Piraea
Piraean Republic Πειραιηκή Δημοκρατία Pireikí Dimokratía (Piraean) | |
|---|---|
Motto: «Ελευθερία ή Θάνατος» "Elefthería í Thánatos" "Freedom or Death" | |
Anthem: «Ύμνος προς την Ελευθερίαν» "The Homeland" | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | |
| Official languages | Piraean |
| Recognised regional languages | Etrurian, Novalian, Amathian, Galenian and Montsurian |
| Religion | See Religion in Piraea |
| Demonym(s) | Piraean |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
| Pavlos Kassapidis Stella Davakis Stefanos Xanthos | |
• Premier | Stamatios Panopoulos |
| Konstantinos Baltas | |
| Legislature | Piraean Senate |
| Establishment | |
• 1st Piraean Empire | 639 - 884 |
• 2nd Piraean Empire | 1012 - 1368 |
• Grand Duchy of Alikianos | 1729 |
• Kingdom of the Piraese | 1857 |
| 1938 | |
| 1948 | |
• Third Republic | 1979 |
| Area | |
• | 86,553.60 km2 (33,418.53 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | |
• 2017 census | 7,484,889 |
• Density | 86/km2 (222.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $207.062 billion |
• Per capita | $27,664 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $113.299 billion |
• Per capita | $15,137 |
| Gini (2020) | low |
| HDI (2020) | very high |
| Currency | Piraese Lira (₺) [a] (LIR) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +42 |
| Internet TLD | .pr |
Piraea (Pireás: Πειραεάς, tr. Peiraeás), officially the Piraean Republic (Pireás: Πειραιηκή Δημοκρατία, tr. Pireikí Dimokratía) is a country in Southern Euclea located along the Acheloian Sea. It borders Amathia to the north, Etruria to the east and the disputed territory of Tarpeia to the south. Piraea has a population of approximately 7.4 million, which are concentrated in urban areas along the coast. Alikianos is the capital and largest city of the country, and is followed by Kissamos, Hersonissos and Tylissos.
Piraea is recognised as one of the oldest civilisations in Euclea, its presence along the Acheloian and Solarian seas as well as Aurean Straits is well documented in numerous texts that highlight the extent of the Piraese city-states along both sides of the straits from at least 600 BCE. This form of political organisation was crucial for Piraea in the development of the first forms of democracy and innumerable mathematical advances. However, between the year 300 and 200 BCE, city-states will progressively fall under Solarian influence, with the fall of Prassa marking the end of the period. Developments that characterised city-states in the areas of literature, philosophy, medicine and mathematics were later used as inspiration during the Solarian period in a moment of massive advances particularly in the arts. The collapse of Solaria in 424 forced the formation of the First Piraean Empire, which centralised and unified different territories across what is today Piraea; the empire would last several centuries until the invasion of the Tagamic hordes. A Second Piraese Empire was re-established, although a weakened army and internal turmoil due to a lack of identification took it to the collapse, which was used by neighbouring foreign powers to rule over Piraese during several centuries.
In 1820, under the control of the Kingdom of Vespasia, ethnic Pirese joined in what is known as the October Uprising, which led to a War of Independence that lasted five years and proved effective in building a national narrative for Piraese identity. The revolution will last until 1925, when diplomatic intervention of Euclean powers concluded with the effective establishment of the Kingdom of Piraea and the crown of a foreign monarch. At the burst of the Great War, Piraea joined the Entente, supporting Gaullica and declaring war on Etruria; however, the high costs of the war amid poor living conditions questioned the continuity of the monarchy and put the government under pressure with different internal conflicts. At the end of the war, the Entente was defeated and Piraea faced the invasion of Etruria, which forced it to hand in the territory of Tarpeia, committing in the subsequent years, the Piraean Genocide. During 1938, Nikolaos II of Piraea was forced to abdicate and fled the country in exile proclaiming the First Piraese Republic, which saw the creation of the first anarchist communes and the leadership of socialist and workers' political parties. The period was characterised by a relative stability, which served for progressive reforms, wealth redistribution and the industrialisation of the country; however, in 1948, a coup d'etat ignited a short civil war, which faced conservatives and socialists. Backed by far-right militias and armies in Etruria and Amathia, the Second Piraese Republic was proclaimed under the authoritarian rule of Konstantinos Athanopoulos and his military junta. The regime led the country until 1979, having introduced several economic and social reforms that exalted conservative values and ties with the Episemialist Church, but nearing the 1970s, the regime faced a period of social discontent, economic downturns and regional isolation, concluding in 1979 with a plebiscite that sought to renew the junta's power. The defeat of the regime ignited the democratic transition, which concluded a year later with the election of Ioannis Apostolou as Premier of Piraea, who later handed in power to Leonidas Palaiotis, first socialist Premier since 1948.
Today, Piraea is a unitary parliamentary republic and developed country with a high standard of living. It tends to rank high in metrics like women participation, press freedom, civil liberties and overall quality of life. The country is a member of the Community of Nations, International Council for Democracy, Euclean Defence Treaty Organisation, Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs, and the International Trade Organisation; as of 2021, the country has formalised its intentions to be a member state of the Euclean Community and is a recognised candidate.
Etymology
The name Piraea comes from the Ancient Piraese name Πειραιεύς (Peiraieús), which roughly means 'the place over the passage'. Over time the Ancient Piraese evolved into the modern Πειραιάς (Piraeus). Piraea is the embricized version of Piraeus.
History
Classical period
Solarian rule (300 BCE-500 AD)
Middle Ages and Empires (500 AD-1368)
Duchy of Alikianos and Kingdom of Piraea (1729-1857)
Industrialisation and Great War (20th century)
First Republic (1938-1948)

On 26 July 1938, the Piraean First Republic was proclaimed in Alikianos. Shortly after the abdication of Nikolaos II of Piraea, an interim government led by the PSEE assumed the administration until the celebration of elections two months later. The government of Stephanos Vitalopoulos was in charge of the introduction of the constitution of the first republic as well as initial reforms aimed to modernise the state from an egalitarian and social view. During the elections of that same year, the coalition formed by the PSEE, the Piraese Section of the Workers' International and several other centre-left and leftists parties, became victorious and led the country during the next five years under the leadership of Themistoklis Ioannopoulos.

Ioannopoulos introduced several deep reforms that put the republican government against the Metropolitanate of Piraea and military authorities, which founded conservative allies on the senate's opposition. Between 1938 and 1943, the Ioannopoulos granted women's vote, expanded the agrarian reform started by Vitalopoulos that benefited cooperatives, granted the right to strike and the activity of trade unions and introduced collective agreements; however, the government faced several crisis when it sought to reform the military and complete the secularisation of the nation. The new republic was born in egalitarianism and the avocation of a strong social state; cooperatives spread anarchist thought across the country and both the GSEP and PSEE were heavily influenced by it. In 1938, the military oath was changed in order to eliminate monarchic connotations and a year later, the government passed a bill that aimed to reduce the number of generals and change the organic composition of the armed forces; a year later, Ioannopoulos nationalised hospitals and cemeteries from the church and reduced the amount of lands without use owned by the Metropolinate.
In 1943, new elections took place in a highly divided and polarised society, which gave the conservative wing a larger role in the Senate. Led by Kyriakos Kanopoulos, the National Party of Piraea became the largest force in the Senate and was allied with other traditionalist and conservative groups on its right to form government. Kanopoulos' main aim and electoral promise was to leave on standby several of the leftist reforms made by the PSEE and recover traditional values throughout the country; as it found strong mobilisation and opposition, it became further aligned with the church and military. At the end of the government, Piraeans found themselves in an algid social situation that favoured the left coalition during elections. The new government of Aristeidis Kontolis, again of the PSEE, lasted a few months before the start of the Piraese Civil War against conservatives.
Military rule (1948-1979)

At the start of 1948, Kanopoulos' cabinet, advised by the return of socialists to government, pushed repressive measures, limiting liberties and starting to persecute trade unions and leftist movements. The elections of 1948 gave another victory to the left coalition, which governed during some months before the burst of the civil war, when military generals upraised against Kontolis' first measures. Conservative forces were largely backed by the Kingdom of Amathia and other paramilitary far-right forces from Etruria, supports that proved decisive in the short civil conflict that ended giving a civic-military junta the government of Piraea. On 19 September 1948, the Second Republic of Piraea was proclaimed by Konstantinos Athanopoulos under a Government of National Reorganisation.
The period was marked by a strong repression of movements associated with the First Republic, the PSEE and trade unions; the use of state terrorism and the systematic abuse of the armed forces and the the introduction of torture of dissidents and political opponents. Throughout its history, the junta rule was led by different figures of strong conservative record from military world, although during the final years, civic members were part of it too. Between 1948 and 1953, the junta was composed by the commanders-in-chief of the three branches of the armed forces, until in 1953, the junta allowed a fourth civic position to take position in an effort to project an image of openness towards the exterior. During the first year, the regime supressed the legislature and imposed strict censorship on press and personal freedom, leading to the closure of several radios and newspapers and the exile of political opponents from the left; in the following years, the junta re-established the close relations with the Episemialist Church, which was in exile in Piraea during the years of the Amathian Equalist and Council Republic, granting it great influence in society.
During the 1950s, the popularity of the regime was increased through economic reforms and developmentalism, with which the junta was able to inaugurate infrastructure projects, highways, railways and dams; most of the construction projects, however, were later denounced to have been funded with corruption and dirty money. The junta, seeking to maintain itself in power, used the popularity to strengthen the regime and secure national integrity against a more aggressive Etruria and hostile international environment led by the condemnation from the Community of Nations and the recently founded Euclean Community. In 1958, Nikolas Zaropoulos became the first and only civic member of the junta, who was tasked with the international relations amid a scenario of increasing tensions with Povelia, which finally burst with the invasion of Tarpeia and the Apokoronas in 1961.
Fall of the regime (1961-1979)
The Etrurian invasion of Tarpeia and the Apokoronas, as well as the misinformation campaign carried by Povelia regarding the presence of Novalian terrorists in Piraea, placed the military junta on a tight position, with minimum international attention and witnessing the start of financial problems. A response to Etrurian forces was long waited, but the all these factors produced a poor mobilisation of Piraean forces; at first, the junta tried to censor the information regarding the lack of valuable force, but several foreign newspapers and radios were able to freely speak about it, igniting discontent towards the regime in Piraea. During most of the 1960s, the regime tried to strengthen even more the repression and censorship in Piraea under the leadership of Konstantinos Athanopoulos; however, this was ineffective and the first signs of serious financial shortcomings took people to the first mass protests in several cities in 1967.
The union between workers, students and political movements functioning in the undergrounds were effective on a social level, but not in the political world. In 1969, the junta started a large-scale liberalisation of the economy in order to receive advise and funding from the International Council for Democracy and Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs; a group of Piraean economists taught in Morwall, Estmere, and known as the Morwall boys became part of the advisors board of the Ministry of Economy, and led the transformation of the Piraese economy, which was heavily marked by the conflict with Etruria, corruption and irresponsible spending during developmentalism years. During most of the 1970s, the economy will see important reforms and experience never seen before growth rates known as the Piraean miracle; however, the country suffered an increasing inequality and political repression was still persistent.
In 1978, Athnopoulos, who had been the undisputed leader of the military junta since 1950, died in Alikianos leaving an open door regarding the future of the regime. A year later, the junta, lead by the Commander-in-Chief of the Air Force Ioannis Christodoulopoulos, sought to renew itself in power through a national plebiscite in which the population was asked if whether they approved the candidate of the junta —Christodoulopoulos— or not; with 56.8% of the population voting no, the junta decided to transition towards a democratic regime, allowing the formation of political parties, talks with the centre-left and setting a date for general elections. In 1980, the first elections since 1948 took place and months later, the first new members of the Senate were swearing oath and granting confidence to the first democratically elected Premier, Ioannis Apostolou, a Sotirian democrat from the People's Party.
Third Republic and contemporary history (1979-present)
Ioannis Apostolou became the first democratically elected Premier in 1979 and his administration dealt with the drafting of a new constitution and the transition towards a liberal democracy of Piraea; politically, Apostolou also faced the re-organisation of the right and centre-right under the People's Party and the legalisation of previously censored parties and organisations from the left, like the Piraese Section of the Worker's International and the General Confederation of Piraese Workers. During his government, the new constitution inaugurated the Third Republic, which granted social rights, press and religious freedom and set aims in the Euclean integration of Piraea.
During 1983, general elections brought back the PSEE to the government, which formed a coalition with the Progressive Federation, a small coalition of parties that grouped an alternative left from the PSEE. Leonidas Palaiotis became Premier of the Republic and led the country through economic and social reforms. In 1985, Palaiotis concluded the trials against the military leaders of the junta and those who committed crimes and abuses; a pardon policy initiated by Apostolou was enlarged to all imprisoned during the dictatorship without trials or due to political reasons. Palaiotis was followed by Theodora Procopiou, first female Premier of Piraea, who counted with broad political support in the the first ever large coalition in Piraea; however, PSEE's aims to become part of ECDTO forced the end of her government in 1991, after the Piraese Section and Progressive Federation stepped down from the coalition. Konstantinos Kondoulis followed Procopiou as the second People's Premier; the government was composed also by centrists and liberals, and was the first to introduce neoliberal reforms in the state to reverse economic stagnation, such as reducing social spending and increasing VAT to induce a reduction of inflation rates. During the administration, a referendum was held in 1995 to conclude the membership of Piraea on the Euclean Common Defence Treaty Organisation; the referendum saw the opposition of the Piraese Section and other left political parties, although the PSEE remained ambiguous, which helped the government to conclude the country's ascension.
Between 2005 and 2009, the country suffered its most important financial crisis, which triggered the implosion of the political scenario, forcing the resignation of Evangelos Polakis due to corruption charges and amid massive protests and repression in the streets. Polakis, who had assumed the People's Party leadership year before becoming Premier, had formed government with the far-right Homeland Party, with which the country moved closer to Samorspi. His government faced severe opposition from centre and centre-left sectors and his resignation was followed by his leaving from the legislature in helicopter. The effects of the crisis were crucial in the future political development of Piraea, forcing the creation of new parties and the comeback of the PSEE to the government during the next 13 years until today. The current Piraese agenda is marked by a strong focus on the Euclean Community followed by most parties and the two main ones, PP and PSEE. As of 2021, the country is a recognised candidate for membership of the Euclean Community.
Geography

Piraea extends over a total area of 86,553.60 km2 (33,418.53 sq mi) and it is entirely located in the southern portion of Euclea, bordering Amathia to the north, Etruria to the east and the territory of Tarpeia to the south. The entirity of Piraea's coastline meets the Acheloian Sea to the west. The centre of Piraea tends to be relatively hilly, with valleys providing enough irrigation and sunlight for the formation of vineyards and olive plantations; in the east, south and north, geography presents more difficulties and higher altitudes in what is known as the Tarantines, a sub range of the Aventines that traverse the regions of Foinikas, Lampi and Samariá. The highest point of the country, Mount Zarkos, is part of the Tarantines and is 1,963 mts (6,440 ft) high.
Most of the coastline along the Souda Riviera and Sitia tends to be relatively flat and highly fertile, with only a mild undulation. The country has three main rivers: the Erymanthos, which is born in a Tarantine peak near the border with Amathia, the Parnos, which makes its way through most of Foinikas, and the Arda — the smallest of the three — that is born in Lampi. All of these conclude in the Acheloian and are considered of vital importance to the Piraese eco-system. Nevertheless, the cultural presence of the ocean has always been more prevalent and rivers were not important as in other regions to organise life around them.
Piraea's convergence of climatic and geographical conditions have resulted in a diversity of flora and fauna, with its distinctive regional geographies providing shelter and optimal development conditions for a wide range of species such as the Solarian monk seal, the roe deer the Tarantine lynx and others common of the region. Most, if not all, Piraese flore tends to correlate with that of the Solarian eco-region, although in higher regions, flora tends to assimilate with central Euclean types. The cedar, evergreen oak and olive are some of the most common types.
View of the Larissos Valley.
Rock formations in the coast near Tarpeia.
Urban landscape of the town of Thytos.
Olive plantations in central Sitia.
Climate
Most of the climate of Piraea, if not all, falls into the category of Solarian, with slight differences depending on altitude and proximity to the sea. In general terms, Piraea's territory receives moderate precipitation and counts with summers of high temperature. According to the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification, the coastaline of Piraea and most of Sitia's highlands are described to have hot-summer Solarian climate (Csa) while further inland, summers are milder and are categorised as warm-summer Solarian climate (Csb). A small area east of the region of Lampi bordering Tarpeia is considered by metereologists as the driest spot of the country and is categorised as hot desert climate (BWh).
Average temperatures in most of Piraea tend to vary between 10.2°C (50.4°F) in the coldest month to 29.3°C (84.7°F) in summers. Snowfalls occur during winter season in the interior of Piraea and in most of the mountainous regions; these usually happen between December and February although they can exceptionally extend from November to March. Coastal urban centres, such as Alikianos, also receive brief snowfalls during these months as temperatures abruptly descend to −10.0 °C (14.0 °F) in the higher regions and −6.5°C (20.3°F) in the coasts. These temperatures have largely contributed, together with insolation hours, to Piraea's tourism industry and primary sector of the economy; in average terms, most of Piraea receives 2300 to 3200 hours of sunshine a year, with 4–6 h in winter and 10–12 h in the summer.
| Climate data for Alikianos-Ioannis Apostolou Air Base Station, Alikianos (1991–2020), Extremes (1890–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
28.9 (84.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
44.8 (112.6) |
43.0 (109.4) |
42.6 (108.7) |
38.6 (101.5) |
36.5 (97.7) |
30.5 (86.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
44.8 (112.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
14.2 (57.6) |
17.0 (62.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
34.3 (93.7) |
34.3 (93.7) |
29.6 (85.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.9 (66.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
21.8 (71.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.4 (84.9) |
25.0 (77.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.6 (60.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
19.2 (66.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.1 (44.8) |
7.3 (45.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
17.0 (62.6) |
21.6 (70.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
12.2 (54.0) |
8.7 (47.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.8 (53.2) |
16 (61) |
15.5 (59.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
5.9 (42.6) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 55.6 (2.19) |
44.4 (1.75) |
45.6 (1.80) |
27.6 (1.09) |
20.7 (0.81) |
11.6 (0.46) |
10.7 (0.42) |
5.4 (0.21) |
25.8 (1.02) |
38.6 (1.52) |
70.8 (2.79) |
76.3 (3.00) |
433.1 (17.06) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 72.0 | 70.0 | 66.0 | 60.0 | 56.0 | 50.0 | 42.0 | 47.0 | 57.0 | 66.0 | 72.0 | 73.0 | 60.9 |
| Source: Piraean National Meteorological Service | |||||||||||||
Politics and government
Piraea is a unitary parliamentary republic, which is constituted in the 1979 Constitution of the Third Republic. Exective power is divided between the Head of State and a Head of Government; the first is consolidated in the collective figure of the Presidency, while the second, consists in the figure of Premier, who is appointed by the Chairperson of the Presidency after gaining the confidence of the legislature. As a secular nation, the constitution recognises the preponderant position of the Episemialist Church but grants the state protection of religious freedom; Piraea's constitution recognises important civil and Human Rights, freedom of speech and expression, and the adoption of a social state.
The Premier and members of the Presidency are elected by universal suffrage by all citizens over 18 years old; however, Premiers are required to gain the declared confidence (Piraese: δεδηλωμένη, tr. dedilomeni) to be formally appointed by the chairperson of the Presidency. The Presidency is elected for a fixed term of six years, which is renewable only once, with its three seats being occupied by the two parties with the most votes and a chairperson title rotating every two years; members of the Presidency are tasked with ceremonial activities and usually appoint ministers, dissolve legislatures or sign passed bills. The legislative power of Piraea is vested on the unicameral Piraean Senate, a legislature comprised of 125 members elected every four years through universal suffrage. Members of the Senate grant or not confidence to the Head of Government and can call individual or the whole cabinet to resign, forcing general elections, if a motion of censure achieves the needed majority. The legislature is also tasked with passing laws, supervising the executive and declaring war, among other things. According to the Constitution of the Third Piraese Republic the judicial branch is divided between civil and administrative courts, with the former dealing with ordinary civil and criminal matters and the former with issues regarding institutional competences or individual cases of disputes between the state and citizens, among others. The judicial system is hierarchically structured, with courts of general jurisdiction on first instances and a Supreme Court of Piraea on top of them, below it, both the civil and administrative courts count with their respective Supreme Courts; when contradictory decisions or disputes between the two arise, the Supreme Court of Piraea is in charge of providing an irrevocable statement.
After the return of democracy, the Piraese political world has been dominated by the Piraese Socialist Workers Union (centre-left) and the People's Party (centre-right), which have alternated in power. Coalition governments are common since the 1980s and the existence of minor parties is considered crucial in the governability of Piraea supporting executives through confidence. The current legislature, led by the PSEE as the largest force is also composed by 8 political parties.
Foreign relations

Piraean relations have been constrained to its political past and geopolitical location in the south of Euclea. Over the years, it has shifted its main foreign policy axis, gaining pragmatism that has given it a wide range of nations with which it holds close relations. During the military junta period, Piraea saw an important alignment with other authoritarian and nationalist regimes, like ASUR; however, during the final years of the dictatorship, Piraea's junta was immersed in a state of isolationism in the Euclean scenario. The return of democracy took it to explore a gradual approach with the Euclean Community after an initial failed attempt to gain access to the bloc; during successive socialist governments, the country became gradually aligned with the socialist world and became an observer of the AESE and the AIS; and although it was never considered a member of any of the two, Piraea still holds close ties with Kirenia and Champania.
Since 2008, the most important political parties have reached consensus about the path of accession to the Euclean Community and Piraea has already held talks with communitarian authorities, being recognised as a candidate. In 1994, it was allowed to become a member of the Euclean Common Defense Treaty Organization and the country aims to become part of the EC by 2024, although a persistent but isolated eucloscepticism and the need of institutional reforms might delay the date. The country's claims over Tarpeia and the Apokornas have long been an obstacle on the relations with neighbouring Etruria, with which Piraea still holds fraught relations as it actively claims the jurisdiction over both territories, granted in 1946 by the Treaty of Morwall.
The country is a founding member of the Community of Nations and has an active participation as full member of the ICD, the ECDTO, the GIFA, and the ITO.
Administrative divisions
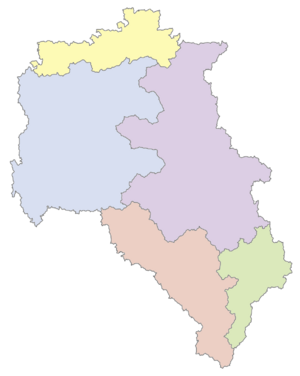
Although conceived as a unitary republic, Piraea is divided into five regions created through the Statute of Autonomy (Piraese: κράτος των αυτόνομων, tr. Krátos Ton Autónomon), which grants devolved powers, the creation of regional legislatures and cabinets led by regional Minister-Presidents. These regions have the right to discuss and enact policy in their territory in diverse matters, such as education, healthcare, welfare urbanism and budgets, while the State acknowledges regional differences and their nature.
Regions are further divided into provinces and these into municipalities, all of them with their smaller models of governing councils, elected by inhabitants of the area for a fixed term of four years. Piraese is the only official language of the country and all of the regions, although in most of them, there is a range of regionally or provincially recognised second language.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Armed forces

The Piraean Armed Forces —Πειραες Ένοπλες Δυνάμεις— are the military defence of Piraea, they consist in three branches; the Piraean Army, the Piraean Navy and the Piraean Air Force, branches that are overseen by the Ministry of Defence and subordinated to the Chairperson of the Presidency, who acts as Commander-in-Chief. The role of the armed forces is defined by the Constitution of the Third Republic as to safeguard independence, sovereignty and the integrity of its territory from foreign interventions; however, in recent years, Piraese armed forces have also been tasked with peacekeeping missions and emergency relief tasks during national disasters. Conscription remained in place until 1989, when it was eliminated via referendum; Piraea sees an average 194 new trainees every year.
Since the entry of the country to the Euclean Common Defense Treaty Organization, the armed forces have also embraced the protection of international peace as a core value on its joint exercises with foreign forces; currently, there are three different deployments of Piraean soldiers abroad in Rahelia and Bahia. Presence and influence of the military in society is an ongoing discussion among political circles in Piraea, which remained reticent to expand the role of the forces after the end of the junta period. As of 2021, the country attributed 1.2% of its total GDP to the military budget.
Economy

Piraea is a developed and high-income economy, with a high standard of living, although still behind other Euclean nations. The country has a GDP (PPP) of $207.062 billion and a per capita of $27,664, it also ranks very high in Human Development Index (0.870) and has a comparably low social inequality according to the Gini index (29.7). Piraeans count with a large welfare net built over the years and the country has developed a high rate of home ownership between the 1970s and 80s; however, the country has a high unemployment rate (15.5% as reported in 2020) and an even higher rate of youth unemployent (33.7% recorded the same year).

The services sector comprises the majority of the Piraean Gross Domestic Product, accounting for a 79.1% of its total output. The sector has a large contribution from tourism, a crucial industry in most Piraean regions, which usually rank among the most visited spots in the Euclean continent; on average years, Piraea approximately welcomes between 14.7 and 19.4 million tourists, mainly from Werania, Estmere, Gaullica, Amathia and Etruria; retail is also considered crucial in the tertiary sector and Piraea counts with numerous retailers that have achieved Euclean presence. Although with a small international projection, the services sector are also see the contributions of a large financial sector, which is mainly focused in Alikianos, and counts with an important presence of the state through regional saving banks that are considered pillars of welfare state. The secondary sector, which accounts for 16.9%, consists on the production of cement, marble and aluminium, as well as a developed chemical industry; shipbuilding, mainly for commercial purposes, is also very important and accounts for a large part of the sector's output. Smaller in comparison but highly profitable, the primary sector of the economy accounts for 4.1% of Piraea's output, but employs 12.6% of the total workforce; the country is a leading exporter in the continent of pistachios, diary products, olives and oils, and several types of fruits and vegetables. The wine industry, one of the largest in the south of Euclea, has been upgraded and is protected nationally.
Piraea is considered to be a welfare state, with extensive social programs and a robust pension system; although severely damaged from budget cuts during the early 2000s and after the 2005 global recession, Piraean governments have achieved to effectively modernise most the welfare state as the political establishment has actively assured macroeconomic stability. At the end of the 1990s and the new millennium, the Kondoulis and Polakis-Kritikiadis administrations assured large privatisation and demonopolisation packages; the accession process to the Euclean Community has assured Piraean governments with stable flows of foreign investment. Piraea's official currency is the Lira (Λίρα; ₺), however, the Euclo is widely used and accepted despite the country's not adherence to the Euclozone.
Labour market

The Piraese labour market has undergone several reforms since the 1990s aimed to make it flexible for both employers and employees and in order to cope with Euclean Community standards. Although the country is considered a developed and high income economy, it faces the struggles of high unemployment rates and a low purchasing power, these factors place Piraese workers with a high average number of working hours. Geographically, unemployment tends to increase in inland regions, which contrast with the coastal reality; similarly, summer season tends to decrease unemployment, especially among the youth. Since 2005, Piraea has introduced temporary layoffs as part of the measures to diminish the impact of the global recession that same year. The Piraese labour market stands out in the region by its small income inequality, often attributed to the proliferation of cooperatives in different sectors.
Piraea counts with an average trade union density (20.8% of the total workforce) and a very high collective agreement coverage (100% in 2020), this gives the main trade union, the General Confederation of Piraese Workers (ΓΣΕΠ), an enormous influence in society and politics. The country has a robust welfare state and spends 23.7% of its total GDP in social welfare spending, mostly directed to support the social security and universal healthcare systems. Tertiary education attainment ranks high when compared in South Euclea but lags behind other Euclean nations, standing between 25% and 30% depending on different age gaps.
Energy and telecommunications

The production of power in Piraea is dominated by the semi-privatised EDE S.A. (Εθνικό Δίκτυο Ενέργειας), which handle most of the energy network, its production and distribution in Piraea. It is one of the few ares in which the state maintains an active influence in order to handle concessions, act as mediator between third companies or lower prices. Energy production benefits from the geographical position of Piraea, which translates in a great use of renewable resources; solar power accounts for 7% of the total energy mix, while hydroelectric dams and wind power represented 31% combined, with the rest being divided with other non-polluting sources (like nuclear energy) and a small percentage of coal and other fossils. Since 1993, the Zakhaz Seredny pipeline provides Piraea with Soravian natural gas.
Piraea's telecommunication sector was liberalised during the late 1990s and early 2000s, eliminating the monopolistic condition of the previously state-owned company and allowing competition. The sector is overseen by the National Authority for Telecommunications and counts with a very high internet and cell-phone penetration, which reach most of the territory. Broadband has also seen a enormous increase in the last 10 years, owed in part to aggressive optical fiber development.
Transport and infrastructure
During the late 1970s and 1980s, Piraea underwent several modernisations on its road networks and transport capacity aimed to put the country on a comparable rank with its other Euclean counterparts. The country has a well expanded and robust motorways (Αυτοκινητόδρομοι) and national roads (Εθνικές Οδοί) network, which are connected to neighbouring nations in different points and provides the country with easy links; most of these tend to be concentrated in the metropolitan area of Alikianos, the Souda Riviera and Sitia, where the most populated centres are found. Major motorways in Piraea are usually privately managed through concessions. The axis of the network is usually attributed to the A1 and A2, which are part of the Euclean road network.
Piraea's railway network is sufficiently expanded through the territory with a varied offer of intercity railways. From Alikianos Kentro, and connected with the rest of the continent, Piraea has an electrified high-speed railway network operated by Trena Piraea. Piraea is serviced by two international airports, the Ioannis Apostolou International Airport in Alikanos and the Hersonissos-Salicea Airport; Alikianos is the largest and busiest of the country, having handled in 2020 some 24.8 million passengers, and is considered a crucial airport in the South Euclea region. Hersonissos-Salicea offers mostly seasonal services during summer to Rahelian and Euclean destinations. Nevertheless, the country is well connected with most of Euclea and Coius; Piraea's flag-carrier, _, is the largest airline and counts with several destinations across the region from its hub airport in Alikianos.
Demographics
Religion
Largest cities
| Rank | Name | Province | Pop. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Alikianos  Kissamos |
1 | Alikianos | Souda Riviera | 1,380,508 |  Hersonissos  Tylissos | ||||
| 2 | Kissamos | Souda Riviera | 324,676 | ||||||
| 3 | Hersonissos | Sitia | 267,121 | ||||||
| 4 | Tylissos | Souda Riviera | 144,046 | ||||||
| 5 | Voula | Foinikas | 120,833 | ||||||
| 6 | Rouvas | Sitia | 96,157 | ||||||
| 7 | Gorgolainis | Foinikas | 82,921 | ||||||
| 8 | [[]] | [[]] | |||||||
| 9 | [[]] | [[]] | |||||||
| 10 | [[]] | [[]] | |||||||
Education
Healthcare
Culture
Architecture
Art
Media

Piraea's public and cultural life are marked by a varied but long standing tradition of paper press. Although heavily restricted during the period of the Second Republic, the constitution of the Third Piraean Republic enshrines press freedom and is committed to protect it from any threat; as such, Piraea has continuously ranked high in press freedom regionally and journalists face little censorship. In 2020, the newspapers with the largest circulation were O Kosmos (newspaper of record generally aligned with the centre-left), Dimokratia (centre-right) and Express (liberal economic newspaper); there are also important newspapers focused in specific issues, Ole (landmark sports newspaper) and political parties usually count with their own outlets. Similarly, newspapers generally count with their magazines.
Cable or satellite TV is well expanded throughout the territory of Piraea, which makes it a valuable market in South Euclea. The country's state-broadcaster, Piraean Radio and Television (Πειραιηκή Ραδιοφωνία Τηλεόραση; PRT), is the most viewed television broadcaster and counts with a dominant position in the radio market with its four three television channels and two radios leading prime times every year; it is a member of the Euclean Union of Broadcasting.
Sports