Philimania: Difference between revisions
m (→Enviroment) |
Philimania (talk | contribs) |
||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{NSNIcon|Philimania}}{{Region_icon_Philimania}} | {{NSNIcon|Philimania}} | ||
{{wip}} | {{Region_icon_Gentu}} | ||
{{Region_icon_Philimania}} | |||
{{Gentu wip}} | |||
{{shift}} | |||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = Republic of Philimania | |conventional_long_name = Republic of Philimania | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
|national_anthem = "[[Toku Nuu]]"<br />({{Lang-en|"My Nation"}})<div style="padding-top:0.5em;" class="center">[[File:Rty.png|frameless|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DWfZ_ydxsHo]]</div> | |national_anthem = "[[Toku Nuu]]"<br />({{Lang-en|"My Nation"}})<div style="padding-top:0.5em;" class="center">[[File:Rty.png|frameless|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DWfZ_ydxsHo]]</div> | ||
|royal_anthem = | |royal_anthem = | ||
|image_map = | |image_map = Philimania Globe.png | ||
|map_width = | |map_width = 250px | ||
|alt_map = | |alt_map = | ||
|map_caption = Location of '''Philimania''' (dark green)<br>– in | |map_caption = Location of '''Philimania''' (dark green)<br>– in [[Flonesia]] (grey) | ||
|image_map2 = | |image_map2 = | ||
|map2_width = | |map2_width = | ||
|alt_map2 = | |alt_map2 = | ||
|map_caption2 = | |map_caption2 = | ||
|capital = [[New Phork|New Phork City]] | |capital = [[New Phork|New Phork City]] | ||
|largest_city = | |largest_city = capital | ||
|official_languages = [[Neragese language|Neragese]] | |||
|regional_languages = [[Hestandan language|Hestandan]] | |||
|official_languages = | |ethnic_groups = 48% [[Philimanian People|Philimanian]]<br>24% [[Hestandan people|Hestandan]]<br>22.2% [[Neragese people|Neragese]]<br>4% Other Oranish<br>1.7% [[Naphto-Philimanian people|Naphto-Philimanians]]<br>0.1% Naphtorans | ||
|regional_languages = | |ethnic_groups_year = 1999 | ||
|ethnic_groups = | | ethnic_groups_ref = | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |||
| ethnic_groups_ref = | |||
|religion = {{ublist |item_style=white-space:nowrap; | |religion = {{ublist |item_style=white-space:nowrap; | ||
| 57% | | 57% [[Terranity]] | ||
| 29% | | 29% [[Hafan]] | ||
| 10% | | 10% No religion | ||
| 2.1% | | 2.1% X | ||
| 1.9% Others | | 1.9% Others | ||
}} | }} | ||
|demonym = Philimanian | |demonym = Philimanian | ||
|government_type = {{wp|Constitutional Federal Republic|Constitutional Federal}}<br>{{wp|Constitutional Federal Republic|Republic}} | |government_type = {{wp|Constitutional Federal Republic|Constitutional Federal}}<br>{{wp|Constitutional Federal Republic|Republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = [[President of Philimania|President]] | |leader_title1 = [[President of Philimania|President]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Nel Karlson]] | |leader_name1 = [[Nel Karlson]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 49: | ||
|lower_house = [[Philimanian House of Representatives|House of]]<br>[[Philimanian House of Representatives|Representatives]] | |lower_house = [[Philimanian House of Representatives|House of]]<br>[[Philimanian House of Representatives|Representatives]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = History | |sovereignty_type = History | ||
|established_event1 = | |established_event1 = [[New Laughton (colony)|Neragese colony]] | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = 14 Hunyo 1551 | ||
|established_event2 = | |established_event2 = [[Colony of Philimania]] | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 23 Phupu 1616 | ||
|established_event3 = | |established_event3 = [[The Philimanian Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] founded | ||
|established_date3 = 6 | |established_date3 = 6 Marto 1654 | ||
|established_event4 = | |established_event4 = First constitution | ||
|established_date4 = | |established_date4 = 15 Marto 1681 | ||
|established_event5 = | |established_event5 = Self-rule | ||
|established_date5 = | |established_date5 = 25 Pusper 1941 | ||
|area_km2 = | |established_event6 = Independence | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |established_date6 = 26 Pusper 1968 | ||
|percent_water = | |established_event7 = Current constitution | ||
|established_date7 = 2 Gunyana 1984 | |||
|area_km2 = 224,805 | |||
|area_sq_mi = | |||
|percent_water = 0.01 | |||
|population_estimate = {{increase}} 13,420,400 | |population_estimate = {{increase}} 13,420,400 | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = 2000 | ||
|population_census = 14,088,100 | |population_census = 14,088,100 | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = 2000 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 62.7 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = 162.3 | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
|GDP_PPP = {{increase}} | |GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $1.301 trillion | ||
|GDP_PPP_rank = | |GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
|GDP_PPP_year = | |GDP_PPP_year = 2000 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $31,422 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = {{increase}} | |GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $1.342 trillion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |GDP_nominal_year = 2000 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $30,120 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini_change = steady | |Gini_change = steady | ||
|Gini = 29 | |Gini = 29 | ||
|Gini_rank = | |Gini_rank = X | ||
|Gini_year = | |Gini_year = 2000 | ||
|Gini_category = | |Gini_category = | ||
|HDI_change = increase | |HDI_change = increase | ||
|HDI = 0.810 | |HDI = 0.810 | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = X | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = 2000 | ||
|currency = [[Philimanian Dollar]] <br>( | |currency = [[Philimanian Dollar|Creit]] <br>(β) | ||
|currency_code = | |currency_code = CET | ||
|time_zone = ( | |time_zone = [[Global Time Standard|MTS+1]] (Philimanian Standard Time) | ||
|utc_offset = | |utc_offset = | ||
|time_zone_DST = | |time_zone_DST = | ||
| Line 99: | Line 104: | ||
|cctld = .ph | |cctld = .ph | ||
|iso3166code = PH | |iso3166code = PH | ||
|calling_code = + | |calling_code = +79 | ||
}} | }} | ||
''' | The '''Republic of Philimania''' (<small>/fɪlɪ'meɪnɪə/ ([[File:Speaker Icon.svg|13px]] [http://ipa-reader.xyz/?text=f%C9%AAl%C9%AAme%C9%AAn%C9%AA%C9%99&voice=Brian listen])</small>), commonly called '''Philimania''', is a {{wp|federal republic}} governed by [[The Philimanian Legislative Council]] (TPLC) in central [[Flonesia]]. Philimania covers over 200 thousand square kilometres and around 532 islands and has a population of over 10 million. The nation consists of 4 provinces. | ||
* History | |||
Philimania is a developed country, with a high national GDP of | Philimania is a developed country, with a high national GDP of $1.342 trillion. The per capita GDP of $30,120 ranks highly in the world. The economy is fueled almost entirely by the private sector, which is quite specialized and led by the Tourism industry, with significant contributions from Book Publishing, Information Technology, and Arms Manufacturing. The average income is $65,825 and evenly distributed, with the richest citizens earning only 2.7 times as much as the poorest. Philimania ranks highly in civil rights, political freedom, and economic freedom. Philimania is a small power, as well as a member of several international organizations, including the [[Union of Realms]]. | ||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
''TBA'' | |||
== History | == History == | ||
=== | === Pre-Oranish history === | ||
Philimania was | According to indigenous [[Philimanian oral tradition]]s, Philimania was first settled by marine nomads known as the [[Runga Puan people]] from modern-day [[Manukaia]] during the [[Novalithic Age]] around 6300 BCE, although there are still many open questions about the specific dates and patterns of human migration into Philimania and many other Nullaric islands. the Runga Puans later saw influences from present-day [[Vashria]] and [[Iolana]] following human migrations brought about by the [[Mutamarma supereruption]] c. 3100 BCE. The first permanent settlement in Philimania was discovered via archaeological in 1986 in [[Dioran]] dating back to atleast 1200 BCE. | ||
In | In 837 CE, the [[Vashrian Empire]] was established in [[Vashria]]. This brought Vashrian and [[Proto-Iolonan people|Proto-Iolonan]] customs and languages to Philimania. By then, the Runga Puans had evolved into the indigenous [[Philimanian people]] similar to the Philimanian people of the modern-day. | ||
In the subsequent centuries, Philimania became a melting pot of Flonesian culture due to its geographical location between east and west [[Flonesia]]. Philimanians also constructed large, elegant watercraft, with rigged sails called ''{{wp|drua}}'' and exported some of them to Vashria. Philimanians also developed a distinctive style of village architecture, including communal and individual ''[[xagona]]'' housings, and an advanced system of ramparts and moats that were usually constructed around the more important settlements. Additionally, pigs were domesticated for food during the early 3rd century, and a variety of agricultural plantations, such as banana plantations, existed since the early stages of the Runga Puan civilisation. Philimanians lived in societies led by chiefs, elders and notable warriors. Magicians often called ''[[daucaka]]s'', were also important cultural figures, and the production and consumption of {{wp|kava}}s was part of their ceremonial and community rites. | |||
[[ | Following the collapse of the Vashrian Empire in 1481, Philimania was plunged into a convoluted conflict known as the [[Veivala War]]. During this period, Philimania was ruled by numerous chiefdoms the most well-known of which is the [[Chiefdom of Dyoruna]]. | ||
With the arrival of Oranishmen during the 16th century, many indigenous Philimanian traditions were suppressed. Early colonists and missionaries pointed to the practice of {{wp|cannibalism}} in Philimania as providing a moral imperative justifying colonization. Oranish colonisers labelled many native Philimanian customs as debased or primitive, enabling many colonists to see Philimania as a "paradise squandered by barbaric cannibals". On the other side of the spectrum, [[Wilhelm Lustig]], the governor of [[New Laughton (colony)|New Laughton]] (1551-1616), wrote that the tasting of the flesh of the enemy was done only on rare occurrences, and only "to indicate supreme hatred and not out of relish for a gastronomic treat". | |||
=== Early colonialism === | |||
Philimania was first discovered by [[Seronia-Sotha]]n explorer [[Vincent Eichinger]] in 1536, sighting a southern island now part of [[Dioran]]. He made landfall on the island in the late afternoon of the 17th of Phupu, giving it the name "[[Eichinger's Island]]". | |||
[[ | However, what is now Philimania was not mapped until the [[Flonesian Scramble]] in 1551 by [[Neragon|Neragese]] explorer [[George Kellerman]] who also established the colony of [[New Laughton (colony)|New Laughton]] near present day [[Lensaw]] on 14 Hunyo the same year. The rest of central Philimania was fully colonised in 1564 following numerous conflicts with indigenous people as well as the end of the Veivala War in the autumn of 1560. As a result, thousands of native Philimanians were put into slavery and sold at auction to {{wp|tobacco plantations}} in New Laughton. This provided a source of revenue for the Neragese colonial government and also dispersed the natives to different, often isolated islands where they could not organise and rebel. The land that was occupied by these people before they became slaves was then also sold for additional revenue. In total, an estimated 78,000 Philimanians were sold into slavery. | ||
During this period, settlements such as [[Phorktown]] (1562), [[Phrakingdale]] (1567), [[Esterham]] (1574), and [[Harpville]] (1580) were founded. | |||
In Gunyana of 1571, a group of settlers were killed near the river [[Brades]] by native Philimanians of the [[Malulu tribe]], prompting a large {{wp|punitive expedition}} of Oranish farmers, army veterans and other civilians to be organised. This group of around 300 armed vigilantes, including veterans of the Five Years' War, participated in the [[Battle near Croufield]] against the Malulu tribe. Both sides suffered few casualties and although the Malulus were forced to retreat, they responded with frequent raids on colonial settlements throughout the following weeks. | |||
Although the New Laughton government did not approve of civilians taking justice into their own hands, it did want the Malulu tribe subjugated and their land sold. This resulted in the formation of the [[New Laughton Army]], the predecessor of the [[Philimanian Armed Forces]], under [[Arthur Sudfries]]. | |||
This marked the beginning of the so-called [[Brades War]] lasting from Gunyana of 1571 to 1573. During this time, a force of about 600 men led by Sudfries campaigned through the Philimanian interior in order to annihilate the Malulu tribe. The combined force of the different clans of the Malulu made a last stand at the village of Wataani where they were ultimately defeated by the 16 Memesa 1573 and surrendered to Sudfries's army. About 2,000 of the prisoners (men, women and children) were sent to Phrakingdale where some were hanged and the rest were sold into slavery and forced to work on various plantations throughout the islands. | |||
Although [[Neragon]] did not officially participate in the [[Flonesian War]], Philimania's waterways became the battlegrounds of numerous military actions including the infamous [[Battle of King Henry's Strait]] in 1584 between the [[Serono-Sotha]]n fleet led by [[Johann Lager]] and the [[Omaran Empire|Omaran]] colonial navy resulting in a decisive victory for Seronia-Sotha, serving as a turning point in the war against the Omaran and [[Paloa]]. | |||
During | During the [[War of 1602]], an invasion of Philimania was attempted by the Paqueons following their victory at the [[Battle of Verano]] on the 16 Gunyana 1604. In the morning of 20 Gunyana, Philimanian coast guards near the southside of [[Eichinger’s Island]] sighted a fleet of Paqueon ships heading towards Philimania. Two hours later, the fleet bombarded the island which led to its capture and the small fleet of Neragese ships at the island to retreat to the nearby [[Prince Edward’s Island]]. | ||
In the following weeks, the Paqueon fleet made its way north capturing Prince Edward’s Island on the 26th of Gunyana and [[Waraki’i Island]] 4 days later. Although the New Laughton government possessed an army, they were unable to match against the Paqueon fleet who by 3 Okjatab had begun to {{wp|bombardment|bombard}} cities in [[Dioran]] such as [[Phrakingdale]], [[Sudville]] and [[New Weissburg]]; and had blockaded most of Philimania from the rest of Neragons colonial holdings in [[Flonesia]]. | |||
[[File:Battle near Petrali Island.jpg|thumb|17th century depiction of the [[Battle near Petralia Island]].]] | |||
However, Paqueon forces weren’t able to advance further north after the fleet was defeated by a Neragese fleet led by Arthur Sudfries at the [[Battle near Petrali Island]] in Memesa of 1605. This led to a stalemate between the Neragese in Paqueons which was resolved in 1607 when a coordinated attack by Serono-Sothans and Neragese forces from [[New Sotha]], [[New Rubenis]]; and [[Colony of Iolana|Iolana]] respectively broke through the Paqueon blockade on the Philimanian archipelago and drove out invading Paqueon forces by the middle of Marto the same year. | |||
By the end of the war, some 100,000 civilians were killed while about 1,340,000 soldiers were killed on both sides of the conflict. Additionally, around 700,000 houses and other structures were damaged or destroyed due to Paqueon bombing. | |||
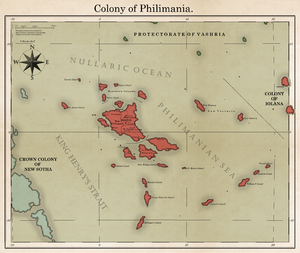
=== Colony of Philimania === | |||
[[File:Colony of Philimania.png|thumb|Map of the [[Colony of Philimania]] shortly after the founding of [[The Philimanian Legislative Council]].]] | |||
''TBA'' | |||
=== Self-rule and independence === | |||
''TBA'' | |||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
{{Main|Geography of Philimania}} | {{Main|Geography of Philimania}} | ||
[[File:Geography map.png|thumb|Physical map of Philimania]] | <!--[[File:Geography map.png|thumb|Physical map of Philimania]]--> | ||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--The land area of Philimania is 224,805 km² (88,200 sq mi) and is bordered by the Nullaric Ocean on all sides. Philimania is 150.3 kilometres (93.4 miles) north of the {{wp|equator}} and comprises of 3 islands, Philimania, [[West Island]], and [[North Island]]. The islands is surrounded by a coral reef, which is exposed at low tide and dotted with pinnacles. The tallest point in Philimania is [[Mount Phanes]] standing at 976 meters in the West of [[North Philimania]]. The most of inland Philimania is covered by the [[Harodan Rainforest]]. [[North Island]] is mostly covered in swamp known as the [[Retop Lagoon]]. There are 4 rivers in Philimania with the longest of which is the [[Brades River]] which runs from [[Mount Naro]] to the west coast of Philimania.--> | |||
=== Enviroment === | |||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--[[File:West Island reserve.jpg|thumb|left|The West Island Wildlife Reserve.]] | |||
Philimania has a history of strong environment conservation. For example, The northern part of the [[West Island]] are protected under the [[West Island Wildlife Preserve]], which was established in 1957. | |||
While much of Philimania remains free of environmental degradation, areas of concern include illegal {{wp|Blast fishing|dynamite fishing}}, inadequate {{wp|Waste management|solid waste disposal}} facilities in [[Dioran]] and extensive sand and coral dredging in the [[Retop Lagoon]].--> | |||
=== Biodiversity === | |||
Philimania is one of X megadiverse countries in Gentu according to X, and it has the X-most biodiversity per square kilometer of any nation. | |||
Philimania | Philimania has 900 bird species. In addition to more than 10,000 species of plants, the country has 97 endemic reptiles, 138 endemic amphibians, and 4,000 species of butterfly. As of the writing of the plan in 2005, 12% of Philimania's land area was in a protected area; however, the plan also states that 35% of the land must be protected in order to truly preserve the nation's biodiversity. Current [[List of Protected Areas in Philimania|protected areas]] include 10 national parks, 12 wildlife refuges, 7 ecological reserves, and other areas. | ||
=== Climate === | === Climate === | ||
Philimania experiences a humid tropical climate with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round. | Philimania experiences a humid tropical climate with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round. Because of the nations close proximity at the equator, Philimania experiences little variation in daylight hours during the course of a year. Both sunrise and sunset occur each day at the two six o'clock hours. | ||
The temperature in Philimania ranges between 30 and 35 °C (86 and 95 °F) at the coast and 30 and 31 °C (86 and 87.8 °F) inland during the day and is quite stable at around 24 °C (75.2 °F) at night. | |||
{{Weather box|location = Philimania | {{Weather box|location = Philimania | ||
| Line 233: | Line 271: | ||
|Nov sun = 183.0 | |Nov sun = 183.0 | ||
|Dec sun = 182.9 | |Dec sun = 182.9 | ||
|date=Tebax 2010}} | |||
=== | === Administrative divisions === | ||
[[ | ''TBA'' | ||
<!--Philimania is divided into 4 provinces, [[North Philimania]], [[West Islands]], [[Dioran]], and [[New Laughton]] which are then divided into numerous counties. | |||
Philimania | {| class="wikitable" style="width:808px;text-align:center;" | ||
|- | |||
!Current map | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
[[File:Philimania Provinces.png||center|frameless|800px|Provincial map of Philimania]] | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|}--> | |||
== Transport and infrastructure == | |||
[[File:Philimania Road.jpg|thumb|A road in the north coast of Philimania.]] | |||
[[ | [[Foster International Airport]] in [[New Phork]] is the only public airport in Philimania. It provides scheduled direct flights with X, X, X and X. | ||
Freight, military and cruise ships often call at [[Phrakingdale Harbor]], [[Gardton Harbour]], or [[Harpville Harbour]]. Philimania has around 1906 km or 1184.3 mi of highways, only 456 km or 283.3 mi are paved. Driving is on the left and the speed limit is 100 km/h (62 mph) on most highways. | |||
The railroad network of Philimania is 1626 km long and is traversed daily by up to 30,000 passenger and cargo trains. The partially state-owned largest railroad company [[Philimanian Rail Company]] serves and oeprates a large number of trains, passengers and infrastructure components. Most of the railroad infrastructure is maintained, operated and financed by the [[Philimanian Ministry of Infrastructure|Ministry of Infrastructure]] since 1964. The network is used by regular and high speed trains, most notably the InterCity trains travelling at between 240 km/h (149 mph) to under 370 km/h (230 mph), providing expansive domestic and international rail connections. | |||
[[ | Confined urban underground rapid transit such as the [[New Phork Underground]] are used by approximately 1.757 million passengers daily. Taxis and public transport in general are all well developed mostly in major Philimanian cities but some in smaller cities as well such as [[Bridging]], [[Seerno]] and [[Lensaw]]. | ||
== Demographics == | |||
<!--[[File:Population of Philimania.png|thumb|left|Total population growth of Philimania 1800-2000.]]--> | |||
{{Pie chart | |||
|caption = Ethnic Groups in Philimania (2000) | |||
|label1 = [[Philimanian people|Philimanian]] | |||
|value1 = 48 | |||
|color1 = Blue | |||
|label2 = [[Hestandan people|Hestandan]] | |||
|value2 = 24 | |||
|color2 = Gold | |||
|label3 = Other Oranish (Including Neragese) | |||
|value3 = 22.2 | |||
|color3 = Green | |||
|label4 = [[Hesterath Lowlands]] people | |||
|value4 = 4 | |||
|color4 = Red | |||
|label5 = [[Naphto-Philimanian people|Afro-Philimanians]] | |||
|value5 = 1.7 | |||
|color5 = Black | |||
|label6 = Others | |||
|value6 = 0.1 | |||
|color6 = Grey | |||
}} | |||
Philimania's population is ethnically diverse and the 2000 census put Philimania's population at 14,088,100. The largest ethnic group (As of 2000) are the [[Philimanian people|Philimanians]], who are mixed race people of [[Neragese people|Neragese]], [[Hestandan people|Hestandan]], and [[Iolonan people|Iolonan]] descent and constitute about 48% of the population. The [[Hestandan people|Hestandan]]s are the second largest ethnic group accounting for 24% of the population. The rest of Philimania's population is a result of a mixture of Oranish immigrants, predominantly from [[Oliea]] and [[Veragon]] with people from [[Cavala]], [[Paloa]], and [[Neragon]] who have settled in the early 20th century. Philimania also has a small population of Hesterish origins, mainly those from the lowlands regions, such as [[Qiuhua]] and [[Samin]] which collectively makes up 4% of the population and whose ancestors arrived as miners, factory workers and fishermen in the mid 19th century during the [[Industrial Revolution (Gentu)|Industrial Revolution]]. The [[Naphto-Philimanian people|Afro-Philimanians]] are a minority population (1.7%) in Philimania, largely based in [[Newton]] and to a lesser degree in X. The remaining 0.1% consists of immigrants from the Domicas and Naphtora. | |||
Philimania has a {{wp|population density}} of 61.6/km² (159.5/sq mi). Being a developed country, Philimania has a {{wp|life expectancy}} of around 80.05 years, 79.72 years for men and 81.94 years for women. Philimania additionally has a very low infant mortality rate of 3.6 boys and 3.3 girls per 1,000 births. Historically the rate of reproduction remained above-average with 1.8 children in the mid 1900s, but deteriorated significantly since then with a period of the {{wp|death rate}} of Philimania exceeding its birth rate and a slightly shrinking population between 1950 and 1970. However, Philimania since then advocated immigration to the country and introduced efforts to stimulate population growth; increased {{wp|birth rates}} and migration numbers curbed the low fertility rate and supported population growth since 1970. | |||
Philimania | Philimania is one of the most important immigration destinations in the world. In a 1999 census, around 4.7 million people (or close to 33.5%) were either of immigrant or partially immigrant descent, and in 2013, 42.9% of all newborn children had atleast one parent born in a foreign country, and 27% atleast one born outside of [[Flonesia]]. Immigration to Philimania is a key factor in supporting its population growth and supply of work forces in light of its aging population. | ||
=== Language === | === Language === | ||
The most widely used language is [[Neragese language|Neragese]] which is also the de facto national language. Approximately 80% of the population speaks Neragese as a first language, with another 9% speaking Hestandan as a first language with only 11% of the population speaking their own native language as a first language. | |||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--Languages introduced to Philimania by {{wp|immigrants}} are numerous and often treated as "unofficial official languages." While the descendants of older migration waves have largely adapted to the linguistic environment of Philimania, immigrants of previous decades, more often factory workers and miners, still frequently use their mother language in their daily lives, most notably {{wp|Chinese}} and {{wp|German}}. Other such "unofficial official languages" includes {{wp|Irish}}, introduced by a large diaspora of Irish people brought by the {{wp|Great Irish Famine}}, {{wp|French}}, and {{wp|Malay}}. The prioritized foreign language taught at public schools is {{wp|Spanish}}, and the second foreign language is often {{wp|French}}, or {{wp|Mandarin}}, more rarely {{wp|German}}.--> | |||
=== Religion === | === Religion === | ||
The | [[File:Watchingham Cathedral.jpg|thumb|The Loransk Cathedral in [[Watchingham]], largest cathedral in Philimania and a symbol of [[Terranity]] built in 1878.]] | ||
{{Bar box | |||
|title=Religions in Philimania (2000 census) | |||
|float=left | |||
|bars= | |||
{{Bar percent|[[Terranity]]|#0400FF|57}} | |||
{{Bar percent|[[Hafan]]|#FF7B00|29}} | |||
{{Bar percent|No religion|#CECECE|10}} | |||
{{Bar percent|X|#CC005B|2.1}} | |||
{{Bar percent|Other religion|#F7CD45|1.7}} | |||
{{Bar percent|Unanswered|#808080|0.2}} | |||
}} | |||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--The majority of Philimania's population identifies as {{wp|Christian}}. With 57% identify as {{wp|Protestant}}, and 29% identifying as {{wp|Catholics}}. The nonreligious account for 10% of the population, while {{wp|Judist}} make up 2.1%. All other faiths such as {{wp|Islam}} and {{wp|Taoism}} collectively make up 1.9% of the population. | |||
The | The 6th Amendment of Philimania guarantees {{wp|freedom of religion}} as an individual {{wp|constitutional right}} and institutional {{wp|separation of church and state}}. Thus the religious view of the state is determined to be neutral and the right of self-determination for religious groups upheld. While the government refrains from recognizing any certain rights of a religious group, and these groups are expected to reject any interaction with politics, church and state rather act as partners: they maintain substantial ties in social, educational and cultural affairs, for example by kindergartens, schools, hospitals or retirement homes overseen by religious actors but state-financed.--> | ||
=== Largest Cities === | === Largest Cities === | ||
Philimania is a highly {{wp|urbanisation|urbanized}} country. Its largest cities include [[New Phork]], [[Phorktown]], [[Stefshire]], [[Shewood]], [[Croufield]], [[Meucester]], [[Phrakingdale]], [[Watchingham]], [[Harpville]], and [[Gardton]] features a number of large {{wp|metropolitan area|metropolitan areas}} summing up {{wp|urban agglomeration|urban agglomerations}}, such as the Greater New Phork. | Philimania is a highly {{wp|urbanisation|urbanized}} country. Its largest cities include [[New Phork]], [[Phorktown]], [[Stefshire]], [[Shewood]], [[Croufield]], [[Meucester]], [[Phrakingdale]], [[Watchingham]], [[Harpville]], and [[Gardton]] features a number of large {{wp|metropolitan area|metropolitan areas}} summing up {{wp|urban agglomeration|urban agglomerations}}, such as the Greater New Phork. Geographically, most urban regions are concentrated along rivers or on the coastal regions of the country due to the dense jungle in the central region of the country. | ||
{{Largest cities | ''TBA'' | ||
<!--{{Largest cities | |||
| name = Largest cities of Philimania | | name = Largest cities of Philimania | ||
| country = Philimania | | country = Philimania | ||
| stat_ref = '' | | stat_ref = ''2000 census'' | ||
| list_by_pop = | | list_by_pop = | ||
| class = info | | class = info | ||
| Line 296: | Line 380: | ||
|city_2 = Phorktown | |city_2 = Phorktown | ||
|div_2 = New | |div_2 = New Laughton | ||
|pop_2 = 2,103,200 | |pop_2 = 2,103,200 | ||
|img_2 = Https_specials-images.forbesimg.com_imageserve_1075517408_0x0.jpg | |img_2 = Https_specials-images.forbesimg.com_imageserve_1075517408_0x0.jpg | ||
| Line 315: | Line 399: | ||
|city_6 = Meucester | |city_6 = Meucester | ||
|div_6 = New | |div_6 = New Laughton | ||
|pop_6 = 606,854 | |pop_6 = 606,854 | ||
|city_7 = Phrakingdale | |city_7 = Phrakingdale | ||
|div_7 = New | |div_7 = New Laughton | ||
|pop_7 = 454,471 | |pop_7 = 454,471 | ||
| Line 343: | Line 427: | ||
|city_13 = Lensaw | |city_13 = Lensaw | ||
|div_13 = New | |div_13 = New Laughton | ||
|pop_13 = 92,040 | |pop_13 = 92,040 | ||
| Line 363: | Line 447: | ||
|city_18 = Esterham | |city_18 = Esterham | ||
|div_18 = New | |div_18 = New Laughton | ||
|pop_18 = 15,342 | |pop_18 = 15,342 | ||
| Line 373: | Line 457: | ||
|div_20 = West Island | |div_20 = West Island | ||
|pop_20 = 12,980 | |pop_20 = 12,980 | ||
}} | }}--> | ||
== Politics == | |||
=== Government === | |||
[[File:Nel_Karlson.jpg|thumb|[[Nel Karlson]], current president of Philimania.]] | |||
The Republic of Philimania is a [[constitutional federal republic]] | The Republic of Philimania is a [[constitutional federal republic]] with the [[Philimanian Constitution]] being the supreme law of the land. Exercising the {{wp|separation of powers}}, the {{wp|political system}} of the country is divded into the {{wp|executive}}, {{wp|legislative}} and {{wp|judiciary}} branch, each controlled by a separate institution. The executive branch is headed by the [[President of the Legislative Council Philimania|President of Philimania]]. Can veto legislative bills, appoint cabinet members and Supreme Court Justices. The legislative branch is made up of the [[The Philimanian Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] and the [[Philimanian House of Representatives|House of Representatives]]. Makes federal law, declares war, allocates federal funds and approves treaties. The judicial branch makes up the Supreme Court and lower federal courts. Has the power of judicial review, and is the highest legal authority after the Constitution. | ||
The [[President of the Legislative Council Philimania|President of Philimania]] is elected directly by the public, and formally approved by the [[The Philimanian Legislative Council|Legislative Council]]. The ministers of the cabinet are then proposed by the president, who are in turn either approved or rejected by the [[The Philimanian Legislative Council|Legislative Council]]. The current president and vice-president since 2000 is [[Nel Karlson]] and [[Henry Field]] of the [[Philimanian Liberal Party]] (PLP). | |||
' | In Philimania's political history, since the founding of the [[The Philimanian Legislative Council|Legislative Council]] in 1654, the [[Philimanian Liberal Party]] (PLP) was most popular party and kept its status until the [[1989 Philimania legislative election]] when the [[Philimanian Democratic Party]] (PDP) surpassed them for the first time and had held its superior status until the [[1999 Philimania legislative election|1999 election]]. Since 1654, 74 Legislative Council elections have been held, with the most recent election being held on 28 Memesa 1999. | ||
=== Foreign Relations === | |||
The | ''TBA'' | ||
<!--Since 1700, Philimania as a small political, economic and military power has established often extensive and diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including many of its Pacific neighbors, like {{wp|Micronesia}} and {{wp|Australia}} and with almost every {{wp|South American}} country. 32 countries maintains an embassy in [[New Phork]] and further consulates in other major Philimanian cities. On 25 Pulungana 1978, the United Nations Security Council passed Resolution 440 recommending Philimania's admission to the United Nations. The United Nations General Assembly approved admission for Philimania pursuant to on 6 Disemba 1978. Philimania has since joined several other international organizations. | |||
'' | The country has played an influential role throughout much of modern {{wp|Pacific}}'s history during the mid 20th century. Especially with Philimania's role during the [[World War II (Philimania)|Second World War]], which had led to a maintained relation with nations such as the {{wp|United States}}, {{wp|Australia}} and {{wp|Ecuador}}. | ||
In international politics, Philimania often votes with {{wp|Ecuador}} on {{wp|United Nations General Assembly}} resolutions. Philimania has also maintained close ties with Brazil, which has funded infrastructure projects including the [[West Island Wildlife Preserve]]. Philimania is also a member of the {{wp|Nauru Agreement}} for the Management of Fisheries. {{wp|Peru}}, an ally of Philimania to the east, has expressed its intent to back Philimania if ever it wishes to join the {{wp|Union of South American Nations}}.--> | |||
=== Military === | |||
[[File:Nws dfs 171212 01-001.jpg|thumb|2 A-11 ''Tomlinson'' during a tactical exercise above the [[Brades River]].]] | |||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--With the exception of The {{wp|Seven Years War}}, the [[Long Kingdomian Revolution]], and [[World War II (Philimania)|World War II]], Philimania has been officially neutral in all armed conflicts since its founding. Philimania's annual military expenditure was at US$28.6 billion, or 2.2% of its GDP, making it the 12th largest global military spender, only behind {{wp|Italy}} and the 1st largest in {{wp|South America}}; it has formally suspended the use of conscription in 1950. The [[Philimanian Armed Forces]] is overseen by the [[Ministry of Defense (Philimania)|Ministry of Defense]]. The commander-in-chief of the Philimanian military is [[Muskaan Velasquez]], who is head of the [[Ministry of Defense (Philimania)|Ministry of Defense]]. | |||
The [[Philimanian Armed Forces]] is the {{wp|military}} and {{wp|paramilitary}} organization of Philimania responsible for its external protection and military actions. It consists of the [[Philimanian Army]], the [[Philimanian Navy]], the [[Philimanian Air Force]], and the [[Philimanian Marines]]. All branches serve professionally and have no other occupation. | |||
Philimania has | Philimania's military is supported by a large complex of civil companies and therefore stimulates one of the largest arms and {{wp|aerospace industries}} in the world. It has also collaborated on a number of international projects with other countries, most notably the other Pacific nations and {{wp|Ecuador}}, but generally prefers the use of domestically produced arms and equipment as opposed to foreign import.--> | ||
== Economy == | |||
{{main|Economy of Philimania}} | |||
{{wp| | with a GDP of $1.342 trillion and a GDP per capita of $30,120, the [[Economy of Philimania]] is the Xth largest in both the world and [[South Domica]]. Philimania is considered to be a developed country with the Xth highest {{wp|Human Development Index}} of the world and boasting one of the largest rates of nominal GDP per capita in any country. The private sector is estimated to constitute 91% of the economy, with federal, regional, and local government accounting for 8.1%. Philimania employed its largest labour force of 11.4 million people in 1998, or 85% of the population, in its history; its unemployment rate was estimated at 0% in 1998, largely due to excellent employment regulations throughout the country. | ||
Philimania's {{wp|economy}} consists primarily of {{wp|tourism}}, {{wp|subsistence agriculture}} and {{wp|fishing}}. While the couuntry has access to some {{wp|resource}} deposits such as {{wp|coal}} and a long history of mining, it is crucially dependant on the import of resources and energy assets from abroad. The most competitive sectors of the Philimanian industry are considered to be the {{wp|automobile}}, {{wp|agriculture}} and the {{wp|fishing}} sectors. The most important trading partners of Philimania in 1999 were X at a trading volume of $151.37 billion, X with $146.60 billion, X with $126.71 billion, and X with $119.28 billion. | |||
The income tax has three brackets with progressive rates of 9.3 percent, 15 percent, and 19.6 percent respectively. Corporate tax is four percent, and the sales tax is zero. There are no property taxes. | |||
=== Tourism === | |||
[[File:100s1f000001gx47fB08D.jpg|thumb|The Stefshire Grotto, the most well known scuba diving spot in Philimania.]] | |||
Philimania is the Xth most visited country in the world, with tourist arrivals numbered some 35.9 million in 1998. Tourism as an economic sector made a considerable contribution to the national economy, generating a revenue of $135 billion, or 10.4% of Philimania's GDP in 1999. 27 of Philimania's counties are registered in some form of tourist agency. 2,842 museums, 94 theatres, 7 amusement parks, 45,940 tennis courts, approximately 87 beaches. 301 golf courses, more than 17,000 kilometres of hike trails and 9,000 kilometres of biking ways, and numerous {{wp|scuba diving}} and {{wp|snorkeling}} spots are all available and accessible to tourism activities. Additionally, long-term prospects for the key tourist sector have been greatly bolstered by the expansion of {{wp|air travel}} in the Nullaric. | |||
{{ | |||
=== Agriculture === | |||
While the agricultural industry gradually diminished in their importance to the national economy, it is still considered internationally relevant in generating a wide array of products, being the fourth-largest exporter of agricultural products in [[Flonesia]]. The domestic agricultural industry is extremely productive in that it is able to sustain and cover more than 85% of the Philimanian population's needs for food in 2019, mainly due to extensive fertile soils in northern Philimania and sophisticated modern technology used in agriculture. | |||
Philimania | Principal agricultural exports of Philimania include products of lifestock, including {{wp|poultry}}, {{wp|beef}} and {{wp|pork}}, {{wp|dairy}} products, {{wp|wheat}}, {{wp|potatoes}}, and {{wp|fruit}}. Processed food such as variations of {{wp|cheese}} and {{wp|bread}} are also important, and form staples of Philimanian cuisine. | ||
=== Science and technology === | |||
[[File:Joseph Hinderman.jpg|thumb|Philimanian theoretical physicist [[Joseph Hinderman]] (1796-1877).]] | |||
Philimania is an internationally significant and renowned location of technology and science. Since the Industrial Revolution, Philimanian scientists participated immensly in the foundation of modern science; especially the economic productivity of multiple industrial sectors and the transfer of knowledge to practical use proved pivotal in the scientific development of the Philimanian academic field. Publications of scientific matters receive international acclaim and domestic public popularity; scientific journals published in Philimania include [[Harefind]] and [[Archaringe]], while Philimania as a research host produced more than 2% of the world's scientific research papers in 2000. | |||
Philimania | Institutions of research and science in Philimania are embodied through {{wp|universities}}. Most of which are in public ownership and service, but their research activities are often financed by third parties such as foundations, companies, and other. The [[University of New Phork]] and the [[International University of Philimania]] remain one of the most renowned and prestigious universities in the world. Apart from the country's universities, a large number of research organizations are active across Philimania and abroad, represented and coordinated through associations and councils in compliance with the [[Philimanian Ministry of Education|Ministry of Education]] and each university. the most famous of which include the Joseph Hinderman Society for basic research, the Craftsman Society as the country's largest scientific society, and the Alban Society for applied research. | ||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
Philimania is home to a variety of cultures, a result of a liberal immigration policy. Philimanian culture is generally considered | Philimania is home to a variety of cultures, a result of a liberal immigration policy. Philimanian culture is generally considered "western", derived from traditions of [[Oranland|Oranish]] and [[Iolona]]n culture. Like other Domican nations, Philimania has been described as a melting pot where several cultures join into one. | ||
Philimanians have been described as very compassionate, hard-working, and competitive. This has resulted in great economic productivity and a libertarian form of government. This has also made Philimania a popular destination for immigrants. Philimanians are also firm believers in equality and do not think that one social class should have more rights than others. | Philimanians have been described as very compassionate, hard-working, and competitive. This has resulted in great economic productivity and a libertarian form of government. This has also made Philimania a popular destination for immigrants. Philimanians are also firm believers in equality and do not think that one social class should have more rights than others. | ||
| Line 439: | Line 529: | ||
[[File:Zncdv3K.png|thumb|Philimanian Curry]] | [[File:Zncdv3K.png|thumb|Philimanian Curry]] | ||
[[File:Shutterstock-392257240.jpg|thumb|left|A night market in [[Phrakingdale]].]] | |||
Philimania is home to many different cuisines, a result of a liberal immigration policy. But mainstream Philimanian cuisine is similar to that in Iolona cultures with some aspects coming from [[Oranland]]. The [[Wee-Wee Fish]], an also an important part of Philimanian cuisine and is often fried, boiled, and minced into small [[Pastocho|Pastochos]], a type of tart made in Philimania. Philimanian cuisine also features dishes such as pineapple pie, Philimanian curry, panipopo, and coconut cake. Bread is also an important part in Philimanian cuisine, dishes wih bread in Philimania includes Luau Bread, Cassavon, and Po'eo. | |||
Places serving Philimanian cuisine can be found all over the country in {{wp|foodstand|foodstands}}, {{wp|restaurant|restaurants}}, and {{wp|shopping mall|shopping malls}}. Philimanian cuisine are also sold in {{wp|night markets}} which would appear during the weekends and holidays. | |||
=== Sports === | === Sports === | ||
Philimania's market for professional sports is roughly P$16 billion. While the most popular spectator sport is {{wp|football}} (soccer), the national sport is considered to be {{wp|Basketball}}. Philimanian athletes have set several world records and won | [[File:8688.jpg|thumb|Triman Stadium in [[Phorktown]].]] | ||
''TBA'' | |||
<!--Philimania's market for professional sports is roughly P$16 billion. While the most popular spectator sport is {{wp|football}} (soccer), the national sport is considered to be {{wp|Basketball}}. | |||
In 2011, approximately 3.7 million people were organized in 7,000 sports and gymnastics clubs in Philimania. Football remains the most popular sport in Philimania. Philimania has hosted the {{wp|FIFA World Cup}} in 1934, and [[2018 FIFA World Cup|2018]] and became one of the largest and most successful sports associations worldwide. The [[Philimanian national football team]], while internationally renowned and regarded, lags behind other football teams and thus only gained one victory in the [[1998 FIFA World Cups]]. | |||
Philimanian athletes have set several world records and have won a total of 543 Olympic medals in athletics alone. In addition, the {{wp|2000 Olympic Games}} were held in Phorktown. {{wp|Hockey}}, {{wp|baseball}}, and {{wp|tennis}} are also popular sports in Philimania.--> | |||
=== Education === | === Education === | ||
[[File:Campus Wide Shot.jpg|thumb|Philimanian Community College]] | ''TBA'' | ||
<!--[[File:Campus Wide Shot.jpg|thumb|Philimanian Community College]] | |||
Primary | Educational affairs at large are the responsibility for the supervision of the individual provinces, but is often co-ordinated by an annual nationwide conference of education {{wp|minister|ministers}} who also agree on educational standards. Kindergarten education is optional and dependant for each state, but higher school attendance for nine to thirteen years are compulsory. {{wp|Primary school}} attendance is atleast six years long. Schools include both public and private institutions as well as some fields of study available at [[Philimania Community College]]. For further undergraduate, graduate and professional programs, students would attend tertiary institutions. Popular choices among Philimanian scholars include the [[University of New Phork]], [[International University of Philimania]], [[Gapan University]], and [[Oton University]].--> | ||
=== Architecture === | === Architecture === | ||
[[File:Admira Center.jpg|thumb|The Admira Centre, one of the most prominent examples of buildings with all-glass shells.]] | [[File:Admira Center.jpg|thumb|left|The Admira Centre, one of the most prominent examples of buildings with all-glass shells.]] | ||
The architecture of Philimania is a mixture of | ''TBA'' | ||
<!--The architecture of Philimania is a mixture of English, {{wp|North American}}, modern, and postmodern architecture mix. Philimania's notable buildings such as the [[Philimanian Legislative Council Complex]] were built around the 18th and early 19th centuries. These buildings were designed in a number of styles – Mock Tudor, Neo-Gothic or Grecian-Spanish style architecture. Most of the styling has been modified to use local resources and acclimatised to the local climate, which is tropical and humid all year around. | |||
Late modern and postmodern architecture began to appear in the earky-1960s and early-1980s. With the economic development, old buildings have been razed to make way for new ones. Buildings with all-glass shells exist throughout the city, with the most prominent examples being the [[Admira Centre]] in [[Phorktown]]. | Late modern and postmodern architecture began to appear in the earky-1960s and early-1980s. With the economic development, old buildings have been razed to make way for new ones. Buildings with all-glass shells exist throughout the city, with the most prominent examples being the [[Admira Centre]] in [[Phorktown]].--> | ||
=== Social Media === | === Social Media === | ||
''TBA'' | |||
[[Category:Countries]] | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
[[Category:Philimania]] | [[Category:Philimania]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Countries in Gentu]] | ||
[[Category:Flonesia]] | |||
{{Template:Philimaniatopics}} | {{Template:Philimaniatopics}} | ||
{{Template:GentuInfo}} | |||
Latest revision as of 17:32, 13 January 2023
This article is a work in progress. Any information here may not be final as changes are often made to make way for improvements or expansion of lore-wise information about Gentu. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, contact User:Philimania. |
This article and its associate pages are undergoing a shift in multiverse, texts in this article may conflict with other pages taking place in the same universe. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. |
Republic of Philimania | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Vita Frui ("Enjoy Life") | |
| Anthem: "Toku Nuu" (English: "My Nation") | |
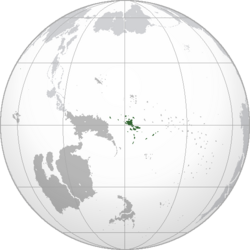 Location of Philimania (dark green) – in Flonesia (grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | New Phork City |
| Official languages | Neragese |
| Recognised regional languages | Hestandan |
| Ethnic groups (1999) | 48% Philimanian 24% Hestandan 22.2% Neragese 4% Other Oranish 1.7% Naphto-Philimanians 0.1% Naphtorans |
| Religion | |
| Demonym(s) | Philimanian |
| Government | Constitutional Federal Republic |
| Nel Karlson | |
| Henry Field | |
| Legislature | |
| Legislative Council | |
| House of Representatives | |
| History | |
| 14 Hunyo 1551 | |
| 23 Phupu 1616 | |
• Legislative Council founded | 6 Marto 1654 |
• First constitution | 15 Marto 1681 |
• Self-rule | 25 Pusper 1941 |
• Independence | 26 Pusper 1968 |
• Current constitution | 2 Gunyana 1984 |
| Area | |
• Total | 224,805 km2 (86,798 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.01 |
| Population | |
• 2000 estimate | |
• 2000 census | 14,088,100 |
• Density | 62.7/km2 (162.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2000 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2000 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2000) | low (X) |
| HDI (2000) | very high (X) |
| Currency | Creit (β) (CET) |
| Time zone | MTS+1 (Philimanian Standard Time) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +79 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH |
| Internet TLD | .ph |
The Republic of Philimania (/fɪlɪ'meɪnɪə/ ( listen)), commonly called Philimania, is a federal republic governed by The Philimanian Legislative Council (TPLC) in central Flonesia. Philimania covers over 200 thousand square kilometres and around 532 islands and has a population of over 10 million. The nation consists of 4 provinces.
- History
Philimania is a developed country, with a high national GDP of $1.342 trillion. The per capita GDP of $30,120 ranks highly in the world. The economy is fueled almost entirely by the private sector, which is quite specialized and led by the Tourism industry, with significant contributions from Book Publishing, Information Technology, and Arms Manufacturing. The average income is $65,825 and evenly distributed, with the richest citizens earning only 2.7 times as much as the poorest. Philimania ranks highly in civil rights, political freedom, and economic freedom. Philimania is a small power, as well as a member of several international organizations, including the Union of Realms.
Etymology
TBA
History
Pre-Oranish history
According to indigenous Philimanian oral traditions, Philimania was first settled by marine nomads known as the Runga Puan people from modern-day Manukaia during the Novalithic Age around 6300 BCE, although there are still many open questions about the specific dates and patterns of human migration into Philimania and many other Nullaric islands. the Runga Puans later saw influences from present-day Vashria and Iolana following human migrations brought about by the Mutamarma supereruption c. 3100 BCE. The first permanent settlement in Philimania was discovered via archaeological in 1986 in Dioran dating back to atleast 1200 BCE.
In 837 CE, the Vashrian Empire was established in Vashria. This brought Vashrian and Proto-Iolonan customs and languages to Philimania. By then, the Runga Puans had evolved into the indigenous Philimanian people similar to the Philimanian people of the modern-day.
In the subsequent centuries, Philimania became a melting pot of Flonesian culture due to its geographical location between east and west Flonesia. Philimanians also constructed large, elegant watercraft, with rigged sails called drua and exported some of them to Vashria. Philimanians also developed a distinctive style of village architecture, including communal and individual xagona housings, and an advanced system of ramparts and moats that were usually constructed around the more important settlements. Additionally, pigs were domesticated for food during the early 3rd century, and a variety of agricultural plantations, such as banana plantations, existed since the early stages of the Runga Puan civilisation. Philimanians lived in societies led by chiefs, elders and notable warriors. Magicians often called daucakas, were also important cultural figures, and the production and consumption of kavas was part of their ceremonial and community rites.
Following the collapse of the Vashrian Empire in 1481, Philimania was plunged into a convoluted conflict known as the Veivala War. During this period, Philimania was ruled by numerous chiefdoms the most well-known of which is the Chiefdom of Dyoruna.
With the arrival of Oranishmen during the 16th century, many indigenous Philimanian traditions were suppressed. Early colonists and missionaries pointed to the practice of cannibalism in Philimania as providing a moral imperative justifying colonization. Oranish colonisers labelled many native Philimanian customs as debased or primitive, enabling many colonists to see Philimania as a "paradise squandered by barbaric cannibals". On the other side of the spectrum, Wilhelm Lustig, the governor of New Laughton (1551-1616), wrote that the tasting of the flesh of the enemy was done only on rare occurrences, and only "to indicate supreme hatred and not out of relish for a gastronomic treat".
Early colonialism
Philimania was first discovered by Seronia-Sothan explorer Vincent Eichinger in 1536, sighting a southern island now part of Dioran. He made landfall on the island in the late afternoon of the 17th of Phupu, giving it the name "Eichinger's Island".
However, what is now Philimania was not mapped until the Flonesian Scramble in 1551 by Neragese explorer George Kellerman who also established the colony of New Laughton near present day Lensaw on 14 Hunyo the same year. The rest of central Philimania was fully colonised in 1564 following numerous conflicts with indigenous people as well as the end of the Veivala War in the autumn of 1560. As a result, thousands of native Philimanians were put into slavery and sold at auction to tobacco plantations in New Laughton. This provided a source of revenue for the Neragese colonial government and also dispersed the natives to different, often isolated islands where they could not organise and rebel. The land that was occupied by these people before they became slaves was then also sold for additional revenue. In total, an estimated 78,000 Philimanians were sold into slavery.
During this period, settlements such as Phorktown (1562), Phrakingdale (1567), Esterham (1574), and Harpville (1580) were founded.
In Gunyana of 1571, a group of settlers were killed near the river Brades by native Philimanians of the Malulu tribe, prompting a large punitive expedition of Oranish farmers, army veterans and other civilians to be organised. This group of around 300 armed vigilantes, including veterans of the Five Years' War, participated in the Battle near Croufield against the Malulu tribe. Both sides suffered few casualties and although the Malulus were forced to retreat, they responded with frequent raids on colonial settlements throughout the following weeks.
Although the New Laughton government did not approve of civilians taking justice into their own hands, it did want the Malulu tribe subjugated and their land sold. This resulted in the formation of the New Laughton Army, the predecessor of the Philimanian Armed Forces, under Arthur Sudfries.
This marked the beginning of the so-called Brades War lasting from Gunyana of 1571 to 1573. During this time, a force of about 600 men led by Sudfries campaigned through the Philimanian interior in order to annihilate the Malulu tribe. The combined force of the different clans of the Malulu made a last stand at the village of Wataani where they were ultimately defeated by the 16 Memesa 1573 and surrendered to Sudfries's army. About 2,000 of the prisoners (men, women and children) were sent to Phrakingdale where some were hanged and the rest were sold into slavery and forced to work on various plantations throughout the islands.
Although Neragon did not officially participate in the Flonesian War, Philimania's waterways became the battlegrounds of numerous military actions including the infamous Battle of King Henry's Strait in 1584 between the Serono-Sothan fleet led by Johann Lager and the Omaran colonial navy resulting in a decisive victory for Seronia-Sotha, serving as a turning point in the war against the Omaran and Paloa.
During the War of 1602, an invasion of Philimania was attempted by the Paqueons following their victory at the Battle of Verano on the 16 Gunyana 1604. In the morning of 20 Gunyana, Philimanian coast guards near the southside of Eichinger’s Island sighted a fleet of Paqueon ships heading towards Philimania. Two hours later, the fleet bombarded the island which led to its capture and the small fleet of Neragese ships at the island to retreat to the nearby Prince Edward’s Island.
In the following weeks, the Paqueon fleet made its way north capturing Prince Edward’s Island on the 26th of Gunyana and Waraki’i Island 4 days later. Although the New Laughton government possessed an army, they were unable to match against the Paqueon fleet who by 3 Okjatab had begun to bombard cities in Dioran such as Phrakingdale, Sudville and New Weissburg; and had blockaded most of Philimania from the rest of Neragons colonial holdings in Flonesia.

However, Paqueon forces weren’t able to advance further north after the fleet was defeated by a Neragese fleet led by Arthur Sudfries at the Battle near Petrali Island in Memesa of 1605. This led to a stalemate between the Neragese in Paqueons which was resolved in 1607 when a coordinated attack by Serono-Sothans and Neragese forces from New Sotha, New Rubenis; and Iolana respectively broke through the Paqueon blockade on the Philimanian archipelago and drove out invading Paqueon forces by the middle of Marto the same year.
By the end of the war, some 100,000 civilians were killed while about 1,340,000 soldiers were killed on both sides of the conflict. Additionally, around 700,000 houses and other structures were damaged or destroyed due to Paqueon bombing.
Colony of Philimania
TBA
Self-rule and independence
TBA
Geography
TBA
Enviroment
TBA
Biodiversity
Philimania is one of X megadiverse countries in Gentu according to X, and it has the X-most biodiversity per square kilometer of any nation.
Philimania has 900 bird species. In addition to more than 10,000 species of plants, the country has 97 endemic reptiles, 138 endemic amphibians, and 4,000 species of butterfly. As of the writing of the plan in 2005, 12% of Philimania's land area was in a protected area; however, the plan also states that 35% of the land must be protected in order to truly preserve the nation's biodiversity. Current protected areas include 10 national parks, 12 wildlife refuges, 7 ecological reserves, and other areas.
Climate
Philimania experiences a humid tropical climate with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round. Because of the nations close proximity at the equator, Philimania experiences little variation in daylight hours during the course of a year. Both sunrise and sunset occur each day at the two six o'clock hours.
The temperature in Philimania ranges between 30 and 35 °C (86 and 95 °F) at the coast and 30 and 31 °C (86 and 87.8 °F) inland during the day and is quite stable at around 24 °C (75.2 °F) at night.
| Climate data for Philimania | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.6 (87.1) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.0 (87.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.3 (81.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.6 (81.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 23.9 (75.0) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.2 (75.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 271.8 (10.70) |
231.6 (9.12) |
208.3 (8.20) |
220.2 (8.67) |
304.5 (11.99) |
438.7 (17.27) |
458.2 (18.04) |
379.7 (14.95) |
301.2 (11.86) |
352.3 (13.87) |
287.5 (11.32) |
304.3 (11.98) |
3,758.3 (147.97) |
| Average rainy days | 19.0 | 15.9 | 16.7 | 14.8 | 20.0 | 21.9 | 21.0 | 19.8 | 16.8 | 20.1 | 18.7 | 19.9 | 224.6 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 198.4 | 194.9 | 244.9 | 234.0 | 210.8 | 168.0 | 186.0 | 176.7 | 198.0 | 179.8 | 183.0 | 182.9 | 2,357.4 |
Administrative divisions
TBA
Transport and infrastructure
Foster International Airport in New Phork is the only public airport in Philimania. It provides scheduled direct flights with X, X, X and X.
Freight, military and cruise ships often call at Phrakingdale Harbor, Gardton Harbour, or Harpville Harbour. Philimania has around 1906 km or 1184.3 mi of highways, only 456 km or 283.3 mi are paved. Driving is on the left and the speed limit is 100 km/h (62 mph) on most highways.
The railroad network of Philimania is 1626 km long and is traversed daily by up to 30,000 passenger and cargo trains. The partially state-owned largest railroad company Philimanian Rail Company serves and oeprates a large number of trains, passengers and infrastructure components. Most of the railroad infrastructure is maintained, operated and financed by the Ministry of Infrastructure since 1964. The network is used by regular and high speed trains, most notably the InterCity trains travelling at between 240 km/h (149 mph) to under 370 km/h (230 mph), providing expansive domestic and international rail connections.
Confined urban underground rapid transit such as the New Phork Underground are used by approximately 1.757 million passengers daily. Taxis and public transport in general are all well developed mostly in major Philimanian cities but some in smaller cities as well such as Bridging, Seerno and Lensaw.
Demographics
Ethnic Groups in Philimania (2000)
Philimania's population is ethnically diverse and the 2000 census put Philimania's population at 14,088,100. The largest ethnic group (As of 2000) are the Philimanians, who are mixed race people of Neragese, Hestandan, and Iolonan descent and constitute about 48% of the population. The Hestandans are the second largest ethnic group accounting for 24% of the population. The rest of Philimania's population is a result of a mixture of Oranish immigrants, predominantly from Oliea and Veragon with people from Cavala, Paloa, and Neragon who have settled in the early 20th century. Philimania also has a small population of Hesterish origins, mainly those from the lowlands regions, such as Qiuhua and Samin which collectively makes up 4% of the population and whose ancestors arrived as miners, factory workers and fishermen in the mid 19th century during the Industrial Revolution. The Afro-Philimanians are a minority population (1.7%) in Philimania, largely based in Newton and to a lesser degree in X. The remaining 0.1% consists of immigrants from the Domicas and Naphtora.
Philimania has a population density of 61.6/km² (159.5/sq mi). Being a developed country, Philimania has a life expectancy of around 80.05 years, 79.72 years for men and 81.94 years for women. Philimania additionally has a very low infant mortality rate of 3.6 boys and 3.3 girls per 1,000 births. Historically the rate of reproduction remained above-average with 1.8 children in the mid 1900s, but deteriorated significantly since then with a period of the death rate of Philimania exceeding its birth rate and a slightly shrinking population between 1950 and 1970. However, Philimania since then advocated immigration to the country and introduced efforts to stimulate population growth; increased birth rates and migration numbers curbed the low fertility rate and supported population growth since 1970.
Philimania is one of the most important immigration destinations in the world. In a 1999 census, around 4.7 million people (or close to 33.5%) were either of immigrant or partially immigrant descent, and in 2013, 42.9% of all newborn children had atleast one parent born in a foreign country, and 27% atleast one born outside of Flonesia. Immigration to Philimania is a key factor in supporting its population growth and supply of work forces in light of its aging population.
Language
The most widely used language is Neragese which is also the de facto national language. Approximately 80% of the population speaks Neragese as a first language, with another 9% speaking Hestandan as a first language with only 11% of the population speaking their own native language as a first language.
TBA
Religion

TBA
Largest Cities
Philimania is a highly urbanized country. Its largest cities include New Phork, Phorktown, Stefshire, Shewood, Croufield, Meucester, Phrakingdale, Watchingham, Harpville, and Gardton features a number of large metropolitan areas summing up urban agglomerations, such as the Greater New Phork. Geographically, most urban regions are concentrated along rivers or on the coastal regions of the country due to the dense jungle in the central region of the country.
TBA
Politics
Government

The Republic of Philimania is a constitutional federal republic with the Philimanian Constitution being the supreme law of the land. Exercising the separation of powers, the political system of the country is divded into the executive, legislative and judiciary branch, each controlled by a separate institution. The executive branch is headed by the President of Philimania. Can veto legislative bills, appoint cabinet members and Supreme Court Justices. The legislative branch is made up of the Legislative Council and the House of Representatives. Makes federal law, declares war, allocates federal funds and approves treaties. The judicial branch makes up the Supreme Court and lower federal courts. Has the power of judicial review, and is the highest legal authority after the Constitution.
The President of Philimania is elected directly by the public, and formally approved by the Legislative Council. The ministers of the cabinet are then proposed by the president, who are in turn either approved or rejected by the Legislative Council. The current president and vice-president since 2000 is Nel Karlson and Henry Field of the Philimanian Liberal Party (PLP).
In Philimania's political history, since the founding of the Legislative Council in 1654, the Philimanian Liberal Party (PLP) was most popular party and kept its status until the 1989 Philimania legislative election when the Philimanian Democratic Party (PDP) surpassed them for the first time and had held its superior status until the 1999 election. Since 1654, 74 Legislative Council elections have been held, with the most recent election being held on 28 Memesa 1999.
Foreign Relations
TBA
Military

TBA
Economy
with a GDP of $1.342 trillion and a GDP per capita of $30,120, the Economy of Philimania is the Xth largest in both the world and South Domica. Philimania is considered to be a developed country with the Xth highest Human Development Index of the world and boasting one of the largest rates of nominal GDP per capita in any country. The private sector is estimated to constitute 91% of the economy, with federal, regional, and local government accounting for 8.1%. Philimania employed its largest labour force of 11.4 million people in 1998, or 85% of the population, in its history; its unemployment rate was estimated at 0% in 1998, largely due to excellent employment regulations throughout the country.
Philimania's economy consists primarily of tourism, subsistence agriculture and fishing. While the couuntry has access to some resource deposits such as coal and a long history of mining, it is crucially dependant on the import of resources and energy assets from abroad. The most competitive sectors of the Philimanian industry are considered to be the automobile, agriculture and the fishing sectors. The most important trading partners of Philimania in 1999 were X at a trading volume of $151.37 billion, X with $146.60 billion, X with $126.71 billion, and X with $119.28 billion.
The income tax has three brackets with progressive rates of 9.3 percent, 15 percent, and 19.6 percent respectively. Corporate tax is four percent, and the sales tax is zero. There are no property taxes.
Tourism
Philimania is the Xth most visited country in the world, with tourist arrivals numbered some 35.9 million in 1998. Tourism as an economic sector made a considerable contribution to the national economy, generating a revenue of $135 billion, or 10.4% of Philimania's GDP in 1999. 27 of Philimania's counties are registered in some form of tourist agency. 2,842 museums, 94 theatres, 7 amusement parks, 45,940 tennis courts, approximately 87 beaches. 301 golf courses, more than 17,000 kilometres of hike trails and 9,000 kilometres of biking ways, and numerous scuba diving and snorkeling spots are all available and accessible to tourism activities. Additionally, long-term prospects for the key tourist sector have been greatly bolstered by the expansion of air travel in the Nullaric.
Agriculture
While the agricultural industry gradually diminished in their importance to the national economy, it is still considered internationally relevant in generating a wide array of products, being the fourth-largest exporter of agricultural products in Flonesia. The domestic agricultural industry is extremely productive in that it is able to sustain and cover more than 85% of the Philimanian population's needs for food in 2019, mainly due to extensive fertile soils in northern Philimania and sophisticated modern technology used in agriculture.
Principal agricultural exports of Philimania include products of lifestock, including poultry, beef and pork, dairy products, wheat, potatoes, and fruit. Processed food such as variations of cheese and bread are also important, and form staples of Philimanian cuisine.
Science and technology

Philimania is an internationally significant and renowned location of technology and science. Since the Industrial Revolution, Philimanian scientists participated immensly in the foundation of modern science; especially the economic productivity of multiple industrial sectors and the transfer of knowledge to practical use proved pivotal in the scientific development of the Philimanian academic field. Publications of scientific matters receive international acclaim and domestic public popularity; scientific journals published in Philimania include Harefind and Archaringe, while Philimania as a research host produced more than 2% of the world's scientific research papers in 2000.
Institutions of research and science in Philimania are embodied through universities. Most of which are in public ownership and service, but their research activities are often financed by third parties such as foundations, companies, and other. The University of New Phork and the International University of Philimania remain one of the most renowned and prestigious universities in the world. Apart from the country's universities, a large number of research organizations are active across Philimania and abroad, represented and coordinated through associations and councils in compliance with the Ministry of Education and each university. the most famous of which include the Joseph Hinderman Society for basic research, the Craftsman Society as the country's largest scientific society, and the Alban Society for applied research.
Culture
Philimania is home to a variety of cultures, a result of a liberal immigration policy. Philimanian culture is generally considered "western", derived from traditions of Oranish and Iolonan culture. Like other Domican nations, Philimania has been described as a melting pot where several cultures join into one.
Philimanians have been described as very compassionate, hard-working, and competitive. This has resulted in great economic productivity and a libertarian form of government. This has also made Philimania a popular destination for immigrants. Philimanians are also firm believers in equality and do not think that one social class should have more rights than others.
Cuisine

Philimania is home to many different cuisines, a result of a liberal immigration policy. But mainstream Philimanian cuisine is similar to that in Iolona cultures with some aspects coming from Oranland. The Wee-Wee Fish, an also an important part of Philimanian cuisine and is often fried, boiled, and minced into small Pastochos, a type of tart made in Philimania. Philimanian cuisine also features dishes such as pineapple pie, Philimanian curry, panipopo, and coconut cake. Bread is also an important part in Philimanian cuisine, dishes wih bread in Philimania includes Luau Bread, Cassavon, and Po'eo.
Places serving Philimanian cuisine can be found all over the country in foodstands, restaurants, and shopping malls. Philimanian cuisine are also sold in night markets which would appear during the weekends and holidays.
Sports

TBA
Education
TBA
Architecture
TBA
Social Media
TBA