaller ports. Its airport, Mambiza–Charles Dumont International Airport, has two runways and services a multitude of international destinations in all of the world's continents.
The city also has a unique public transport city known as the SRM (Service de la rivière Mambesa; "Mambiza River Service"), which consists of large boats and smaller ferries travelling up the Gonda delta to a series of destinations along its banks. The SRM currently services five main routes for the five main settled rivers of the delta in the city, Trente-Avril–Villefavard du Ouest, Chalandray–Villefavard du Est, Gambeiseuil–Mutasa Village, Izé–Gare d'Hourege and Maimbeville–Chauruka. The SRM has a daily ridership of around 175,000, and is mainly used a tourist or sightseeing attraction, with the metro being favoured for high-speed travel. The SRM has recently had funding issues as a result of decreasing daily ridership in favour of the metro and the city's motorways.
Twin towns – Sister cities
 Stajnensby, Azmara (2009)
Stajnensby, Azmara (2009) Castelonovo, Belmonte (2001)
Castelonovo, Belmonte (2001) Spálgleann, Caldia (1993)
Spálgleann, Caldia (1993)- File:ImaguaFlag.png Cuanstad, Imagua and the Assimas (1999)
Verlois, Gaullica (1978)
 Ealaghleann, Halland (1978)
Ealaghleann, Halland (1978)- File:RwizikuruFlag.PNG Port Fitzhubert, Rwizikuru (1945–1969, 1980–)
 Zahedan, Zorasan (2006)
Zahedan, Zorasan (2006)
References
- ↑ IMG, Mambiza climate data (1970-2000), Institut météorologique de Garamboure, 17 January 2000, Retrieved 20 March 2020