Etruria
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
United Etrurian Federation
3 other official names
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Motto:
| |||||||
Anthem:
| |||||||
 Location of Etruria (in light green), within Euclea (light grey) | |||||||
 | |||||||
| Capital | Poveglia | ||||||
| Largest city | Tyrrhenus | ||||||
| Official languages | Italian Croatian Slovenian | ||||||
| Ethnic groups (2016) |
| ||||||
| Religion (2016) | 96% Poveglian Catholic 2% Atheist 1% Other | ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Etrurian | ||||||
| Government | Constitutional parliamentary federal republic | ||||||
| Francesco Carcaterra | |||||||
| Vittoria Vasari | |||||||
| Ivano Balić | |||||||
| Legislature | Senate of the Federation | ||||||
| State Council | |||||||
| Chamber of Representatives | |||||||
| Formation | |||||||
| 10 November 1736 | |||||||
| 18 September 1793 | |||||||
• Monarchy restored | 3 April 1810 | ||||||
| 10 May 1888 | |||||||
• Treaty of Kesselbourg | 12 February 1935 | ||||||
• Current constitution | 1 July 1983 | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
• | 548,549 km2 (211,796 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 2017 estimate | |||||||
• 2014 census | 63,888,987 | ||||||
• Density | 119.58/km2 (309.7/sq mi) | ||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| Gini | 46.9 high | ||||||
| HDI | 0.843 very high | ||||||
| Currency | Etrurian florin (₣) | ||||||
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy | ||||||
| Driving side | left | ||||||
Etruria, officially the United Etrurian Federation or UEF (Vespasian: Federazione Etruriana Unita; Novalian: Sjedinjene Etruriska Federacija; Carinthian: Združena Etruriska Federacija) is a sovereign parliamentary federal republic, made up of three constituent states: Vespasia, Novalia and Carinthia and six autonomous federal regions; Carvagna, Torrazza, Ossuccio, San Eugenio and Tarpeia, and several islands, the largest being Aeolia and Apocorona. Etruria is located in southern Euclea. Its is bordered (clockwise) by Amathia to the north, Gaullica to the north-east, Florena to the east, to south, Gibany to the south, and Piraea to the west. Etruria is home to 65.5 million people, its federal capital is Poveglia and largest city is Tyrrhenus.
Since classical times, its central geographic location in Euclea and the Mazdan and Solarian Seas, Etruria has historically been home to a myriad of peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient Vespasian tribes and Vespasic peoples dispersed throughout the Etrurian interior and insular Etruria, beginning from the classical era, Pireans, XX and XX established settlements in the south of Etruria, with Vicalvii and Gaullics and Iberialcelts inhabiting the centre and the north of Etruria respectively. The Vespasic tribe known as the Solarians formed the Solarian Kingdom in the 8th century BC, which eventually became a republic that conquered and assimilated its neighbours, including the powerful and wealthy Viclavii. In the first century BC, the Solarian Empire emerged as the dominant power in the Solarian-Mazdan Basin and became the leading cultural, political and religious centre of Euclean civilisation. The legacy of the Solarian Empire is widespread and can be observed in the global distribution of civilian law, republican governments, Sotirianism and the Solarian script.
During the Middle Ages, Etruria suffered sociopolitical collapse amid calamitous barbarian invasions, but by the 11th century, numerous rival city-states and maritime republics rose in Vespasia to great prosperity through shipping, commerce, and banking, laying down the groundwork for modern capitalism, however the areas of modern Novalja and Carinthia continued to decline. These independent statelets often enjoyed a greater degree of democracy and wealth in comparison to the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Euclea at the time. By the 13th century, modern Etruria became dominated by three states, the Exalted Republic of Poveglia, Grand Duchy of Carvagna and the Ecclesiastical States.
The Renaissance spread across Etruria from Povelia, bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration and art. Vespasian culture flourished at this time, producing famous scholars, artists and polymaths such as "Great people". The influence and commercial power of the maritime republics began to dominate the monarchies of the interior, culminating in the Povelian victory in the Etrurian Wars and becoming the dominant power in Etruria, leading to the Pax Poveliae. Povelian colonisation of the Asterias soon followed, introducing New World treasures to Etruria. The sudden rise of the Principality of Tyrrenhus in the south added pressure to Povelia. In the 18th century, Povelia’s decline began, hastened by the immense cost paid during the Ten Year’s War. This decline led to the Central Etrurian Wars and the Torazzi War between Povelia and Tyrrenhus, bankrupting and disrupting vast swathes of Etruria. The famine, debt and corruption led to the overthrow of the monarchy in Tyrrenhus, sparking the Etrurian Revolution (1783-1785) and the establishment of the Etrurian First Republic, creating one of the earliest republics in history. The Republic would go on to unite Etruria and for the next fifteen years, engage in the Etrurian Revolutionary Wars, spreading republican tradition and values across southern Euclea. The constant warfare, poor governance and state-terror would lead to the restoration of monarchy in 1810 and the United Kingdom of Etruria.
From 1810 until 1880 would enjoy prosperity, growth and development. Etruria would establish one of the largest colonial empires, while federalism was greatly expanded and refined. However, debt, a poor economy and authoritarianism resulted in the 1880 Revolution and the establishment of the Second Etrurian Republic. Etruria was a major participant in the Great War, from which it emerged victorious, however, poor territorial gains and political instability led to the emergence of the Etrurian Revolutionary Republic and the Solarian War, which saw Etruria defeated. The Third Etrurian Republic emerged in the aftermath, rebuilding the country and establishing a fixed regime of civil rights and freedoms before being overthrown by the military which established a Junta in wake of the Western Emergency. Democracy would be restored in 1983 with the current Fourth Republic.
Today, Etruria has a mixed market economy based around finance, industry and agriculture. It has the XX largest economy in Euclea, and XX largest in the world. It is widely considered a newly-industrialised economy, a regional power and middle power. It is a council member of the Community of Nations, GIFA, NAC and the ITO.
Etymology
The assumptions on the etymology of the name "Etruria" are very numerous and the corpus of the solutions proposed by historians and linguists is very wide. Many historians note that the Etrurian mountain range that extends across northern Etruria and rising up east of Sea/Lake X then southwards along the border with Sardenya were prominent features of Vespasic faiths in ancient history. Etruria in ancient Vespasic (Etrúra) meant "Sacred Rock" and since the Aventine mountains meet the Etrurians roughly in the central region of the north and push south towards the X Sea, many historians surmise that as the Vespasic tribes expanded, they considered the Aventines and the Etrurians to be one and the same and extended the name Etrúra to the rest of the country. As Vespasic developed into latin, Etrúra evolved into Etruria and the name has remained in use since.
The term Transetruria or Transetrurian was only introduced in the 19th century to refer to Vespasia and its territories in Carinthia and Novalia and remained in use within officialdom, eventually being adopted as the official title of the federation in 1921, as a means of unifying the three constituent states.
History
Pre-history
Excavations throughout Etruria revealed a hominid presence dating back to the Palaeolithic period, some 210,000 years ago, modern Humans appeared about 48,000 years ago. Much of the pre-history presence is concentrated around the Poveglian Basin in the north and the Alluvian plains in southern Etruria.
The Ancient peoples of pre-Solarian Etruria– such as the Torians, the Vepasii (from which the Solarians emerged), Vicalvii, Otians, Samanians, Sorines, the Guallics, the Suratii, and many others. Other peoples were identified as the primarily mountainous, Novarians, Carumnii and the southern and coastal focused Aeoluii.
Between the 17th and the 11th centuries BC XX established contacts with Etruria and in the 8th and 7th centuries BC a number of XX colonies were established all along the coast of Vespasia and the southern part of the Aeolian Peninsula, that became known as XX. During this time, the Vespasii were rapidly growing in and around what would become Solaria, while north of them, the Vicalvii had cleared land around the seven-hills of Vicalvus.
Ancient Solaria and Vicalvus
Solaria, a settlement on the coast of the Bay of Lasa Vecuvia conventionally founded in 757 BC, was ruled for a period of 239 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of Vespasii and Torian origin, later by Vicalvii kings. The tradition handed down seven kings: Romulus, Verus Tanis, Horius Antonius, Marcus Marcellius, Eugenius Prascus, Ceserius Tullius and Hadrianus Lutorius. In 511 BC, the Solarians expelled the last Vicalvii king from their city and established an oligarchic republic.
To the north of Solaria, Viclavus, a settlement built around the ford of the Metaia River rapidly grew under a series of successive kings, it dramatically expanded its territories to cover the entire Vicalvian Plain. Vicalvus' dominant position allowed it to influence Solaria until the expulsion of Hadrianus Lutorius. With the establishment of the Solarian Republic, Vicalvus found a serious challenger to domination over southern Vespasia. The two cities would fight numerous wars known as the Wars of the Two Cities, the wars ended in 256 BC when Vicalvus was defeated at the Battle of Veii, resulting in the city's annexation by Solaria. Vicalvii culture would fuse with Solarian, creating the long-lasting Solarian culture that spread with the empire's growth. The Solarian Republic until the first century B.C. would expand to encompass all of modern day Etruria and western Florena, crossing the Solarian sea to establish colonies on the coasts of XX and XX by 89 BC.
In the wake of rebellion by Tarchon Parusna in the first century B.C., Solaria grew over the course of centuries into a massive empire stretching from XX to the borders of XX, and engulfing the whole Solarian and Mazdan basins, in which the Vicalvii-Solarian and Helleneo and many other cultures merged into a unique civilisation. The Solarian Peninsula was named Etruria was declared "Terra Saena" (Sacred Soil), granting special status compared to other imperial provinces. The long and triumphant reign of the first emperor, Tarvinius, began a golden age of peace and prosperity.
The Solarian Empire was among the most powerful economic, cultural, political and military forces in the world of its time. It was one of the largest empires in world history. At its height under Velturius, it covered 5 million square kilometres. The Solarian legacy has deeply influenced the Euclean civilisation, shaping most of the modern world; among the many legacies of Solarian dominance are the widespread use of the Vespasic languages derived from Vepsasii, the numerical system, the modern Western alphabet and calendar, and the emergence of Christianity as a major world religion.
Decline and end...
Middle Ages
After the fall of the Solarian Empire, Etruria fragmented, falling to both domestic and foreign rule, from north Gaullic and Marolev tribes advanced south to dominate much of the country, ending political unity in Etruria for the next 1,300 years. In the south, the Papacy in Solaria emerged as an independent force, using wealth and political maneuverings to coalesce the small fiefdoms around the city under its control, while in the north, the city of Poveglia which maintained some semblance of the former Empire slowly guaranteed its independence and moved to expand its own territory.
It was during this chaotic era that Vespasian towns saw the rise of a peculiar institution, the medieval commune. Given the power vacuum caused by extreme territorial fragmentation and the struggle between these polities and the growing power of the Papacy, local communities sought autonomous ways to maintain law and order, this gave way to numerous city-states and small states.
In coastal and southern areas, the maritime republics grew to eventually dominate the Solarian Sea and monopolise trade routes to between Euclea and northern Coius. They were independent thalassocratic city-states. All these cities during the time of their independence had similar systems of government in which the merchant class had considerable power. Although in practice these were oligarchical, and bore little resemblance to a modern democracy, the relative political freedom they afforded was conducive to academic and artistic advancement.
The four most prominent maritime republics were Poveglia, Accadia, Casperia and Valestra, while less known are Apricena, Leverano and Andrano. Poveglia and Accadia were Euclea's prominent gateways to trade with the South, and a producer of fine glass, while Stazzona was a capital of silk, wool, banks and jewelry. The wealth such business brought to Vespasia meant that large public and private artistic projects could be commissioned. While Vespasia was predominately fractured and balkanised, Novalia and Carinthia rapidly united into the current forms under monarchies. These two kingdoms would maintain their independence and form until the early 18th century, when their conquest by the Floren Empire under Nèstor Pereramon, then the eventual unification of Etruria under Poveglia following Pereremon's death.
Early Modern

In the 14th and 15th centuries, Etruria was divided into numerous warring states, the most powerful of these being Poveglia, Carvagna, Fauglia, Ecclesiastical States and the Valtapinia. This time was marked by the fierce rivalry between Poveglia, Carvagna and Valtapinia. The remaining states usually be fluid alliances preserved their independence form the major states, while others used marriages and lucrative trade to gain favour. The strongest among these city-states gradually absorbed the surrounding territories giving birth to the Signorie, regional states often led by merchant families which founded local dynasties. These families would use patronage of the arts and science to compete for prestige, this not only fostered the Etrurian renaissance but expanded scientific and cultural development. War between the city-states was endemic, and primarily fought by armies of mercenaries known as "Soldati di Ventura", bands of soldiers drawn from around Euclea, especially Gaullica and the neighboring Floren states, led largely by Vespasian captains. However, Poveglia and the Ecclesiastical States were the only two states known to use domestically raised forces during war. Decades of fighting eventually saw Carvagna, Fauglia and Poveglia emerged as the dominant players that agreed to the Concordat of Lake Imperia in 1489, which saw relative calm brought to the region for the first time in centuries.
This peace would hold for the next forty years. Prior to the Lake Imperia Peace, the 1470s and 1480s were dominated by Poveglian expansion along the Vespasian coastline, frequent clashes between Carvagna and Torrazza and Papal conflict with Novalia. However, as time went on the dominant position of Poveglia would be further enhanced by expansion across the Coian and Hydanian coastlines, securing more lucrative trade routes, while its naval power grew immeasurably during the 1500s.
Throughout the 15th and early 16th centuries, Poveglia would engage in bitter maritime conflicts with the Gorsanid Empire based in Zorasan, these wars, coinciding with Gorsani raids on southern Euclea became known as the War of the Seas and further fuelled the naval domination of Poveglia, who used the naval conflict to innovate new naval designs and weaponry. These developments would prove vital toward the 16th century, as Poveglia sought out its own trade routes to the Asterias. In 1522, Poveglia dispatched Raffaele di Mariran, he would land in what would become Marirana. Steady development of Poveglia's Asterian colony saw significant return in gold and silver, which the republic used to modernise its fleet, army and infrastructure. It was during this time that Poveglia began to foster ambitions of unifying Etruria, however, this would be off-set by rising pressures to the south, where a resurgent Gorsanid Empire sought to evict Poveglia from its Coian territories.
Poveglia would dramatically expand in Etruria proper during the 1550s and 1580s with the War of Santa Cecilia, in which the Poveglian armies decisively defeated the League of Villa Barbarigo, annexing the Duchies of Fauglia and Eratia, while a second war against the Kingdom of Carinthia and the Grand Duchy of Serona, saw the Republic gain control over all of northern Etruria. Rivalry and intermittent conflict with Gaullica in what became known as the Aventine Wars would remain commonplace well into the 18th century. However, due to rising capabilities among its rival Etrurian powers, steady defeats at the hands of the Gorsanids and colonial unrest, Poveglia entered a period of decline. Forced to focus ever limited forces across three continents, Poveglia was fearful of the now united Pereramonic Florena, securing the backing of its Etrurian rivals, it led an expedition into Transmutanya in 1711. Despite early success, the Etrurian coalition was deceisvely defeated at the Battle of Oclava in 1713. Nèstor Pereramon counter-attacked and subjugated the entirety of Etruria by 1716, ending centuries of city-state rule, the collapse of Poveglia saw Mariranian independence.
Revolutionary Etruria (1790–1810)
The dramatic expansion of the Kingdom of Vicalvi throughout the 18th century had ruptured the socio-political fabric of Etrurian life that had remained relatively static since the 12th century. The fall of Carvagna in 1759 to Vicalvi saw the demise one of Euclea’s most influential cultural hubs and the significant losses suffered by Poveglia saw a further loss of economic influence due to the ceding of Poveglia’s colonies to Vicalvi. Most importantly, the Central Etrurian Wars had destabilised food production in Vicalvi’s territory, while also undermining support for the absolute monarchy. In 1781, war erupted between Vicalvi and Poveglia as the latter sought to reclaim its lost territories in northern Vespasia. Eager to fund his campaigns, King Alessandro III increase taxation, causing immense hardship among the peasantry and eventually the middle classes. The rubber-stamp Senate of Vicalvi denounced the taxation increase in 1782, bemoaning its failure to confront the Kingdom’s debt crisis. Their criticism falling on deaf-ears and royal obstructionism leads to the emergence of constitutionalist movements within the Senate.
Between 1783 and 1784, tensions between the King and the Senate grew exponentially, with the emergence of middle-class dominated secret societies that agitated for a constitutional monarchy or an outright republic. Yet, the continued famine, high taxation and authoritarianism against the peasantry resulted in mass uprisings by the lower classes in 1784. The popular uprisings eventually overthrew the King, transferring power to the senate, which proclaimed the Etrurian First Republic on 19 September 1784.

The new republic was gripped with chaos and political infighting, with various factions of republicans competing for control over the new government. The situation stabilised with the emergence of the Aventine Triad, consisting of Francesco Cassio Caciarelli, Giovanni-Paolo Danova and Massimiliano Malaspina. The Triad soon found itself leading the republic into war, with the outbreak of the Etrurian Revolutionary Wars in early 1785. Facing isolation and enemies on three fronts, the Republic rapidly fell into a “fanatical state of mind.” As generals loyal to Caciarelli scored major victories against the monarchies of Etruria, his influence over the Triad increased, as he did so, his Society of the Pantheon’s fervently Catholic Republicanism became more popular among the revolutionary classes. Over the course of six months, the Pantheonista government abolished aristocratic privalege, such as personal serfdom and exclusive hunting rights.

In 1786, the Revolutionary Armies fell under the complete command of Patheonistas, sensing an opportunity to remove the anti-clerical factions from the Triad and wider government, Caciarelli and his allies staged a coup and purged the republican government of its rivals. The Pantheonista Domination would see the greatest violent excesses of the revolution and an escalation of the Revolutionary Wars. The La Tempsta began shortly after the Pantheonista coup, which would see an estimated 85,000 people executed for being “enemies of the revolution”, the proclamation of the “Republic of Heaven” and a Catholic religious fervency not seen in Etruria since the Reformation. In 1787, the Republic captured Solaria, annexing the Ecclesiastical States. Despite their reverance for the Papacy, Pope TBD XI refused to offer his support and fled to Rayenne in Gaullica.
This fervency gave the Revolutionary Armies the morale boost to begin expanding the Republic’s borders at a rapid pace. By late 1786, all of modern Etruria had fallen under the Republic’s control. The emergence of wider Euclean alliances against the Republic gave way to expeditions and invasions of neighbouring countries. As the Republic expanded it exported its revolutionary republicanism, establishing Sister Republics, in Florena, Amathia and southern Gaullica. For the next decade, the Republic would engage in endless war with its Euclean rivals and neighbours, while the violent excesses of the government in pursuit of establishing the Republic of Heaven proved highly destructive. With the turn of the 19th century, the Republic's fortunes began to turn, with renewed offensives by the Gaullican League and rising unrest at home. By 1809, the situation was so severe that formerally loyal revolutionaries coalesced around Caio Amadeo Caltarini, who organised a coup against the Republican government under Francesco Cassio Caciarelli. On January 18 1810, the Republic was overthrown and Caltarini proclaimed himself King of the United Kingdom of Etruria. King Caio Amadeo I instituted many constitutional reforms, establishing one of the first constitutional monarchies.
Royal Restoration and 19th century (1810–1888)

Followign the royal restoration in 1810, the newly formed United Kingdom of Etruria emerged as a rising Euclean great power. Under the reign of Caio Aurelio I, the kingdom was successfully consolidated and one of the first constitutional monarchies emerged. The royal household was keen to protect its power from any resurgence of republicanism and as a result purused a two-pronged strategy - maintaining constitutionalism and uniting the country through imperialism and colonialism. This strategy began in earnest with the annexation of Emessa in 1814 as part of the Kingdom's operations against piracy. This was followed by the acquisition of several treaty ports in modern-day Zorasan and Subarna. Between 1810 and 1830, the relationship between the Vespasian, Carinthians and Novalians was redefined and made more equal, further aiding the monarchy in consolidating its rule and Etruria as a great colonial power.
In 1847, the Kingdom's constitution was amended by Caio Eugenio II, which dramatically expanded the basic rights and freedoms of the state, but electoral laws continued to exclude the non-propertied and uneducated classes from voting. These reforms resulted in the rising domination of liberal forces. This was followed by a resurgence in Etrurian contributions to science and technological discovery. Industrialisation in the south and central regions of the country left the rural north underdeveloped and overpopulated, resulting in decades of construction and engineering to expand industrialisation to the larger cities of the north. This uneven industrialisation led to the rise of the Etrurian Socialist Party, which would come to challenge the conservative-liberal tradition from strongholds in the north.

Starting from the last four decades of the 19th century, Etruria developed into a colonial power by forcing under its rule on vast swathes of northern Coius. Successive Etruro-Pardarian Wars saw the annexation of the Gorsanid Empire by 1860. This was followed by the annexation of territories in Satria, in 1863, Etruria's colonial possessesion were reformed, establishing Satria Etruriana, Satria Libera, Cyrcana, Bahia Etruriana with colonial protectorates over the Pardaran and Ninavina. Colonial tensions with Estmere resulted in the Etruro-Estmerish Wars and the development of the Royal Etrurian Navy into one of the most advanced and largest of the Euclean powers. The period between 1850 and 1880 marked the zenith of the United Kingdom, being marked by territorial expansion, socio-political and cultural modernisation of Etruria and its society.
In 1882, Caio Augustino ascended to the throne aged 17, falling rapildy under the influence and control of Prime Minister Girolamo Galba. Galba's control over the monarch was so profound that when the Senate sought to curtail the prime minister's power, he had the senate dissolved on three occassions, sparking elections that further entrenched Galba's power. Popular opposition to Galba grew between 1884 and 1886, which was deepened due to chronic shortages of capital and an emerging debt crisis. Galba responded with heavy handed tactics using royal ascent, in turn souring the once close relationship between monarchy and subject. In 1887, the anti-Galba movement fell under the leadership of Cardinal Romolo Caio Alessandri, a popular and high-ranking Etrurian cardinal, and Pantheonista. In 1888, this opposition erupted into the San Sepulchro Revolution following the arrest and death of three elder Senators, blamed on Galba. In the ensuing chaos, Galba fled Etruria for neighboring Gaullica, while under pressure from his family and facing threats of regicide from the revolutionaries, King Caio Augistino abdicated. Cardinal Alessandri was proclaimed interim Chief of State (Capo di Stato). This marked the end of monarchy in Etruria and the establishment of the Etrurian Second Republic.
Second Republic (1888–1937)
Following the establishment of the Etrurian Second Republic under Cardinal Romolo Alessandri, Etruria rapidly began to reform toward establishing a wider democracy and civil liberties. Between 1888 and 1900, male suffrage was repeatedly expanded while new laws guaranteeing the freedom of speech, thought and religion were passed. The new democracy established a “federal-union” of three constituent states, granting equal power and representation to the three peoples of Etruria. This new political freedom enabled the rise of organised trade unionism and the political left. In 1899, Cardinal Alessandri died, sparking a general election that saw the victory of the National Liberal Union under Alfredo Di Rienzo. The new government fostered further expansions of male suffrage, before ultimately introducing universal male suffrage for those aged 21 and above in 1902. This was followed by economic reforms that led to significant growth and modernisation.
The 1910s would see repeated crises in the colonies, with the Khordad Rebellion in Pardaran from 1912. These colonial uprisings played a significant role in a sense of “systemic failure” which was exacberated by the Great Collapse, which sparked a global economic recession. The economic crisis led to a rise and increasing militancy among the Etrurian left-wing parties, specifically the Etrurian Section of the Worker’s Internationale. The rise of the Liberal Republics in the 1916 election under Alessandro Luzzani saw major economic reforms and crackdowns on the far left, culminating in 1924 Schiatarella Crackdown that destroyed the ESWI. This had the effect of leaving the far-right as the only alternative to the liberal-conservative tradition.

The 1920s was dominated by rising global tensions, led by the rise of functionalist Gaullica. The same period saw significant divisions within Etruria between functionalist movements and those who opposed the totalitarian ideology. So profound was the division in Etruria, that the government was forced to purge the armed forces of pro-Gaullican officers from the mainland to colonial postings. Etruria, nominally allied with Estmere and Werania in the Grand Alliance failed to enter the war in 1927 owing to its ideological split. However, following the removal of pro-Gaullican figures from power and influence and a series of promises for territorial expansion, Etruria entered the Great War in 1928. The country gave a fundamental contribution to the victory of the conflict as one of the "Big Three" top Allied powers. The war was initially inconclusive, as the Etrurian army got stuck in a long attrition war in the Aventines, making little progress and suffering very heavy losses. Etruria saw greater success against Amathia and Piraea in the west and in halting the Gaullican advance in Florena. In Coius, Etruria’s colonies initially came under immense pressure and facing the threat of being evicted from its colonies, the Etrurian army was reorganised. Leadership changes and the mass conscription of all males turning 18 led to more effective Etrurian operations and victories in key major battles. The Etrurian Navy re-established dominance over the Solarian Sea, enabling the mass deployment of forces to the colonies. Eventually, in December 1934, the Etrurians launched a massive offensive against Gaullica, culminating in the victory of Vittorio Rivodutri. The Etrurian victory marked the end of the war on the Aventine Front, while smaller engagements saw Etruria push Gaullica out of Florena. Combined these victories proved instrumental in ending the war three months later.

During the war, more than 680,000 Etrurian soldiers and civilians died, leaving the country on the verge of bankruptcy and famine. The failure by the victorious allies to award most of Etruria’s promised territories led to a significant rupture in the political stability of the Etrurian government. Nationalists, many of whom were pro-Gaullican prior to the Great War returned home to agitate against the government. This led to the emergence of the Great Betrayal theory. The war also saw a resurgence in the far left, leading to political violence across the country.
National Solarian period (1937-1946)
As the post-war situation worsened, the far-right which boasted significant support among the military, most of whom feared a far-left revolution owing to economic crisis, began to plot against the republic. In late 1936, an Emergency Government for Peace was established with President Marco Antonio Ercolani remaining as a figurehead. This military government slowly eroded institutions and played a pivotal role in the Legionary Reaction of 1937, in which the Revolutionary Legion of Etruria assumed power under the co-leaders of Ettore Caviglia and Aldo Aurelio Tassinari. The Second Republic was replaced with the single-party totalitarian Solarian Republic of Etruria. Between 1937 and 1943, the SRE focused entirely on rebuilding the economy and Etruria’s military might. The National Solarian regime also restored control over the country’s colonial possessions while rallying the people for conflict in order to “avenge the great betrayal” and to seize territories promised to Etruria. The same period saw violent repressions of political opposition and criticism, as well as the Etrurianisation of Tarpeia and Emessa.
In 1943, the Solarian War broke out with Etruria’s invasion of Piraea, followed by attacks on colonial mandates in Tsabara, Satria, and later invasions of neighboring XX to the east. The war saw Etruria face a coalition under the leadership of the Community of Nations, which steadily overwhelmed and defeated Etruria in Coius. In 1946, with Gaullica’s entry in the war against Etruria, the country itself came under direct attack. The invasion of Etruria proper led to the collapse of the SRE with the overthrow of the regime by popular revolt. Etruria unconditionally surrendered on May 16 1946.
The Solarian War left over 500,000 Etrurian soldiers and as many civilians dead, Etruria saw the total loss of its colonial possessions who were granted independence by the CoN and the Etrurian economy had been all but destroyed; per capita income in 1946 was at its lowest point since the beginning of the 20th century. The war also saw numerous atrocities committed by Etruria against occupied territories, including the Piraean Genocide. The National Solarian regime was succeeded by a Community of Nations led provisional government who oversaw the restoration of democracy and the rise of the Etrurian Third Republic.
Third Republic (1946-1960)
In late 1946, the Third Republic was officially formed in wake of free elections and the adoption of a new CoN devised constitution. President Giuseppe Zappella sought to use the reconstruction of Etruria to re-establish the country as one of Euclea’s great economic powers. However, the Solarian War had left organised crime syndicates and the mafia with immense power and influence over Etrurian industry, corruption at every level of government, driven by the devastation and destitution of the war significantly undermined progress. The economic devastation led to the emergence of far-left movements in Carinthia and Novalia, who saw little to no resources from which to rebuild. These movements grew in popularity and by 1950 began to agitate for secession from Etruria.

The crisis over secessionism escalated during the 1950s as Etruria also struggled to recovery economically from the war, far-left groups began to opt for violent militancy over independence. Mass unemployment led to widespread social and moral decline across the rest of the country. Many of Etruria’s major cities were marked by violence, criminality and poverty, a general sense of declinism and malaise gripped Etrurian society. In 1958, the Novalian People’s Liberation Front attacked a series of police stations and army bases, distributing weapons to its members. This was followed by similar actions in Carinthia, led by the Carinthian Popular Army, sparking the Western Emergency. The government response was poorly conducted with Etruria witnessing successive presidents and governments, who struggled to confront the economic and secessionist crises.
Facing the fracturing of the country and the threat of far-left terrorism in Vespasia, the Etrurian military staged a bloodless coup d’état in 1960, establishing the Supreme Council for Order and Peace. The coup resulted in the demise of the Etrurian Third Republic and twenty-three years of military dictatorship.
Military dictatorship (1960-1983)
The new military regime upon seizing power immediately dissolved the senate, abolished the 1946 constitution and stripped the country of its civil liberties. The regime instituted censorship, military courts and martial law across Carinthia and Novalia. Oppression was not limited to the restive western states, but also reached institutional opponents, artists, journalists and other members of civil society, inside and outside the country. The regime's use of brutal and often indiscriminate tactics in the west soon saw the far-left secessionist groups lose ground and support. Throughout the Western Emergency, the military dictatorship was accussed of conducting mass killings and executions against supporters of the separatists. The dictatorship was also known to use nationalist loyalist militias in Carinthia an Novalia.
As the regime consolidated its control by 1961, it sought to distract and unify society. This was first achieved in 1962, when Etruria invaded the Apocorona Islands, seizing them from Piraea. This was swiftly followed by Operation Lexicon in which Etruria seized control over disputed regions of Tarpeia, which was officially justified as part of Etruria's struggle against far-left separatists. The two operations further increased the regime's popularity and denied the separatists areas of relative safety. The country's tough stance against communism and separatism led to dramatic improvements in relations with key Euclean governments, such as Werania and Estmere. The re-emergence of Etruria from post-war isolationism also enabled the military government to step up economic reforms, aided by growing investment from the Euclean Community. Between 1965 and 1975, Etruria emerged as one of the fastest growing Euclean economies, dubbed the Etrurian economic miracle. The late 1960s saw a transition by the separatist movements, who in face of successive losses to the Etrurian army, began to resort to terrorist attacks in Vespasia. In 1966, 22 people were killed in the Piazza Caciarelli bombing, 92 were killed in the 1967 Piazza della Vergine Maria bombing and 111 were killed in the 1969 San Alessandro Train Station bombing. This bombings etrenched popular opposition to the separatists and emboldened the military regime to step up its draconian measures against the separatists. By 1972, the crisis had come to an end with the collapse of separatism and the surrender of senior leaders. This alongside the economic miracle marked the peak of the regime's popularity. The regime is widely blamed for the disappearance of over 8,000 people during its twenty-three year long rule, this does not include the 1,582 people officially documented to have been killed by the regime's secret services. At least 16,000 people were killed as a result of the Western Emergency between 1958 and 1972.
Slowly however, the wear and tear of years of dictatorial power that had not slowed the repression, even after the defeat of the leftist guerrillas, plus the inability to deal with the new global econmomic crises of the period and popular pressure, made an opening policy inevitable, which from the regime side was led by Gennaro Aurelio Altieri. In 1978, he passed the Amnesty Law for political crimes committed for and against the regime. He had secured agreement from other military chiefs in 1980, to begin the "return to peace", striking up negotiations with opposition groups and political parties to restore democracy. However, the slow progress resulted in massive popular demonstrations in the streets of the main cities of the country, the first free elections in 21 years were held for the national legislature in 1981. In 1983, another election was held, this time to elect a new government, being contested without military oversight or interference, which was won by the Etrurian Socialist Party, with Miloš Vidović becoming president. Since then, the military has remained under control of civilian politicians, with no official role in domestic politics.
Contemporary (1983-present)
The return of democracy in 1983 was followed by widespread economic and social reforms led by President XX. The 1983 Constitution proved highly versatile in comparison to the 1946 constitution, delivering Etruria strong and capable coalition governments. By 1990, Etruria had returned as one of the largest industrial economies in the world and in Euclea. In 1991, XX was defeated by Enrico Biava of the centre-right Federalist Party, who entered into coalition with the Sotirian Democratic Party. The Biava government continued the neo-liberal reforms of the centre-left government under XX, seeing Etruria achieve significant improvements to living standards and per capita incomes.
In 1996, however, a group of investigative journalists published the Capo del Leone Scandal, in which it was discovered both parties had engaged in a highly lucrative embezzlement plot involving the new town of Capo del Leone. The ensuing fallout forced the resignation of Biava and a restructuring the major parties. In the subsequent election, the Sotiran Democratic Party won the election, entering the government alongside the Workers and Farmers Union under Marko Stepanovic. Strident anti-corruption laws were introduced and public confidence in the political system was relatively restored by 2003.
The 2005 Global Recession hit Etruria hard, forcing the country into facing 23 months of recession. Much of the economic progress made in the 1990s was lost and many commentators argued that the situation was worsened by the corrupt practices of Etrurian companies, especially the banking system. The 2006 snap election saw the return of the Socialist Party under Urbano Onoforio, who instituted numerous reforms and stimulus packages. By 2007, Etruria had returned to strong economic growth, with manufacturing replacing services as the key driver of Etrurian economic output.

In 2011, Onoforio was defeated by Emiliano Reali and the Etrurian Federalist Party who entered into coalition with the Veritas party. This coalition led to a splinter group of the EFP forming into the Citizens’ Alliance. Invoking the closer relationship with the Euclean Community, Reali’s government announced plans in 2013, for a popular referendum on Etruria joining the bloc. This provoked a surge in support for right-wing populist parties, which united to form the Coalition of the Right alliance, led by National Action. Still requiring time to meet Euclean standards to achieve membership, the gap between announcing the referendum and holding the vote was extended to three years. During this time repeated corruption and personal scandals hit the Reali government, this would lead to the undermining of the government. In the 2016 referendum, the No-campaign defeated the government led-Yes campaign, stalling Etrurian membership of the bloc indefinitely.
Following the rejection of EC membership, the centre-right government collapsed in August, leading to the 2016 election, which saw a surprise landslide victory by the right-wing populist Tribune Movement, which entered government in coalition with the Workers and Farmers Union, with Francesco Carcaterra as president. Between 2016 and 2018, the Tribune Movement government instituted a series of reforms, including the restoration of capital punishment, federalising law enforcement, electoral reform and abolishing a series of government offices charged with securing EC membership. In 2018, during the EC-Etrurian Crisis, a snap election saw the Tribune Movement re-elected using its newly introduced electoral system, allowing the party to form the first ever single-party government since 1983. This was followed by Operation Gladio, which devastated organised crime and provoked a crisis over civil liberties. The government also passed legislation limiting debate over Etrurian war crimes during the Solarian War, increased federal control over universities and in 2020, effectively banned abortion.
Geography
Etruria is located in Southern Euclea. To the north, Etruria borders Gaullica which is dominated by the Aventine Mountaines which also encloses the Eugenian Plain to the east, which borders Florena. The Aventine Mountains are met in the north by the Etrurian Mountains which run through roughly centrally through the country to the south, flanked on both sides by wide plains, which however are marked by hilly regions, before dropping in altitude along the coasts. In the north are two major lakes, Lake Imperia and Lake Jovia. Etruria is also includes one large islands; Aeolia and numerous smaller islands.
The country's total area is 548,549 km² (211,796 sq mi). Including the islands, Etruria has a coastline of 2,636 kilometres (1,637 miles) on the Solarian and Mazdan seas.
The Aventine Mountains form Etruria's backbone and the Eturians form most of its northern and eastern boundary, Etruria's highest point is located on Monte Tinia (4,810 m or 15,780 ft) in the northern reaches of the range. The Volterra, Etruria's longest river (1,114 kilometres or 692 miles), flows from the Etrurians on the northern border with Guallica and crosses the Novalian plain on its way to the Solarian Sea. The five largest lakes are, in order of diminishing size: Imperia (1,000 km2 or 386 sq mi), Jovia (212.51 km2 or 82 sq mi), San Paolo (145.9 km2 or 56 sq mi), San Pietro (124.29 km2 or 48 sq mi) and Balestra (113.55 km2 or 44 sq mi).
The country is situated at the meeting point of the XXX Plate and the XXX Plate, leading to considerable seismic and volcanic activity. There are 17 volcanoes in Etruria, three of which are active: Vosca, Stalleria, Vesano and Veturius, which last erupted in 2015.
Because of the great longitudinal extension of the peninsula and the mostly mountainous internal conformation, the climate of Etruria is highly diverse. In most of the inland northern and central regions, the climate ranges from humid subtropical to humid continental and oceanic. In particular, the climate of the Eugenian Plain geographical region is mostly continental, with harsh winters and hot summers.
The coastal areas of Torrazza-Carvagna, Solarita and most of the South generally fit the Solarian climate stereotype (Köppen climate classification Csa). Conditions on peninsular coastal areas can be very different from the interior's higher ground and valleys, particularly during the winter months when the higher altitudes tend to be cold, wet, and often snowy. The coastal regions have mild winters and warm and generally dry summers, although lowland valleys can be quite hot in summer. Average winter temperatures vary from 0 °C (32 °F) on the Alps to 12 °C (54 °F) in Sicily, so average summer temperatures range from 20 °C (68 °F) to over 25 °C (77 °F). Winters can vary widely across the country with lingering cold, foggy and snowy periods in the north and milder, sunnier conditions in the south. Summers can be hot and humid across the country, particularly in the south while northern and central areas can experience occasional strong thunderstorms from spring to autumn.
Government and politics
Etruria is a federal parliamentary republic governed under the 1983 Constitution, recently amended in 2017, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. Unlike other presidential republics the President is both head of state and head of government and depends for his tenure on the confidence of Parliament. It is a constitutional federal republic and representative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law".
Federalism in Etruria defines the power distribution between the federal government and the constituent states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances, which however have never been considered overly strong. The Constitution of Etruria, which came into effect on 1 July 1983, states in its preamble that Etruria is "a sovereign, Solarian Catholic democratic republic and union of three states". Etruria's form of government, traditionally described as "quasi-federal" with a strong centre and weak constituent states, has grown increasingly federal since the late 1980s as a result of political agitation at the constituent level. However, since 2016, the level of separation between federal and state has significantly declined.
Branches of government
Executive: The President of Etruria is the head of state and head of government and is supported by the party or political alliance holding the majority of seats in the lower house of the senate. The executive branch of the Etrurian government consists of the president, the vice president, and the Federal Cabinet—this being the executive committee—headed by the president. The president is mandated to select his deputy and his Federal Cabinet, however the cabinet must receive the confidence of the state council to be confirmed. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of one of the houses of congress. In the Etrurian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature; the president and his council are directly responsible to the lower house of the congress (the chamber of representatives).
The president and the cabinet may be removed by the senate by a motion of no confidence. There are no term limits for the presidency.
 |
|
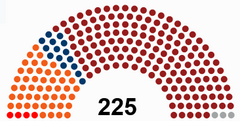
Government (194) Tribune Movement (194) People's Opposition (99) Citizens' Alliance (71) Workers and Farmers Union (14) Etrurian Greens (11) |
 |
|
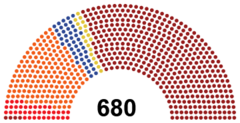
Government (414) Tribune Movement (414) People's Opposition (266) Citizens' Alliance (160) Democratic Alternative for Etruria (45) Etrurian Socialist Party (38) Workers and Farmers Union (19) Popular Renewal (4) |
Legislature: the legislative branch of Etruria is based on the adversarial model of parliament, as such the federal legislature is parliamentary. The Senate is split into two houses: the State Council and the Chamber of Representatives. The Chamber of Representatives is the lower house and is the more powerful. The State Council is the upper house and although it can vote to amend proposed laws, the chamber can only vote to overrule its amendments should the state council reject the bill more than twice. Although the State Council can introduce bills, most important laws are introduced in the Chamber – and most of those are introduced by the government, which schedules the vast majority of parliamentary time in the Chamber. Parliamentary time is essential for bills to be passed into law, because they must pass through a number of readings before becoming law. Prior to introducing a bill, the government may run a public consultation to solicit feedback from the public and businesses, and often may have already introduced and discussed the policy in the president's State of the Union address, or in an election manifesto or party platform.
The Chamber has 680 voting members, each representing a senatorial district for a four-year term without term limits. Chamber seats are apportioned on the basis of population, with Vespasia holding 480, Novalja holding 145 and Carinthia holding 55.
The State Council has 290 members, with each constituent state providing 90 representatives each. All state councillors are elected for parallel terms to the Senate. The duty of the senate is to scrutinise all legislation, confirm appointments and ratify all international agreements. The State Council is able to table legislation over certain issues, these being; the constitution, limits of federal power, the separation between state and federal power, foreign policy and defence.
Judiciary:
Political parties
The political parties of Etruria operate at all three levels, federal, national constituent and local, however some parties operate exclusively at the constituent level. Nationally, the country is dominated by the Tribune Movement, a right-wing nationalist and populist party that won a landslide in the 2016 general election. The main opposition party is the centrist Citizens' Alliance, followed by the Novalian-dominated Farmers and Workers Union, the centre-right Democratic Alternative for Etruria, Etrurian Federalist Party, the centre-left Etrurian Socialist Party, the far-left Popular Renewal and the Etrurian Greens.
At the constituent level, Vespasia is dominated by the Tribune Movement, with the Citizens' Alliance being the other party represented in the Vespasian Assembly, this corresponds at the local level also. In Novalia, the country is dominated by the Workers and Farmers Union, although it has an legislative cooperation agreement with its branch of the PSP. In Carinthia, the state is also dominated by the Tribune Movement, being the region that first saw its breakthrough at the state-level.
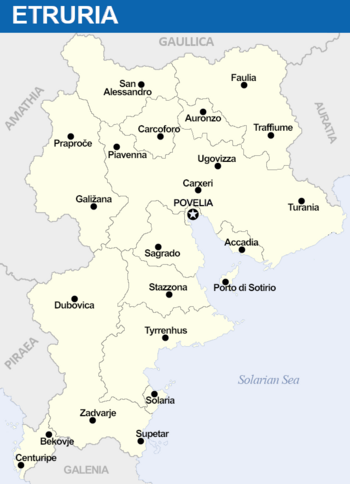
Constituent states
Internally, the Etrurian Federation is divided into three constituent republics and five Autonomous Federal Regions; four under Vespasia and one under Novalia. The federal capital is Poveglia. All states, as well as the Autonomous Federal Regions, have elected legislatures and governments, both patterned on the national model. Both the constituent states and autonomous regions are divided further into Regions (Regione) and then into Communes (Communi).
In order of population, the states are:
| Map | Name and flag | Administrative centre | Population | Governor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States of Etruria | |||||
| Praproče | 5,231,529 | Davo Karničar (TM) | |||
| San Alessandro | Augustina Faustini (CA) | ||||
| Auronzo | Enrico Volpe (CA) | ||||
| Carcoforo | Emmanuele Angrisani (CA) | ||||
| Faulia | Alessandro Garavoglia (CA) | ||||
| Carxeri | Marco Antonio Cristofori (TM) | ||||
| Porto di Cristo | Luciano Giustiniani (TM) | ||||
| Sagrado | 3,114,504 | Simone Parro (TM) | |||
| Stazzona | 3,586,111 | Annalisa Taddei (CA) | |||
| Tyrrenhus | Pietro Andrea Ercolani (TM) | ||||
| Solaria | Vittore Amadeo Varro (TM) | ||||
| Vilanija | 8,603,451 | Franjo Sarič (FWU) | |||
| Federal Districs Etruria | |||||
| Povelia | Giuliano Aurelio Vinci (TM) | ||||
| Centuripe | 1,685,000 | Nero Orlando (TM) | |||
The 1983 Constitution and more specifically the 1986 Convention Amendment laid out more clearly the federal system of Etruria, openly stating that the Federal Government is the governing authority of a federal union of three states and five autonomous regions.
The government of Etruria is based on a 3 tiered system, in which the Constitution of Etruria delineates the subjects on which each tier of government has executive powers. The Constitution originally provided for a two-tier system of government, the Federal Government (also known as the Union-Authority), representing the nation. Later, a third tier was added in the form of Municipalities. In the current arrangement, Article 15 of the constitution delimits the subjects of each level of governmental jurisdiction, dividing them into three lists:
- National List: includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, law enforcement, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. The Federal Government alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the National List.
- Constituent State List: contains subjects of State and local importance such as trade, commerce, agriculture and irrigation. The State Governments alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the State List.
- Concurrent List: includes subjects of common interest to both the Federal Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Federal as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Federal Government will prevail.
- Autonomous List: in effect replicates the constituent state list for the autonomous federal regions, with the concurrent list subordinated to ensure the constituent state's laws prevail over the AFR's.
Foreign relations and military
Military
The Etrurian Land Force, Etrurian Naval Force, Etrurian Air Force and the Auxiliary Defence Force collectively form the Etrurian Defence Force, under the Supreme Command (Commando Supremo), presided over by the First Citizen of Etruria. The armed forces is both voluntary and conscripted, as of 2016 the armed forces had 385,600 active personnel and 550,000 reserve, with a defence budget of $60.79 billion.
TBD..
The final branch of the armed forces is the Auxiliary Defence Force, which is a popular militia that also serves as the country's gendarme in times of national emergency. The ADF is subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior during peace-time and in war-time, it is subordinate to the Supreme Command. As of 2016, the ADF had a strength of 55,000 active members and an estimated 255,000 reserve members. Since 2010, the ADF has also served as an emergency response force, assisting in the aftermaths of earthquakes. Most recently several ADF units were engaging in confronting several separatist movements in Carinthia and Marolev-ethnic armed groups, including the Battle of Starše in 2011.
Economy
Etruria is the world's nth largest economy as of 2018, with a nominal GDP of approximately $1.025 trillion. Etruria has a capitalist mixed economy. The GDP per capita as of 2017 is $15,637 (nominal) and $33,747 (PPP). Etruria has emerged as a leading country in world trade and exports, it still records strong growths in manufacturing, indicative of its recent upgrade from a newly-industrialised economy in 1998. It is a well-developed country, with the world's nth highest quality of life in 2015 and the nth Human Development Index. The country is well known for its creative and innovative business, its state supported manufacturing sector, a large and competitive agricultural sector (Etruria is the world's nth largest wine producer), and for its influential and high-quality automobile, machinery, food, design and fashion industry. Since 2003, it has become a strong producer of commercial aircraft, with the company Caviglia Aeronautics becoming a major world brand.
Etruria has a strong mining sector, focused on mining coal, tungsten and several rare earth elements such as cobalt, coltan, cassiterite and ores of tantalum and tin. However this deposits have reduced in size, limiting the role mining plays within the Etrurian economy.
Etruria is one of the world's largest manufacturing countries, characterised by a smaller number of global multinational corporations than other economies of comparable size and a large number of dynamic small and medium-sized enterprises, notoriously clustered in several industrial districts, which are the backbone of the Etrurian industry. This has produced a manufacturing sector often focused on the export of niche market and luxury products which focuses on high quality products, however since the early 2000s, the Etrurian economy has pushed for cheaper goods production in Novalia and Carinthia where wages are lower. Etruria has the highest levels of economic growth in southern Euclea, growing on average between 4.5%-5.5% between 2003 and 2017.
The Etrurian economy has been noted to suffer from extensive levels of corruption in civil and political society, which at times has hindered foreign investment. Efforts to confront corruption during the 1990-2016 period were often described as "lackluster" by domestic and foreign commentators. Further issues include Intellectual Property theft, weak business and investment protection laws and weaker auditing systems. Since 2016, efforts to confront these systemic issues has gained pace.
Industry
Etruria has a sizeable automotive industry, which produced over 1.3 million motor vehicles in 2015, ranking as the Nth largest producer in the world. Etrurian shipbuilding exports were worth $4.2 billion in 2016, through Nettuno Nazionale Marittimo and Arsenale di Poveglia Unito. Etrurian shipyards have 18 floating docks of different sizes and six dry docks. Centuripe, Accadia, and Solaria have developed into dynamic shipbuilding centres. In 2016, there were 111 active shipyards in Etruria, with another 33 being built, including a major expansion of the drydocks in Turania. Etrurian shipyards are highly regarded both for the production of chemical and oil tankers up to 10,000 dwt and also for their mega yachts and passenger cruises.
Etrurian brands like Casa and N&Z are among the largest producers of consumer electronics and home appliances in Euclea, and invest a substantial amount of funds for research and development in new technologies related to these fields.
Etruria also possesses the Caviglia Group, a conglomerate which includes Caviglia Aeronautica and Caviglia Rotaia, which manufacture aircraft and locomotives respectively. Caviglia Aeronautica for its part has become one of the largest producers of regional-range and private aircraft, with government support in 2016 it revealed its first trans-oceanic passenger aircraft.

Other key sectors of the Etrurian economy are banking, construction, home appliances, electronics, textiles, oil refining, petrochemical products, food, mining, iron and steel, and machine industry. In 2010, the agricultural sector accounted for 9 percent of GDP, while the industrial sector accounted for 28 percent and the services sector for 64 percent. However, agriculture still accounted for a quarter of employment, by 2016 this had fallen to 18%. Etrurian manufacturers receive significant support from the federal government, through competitive grants, direct investment and energy subsidies, this level of state-aid has led to the establishment of several major national champions.
Tourism
Etruria is the Nth most visited country in the world, with a total of 50.3 million international arrivals in 2016. The total contribution of travel & tourism to GDP (including wider effects from investment, the supply chain and induced income impacts) was ₣122.7bn in 2017 (10.1% of GDP) and generated 1,082,000 jobs directly in 2017 (4.8% of total employment).
Etruria is well known for its cultural and environmental tourist routes. Vicalvi is the 6th most visited city in Euclea and the 15th in the world, with an average of 7.65 million international arrivals in 2016 while San Alessandro is the 8th and 16th resptectively, with 7.12 million toruists. In addition, Poveglia and Stazzona are also among the world's top 100 destinations. The tourism industry saw significant state and federal investment during the 1980s and 1990s, with the subsidised construction of hundreds of resorts and hotels across the country.
Agriculture
According to the last national agricultural census, there were 1.9 million farms in 2010 (−22.4% since 2000) covering 14.7 million hectares (63% of which are located in Southern Vespasia and Novalia). The vast majority (80%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size, the remaining 20% are Government-supported Cooperatives covering up to 100 hectares. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), grain fields take up 31%, olive tree orchards 8.2%, vineyards 5.4%, citrus orchards 3.8%, sugar beets 1.7%, and horticulture 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%).
Etruria is one of the world's top wine producer, and one of the leading in olive oil, fruits (apples, olives, grapes, oranges, lemons, pears, apricots, hazelnuts, peaches, cherries, plums, strawberries and kiwifruits), and vegetables (especially artichokes and tomatoes). The most famous Etrurian wines are probably the Cavantine Chianti and the Poveglian Barolo. Other famous wines are Marollesco, Balboni d'Revi, Amacini, Farinacci della Valle, Frutto di Bacco, Vossecello, and the sparkling wines Gennarollo and Terrasocco. Quality goods in which Etruria specialises, particularly the already mentioned wines and regional cheeses, are often protected under federal quality assurance labels.
Infrastructure
In 2014 the transport sector in Etruria generated a turnover of about ₣119.4 billion, employing 935,700 persons in 153,700 enterprises. Regarding the national road network, in 2012 there were 668,721 km (415,524 mi) of serviceable roads in Etruria, including 7,487 km (4,652 mi) of motorways, state-owned but privately operated by Genesi. In 2015, about 34,667,000 passenger cars (590 cars per 1,000 people) and 4,015,000 goods vehicles circulated on the national road network.[179]
The national railway network, state-owned and operated by Amministrazione Ferroviaria Federale Etruria, in 2006 totalled 16,529 km (10,271 mi) of which 11,727 km (7,287 mi) is electrified, and on which 4,802 locomotives and railcars run.
The national inland waterways network comprised 1,977 km (1,228 mi) of navigable rivers and channels in 2002. In 2014 there were approximately 30 main airports ,including the two hubs of Ravello International in Castello Nero and Pietramontecorvino International in Vicalvi, and 43 major seaports, including the seaport of Accadia, the country's largest and largest on the Solarian Sea. In 2015 Etruria maintained a civilian air fleet of about 389,000 units and a merchant fleet of 581 ships.
Etruria as of 2016 required to import 80% of its energy requirements, this fell to 70% in 2018 with the completion of six major windfarms and improvements to efficiency in domestic production.
Etruria does not invest enough to maintain its drinking water supply. The Acqua per la Vita Law, passed in 1999, aimed at raising the level of investment and to improve service quality by consolidating service providers, making them more efficient and increasing the level of cost recovery through tariff revenues. Despite these reforms, investment levels have declined and remain far from sufficient. This has caused significant problems in the Poveglian Basin and Novalian Valleys during hot summers, with water shortages often being recorded. In 2017, the Etrurian government launched the Sicurezza dell'Acqua project aimed at modernising pumps, expanding access to aquifers and re-routing rivers and streams for greater access.
Science and technology
Through the centuries, Etruria has fostered the scientific community that produced many major discoveries in physics and the other sciences. During the Renaissance Vespasian polymaths especially, such as Alessandro Tiberio Volci (1452–1521), Francesco della Caprese (1475–1564) and Michele Caio Solariano (1404–1472) made important contributions to a variety of fields, including biology, architecture, and engineering. Aurelio Schirinzi (1564–1645), a physicist, mathematician and astronomer, played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include key improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations, and ultimately the emergence of new scientific methods.
During the Industrial Revolution, Etruria further fostered the industrial, scientific and engineering communities to aid the process, this also led to the emergence of prominent physicists and biologists. Within these communities were, Matteo Giovanni Abasta (inventor of barometer), Vittore Volta (inventor of electric battery), Ugo Sforza (inventor of radio), Genaro Gambini and Stepan Vlatko, pioneers of the induction motor, Giovanni-Paolo Zanni, pioneer of light bulb Urbano D'Santis is known for developing a voice-communication device which is often credited as the first telephone.
Today, Etruria is host to several major institutions and research groups that focus on engineering, energy, robotics and communications. The Innocenzo Dametto Institute is one of Euclea's leading research and development bodies, looking into cleaner energy production. The New Century Group is a state-backed series of R&D institutions dedicated to pioneering future technologies, primarily Artificial Intelligence, Quantum computing, information technology and robotics. As of 2018, the Etrurian government spent $23.5 billion on R&D, a 11% increase from 2016, ranking Etruria as one of the highest spenders on research and development.
Demographics
At the end of 2017, Etruria had an estimated 65,596,083 inhabitants, the third largest in Euclea. The resulting population density, at 119.58/km2 (309.7/sq mi), which is lower than most in eastern Euclea. However, the distribution of the population is widely uneven. The most densely populated areas are the Eugenian Plain (that accounts for almost a half of the national population) and the Bay of Solaria Region, while vast regions such as the Etrurian and Aventine highlands, the hills of Carinthia and Novalia and insular Etruria are sparsely populated.
The population of Italy almost doubled during the 20th century, but the pattern of growth was extremely uneven because of large-scale internal migration from the rural Carinthia and Novalia to the industrial cities of Vespasia, a phenomenon which happened as a consequence of the post-war economic boom and the Western Emergency. High fertility and birth rates persisted until the 1990s, after which they started to decline, however ferility rates began to increase again from the late 1990s. Despite the decline, the population remained relatively young with the average age increasing from 26 to 38. As of 2016, the average age of Etruria fell to 28, making it the youngest population in Eastern Euclea. As of 2017, the total fertility rate was recorded at 2.3, above the 2.1 replacement rate. In 2019 it is estimated that the TFR increased to 2.5, though considerably below the high of 5.08 children born per woman in 1889. Etruria's population is expected to surpass 70 million by 2030. The steady birthrate is being led by Novalia, which has a TFR of 2.4, and Vespasia with a TFR of 2.25.
Ethnic groups
The constitution of the Etruria recognises "nations" (nazioni) and "nationalities" (nazionalità) separately; the former included the constituent state peoples, while the latter included other non-federation ethnic groups such as Piraeans, Gaullicans and immigrants from select countries; however to be recognised as a nationality, a minority must exceed 550,000 citizens. The three "nations" recognised are the Vespasians, Novalians and Carinthians whilst Piraeans, Gaullicans, Maruvians, Badawiyans and Pardarians are recognised as nationalities. There is also an Etrurian ethnic designation, for the people who want to identify with the entire country, including people who were born to parents in mixed marriages.
According to the 2013 census, 65.14% were identified as Vespasian, 14.03% were identified as Novalian, 11.03% were identified as Carinthian and 9.8% were recognised as "other"; of which included 3.88% identified as Maruvian, 2.13% identified as Piraean and 1.48% as Badawiyans, 1.47% as other, 1.11% as Pardarians and 0.22% as Gaullican. However of these groups, 69.6% identified themselves as Etrurian, rather than their ethnic group.
From 1991 to 2018, immigration to Etruria had steadily increased, with most coming from countries in Bahia and Badawiya. In recent years, especially since 2018, the Etrurian government has significantly restricted access to the country for immigrants from these regions.
Languages
The population of Etruria speaks mainly three languages: Vespasian, Novalian and Carinthian. The Vespasian language was spoken by all the constituent republics either as a first language (in Vespasia's case) or as the second language, Novalian is spoken primarily in Novalia and Carinthian in Carinthia.
Both Novalian and Carinthian belong to the same language group and are thus similar, allowing most people from the two areas to understand each other. Due to this, schools in both Novalia and Carinthia opt to teach Vespasian as the primary language for secondary use over their respective languages. As such, Vespasian is the second language of 88.5% of Novalia and Carinthia combined, whilst Novalian is spoke as a second language by 62% of Vespasians and Carinthian at 30%. Vespasian is widely recognised as the lingua-franca in official circles.
The Novalian language was adapted for use of the Latin alphabet to be used more efficiently with both Vespasian and Carinthian, use of Cyrillic was banned in 1922 to limit ways of separatists of Novalian nationalists from expressing their ideas.
Religion
While Etruria is a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual state, religion remains not only limited in diversity, but also a source of criticism and controversy. 91.7% of the population are recorded as practicing Solarian Catholics, the overwhelming dominance of Catholicism, while historically rooted, especially in the long-standing residence of the Holy See within the boundaries of Solaria, is also explained through centuries of state-backed protection of the Catholic faith.

From 1765 until 1983, non-Catholics were barred from working in the federal civil service, while similar bans were enacted in Novalia and Vespasia at the state-level. While the 1983 constitution recognised minority faiths as “integral traditions of the nation”, it failed deliver set equality. Today, this legalistic discrimination remains a source of contention, while Carinthia’s state government has re-introduced restrictions on the number of non-Catholics employed by state services.
Despite the presence of restrictions on employment, there remains some sizeable religions minorities. The largest religious minority is Episemialism, approximately 4.43% of the population are recorded as adherents. Episemialists face the strongest levels of legalistic discrimination, which also rooted in long-standing discrimination toward the Marolev and Hellenic minorities. The Episemialist population is densely concentrated in south-western Etruria, in line with the geographic distribution of the Marolev population.
The next largest faith is Atudism at 2.66%, Vespasia has always held a significant Atudite population from ancient Solaria through to the Reniassance. The vast majority of the country’s Atudite population reside in and around Solaria, over 45,000 live in the Quartiere Atudito (Atudite Quarter), a cosmopolitan and wealthy suburb of the city. The Atudites are the only significant non-Catholic population to not face legalistic discrimination.
The third largest religious minority are classified as the “Protestante-Riformista” (Protestant-Reformist), and includes Pentecostals, Evangelicas, Jehovah Witnesses, Waldensians, Seventh-day Adventists, Mormons, Baptists, Lutherans and Methodists. Since they are not recorded as individual faiths, collectively they represent 1.04% of the population.
The smallest religious minority are Athiests, at 0.17%. Atheists also face some discrimination, with Atheists being banned from teaching up until 1999, however repeated efforts have been made in Novalia and Vespasia to restore the ban, with many state-level politicians claiming that Atheists "make bad teachers."
Education
Education in Etruria is free and mandatory from ages six to eighteen, and consists of five stages: kindergarten (scuola dell'infanzia), primary school (scuola primaria), lower secondary school (scuola secondaria di primo grado), upper secondary school (scuola secondaria di secondo grado) and university (università).
Primary education lasts eight years. The students are given a basic education in Vespasian, another federal language (either Novalian or Carinthian), mathematics, natural sciences, history, geography, social studies, religious studies, physical education and visual and musical arts. Secondary education lasts for five years and includes three traditional types of schools focused on different academic levels: the liceo prepares students for university studies with a classical or scientific curriculum, while the istituto tecnico and the Istituto professionale prepare pupils for vocational education. A wide gap exists between Vespasian schools, which performed significantly better than the national average (among the best in the world in some subjects), and schools in Novalia and Carinthia, that had much poorer results.
Tertiary education in Etruria is divided between public universities, private universities and the prestigious and selective superior graduate schools, such as the Scuola Normale Superiore di Urbisalia and prestigious Church run academies such as the Scuola del Corpo di Cristo and Accademia degli Apostoli. The university system in Etruria is regarded as highly elitist and divided by quality and funding, however the new government in 2016 has announced major reforms of the university system and greater federal funding for struggling universities in Novalia and Carinthia.
Health
The Eturian federal state runs a universal public healthcare system since 1956. However, healthcare is provided to all citizens and residents by a mixed public-private system. The public part is the Servizio Sanitario Federale, which is organised under the Ministry of Health and administered on the constituent-state basis. Since 1994, the SSF has been greatly devolved, in which public healthcare is provided directly to the most deprived areas of the country, where citizens can't afford health-insurance. And since 2003, the SSF has been charged with managing funding for the state-level services. Life expectancy in Etruria is 80 for males and 85 for females (however it averages at 76 for males and 78 for females in Novalia), placing the country nth in the world for life expectancy. Etruria has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), probably thanks to the health benefits of the mediterranean diet and an extensive government led and organised public exercise regime. The proportion of daily smokers was 28% in 2012, up from 24.4% in 2000. Smoking in public places including bars, restaurants, night clubs and offices has been restricted to specially ventilated rooms since 2005.
Functional urban areas
| Rank | Region | Pop. | Rank | Region | Pop. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tyrrhenus  Solaria |
1 | Tyrrhenus | Palestrina | 5,981,640 | 11 | Poveglia | Àdexe | 823,997 |  San Alessandro  Fauglia |
| 2 | Solaria | Aventina | 5,573,217 | 12 | Stazzona | Carvagna | 710,343 | ||
| 3 | San Alessandro | Lamuria | 3,772,475 | 13 | Galižana | Štinjan | 694,683 | ||
| 4 | Fauglia | Dinara | 2,403,919 | 14 | Piavenna | Ossuccio | 614,111 | ||
| 5 | Accadia | San Pietro | 1,998,187 | 15 | Centuripe | Tarpeia | 500,735 | ||
| 6 | Dubovica | Krivaja | 1,431,383 | 16 | Sagrado | Torrazza | 499,324 | ||
| 7 | Turania | Moresco | 1,392,003 | 17 | Castello Nero | Valle di Conti | 494,007 | ||
| 8 | San Francesco | Meloria Superiore | 1,376,113 | 18 | Bekovje | Kopriva | 470,561 | ||
| 9 | Praproče | Kapitala | 994,537 | 19 | Auronzo | Valle dei lupi | 379,886 | ||
| 10 | Auronzo | Falerone Inferiore | 969,897 | 20 | Ugovizza | Gniva | 371,990 | ||
Culture
For centuries divided by politics and geography until its eventual unification in 1736, Etruria's culture has been shaped by a multitude of regional customs and local centres of power and patronage, but also its multicutural make-up with centuries of imersion of its three distinct cultures. Italy had a central role in Eastern Euclean culture for centuries and is still recognised for its cultural traditions and artists. During the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, a number of magnificent courts, including the Papacy competed for attracting the best architects, artists and scholars, thus producing a great legacy of monuments, paintings, music and literature. Despite the political and social isolation of these courts, Etruria's contribution to the cultural and historical heritage of Euclea and the world remain immense.
From the 18th century onward, the cultural mix of Etruria coalesced into forming a unique blend of Vespasia, Carinthian and Novalian works, often incorporating elements from all three, this is no more evident in architecture, music and literature. This fusion of culture is considered to be one factor in the socio-political success of the union of three distinct peoples and cultures.
Etruria has more WEHO World Heritage Sites (58) than any other country in the world, and has rich collections of art, culture and literature from many periods. The country has had an expansive cultural influence worldwide, also because numerous Etrurians emigrated to other places during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Furthermore, Etruria has, overall, an estimated 150,000 monuments of any sort (museums, palaces, buildings, statues, churches, art galleries, villas, fountains, historic houses and archaeological remains), 100,000 of which are located in Vespasia alone.
Arts and literature
Cuisine
Sport
The most popular sport in Etruria is football. Etruria's national football team is one of the world's most successful teams with TBD XXX Coupe victories (XXXX, XXXXX). Etrurian clubs have won numerous major Euclean trophies, making Etruria one of the most successful countries in Euclean football. Etruria's top-flight club football league is named Lega A and is followed by millions of fans around the world.
The second most popular team sport in Etruria is a rugby, which has a long tradition in northern Vespasia. Etruria's national team competes in major Euclean competitions and the internationals. Etruria ranks as a tier-one nation in Rugby, while also boasting significant wins and competiveness in volleyball. Mens' and womens' volleyball is popular among young Etrurians and has a popular following in Novalia and Carinthia.
Etruria has a long and successful tradition in individual sports as well. Bicycle racing is a very familiar and popular sport in the country, with the Giro d'Etruria held every July and lasting three weeks. Aventine skiing is also a very widespread sport in Etruria, and the country is a popular international skiing destination, known for its ski resorts. Etrurian skiers achieved good results in Winter Invictus Games, Aventine Ski World Cup, and World Championship. Motorsports are also extremely popular in Etruria owing to the cultural affection for automobiles and motorcycles. The Fiorena Grand Prix is one of the most prestigious motorsports events held annually.

Historically, Etruria has been successful in the Invictus Games, which is widely agreed to have begun in Ancient Solaria, taking part from the first Invictus and in XX Games out of XX. Etrurian sportsmen have won 503 medals at the Summer Invictus Games, and another 101 at the Winter Invictus Games, for a combined total of 606 medals with 219 golds, which makes them the XXX most successful nation in Invictus history for total medals. The country hosted XX Winter Invictus and XX Summer Games (X, X, X).
Public holidays
Citizens of Etruria enjoy a large number of public holidays, officially known as Federal Holidays. The origins of the holidays are varied; some are cultural holidays, steeped in Eturian history, while a majority are derived from the Solarian tradition, and others are derived from the country's modern history. There are currently 19 official public holidays, all of which are non-working day
| Date | Estmerish name | Official Etrurian name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day | Capodanno | |
| 6 January | Epiphany | Epifania | |
| 10 February | Rivodutri Victory | Vittoria Rivodutri | Final battle of the Great War, resulting in a victory over Gaullica |
| A Sunday in spring | Easter | Pasqua | |
| Monday after Easter | Easter Monday | Lunedì dell'Angelo, Lunedì in Albis or more commonly Pasquetta | |
| 1 May | International Workers' Day | Festa del Lavoro (or Festa dei Lavoratori) | |
| 10 May | Day of Serenity/Union Day | Giorno della Serenità or Giorno Unione | Birth of the Etrurian Federation, 1888 |
| 4 June | Liberation and Unification Day | Liberazione e Unificazione | Celebrates the unification of modern day Etruria following the Pereramonic Wars |
| 15 August | Ferragosto/Assumption Da | Ferragosto or Assunzione | |
| 1 November | All Saints' Day | Tutti i santi (or Ognissanti) | |
| 26 November | Sons of Romulus Day | Figli di Giorno Romolo | Celebration of the Etrurian Armed Forces |
| 8 December | Immaculate Conception | Immacolata Concezione (or just Immacolata) | |
| 25 December | Christmas Day | Natale | |
| 26 December | Saint Stephen's Da | Santo Stefano |