Tyreseia: Difference between revisions
m (→Salons) |
|||
| Line 196: | Line 196: | ||
===Salons=== | ===Salons=== | ||
Political parties were outlawed in 1880 under the transitional military rule of Tyreseian strongman Azmelqart Šidduni. The proscription was directly inspired by the entrenchment of parties and self-interest of political machines in pre-unification republics like Oyat and Adramut. Trade unions and federations, therefore, tend to fill many of the roles of a political party in the Tyreseian system. Their influence, however, is often limited to issues regarding their represented profession, and as such entities known as political salons have come into being. Much more loosely-organized and unofficial than political parties, the salons act as informal collections of intellectuals and elected Assembly members, brought together by either a single hot-button issue or a range of political ideals. | Political parties were outlawed in 1880 under the transitional military rule of Tyreseian strongman Azmelqart Šidduni. The proscription was directly inspired by the entrenchment of parties and self-interest of political machines in pre-unification republics like Oyat and Adramut. Trade unions and federations, therefore, tend to fill many of the roles of a political party in the Tyreseian system. Their influence, however, is often limited to issues regarding their represented profession, and as such entities known as political salons have come into being. Much more loosely-organized and unofficial than political parties, the salons act as informal collections of intellectuals and elected Assembly members, brought together by either a single hot-button issue or a range of political ideals. Such collections may have full-time dedicated members and regular meetings, though Assemblymen and other politically-involved individuals are just as likely to frequent multiple salons, or even no salons at all. | ||
For much of Tyreseia's history, political salons were an event more than a permanent group. Beginning as ''ad hoc'' gatherings of like-minded politicians, | |||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
Revision as of 06:07, 2 December 2021
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Workers' Federation of Tyreseia Foederatio Proletariae Tyreseiae (Latin) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Hymnus Proletariae" "Hymn of the Proletariat" | |
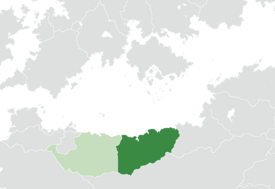 Location of Tyreseia on the Periclean Basin in North Scipia | |
 | |
| Capital | none specified |
| Largest city | New Tyria |
| Official languages | none at national level |
| Recognised national languages | Tyrian, Latin, Tamaziɣt, Hebrew |
| Ethnic groups (2020) |
|
| Religion | Secular state |
| Demonym(s) | Tyreseian, Tyrian (outdated) |
| Government | Syndicalist directorial federation |
• President of the Supreme Workers' Council | Yoana Wechsler |
| Legislature | Supreme Workers' Council |
| Establishment | |
• Foundation of Tyrian city-state | c. 800s BCE |
• Proclamation of Tyreseian Nation | 1861 |
| Area | |
• | 527,552 km2 (203,689 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 5.04 |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 33,275,404 |
• Density | 63.075/km2 (163.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $714,373,343,528 |
• Per capita | $21,468.51 |
| Currency | Tyreseian piaster (TYP) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (Central Scipian Time) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .tyr |
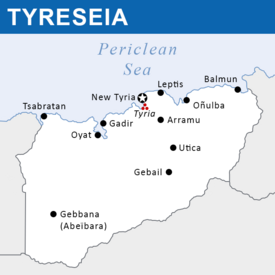
Tyreseia, formally known as the Workers' Federation of Tyreseia, is a sovereign state in northern Scipia, along the shores of the Periclean Sea. It borders that sea on the north, the Charnean Empire on the south, and Aɣmatia on the west. Tyreseia is a decentralized, worker-led federation laid out along syndicalist principles. The nation is home to a diverse number of ethnicities, religions and languages, all reflecting the various empires, kingdoms, tribes and other civilizations that have inhabited the region over millennia. In Tyreseia's north, large, bustling cities like New Tyria hug the coast, sandwiched between vineyards, farms, and drydocks. In the south, The Axos Mountains dominate the skyline and halt the encroaching Ninva desert, itself dotted with river valleys, oases, trade posts, and numerous nomadic tribes who make the hinterlands their home.
In antiquity, the region now known as Tyreseia was ruled by the Tyrian civilization, a conglomerate of city-states led by the eponymous Tyria. The Tyrians were known for their extensive thalassocracy and distinctive purple dye, which remains a symbol of the Tyreseian people to this day. After a fall from grace and a decline in Periclean trading power, the entire region was subsumed by the Latin Empire in the 2nd century BCE. Tyreseia fluorished again under Latin control and cultural influence until the Empire shrank away from the area under both internal and external pressure in the 6th century CE. Following this, the region fractured into various petty kingdoms, chiefdoms, merchant republics, and pirate havens, with a united Tyreseia not to be seen until the mid-19th century.
Over the intervening centuries, the Tyreseian region was plagued by disease, banditry, and factionalism punctuated by repeat Charnean invasions in a time known to Tyreseian historiographers as the Medieval Period or the Dark Ages. These times came to an end when intellectuals like Hanno of Tyria jumpstarted the Tyreseia Movement, a coffeehouse ideology that eventually formed the sociopolitical and philosophical basis for a modern-day Tyreseian state. In a period known as the Springtime of Tyreseia, a series of bloody wars and revolts of unification coincided with a mass resurgence in nearly-extinct Tyrian culture, culminating in the establishment of the Workers' Federation of Tyreseia at the National Proclamation of 1861.
Today, Tyreseia is a stable nation, weathering the transition to a post-industrial economy, fueled by an influx of tourism. Tyreseia is a member of the Forum of Nations, the Kiso Pact, and the Society of Latin Peoples and States, and engages regularly in international trade and diplomacy.
Etymology
Tyreseia, as a term, is wholly artifical and derives from the 19th century. The term was invented by the philosopher(s) Hanno of Tyria in order to create a name that would encompass the Tyreseian region, but be ethnically neutral and not serve to exclude the Latins, Jews, or other groups.
History
The area known today as Tyreseia was likely first inhabited by nomadic tribes around 5000 BCE. Farming techniques originating from western Scipia likely came soon after, with more peoples then settling both along the Periclean and in fertile river valleys. Very little is known about these First Peoples of Tyreseia, as no writing system has ever been found predating the Aradian migration. Early sites at x and y contain both copper and ivory tools, indicating that these peoples engaged in trade with neighboring groups of people. Additional finds suggest a reliance on a diet of fish and cereals, supplemented by a meager supply of pastoral beef; this supply seems to have disappeared around the beginning of the Bronze Age.
The utter lack of solid evidence as to these early peoples' lives is likely compounded by their lifestyles. A site 50 kilometers southeast of Gebayl, is likely the remnants of a Middle Bronze Age city, and one of the best-preserved ruins from the period.
Ancient Tyria
Archaeologists debate the circumstances and exact year in which the city-state of Tyria was founded. 814 BCE, 842 BCE, and 812 BCE have all been floated as possible founding dates, based on varying corroborations of archaeological digs and the testimonies of Tyro-Latin historians writing on the period. According to Tyrian myth, the city was founded by Aradian settlers fleeing the eruption of a volcano in their homeland, generally believed by archaeologists to be the city of Gadir to the west. As the legend goes, the future site was revealed when Baʿal Ḥammon, the chief god of the Aradian mythos and controller of weather, parted the mists and raised the foundations of the gleaming city walls from the silt of the river delta. While the historicity of this creation myth is dubious, excavations around the walls of Tyria indicate that the lower layers were built much earlier than the 9th century BCE. X scholar of the National University of Tyreseia theorizes that a previous civilization may have colonized the TBD River Valley between the First Peoples and the Aradian migration, though this is disputed by others, who suggest that Tyria was built on the site of a yet-unknown First Peoples city.
Regardless of origin, Tyria would quickly prove a jewel in the Aradian crown, as its strategic location at the junction of the TBD River and Periclean Sea trade networks led to a rapid explosion in economic and political power in the following centuries. As the Aradian civilization fell to repeated assaults in XXX BCE, the Tyrian civilization filled the power vacuum and rose to become a Periclean power in its own right. At its territorial peak around 300 BCE, the confederation of Tyrian city-states spanned much of the southern Periclean basin, with a vast patchwork of satellites, colonies, and trading outposts asserting the civilization's mercantile power throughout the rest of the region. Tyreseians often cite this period as the origin of their strong maritime tradition, thanks to the commanding presence Tyria held in early antiquity.
While nominally under the command of the city of Tyria, city-states on the periphery of the polity would often function on a tribute system, sometimes with the autonomy to wage their own wars and hire their own mercenary armies. Generally, though, the inner cities would be governed by a shofeṭ (Tyrian: šūfeṭ), elected from the wealthy merchant families much like an ancient Latin consul. These shofeṭim would meet in Tyria and run the Tyrian mercantile empire through the Senate (Tyrian: Drm), similar to the contemporary Latin Senate, but without a figurehead monarch to rule them. Indeed, the power of the Tyrian merchant families was profound and deep-seated, with power conflicts between the two sometimes erupting into violence and full-blown civil wars. Outside of Tyria itself, these families often maintained extensive connections and properties throughout the Periclean both to express their wealth and secure their mercantile holdings. These families would often finance their own armies of citizens and mercenaries in times of both interstate and intrastate conflict, often far dwarfing the size of the Tyrians' standing army, the Sacred Band. The Tyrian navy, however, was almost always in state hands, and was one of the few standing navies in the ancient world. Historians have credited the navy and its capable commanders with singlehandedly bolstering ancient Tyria's military might and with ushering in a golden age of maritime trade that coincided with the peak of Tyria's territorial expansion around the end of the 4th century BCE.
Tyria's downfall came during the time of the XXXth Council (in XXX BCE). The mercantile Houses of Hiram and Eshmun had, by this time in history, become the most wealthy families in Tyria, with each patriarch being valued as among the richest men in world history and controlling the local politics of several cities. Their rivalry had lasted for centuries, and frequently boiled over into conflict that had crippled the state's treasury and nearly destroyed the once-mighty Tyrian navy. During that year's shofeṭ elections, an attempt by the Hiramites to finance a candidate in a typically Eshmunite-controlled city broke out into civil war. As families and their associated cities began taking sides, the Latin Empire, long jealous of the Tyrian power in the Periclean, began preparations to invade. The Eshmunites consolidated their position within the city of Tyria, while the Hiramites took over the western cities around Tsabratan and appealed to Latium for assistance.
Latin Tyria
The Latin period came to a close around the late 8th century CE, in the midst of a period of mass retreat across the empire. The first signs of trouble came as
Dark Ages
See also: Dictators of Tyria
The Tyreseian region produced numerous vessels and fleets throughout the early modern period. These ships were highly sought-after for their versatility and high cargo capacity, while the sailors were sought after both for their experience and linguistic ability, with most sailors speaking multiple languages in their homeland. The introduction of oceangoing ship technology from the Rezese in the 7th century CE via Latium led to the modernization of Tyreseia's shipyards while under Latin rule. As the Greater Tyrian region fell away from the Latin empire in the late 8th century CE, the ships similarly fell from central control. As the new breakway statelets could not afford to maintain all of these ships, many were hired out on contract or sold outright to other nations, often with crews included on retainer. This contract system was originally limited to deals with Latium, but gradually extended to other Belisarian and North Scipian nations, and eventually to states across the Oorupaqi and the Salacian Ocean. By the 1200s, Tyreseian ships were the primary ferries of Latin troops in the Belfrasian Crusades. Ships both owned by other nations crewed by Tyreseians and owned by Tyreseian states themselves dominated trans-Oorupaqi trade from the 900s onward.
These traders and transports could just as easily turn to piracy, and the line between trader and raider was often thin and always blurred. Numerous pirate havens have been recorded across the region, with many originating from Onigamyg raiders from modern-day Wazheganon in the 9th century CE. These havens were often transient and temporary, but some had the permanence and political capital to organize into full-fledged statelets. Tyreseian pirates were also seen across the Oorupaqi trade networks, either crewing their own vessels or working alongside with Latin, Mutulese, Kayahallpan, Rezese, and Zacapine sailors in multinational pirate crews. Tyreseians were also the targets of piracy, as well. Tyreseian sailors were highly sought-after by Mutulese and Rezese slavers for their experience and skills. Rezese slavery functioned on a ten-year contract system, but often left Tyreseian former slaves with no way to return home after their servitude ended. As many Tyreseian sailors, and subsequently Rezese slaves, were women, these communities of former slaves were uniquely equipped to self-perpetuate in Sante Reze, especially in the port city of Eporte Kiriz in the Nine Cousins. The Eporte Kiriz community of Tyreseians still exists to this day, while other, smaller communities have mixed into both the freeborn and slave creole groups in the intervening centuries. In the Mutul as well, communities of slaves and ex-slaves of Tyreseian extraction formed self-sustaining and insular communities that persisted for centuries following their establishment, though the practice of ritual human sacrifice initially thinned the numbers of prisoners captured through conflict by the Mutulese. Various communities formed by slaves, expatriates, pirates and immigrants existed in other realms across Norumbia and Oxidentale throughout the Fragmentary Period and beyond, with some persisting into the modern day but the rest assimilating into wider society or mixing with other immigrant groups to form mixed creole societies.
Reunification
Modern Period
Geography
Administrative Divisions
Government
Legislature
As Tyreseia lacks an actual head of state or government, the Supreme Workers' Assembly serves many of the functions an executive branch would normally perform. The body is made up of 708 members, divided equally between communes and municipalities. Members are selected by local governments or, in rural communes, by local branches of the Magonic Society, then elected by the populace at large. Terms last for two years; Assemblymen are allowed one consecutive re-election before being forcibly barred from office. As of the 1970 National Reforms, Tyreseia is also one of the few nations to practice staggered elections for a national assembly, with half of the seats being elected on odd-numbered years and half on even-numbered years. Division between "odd" and "even" seats is as evenly distributed across the nation's constituencies as possible. Citizens in a representative's constituency are allowed to start petitions of recall at any time during that representative's term, which will trigger a snap election.
The Supreme Workers' Assembly is responsible for passing all federal laws in the nation. Laws may also be put before the Assembly for voting by petitions of initiative, which require 30,000 signatories from across at least two constituencies to pass.
Salons
Political parties were outlawed in 1880 under the transitional military rule of Tyreseian strongman Azmelqart Šidduni. The proscription was directly inspired by the entrenchment of parties and self-interest of political machines in pre-unification republics like Oyat and Adramut. Trade unions and federations, therefore, tend to fill many of the roles of a political party in the Tyreseian system. Their influence, however, is often limited to issues regarding their represented profession, and as such entities known as political salons have come into being. Much more loosely-organized and unofficial than political parties, the salons act as informal collections of intellectuals and elected Assembly members, brought together by either a single hot-button issue or a range of political ideals. Such collections may have full-time dedicated members and regular meetings, though Assemblymen and other politically-involved individuals are just as likely to frequent multiple salons, or even no salons at all.
For much of Tyreseia's history, political salons were an event more than a permanent group. Beginning as ad hoc gatherings of like-minded politicians,
Military
Foreign Affairs
Tyreseia maintains embassies or other diplomatic nations in nearly every nation in the world. In addition, Tyreseia participates in numerous international organizations such as the Forum of Nations, the Kiso Pact, and the Society of Latin Peoples and States. The national government engages actively in foreign affairs through the People's Commissariat of Foreign Affairs.
In geopolitics, Tyreseia sees itself as part of the broad leftist and republican vanguard. Though it maintains cordial relations with the Western and Eastern Monarchies, Tyreseia's closest allies are its fellow members of the Kiso Pact. Foremost among Tyreseia's allies is the Messidor Union, its western neighbor. Their ideological closeness and geographical proximity led to Tyreseian volunteers fighting alongside Messidorian troops in most of its conflicts, and vice versa. The two nations maintain a healthy friendship to this day.
Tyreseia's southern neighbor, the Charnean Empire, serves as the country's biggest existential threat. Charnea's predecessor states have attempted perennial invasions of the Tyreseian region for centuries, with varying amounts of success. Large communities of Amaziɣ and Imuhaɣ peoples also exist south of the Axos Mountains in Tyreseia, a product of trade and said invasions; these communities have long been a source of national security concerns under Tyreseian governments who feared that the Charnean government might use them as justification for an invasion or annexation. Modern-day security concerns now stem more from Charnea's internal instability rather than any fears of a state-level invasion. Smuggling out of northern Charnea into Tyreseia, both as a destination point and as a transit point through its ports to southern Belisaria, has been an issue for decades. The practice reached a crescendo during the Ninvite War, but was temporarily lessened following Operation Baggage, when elements of the Tyreseian Workers' Navy occupied parts of northern Charnea until the end of the conflict.
Tyreseia maintains a unique relationship with the Latin Empire.
Unions
Trade unions, also known as Societies or Federations, serve as both the economic and political backbone of Tyreseia. The national headquarters of these federations will host Trade Union Congresses (TUCs) once or twice a year, made up of representatives from every municipality, to plan overarching goals for their set industry and to share new innovations and processes. Local industries, such as factories, are governed by local branches of unions. These branches are horizontally managed and are responsible for paying for members' transportation, recreation, childcare, and other needs and wants through profit-sharing agreements and financial management. Depending on the union, membership dues might also be required and passed up the chain to the national level. Local unions will also be required to equip certain numbers of personnel for the Workers' Militia, with the government reimbursing purchases of required firearms, ammunition, supplies, and vehicles. Union militias are typically consolidated in their local commune or municipality, and can be raised and/or merged into regular Naval Infantry units in times of crisis. As such, a minuteman-like network of small Militias exists across Tyreseia, cheaper to equip than a regular army but consequently less effective. The exception to this process is the Society of Neptune, which governs longshoremen, merchant mariners, shipbuilders, and other maritime personnel. The Society is required to furnish people for the Naval Fleet Reserve rather than the Workers' Militias. The Society will therefore maintain mothballed ships and Fleet facilities in peacetime, and man and repair ships in wartime.
On a local level, unions also play a crucial role in government. In municipalities, all unions within are required to put potential representatives up in a general election to serve on a Municipal Assembly, which serves as the region's self-government. These assemblies act as both the legislative and executive branch of local government, and wield a great amount of power in how the city is run, where new projects are built, allocating funds, and electing representatives for the Supreme Workers' Assembly. Given this power, both local unions and assorted petitioners can institute a recall election at any time. Supreme Workers' Assemblymen are subject to the same recall rules via their local constituents and Municipal Assembly. In rural communes, the plethora of unions are replaced by a local branch of the Magonic Society, which serves as the agricultural workers' union. Magonic branches are thus the direct local governance for these communes, and elect representatives directly to the Supreme Workers' Assembly.
Issues have arisen over the creation of new industries and municipalities in previously uninhabited areas, particularly during the 20th-century petrochemical boom. [Insert examples here.] [Then describe how the problem was/wasn't solved.] Similarly, though more rarely, municipalities have dropped in population and have reverted to communes. [Insert examples here.] [Then describe how the problem was/wasn't solved.] Another issue comes with industrial disaster areas or other places rendered uninhabitable.[Insert examples here.] [Then describe how the problem was/wasn't solved.]
Education

Childcare and education is guaranteed as a right by the state, and so it serves as a perennial subject of review and reform. As a baseline, the national literacy rate is 99.6%, with nearly equal gender parity. National groups like the Tyreseian Congress of Educators and the Higher Education Federation often form baselines to ensure that children across the nation receive a similar education. The aforementioned unions staff all schools in Tyreseia, and the regular Trade Union Congresses ensure that new innovations in the field of education are shared uniformly across the nation. Schools are often funded by a mixture of payments from municipal unions and government subsidies, with the latter being the near-exclusive funding source for numerous major universities.
The basic structure of Tyreseian education closely follows the Latin model. Children are required to enter the first stage of school, nursery (seminarium), at the age of 3. From there, students will enroll in schola primaria, for ages 5 to 11 (Years 1 through 6). Students will receive elementary instruction in subjects such as their native language's grammar, history, the sciences, arithmetic, geography, the arts, music, and physical education. Many of these subjects will carry into the students' further studies at the level of the gymnasium inferiorum, or the Lower Gymnasium. The Lower Gymnasium, consisting of Grades 1 through 4 and ages 11 through 15, exposes students to elective courses like foreign languages and home economics to prepare them for the gymnasium superiorum, or the Upper Gymnasium. Students are required to learn at least one language at this level and beyond. The most common foreign languages studied by Tyreseian students are Audonian, Anglic, Tsurushimese, Hellenic, and Nahuatl. Following matriculation from Grade 4, students are required to take an aggregate exam based on international standards, designed to gauge both their progress and the efficacy of the Tyreseian education system. Finally, in the Upper Gymnasium (Grades 5 through 7, ages 15 through 18), students experiment with future career paths or potential college degrees, with schools offering numerous electives ranging from the social sciences to the industrial arts. From matriculation at age 18, the Tyreseian student has completed their compulsory education and may choose to either pursue college education after taking a General Education Exam. Departure from school before graduation is extremely uncommon, as even students who are ill, injured or incarcerated in some fashion are expected to finish their studies as soon as they are able.
Higher education is popular in Tyreseia, as tuition payments are subsidized by the national government. Traditionally, students sign on with a union of their choice before entering university, then will pursue degrees and career paths that local unions might need in exchange for their remaining tuition being paid off by the union. This practice, though still common, is growing less popular as parents have begun investing savings into their offspring's education to ensure they may pursue a career that they choose. Colleges and universities, even technical or other specialized schools, require numerous general education courses to create well-rounded students. Room and board costs are covered by the government for all Tyreseian citizens; international students must pay for these and for tuition, but may receive financial aid to cover these costs if they are of low means. Scholarship funds exist through the work of unions and private individuals to help pay for the education of traditionally marginalized groups in Tyreseian society.
International exchange students make up a large percentage of tertiary students in Tyreseia, especially at the National University of Tyreseia in New Tyria. Numerous left-wing educators and intelligentsia fled Latium in the aftermath of the Social War, with many flocking to the welcoming arms of Tyreseian higher education. There, they brought large amounts of knowledge from the cutting edge of Latin academia, and established attractive Latin-language curriculae at their new homes. In the following decades, tensions cooled and Tyreseia opened up its borders for more and more Latin exchange students. In the modern day, low consumer costs, tolerable climate, and widespread use of the Latin language have all made Tyreseia a favorite for Latin college students looking to study abroad. To a lesser extent, students from Yisrael and the Jewish diaspora find the widespread use of Hebrew, especially in the Jewish Quarter of New Tyria, attractive. The interplay bewtween numerous cultures over Tyreseia's history has also encouraged students of the social sciences from around the world to visit Tyreseian universities to study firsthand.
Economy
The economy of Tyreseia is structured primarily around the idea of workplace democracy, an idea held as sacrosanct. As such, all businesses function as localized collectives, with horizontal management structures and profit-sharing-based payout schemes.
Grey Market
As most individual-based taxes are levelled on luxury commodities and high-income persons, most people only experience state taxation through production taxes on their union. As such, a grey market of freelancers, handymen and other itinerant workers has become pervasive in Tyreseia. As monetary payment through this system has been heavily discouraged or even outlawed throughout various points in the nation's history, mutual aid has become the driving force behind this secondary market. Ad hoc exchanges of goods or services between individuals
Energy
Tyreseia possesses two nuclear power plants.
Culture
Ethnic Groups
Small but stable Onigamyg-descended communities exist throughout Tyreseia, but are traditionally centered around the city of Leptis. Their numbers are around XTHOUSAND now, and have remained stable in recent times thanks to government efforts to connect them with cultural resources in Wazheganon.
Religion
See also: Coptic Nazarism
Religiosity in Tyreseia has been on a steady decline since the institution of state secularism in the 1900s, with a sharp acceleration towards the turn of the century. "Irreligious" overtook Coptic Nazarism as the largest religious self-identity in Tyreseia following the 2000 Census. As of 2021, it is estimated that a full 44% of Tyreseia's population does not follow an organized religion. Religion often plays a minimal part in the average citizen's life, even if they profess belief. A recent survey by a non-governmental organization identified that only 25% of people stated that their primary values in life were based on their faith, and only 22% stated they were "absolutely certain" that their religion was correct over all others. Historically, Tyreseians have also been known to mix and syncretize various religious celebrations and rituals into their lifestyles.
The plurality religion in Tyreseia is Coptic Nazarism, a wholly indigenous form of Gnosticism. Around 30% of Tyreseians are Coptic, according to the 2020 Census. The second religion in terms of adherents is Judaism, which 15% of the population adheres to according to the 2020 Census.






