Huang dynasty: Difference between revisions
m (→Military) |
m (→Military) |
||
| Line 174: | Line 174: | ||
== Military == | == Military == | ||
{{Main|Everlasting Army|Paramilitary forces of Da Huang|Everlasting Army Ground Force under Cao Fang}} | {{Main|Everlasting Army|Paramilitary forces of Da Huang|Everlasting Army Ground Force under Cao Fang}} | ||
[[File:J-94 4th Generation Prototype Fighter.jpg|thumb|[[Anxi J-94]] {{wp|Fourth-generation jet fighter|4th generation}} prototype fighter used in limited quantity by the [[Everlasting Army Air Force|EAAF]]]]]] | |||
The Everlasting Army ([[Simplified Jin characters|Jin]]: 永固军; {{wp|Pinyin|pinyin}}: ''Yǒnggùjūn''), more fully called the Everlasting Royal Army of Jin (中国皇家永固军; ''zhōngguó huángjiā yǒnggùjūn'') constitutes the military of Da Huang and is amongst the world's largest militaries. It consists of the [[Everlasting Army Ground Force|Ground Force]] (EAGF), the [[Everlasting Army Navy|Navy]] (EAN), the [[Everlasting Army Air Force|Air Force]] (EAAF), and various {{wp|Paramilitary|paramilitary}} forces that serve as the {{Gendarmerie|gendarmerie}} during peacetime. | The Everlasting Army ([[Simplified Jin characters|Jin]]: 永固军; {{wp|Pinyin|pinyin}}: ''Yǒnggùjūn''), more fully called the Everlasting Royal Army of Jin (中国皇家永固军; ''zhōngguó huángjiā yǒnggùjūn'') constitutes the military of Da Huang and is amongst the world's largest militaries. It consists of the [[Everlasting Army Ground Force|Ground Force]] (EAGF), the [[Everlasting Army Navy|Navy]] (EAN), the [[Everlasting Army Air Force|Air Force]] (EAAF), and various {{wp|Paramilitary|paramilitary}} forces that serve as the {{Gendarmerie|gendarmerie}} during peacetime. | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 9 April 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Great Huang | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: 永固军軍歌 Yǒnggùjūn jūngē "Anthem of the Everlasting Army" | |
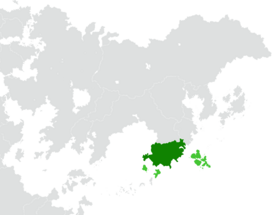 Territory controlled by the Huang dynasty is shown in dark green; territory claimed but not controlled is shown in light green. | |
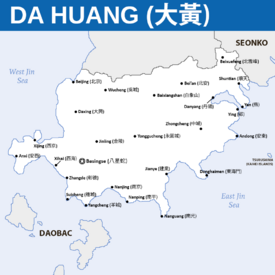 Political Map of Da Huang | |
| Capital | Basingse |
| Largest city | Xi'hai |
| Official languages | Standard Jin |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Official script | Simplified Jin |
| Ethnic groups (2022) | |
| Religion (2022) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Jin |
| Government | Unitary parlimentary anocratic semi-consitutional monarchy |
• Emperor | Yingjie Emperor |
• Prince Regent | Shunwang, Prince Huang |
• Prime Minister | Cheng Pu |
| Legislature | Advisory Council |
| Formation | |
• First pre-imperial dynasty | c. 2070 BCE |
• First Imperial dynasty | c. 221 BCE |
• Conquest by the Bayarids | 932 CE |
• Establishment of the Great Khan's Court-in-Taizhou | 1145 CE |
• Great Kra Invasion | 1346—1358 |
• Establishment of the Kra—Na dynasty | 1358 |
• Five Pecks of Rice Rebellion | 1672—1674 |
• Establishment of the ethnic Jin—Huang dynasty | 1674 |
• Wucheng Heavenly Rebellion | 1900—1908 |
• Republic of Jin established | 1902—1931 |
• Corrective Movement | 1931—1943 |
• End of the Republic and Reestablishment of the Huang dynasty | 12 February 1943 |
• Current constitution (1991) | 29 August 1991 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,125,344 km2 (434,498 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 121,648,117 |
• Density | 108.1/km2 (280.0/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $1.387 trillion |
• Per capita | $11,400 |
| Gini (2022) | 36.4 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high |
| Currency | Yuan (元/¥) (JY) |
| Time zone | (GST+8) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+7 ((GST+7)) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy CE |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +16 |
| Internet TLD | .jn |
The Huang dynasty, officially the Great Huang (Jin: 大黄; pinyin: Dà Huáng), is a sovereign state in Southeast Ochran, situated in the Jin Peninsula, spanning 1,125,344 square kilometres (434,498 sq mi), with a population of 121,648,117. The country is bordered to the northeast by Seonko and shares maritime borders with Daobac to the south and Tsurushima through the Kaihei islands to the east. The national capital is Basingse, and the most populous city and largest financial centre is Xi'hai.
Modern Jin traces their origins to a cradle of civilisation in the fertile Yellow River basin in the Central Jin Plain. Their long occupation, initially in varying forms of hunter-gatherers, emerged into settled life as early as 7000 BCE, gradually evolving into multiple early Jin civilisations. The interactions of different and distinct cultures and ethnic groups influenced each other's development; specific cultural regions that developed the early Jin civilisation were the Huanghe civilisation, the Chiangjiang civilisation, and the Nanbei culture.
These early civilisations would set the foundations of several regional cities, eventually turning into city-states and petty kingdoms. The semi-legendary kingdom of Wei in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Zhang and Liao states developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies known as dynasties. Jin writing, Jin classic literature, and the Hundred Schools of Thought emerged during this period and influenced Da Huang and its neighbours for centuries to come.
Early Jin historians attributed to the notion of one dynasty succeeding another; however, current archaeological, geological, and anthropological findings have shown that the political situation in the Jin peninsula was much more complicated. These political entities existed concurrently and would remain disunited until the third century BCE when the King of Wu, Wu Shi Huang, founded the first Jin empire, the short-lived Wu dynasty. The more stable Jin dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE) followed the fall of the Wu and established a model for nearly two millennia in which the Jin empire was one of the world's foremost economic power.
Throughout its existence, the Jin dynasty expanded, fractured, and reunified; was conquered and reestablished; absorbed foreign religions and ideas; and made world-leading scientific advances, such as the Four Great Inventions: gunpowder, paper, the compass, and printing[a]. However, by the late 6th century CE, centuries of disunity led to the fall of the Jin. The following Zhou (581–618) and the Later Wei (618–907) dynasties would reunify the empire. The xenophilic Later Wei welcomed foreign trade and culture across the Kayatman Sea and the Jade Road and adapted N'nhivaranism to Jin culture.
The Song dynasty (907–932) would replace the Later Wei and see an increasingly urban and commercialised economy in the empire. During this period, the civilian scholar-officials, or the literati class, would emerge and replace the military aristocrats of earlier dynasties with the introduction of the Song Imperial examination system. The Song emperors sought to avoid the same mistakes that had led to the downfall of their predecessors and introduce wide-ranging reforms to curb the power of the military. However, in 932, the Bayarid invasion cut short the Song reforms and established the Great Khan's Court in Taizhou, also known as the Zhen dynasty (932–1358), by Jin historians. Another foreign culture would conquer the Bayarid-led Zhen dynasty, the Kra, establishing the Kra–Na dynasty (1358–1674) before the Huang dynasty (1674–1902) reestablished ethnic Jin control.
The Jin monarchy collapsed in 1902 with the Wucheng Heavenly Rebellion when the Republic of Jin (ROJ) replaced the Huang dynasty. In its early years as a republic, the country underwent a period of instability known as the Warlord Era before mostly reunifying in 1913 under a Nationalist government with the Huang royalist forces spread and contained in the central and northern mountains. With financial and military aid from the Empire of the Latins, the Republic of Jin recovered from the disastrous Cross-Strait war before participating in the Hanaki War in 1927 to conquer their claimed lands. However, the Hanaki War ended in another failure for the Jin. The surrender left a power vacuum in the country, leading to renewed fighting between the scattered remnant armies and a reinvigorated royalist army. The civil war culminated into the Corrective Movement (1931–1943) and ended with a royalists coup from disaffected republican generals and civil servants who wanted an end to the instability. The Huang emperor was reinstated to the throne, and the military and civil servants reestablished the dynasty on 12 February 1943.
Da Huang has since periodically alternated between civil, monarchic and military rule. Whilst the emperor has been seen as the Son of Heaven and an undisputed autocrat of all under Heaven, this archaic belief in the emperor's divinity has slowly faded away from the new bureaucrats of the late 20th century. Dissent among government officials has led to the stagnation of the empire's recovery leading to foreign economic exploitation and civil unrest between the literati and the military, alongside a resurging Kra rebellion in the northern provinces. To circumnavigate this byzantine bureaucracy, the Yingjie emperor introduced the 1991 constitution as a compromise between the three estates, allowing some form of democratic rule to modernise its bureaucracy.
Da Huang is currently governed as a parlimentary constitutional monarchy; in practice, however, structural advantages in the constitution due to the compromise in the 1991 constitution have resulted in a complex parliamentary anocratic semi-constitutional monarchy system balanced between the military, the literati, and the monarchist. Da Huang is a middle power in global affairs and ranks moderately on the Human Development Index. It is also classified as a newly industrialised economy, with manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism as leading sectors.
Etymology

The name Dà Huáng (大黄; lit. "Great Yellow") in its national language, Standard Pūrvī, has been used by native Jin since the dynasty's foundation. Its origin is generally accepted to be named after the Yellow River though some modern scholars attributed the name directly to the founder of the early Huang dynasty, Huang Junyan. Another accepted argument for the source of the word is that it was adapted from the poem Mother River (Jin: 母河; pinyin: mǔ hé) authored by the famous 10th-century CE poet Wang Wei. The old Jueju style poetry depicts the Yellow River as the "Mother River" and the "cradle of Jin civilisation":
| 《母河》 | Mother River |
|---|---|
|
|
While the name Da Huang has been used natively since the 17th century, foreigners did not use this name during this period. The Jin peninsular includes many contemporary and historical appellations in various languages for the Southeast Ochran country. Of the most common, the word "Jina" has appeared on many foreign maps and records from the world's western hemisphere. Its origin has been traced through Latin, Mutli, and Tyreseian back to the Uthire word Jindā, used in the Tahamaja empire. "Jina" appears in Akutze Selenecha's 1516 translation of the 1346 journal of the Tyresene explorer Ahumm Bōdashtarti. Bōdashtarti's usage was derived from the Scipio-Latinic word Jiña, which was in turn derived from Uthire Jindā (जिन्दा). Jindā was first used in early N'nhivara scripture, including the Tuntutan Roh (805 BCE) and the Tuntutan Kuasa (850 BCE). In 1655, Clímaco Casados suggested that the word Jina is derived ultimately from the name of the Jin dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). Although usage in Tahamaja sources precedes this dynasty, various sources still give this derivation. According to the Latin Dictionary, the origin of the Uthire word is a matter of debate.
Da Huang is also sometimes referred to by its informal name "Zhongguo" (simplified Jin: 中国; traditional Jin: 中國; pinyin: Zhōngguó) from zhōng ("central") and guó ("state"), a term developed under the Western Liao dynasty in reference to its royal demesne. The name Zhongguo is also translated to "Middle Kingdom" in Latin and was used as a cultural concept to distinguish the Jinxia people from perceived "barbarians". It was then applied to the area around Qinjing (present-day Daxing) during the Eastern Liao dynasty and then to the Central Jin Plain before being used as an occasional synonym for the state under the Zhen dynasty (also known as the Great Khan's Court in Taizhou).
History
- For a chronological guide, see Timeline of Da Huang history
Prehistory

Geography
Politics
Military
]]
The Everlasting Army (Jin: 永固军; pinyin: Yǒnggùjūn), more fully called the Everlasting Royal Army of Jin (中国皇家永固军; zhōngguó huángjiā yǒnggùjūn) constitutes the military of Da Huang and is amongst the world's largest militaries. It consists of the Ground Force (EAGF), the Navy (EAN), the Air Force (EAAF), and various paramilitary forces that serve as the Template:Gendarmerie during peacetime.
The Everlasting Army have a combined manpower of 406,000 active duty personnel and another 345,000 active reserve personnel. The head of the Everlasting Army is the emperor, although this position is only nominal and highly contentious in the current political climate. Under the 1991 constitution, the armed forces were to be managed by the Board of War, which is jointly headed by the Minister of the Army (Da Huang) and the Minister of the Navy (Da Huang) under the direct supervision of the emperor. In reality, however, the armed forces are split between those loyal to the dajiang (大将; lit. Grand General) Cao Fang of EAGF and the Royalist party, with some junior officers dedicated to the Constitutionalists. Da Huang's official military budget for 2022 totalled JY¥54.09300 billion, accounting for 3.9 per cent of the annual GDP.
According to the constitution, serving in the armed forces is the duty of all Jin citizens. Da Huang still uses the active draft system for males over the age of 18, except those with a criminal record or who can prove that their loss would bring hardship to their families. Males who have not completed their pre-university education, are awarded the Public Service Commission (PSC) scholarship, or are pursuing a medical degree can opt to defer their draft. However, this deferment is subject to varying degrees of success; well-to-do citizens have been known to bribe draft officials, most notably from the EAGF, to dodge the draft entirely. Hence, the poor and less educated are often subjected to varying lengths of active service, with some serving for as long as the maximum five years of reserve training as a Territorial Defence Soldier. This practice has long been criticised, as some media question its efficacy and value. It is alleged that conscripts of the EAGF end up as servants to senior officers or clerks in military cooperative shops. In a report issued in April 2019, EAGF military conscripts are found to have faced institutionalised abuse systematically hushed up by the army authorities.
Historically, Da Huang's military has been mired in corruption and nepotism; the Internal Security Operations Command of the EAGF functions as the political arm of the EAGF military authorities. It has overlapping social and political tasks with civilian bureaucracy, adopting an anti-democratic ideology recently. The military is also notorious for numerous corruption incidents, such as accusations of illegal trafficking, promotion of high-ranking officers in the form of nepotism, and deeply entrenching themselves into the Jin civilian politics.
Economy
Science and technology
Infrastructure
Demographics
Culture and Society
Notes
- ↑ The Four Great Inventions (simplified Jin: 四大发明; traditional Jin: 四大發明; pinyin: sì dà fā míng) are inventions from ancient Jin that are celebrated in Jin culture for their historical significance and as symbols of Jin's golden age. However, modern scholars have disputed the veracity that the Jin was the first to develop these innovations. The historical facts regarding the origin of some of these inventions remain scant, and several competing arguments have been raised to challenge these claims. Most notably:
- Gunpowder has been used extensively in the Tahamaja empire since the mid-11th century. The medieval navies of the Tahamaja were recorded to have mastered using rudimentary artillery to solidify their rule across their vast maritime empire. While the Song dynasty (907–932) in Da Huang has been purported to have used explosive substances in cannons, fire arrows, and other military weapons, scholars have posited that their military use was not as extensive as once thought and that these weapons only saw comprehensive service during the Zheng dynasty (932–1358) in the late 13th century. There is an increasingly growing argument that the Tahamaja empire was the first to discover the invention of gunpowder, and its manufacturing methods were brought to Da Huang by their interaction. Another purported argument is that the innovation was concurrent, and both the ancient Jin and Tahamaja developed gunpowder simultaneously around the same time.