Lavana: Difference between revisions
| (126 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Region icon Kylaris}} | {{Region icon Kylaris}} | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = People's Republic of Lavana | |conventional_long_name = People's Republic of Lavana | ||
|native_name = ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາຊົນລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ <!--Country's name (usually full name) in its native language, hence in italics (double quotemarks)--> | |native_name = ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາຊົນລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ<br>''Javunganiboga''<br>''Bügd Nairamdakh Lavana Uls''<br>''Lavana Xalıq Respwblïkası''<br>''République Populaire de Lavana'' <!--Country's name (usually full name) in its native language, hence in italics (double quotemarks)--> | ||
|common_name = Lavana <!--Common name in English (used for wikilinks and to produce a default iso3166 code)--> | |common_name = Lavana <!--Common name in English (used for wikilinks and to produce a default iso3166 code)--> | ||
|image_flag = | |image_flag = | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|alt_coat = | |alt_coat = | ||
|symbol_type = Seal | |symbol_type = Seal | ||
|national_motto = "ຈາກແມ່ນ້ ຳ ທີ່ຍິ່ງໃຫຍ່" ''"From the Mighty Rivers"''<!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | |national_motto = "ຈາກແມ່ນ້ ຳ ທີ່ຍິ່ງໃຫຍ່"<br> | ||
|national_anthem = {{wp|The_Red_Sun|ດວງຕາເວັນແດງຂອງລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ (The Red Sun of Lavana)}}<br>[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OjNpRbNdR7E|200px]] | ''"From the Mighty Rivers"''<!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|national_anthem = {{wp|The_Red_Sun|ດວງຕາເວັນແດງຂອງລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ <br>(The Red Sun of Lavana)}}<br>[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OjNpRbNdR7E|200px]] | |||
|image_map = Location of Lavana.png | |image_map = Location of Lavana.png | ||
|map_width = 275px | |map_width = 275px | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|capital = [[Pers]] <!--Name of country/territory's capital, wikilinked if link exists--> | |capital = [[Pers]] <!--Name of country/territory's capital, wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|largest_city = [[Pers]] <!--Name of country/territory's largest city. Use "capital" (without quotemarks) if it's the capital.--> | |largest_city = [[Pers]] <!--Name of country/territory's largest city. Use "capital" (without quotemarks) if it's the capital.--> | ||
|national_languages = {{wp|Lao_language| | |national_languages = {{wp|Lao_language|Kachai}}<br/> | ||
|ethnic_groups = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lao_people| | [[Ziba]]<br/> | ||
[[ | {{wp|Mongolian_language|Ukilen}}<br/> | ||
{{wp| | {{wp|Kazakh_language|Majgars}}<br/> | ||
{{wp| | {{wp|French_language|Gaullican}}<br/> | ||
|ethnic_groups = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lao_people|Kachai}} 52% <br/> | |||
[[Ziba|Dhavoni]] 21% <br/> | |||
{{wp|Mongols|Ukilen}} 11%<br/> | |||
{{wp|Kazakhs|Majgars}} 9%<br/> | |||
{{wp|Malaysian_Malay|Male}} 3%<br/> | |||
{{wp|Azerbaijanis|Kiziks}} 2%<br/> | |||
Other 2%<br/> | |||
|religion = | |religion = | ||
[[Badi]] | [[Badi]] 56% <br/> | ||
{{wp|Irreligion}} | {{wp|Irreligion}} 21%<br/> | ||
[[Solarian Catholic Church]] | [[Solarian Catholic Church]] 12%<br/> | ||
Other | [[Irfan]] 10% <br/> | ||
Other 1%<br/> | |||
|demonym = Lavanan <!--Term/s describing those associated with the country/territory (e.g. "Belgian" for the country Belgium)--> | |demonym = Lavanan <!--Term/s describing those associated with the country/territory (e.g. "Belgian" for the country Belgium)--> | ||
|government_type = Council | |government_type = [[Council republic]] <!--(often a compound multi-wikilinked term, e.g. "Federal semi-presidential constitutional republic", etc)--> | ||
|leader_title1 = Premier | |leader_title1 = [[Premier of Lavana|Premier]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[ | |leader_name1 = [[Emmanuel Bakhtzhany]] | ||
|leader_title2 = Vice-Premier | |leader_title2 = Vice-Premier | ||
|leader_name2 = [[Trang Dong]] | |leader_name2 = [[Trang Dong]] | ||
|legislature = [[ | |legislature = [[Congress of Lavana]] | ||
|established_event1 = Establishment of the Republic of Lavana | |||
|established_date1 = 1940 | |||
|established_event1 = | |established_event2 = Establishment of the People's Republic of Lavana | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date2 = 1960 | ||
|established_event2 | |area = | ||
|area_km2 = 731,189 | |||
| | |||
|area = | |||
|area_km2 = | |||
|population_estimate = | |population_estimate = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = {{increase}} 135,022,931 | ||
|population_census_year = 2020 | |population_census_year = 2020 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 189 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $1.920 trillion | |GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $1.920 trillion | ||
|GDP_PPP_rank = | |GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
|GDP_PPP_year = 2020 | |GDP_PPP_year = 2020 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $ | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $14,220 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $640.2 billion | |GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $640.2 billion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2020 | |GDP_nominal_year = 2020 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $ | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $4,740 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|HDI = | |HDI = 0.806 | ||
|HDI_year = 2020 | |HDI_year = 2020 | ||
|currency = Lavanan | |currency = Lavanan dunan ({{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_4217|LAD}}) | ||
|time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | |time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | ||
|date_format = dd-mm-yyyy | |||
|date_format = dd-mm-yyyy | |drives_on = Right | ||
|drives_on = Right | |cctld = .la | ||
|cctld = . | |calling_code = [[+420]] | ||
|calling_code = [[+420]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Lavana''' ({{wp|Lao_language| | '''Lavana''' ({{wp|Lao_language|Kachai}}:ລະຫວ່າແ, Lavanga; [[Ziba]] Javunga ) officially the '''People's Republic of Lavana''' ({{wp|Lao_language|Kachai}}:ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາຊົນລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ, Sathalanalad Pasasonlad Lavanga; [[Ziba]] Javunganiboga) is a sovereign state in [[Southeast Coius|Southeastern Coius]]. It borders [[Dezevau]] to the north, the Brown Sea to the east, [[Hacyinia]], and the {{wp|Diplomatic recognition|unrecognised breakaway socialist state}} of the [[Yoloten]] to the west, and tbd to the south. With a total area of 731,189 km2, and population of 135 million people, it is one of the largest countries by population in the world. Its capital and largest city is [[Pers]], which is also the country's economic, political and cultural centre. It stands besides the city of Ban Sao which was the historical center of government of several empires in the region | ||
Inhabited since antiquity | Inhabited since antiquity, agriculture and language was brought by [[Ziba]] speaking settlers from [[Dezevau]], which utilized wide river system to establish centers of trade and the establishment of the first city states in the inland regions. The city states would eventually band together in various federations and empires usually centered on the centrally located city of Zebedize and Jaudau Sao (modern Pers) from which the Sasuanan empire began emanating power and influence from the 4th century BCE onwards. The Sasuanan Empire established the tradition of a centrally located aristocracy and center of power centralized on a Sao comparable to an emperor, such traditions would continue for several centuries. The {{wp|Lao_people|Kachais}} originally from the areas surrounding modern day [[Kuthina]] would begin their migration around the 8th century CE with many finding their ways as mercenaries towards the warring factions following the collapse of the Zibinego empire, Kachai influence would reach its highest point when aristocrats and military leaders of Kachai descent would establish a Kachai king during the reign of the Damrog Empire in the 11th century. Kachais would settle in the east and centre of the country. Weakening Damrog Empire influence and power would result in the rise the [[Aguda Empire]] in southern Dezevau and Northern Lavana, from former Damrog holdings which would grow onto control most of Southeast Coius. | ||
The arrival of [[Euclea|Eucleans]] mainly[[Gaullica | The Aguda Empire would reach its apex in the 16th century when it held vast influence and land throughout Coius, the arrival of [[Euclea|Eucleans]] mainly [[Gaullica]]ns into the region began a slow decline as foreign influences weakened its internal structure. Where at points the Agudan Empire existed solely on paper while entities such as the [[Saint Bermude's Company]] from Gaullica managed the lands of the former Agudans as colonial holdings. Eventually the [[Bureau for Southeast Coius]] would manage a variety of breakaway puppet states in the former Agudan territories. Following the defeat of Gaullica in the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], the Bureau would be managed by [[Estmere]]. Suffering from growing costs and resistance, Estmere would [[Partition_of_Southeast_Coius|partition]] the bureau in 1940. Lavana became a democratic republic however internal strife, and tensions with its neighbors would result in Lavana undergoing a revolution in 1959-1961 that would result in the establishment of the {{wp|One-party state}} People's Republic under the [[Lavanan Section of the Workers International]]. | ||
Lavana would integrate into the international socialist movements alongside it's two close Socialist neighbors in Dezevau and [[South Kabu]] founding the [[Brown Sea Community]] | Lavana holds large ethnic minorities in the country primarily [[Dhavoni]], {{wp|Mongols|Ukilen}} and {{wp|Kazakhs|Majgar}} minorities in the north, and west of the country. These populations historically marginalized by the central Kachai government, were in involved in a series of uprisings, insurgencies, and conflict between Lavanas central government, its minorities, and foreign states such as [[Hacyinian-Lavanan wars and conflicts|Hacyinia]]. This conflict reached its greatest point when on 1992, Lavana invaded Hacyinia establishing the [[Yoloten|People's Republic of Yoloten]]. The backlash from this conflict, and foreign toppling of Socialist governments caused Lavana to undergo its own reforms in 1994, which established a more liberal socialist state. Today Lavana is considered a liberal and developing socialist country, although it still struggles with corruption, and censorship. | ||
Lavana would integrate into the international socialist movements alongside it's two close Socialist neighbors in Dezevau and [[South Kabu]] founding the [[Brown Sea Community]] 1981. The country today is a developing economy, with close ties to it's Northern neighbor and other socialist states, the government has followed the trend of liberalization and opening up which followed after decline of Socialist countries in the 1980's and 90's. It has been a member of the [[Association for International Socialism|AIS]] since its inception in 1980. On March 6th 2022, it underwent a violent [[2022 Lavana coup d'état|coup]], along in [[2022 Hacyinia-Lavana war|2022]] Lavana would invade Hacyinia, sparking tensions in the region. | |||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
The term originates from the | The term '''Lavanga''' (Lavana in {{wp|English Language|Estmerish}}) originates from the Kachai combination of between '''lavang (ລະຫວ່າງ)''' and river '''aemn am (ແມ່ນ້ ຳ)''', thus Lavana means "between rivers" in the Kachai language. The term gained traction in the 11th and 12th centuries, as the territories inhabited by the Kachais which were marked as being between the Siadng and Kalani rivers. The term never entered official use, but was returned to public conscience in the establishment of the [[Lavanan Section of the Workers International]], and the [[Confederation of Free Lavana]] in the 1910's. These groups had exclusive Kachai membership, and thus why they used an exclusively Kachai term. Kachai's successfully established that Lavana referred to the land between the Siadng and Kalani rivers, which now are the borders of the modern state. The term was chosen as the Kachai refused to use a Ziba name, as they were the majority in the new country. | ||
Prior to the arrival of the Kachai, the region of modern Lavana and southern Dezevau was known as "Dhabovozuigi" in Ziba, which translates to southern fountain/centre/capital. This term was used to refer to the lowlands south of the Zedenge valley, and ending near the Kalani river. It also makes reference to the more centralized states that emanated from Zebedize and Jaudau Sao, modern Pers. The meaning of fountain also makes emphasis on the rivers of the region. The direct translation of Dhabovozuigi in Kachai is ສູນພາກໃຕ້ (Sunphakta), and was the name used by early Kachai settlers until the 10th century CE, when Lavana became more favored to represent the Kachai populations which had settled between the Siadng and the Kalani rivers. The term fell out of favor during the Aguda Empire. | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
{{main|History of Lavana}} | |||
=== Pre-history === | === Pre-history === | ||
{{sidebar | {{sidebar | ||
| Line 97: | Line 106: | ||
| row1style=background-color:#eee; vertical-align:bottom; | | row1style=background-color:#eee; vertical-align:bottom; | ||
| [[File:Angkor - Prasat Kravan.jpg|150px|Lavanan temple to the 20 sisters]]<br>[[File:ThangLong-KeCho.jpg|150px|Dabadonga in the 16th century]] | | [[File:Angkor - Prasat Kravan.jpg|150px|Lavanan temple to the 20 sisters]]<br>[[File:ThangLong-KeCho.jpg|150px|Dabadonga in the 16th century]] | ||
| [[File:Cổng trái Đoan Môn, Hoàng thành Thăng Long, Hà Nội 001.JPG|150px| | | [[File:Cổng trái Đoan Môn, Hoàng thành Thăng Long, Hà Nội 001.JPG|150px|Ban Sao]]<br>[[File:Vientianne1973.jpg|150px|Socialist forces entering Pers]] | ||
| Ancient Lavana | prehistory-9th century BCE | | Ancient Lavana | prehistory-9th century BCE | ||
| Duh Hoc Culture and early Lavanan city states | 9th century- | | Duh Hoc Culture and early Lavanan city states | 9th century BCE-33 CE | ||
| | | Sayak Dynasty | 33-109 CE | ||
| | | Dhijivodhi Empire | 109-470 CE | ||
| Warring Kingdoms period | | | Zibinego Kingdom | 470-763 CE | ||
| | | Warring Kingdoms period | 763-875 CE | ||
| | | Gevuine Empire | 875-1272 CE | ||
| Rasuvong Empire | 1272-1495 CE | |||
| [[Aguda Empire]] | 1476-1886 CE | | [[Aguda Empire]] | 1476-1886 CE | ||
| | | [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] colonial control | 1820-1935 CE | ||
| Republic of Lavana| | | [[Estmere|Estmerish]] colonial control | 1935-1940 CE | ||
| People's Republic of Lavana | | | Republic of Lavana| 1940-1960 CE | ||
| Lavanan civil War| 1959-1961 CE | |||
| People's Republic of Lavana | 1960-Present}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:Ebene der Tonkrüge Laos.JPG|thumb|left|Jars from the Duh Hoc | [[File:Ebene der Tonkrüge Laos.JPG|thumb|left|Jars from the Duh Hoc civilization]] | ||
Lavanan pre-history can trace itself to | Lavanan pre-history can trace itself to migrating {{wp|Hunter-gatherer|Hunter gatherers}} which hunted various animals in the fertile regions of Lavana, where ample grazing areas for animals was present. Archaelogical evidence shows use of early-prehistoric bone {{wp|tools}} almost 1 million years ago, and other discoveries such as fossilized teeth to 125,000–80,000 years ago. The discovery of {{wp|agriculture}} can trace its origins to [[Dezevau]], rice was the primary crop grown in the numerous fertile rivers and remains to this day its most important. The Duh-Hoc {{wp|civilization}} is the earliest settled society in Lavana with a written record, the Duh-Hoc society is believed to have been first established in the 9th century B.C.E. along the banks of the Siadng river, this civilization utilized the vast waterways for communication and trade. They're most well known for their jars, which have been suspected to serve a ceremonial purpose, many jars have been found holding possessions along with the remains of individuals, which could show early {{wp|Funeral|funerary rites}}. To ensure the free and safe passage of trade and goods, fortified settlements were constructed alongside rivers to defend them, along with the collection of {{wp|taxes}} in the form of rice. Early texts describe this system of taxation. | ||
=== | |||
The Duh-Hoc civilization experienced an eventual fragmentation as it spread throughout the land, eventually numerous {{wp|City-state}}s would be established around the 8th-6th centuries BCE, a trend that would continue through the regions history. The Sao, was a titled designated to the leader of a city state, and was commonly associated with someone of minimal control outside of city walls, the term grew in significance throughout the ages, and its meaning was replaced and adapted. During this time as well, the {{wp|Austronesian_peoples#Migration_and_dispersion|!Austronesian migrations}}, which date from the 8th through 4th century BCE, originated from the South of Coius around [[Kuthina]]. They settled primarily in the coasts of the country and established well connected wealthy coastal cities, which usually demanded {{wp|tribute}} from upstream cities to access their vast rudimentary trading network. War was common for this early societies, and numerous conflicts were fought for control of farmland, access to bodies of water, and trading routes. Cultural differences were observed in the early Dhavoni society in Lavana, which unlike modern belief remained a vastly diverse group, only united in a similar {{wp|Writing_system|writing system}}. During this time many {{wp|Animism|animist}} beliefs were held throughout the land, many texts survive telling of rituals and ceremonies in early Lavana, construction of temples was also commonplace. | |||
=== Rising power and Sayak Dynasty (3rd Century B.C.E-109 C.E.) === | |||
At the start of the 3rd century BCE, 3 major city-states became centers of powers in the region, Jaudau Sao, Dezenhua, and Bouna. These 3 cities maintained vast relationships with smaller city-states and principalities. The most prominent of these centers of powers was Jaudau Sao which controlled most trade coming in from the west of the region through the numerous tributaries of the Kung river. These cities avoided direct conflict do to the loose relationships that were maintained with principalities, which in some instances paid tribute to multiple entities. [[Ziba#Old_Ziba|Old Ziba]] is expected to have been introduced in the 1st century CE, as a {[wp|Prestige_(sociolinguistics)|prestige language}} in noble courts. | |||
[[File:Han Dynasty ceramic prancing horse.jpg|thumb|right|Ceramic horses depicting Ashinan horses]] | |||
Around the 1st century BCE, Jaudau Sao began employing the services of {{wp|Xiongnu|Ashinan}} mercenaries, to enforce greater control over their neighbors and rivals. Jaudau Sao came to rely on these {{wp|Turkic_peoples|Proto-Oroqic}} groups for warfare, and internal security. The term of Sao began to be used as a sign of ranking on the King of the 3 major city states. Charismatic and well connected Sao's in Jaudau Sao ensured the cities dominance over its rival peers during the 1st century BCE. Declining influence on the 1st century CE however would result in great instability for Jaudau Sao, which would result in Lao Va the leader of a band of Ashinan mercenaries to seize control of Jaudau Sao and establish the Sayak Dynasty on 33 CE. | |||
The Sayak Dynasty coincided with an increase in violence, as the Sayak's sought to dominate by whichever way possible their rivals, and expand influence. Infighting among the Sao and his Ashinan counterparts would result in internal instability, finally culminating in general anarchy and conflict between 50 CE and 97 CE. During this period numerous warlords arose and carved petty kingdoms, with differing levels of centralization. This period would end when Pae Halin was crowned as Sao, establishing the Dhijivodhi empire with the Dhijivodhi dynasty at its head in 109 CE on the city of Jaudau Sao, which now attempted to enact greater territorial control over the other major centers of power. | |||
=== Dhijivodhi empire (109-470)=== | |||
=== Zibinego kingdom (470-763)=== | |||
=== | Burning of Jaudau Sao in 763 | ||
=== Aguda Empire (1476-1886)=== | |||
=== Colonialism (1820-1940)=== | |||
Growing [[Gaullica]]n control over the Aguda Empire, coincided with dwindling commercial prospects in the major cities of the Kung river. Gaullican authorities favored coastal trading cities, and resource exploitation everywhere else. The 3 cities of Zebedize, Jaudau Sao, and Khaimuk suffered significant depopulation between 1820 and 1880, losing up to an estimated 400,000 people. The coastal cities of Dezebenhua and Ban Vuga swelled in population, although the vast majority of urban regions suffered widespread emigration. Ziba increasingly became sidelined by colonial authorities who encouraged Kachai populations to utilize Kachai as the language of administration alongside {{wp|French Language|Gaullican}}. | |||
=== Independence (1940-1959)=== | |||
On October 3rd 1940, the Republic of Lavana came into existence following the first part of the [[Partition of Southeast Coius]], which divided the territories of both former Gaullican and Estmerish territories in Southeast Coius. In a bid to reduce of influence of Socialist Dezevau, and establish a strong anti-Socialist state, the Republic of Lavana was made independent 3 months before the rest of the region was. Lavana was to negotiate independently with Hacyinia for territory exchanges, and migration agreements, along with the numerous Zejas that now existed in the territory. Hacyinia unable to obtain a favorable agreement that granted it control of the Oroqic lands now under Lavanan control, proceeded to invade Lavana on October 21st 1940 in the [[Hacyinian-Lavanan_wars_and_conflicts#First_Galshir_Conflict_.281940.29|First Galshir war]], where Lavana lost 1/3 of its country to Hacyinia. During this time, the Lavanan government struggled under the weight of migrations out of Dezevau, internal infighting, general inability of its government and armed forces to defend Lavana both from Hacyinia and an expected Dezevauni invasion. The invasion of Lavana would mark the highest extent of Hacyinia, and to this day is claimed by that country, it began the [[Hacyinian-Lavanan_wars_and_conflicts|Hacyinian-Lavanan conflicts]] which continue to this day. | |||
[[ | |||
The end of the government was spelled in the increasing unpopularity of the Anti-Socialist coalition led by Nayaga Nurzhavong, with the centrist opposition, and Leftist coalitions strongly positioned in the upcoming elections. At the end of 1958, both the SDP, and NDP had lost support for Nurzhavong, and sought to form a majority government with the Centrist opposition with one of the two at the head, following an expected negative result for the FLC. Election night on March 1st, 1959 however came with extreme surprises as rural support for the LSWI ensured that the party would be the largest in Congress. The results sparked chaos in the ruling coalition and opposition at the face of a minority LSWI led government, although the FLC, SDP, and NDP agreed to a SDP led coalition government they could not obtain sufficient votes a 2/3 majority, to overturn the granting of government making powers to the LSWI, which was automatically done to the largest party. Nurzhavong along with Supreme Army General Oke Syrypanha, agreed that the LSWI could not be allowed to form a government, along with support from the President, and the SDP. Nurzhavong who was still Premier suspended the constitution and established martial law, in the hopes of arresting most of the LSWI top leadership inside Pers, as Army units rushed into the city and police blocked all entry and exit ways of the capital on March 13th, 1959. The plan however had been leaked and numerous LSWI leaders including Goube had escaped. | |||
=== Civil War (1959-1961) === | |||
[[File:An ARVN outpost on the My Chanh Line, May 1972.jpg|thumb|right|Army outpost outside Dezebenhua, 1959]] | |||
Looking to prevent the rise of a LSWI government. The military and ruling government conducted a coup attempt on July 11, 1959. The coup attempt failed, allowing LSWI leaders and commanders to exit Pers, with Goube establishing a government in the northern city of Zadou that LSWI had taken. Moderate members of the government moved to the LSWI, and internationally Goube presented himself as leading the legitimately elected government. LSWI forces enjoyed support from [[Dezevau]], [[Valduvia]], and [[Chistovodia]], in the form of manpower, trainers, and equipment. LSWI forces were trained in Dezevau, and equipped before crossing the border. | |||
LSWI forces quickly secured the northern provinces, but were unable to secure major city centers such as Dezebenhua, and Dabadonga. With LSWI forces struggling to overcome Republican resistance. Hacyinian forces were involved in providing aid to the Republican forces, and LSWI fears of sudden invasion by Hacyinian forces were prominent. After LSWI forces were unable to storm Dezebenhua on October 1959, Dezevauni regulars entered the country. A major offensive on December 1949 resulted in the surrender of Dabadonga and all territory north of the Siadng although Dezebenhua evaded LSWI forces during the entire war. LSWI forces made thorough progress south of the country, and by June 1960 had reached Pers. LSWI forces stormed the city in July and August, before Republican forces abandoned the city. Republican forces having stopped LSWI forces on Pers, conducted a major offensive during November-January 1961, that culminated in massive losses for the LSWI, however Republican resources had been exhausted. After a period of rest, and Republican infighting, LSWI forces conducted a major offensive overwhelming Republican forces, retaking Pers in September. Republican forces began negotiating for the end of the war. | |||
=== People's Republic (1961-1970) === | |||
[[File:Mao Proclaiming New China.JPG|thumb|right|Goube proclaiming the People's Republic of Lavana]] | |||
Goube declared the People's Republic of Lavana, and declared it a one-party state, ending the multiparty coalition of leftist and Worker International parties in the country. Goube reformed numerous aspects of the Lavanan Congress, primarily the reduction in freedom of the body, and scope. Elections were no longer free and open, and instead citizens voted on single candidate races. The Congress of the LSWI was established as a parallel structure to the Lavanan Congress, which allowed inner party politics to remain inside the confines of the party. Goube quickly entered the International Socialist order, and foreign specialists arrived to the country. | |||
[[File:Hanoi, The uprising on August 19, 1945.jpg|thumb|right|Storming of the Presidential residence by civilians in 1959]] | |||
=== 1970's === | |||
=== 1990's === | |||
[[File:KNLA medic treating displaced civilians (Steve Sandford-VOA).jpg|thumb|right|Medical care provided to refugees displaced by the [[Yoloten|Yoloten Conflict]]]] | |||
Tensions between Lavana and Hacyinia remained high as Lavanan support for Ukilen and Majgar Workers International increased. On December 1991, 32 Ukilen soldiers trained inside Lavana were arrested trying to enter Hacyinia, leading to a diplomatic spat between both nations, with Hacyinia shelling Lavanan border crossing throughout the month. Dezevau had become increasingly worried about the situation in Hacyinia and worried that Lavana might launch a full scale invasion of the country, and stated that they would not support an invasion. Inthavongsa frustrated with Dezevauni reluctance and with limited support at home, refrained from invading Hacyinia but shelling between both sides continued until February its longest period since 1986. In the town of Shieli near the Lavanan border, Majgar insurgents were cornered and shelled throughout March and April, with large civilian populations unable to leave the town. Fearing heavy casualties in retaking the town, Hacyinian forces used {{wp|Sarin}} gas to dislodge the defenders. The attack left 300 insurgents dead and 500 civilians killed after the Sarin was accidentally dropped on a civilian hospital. Inthavongsa quickly used the attack as a justification to mobilize the armed forces and to shore up support from Dezevau, which agreed to not oppose Lavanan intervention in Hacyinia. | |||
Pers Acts 1994 reforms | |||
=== 2000's === | |||
=== | === 2010's === | ||
=== | |||
[[File:ThuyDienSonLa2010.JPG|thumb|right|Lav San Dam under construction in 2010]] | [[File:ThuyDienSonLa2010.JPG|thumb|right|Lav San Dam under construction in 2010]] | ||
The need of further electricity for Lavana, and further expanding it's energy diversity the Lavanan | The need of further electricity for Lavana, and further expanding it's energy diversity the Lavanan Congress approved in 2004 a wide variety of projects including the construction of along with numerous other projects including 4 nuclear reactors, and 2 wind farms but most prominently a dam in the Lav San river in the north of the country, which had been marked for possible hydroelectric potential in a study in 1994. The dam began construction in 2005, with help from Dezevau, the dam finished building in 2014, becoming the largest dam in Southeast Coius. | ||
On November 11th, 2019 Premier Loe Vatthana died of a heart attack, and was succeeded by Vice-Premier [[Laina Keomany]]. | |||
=== 2022 Lavana coup d'état and aftermath === | |||
{{Main|2022 Lavana coup d'état}} | |||
Following Vatthanas death in 2019, Keomany became Premier and initially crashed with General Secretary of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International who holds power over the democratically elected government and is directly solely by the party elite and its members. Keomany attacked Goubist faction members, and was seen as a threat against the old guard of the party. Khudu Narinamoa was elected on 2020 as General Secretary to counter Keomany as both of them were connected through the marriage of immediate family. The connection was abruptly ended by the death of Vinliam Keomany, Lainas Grandson on October, fearing renewed interest by Keomany to challenge the old guard he approved new election rules which would had given the party elite greater power to elect his position.<ref name="November 7">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=39369347#p39369347 |work=[[Coius|Coius Monitor]] |title=Proposed party election changes in Lavana, and what it means for the country. |date=7 December 2021 |access-date=14 March 2022}}</ref> The Reform faction increasingly began challenging and attacking the Goubists for such a move, and the election of Narinamoa was expected on March 1st, he quickly replaced key Keomany allies and sought to cripple her power in the party. Military movements throughout the country in the leadup to the election were noted in foreign press.<ref name="Rizealand Military News">{{cite news |url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Rizealand |work=[[Rizealand|Foreign Affairs of the World]] |title=Abnormal military movements reported in Lavana, possible coup? |date=6 March 2022 |access-date=14 March 2022}}</ref> | |||
On March 6th 2022, Khudu Narinamoa [[General Secretary of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International]] legally removed Premier Laina Keomany from her position and appointed a replacement Premier. The move was seen as a coup, and Keomany called on the army and people to defend Lavanan democracy citing the removal as illegal, and launched a countercoup. Soldiers loyal to the central government and Keomany fought throughout Lavana, primarily in Pers where large scale fighting and civil protest took place. Keomany was able to elude capture and with sizeable military and civilian casualties throughout the country, Narinamoa surrendered on the 7th of March after coup forces penetrated into Pers. Sporadic fighting continued until the 9th. The coup left about 1,000 soldiers and civilians dead throughout the country.<ref name="">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?f=4&t=418954&start=2200 |work=[[Coius|Coius Monitor]] |title=Lavanan Government releases new casualty figures following coup |date=14 March 2022 |access-date=13 August 2022}}</ref> | |||
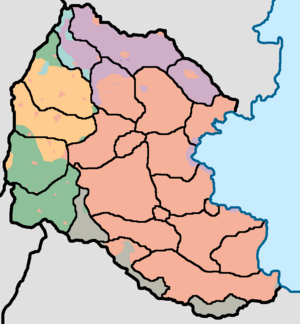
[[File:Provincial Map of ethnics in Lavana.png|thumb|right|Lavana adopted a new constitution on October 2022, expanding the number of provinces in the country up to 24. To better represent minorities.]] | |||
Keomany called the coup a vile attempt to remove democracy from Lavana, and stated that [[Champania]] had supported Narinamoa on his coup attempt. Keomany took on the role of General Secretary, and published lists of individuals which were connected to Narinamoa and the coup. About 38,941 were detained of which 30,159 were arrested on numerous crimes such as {{wp|treason}}, {{wp|corruption}}, and {{wp|Espionage}} in total 98,291 government officials and workers were suspended or fired over their role in the coup.<ref name="Government suspended arrested">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=39430366#p39430366 |work=[[Lavana|Paper of the Lavanan Worker]] |title=phak pheu cha kamchad khon thola nyod |trans-title=Party to be rid of traitors |date=13 March 2022 |access-date=13 August 2022}}</ref> The LSWI and the Lavanan Congress had hundreds of high ranking members removed from power and arrested. Over 300 members of the Lavanan Congress were removed, and Keomany appointed allies to the vacant seats using emergency powers given by herself by announcing a 3 month emergency period. Which she used to approve a temporary new constitution giving her position increased powers, and removing any possible attempt by the party to remove her from the position. The ability to deeply reform the Lavanan state, including several rules to allow for Democratic elections were also included in the constitution.<ref name="March 13">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=39439889#p39439889 |work=[[Coius|Coius Monitor]] |title=Keomany announces new constitutional changes. |date=13 March 2022 |access-date=14 March 2022}}</ref> Keomany stated her intentions to reform Lavana to be a more fair and democratic country, announcing the first multiparty elections since 1959. <ref name="Coian Monitor Interview">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=39514259#p39514259 |work=[[Coius|Coius Monitor]] |title=Exclusive interview with Lavanan Premier Laina Keomany |date=10 April 2022 |access-date=13 August 2022}}</ref> Keomany ran on a platform of deeply reforming the Lavanan state, and expanding the rights of minorities to defend and uphold their cultural values. [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Elections]] were held on September 1st 2022, with the LSWI establishing a minority led government with several other parties. On October 7th, 2022 a new constitution was permanently voted on and entered into force on October 1st of that year. | |||
On October 1st a {{wp|car bomb}} outside the [[Pers|Mei Phong Mall car bomb attack]] in central Pers, detonated.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Deadly blast in Lavana threatens stability in the region.|url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=40001395#p40001395 |newspaper=[[Vinalia|Free Press]] |date=1 October 2022 |access-date=25 October 2022|first=Mariya|last=Nazarivna}}</ref>killing 26 people and injuring 33. Shelling in the breakaway republic of the Yoloten, by Pro-Hacyinian militias was alo reported. Lavana claimed that Hacyinia had violated the 2004 agreement by failing to properly deal with militias in the demilitarized zone separating the Hacyinian army and the PAMFY, which had launched the attacks. <ref>{{Cite news |title=Hacyinian diplomats meet with Lavanan Premier|url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=40002198#p40002198 |newspaper=[[Coius|Coian Monitor]] |date=2 October 2022 |access-date=25 October 2022}}</ref> This prompted Lavana to begin building up troops alongside its border with Hacyinia and the Yoloten. On November 8th, Lavana [[2022 Hacyinia-Lavana war|invaded]] Hacyinia and moved troops into the Yoloten, kickstarting the [[2022 Hacyinia-Lavana war|Second Yoloten war]]. It sought to prevent further border incursions and defend the Yoloten from foreign incursions. Lavana made mention of imminent terrorists attack on Lavana utilizing Chemical weapons but this has been contested internationally. Following the announcement of a ceasefire on November 18th, as a result [[2022 Lavanan protests|anti-government protests in Lavana]] begun, leading to the resignation of Premier Laina Keomany, and the confirmation of former Minister of Economy [[Emmanuel Bakhtzhany]]. | |||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
[[File:Geographic Map of Lavana.png|thumb|right|Geographic Map of Lavana]] | [[File:Geographic Map of Lavana.png|thumb|right|Geographic Map of Lavana]] | ||
Lavana | Lavana is located between {{wp|Latitude|latitudes}} 7° and 17°S, and {{wp|Longitude|longitudes}} 59° and 83°W in the eastern portion of Coius. It borders Dezevau to the north, the Brown Sea to the east of the country, X to the south, Hacyinia and the Yoloten to the west of the country. Lavanas total area is 731,189 km2 (282,313 sq mi), making it a relatively large country in the world, Lavana has a long coastline with the Brown sea holding sovereignty over several islands, however most of these are small islands off the coast. | ||
[[ | |||
Lavanas borders mostly stem historical precedent which defined the nation of the Kachais from the Siadng river in the north and the Kalani river to the south, with most of its western border a result of colonial rule which defined the border without taking into account the ethnic makeup of the area. Its Northern border was the subject of much controversy during the partition of the Aguda Empire and the latter independence of Lavana and Dezevau, both nations have since defined the border. Although the greatest controversy stems from the border of Lavana with Hacyinia. Currently Lavana recognizes the modern border as their defacto borders, while Hacyinia claims the borders following the 1940 Galshir War. | |||
<gallery mode=packed heights= | |||
File: | Lavana is a relatively flat country with mountainous and hilly regions to the north and west of the country, the Gezije range defines most of the northwest of the country where its mountainous territory spills between both Lavana and Dezevau. The Gezije ranges gives way to hilly regions to the west of the country called the Nayzabeler which eventually give way to the steppe reminiscent of the [[Great Steppe]], powerful rivers traverse the southwest corner of the country eventually drain into the Ikaika lake, the Kung and Phankham rivers originate west of the Nayzabelers. To the east of the Gezije the Zedenge valley along the Siadng river gives way near the coast to remnants of Bouvai Massif stretching from Dezevau. The rest of the country is relatively flat with vast rivers the most prominent of which is the Kung river transversing the land. The Kung river water basin covers large parts of the country and has served the role of the central artery to civilization in Lavana since ancient times, large sections of arable land can be found to its sides and the seasonal flooding of the Kung river has provided ample nutrients to agricultural operations for centuries. Most of Lavana receives large amounts of rain, and thus large jungles and forests exist in the country, swamplands are common in several parts of the country most importantly near the mouth of Lavanas numerous powerful rivers. To the west of the country the jungle of the lowlands gives way to vast and open plains which enjoy calm weather. Lavanas highest point is Mount Zirjia 1,694 m (5,558 ft) in the Gezije range and its lowest is Jaudau Panna −4 m (−13 ft) to the east of the country in the Zedenge valley. | ||
File: | <gallery mode=packed heights=170 style="font-size:88%;line-height:120%"> | ||
File: | File:20171111 Luang Prabang Mekong 1487 DxO.jpg|150px|Mountains of the Gezije range. | ||
File: | File:Path and trees in green paddy fields, at golden hour, in Don Det, Laos.jpg|150px|{{wp|Rice paddy}} field in Bantafa province. | ||
File: | File:Tad Hang waterfalls, Tad Lo village, Bolaven Plateau, Laos.jpg|150px|Koa Syvongsa waterfall in Thaviang province. | ||
File: | File:Water reflection of a green island at sunrise with blue sky and pirogue in Don Det Laos.jpg|150px|The Kung River in Sainyabuli province. | ||
File:Saracen Bay panoramic view, Koh Rong Sanloem, Cambodia, June 2014.jpg|150px|Falino bay to the south of Panitch | |||
File:20171116 Ponds near Phonsavan, Laos 2952 DxO.jpg|150px|Coastal wetlands in Cha Ha | |||
File:Karst peaks with sea of clouds at sunrise, South view from the top of Mount Nam Xay, Vang Vieng, Laos.jpg|150px|Mountains in Daonga province | |||
File:Li Phi falls at dusk with yellow sky in Don Khon Si Phan Don Laos.jpg|150px|Deilang River in Diahai Province. | |||
File:Niebo nad stepem w Karakorum (02).jpg|150px|Steppe in Galshir Province. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Climate=== | |||
{{Weather box | |||
|location = Lavana (records from all meteorological stations) | |||
|collapsed = | |||
|metric first = Y | |||
|single line = Y | |||
|Jan record high C = 25.8 | |||
|Feb record high C = 27.8 | |||
|Mar record high C = 28.7 | |||
|Apr record high C = 29.1 | |||
|May record high C = 30.9 | |||
|Jun record high C = 32.6 | |||
|Jul record high C = 32.5 | |||
|Aug record high C = 31.8 | |||
|Sep record high C = 30.7 | |||
|Oct record high C = 28.2 | |||
|Nov record high C = 26.6 | |||
|Dec record high C = 24.4 | |||
|year record high C = 29.9 | |||
=== | |Jan record low C = 20.7 | ||
|Feb record low C = 20.9 | |||
|Mar record low C = 22.7 | |||
|Apr record low C = 25.8 | |||
|May record low C = 26.1 | |||
|Jun record low C = 27.7 | |||
|Jul record low C = 28.6 | |||
|Aug record low C = 27.5 | |||
|Sep record low C = 25.7 | |||
|Oct record low C = 22.4 | |||
|Nov record low C = 20.5 | |||
|Dec record low C = 19.1 | |||
|year record low C = 23.9 | |||
|source = Ministry of the Interior | |||
|date=January 2017 | |||
}} | |||
=== Biodiversity === | |||
{{multiple image|perrow = 2|total_width=325 | |||
| align = left | |||
| image1 = Saras crane by Sanjay Tha Shrestha.jpg | |||
| image2 = Asian_elephant_walking_in_Tad_Lo_river_at_golden_hour,_Bolaven_Plateau,_Laos.jpg | |||
| image3 = Sun_bear_medan_old_zoo_standing.jpg | |||
| image4 = Panthera_tigris_corbetti_02.jpg | |||
| image5 = White-handed_Gibbon_(Hylobates_lar)_female_with_baby_(7105681909).jpg | |||
| image6 = Bengal_monitor_(Varanus_bengalensis).jpg | |||
| image7 = Pelochelys cantorii.jpg | |||
| image8 = Spinners.png | |||
| footer = A biodiverse country, Lavana is home to a variety of animal species. | |||
}} | |||
Lavanan can be subdivided between several ecoregions because of its climate and geomorphology. The country is rich in terms of {{wp|biodiversity}}, and several native species exist in the country. It has numerous ecoregions, ranging from {{wp|Jungles}} in most of the center of the country, and northwest, to {{wp|wetland}}s | |||
among the Kung River, and the coasts. The country has 27 {{wp|national park}}s, 15 {{wp|Nature_reserve|reservations}}, and 5 {{wp|natural monument}}s. The largest of this protected areas is the {{wp|Sarus_crane|Red great Crane}} National Park at 641.5 km2, which was added to the World Heritage list in 2015, the site has been a protected site since 1911. | |||
== | Lavana is a country of distinct {{wp|Fauna}}. It has some 15,600 animal species, including at least 2,423 {{wp|Bird}} species, 1,900 {{wp|Amphibian}} species, 1,610 {{wp|Mammal}} species, and 1,427 {{wp|Reptile}} species, of which 5,000 are {{wp|endemism|endemic}} to Lavana. Including large quantities of {{wp|insect}}s. Some native birds include the {{wp|Black-throated_bushtit|Black-throated tit}}, {{wp|Black-winged stilt}}, {{wp|Common emerald dove}}, {{wp|Crested Treeswift}}, {{wp|Greater adjutant}}, {{wp|Greater flameback}}, {{wp|Knob-billed duck}}, {{wp|Long-tailed shrike}}, {{wp|Vietnamese crested argus|Nainan crested argus}},{{wp|Sarus_crane|Red great Crane}}, {{wp|Silver pheasant}}, {{wp|Tawny fish owl}}, {{wp|Yellow-vented green pigeon}}. With the Red Great Crane being Lavanas national animal and featured in the flag of the country. Amphibians include the {{wp|Amolops_chunganensis|Chungus sucker frog}}, {{wp|Quasipaa spinosa|Giant spiny frog}}, {{wp|Tylototriton_notialis|Lavanan knobby newt}}, {{wp|Laos_warty_newt|Lavanan Warty newt}}, {{wp|Upper_Laos_caecilian|Upper Lavanan caecilian}}, along with a variety of {{wp|Salamanders}}, most Amphibians in the country were discovered within the last decade. Native mammals include the {{wp|Clouded leopard}}, {{wp|Asian_elephant|Coian elephant}}, {{wp|Disk-footed bat}}, {{wp|Horse|Great Steppe Horse}}, {{wp|Large-spotted civet}}, {{wp|Indochinese_tiger|Lavanan tiger}}, {{wp|Northern treeshrew}}, {{wp|Smooth-coated otter}}, {{wp|Spinner dolphin}}, {{wp|Sun bear}}, {{wp|Sunda pangolin}}, {{wp|Wild water buffalo}}, including several {{wp|Primates}} such as the {{wp|Crab-eating macaque}}, {{wp|Snub-nosed monkey}}, and {{wp|Lar gibbon|White gibbon}}. Reptile species native to Lavana include the {{wp|Calotes_mystaceus|Blue-crested lizard}}, {{wp|Asian_giant_softshell_turtle|Coian giant softshell turtle}}, {{wp|Siamese_crocodile|East Coian Crocodile}}, {{wp|Chrysopelea_ornata|Golden flying snake}}, {{wp|Scincella_reevesii|Kung's smooth skink}}, {{wp|Bengal monitor|Lavanan monitor}}. Hundreds of {{wp|Freshwater fish|Freshwater}}, and {{wp|Saltwater fish|Saltwater}} {{wp|Fish}} live in the countries numerous rivers, lakes, and seas. | ||
Lavana has suffered with issues of {{wp|deforestation}} and {{wp|poaching}} since the 1950's. Lavana had amongst the highest rates of deforestation between 1960 and 1970, with international alarm raised at the rate Lavana was losing its forests. Following concerns regarding deforestation near the Red Great Crane National Park in 1989 led to the government to enact reforms and law which prevented deforestation and {{wp|Habitat loss} in large sections of the country. The country expanded upon this in 2000 with further laws enacted to defend Lavanas biodiversity. Endangered wildlife is protected by law, and as of 2020, 1,736 species were protected by the state. | |||
== Politics == | |||
{{main|Cabinet of Lavana}} | |||
{{multiple image | {{multiple image | ||
|align= | |align=left | ||
|image1= | |image1=Prayuth 2018 cropped.jpg | ||
|width1=150 | |width1=150 | ||
|caption1=[[ | |caption1=[[Emmanuel Bakhtzhany]]<br><small>[[Premier of Lavana|Premier]]</small> | ||
|alt1= | |alt1= | ||
|image2= | |image2=Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân.jpeg | ||
|width2=150 | |width2=150 | ||
|caption2= | |caption2=[[Laina Keomany]]<br><small>[[General Secretary of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International|General Secretary]]</small> | ||
|alt2= | |alt2= | ||
}} | }} | ||
Lavana is constitutionally | |||
The Lavanan constitution states that the People's Republic of Lavana "is a democratic socialist state governed by a people's democratic government that is led by the working class and based on an alliance of all Lavanans," and that the state institutions "shall practice the principle of democracy." Lavana is constitutionally a {{wp|parlimentary}}, {{wp|multi-party_state|multi-party}}, {{wp|Representative_democracy|representative}} [[Council republic]]. The [[Premier of Lavana|Premier]] is the nations {{wp|head of state}}, {{wp|Head of government}}, and {{wp|Commander-in-chief|Chairman}} of the armed forces, elected by the {{wp|Unicameral}} [[Lavanan Congress]]. The Premier is the head of the [[Lavanan Cabinet]] and appoints its members. The incumbent Premier is [[Emmanuel Bakhtzhany]], who was elected to the position in 2022. Her Vice-Premier is Trang Dong. Under the 2022 constitution, Lavana is officially a multi-party state, although in reality the [[Lavanan Section of the Workers International]] (LSWI) asserts their role in all branches of the country's politics and society. | |||
Although the LSWI describes Lavana as a "free liberal socialist democracy", the country is commonly described as an {{wp|authoritarian}} {{wp|One-party_state|single-party}}, and a {{wp|Despotism|Depostic}} {{wp|dictatorship}}. Its current political, ideological and economic system has been termed by its leaders as a "{{wp|Socialism|Liberal Councilist state}}", "{{wp|Socialism|People's Liberal Democracy}}", "{{wp|Socialism|Socialist Market economy with Lavanan characteristics}}" respectively. Lavana saw the highest democratic rating since 1959, in 2022, the first such change since 1994. Although it is still described as unfree country. | |||
Political concerns in the country include: Corruption, minority rights, religious freedom, and the economy. Laina Keomany is still highly popular, however her involvement in the invasion of Hacyinia, and the ensuing defeat, her position was no longer solid, and she resigned in favor of Emmanuel Bakhtzhany, her former Minister of Economy. Bakhtzhany is cited as the mastermind of Lavanas post-coup economy, and he is believed to have opposed the invasion of Hacyinia leaving him untouched by the fallout. | |||
=== Lavanan Section of the Workers International === | |||
The General Secretary of the LSWI performs numerous key administrative functions, controlling the party's national organization, and direction. The current general secretary is former Premier [[Laina Keomany]], the first individual to hold both positions since 1994. LSWI membership elects the parties General Assembly, who elects the General Secretary and decides on policy and goals for the LSWI. Local LSWI Assemblies are directly elected, and higher levels of LSWI Assemblies up to the General Assembly are indirectly elected by the Assembly of the level immediately below. One can be a member of the democratically elected councils and congress and the LSWI structure, and close to 90% of all elected members serve in some capacity in both systems, primarily in lower levels. | |||
Following the 2022 coup, the LSWI experienced its greatest reform since 1994. The party lost most of its ability to directly affect the democratically elected government, which had caused the government crisis and subsequent coup. Although officially a multi-party state, the LSWI still controls the legality of political parties in the country by appointing or removing members of the Electoral commission, through the Premier. Effectively ensuring no proper opposition arises. Several parties were founded in the aftermath of the new rules, which represented previous ideological sections in the LSWI, such as the [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Worker-Labour Front]], and [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Great Crane Association]], which competed in the 2022 elections. These parties are equally organized as the LSWI, although in a lesser scale. | |||
{{Sidebar | {{Sidebar | ||
| name = Lavana | | name = Lavana | ||
| outertitle = [[Lavanan | | outertitle = [[Lavanan Congress]] | ||
| topimage = | | topimage = | ||
| pretitle = | | pretitle = | ||
| Line 210: | Line 297: | ||
[[File:LavaParliament.png|240px|center]] | [[File:LavaParliament.png|240px|center]] | ||
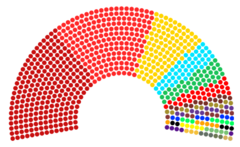
'''Government ( | '''Government (753)'''<br> | ||
<br>{{colorbox|#c1152e}} [[Lavanan Section of the Workers International|LSWI]] (315) | |||
[[ | <br>{{colorbox|#31287f}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Worker-Labour Front (WLF)]] (113) | ||
<br>{{colorbox|#3a1369}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Dhavoni People’s Party (DPP)]] (75) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#9c5494}} [[Ukilen Section of the Workers International|Ukilen Section of the Workers International (USWI)]] (71) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#D46714}} [[Majgar Section of the Workers International|Majgar Section of the Workers International (MSWI)]] (57) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#7613ec}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Socialist-Solarian Understanding party (SSUP)]] (53) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#F1a734}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Yoloten-Friendship Party (Y-FP)]] (40) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#21f7ec}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Great Crane Association]] (29) | |||
<br>'''Confidence and supply (42)'''<br> | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#B53770}} [[2022 Lavanan General Election|Maral Gavagamu Alliance]] (26) | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#B2BEB5}} {{wp|Independent_politician|Independents}} (16) | |||
<br>'''Opposition (6)'''<br> | |||
<br>{{colorbox|#B2BEB5}} {{wp|Independent_politician|Independents}} (6) | |||
}} | |||
=== Government === | |||
The [[Lavanan Congress]] is the unicameral state legislature composed of 801 members. Headed by the Premier, it is superior to both the executive and judicial branches. 2 members are elected by municipality using {{wp|Ranked voting}}, to the congress to serve 5 year terms, 3 seats are reserved for 3 members of all 24 Provincial councils. Seats for all ethnic groups in the country, distribution seats for municipalities that are highly populated, along with abroad seats fill out the remaining seats in the Congress. Provincial councils function in the same way as the Congress with certain duties granted to them by the constitution, Municipal and city level councils are elected as well, all using Ranked voting. Unlike with the LSWI structure, all citizens 18 and older are granted the right to vote on Legislative elections, unlike in LSWI where only party members are allowed to vote. | |||
Currently the LSWI rules in a collision government with all other parties, and some independents. Currently a 753 Coalition government exists, with numerous members in {{wp|confidence and supply}} roles, or serving in the opposition. Currently only 6 independent politicians are members of the opposition. | |||
The Supreme Court of Lavana, headed by a chief justice, is the country's highest court of appeal, though it is also answerable to the Congress, and the Premier. Its a 15 member court with members elected for single 10 year terms. Members are appointed by the Premier. Beneath the Supreme Court stand the provincial, municipal courts and city level courts. Military courts possess special jurisdiction in matters of state security. Lavana maintains the death penalty for numerous offences, although it has not charged anyone since 2009 and carried out an execution since 2013. | |||
Lavanas Socialist constitution takes its roots from the 1961 revolution, which granted wide powers to the LSWI and limited democratic involvement. Following internal instability within the LSWI, and widespread protests during the 80s and 90s a group of reformists led by [[Keo Sitwat]] came to control the LSWI and resulted in the election of Sitwat as both General Secretary and Premier, Sitwat ushered in a new constitution in 1994, which reformed the Lavanan state. This reforms were welcomed, by the LSWI and the population which allowed Lavana to survive the end of the 20th Century which saw numerous Socialist states collapse. Sitwat's successor [[Hatsadi Lor]] continued Sitwat's successful reforms, but he desired further democratization and reduction of power for the LSWI causing major frictions inside the LSWI. Major Reformist and Conservative factions arose within the LSWI. Traditional groups of LSWI members have been members of several distinct "Sections" with differing goals and beliefs, ranging from {{wp|Market_socialism|Market socialists}} to {{wp|Authoritarian_socialism|Authoritarian socialists}}. The two major sections that of the United People's and that of the Gouve Section were the largest sections in the country, where they contested the position of General Secretary and Premier usually, they're the party leaders of the Reform and Conservative factions respectively. | |||
The struggle between factions led to the 2022 coup, where Conservative factions feared an immediate loss of power, and sought through the General Secretary of the LSWI to remove Premier Laina Keomany the leader of the Reform faction. The failure of the Conservative attempt to mantain power, resulted in the major purge of the LSWI of members of the Conservative faction and rivals to Keomany. The Premier quickly filled positions with loyalists, and members of the reform faction, which rallied around her. Experts believe that 10% of the Conservative faction remain in the country, with the rest having been purged from government positions, and civilian positions. | |||
=== Administrative divisions === | |||
{{main|Administrative divisions of Lavana}} | |||
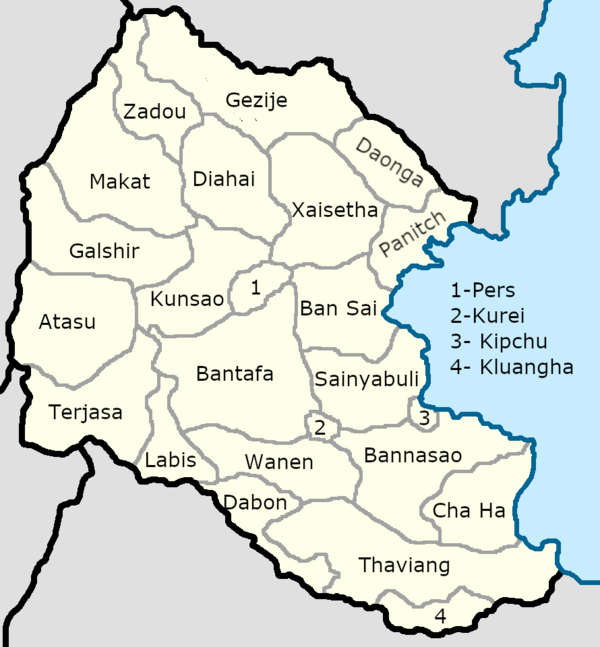
Lavana a {{Wp|unitary state}}, with partial {{wp|devolution}} consisting of 24 provinces (ແຂວງ ; Aekhuang). The most populous of which is the Capital province holding 10 million people. With the largest geographically being that of [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Thaviang]]. | |||
Provinces each with their own elected Provincial council headed by a {{wp|Governor}} (ເຈົ້າແຂວງ ; Chaoaekhuang) located in the provincial capital. Provinces are further divided into Municipalities (ເທດສະບານ; Thedsaban) of which there are 350. They're governed by a Municipal council, who elect a rotating leader to represent the municipality within Provincial councils. Municipalities are further divided into City "level" subdivisions, of which there are 1,425 in the country. This city "level" divisions include County (ຄາວຕີ້ ; Khav ti), City (ເມືອງ ; Meuong), Village (ບ້ານ ; Banla), and Ward (ອຸປະຖໍາ ; Upathoa). Which elect their own councils and representatives to the Municipal council. | |||
'''Population not updated''' | |||
[[File:Lavana-Provinces1.png|600px|center]] | |||
<center> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
|- | |||
! scope="col" | Province | |||
! scope="col" | Capital | |||
! scope="col" | Population | |||
! scope="col" | Province | |||
! scope="col" | Capital | |||
! scope="col" | Population | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Atasu]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Hara]] | |||
| 4,045,573 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Gezije]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Diuhai]] | |||
| 3,315,301 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Sai]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Nang Ha]] | |||
| 3,911,425 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Kluangha]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Dalat]] | |||
| 355,644 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Vuga]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Vuga]] | |||
| 4,951,125 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Kunsao]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Moc]] | |||
| 4,774,141 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Bannasao]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Sikeut]] | |||
| 4,755,567 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Labis]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Arachzharga]] | |||
| 881,031 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Bantafa]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Lao]] | |||
| 4,056,772 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Makat]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Hatgna]] | |||
| 3,676,311 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Biyaosa]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Biyaosa]] | |||
| 3,169,377 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Panitch]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Dezebenhua]] | |||
| 5,163,356 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Capital]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Pers]] | |||
| 10,055,673 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Sainyabuli]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Pong Det]] | |||
| 4,416,884 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Cha Ha]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Bouna]] | |||
| 4,889,530 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Terjasa]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ulzit]] | |||
| 2,687,853 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Dabon]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Yong Peng]] | |||
| 452,778 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Thaviang]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Thaheu]] | |||
| 4,536,888 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Daonga]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Dabadonga]] | |||
| 2,629,185 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Wanen]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Pasao]] | |||
| 954,602 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Diahai]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Ban Leum]] | |||
| 3,497,316 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Xaisetha]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Jaudau Fai]] | |||
| 4,318,736 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Galshir]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Karatau]] | |||
| 3,628,518 | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Zadou]] | |||
| [[Administrative_divisions_of_Lavana#Provinces|Zadou]] | |||
| 1,719,156 | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
</center> | |||
=== Military === | === Military === | ||
{{multiple image |perrow=2 |total_width=400 | |||
|image1=Royal Malaysian Air Force MiG-29's show off during the 2012 Singapore Airshow 120215-F-MQ656-003.jpg |width1=200 | |||
|image2=TankExercise2018-12.jpg |width2=200 | |||
|image3=Vietnamese Navy Petya II Class Frigate (HQ-15).jpg |width3=200 | |||
|image4=Ministro da Defesa, Jaques Wagner, visita a Base Aérea de Porto Velho - RO (16917248811).jpg|width4=200 | |||
|footer=Top row: {{wp|Mikoyan_MiG-29|TRA-21's}} on parade and {{wp|T-72|Type-59}} tanks in an exercise.<br>Bottom row: {{wp|TT-400TP_gunboat|Lo-15}} gunboat and a {{Wp|Mil_Mi-24l|Sin-201}} attack helicopters. | |||
}} | |||
The Lavanan People's Armed Forces consist of the Lavanan People's Army (LPA), Lavanan People's Navy (LPN), Lavanan People's Airforce (LPAF), the Lavanan People's Public Security (LPPS), which is divided between the Lavanan Coast Guard, Lavanan Border Force, and National Defence Units (NDU). In total it is composed of about 750,000 soldiers. All 4 branches fall within control of the Ministry of Defence, and are presided over by the [[Premier of Lavana]]. Lavana spends about 2% of its GDP or $39.4 Billion on its armed forces, it accounts for about 10% of government spending. | |||
The | The LPA is by far the largest branch of the Armed Forces, as it stands at 400,000 total soldiers including 100,000 reserves. It is by far the most important branch in the Armed Forces. The LPN and LPAF are smaller in size, the navy operates limited {{wp|Blue-water_navy|blue water}} capabilities with 5 {{wp|Submarine#Diesel-electric_transmission|Diesel}} {{wp|attack submarine}}s, 10 {{wp|Destroyers}} mostly older models, along with numerous smaller vessels. The LPN operates mostly {{wp|Brown-water_navy|brown water}} capable vessels, owing to the countries vast inland waterways, with hundreds of {{wp|Gunboat}}s. The LPAF relies on older aircraft including the {{wp|Mikoyan_MiG-29|TRA-21}} {{wp|Fighter aircraft}}, {{Wp|Mil_Mi-24l|Sin-201}} {{wp|attack helicopter}}, and {{wp|Antonov_An-24#Antonov_An-24|TRA-09}} {{wp|Military_transport_aircraft|transport aircraft}}. The LPPS serves the role of {{wp|Public security}} in the country. It totals 270,000 soldiers, with the Coast Guard polices the Lavanan waterways and helps in {{wp|Search and rescue}} operations, while the Border Force operates all entry points into Lavana, and patrols the borders of the country. The National Defence Units (NDU), are the former military arm of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International, and operated as a {{wp|paramilitary}} force from the revolution until 1995, when it was incorporated formally into the armed forces. The NDU operates as a {{wp|Gendarmerie}}, and police force at the national level mostly to provide additional security to rural localities. | ||
Lavana obtains most of its equipment from other Socialist states, most prominently [[Chistovodia]], [[Dezevau]], and [[Kirenia]]. Lavana conducts regular exercises with its Brown Sea Community allies, Dezevau and [[South Kabu]] on a regular basis. Lavana allows South Kabu to utilize its airspace and facilities to train members of the South Kabuese Airforce, and agreements between both armed forces exist. {{wp|Conscription}} in Lavana was ended in 1995 with the new constitution, and the armed forcs moved towards a fully {{wp|Standing_army|professional}} force, along with reducing its size from 900,000 total personnel to 700,000. Lavanas close relationship within the Brown Sea Community resulted in little need for advanced forces so long as the Lavanan army was able to remain more advanced than its neighbors. Following 2016, Lavana embarked on an modernization effort primarily for its {{wp|T-72|Type-59}} tanks, and the equipment of the Armed forces. The country has maintained interest in expanding the LPN, and LPAF and was a driving reason for the 2021 Government budget, which would allow Lavana to acquire a new fighter aircraft, along with expanding its Blue-water capabilities. Lavana is the primary developer on the | |||
=== Foreign Relations === | === Foreign Relations === | ||
{{multiple image | |||
|align=left | |||
|image1=Diplomatic Relations of Lavana.png | |||
|width1=140 | |||
|caption1=Diplomatic relations of Lavana |alt1= | |||
|image2=Entry Policy of Lavana.png | |||
|width2=150 | |||
|caption2=Visa requirements for entry to Lavana | |||
|alt2= | |||
}} | |||
Lavanas Socialist leanings have dictated the countries foreign policy since the revolution. Lavana today is a prominent member of the [[Association of International Socialism]] of which the country is a founding member, and 3rd most populous member. Lavana is also a member of the Brown Sea Community with socialist neighbors Dezevau and [[South Kabu]], Lavana maintains through the BSC cultural, economical, and military ties with both nations. Lavana does not recognize the sovereignty of [[North Kabu]], and supports South Kabuese territorial claims on Gaullican and Estmerish controlled territories, which has caused controversy. Dezevau is Lavanas closest ally, and both nations maintain deep diplomatic, cultural, economic, and military connections. | |||
Following the liberalization of the country, Lavana normalized diplomatic relations with non socialist states, and opened its first foreign embassy in a previously not socialist country in 1993 in [[Werania]]. Lavana has diplomatic relations with over 50 countries and maintains embassies in over 20. Lavana maintains several agreements with [[Vinalia]], and is the countries closest non-socialist tie. The nation maintains additional diplomatic relations with non-socialist states in [[Kuthina]], [[Garambura]], and [[Mabifia]]. The country along with the BSC maintain difficult relations with [[Nainan]] do to that countries persecution of Socialists, although efforts between both states in cultural matters have been made. Lavana provides foreign aid to nations in [[Bahia]] mainly focused in the development of agricultural, and food security in the region, Lavanan doctors frequently make trips to Bahia to provide medical aid to the population, the largest of this efforts involved 100 medical personnel deployed to Garambura from 2007 to 2009. | |||
Lavana holds complicated relations with its neighbor [[Hacyinia]], both nations have fought [[Hacyinian-Lavanan wars and conflicts|several wars and conflicts]] since Lavanan independence in [[Hacyinian-Lavanan_wars_and_conflicts#First_Galshir_Conflict_.281941.29|1941]]. Conflicts stem from issues regarding the partition of Estmerish holdings, and Princely states, but it has since expanded to the treatment of Ethnic minorities, Geopolitical influences, and military intervention in internal affairs. Hacyinia claims 1/3rd of Lavana, which it gained in 1941 and subsequently lost between 1942 and 1963. Lavana invaded Hacyinia in 1992, and established the [[Yoloten|People's Republic of Yoloten]] (PRY), which is recognized by a couple of friendly Socialist countries. In 2005 Lavana reached an agreement with Hacyinia that removed all Lavanan troops from the Yoloten. Lavana holds close economic ties with the Yoloten, which ruling party the Provisional Administrative and Military Front of the Yoloten (PAMFY) has been described as a Lavanan puppet. The PRY is located in a former princely state whose ruler sought to join Lavana during the partition before the state was invaded and annexed into Hacyinia. | |||
Lavana terminated all relations with [[Champania]] following its coup on March 2022, where it blamed the Champanian government for supporting the removal of Keomany. Relations were reopened on August 2022 between both Lavana and Champania, although considerably less friendly than before. Lavana clarified the situation by stating that Champania had provided information that disproved the claims of the administration of Champanian support for the coup, with Keomany publicly walking back her accusations.<ref name="November 7">{{cite news |url=https://forum.nationstates.net/viewtopic.php?p=39878787#p39878787 |work=[[Champania|L'Humanite]] |title=Foreign Office announcement regarding Champanian-Lavanan relations. |date=12 August 2022 |access-date=13 August 2022}}</ref> | |||
Lavana is a member of the [[Community of Nations]], [[Association of Gaullophone States]], [[Estmerish Council]] among other international communities. | |||
== Economy == | |||
[[File:Rice terraces in Lao Chải 06.jpg|thumb|right|Rice paddies in the Gezije Range]] | |||
Generally considered a {{wp|developing economy}}, Lavana has a {{wp|Gross_domestic_product#Nominal_GDP_and_adjustments_to_GDP|nominal}} {{wp|gross domestic product|GDP}} of $640.2 billion as of 2020, and a {{wp|Purchasing_power_parity|PPP}} GDP of $1.920 trillion, with a nominal per capita at $4,740, and $14,220 PPP per capita. It has an above average {{wp|Human Development Index}} score of .806. The country has showcased strong economic growth, posting good economic growth around 4% and peaking at 9% in 2014 since 2001, the countries economy grew by 3% in 2020. However the [[Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs]] estimates that, as of 2020, roughly 21.6% of Lavanas population lives on less than $5.50 a day, a considerable reduction from 70% in 1993. The country's {{wp|unemployment rate}} was estimated at 4.2% in 2019, its lowest in history. | |||
=== Agriculture and fishing === | |||
[[File:Coffee Harvest Laos.jpg|thumb|right|Coffee harvesters]] | |||
Agriculture has historically been a major sector in Lavanan economy, Lavanas vast system of rivers and estuaries with additional man made water ways such as canals, Lavanan farmers have always had access to vast fertile lands and ways to transport goods using the rivers. Lavanas has always been a major producer of rice through the use of {{wp|Paddy_field|paddy fields}}, and it has been a major part of Lavanan diet for centuries. Lavana is a major exporter of rice in the world, but it has seen a decline as other products such as coffee, and nuts increase in value. Lavana alone is the worlds biggest producer of {{wp|Cashew}} nuts, and is a top producer of coffee. Coffee has become a major part of Lavanan agriculture following its introduction in 1870 by Gaullican authorities which sought to establish profitable plantations in the country, the Socialist government has sought to increase coffee production as the demand of the product grows both at home and at broad. Other products produced in great quantities include peppers, rubber, cotton, sugar, coconuts, among others. Lavanan attempts at diversifying its agricultural output have been greatly successful with Lavana holding among the most resilient agricultural sectors in the world. | |||
[[File:Fish-farms-vietnam.jpg|thumb|left|Fish farming village in the Kung river]] | |||
Fishing has historically been a key part in the economy of Lavana, fish farming in Lavana traces its history to antiquity where fishing villages known as {{wp|Kelong|Kelongs}} appeared on the rivers of the country usually close to markets with farmers managing fields then returning to their houses to feed fish held in large metal containers. Such fishing villages have been impacted by river pollution along with higher costs than fish grown in land based farms. Land based fish farms have grown greatly since the 80's with government subsided farms cropping up across the country, and making it easier for {{wp|Rice-fish_system|rice and fish}} farms to grow and expand. Many villages in the coastal regions still largely depend on fishing, which has led to overfishing in some areas. Fishing of {{wp|Sea_cucumber|sea cucumbers}} has seen increasing growth, although much of this is performed illegally the high price of the sea cucumber makes it hard for government authorities to regulate, attempts at farming the sea cucumbers have mostly had low results, and attempts at {{wp|polyculture}} growing both sea cucumbers and {{wp|prawns}} have had little success. Highly profitable {{wp|shrimp}} farms have seen a massive investment in the country with large amounts of public and private money invested into the industry, making the country among the leading producers of shrimp. | |||
=== Energy === | |||
{{Pie chart | |||
| thumb = right | |||
| caption = Electricity production in Lavana (2021) | |||
| other = | |||
| label1 = {{wp|Coal-fired_power_station|Coal}} | |||
| value1 = 40 | |||
| color1 = Black | |||
| label2 = {{wp|Nuclear energy|Nuclear}} | |||
| value2 = 28 | |||
| color2 = Red | |||
| label3 = {{wp|Petroleum|Oil}} | |||
| value3 = 15 | |||
| color3 = brown | |||
| label4 = {{wp|Hydro energy|Hydro}} | |||
| value4 = 14 | |||
| color4 = Blue | |||
| label5 = {{wp|Wind energy|Wind}} | |||
| value5 = 2 | |||
| color5 = Green | |||
| label6 = {{wp|Solar energy|Solar}} | |||
| value6 = 1 | |||
| color6 = Yellow | |||
}} | |||
Lavana consumes some estimated 330,437 {{wp|Kilowatt-hour#Multiples|Gw}} a year, with an average consumption of 3,805 {{wp|Kilowatt-hour|kWh}} per person, making it one of the largest electrical consumers in the world. Lavana obtains its energy mainly from {{wp|Coal-fired_power_station|Coal}} and {{wp|Nuclear energy|Nuclear}} power at 40% and 28% respectively, {{wp|Petroleum|Oil}} makes up 15%, with the remaining 17% made up of {{wp|renewable energy}} primarily {{wp|Hydro energy|Hydroelectric}} at 85%, {{wp|Wind energy|Wind}} at 10%, and {{wp|Solar energy|Solar}} at 5%. | |||
Lavana has historically relied on {{wp|Coal-fired_power_station|Coal}} for its energy needs, and today it remains its largest source of energy at 40%. Increased desire to diversify and combat pollution lead to government development of alternative energy sources. Today coal makes the least percentage of the energy grid in its history, although the amount of coal generated energy and thus consumption has increased. Lavana has promised to stop building new {{wp|Coal-fired_power_station|coal power plants}} by 2025, and to phase out all of its coal power plants by 2035. | |||
Lavana operates 12 {{wp|Nuclear_reactor|reactor}}s in 4 {{wp|Nuclear Power plant}}s. Lavana has expressed great interest in nuclear energy and between 2005-2020 the nation built 4 reactors, and announced its intention on keeping the 2 Min La reactors first built in 1985 online until 2040, Lavana also stated its intention in building a further 3 reactors in a brand new facility between 2020 and 2030. Lavanas growing energy needs and desire to become more energy independent resulted in it stating its desire to have 50% of Lavanan power produced through nuclear energy by 2050, with plans for the construction of up to 12 new reactors to be constructed, effectively doubling the amount of reactors in Lavana. | |||
Renewable energy has been a growing field in the country, primarily hydroelectric power, Lav San Dam first started building in 2004 and finished in 2015 is the largest dam in Southeast Coius, and provides 80% of Lavana's total hydroelectric power output. The dam was seen as a highly ambitious project as it was the first large scale dam project in Lavana, but its successful construction and results have led to wider development in the area, with multiple projects seeking to expand on the success of the dam. Other sources of energy although limited have slowly grown in importance, the government has approved 10 Gw worth of {{wp|Photovoltaic_power_station|solar farms}} in the nation to be installed between 2015-2025, the move marked as highly ambitious has met great results with a steady rise in solar power produced and a general decline in the cost of electricity primarily in the west of the country where nuclear energy is not as efficient, and issues with the transportation of electricity from the coastal plants. | |||
[[File:Lavanan Oil.png|thumb|left|Map of Oil deposits and fields in Lavana]] | |||
Lavana maintains a production of 150,000 {{wp|Barrel_(unit)|barrels}} of {{wp|petroleum|oil}} per day, while having {{wp|proven reserves}} of 1.5 million barrels, although PetroLav maintains that the country has 5.3 million barrels in reserve, this figure is hotly contested. All Lavanan oil is managed by the state-owned PetroLav company. Lavana obtains most of its oil from {{wp|Offshore drilling}} in the Brown Sea, along with some oil fields in the mainland. Lavana was the center of major AIS Petro-chemical development spurred by government interest in the 60's and 70's for the exploitation of the resource, oil was seen as a possible driver of the Lavanan economy although no major sources of Oil could be found until the discovery of Oil deposits in the Brown Sea. Oil served as another way for Lavana to obtain foreign currency until Lavana stopped exporting oil in 2005, do to the rise in the cost of oil, that made historically expensive Lavanan oil uncompetitive in the foreign market. Lavana has some {{wp|Natural gas}} reserves, although they have not been exploited do to high development costs. Lavana will open its first {{wp|Gas-fired_power_plant|natural gas power plant}} in the outskirts of Dezebenhua in 2022, with goals to make natural gas represent 10% of the grid by 2040. PetroLav owns a considerable amount of Oil in the Yoloten, with 80% of its extraction under its control, and 100% of its refining capacity. | |||
{{multiple image | |||
| align = center | |||
| image1 = Sơn La Dam reservoir.JPG | |||
| image2 = Hengchun Taiwan Maanshan-Nuclear-Power-Plant-02.jpg | |||
| image3 = Zigui-Sinopec-boat-fuel-station-4959.jpg | |||
| footer = (Left) Lav San {{wp|Dam}}. (Center) Min La {{wp|Nuclear Power Plant}}. (Right) A floating {{wp|Filling station|fuel station}} on the Pekelo river. | |||
}} | |||
=== Mining === | |||
Although mining has existed since antiquity it has not been a key sector in the Lavanan economy, Gaullican attempts at increasing production of {{wp|coal}} reserves found in the Gezije range were largely unsuccessful, and Lavanan has primarily mined minor amounts of {{wp|iron}}, and {{wp|copper}}. In the 1970's growing interest in the sector resulted in studies conducted by the central government which found unexploited reserves of {{wp|bauxite}}, {{wp|chromium}}, and {{wp|zinc}} resulted in wide investment by the central government, this resulted in the establishment of the ສະພາຂຸດຄົ້ນບໍ່ແຮ່ແຫ່ງຊາດ (National Mining Council), a state owned enterprise tasked with managing the mineral resources of the country. By 1996, Lavanan production of bauxite, chromium, and copper had nearly quadrupled, with the nation becoming a key exporter of bauxite on the global market with large reserves still unexploited. This rapid expansion was seen favoredly by the central government as a key way of obtaining foreign {{wp|Hard_currency| hard currency}}, and allowing for warmer relations between Lavana and foreign buyers. Mining is conducted wholly by the state owned NMC, and foreign investment and acquisition is carefully regulated. | |||
The expansion of mining has caused severe environmental issues, with waste from mineral operations usually dumped into the countries rivers, following government regulation this problem has been majorly eliminated by environment degradation, and deforestation remain a key issue. As most minerals are mined and transported through the river system for either export or processing, spills and leaks have occurred. In 2014 an iron ore transporting vessel collided with a fishing village on the Kung river capsizing and releasing several tons of the ore into the river causing great pollution along with several deaths, attempts at changing the transportation of minerals through railway has seen some success but still large amounts of minerals are transported via waterways. | |||
=== Transportation === | |||
[[File:Da Nang Dragon Bridge (II).jpg|thumb|right|Bridge of the Yellow Dragon over the Kung river]] | |||
Prior to Gaullican colonization most of Lavana relied on waterways for transportation with some stone roads connecting major cities and centers of trade. Gaullican authorities made use of the countries vast river system as previously done through the centuries. The first railroad in Lavana was laid in 1890 between Pers and Kipchu although it served primarily for passenger transport as river transport was incredibly cheap. A major explosion in infrastructure occurred in the 1920's as Gaullican authorities desired to create a vast system of roadways to aid in mobilizing soldiers and resources, such a system had been mostly completed by the start of the Great war, although further plans remained uncompleted and neglected following the war. The Socialist government launched a major campaign constructing infrastructure throughout the nation. | |||
Lavana has a vast motorway network, with national managed roadways (4-6 total lanes) connecting major cities, and provincial managed roadways (2-4 total lanes) connecting other areas of the country, in 2017 all provincial roadways were paved, while municipal roadways (2 total lanes) cover the rest of the country with varying levels of maintenance and paving depending on the municipality. The central government began construction on an {{wp|Controlled-access_highway|expressway}} system (6-8 total lanes) in 2010 and construction was underway, with the first section of the route K1 Pers-Ban Vuga expected to finish in 2021, with K2 Pers-Biyaosa, K3 Pers-Dezebenhua, and K4 Pers-Kurei expected to be finished by 2022, the central government expects to finish the expressway system by 2035 with routes K1 to K6. Congestion has been a major issue for the country as large sections of Pers can be completely gridlocked during rush hour, the increase in commuters and car ownership have been blamed for such issues, but poor management of municipal roadways inside the city are also a cause, the government has attempted to limit the amount of cars on the roads but has faced backlash. Large parts of Lavanans still mobilize using {{wp|Motorcycle|motorcycles}}. | |||
[[File:CR300AF-0003位于北京环形铁道.jpg|thumb|right|Gavujuju-Pers express train entering Dabadonga Central station]] | |||
Railroad connections in the country have also seen great importance, with several thousands of kilometers of track laid down. Passenger rail is more developed than freight rail, a situation the country has sought to solve with the construction of a freight train only line between Zadou-Dabadonga-Dezebenhua which was completed in 2015, although plans to expand this freight only system remain mostly delayed as the nation has sought other alternatives to its growing freight needs. Construction on a freight only line between Pers-Ongoya-Dabadonga began in 2018, with a Kurei-Laitaka line beginning construction in 2020. A {{wp|High-speed_rail|high-speed rail}} connection with Dezevau was inaugurated in 2015 the [[Bazadavo]]-[[Pers]] express via Mhidyzai, Viodhoumi, and Dabadonga was a major success for both nations, as the difficult geography of the area threatened to reduce speeds for the project but the link was completed with minimal speed loss. Such a success was celebrated through the issue of stamps across members of the AIS. {{wp|Rapid_transit| Rapid transit}} in the form of metro lines has also seen keen development as the nation has sought to construct metro systems in its 3 largest cities, the Pers metro opened in August 2020 with its green line, further expansions are planned and expected to finish no later than 2032. Metro systems in Kurei and Kipchu are expected to begin operations in 2025 and 2026 respectively. | |||
Lavana operates some 36 national airports including 4 international airports: Kanoa Somphon in Pers, Vongvichit International Airport in Kurei, Arath Khouph International Airport in Kipchu, and Laitaka International Airport. Kanoa Somphon is the countries largest airport handling much of its international passengers. Domestic flights to Pers-Ban Sao were moved to the smaller Keolamalay airport in 2018, which has reduced congestion in Kanoa Somphon. Lavana's national carrier is the state owned Lavanian Airways, which operates close to 70 aircraft, Lavanian Airways flew to some 60 destinations all in Coius and Euclea. Private carriers exist in Lavana as well. | |||
Lavanas important relation with waterways has resulted in sizeable amounts of cargo and passengers still utilizing the water systems although this amount has reduced for several years following government attempts at improving water quality and other methods of transportation, and nowadays the river are mainly used by rural populations and the mining sector. The largest sea port in Lavana is that of Kipchu, which has always historically been the largest port in the country, Laitaka and Dezebenhua follow Kipchu both in importance and tonnage which passes through. Laitaka has become an important {{wp|Cruise_ship|cruise}} stop with numerous cruise ships stopping at the port during the summer months bringing in international tourists. | |||
Lavana | === Tourism === | ||
<gallery mode=packed heights=150 style="font-size:88%;line-height:120%"> | |||
File:Kleine Bonaire-Underwater life(js).jpg|{{wp|Coral_reef|Brown Sea shadowed coral reefs}} World Heritage site is a popular spot for scuba divers. Site is jointly managed by Lavana and Dezevau | |||
File:Sarus Cranes (Grus antigone)- Calling in Display near Hodal I Picture 2023.jpg|Kung river {{wp|Sarus_crane|Red great crane}} breeding grounds was added to the World Heritage list in 2015, the site has been a Lavanan National park since 1911. | |||
File:Plaine des Jarres (4345423217) (2).jpg|{{wp|Plain_of_Jars|Duh Hoc culture jars}} encompass the numerous jars dating back to the 9th century B.C.E. Duh Hoc culture in western Lavana. | |||
File:Great-zim-aerial-looking-West.JPG|Part of the greater Zedenge Canal World heritage site {{wp|Great_Zimbabwe|Dabadonga}} was the capital of the Agudan Empire. The site is jointly administered by Lavana and Dezevau | |||
File:Citadelle de Hanoï (4).jpg|The {{wp|Imperial_Citadel_of_Thăng_Long|Ban Sao Historical center}} in the center of Ban Sao showcases the ancient capital of the Sao's which ruled over modern Lavana. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
'''Population not updated''' | |||
{{Historical populations | |||
|title = | |||
|type = | |||
|align = left | |||
|direction = | |||
|width = | |||
|state = | |||
|shading = | |||
|pop_name = | |||
|percentages = | |||
|footnote = | |||
|source = Ministry of the Interior | |||
|1900| 30500000 | |||
|1915| 38392000 | |||
|1930| 48738000 | |||
|1945| 61931000 | |||
|1960| 72524000 | |||
|1975| 89721000 | |||
|1990| 107384000 | |||
|2005| 122534000 | |||
|2020| 135022931 | |||
}} | |||
{{multiple image|perrow = 3|total_width=375 | |||
| align = right | |||
| image1 = Người Lự và người Lào.jpg | |||
| image2 = People of Kazakhstan in Zailiysky Ala-Tau mountains.png | |||
| image3 = Pgs sấdasdas.jpg | |||
| image4 = Üzemchin.jpg | |||
| image5 = Rice 02.jpg | |||
| image6 = 20200206 150859 Mon Girls in Mawlamyaing Myanmar anagoria.JPG | |||
| footer = Lavana is a multi-ethnic country. | |||
}} | |||
As of the 2020 census Lavana had a population of 135022931, making it the 14th largest country in the world by population. The Kung River basin has historically been heavily populated, and thus Lavana has had large populations historically. 19th century Aguda Census placed Lavanas population at 13.5 million people. However such censuses were discontinued during the colonial era. A 1935 census by Estmerish authorities estimated some 50 million people, although many have questioned such values. In 1960 the first comprehensive census was conducted, and has been conducted every 15 years since then. Lavanan officials released in 2021 an attempt to calculate Lavanan demographics since 1900. | |||
Lavana has a population density of 189 (ppl/km2), making it the 12th most densely populated country in the world. About a third of the population lives in Urban areas with some 37.14% of the population, the largest of which is Pers and Kurei with 13.1 million and 5.95 million respectively. The Pers Metropolitan area houses some 15 million people and is among the largest metropolitan areas in the world, along with one of its densest. Lavanan life expectancy sits around 73.7 years of age, and has been steadily increasing since the 1980's. | |||
Lavanan demographics are impacted by {{wp|Natalism|Natalist}} policies that sought to increase the size of the population. Lavana experimented with a "Child Provision" which sought to grant tax breaks, and in some instances direct income for each child a couple had. This campaign initially launched in 1962, proved successful in increasing the Lavanan fertility rate. This {{wp|Population_growth|population boom}}, greatly increased the {{wp|Workforce|working population}} in the country and allowed it to increase its {{wp|Gross_domestic_product|GDP}} considerably since 1990. Growing cost, and fear of {{wp|Overpopulation}} lead to the abandonment of the Natalist policies, although the government has not sought to actively restrict population growth as had initially been thought. Since 1990 Lavana has grown by 25.74% or 27.6 million people. | |||
=== Ethnic groups === | |||
{{Pie chart | |||
| thumb = right | |||
| caption = Demographic Groups of Lavana (2020) | |||
| other = | |||
| label1 = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lao_people|Kachai}} | |||
| value1 = 52 | |||
| color1 = Red | |||
| label2 = [[Ziba|Dhavoni]] | |||
| value2 = 21 | |||
| color2 = Purple | |||
| label3 = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mongols|Ukilen}} | |||
| value3 = 11 | |||
| color3 = Yellow | |||
| label4 = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kazakhs|Majgars}} | |||
| value4 = 9 | |||
| color4 = Orange | |||
| label5 = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malaysian_Malay|Male}} | |||
| value5 = 3 | |||
| color5 = Green | |||
| label6 = {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Azerbaijanis|Kiziks}} | |||
| value6 = 2 | |||
| color6 = Blue | |||
| label7 = Other | |||
| value7 = 2 | |||
| color7 = Grey | |||
}} | |||
Lavana is a multi-etnic country, with numerous people of differing ethnic, linguistic, and cultural backgrounds. According to the 2020 census established the {{wp|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lao_people|Kachai}}s as the largest ethnic group in Lavana at 52% (70.21 million), [[Ziba|Dhavoni]] at 21% (28.35 million), {{wp|Mongols|Ukilen}}s at 11% (13.85 million), {{wp|Kazakhs|Majgars}} at 9% (12.15 million), the {{wp|Malaysian_Malay|Male}} at 3% (4 million), the {{wp|Azerbaijanis|Kiziks}} at 2% (2.7 million), with Other groups at 2% (2.7 million). | |||
The Kachais represent a majority in the state, and are by far the most economically and politically active of all groups in the country. Kachais are found all over Lavana, but dominate primarily in the center and east of the country and all major urban centers. Kachais have been benefitted by settlement in the west of the country, and they represent about 1/3 in most of the western part of the country. The Kachais were part of the wider {{wp|Tai peoples|Kasi}} [[Kasi Migration|migrations]] from the 8th to 10th century CE, the Kachai being the furthest of said migrations. Initially arriving as mercenaries, they were increasingly settled in the urban centers of the country. Their increasing power inside Gevuine empire would culminate in the breakup of the Gevuine Empire and the establishment of a Kachai Empire in the Rasuvong. The Kachai would come to inhabit much of the east and center of the country, with significant populations settling north of the Gezije range. | |||
[[File:Ethnic Map of Lavana.png|thumb|left|Red-{{wp|Lao_people|Kachai}}. Purple-[[Ziba|Dhavoni]]. Yellow-{{wp|Mongols|Ukilen}}. Orange-{{wp|Kazakhs|Majgars}}. Green-{{wp|Malaysian_Malay|Male}}. Blue-{{wp|Azerbaijanis|Kiziks}} ]] | |||
Dhavonis represent the second largest group in the country, and enjoy vast economic and politically active roles in society. Dhavonis inhabit much of the north and major urban centers. Dhavonis is a term that refers to the people which lived in the lowlands South of the Zedenge Valley. The term is utilized by the Lavanan government to separate the Ziba speakers from Lavana and those of Dezevau and abroad, which are considered instead by their nationality. The term originates in the work of Republican Ziba writers which sought to create a distinct Lavanan identity for the Ziba speakers outside of Dezevau, based around a perceived historical difference from their northern neighbours which now represented the majority of the population in newly formed Dezevau. Although less relevant following the Lavanan Revolution in 1959, the distinction is still maintained by Ziba speaking populations. | |||
Ukilens are the 3rd largest group in the country, they have enjoyed greater roles inside Lavanan politics and the economy since the 1980's but remain mostly sidelined. Ukilens make a majority in the West and Southwest of Lavana. Ukilen migrations into other parts of Lavana, primarily urban centers has expanded much of the population, and today about 1/4 of all Ukilens live away from the commonly Ukilen west, centering in Lavanas urban regions. Migrants from Hacyinia have also settled in Lavana in recent years. Majgars represent the 4th largest group, and have much of the same history and role in society as their Ukilen neighbors. About 1/3 of all Majgars inhabit urban centers. Majgars inhabit much of the west of Lavana, and its major urban centers. Ukilen and Majgar populations have increasingly mixed as a result of population shifts throughout the years. Ukilen and Majgar populations have experienced discrimination and political disenfranchisement in the past, leading to bans on cultural and religious practices. Today they suffer issues of political representation, which have seen attempts at fixing by new Lavanan administrations. | |||
The Male inhabit much of the south of Lavana and represent the 5th largest group. Unlike the other groups, they have not migrated in great quantities into the urban centers of Lavana. The Kiziks represent the 6th largest group at 2% and inhabit small pockets in the northwest in the Gezije Range. About 1/2 of all Kiziks have migrated into urban centers in Lavana, primarily Kizik workers coming from Hacyinia. | |||
Other groups in Lavana account for 2% and showcase the widespread diversity in the country. Significant populations of socialist countries exist, [[Kabu|Kabuese]], [[Chistovodia|Chistovodians]], [[Kirenia|Kirenians]], exist in the country. Although the largest group is by far Dezevauni's. Similar situations exist for migrating Hacyinians, which are usually divided between classifying as one of the major ethnic groups in Lavana or as their nationality. A historically important population of [[Shangea]]ns has existed in the country and can trace its history to ancient merchants and administrators that have come to settle into the country, throughout the centuries. [[Vinalia|Vinalians]] have settled in the country in great quantities since the 70's and today maintain small communities in the country. {{wp|Javanese people|Kabuese}} have settled mostly in the eastern coast, or Pers. Most minorities and migrants inhabit the urban centers of the country, mostly concentrated on Pers. | |||
=== Health === | === Health === | ||
Lavana had in 2020 an average {{wp|life expectancy}} at birth of 73.7, which is relatively low but has seen a great increase since the 1980's when it averaged to 65.2 years. The Community of nations estimated that the countries expected life expectancy could reach 75.5 within 10 years, as a result of a stronger healthcare system, and ever increasing {{wp|quality of life}} for Lavanans. Health in Lavana is provided by the state free of charge, and is administered at the national and provincial levels, with the state operating more specialized services, with provincial being suited to more general services. Health in the country is administered by the Ministry of Health, its minister must be by law a health worker. Small clinics are run by provincial authorities and usually serve to treat general issues and concerns, also serving the role of family clinics, and walk-in clinics. Provincial health systems also maintain general hospitals in their territory which serve more advanced needs of the population, such as {{wp|Surgery}}, {{wp|Maternity Ward}}, {{wp|Intensive care}}, and {{wp|Medical laboratory}}. The national government maintains specific hospitals with specialized needs, such as {{wp|Cardiovascular surgery}} facilities, {{wp|Child hospital}}s, {{wp|Cancer treatment}}, {{wp|MRI}} facilities, and research institutions. | |||
[[File:Students assisting surgery.JPG|thumb|right|Medical students assisting a live surgery conducted by Dezevauni doctors]] | |||
Lavana throughout its history has struggled with {{wp|famine|famines}}, {{wp|malnutrition}}, and {{wp|food security|food insecurity}}. Which have led to instances of high {{wp|child mortality}}, and a lower life expectancy. Some 500,000 have been estimated to have died as a result of the 1956 famine, which led to wide reform on the Lavanan economy, but remained of minimal impact, by the rise of the Socialist government and as a result of the civil war some 35% of all Lavanans held some sort of food insecurity, and some 8% were considered on famine like conditions. Socialist reforms and strong programs in the support of farmers primarily subsidies improved the food security in the country, primarily its western areas where famines had appeared on a cycle as a result of negligence on part of colonial authorities. Although progress was made, conflict and instability led to issues during the 70's and 80's in the west. Today under 10% of Lavanans experience some sort of Food insecurity during any given year, in a declining trend, malnutrition has also been heavily attacked primarily by introducing new foods into the diets of rural populations, which historically relied primarily on rice. The increase in unique crops grown, and imported have helped reduce Lavanas malnutrition rates, along with greater economic resources and nutritional information. Lavana and Champania collaborated extensively, with a large quantity of Lavanan doctors being trained in Champanian institutions. Such programs have faced extreme pressure do to Lavanan-Champanian strained relations stemming from the aftermath of the [[2022 Lavana coup d'état]]. | |||
As a result of the Lavanan civil war a large {{wp|Human_capital_flight|brain drain}} was experienced, particularly in the health sector as thousands of medical practitioners immigrated to other countries, thus creating a strain on the ability of Lavana to meet its increasing health needs. Lavana has historically experienced high rates of {{wp|Tropical disease}} such as {{wp|Malaria}}, {{wp|Typhoid Fever}}, {{wp|Dengue Fever}}, and {{wp|Tuberculosis}}. To combat the lack of doctors and the government ever increasing desires to combat disease, a program was started in conjunction with the AESE where Lavanan doctors were trained in AESE countries primarily Kirenia, Chistovodia, [[Champania]] and Dezevau to increase their effectiveness. Such a program along with incentives for any desiring doctors increased the efficiency and amount of doctors in the country. Lavanan institutions have since maintained close ties with health institutions in other Socialist countries, Lavanan doctors have worked closely in [[North Vinalia]] (later Vinalia), Champania, and Dezevau to develop strategies for combating a variety of tropical diseases, primarily {{wp|mosquito-borne_disease|Mosquito borne diseases}} which are a great issue in this countries and abroad. Lavana had begun working closely with Vinalia in 2014 to develop strategies and treatments for the prevention and treatment of the {{wp|Zika}} virus which had experienced an outbreak in the country that year, Vinalia aided the Lavanan government in implementing preventive strategies with great success. Lavana succesfully declared the country Zika free in 2016. | |||
Smoking in the country has since 2008 been heavily regulated, following higher rates of {{wp|Lung_cancer| lung cancer}} than the global average. Such measures have heavily curtailed the rates of lung cancer in the country, and has been one of the factors in Lavanas ever increasing life expectancy. | |||
=== Education === | === Education === | ||
[[File:Uttaradit Rajabhat University 04.JPG|thumb|right|Faculty of Science at the national university]] | |||
Since 1980 {{wp|Primary_school|primary}}, and {{wp|Middle_school|secondary}} education are compulsory for all students, which together account for 10 years in total. Tertiary education comprises students attending a 2 year University Preparatory school, some 69.7% of students continue into tertiary education in 2010. Students must then pass the Kathomtua or National Preparatory Test to enter into {{wp|University}}. Since 1980 primary and secondary education have been fully free, and since 2010 all tertiary and university education are free as well. | |||
As of 2020 98% of the population over 15 were literate, this comes at a great improvement over the 13% literacy rate in 1941, and 58% in 1980. Free primary and secondary education are the main drivers in such high literacy rates in the country since 1980. Lavanan students have increasingly improved in their test scores, although they still lag behind other AIS states such as Kirenia, Chistovodia, and Dezevau. | |||
Lavanas most prominent and prestigious university is the National University of Pers, which consistently ranks as among the best in Coius and the world. Other universities and colleges of importance are the Workers College in Kipchu, University of the East in Laitaka, and Pers University. Lavana has had an increasing level of higher university graduates and professionals, although Lavana holds a higher than average rate of migration in this area, primarily to other AIS countries such as Dezevau. In 2009 university graduate that speaks Ziba as a native tongue is 50% more likely to migrate to Dezevau upon completing their education than any other specific group in Lavana, something which has prompted concern for the government. | |||
=== Religion === | === Religion === | ||
[[File:Ananda Myitta Buddha Temple at Moheshkhali,Cox's Bazar.jpg|thumb|left|Badi temple near | [[File:Ananda Myitta Buddha Temple at Moheshkhali,Cox's Bazar.jpg|thumb|left|Badi temple near Dabadonga, established in the 15th century.]] | ||
[[File:Wooden buddhist house of Don Loppadi.jpg|thumb|right|Wooden Badi house.]] | |||
{{Pie chart | {{Pie chart | ||
| thumb = right | | thumb = right | ||
| Line 240: | Line 643: | ||
| other = | | other = | ||
| label1 = [[Badi]] | | label1 = [[Badi]] | ||
| value1 = | | value1 = 56 | ||
| color1 = Green | | color1 = Green | ||
| label2 = {{wp|Irreligious}} | | label2 = {{wp|Irreligious}} | ||
| value2 = | | value2 = 21 | ||
| color2 = Grey | | color2 = Grey | ||
| label3 = [[Solarian Catholic Church]] | | label3 = [[Solarian Catholic Church]] | ||
| value3 = | | value3 = 12 | ||
| color3 = purple | | color3 = purple | ||
| label4 = | | label4 = [[Irfan]] | ||
| value4 = | | value4 = 10 | ||
| color4 = white | | color4 = Red | ||
| label5 = Other | |||
| value5 = 1 | |||
| color5 = white | |||
}} | }} | ||
Lavana | The 2020 census registered that ranking first at 56% (75.6 million) were believers of [[Badi]], ranking second at 21% (28.35 million) are declared as having {{wp|Irreligious|no religion}}, ranking third at 12% (16.2 million) as being members of the [[Solarian Catholic Church]], at fourth at 10% (13.5 million) is [[Irfan]], 1% (1.35 million) people are members of other religions such as [[Amendism|Amendist]] denominations, [[Orthodox Church of the South]], [[Episemialist Church]], [[Atudism]] among others. | ||
Badi is the largest religion in Lavana at 56% or 75.6 million people. Lavana is one of the largest Badist countries in the world being the [[Badi by country|3rd largest]] in total followers, and largest percent wise. Badi has a long history in Lavana starting from the 1st century B.C.E. when the practice and preaching of which was heavily banned by central authorities, however during the Dhijivodhi Empire, Badi was decriminalized and grew to become the main religion in Lavana supplanting earlier Lavanan religions. Lavanan missionaries would go on to travel into the steppe spreading Badi, and many Badi temples and churches can be traced back to Lavanan missionaries. The Kachai were converted into Badi in the 9th century CE, the Kanchai increasingly combined aspects of their own former [[Zohism|Zohist]] faith into the beliefs and teaching of Badi. Badi was the dominant religion in modern Lavana until the arrival of Eucleans where Catholicism was greatly supported, numerous Badi practices such as the use of hallucinogenics were banned under colonial rule. Lavanan Socialism accepted Badi as an innate part of Lavanan society, but it did seek to regulate Badist sects and beliefs to better incorporate into Lavanan political and social goals, and prevent Badi from being a force against Socialist secularism. The Lavanan socialism government however did act against Badi, when on 1973 it banned and imprisoned followers of the [[Badist_sects#Thin_Air|Thin Air]] sect, which was the dominant sect in Ukilen and Majgar communities in a manner similar to how Irfanics were prosecuted decades prior. Such a ban was lifted in 1980, and imprisoned priests let go. Today Badists in Lavana similar to their brethren in Dezevau hold a less dominant role in society, as government is completely secularized. | |||
About 21% or 28.35 million people declared themselves as having {{wp|Irreligious|no religion}}. Irreligion stems from secular ideals during the Colonial period, which sought to separate the country from Badi which had been dominant for centuries. Initially irreligion stemmed from a support in Euclean anti-Badi policies and beliefs and a rejection of Euclean catholicism. The Republic of Lavana in 1940 was established officially as a secular state, with the People's Republic in 1960 holding the same secular beliefs. The removal of both Badi and Catholicism from public education in the 1940's, along with some restrictions on Badist beliefs created an environment for rapid expansion of the irreligious population, although with less speed and impact as in Dezevau. | |||
About 12% or 16.2 million people were registered as being members of the [[Solarian Catholic Church]]. Catholicism initially arrived to the Aguda Empire in the 17th century in the form of {{wp|Christian mission|missionaries}}. The entry of Gaullican interests and later colonial rule quickly expanded the importance of Catholicism in the country, as much of the colonial bureaucracy converted to the religion, and Badist practices and beliefs were discouraged, although it never represented more than 20% of the country. The independence of Lavana, reduced the importance of Catholicism as individuals were no longer favored for their beliefs. Solarians however came to represent an important political force do to their wealth and power, and sided with the Republicans during the civil war. Their defeat resulted in initial opposition to the Solarian church, although by 1965 the church was returned certain freedoms. Solarians are prevalent in all ethnic groups although they congregrate in urban areas and thus Kachais and Dhavonis represent the largest ethnic followers in the country. Solarians were legally allowed to enter political office when in 1994, the provisions that rejected the joining of Solarians into the Lavanan Section of the Workers International (a requirement in being able to be in any position of the government prior to 2022) were removed. Today Solarians hold public offices, and are part of the wider society. | |||
[[File:Mosque in HCMC.jpg|thumb|left|A Mazar in Pers]] | |||
Irfan is the 4th largest group in the country with 10% and 13.5 million followers nationwide. Irfan initially arrived to Lavana in the north, and mainly Ukilen and Majgars in rural regions of the steppe were of Irfan belief. At independence, Irfan was located almost exclusively inside these two groups. The Republican government believed most Irfanics held beliefs of a pan-Majgar and pan-Ukilen state, and sought to control such rhetoric. The Socialist government upon taking power launched its largest religious campaigns against Irfan, closing down and defacing Mazars. From 1960 to 1985 all Irfanics were required to carry identifications that identified them as such, and made it legal for them to be questioned by authorities, or imprisoned on "suspicion" of illegal activities, several restrictions regarding dress and beliefs were also imposed. Some restrictions against Irfanics were lifted in 1985, although the last restrictions on Irfanics, including ability to join the LSWI and thus the government in 1994. Today Irfanics remain mostly Ukilens and Majgars, although they hold higher negative connotations than Ukilens and Majgars who are any other religion. Irfanics are severely underrepresented in government, civil positions; and almost never hold positions outside of Irfanic majority areas. In 2022 out of 760 members of the Lavanan Congress, only 22 are Irfanic of which only 9 were not appointed by a provincial council or by the Premier to fill vacant seats. Only about 35% of Irfanics live in one of Lavanas top 15 largest cities, and 50% in its top 30 largest. | |||
=== Language === | === Language === | ||
=== | === Urbanisation === | ||
About 26% of Lavanans live in the 10 largest cities. With the vast majority living in Pers. Lavana is highly centralized in the Pers metro area home to some 15 million people, which makes up 11% of the total Lavanan population. Urban growth has been concentrated primarily in the Kachai and Dhavoni majority territories of Lavana. The countries urbanisation rate of 37.14 (50.1 million) with 68% of the urban population living in the top 10 cities. | |||
Lavanan cities have seen considerable growth primarily from migration from rural regions, which has created a lack of housing in some cities, primarily Pers. Government attempts at curtailing or slowing such migration have so far not been succesful. Issues regarding {{wp|pollution}}, {{wp|water sanitation}}, {{wp|congestion}}, among others have been difficult challenges for Lavanan authorities to curtail. | |||
Cities in Lavana tend to have both an official and a local name, although in some instances the same name is used in both contexts. The city of Ban Vuga has its official name with "Ban" (city in Kachai), while its local name is Vuga. In the case of Ban Vuga both the official and local name are the same, as defined by law. In the case of Dezebenhua, the local name is Dezebenhua while the official name is Jaudau Dezebenhua, with "Jaudau" (Ziba for ''magnificent city'') being used. The literal name of Ban Vuga is, City of Vuga. While Dezebenhua is, Magnificent city of Dezebenhua. Local names are used where applicable. | |||
'''Population not updated''' | |||
{| class="infobox" style="text-align:center; width:97%; margin-right:10px; font-size:90%" | {| class="infobox" style="text-align:center; width:97%; margin-right:10px; font-size:90%" | ||
! colspan="8" style="background:#e9e9e9; padding:0.3em; line-height:1.2em;"|Largest urban centers by population | ! colspan="8" style="background:#e9e9e9; padding:0.3em; line-height:1.2em;"|Largest urban centers by population | ||
| Line 261: | Line 681: | ||
!rowspan=11| | !rowspan=11| | ||
[[File:Han River from the Han River Bridge 3.jpg|220px]]<br /><small>[[Pers]]</small><br /> | [[File:Han River from the Han River Bridge 3.jpg|220px]]<br /><small>[[Pers]]</small><br /> | ||
[[File:Phnom Penh Evening Aerial View.png|220px]]<br /><small>[[ | [[File:Phnom Penh Evening Aerial View.png|220px]]<br /><small>[[Ban Vuga]]</small><br /> | ||
! style="text-align:center; background:#f5f5f5;"| <small>#</small> | ! style="text-align:center; background:#f5f5f5;"| <small>#</small> | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#f5f5f5;"| Settlement | ! style="text-align:left; background:#f5f5f5;"| Settlement | ||
! style="text-align:center; background:#f5f5f5;"| Population | ! style="text-align:center; background:#f5f5f5;"| Population | ||
!rowspan=11| | !rowspan=11| | ||
[[File:Catbi building.jpg|220px]]<br /><small>[[ | [[File:Catbi building.jpg|220px]]<br /><small>[[Dezebenhua]]</small><br />[[File:Patuxai.jpg|220px]]<br /><small>[[Biyaosa]]</small> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 1 ||align=left | '''[[Pers]]''' || | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 1 ||align=left | '''[[Pers]]''' || 13,155,673 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 2 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 2 ||align=left | '''Ban Vuga''' || 5,951,125 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 3 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 3 ||align=left | '''Dezebenhua''' || 3,863,356 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 4 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 4 ||align=left | '''Biyaosa''' || 3,469,377 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 5 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 5 ||align=left | '''Bouna''' || 3,362,753 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 6 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 6 ||align=left | '''Nang Ha''' || 1,724,136 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 7 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 7 ||align=left | '''Dabadonga''' || 1,100,633 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 8 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 8 ||align=left | '''Karatau''' || 793,842 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 9 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 9 ||align=left | '''Attapeu''' || 691,853 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background:#f0f0f0"| 10 ||align=left | ''' | | style="background:#f0f0f0"| 10 ||align=left | '''Zadou''' || 583,631 || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
== | == Culture == | ||
=== Cuisine === | |||
=== | [[File:Nhân nem.jpg|thumb|right|Raw ingredients to make filling of {{wp|Chả_giò|Spring rolls}} before mixing together. They represent the five-element principle of Lavanan cuisine.]] | ||
[[File: | Lavanan dishes are traditionally crafted on a 5 element principle, which is called ອາຫານປະກອບ; ahan pakob or "Elemental foods". This concept has its roots on the [[Badi#Elemental_theory|Badist elemental theory]], but it has moved into a cultural practice rather than religious practice. The principle involves the use of 5 elements to make a dish, although by elements it can mean the origin of an ingredient, or a process during the preparation or cooking of the dish. Although theres no set guides for what elements to use, or which ingredients go where, the main elements are: Animal for products made from animals such as {{wp|meat}}, {{wp|milk}}, {{wp|cheese}}; Earth and Plant for {{wp|rice}}, {{wp|vegetable|vegetables}}, {{wp|fruit|fruits}}, among others; Heat is usually used to refer to the cooking process of the dish; Oil for the {{wp|Cooking oil}} used in the cooking of the dish, Seasoning for the process of seasoning the food; Time if the process of cooking the dish involves long periods of time such as {{wp|fermentation}}; and Water to signify water in either the dish (such as a soup), or an accompanying drink. The concept is today is more used in the crafting of meals for family gatherings and special events, rather than individual dishes but many traditional dishes were made on the 5 element principle. | ||
Popular dishes in the country include {{wp|Larb#Lao/Isan_style|Larb}}, a dish made of meat and vegetables, served with {{wp|Glutinous_rice|sticky rice}}. {{wp|Green_papaya_salad|Tam som}} a dish made of shredded {{wp|papaya}} which can be greatly customized with additional ingredients. {{wp|Chả_giò|Spring rolls}} which is usually served as an {{wp|appetizer}} and is made of ground meat, usually {{wp|pork}} or {{wp|Lamb_and_mutton|mutton}}, wrapped in rice paper and deep-fried. Other foods of importance include {{wp|Bún_bò_Huế|rice and beef soup}}, {{wp|Khorkhog}}, {{wp|Shelpek}}, {{wp|Kai yang}}, {{wp|Pho|Feu}} and many more. Lavanan cuisine is varied, and dishes usually change inside the region, with the Dezevauni populations in the north favoring food with more spices, and vegetables and less meat, while those in the west favor meat over vegetables, while the Kachai population varies on preference. | |||
Various animals are consumed in the nation, not usually found in other countries such as {{wp|Qazı|Horse}}, {{wp|Grasshopper#As_food|Grasshopper}} {{wp|Crocodile#Crocodile_products|Crocodile}}, {{wp|Snake_soup|Snake}}, and {{wp|Shark_meat|Shark}} can be found in street markets and grocery stores as is the case with Horse meat and Grasshoppers, while the others are considered a {{wp|delicacy}} in local cuisine. Although the consumption of {{wp|dog meat}} is banned by the government since 1990, an illegal trade in the country exists, similar situations exist in regards to {{wp|Elephant meat}}, {{wp|Monkey meat}}, and {{wp|Turtle#As food, traditional medicine, and cosmetics|Turtle meat}}. Government attempts at cracking down the illegal meat trade in the country have been met with great success. In 1990 the Lavanan Congress decreed that the illegal meat trade of protected species, was the greatest threat to Lavanan fauna, a decree that has been upheld since. | |||
[[File:Can Tho, Vietnam, Floating Market, Boats.jpg|thumb|right|Floating market on the Pekelo River]] | [[File:Can Tho, Vietnam, Floating Market, Boats.jpg|thumb|right|Floating market on the Pekelo River]] | ||
Popular drinks in the country include {{wp|coffee}}, {{wp|sugarcane juice}}, {{wp|tea}}, and {{wp|Oliang|iced coffee}}. alcoholic drinks consumed in the country include {{wp|Beerlao|beer}}, {{wp|Lao-Lao|whiskey}}, and {{wp|wine}}. Lavanan beer is highly celebrated and acclaimed, it has successfully been exported abroad, and is one of the most recognizable symbols of Lavana. {{wp|Turkish coffee|Dezevauni coffee}} is incredibly popular in Lavana, and is commonly served in [[Ganome|Ganomes]] throughout the country. Although areas with high Dezevauni populations, Ganomes are the same as in Dezevau and share many common values, in other parts of the country they serve the explicit purpose of a {{wp|coffeehouse}} only, with many locations adopting the name as a {{wp|marrketing}} tool but sharing no values with the original concept of a ganome. | |||
Floating markets are a staple of Lavanan cuisine and culture, although they have reduced their importance through grocery stores, and other conveniences. Eating aboard boats and floating markets has become a popular attraction for tourists and many floating markets and restaurants exist to cater to tourists, {{wp|floating restaurants}}, are a common sight in Lavanan cities, and many high-class restaurants operate as floating restaurants. | |||
=== Music === | === Music === | ||
=== Art === | |||
Something something [[Goaboabanga]] | |||
=== Literature === | === Literature === | ||
=== Cinema === | === Cinema === | ||
[[File:GladisSaenbouthalathpicture .jpg|thumb|right|Gladis Saenbouthalath is the most prominent Lavanan Actress]] | |||
Cinema was brought to Lavana in 1923 as a theater was built in Pers for Gaullican colonial administrators and businessmen. The first film to be shot in Lavana was the Gaullican directed 1926 film [[Gaullica|Robe blanche sur la rivière]] (White dress on the River). Following independence Lavanan film making began although mostly centered around Kachai cinema, the first film to be made in the country was ນ້ໍາໃນຂອບເຂດ (Water on the horizon) in 1943. Dezevauni migrants began a Ziba based film industry with the release of Dezevauboga in 1948, a film criticizing Socialism meant to be illegally distributed in Dezevau. By the time of the civil war, theatres existed throughout the nation although they showed mostly Gaullican films with a minority of Kachai films. | |||
Following the revolution, Zadavana Goube approved in 1961 the Division of Cinema (DC), which censored films in Lavana and allowed for government films to be made. All movies made prior to that were banned, and cinemas switched to showing only Kachai and Ziba films. Socialist films from Dezevau dominated the Ziba market, and foreign films from [[Chistovodia]], [[North Vinalia]], [[Champania]] were shown as well. Commercial film makers were allowed to make films in 1966, although all films were closely connected with the socialist government and policy. In 1973 the Kachai-Ziba epic ເລື່ອງຂອງຂ້ອຍ (My story) was made, it's the most expensive Lavanan film ever made; it follows the life of Zadavana Goube. Lavanan propaganda films were the sole films made in Lavana from 1961 to 1994. | |||
Starting in 1994, the DC was reduced in scope and private films were reintroduced in the country. Commercial Lavanan films have participated sporadically in foreign film festivals such as the [[Montecara Film Festival]] since 2000. Today the Lavanan film industry is steadily growing, its primarily language based with Kachai, Ziba, Ukilen, and Majgar films being made and distributed throughout the country. The Lavanan government still makes around 1/4th of all films distributed in the country. Dezevauni films are regularly shot in the country and distributed abroad. In 2009 the Gaullican film [[Gaullica|Le Radeau sur le Kung]] was the first Gaullican film to be shot in Lavana since 1949. All foreign films are still subject to censorship by the DC. About 12 films are shot inside Lavana each year. Gladis Saenbouthalath is the most prominent Lavanan Actress, having appeared in Lavanan, Dezevauni, and Gaullican films. | |||
=== Sports === | === Sports === | ||
[[File:上海虹口足球场全貌.jpg|thumb|right|National Workers stadium in Pers]] | |||
Lavana does not maintain a national sport but {{wp|Association_football|football}} is the most popular sport in the country, represented in the Lavanan Top League. {{wp|Basketball}} is another popular sport in the country with many youths practicing the sport, and the Lavanan national team competing in highly prestigious competitions in the international stage. The Lavanan National Football team plays in the National Workers stadium built in 2010, its also the largest stadium by size and seating capacity in the country. The Lavanan A League is the top level football league in the country with 14 teams, the most prominent of which is Dabadonga F.C. which have won the league some 20 times in the leagues 50 year history. | |||
{{multiple image | |||
| align = left | |||
| image1 = 2018-10-09 Rowing Training at 2018 Summer Youth Olympics (Martin Rulsch) 43.jpg | |||
| image2 = Biathlon at the 2020 Winter Youth Olympics – Boys' individual 0465.jpg | |||
| width2=150 | |||
| footer = (Left) Laila Manwilaivong, and Malo Thonemany are Lavanas most successful Invictus medalists in history. (Right) [[Konala Vsevolodovych]] following his bronze medal winning race in the [[Scovern|2016]] Winter Invictus games, Lavanas only Winter medal. | |||
}} | |||
[[Lavana_at_the_Invictus_Games|Lavana]] has participated in all Summer [[Invictus Games]] since [[Eldmark|Hammarvik 1954]], with the exception of [[Estmere|Jindao 1958]]. Lavana has won a total of 54 medals 53 in the Summer editions of the games, and 1 medal in the Winter editions, including 13 golds all from the Summer games. Lavana has earned 11 out of its 13 gold medals, and 27 out of its 54 total medals in {{wp|Rowing}}, where Lavana has historically dominated. Lavanas most successful Invictus medalists are the rowing pair of Laila Manwilaivong, and Malo Thonemany which have won 5 medals each, including 3 gold medals each in rowing. Lavana has participated sporadically in the Winter Invictus games, sending its largest representation in [[2020 Winter Invictus Games|Ulan Khol 2020]] when it sent 6 athletes, Lavana however is one of the few tropical countries in the world to win a Winter Invictus medal, when [[Konala Vsevolodovych]] won the bronze medal on the Men's 20 km individual {{wp|Biathlon}} event in [[Scovern|Linå 2016]]. Lavana has made it a national priority to send at least one athlete to the Winter games, following 2020, and the government has funded athletes who live in countries which allow for training in Winter Sports, most prominently Chistovodia, and Kirenia. | |||
=== Holidays === | === Holidays === | ||
[[File:Yasothonrocketfloat01.JPG|thumb|right|River Festival float near Laitaka]] | |||
Numerous holidays and festivals are celebrated in Lavana. | |||
{| class=wikitable | |||
!Date !! Name !! Native Name !! Public Holiday !! Notes | |||
|- | |||
|January 1 || {{wp|New Year's Day}} || ມື້ປີໃຫມ່;''mu pi haim''|| {{ya}} || Celebration of the Euclean new year. | |||
|- | |||
|January 7 || {{wp|Christmas|Nativity}} || ວັນຄຣິດສະມາດ; ''van khrid samad'' || {{na}} || Celebration of the Nativity, practiced by Solarian Lavanans | |||
|- | |||
|February 1 || {{wp|Boun Khun Khao|Day of the Harvest}} || ບຸນຄູນ ຄຳ;''Boun Khun Khao''|| {{ya}} || Celebration of the new harvest, usually of rice. | |||
|- | |||
|February 22 || {{wp|Armed Forces Day}} || ມື້ປີໃຫມ່;''mu pi haim''|| {{ya}} || Celebration of the new year. | |||
|- | |||
|March 19 || {{wp|Armed Forces Day}} || ວັນ ກຳ ລັງປະກອບອາວຸດ;''van kam lang pakoboavud'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the Armed forces of Lavana | |||
|- | |||
|April 13{{ndash}}15 || {{wp|Lao_New_Year|New Year}} || ປີໃຫມ່;''pi haim'' || {{ya}} || Celebration of the new year based on the Lunar calendar of the Damrog Empire. | |||
|- | |||
|May 1 || {{wp|International Workers' Day}} || ວັນ ກຳ ມະກອນສາກົນ;''van kam ma kon sakon'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the workers of Lavana. | |||
|- | |||
|May 27{{ndash}}30 || {{wp|Rocket_Festival|River festival}} || ບຸນຊ່ວງເຮືອ;''Bunsuangheu'' || {{ya}} || Holiday with Lavanan Folk origins, which celebrates water and its importance to Lavana and its society. | |||
|- | |||
|June 3 || [[Lavanan Civil War|Day of the Republic]] || ວັນປະຕິວັດ;''Vanpativad'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the establishment of the People's Republic of Lavana in 1960. | |||
|- | |||
|July 12 || [[Lavanan Civil war|Day of the Revolution]] || ວັນປະຕິວັດ;''van pativad'' || {{ya}} || Commemorate the start of the Lavanan Civil War. | |||
|- | |||
|September 19 || [[Lavana#Demographics|People's Day]] || ມື້ປະຊາຊົນ;''mupasason'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the people and culture of Lavana | |||
|- | |||
|October 3 || [[Partition of Aguda|Independence Day]] || ວັນເອກະລາດ;''van ekalad'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the independence of Lavana, and the end to colonization. | |||
|- | |||
|November 25 || [[Lavanan civil War|End of Civil Struggle Day]] || ສິ້ນສຸດວັນຕໍ່ສູ້ພົນລະເຮືອນ;''sinsud van tosu phonla heuon'' || {{ya}} || Celebrate the end of the [[Lavanan Civil War]] in 1961. | |||
|- | |||
|December 31 || {{wp|New Year's Eve}} || ປີ ໃໝ່ ລາວ;''pi mai lav'' || {{na}} || Day before the Euclean new year. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
{{Template:Lavana topics}} | |||
[[category:Kylaris]] | [[category:Kylaris]] | ||
[[category:Lavana]] | [[category:Lavana]] | ||
[[category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | [[category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:06, 27 August 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
People's Republic of Lavana ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາຊົນລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ Javunganiboga Bügd Nairamdakh Lavana Uls Lavana Xalıq Respwblïkası République Populaire de Lavana | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "ຈາກແມ່ນ້ ຳ ທີ່ຍິ່ງໃຫຍ່" "From the Mighty Rivers" | |
| Anthem: ດວງຕາເວັນແດງຂອງລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ (The Red Sun of Lavana) | |
 Location of Lavana on Kylaris in dark green | |
| Capital and largest city | Pers |
| Recognised national languages | Kachai Gaullican |
| Ethnic groups | Kachai 52% Dhavoni 21% |
| Religion | Badi 56% Irreligion 21% |
| Demonym(s) | Lavanan |
| Government | Council republic |
• Premier | Emmanuel Bakhtzhany |
• Vice-Premier | Trang Dong |
| Legislature | Congress of Lavana |
| Establishment | |
• Establishment of the Republic of Lavana | 1940 |
• Establishment of the People's Republic of Lavana | 1960 |
| Area | |
• Total | 731,189 km2 (282,314 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | |
• Density | 189/km2 (489.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| HDI (2020) | 0.806 very high |
| Currency | Lavanan dunan (LAD) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +420 |
| Internet TLD | .la |
Lavana (Kachai:ລະຫວ່າແ, Lavanga; Ziba Javunga ) officially the People's Republic of Lavana (Kachai:ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາຊົນລັດ ລະຫວ່າແ, Sathalanalad Pasasonlad Lavanga; Ziba Javunganiboga) is a sovereign state in Southeastern Coius. It borders Dezevau to the north, the Brown Sea to the east, Hacyinia, and the unrecognised breakaway socialist state of the Yoloten to the west, and tbd to the south. With a total area of 731,189 km2, and population of 135 million people, it is one of the largest countries by population in the world. Its capital and largest city is Pers, which is also the country's economic, political and cultural centre. It stands besides the city of Ban Sao which was the historical center of government of several empires in the region
Inhabited since antiquity, agriculture and language was brought by Ziba speaking settlers from Dezevau, which utilized wide river system to establish centers of trade and the establishment of the first city states in the inland regions. The city states would eventually band together in various federations and empires usually centered on the centrally located city of Zebedize and Jaudau Sao (modern Pers) from which the Sasuanan empire began emanating power and influence from the 4th century BCE onwards. The Sasuanan Empire established the tradition of a centrally located aristocracy and center of power centralized on a Sao comparable to an emperor, such traditions would continue for several centuries. The Kachais originally from the areas surrounding modern day Kuthina would begin their migration around the 8th century CE with many finding their ways as mercenaries towards the warring factions following the collapse of the Zibinego empire, Kachai influence would reach its highest point when aristocrats and military leaders of Kachai descent would establish a Kachai king during the reign of the Damrog Empire in the 11th century. Kachais would settle in the east and centre of the country. Weakening Damrog Empire influence and power would result in the rise the Aguda Empire in southern Dezevau and Northern Lavana, from former Damrog holdings which would grow onto control most of Southeast Coius.
The Aguda Empire would reach its apex in the 16th century when it held vast influence and land throughout Coius, the arrival of Eucleans mainly Gaullicans into the region began a slow decline as foreign influences weakened its internal structure. Where at points the Agudan Empire existed solely on paper while entities such as the Saint Bermude's Company from Gaullica managed the lands of the former Agudans as colonial holdings. Eventually the Bureau for Southeast Coius would manage a variety of breakaway puppet states in the former Agudan territories. Following the defeat of Gaullica in the Great War, the Bureau would be managed by Estmere. Suffering from growing costs and resistance, Estmere would partition the bureau in 1940. Lavana became a democratic republic however internal strife, and tensions with its neighbors would result in Lavana undergoing a revolution in 1959-1961 that would result in the establishment of the One-party state People's Republic under the Lavanan Section of the Workers International.
Lavana holds large ethnic minorities in the country primarily Dhavoni, Ukilen and Majgar minorities in the north, and west of the country. These populations historically marginalized by the central Kachai government, were in involved in a series of uprisings, insurgencies, and conflict between Lavanas central government, its minorities, and foreign states such as Hacyinia. This conflict reached its greatest point when on 1992, Lavana invaded Hacyinia establishing the People's Republic of Yoloten. The backlash from this conflict, and foreign toppling of Socialist governments caused Lavana to undergo its own reforms in 1994, which established a more liberal socialist state. Today Lavana is considered a liberal and developing socialist country, although it still struggles with corruption, and censorship.
Lavana would integrate into the international socialist movements alongside it's two close Socialist neighbors in Dezevau and South Kabu founding the Brown Sea Community 1981. The country today is a developing economy, with close ties to it's Northern neighbor and other socialist states, the government has followed the trend of liberalization and opening up which followed after decline of Socialist countries in the 1980's and 90's. It has been a member of the AIS since its inception in 1980. On March 6th 2022, it underwent a violent coup, along in 2022 Lavana would invade Hacyinia, sparking tensions in the region.
Etymology
The term Lavanga (Lavana in Estmerish) originates from the Kachai combination of between lavang (ລະຫວ່າງ) and river aemn am (ແມ່ນ້ ຳ), thus Lavana means "between rivers" in the Kachai language. The term gained traction in the 11th and 12th centuries, as the territories inhabited by the Kachais which were marked as being between the Siadng and Kalani rivers. The term never entered official use, but was returned to public conscience in the establishment of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International, and the Confederation of Free Lavana in the 1910's. These groups had exclusive Kachai membership, and thus why they used an exclusively Kachai term. Kachai's successfully established that Lavana referred to the land between the Siadng and Kalani rivers, which now are the borders of the modern state. The term was chosen as the Kachai refused to use a Ziba name, as they were the majority in the new country.
Prior to the arrival of the Kachai, the region of modern Lavana and southern Dezevau was known as "Dhabovozuigi" in Ziba, which translates to southern fountain/centre/capital. This term was used to refer to the lowlands south of the Zedenge valley, and ending near the Kalani river. It also makes reference to the more centralized states that emanated from Zebedize and Jaudau Sao, modern Pers. The meaning of fountain also makes emphasis on the rivers of the region. The direct translation of Dhabovozuigi in Kachai is ສູນພາກໃຕ້ (Sunphakta), and was the name used by early Kachai settlers until the 10th century CE, when Lavana became more favored to represent the Kachai populations which had settled between the Siadng and the Kalani rivers. The term fell out of favor during the Aguda Empire.
History
Pre-history
| Lavana Timeline of Significant Eras | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lavanan pre-history can trace itself to migrating Hunter gatherers which hunted various animals in the fertile regions of Lavana, where ample grazing areas for animals was present. Archaelogical evidence shows use of early-prehistoric bone tools almost 1 million years ago, and other discoveries such as fossilized teeth to 125,000–80,000 years ago. The discovery of agriculture can trace its origins to Dezevau, rice was the primary crop grown in the numerous fertile rivers and remains to this day its most important. The Duh-Hoc civilization is the earliest settled society in Lavana with a written record, the Duh-Hoc society is believed to have been first established in the 9th century B.C.E. along the banks of the Siadng river, this civilization utilized the vast waterways for communication and trade. They're most well known for their jars, which have been suspected to serve a ceremonial purpose, many jars have been found holding possessions along with the remains of individuals, which could show early funerary rites. To ensure the free and safe passage of trade and goods, fortified settlements were constructed alongside rivers to defend them, along with the collection of taxes in the form of rice. Early texts describe this system of taxation.
The Duh-Hoc civilization experienced an eventual fragmentation as it spread throughout the land, eventually numerous City-states would be established around the 8th-6th centuries BCE, a trend that would continue through the regions history. The Sao, was a titled designated to the leader of a city state, and was commonly associated with someone of minimal control outside of city walls, the term grew in significance throughout the ages, and its meaning was replaced and adapted. During this time as well, the !Austronesian migrations, which date from the 8th through 4th century BCE, originated from the South of Coius around Kuthina. They settled primarily in the coasts of the country and established well connected wealthy coastal cities, which usually demanded tribute from upstream cities to access their vast rudimentary trading network. War was common for this early societies, and numerous conflicts were fought for control of farmland, access to bodies of water, and trading routes. Cultural differences were observed in the early Dhavoni society in Lavana, which unlike modern belief remained a vastly diverse group, only united in a similar writing system. During this time many animist beliefs were held throughout the land, many texts survive telling of rituals and ceremonies in early Lavana, construction of temples was also commonplace.
Rising power and Sayak Dynasty (3rd Century B.C.E-109 C.E.)
At the start of the 3rd century BCE, 3 major city-states became centers of powers in the region, Jaudau Sao, Dezenhua, and Bouna. These 3 cities maintained vast relationships with smaller city-states and principalities. The most prominent of these centers of powers was Jaudau Sao which controlled most trade coming in from the west of the region through the numerous tributaries of the Kung river. These cities avoided direct conflict do to the loose relationships that were maintained with principalities, which in some instances paid tribute to multiple entities. Old Ziba is expected to have been introduced in the 1st century CE, as a {[wp|Prestige_(sociolinguistics)|prestige language}} in noble courts.
Around the 1st century BCE, Jaudau Sao began employing the services of Ashinan mercenaries, to enforce greater control over their neighbors and rivals. Jaudau Sao came to rely on these Proto-Oroqic groups for warfare, and internal security. The term of Sao began to be used as a sign of ranking on the King of the 3 major city states. Charismatic and well connected Sao's in Jaudau Sao ensured the cities dominance over its rival peers during the 1st century BCE. Declining influence on the 1st century CE however would result in great instability for Jaudau Sao, which would result in Lao Va the leader of a band of Ashinan mercenaries to seize control of Jaudau Sao and establish the Sayak Dynasty on 33 CE.
The Sayak Dynasty coincided with an increase in violence, as the Sayak's sought to dominate by whichever way possible their rivals, and expand influence. Infighting among the Sao and his Ashinan counterparts would result in internal instability, finally culminating in general anarchy and conflict between 50 CE and 97 CE. During this period numerous warlords arose and carved petty kingdoms, with differing levels of centralization. This period would end when Pae Halin was crowned as Sao, establishing the Dhijivodhi empire with the Dhijivodhi dynasty at its head in 109 CE on the city of Jaudau Sao, which now attempted to enact greater territorial control over the other major centers of power.
Dhijivodhi empire (109-470)
Zibinego kingdom (470-763)
Burning of Jaudau Sao in 763
Aguda Empire (1476-1886)
Colonialism (1820-1940)
Growing Gaullican control over the Aguda Empire, coincided with dwindling commercial prospects in the major cities of the Kung river. Gaullican authorities favored coastal trading cities, and resource exploitation everywhere else. The 3 cities of Zebedize, Jaudau Sao, and Khaimuk suffered significant depopulation between 1820 and 1880, losing up to an estimated 400,000 people. The coastal cities of Dezebenhua and Ban Vuga swelled in population, although the vast majority of urban regions suffered widespread emigration. Ziba increasingly became sidelined by colonial authorities who encouraged Kachai populations to utilize Kachai as the language of administration alongside Gaullican.
Independence (1940-1959)
On October 3rd 1940, the Republic of Lavana came into existence following the first part of the Partition of Southeast Coius, which divided the territories of both former Gaullican and Estmerish territories in Southeast Coius. In a bid to reduce of influence of Socialist Dezevau, and establish a strong anti-Socialist state, the Republic of Lavana was made independent 3 months before the rest of the region was. Lavana was to negotiate independently with Hacyinia for territory exchanges, and migration agreements, along with the numerous Zejas that now existed in the territory. Hacyinia unable to obtain a favorable agreement that granted it control of the Oroqic lands now under Lavanan control, proceeded to invade Lavana on October 21st 1940 in the First Galshir war, where Lavana lost 1/3 of its country to Hacyinia. During this time, the Lavanan government struggled under the weight of migrations out of Dezevau, internal infighting, general inability of its government and armed forces to defend Lavana both from Hacyinia and an expected Dezevauni invasion. The invasion of Lavana would mark the highest extent of Hacyinia, and to this day is claimed by that country, it began the Hacyinian-Lavanan conflicts which continue to this day.
The end of the government was spelled in the increasing unpopularity of the Anti-Socialist coalition led by Nayaga Nurzhavong, with the centrist opposition, and Leftist coalitions strongly positioned in the upcoming elections. At the end of 1958, both the SDP, and NDP had lost support for Nurzhavong, and sought to form a majority government with the Centrist opposition with one of the two at the head, following an expected negative result for the FLC. Election night on March 1st, 1959 however came with extreme surprises as rural support for the LSWI ensured that the party would be the largest in Congress. The results sparked chaos in the ruling coalition and opposition at the face of a minority LSWI led government, although the FLC, SDP, and NDP agreed to a SDP led coalition government they could not obtain sufficient votes a 2/3 majority, to overturn the granting of government making powers to the LSWI, which was automatically done to the largest party. Nurzhavong along with Supreme Army General Oke Syrypanha, agreed that the LSWI could not be allowed to form a government, along with support from the President, and the SDP. Nurzhavong who was still Premier suspended the constitution and established martial law, in the hopes of arresting most of the LSWI top leadership inside Pers, as Army units rushed into the city and police blocked all entry and exit ways of the capital on March 13th, 1959. The plan however had been leaked and numerous LSWI leaders including Goube had escaped.
Civil War (1959-1961)
Looking to prevent the rise of a LSWI government. The military and ruling government conducted a coup attempt on July 11, 1959. The coup attempt failed, allowing LSWI leaders and commanders to exit Pers, with Goube establishing a government in the northern city of Zadou that LSWI had taken. Moderate members of the government moved to the LSWI, and internationally Goube presented himself as leading the legitimately elected government. LSWI forces enjoyed support from Dezevau, Valduvia, and Chistovodia, in the form of manpower, trainers, and equipment. LSWI forces were trained in Dezevau, and equipped before crossing the border.
LSWI forces quickly secured the northern provinces, but were unable to secure major city centers such as Dezebenhua, and Dabadonga. With LSWI forces struggling to overcome Republican resistance. Hacyinian forces were involved in providing aid to the Republican forces, and LSWI fears of sudden invasion by Hacyinian forces were prominent. After LSWI forces were unable to storm Dezebenhua on October 1959, Dezevauni regulars entered the country. A major offensive on December 1949 resulted in the surrender of Dabadonga and all territory north of the Siadng although Dezebenhua evaded LSWI forces during the entire war. LSWI forces made thorough progress south of the country, and by June 1960 had reached Pers. LSWI forces stormed the city in July and August, before Republican forces abandoned the city. Republican forces having stopped LSWI forces on Pers, conducted a major offensive during November-January 1961, that culminated in massive losses for the LSWI, however Republican resources had been exhausted. After a period of rest, and Republican infighting, LSWI forces conducted a major offensive overwhelming Republican forces, retaking Pers in September. Republican forces began negotiating for the end of the war.
People's Republic (1961-1970)
Goube declared the People's Republic of Lavana, and declared it a one-party state, ending the multiparty coalition of leftist and Worker International parties in the country. Goube reformed numerous aspects of the Lavanan Congress, primarily the reduction in freedom of the body, and scope. Elections were no longer free and open, and instead citizens voted on single candidate races. The Congress of the LSWI was established as a parallel structure to the Lavanan Congress, which allowed inner party politics to remain inside the confines of the party. Goube quickly entered the International Socialist order, and foreign specialists arrived to the country.
1970's
1990's

Tensions between Lavana and Hacyinia remained high as Lavanan support for Ukilen and Majgar Workers International increased. On December 1991, 32 Ukilen soldiers trained inside Lavana were arrested trying to enter Hacyinia, leading to a diplomatic spat between both nations, with Hacyinia shelling Lavanan border crossing throughout the month. Dezevau had become increasingly worried about the situation in Hacyinia and worried that Lavana might launch a full scale invasion of the country, and stated that they would not support an invasion. Inthavongsa frustrated with Dezevauni reluctance and with limited support at home, refrained from invading Hacyinia but shelling between both sides continued until February its longest period since 1986. In the town of Shieli near the Lavanan border, Majgar insurgents were cornered and shelled throughout March and April, with large civilian populations unable to leave the town. Fearing heavy casualties in retaking the town, Hacyinian forces used Sarin gas to dislodge the defenders. The attack left 300 insurgents dead and 500 civilians killed after the Sarin was accidentally dropped on a civilian hospital. Inthavongsa quickly used the attack as a justification to mobilize the armed forces and to shore up support from Dezevau, which agreed to not oppose Lavanan intervention in Hacyinia.
Pers Acts 1994 reforms
2000's
2010's
The need of further electricity for Lavana, and further expanding it's energy diversity the Lavanan Congress approved in 2004 a wide variety of projects including the construction of along with numerous other projects including 4 nuclear reactors, and 2 wind farms but most prominently a dam in the Lav San river in the north of the country, which had been marked for possible hydroelectric potential in a study in 1994. The dam began construction in 2005, with help from Dezevau, the dam finished building in 2014, becoming the largest dam in Southeast Coius.
On November 11th, 2019 Premier Loe Vatthana died of a heart attack, and was succeeded by Vice-Premier Laina Keomany.
2022 Lavana coup d'état and aftermath
Following Vatthanas death in 2019, Keomany became Premier and initially crashed with General Secretary of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International who holds power over the democratically elected government and is directly solely by the party elite and its members. Keomany attacked Goubist faction members, and was seen as a threat against the old guard of the party. Khudu Narinamoa was elected on 2020 as General Secretary to counter Keomany as both of them were connected through the marriage of immediate family. The connection was abruptly ended by the death of Vinliam Keomany, Lainas Grandson on October, fearing renewed interest by Keomany to challenge the old guard he approved new election rules which would had given the party elite greater power to elect his position.[1] The Reform faction increasingly began challenging and attacking the Goubists for such a move, and the election of Narinamoa was expected on March 1st, he quickly replaced key Keomany allies and sought to cripple her power in the party. Military movements throughout the country in the leadup to the election were noted in foreign press.[2]
On March 6th 2022, Khudu Narinamoa General Secretary of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International legally removed Premier Laina Keomany from her position and appointed a replacement Premier. The move was seen as a coup, and Keomany called on the army and people to defend Lavanan democracy citing the removal as illegal, and launched a countercoup. Soldiers loyal to the central government and Keomany fought throughout Lavana, primarily in Pers where large scale fighting and civil protest took place. Keomany was able to elude capture and with sizeable military and civilian casualties throughout the country, Narinamoa surrendered on the 7th of March after coup forces penetrated into Pers. Sporadic fighting continued until the 9th. The coup left about 1,000 soldiers and civilians dead throughout the country.[3]
Keomany called the coup a vile attempt to remove democracy from Lavana, and stated that Champania had supported Narinamoa on his coup attempt. Keomany took on the role of General Secretary, and published lists of individuals which were connected to Narinamoa and the coup. About 38,941 were detained of which 30,159 were arrested on numerous crimes such as treason, corruption, and Espionage in total 98,291 government officials and workers were suspended or fired over their role in the coup.[4] The LSWI and the Lavanan Congress had hundreds of high ranking members removed from power and arrested. Over 300 members of the Lavanan Congress were removed, and Keomany appointed allies to the vacant seats using emergency powers given by herself by announcing a 3 month emergency period. Which she used to approve a temporary new constitution giving her position increased powers, and removing any possible attempt by the party to remove her from the position. The ability to deeply reform the Lavanan state, including several rules to allow for Democratic elections were also included in the constitution.[5] Keomany stated her intentions to reform Lavana to be a more fair and democratic country, announcing the first multiparty elections since 1959. [6] Keomany ran on a platform of deeply reforming the Lavanan state, and expanding the rights of minorities to defend and uphold their cultural values. Elections were held on September 1st 2022, with the LSWI establishing a minority led government with several other parties. On October 7th, 2022 a new constitution was permanently voted on and entered into force on October 1st of that year.
On October 1st a car bomb outside the Mei Phong Mall car bomb attack in central Pers, detonated.[7]killing 26 people and injuring 33. Shelling in the breakaway republic of the Yoloten, by Pro-Hacyinian militias was alo reported. Lavana claimed that Hacyinia had violated the 2004 agreement by failing to properly deal with militias in the demilitarized zone separating the Hacyinian army and the PAMFY, which had launched the attacks. [8] This prompted Lavana to begin building up troops alongside its border with Hacyinia and the Yoloten. On November 8th, Lavana invaded Hacyinia and moved troops into the Yoloten, kickstarting the Second Yoloten war. It sought to prevent further border incursions and defend the Yoloten from foreign incursions. Lavana made mention of imminent terrorists attack on Lavana utilizing Chemical weapons but this has been contested internationally. Following the announcement of a ceasefire on November 18th, as a result anti-government protests in Lavana begun, leading to the resignation of Premier Laina Keomany, and the confirmation of former Minister of Economy Emmanuel Bakhtzhany.
Geography
Lavana is located between latitudes 7° and 17°S, and longitudes 59° and 83°W in the eastern portion of Coius. It borders Dezevau to the north, the Brown Sea to the east of the country, X to the south, Hacyinia and the Yoloten to the west of the country. Lavanas total area is 731,189 km2 (282,313 sq mi), making it a relatively large country in the world, Lavana has a long coastline with the Brown sea holding sovereignty over several islands, however most of these are small islands off the coast.
Lavanas borders mostly stem historical precedent which defined the nation of the Kachais from the Siadng river in the north and the Kalani river to the south, with most of its western border a result of colonial rule which defined the border without taking into account the ethnic makeup of the area. Its Northern border was the subject of much controversy during the partition of the Aguda Empire and the latter independence of Lavana and Dezevau, both nations have since defined the border. Although the greatest controversy stems from the border of Lavana with Hacyinia. Currently Lavana recognizes the modern border as their defacto borders, while Hacyinia claims the borders following the 1940 Galshir War.
Lavana is a relatively flat country with mountainous and hilly regions to the north and west of the country, the Gezije range defines most of the northwest of the country where its mountainous territory spills between both Lavana and Dezevau. The Gezije ranges gives way to hilly regions to the west of the country called the Nayzabeler which eventually give way to the steppe reminiscent of the Great Steppe, powerful rivers traverse the southwest corner of the country eventually drain into the Ikaika lake, the Kung and Phankham rivers originate west of the Nayzabelers. To the east of the Gezije the Zedenge valley along the Siadng river gives way near the coast to remnants of Bouvai Massif stretching from Dezevau. The rest of the country is relatively flat with vast rivers the most prominent of which is the Kung river transversing the land. The Kung river water basin covers large parts of the country and has served the role of the central artery to civilization in Lavana since ancient times, large sections of arable land can be found to its sides and the seasonal flooding of the Kung river has provided ample nutrients to agricultural operations for centuries. Most of Lavana receives large amounts of rain, and thus large jungles and forests exist in the country, swamplands are common in several parts of the country most importantly near the mouth of Lavanas numerous powerful rivers. To the west of the country the jungle of the lowlands gives way to vast and open plains which enjoy calm weather. Lavanas highest point is Mount Zirjia 1,694 m (5,558 ft) in the Gezije range and its lowest is Jaudau Panna −4 m (−13 ft) to the east of the country in the Zedenge valley.
Rice paddy field in Bantafa province.
Climate
| Climate data for Lavana (records from all meteorological stations) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.8 (78.4) |
27.8 (82.0) |
28.7 (83.7) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
30.7 (87.3) |
28.2 (82.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
| Source: Ministry of the Interior | |||||||||||||
Biodiversity
Lavanan can be subdivided between several ecoregions because of its climate and geomorphology. The country is rich in terms of biodiversity, and several native species exist in the country. It has numerous ecoregions, ranging from Jungles in most of the center of the country, and northwest, to wetlands among the Kung River, and the coasts. The country has 27 national parks, 15 reservations, and 5 natural monuments. The largest of this protected areas is the Red great Crane National Park at 641.5 km2, which was added to the World Heritage list in 2015, the site has been a protected site since 1911.
Lavana is a country of distinct Fauna. It has some 15,600 animal species, including at least 2,423 Bird species, 1,900 Amphibian species, 1,610 Mammal species, and 1,427 Reptile species, of which 5,000 are endemic to Lavana. Including large quantities of insects. Some native birds include the Black-throated tit, Black-winged stilt, Common emerald dove, Crested Treeswift, Greater adjutant, Greater flameback, Knob-billed duck, Long-tailed shrike, Nainan crested argus,Red great Crane, Silver pheasant, Tawny fish owl, Yellow-vented green pigeon. With the Red Great Crane being Lavanas national animal and featured in the flag of the country. Amphibians include the Chungus sucker frog, Giant spiny frog, Lavanan knobby newt, Lavanan Warty newt, Upper Lavanan caecilian, along with a variety of Salamanders, most Amphibians in the country were discovered within the last decade. Native mammals include the Clouded leopard, Coian elephant, Disk-footed bat, Great Steppe Horse, Large-spotted civet, Lavanan tiger, Northern treeshrew, Smooth-coated otter, Spinner dolphin, Sun bear, Sunda pangolin, Wild water buffalo, including several Primates such as the Crab-eating macaque, Snub-nosed monkey, and White gibbon. Reptile species native to Lavana include the Blue-crested lizard, Coian giant softshell turtle, East Coian Crocodile, Golden flying snake, Kung's smooth skink, Lavanan monitor. Hundreds of Freshwater, and Saltwater Fish live in the countries numerous rivers, lakes, and seas.
Lavana has suffered with issues of deforestation and poaching since the 1950's. Lavana had amongst the highest rates of deforestation between 1960 and 1970, with international alarm raised at the rate Lavana was losing its forests. Following concerns regarding deforestation near the Red Great Crane National Park in 1989 led to the government to enact reforms and law which prevented deforestation and {{wp|Habitat loss} in large sections of the country. The country expanded upon this in 2000 with further laws enacted to defend Lavanas biodiversity. Endangered wildlife is protected by law, and as of 2020, 1,736 species were protected by the state.
Politics
The Lavanan constitution states that the People's Republic of Lavana "is a democratic socialist state governed by a people's democratic government that is led by the working class and based on an alliance of all Lavanans," and that the state institutions "shall practice the principle of democracy." Lavana is constitutionally a parlimentary, multi-party, representative Council republic. The Premier is the nations head of state, Head of government, and Chairman of the armed forces, elected by the Unicameral Lavanan Congress. The Premier is the head of the Lavanan Cabinet and appoints its members. The incumbent Premier is Emmanuel Bakhtzhany, who was elected to the position in 2022. Her Vice-Premier is Trang Dong. Under the 2022 constitution, Lavana is officially a multi-party state, although in reality the Lavanan Section of the Workers International (LSWI) asserts their role in all branches of the country's politics and society.
Although the LSWI describes Lavana as a "free liberal socialist democracy", the country is commonly described as an authoritarian single-party, and a Depostic dictatorship. Its current political, ideological and economic system has been termed by its leaders as a "Liberal Councilist state", "People's Liberal Democracy", "Socialist Market economy with Lavanan characteristics" respectively. Lavana saw the highest democratic rating since 1959, in 2022, the first such change since 1994. Although it is still described as unfree country.
Political concerns in the country include: Corruption, minority rights, religious freedom, and the economy. Laina Keomany is still highly popular, however her involvement in the invasion of Hacyinia, and the ensuing defeat, her position was no longer solid, and she resigned in favor of Emmanuel Bakhtzhany, her former Minister of Economy. Bakhtzhany is cited as the mastermind of Lavanas post-coup economy, and he is believed to have opposed the invasion of Hacyinia leaving him untouched by the fallout.
Lavanan Section of the Workers International
The General Secretary of the LSWI performs numerous key administrative functions, controlling the party's national organization, and direction. The current general secretary is former Premier Laina Keomany, the first individual to hold both positions since 1994. LSWI membership elects the parties General Assembly, who elects the General Secretary and decides on policy and goals for the LSWI. Local LSWI Assemblies are directly elected, and higher levels of LSWI Assemblies up to the General Assembly are indirectly elected by the Assembly of the level immediately below. One can be a member of the democratically elected councils and congress and the LSWI structure, and close to 90% of all elected members serve in some capacity in both systems, primarily in lower levels.
Following the 2022 coup, the LSWI experienced its greatest reform since 1994. The party lost most of its ability to directly affect the democratically elected government, which had caused the government crisis and subsequent coup. Although officially a multi-party state, the LSWI still controls the legality of political parties in the country by appointing or removing members of the Electoral commission, through the Premier. Effectively ensuring no proper opposition arises. Several parties were founded in the aftermath of the new rules, which represented previous ideological sections in the LSWI, such as the Worker-Labour Front, and Great Crane Association, which competed in the 2022 elections. These parties are equally organized as the LSWI, although in a lesser scale.
 |
|
Government (753) Independents (6) |
Government
The Lavanan Congress is the unicameral state legislature composed of 801 members. Headed by the Premier, it is superior to both the executive and judicial branches. 2 members are elected by municipality using Ranked voting, to the congress to serve 5 year terms, 3 seats are reserved for 3 members of all 24 Provincial councils. Seats for all ethnic groups in the country, distribution seats for municipalities that are highly populated, along with abroad seats fill out the remaining seats in the Congress. Provincial councils function in the same way as the Congress with certain duties granted to them by the constitution, Municipal and city level councils are elected as well, all using Ranked voting. Unlike with the LSWI structure, all citizens 18 and older are granted the right to vote on Legislative elections, unlike in LSWI where only party members are allowed to vote.
Currently the LSWI rules in a collision government with all other parties, and some independents. Currently a 753 Coalition government exists, with numerous members in confidence and supply roles, or serving in the opposition. Currently only 6 independent politicians are members of the opposition.
The Supreme Court of Lavana, headed by a chief justice, is the country's highest court of appeal, though it is also answerable to the Congress, and the Premier. Its a 15 member court with members elected for single 10 year terms. Members are appointed by the Premier. Beneath the Supreme Court stand the provincial, municipal courts and city level courts. Military courts possess special jurisdiction in matters of state security. Lavana maintains the death penalty for numerous offences, although it has not charged anyone since 2009 and carried out an execution since 2013.
Lavanas Socialist constitution takes its roots from the 1961 revolution, which granted wide powers to the LSWI and limited democratic involvement. Following internal instability within the LSWI, and widespread protests during the 80s and 90s a group of reformists led by Keo Sitwat came to control the LSWI and resulted in the election of Sitwat as both General Secretary and Premier, Sitwat ushered in a new constitution in 1994, which reformed the Lavanan state. This reforms were welcomed, by the LSWI and the population which allowed Lavana to survive the end of the 20th Century which saw numerous Socialist states collapse. Sitwat's successor Hatsadi Lor continued Sitwat's successful reforms, but he desired further democratization and reduction of power for the LSWI causing major frictions inside the LSWI. Major Reformist and Conservative factions arose within the LSWI. Traditional groups of LSWI members have been members of several distinct "Sections" with differing goals and beliefs, ranging from Market socialists to Authoritarian socialists. The two major sections that of the United People's and that of the Gouve Section were the largest sections in the country, where they contested the position of General Secretary and Premier usually, they're the party leaders of the Reform and Conservative factions respectively.
The struggle between factions led to the 2022 coup, where Conservative factions feared an immediate loss of power, and sought through the General Secretary of the LSWI to remove Premier Laina Keomany the leader of the Reform faction. The failure of the Conservative attempt to mantain power, resulted in the major purge of the LSWI of members of the Conservative faction and rivals to Keomany. The Premier quickly filled positions with loyalists, and members of the reform faction, which rallied around her. Experts believe that 10% of the Conservative faction remain in the country, with the rest having been purged from government positions, and civilian positions.
Administrative divisions
Lavana a unitary state, with partial devolution consisting of 24 provinces (ແຂວງ ; Aekhuang). The most populous of which is the Capital province holding 10 million people. With the largest geographically being that of Thaviang.
Provinces each with their own elected Provincial council headed by a Governor (ເຈົ້າແຂວງ ; Chaoaekhuang) located in the provincial capital. Provinces are further divided into Municipalities (ເທດສະບານ; Thedsaban) of which there are 350. They're governed by a Municipal council, who elect a rotating leader to represent the municipality within Provincial councils. Municipalities are further divided into City "level" subdivisions, of which there are 1,425 in the country. This city "level" divisions include County (ຄາວຕີ້ ; Khav ti), City (ເມືອງ ; Meuong), Village (ບ້ານ ; Banla), and Ward (ອຸປະຖໍາ ; Upathoa). Which elect their own councils and representatives to the Municipal council. Population not updated
| Province | Capital | Population | Province | Capital | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atasu | Hara | 4,045,573 | Gezije | Diuhai | 3,315,301 |
| Ban Sai | Nang Ha | 3,911,425 | Kluangha | Dalat | 355,644 |
| Ban Vuga | Ban Vuga | 4,951,125 | Kunsao | Ban Moc | 4,774,141 |
| Bannasao | Sikeut | 4,755,567 | Labis | Arachzharga | 881,031 |
| Bantafa | Ban Lao | 4,056,772 | Makat | Hatgna | 3,676,311 |
| Biyaosa | Biyaosa | 3,169,377 | Panitch | Dezebenhua | 5,163,356 |
| Capital | Pers | 10,055,673 | Sainyabuli | Pong Det | 4,416,884 |
| Cha Ha | Bouna | 4,889,530 | Terjasa | Ulzit | 2,687,853 |
| Dabon | Yong Peng | 452,778 | Thaviang | Thaheu | 4,536,888 |
| Daonga | Dabadonga | 2,629,185 | Wanen | Ban Pasao | 954,602 |
| Diahai | Ban Leum | 3,497,316 | Xaisetha | Jaudau Fai | 4,318,736 |
| Galshir | Karatau | 3,628,518 | Zadou | Zadou | 1,719,156 |
Military
The Lavanan People's Armed Forces consist of the Lavanan People's Army (LPA), Lavanan People's Navy (LPN), Lavanan People's Airforce (LPAF), the Lavanan People's Public Security (LPPS), which is divided between the Lavanan Coast Guard, Lavanan Border Force, and National Defence Units (NDU). In total it is composed of about 750,000 soldiers. All 4 branches fall within control of the Ministry of Defence, and are presided over by the Premier of Lavana. Lavana spends about 2% of its GDP or $39.4 Billion on its armed forces, it accounts for about 10% of government spending.
The LPA is by far the largest branch of the Armed Forces, as it stands at 400,000 total soldiers including 100,000 reserves. It is by far the most important branch in the Armed Forces. The LPN and LPAF are smaller in size, the navy operates limited blue water capabilities with 5 Diesel attack submarines, 10 Destroyers mostly older models, along with numerous smaller vessels. The LPN operates mostly brown water capable vessels, owing to the countries vast inland waterways, with hundreds of Gunboats. The LPAF relies on older aircraft including the TRA-21 Fighter aircraft, Sin-201 attack helicopter, and TRA-09 transport aircraft. The LPPS serves the role of Public security in the country. It totals 270,000 soldiers, with the Coast Guard polices the Lavanan waterways and helps in Search and rescue operations, while the Border Force operates all entry points into Lavana, and patrols the borders of the country. The National Defence Units (NDU), are the former military arm of the Lavanan Section of the Workers International, and operated as a paramilitary force from the revolution until 1995, when it was incorporated formally into the armed forces. The NDU operates as a Gendarmerie, and police force at the national level mostly to provide additional security to rural localities.
Lavana obtains most of its equipment from other Socialist states, most prominently Chistovodia, Dezevau, and Kirenia. Lavana conducts regular exercises with its Brown Sea Community allies, Dezevau and South Kabu on a regular basis. Lavana allows South Kabu to utilize its airspace and facilities to train members of the South Kabuese Airforce, and agreements between both armed forces exist. Conscription in Lavana was ended in 1995 with the new constitution, and the armed forcs moved towards a fully professional force, along with reducing its size from 900,000 total personnel to 700,000. Lavanas close relationship within the Brown Sea Community resulted in little need for advanced forces so long as the Lavanan army was able to remain more advanced than its neighbors. Following 2016, Lavana embarked on an modernization effort primarily for its Type-59 tanks, and the equipment of the Armed forces. The country has maintained interest in expanding the LPN, and LPAF and was a driving reason for the 2021 Government budget, which would allow Lavana to acquire a new fighter aircraft, along with expanding its Blue-water capabilities. Lavana is the primary developer on the
Foreign Relations
Lavanas Socialist leanings have dictated the countries foreign policy since the revolution. Lavana today is a prominent member of the Association of International Socialism of which the country is a founding member, and 3rd most populous member. Lavana is also a member of the Brown Sea Community with socialist neighbors Dezevau and South Kabu, Lavana maintains through the BSC cultural, economical, and military ties with both nations. Lavana does not recognize the sovereignty of North Kabu, and supports South Kabuese territorial claims on Gaullican and Estmerish controlled territories, which has caused controversy. Dezevau is Lavanas closest ally, and both nations maintain deep diplomatic, cultural, economic, and military connections.
Following the liberalization of the country, Lavana normalized diplomatic relations with non socialist states, and opened its first foreign embassy in a previously not socialist country in 1993 in Werania. Lavana has diplomatic relations with over 50 countries and maintains embassies in over 20. Lavana maintains several agreements with Vinalia, and is the countries closest non-socialist tie. The nation maintains additional diplomatic relations with non-socialist states in Kuthina, Garambura, and Mabifia. The country along with the BSC maintain difficult relations with Nainan do to that countries persecution of Socialists, although efforts between both states in cultural matters have been made. Lavana provides foreign aid to nations in Bahia mainly focused in the development of agricultural, and food security in the region, Lavanan doctors frequently make trips to Bahia to provide medical aid to the population, the largest of this efforts involved 100 medical personnel deployed to Garambura from 2007 to 2009.
Lavana holds complicated relations with its neighbor Hacyinia, both nations have fought several wars and conflicts since Lavanan independence in 1941. Conflicts stem from issues regarding the partition of Estmerish holdings, and Princely states, but it has since expanded to the treatment of Ethnic minorities, Geopolitical influences, and military intervention in internal affairs. Hacyinia claims 1/3rd of Lavana, which it gained in 1941 and subsequently lost between 1942 and 1963. Lavana invaded Hacyinia in 1992, and established the People's Republic of Yoloten (PRY), which is recognized by a couple of friendly Socialist countries. In 2005 Lavana reached an agreement with Hacyinia that removed all Lavanan troops from the Yoloten. Lavana holds close economic ties with the Yoloten, which ruling party the Provisional Administrative and Military Front of the Yoloten (PAMFY) has been described as a Lavanan puppet. The PRY is located in a former princely state whose ruler sought to join Lavana during the partition before the state was invaded and annexed into Hacyinia.
Lavana terminated all relations with Champania following its coup on March 2022, where it blamed the Champanian government for supporting the removal of Keomany. Relations were reopened on August 2022 between both Lavana and Champania, although considerably less friendly than before. Lavana clarified the situation by stating that Champania had provided information that disproved the claims of the administration of Champanian support for the coup, with Keomany publicly walking back her accusations.[1]
Lavana is a member of the Community of Nations, Association of Gaullophone States, Estmerish Council among other international communities.
Economy
Generally considered a developing economy, Lavana has a nominal GDP of $640.2 billion as of 2020, and a PPP GDP of $1.920 trillion, with a nominal per capita at $4,740, and $14,220 PPP per capita. It has an above average Human Development Index score of .806. The country has showcased strong economic growth, posting good economic growth around 4% and peaking at 9% in 2014 since 2001, the countries economy grew by 3% in 2020. However the Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs estimates that, as of 2020, roughly 21.6% of Lavanas population lives on less than $5.50 a day, a considerable reduction from 70% in 1993. The country's unemployment rate was estimated at 4.2% in 2019, its lowest in history.
Agriculture and fishing
Agriculture has historically been a major sector in Lavanan economy, Lavanas vast system of rivers and estuaries with additional man made water ways such as canals, Lavanan farmers have always had access to vast fertile lands and ways to transport goods using the rivers. Lavanas has always been a major producer of rice through the use of paddy fields, and it has been a major part of Lavanan diet for centuries. Lavana is a major exporter of rice in the world, but it has seen a decline as other products such as coffee, and nuts increase in value. Lavana alone is the worlds biggest producer of Cashew nuts, and is a top producer of coffee. Coffee has become a major part of Lavanan agriculture following its introduction in 1870 by Gaullican authorities which sought to establish profitable plantations in the country, the Socialist government has sought to increase coffee production as the demand of the product grows both at home and at broad. Other products produced in great quantities include peppers, rubber, cotton, sugar, coconuts, among others. Lavanan attempts at diversifying its agricultural output have been greatly successful with Lavana holding among the most resilient agricultural sectors in the world.
Fishing has historically been a key part in the economy of Lavana, fish farming in Lavana traces its history to antiquity where fishing villages known as Kelongs appeared on the rivers of the country usually close to markets with farmers managing fields then returning to their houses to feed fish held in large metal containers. Such fishing villages have been impacted by river pollution along with higher costs than fish grown in land based farms. Land based fish farms have grown greatly since the 80's with government subsided farms cropping up across the country, and making it easier for rice and fish farms to grow and expand. Many villages in the coastal regions still largely depend on fishing, which has led to overfishing in some areas. Fishing of sea cucumbers has seen increasing growth, although much of this is performed illegally the high price of the sea cucumber makes it hard for government authorities to regulate, attempts at farming the sea cucumbers have mostly had low results, and attempts at polyculture growing both sea cucumbers and prawns have had little success. Highly profitable shrimp farms have seen a massive investment in the country with large amounts of public and private money invested into the industry, making the country among the leading producers of shrimp.
Energy
Lavana consumes some estimated 330,437 Gw a year, with an average consumption of 3,805 kWh per person, making it one of the largest electrical consumers in the world. Lavana obtains its energy mainly from Coal and Nuclear power at 40% and 28% respectively, Oil makes up 15%, with the remaining 17% made up of renewable energy primarily Hydroelectric at 85%, Wind at 10%, and Solar at 5%.
Lavana has historically relied on Coal for its energy needs, and today it remains its largest source of energy at 40%. Increased desire to diversify and combat pollution lead to government development of alternative energy sources. Today coal makes the least percentage of the energy grid in its history, although the amount of coal generated energy and thus consumption has increased. Lavana has promised to stop building new coal power plants by 2025, and to phase out all of its coal power plants by 2035.
Lavana operates 12 reactors in 4 Nuclear Power plants. Lavana has expressed great interest in nuclear energy and between 2005-2020 the nation built 4 reactors, and announced its intention on keeping the 2 Min La reactors first built in 1985 online until 2040, Lavana also stated its intention in building a further 3 reactors in a brand new facility between 2020 and 2030. Lavanas growing energy needs and desire to become more energy independent resulted in it stating its desire to have 50% of Lavanan power produced through nuclear energy by 2050, with plans for the construction of up to 12 new reactors to be constructed, effectively doubling the amount of reactors in Lavana.
Renewable energy has been a growing field in the country, primarily hydroelectric power, Lav San Dam first started building in 2004 and finished in 2015 is the largest dam in Southeast Coius, and provides 80% of Lavana's total hydroelectric power output. The dam was seen as a highly ambitious project as it was the first large scale dam project in Lavana, but its successful construction and results have led to wider development in the area, with multiple projects seeking to expand on the success of the dam. Other sources of energy although limited have slowly grown in importance, the government has approved 10 Gw worth of solar farms in the nation to be installed between 2015-2025, the move marked as highly ambitious has met great results with a steady rise in solar power produced and a general decline in the cost of electricity primarily in the west of the country where nuclear energy is not as efficient, and issues with the transportation of electricity from the coastal plants.
Lavana maintains a production of 150,000 barrels of oil per day, while having proven reserves of 1.5 million barrels, although PetroLav maintains that the country has 5.3 million barrels in reserve, this figure is hotly contested. All Lavanan oil is managed by the state-owned PetroLav company. Lavana obtains most of its oil from Offshore drilling in the Brown Sea, along with some oil fields in the mainland. Lavana was the center of major AIS Petro-chemical development spurred by government interest in the 60's and 70's for the exploitation of the resource, oil was seen as a possible driver of the Lavanan economy although no major sources of Oil could be found until the discovery of Oil deposits in the Brown Sea. Oil served as another way for Lavana to obtain foreign currency until Lavana stopped exporting oil in 2005, do to the rise in the cost of oil, that made historically expensive Lavanan oil uncompetitive in the foreign market. Lavana has some Natural gas reserves, although they have not been exploited do to high development costs. Lavana will open its first natural gas power plant in the outskirts of Dezebenhua in 2022, with goals to make natural gas represent 10% of the grid by 2040. PetroLav owns a considerable amount of Oil in the Yoloten, with 80% of its extraction under its control, and 100% of its refining capacity.
Mining
Although mining has existed since antiquity it has not been a key sector in the Lavanan economy, Gaullican attempts at increasing production of coal reserves found in the Gezije range were largely unsuccessful, and Lavanan has primarily mined minor amounts of iron, and copper. In the 1970's growing interest in the sector resulted in studies conducted by the central government which found unexploited reserves of bauxite, chromium, and zinc resulted in wide investment by the central government, this resulted in the establishment of the ສະພາຂຸດຄົ້ນບໍ່ແຮ່ແຫ່ງຊາດ (National Mining Council), a state owned enterprise tasked with managing the mineral resources of the country. By 1996, Lavanan production of bauxite, chromium, and copper had nearly quadrupled, with the nation becoming a key exporter of bauxite on the global market with large reserves still unexploited. This rapid expansion was seen favoredly by the central government as a key way of obtaining foreign hard currency, and allowing for warmer relations between Lavana and foreign buyers. Mining is conducted wholly by the state owned NMC, and foreign investment and acquisition is carefully regulated.
The expansion of mining has caused severe environmental issues, with waste from mineral operations usually dumped into the countries rivers, following government regulation this problem has been majorly eliminated by environment degradation, and deforestation remain a key issue. As most minerals are mined and transported through the river system for either export or processing, spills and leaks have occurred. In 2014 an iron ore transporting vessel collided with a fishing village on the Kung river capsizing and releasing several tons of the ore into the river causing great pollution along with several deaths, attempts at changing the transportation of minerals through railway has seen some success but still large amounts of minerals are transported via waterways.
Transportation
Prior to Gaullican colonization most of Lavana relied on waterways for transportation with some stone roads connecting major cities and centers of trade. Gaullican authorities made use of the countries vast river system as previously done through the centuries. The first railroad in Lavana was laid in 1890 between Pers and Kipchu although it served primarily for passenger transport as river transport was incredibly cheap. A major explosion in infrastructure occurred in the 1920's as Gaullican authorities desired to create a vast system of roadways to aid in mobilizing soldiers and resources, such a system had been mostly completed by the start of the Great war, although further plans remained uncompleted and neglected following the war. The Socialist government launched a major campaign constructing infrastructure throughout the nation.
Lavana has a vast motorway network, with national managed roadways (4-6 total lanes) connecting major cities, and provincial managed roadways (2-4 total lanes) connecting other areas of the country, in 2017 all provincial roadways were paved, while municipal roadways (2 total lanes) cover the rest of the country with varying levels of maintenance and paving depending on the municipality. The central government began construction on an expressway system (6-8 total lanes) in 2010 and construction was underway, with the first section of the route K1 Pers-Ban Vuga expected to finish in 2021, with K2 Pers-Biyaosa, K3 Pers-Dezebenhua, and K4 Pers-Kurei expected to be finished by 2022, the central government expects to finish the expressway system by 2035 with routes K1 to K6. Congestion has been a major issue for the country as large sections of Pers can be completely gridlocked during rush hour, the increase in commuters and car ownership have been blamed for such issues, but poor management of municipal roadways inside the city are also a cause, the government has attempted to limit the amount of cars on the roads but has faced backlash. Large parts of Lavanans still mobilize using motorcycles.
Railroad connections in the country have also seen great importance, with several thousands of kilometers of track laid down. Passenger rail is more developed than freight rail, a situation the country has sought to solve with the construction of a freight train only line between Zadou-Dabadonga-Dezebenhua which was completed in 2015, although plans to expand this freight only system remain mostly delayed as the nation has sought other alternatives to its growing freight needs. Construction on a freight only line between Pers-Ongoya-Dabadonga began in 2018, with a Kurei-Laitaka line beginning construction in 2020. A high-speed rail connection with Dezevau was inaugurated in 2015 the Bazadavo-Pers express via Mhidyzai, Viodhoumi, and Dabadonga was a major success for both nations, as the difficult geography of the area threatened to reduce speeds for the project but the link was completed with minimal speed loss. Such a success was celebrated through the issue of stamps across members of the AIS. Rapid transit in the form of metro lines has also seen keen development as the nation has sought to construct metro systems in its 3 largest cities, the Pers metro opened in August 2020 with its green line, further expansions are planned and expected to finish no later than 2032. Metro systems in Kurei and Kipchu are expected to begin operations in 2025 and 2026 respectively.
Lavana operates some 36 national airports including 4 international airports: Kanoa Somphon in Pers, Vongvichit International Airport in Kurei, Arath Khouph International Airport in Kipchu, and Laitaka International Airport. Kanoa Somphon is the countries largest airport handling much of its international passengers. Domestic flights to Pers-Ban Sao were moved to the smaller Keolamalay airport in 2018, which has reduced congestion in Kanoa Somphon. Lavana's national carrier is the state owned Lavanian Airways, which operates close to 70 aircraft, Lavanian Airways flew to some 60 destinations all in Coius and Euclea. Private carriers exist in Lavana as well.
Lavanas important relation with waterways has resulted in sizeable amounts of cargo and passengers still utilizing the water systems although this amount has reduced for several years following government attempts at improving water quality and other methods of transportation, and nowadays the river are mainly used by rural populations and the mining sector. The largest sea port in Lavana is that of Kipchu, which has always historically been the largest port in the country, Laitaka and Dezebenhua follow Kipchu both in importance and tonnage which passes through. Laitaka has become an important cruise stop with numerous cruise ships stopping at the port during the summer months bringing in international tourists.
Tourism
Brown Sea shadowed coral reefs World Heritage site is a popular spot for scuba divers. Site is jointly managed by Lavana and Dezevau
Kung river Red great crane breeding grounds was added to the World Heritage list in 2015, the site has been a Lavanan National park since 1911.
Duh Hoc culture jars encompass the numerous jars dating back to the 9th century B.C.E. Duh Hoc culture in western Lavana.
Part of the greater Zedenge Canal World heritage site Dabadonga was the capital of the Agudan Empire. The site is jointly administered by Lavana and Dezevau
The Ban Sao Historical center in the center of Ban Sao showcases the ancient capital of the Sao's which ruled over modern Lavana.
Demographics
Population not updated
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1900 | 30,500,000 | — |
| 1915 | 38,392,000 | +25.9% |
| 1930 | 48,738,000 | +26.9% |
| 1945 | 61,931,000 | +27.1% |
| 1960 | 72,524,000 | +17.1% |
| 1975 | 89,721,000 | +23.7% |
| 1990 | 107,384,000 | +19.7% |
| 2005 | 122,534,000 | +14.1% |
| 2020 | 135,022,931 | +10.2% |
| Source: Ministry of the Interior | ||
As of the 2020 census Lavana had a population of 135022931, making it the 14th largest country in the world by population. The Kung River basin has historically been heavily populated, and thus Lavana has had large populations historically. 19th century Aguda Census placed Lavanas population at 13.5 million people. However such censuses were discontinued during the colonial era. A 1935 census by Estmerish authorities estimated some 50 million people, although many have questioned such values. In 1960 the first comprehensive census was conducted, and has been conducted every 15 years since then. Lavanan officials released in 2021 an attempt to calculate Lavanan demographics since 1900.
Lavana has a population density of 189 (ppl/km2), making it the 12th most densely populated country in the world. About a third of the population lives in Urban areas with some 37.14% of the population, the largest of which is Pers and Kurei with 13.1 million and 5.95 million respectively. The Pers Metropolitan area houses some 15 million people and is among the largest metropolitan areas in the world, along with one of its densest. Lavanan life expectancy sits around 73.7 years of age, and has been steadily increasing since the 1980's.
Lavanan demographics are impacted by Natalist policies that sought to increase the size of the population. Lavana experimented with a "Child Provision" which sought to grant tax breaks, and in some instances direct income for each child a couple had. This campaign initially launched in 1962, proved successful in increasing the Lavanan fertility rate. This population boom, greatly increased the working population in the country and allowed it to increase its GDP considerably since 1990. Growing cost, and fear of Overpopulation lead to the abandonment of the Natalist policies, although the government has not sought to actively restrict population growth as had initially been thought. Since 1990 Lavana has grown by 25.74% or 27.6 million people.
Ethnic groups
Lavana is a multi-etnic country, with numerous people of differing ethnic, linguistic, and cultural backgrounds. According to the 2020 census established the Kachais as the largest ethnic group in Lavana at 52% (70.21 million), Dhavoni at 21% (28.35 million), Ukilens at 11% (13.85 million), Majgars at 9% (12.15 million), the Male at 3% (4 million), the Kiziks at 2% (2.7 million), with Other groups at 2% (2.7 million).
The Kachais represent a majority in the state, and are by far the most economically and politically active of all groups in the country. Kachais are found all over Lavana, but dominate primarily in the center and east of the country and all major urban centers. Kachais have been benefitted by settlement in the west of the country, and they represent about 1/3 in most of the western part of the country. The Kachais were part of the wider Kasi migrations from the 8th to 10th century CE, the Kachai being the furthest of said migrations. Initially arriving as mercenaries, they were increasingly settled in the urban centers of the country. Their increasing power inside Gevuine empire would culminate in the breakup of the Gevuine Empire and the establishment of a Kachai Empire in the Rasuvong. The Kachai would come to inhabit much of the east and center of the country, with significant populations settling north of the Gezije range.
Dhavonis represent the second largest group in the country, and enjoy vast economic and politically active roles in society. Dhavonis inhabit much of the north and major urban centers. Dhavonis is a term that refers to the people which lived in the lowlands South of the Zedenge Valley. The term is utilized by the Lavanan government to separate the Ziba speakers from Lavana and those of Dezevau and abroad, which are considered instead by their nationality. The term originates in the work of Republican Ziba writers which sought to create a distinct Lavanan identity for the Ziba speakers outside of Dezevau, based around a perceived historical difference from their northern neighbours which now represented the majority of the population in newly formed Dezevau. Although less relevant following the Lavanan Revolution in 1959, the distinction is still maintained by Ziba speaking populations.
Ukilens are the 3rd largest group in the country, they have enjoyed greater roles inside Lavanan politics and the economy since the 1980's but remain mostly sidelined. Ukilens make a majority in the West and Southwest of Lavana. Ukilen migrations into other parts of Lavana, primarily urban centers has expanded much of the population, and today about 1/4 of all Ukilens live away from the commonly Ukilen west, centering in Lavanas urban regions. Migrants from Hacyinia have also settled in Lavana in recent years. Majgars represent the 4th largest group, and have much of the same history and role in society as their Ukilen neighbors. About 1/3 of all Majgars inhabit urban centers. Majgars inhabit much of the west of Lavana, and its major urban centers. Ukilen and Majgar populations have increasingly mixed as a result of population shifts throughout the years. Ukilen and Majgar populations have experienced discrimination and political disenfranchisement in the past, leading to bans on cultural and religious practices. Today they suffer issues of political representation, which have seen attempts at fixing by new Lavanan administrations.
The Male inhabit much of the south of Lavana and represent the 5th largest group. Unlike the other groups, they have not migrated in great quantities into the urban centers of Lavana. The Kiziks represent the 6th largest group at 2% and inhabit small pockets in the northwest in the Gezije Range. About 1/2 of all Kiziks have migrated into urban centers in Lavana, primarily Kizik workers coming from Hacyinia.
Other groups in Lavana account for 2% and showcase the widespread diversity in the country. Significant populations of socialist countries exist, Kabuese, Chistovodians, Kirenians, exist in the country. Although the largest group is by far Dezevauni's. Similar situations exist for migrating Hacyinians, which are usually divided between classifying as one of the major ethnic groups in Lavana or as their nationality. A historically important population of Shangeans has existed in the country and can trace its history to ancient merchants and administrators that have come to settle into the country, throughout the centuries. Vinalians have settled in the country in great quantities since the 70's and today maintain small communities in the country. Kabuese have settled mostly in the eastern coast, or Pers. Most minorities and migrants inhabit the urban centers of the country, mostly concentrated on Pers.
Health
Lavana had in 2020 an average life expectancy at birth of 73.7, which is relatively low but has seen a great increase since the 1980's when it averaged to 65.2 years. The Community of nations estimated that the countries expected life expectancy could reach 75.5 within 10 years, as a result of a stronger healthcare system, and ever increasing quality of life for Lavanans. Health in Lavana is provided by the state free of charge, and is administered at the national and provincial levels, with the state operating more specialized services, with provincial being suited to more general services. Health in the country is administered by the Ministry of Health, its minister must be by law a health worker. Small clinics are run by provincial authorities and usually serve to treat general issues and concerns, also serving the role of family clinics, and walk-in clinics. Provincial health systems also maintain general hospitals in their territory which serve more advanced needs of the population, such as Surgery, Maternity Ward, Intensive care, and Medical laboratory. The national government maintains specific hospitals with specialized needs, such as Cardiovascular surgery facilities, Child hospitals, Cancer treatment, MRI facilities, and research institutions.
Lavana throughout its history has struggled with famines, malnutrition, and food insecurity. Which have led to instances of high child mortality, and a lower life expectancy. Some 500,000 have been estimated to have died as a result of the 1956 famine, which led to wide reform on the Lavanan economy, but remained of minimal impact, by the rise of the Socialist government and as a result of the civil war some 35% of all Lavanans held some sort of food insecurity, and some 8% were considered on famine like conditions. Socialist reforms and strong programs in the support of farmers primarily subsidies improved the food security in the country, primarily its western areas where famines had appeared on a cycle as a result of negligence on part of colonial authorities. Although progress was made, conflict and instability led to issues during the 70's and 80's in the west. Today under 10% of Lavanans experience some sort of Food insecurity during any given year, in a declining trend, malnutrition has also been heavily attacked primarily by introducing new foods into the diets of rural populations, which historically relied primarily on rice. The increase in unique crops grown, and imported have helped reduce Lavanas malnutrition rates, along with greater economic resources and nutritional information. Lavana and Champania collaborated extensively, with a large quantity of Lavanan doctors being trained in Champanian institutions. Such programs have faced extreme pressure do to Lavanan-Champanian strained relations stemming from the aftermath of the 2022 Lavana coup d'état.
As a result of the Lavanan civil war a large brain drain was experienced, particularly in the health sector as thousands of medical practitioners immigrated to other countries, thus creating a strain on the ability of Lavana to meet its increasing health needs. Lavana has historically experienced high rates of Tropical disease such as Malaria, Typhoid Fever, Dengue Fever, and Tuberculosis. To combat the lack of doctors and the government ever increasing desires to combat disease, a program was started in conjunction with the AESE where Lavanan doctors were trained in AESE countries primarily Kirenia, Chistovodia, Champania and Dezevau to increase their effectiveness. Such a program along with incentives for any desiring doctors increased the efficiency and amount of doctors in the country. Lavanan institutions have since maintained close ties with health institutions in other Socialist countries, Lavanan doctors have worked closely in North Vinalia (later Vinalia), Champania, and Dezevau to develop strategies for combating a variety of tropical diseases, primarily Mosquito borne diseases which are a great issue in this countries and abroad. Lavana had begun working closely with Vinalia in 2014 to develop strategies and treatments for the prevention and treatment of the Zika virus which had experienced an outbreak in the country that year, Vinalia aided the Lavanan government in implementing preventive strategies with great success. Lavana succesfully declared the country Zika free in 2016.
Smoking in the country has since 2008 been heavily regulated, following higher rates of lung cancer than the global average. Such measures have heavily curtailed the rates of lung cancer in the country, and has been one of the factors in Lavanas ever increasing life expectancy.
Education
Since 1980 primary, and secondary education are compulsory for all students, which together account for 10 years in total. Tertiary education comprises students attending a 2 year University Preparatory school, some 69.7% of students continue into tertiary education in 2010. Students must then pass the Kathomtua or National Preparatory Test to enter into University. Since 1980 primary and secondary education have been fully free, and since 2010 all tertiary and university education are free as well.
As of 2020 98% of the population over 15 were literate, this comes at a great improvement over the 13% literacy rate in 1941, and 58% in 1980. Free primary and secondary education are the main drivers in such high literacy rates in the country since 1980. Lavanan students have increasingly improved in their test scores, although they still lag behind other AIS states such as Kirenia, Chistovodia, and Dezevau.
Lavanas most prominent and prestigious university is the National University of Pers, which consistently ranks as among the best in Coius and the world. Other universities and colleges of importance are the Workers College in Kipchu, University of the East in Laitaka, and Pers University. Lavana has had an increasing level of higher university graduates and professionals, although Lavana holds a higher than average rate of migration in this area, primarily to other AIS countries such as Dezevau. In 2009 university graduate that speaks Ziba as a native tongue is 50% more likely to migrate to Dezevau upon completing their education than any other specific group in Lavana, something which has prompted concern for the government.
Religion
Religion in Lavana (2019)
The 2020 census registered that ranking first at 56% (75.6 million) were believers of Badi, ranking second at 21% (28.35 million) are declared as having no religion, ranking third at 12% (16.2 million) as being members of the Solarian Catholic Church, at fourth at 10% (13.5 million) is Irfan, 1% (1.35 million) people are members of other religions such as Amendist denominations, Orthodox Church of the South, Episemialist Church, Atudism among others.
Badi is the largest religion in Lavana at 56% or 75.6 million people. Lavana is one of the largest Badist countries in the world being the 3rd largest in total followers, and largest percent wise. Badi has a long history in Lavana starting from the 1st century B.C.E. when the practice and preaching of which was heavily banned by central authorities, however during the Dhijivodhi Empire, Badi was decriminalized and grew to become the main religion in Lavana supplanting earlier Lavanan religions. Lavanan missionaries would go on to travel into the steppe spreading Badi, and many Badi temples and churches can be traced back to Lavanan missionaries. The Kachai were converted into Badi in the 9th century CE, the Kanchai increasingly combined aspects of their own former Zohist faith into the beliefs and teaching of Badi. Badi was the dominant religion in modern Lavana until the arrival of Eucleans where Catholicism was greatly supported, numerous Badi practices such as the use of hallucinogenics were banned under colonial rule. Lavanan Socialism accepted Badi as an innate part of Lavanan society, but it did seek to regulate Badist sects and beliefs to better incorporate into Lavanan political and social goals, and prevent Badi from being a force against Socialist secularism. The Lavanan socialism government however did act against Badi, when on 1973 it banned and imprisoned followers of the Thin Air sect, which was the dominant sect in Ukilen and Majgar communities in a manner similar to how Irfanics were prosecuted decades prior. Such a ban was lifted in 1980, and imprisoned priests let go. Today Badists in Lavana similar to their brethren in Dezevau hold a less dominant role in society, as government is completely secularized.
About 21% or 28.35 million people declared themselves as having no religion. Irreligion stems from secular ideals during the Colonial period, which sought to separate the country from Badi which had been dominant for centuries. Initially irreligion stemmed from a support in Euclean anti-Badi policies and beliefs and a rejection of Euclean catholicism. The Republic of Lavana in 1940 was established officially as a secular state, with the People's Republic in 1960 holding the same secular beliefs. The removal of both Badi and Catholicism from public education in the 1940's, along with some restrictions on Badist beliefs created an environment for rapid expansion of the irreligious population, although with less speed and impact as in Dezevau.
About 12% or 16.2 million people were registered as being members of the Solarian Catholic Church. Catholicism initially arrived to the Aguda Empire in the 17th century in the form of missionaries. The entry of Gaullican interests and later colonial rule quickly expanded the importance of Catholicism in the country, as much of the colonial bureaucracy converted to the religion, and Badist practices and beliefs were discouraged, although it never represented more than 20% of the country. The independence of Lavana, reduced the importance of Catholicism as individuals were no longer favored for their beliefs. Solarians however came to represent an important political force do to their wealth and power, and sided with the Republicans during the civil war. Their defeat resulted in initial opposition to the Solarian church, although by 1965 the church was returned certain freedoms. Solarians are prevalent in all ethnic groups although they congregrate in urban areas and thus Kachais and Dhavonis represent the largest ethnic followers in the country. Solarians were legally allowed to enter political office when in 1994, the provisions that rejected the joining of Solarians into the Lavanan Section of the Workers International (a requirement in being able to be in any position of the government prior to 2022) were removed. Today Solarians hold public offices, and are part of the wider society.
Irfan is the 4th largest group in the country with 10% and 13.5 million followers nationwide. Irfan initially arrived to Lavana in the north, and mainly Ukilen and Majgars in rural regions of the steppe were of Irfan belief. At independence, Irfan was located almost exclusively inside these two groups. The Republican government believed most Irfanics held beliefs of a pan-Majgar and pan-Ukilen state, and sought to control such rhetoric. The Socialist government upon taking power launched its largest religious campaigns against Irfan, closing down and defacing Mazars. From 1960 to 1985 all Irfanics were required to carry identifications that identified them as such, and made it legal for them to be questioned by authorities, or imprisoned on "suspicion" of illegal activities, several restrictions regarding dress and beliefs were also imposed. Some restrictions against Irfanics were lifted in 1985, although the last restrictions on Irfanics, including ability to join the LSWI and thus the government in 1994. Today Irfanics remain mostly Ukilens and Majgars, although they hold higher negative connotations than Ukilens and Majgars who are any other religion. Irfanics are severely underrepresented in government, civil positions; and almost never hold positions outside of Irfanic majority areas. In 2022 out of 760 members of the Lavanan Congress, only 22 are Irfanic of which only 9 were not appointed by a provincial council or by the Premier to fill vacant seats. Only about 35% of Irfanics live in one of Lavanas top 15 largest cities, and 50% in its top 30 largest.
Language
Urbanisation
About 26% of Lavanans live in the 10 largest cities. With the vast majority living in Pers. Lavana is highly centralized in the Pers metro area home to some 15 million people, which makes up 11% of the total Lavanan population. Urban growth has been concentrated primarily in the Kachai and Dhavoni majority territories of Lavana. The countries urbanisation rate of 37.14 (50.1 million) with 68% of the urban population living in the top 10 cities.
Lavanan cities have seen considerable growth primarily from migration from rural regions, which has created a lack of housing in some cities, primarily Pers. Government attempts at curtailing or slowing such migration have so far not been succesful. Issues regarding pollution, water sanitation, congestion, among others have been difficult challenges for Lavanan authorities to curtail.
Cities in Lavana tend to have both an official and a local name, although in some instances the same name is used in both contexts. The city of Ban Vuga has its official name with "Ban" (city in Kachai), while its local name is Vuga. In the case of Ban Vuga both the official and local name are the same, as defined by law. In the case of Dezebenhua, the local name is Dezebenhua while the official name is Jaudau Dezebenhua, with "Jaudau" (Ziba for magnificent city) being used. The literal name of Ban Vuga is, City of Vuga. While Dezebenhua is, Magnificent city of Dezebenhua. Local names are used where applicable. Population not updated
| Largest urban centers by population | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Settlement | Population | |||||
| 1 | Pers | 13,155,673 | |||||
| 2 | Ban Vuga | 5,951,125 | |||||
| 3 | Dezebenhua | 3,863,356 | |||||
| 4 | Biyaosa | 3,469,377 | |||||
| 5 | Bouna | 3,362,753 | |||||
| 6 | Nang Ha | 1,724,136 | |||||
| 7 | Dabadonga | 1,100,633 | |||||
| 8 | Karatau | 793,842 | |||||
| 9 | Attapeu | 691,853 | |||||
| 10 | Zadou | 583,631 | |||||
Culture
Cuisine

Lavanan dishes are traditionally crafted on a 5 element principle, which is called ອາຫານປະກອບ; ahan pakob or "Elemental foods". This concept has its roots on the Badist elemental theory, but it has moved into a cultural practice rather than religious practice. The principle involves the use of 5 elements to make a dish, although by elements it can mean the origin of an ingredient, or a process during the preparation or cooking of the dish. Although theres no set guides for what elements to use, or which ingredients go where, the main elements are: Animal for products made from animals such as meat, milk, cheese; Earth and Plant for rice, vegetables, fruits, among others; Heat is usually used to refer to the cooking process of the dish; Oil for the Cooking oil used in the cooking of the dish, Seasoning for the process of seasoning the food; Time if the process of cooking the dish involves long periods of time such as fermentation; and Water to signify water in either the dish (such as a soup), or an accompanying drink. The concept is today is more used in the crafting of meals for family gatherings and special events, rather than individual dishes but many traditional dishes were made on the 5 element principle.
Popular dishes in the country include Larb, a dish made of meat and vegetables, served with sticky rice. Tam som a dish made of shredded papaya which can be greatly customized with additional ingredients. Spring rolls which is usually served as an appetizer and is made of ground meat, usually pork or mutton, wrapped in rice paper and deep-fried. Other foods of importance include rice and beef soup, Khorkhog, Shelpek, Kai yang, Feu and many more. Lavanan cuisine is varied, and dishes usually change inside the region, with the Dezevauni populations in the north favoring food with more spices, and vegetables and less meat, while those in the west favor meat over vegetables, while the Kachai population varies on preference.
Various animals are consumed in the nation, not usually found in other countries such as Horse, Grasshopper Crocodile, Snake, and Shark can be found in street markets and grocery stores as is the case with Horse meat and Grasshoppers, while the others are considered a delicacy in local cuisine. Although the consumption of dog meat is banned by the government since 1990, an illegal trade in the country exists, similar situations exist in regards to Elephant meat, Monkey meat, and Turtle meat. Government attempts at cracking down the illegal meat trade in the country have been met with great success. In 1990 the Lavanan Congress decreed that the illegal meat trade of protected species, was the greatest threat to Lavanan fauna, a decree that has been upheld since.
Popular drinks in the country include coffee, sugarcane juice, tea, and iced coffee. alcoholic drinks consumed in the country include beer, whiskey, and wine. Lavanan beer is highly celebrated and acclaimed, it has successfully been exported abroad, and is one of the most recognizable symbols of Lavana. Dezevauni coffee is incredibly popular in Lavana, and is commonly served in Ganomes throughout the country. Although areas with high Dezevauni populations, Ganomes are the same as in Dezevau and share many common values, in other parts of the country they serve the explicit purpose of a coffeehouse only, with many locations adopting the name as a marrketing tool but sharing no values with the original concept of a ganome.
Floating markets are a staple of Lavanan cuisine and culture, although they have reduced their importance through grocery stores, and other conveniences. Eating aboard boats and floating markets has become a popular attraction for tourists and many floating markets and restaurants exist to cater to tourists, floating restaurants, are a common sight in Lavanan cities, and many high-class restaurants operate as floating restaurants.
Music
Art
Something something Goaboabanga
Literature
Cinema
Cinema was brought to Lavana in 1923 as a theater was built in Pers for Gaullican colonial administrators and businessmen. The first film to be shot in Lavana was the Gaullican directed 1926 film Robe blanche sur la rivière (White dress on the River). Following independence Lavanan film making began although mostly centered around Kachai cinema, the first film to be made in the country was ນ້ໍາໃນຂອບເຂດ (Water on the horizon) in 1943. Dezevauni migrants began a Ziba based film industry with the release of Dezevauboga in 1948, a film criticizing Socialism meant to be illegally distributed in Dezevau. By the time of the civil war, theatres existed throughout the nation although they showed mostly Gaullican films with a minority of Kachai films.
Following the revolution, Zadavana Goube approved in 1961 the Division of Cinema (DC), which censored films in Lavana and allowed for government films to be made. All movies made prior to that were banned, and cinemas switched to showing only Kachai and Ziba films. Socialist films from Dezevau dominated the Ziba market, and foreign films from Chistovodia, North Vinalia, Champania were shown as well. Commercial film makers were allowed to make films in 1966, although all films were closely connected with the socialist government and policy. In 1973 the Kachai-Ziba epic ເລື່ອງຂອງຂ້ອຍ (My story) was made, it's the most expensive Lavanan film ever made; it follows the life of Zadavana Goube. Lavanan propaganda films were the sole films made in Lavana from 1961 to 1994.
Starting in 1994, the DC was reduced in scope and private films were reintroduced in the country. Commercial Lavanan films have participated sporadically in foreign film festivals such as the Montecara Film Festival since 2000. Today the Lavanan film industry is steadily growing, its primarily language based with Kachai, Ziba, Ukilen, and Majgar films being made and distributed throughout the country. The Lavanan government still makes around 1/4th of all films distributed in the country. Dezevauni films are regularly shot in the country and distributed abroad. In 2009 the Gaullican film Le Radeau sur le Kung was the first Gaullican film to be shot in Lavana since 1949. All foreign films are still subject to censorship by the DC. About 12 films are shot inside Lavana each year. Gladis Saenbouthalath is the most prominent Lavanan Actress, having appeared in Lavanan, Dezevauni, and Gaullican films.
Sports
Lavana does not maintain a national sport but football is the most popular sport in the country, represented in the Lavanan Top League. Basketball is another popular sport in the country with many youths practicing the sport, and the Lavanan national team competing in highly prestigious competitions in the international stage. The Lavanan National Football team plays in the National Workers stadium built in 2010, its also the largest stadium by size and seating capacity in the country. The Lavanan A League is the top level football league in the country with 14 teams, the most prominent of which is Dabadonga F.C. which have won the league some 20 times in the leagues 50 year history.
Lavana has participated in all Summer Invictus Games since Hammarvik 1954, with the exception of Jindao 1958. Lavana has won a total of 54 medals 53 in the Summer editions of the games, and 1 medal in the Winter editions, including 13 golds all from the Summer games. Lavana has earned 11 out of its 13 gold medals, and 27 out of its 54 total medals in Rowing, where Lavana has historically dominated. Lavanas most successful Invictus medalists are the rowing pair of Laila Manwilaivong, and Malo Thonemany which have won 5 medals each, including 3 gold medals each in rowing. Lavana has participated sporadically in the Winter Invictus games, sending its largest representation in Ulan Khol 2020 when it sent 6 athletes, Lavana however is one of the few tropical countries in the world to win a Winter Invictus medal, when Konala Vsevolodovych won the bronze medal on the Men's 20 km individual Biathlon event in Linå 2016. Lavana has made it a national priority to send at least one athlete to the Winter games, following 2020, and the government has funded athletes who live in countries which allow for training in Winter Sports, most prominently Chistovodia, and Kirenia.
Holidays
Numerous holidays and festivals are celebrated in Lavana.
| Date | Name | Native Name | Public Holiday | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | ມື້ປີໃຫມ່;mu pi haim | Celebration of the Euclean new year. | |
| January 7 | Nativity | ວັນຄຣິດສະມາດ; van khrid samad | Celebration of the Nativity, practiced by Solarian Lavanans | |
| February 1 | Day of the Harvest | ບຸນຄູນ ຄຳ;Boun Khun Khao | Celebration of the new harvest, usually of rice. | |
| February 22 | Armed Forces Day | ມື້ປີໃຫມ່;mu pi haim | Celebration of the new year. | |
| March 19 | Armed Forces Day | ວັນ ກຳ ລັງປະກອບອາວຸດ;van kam lang pakoboavud | Celebrate the Armed forces of Lavana | |
| April 13–15 | New Year | ປີໃຫມ່;pi haim | Celebration of the new year based on the Lunar calendar of the Damrog Empire. | |
| May 1 | International Workers' Day | ວັນ ກຳ ມະກອນສາກົນ;van kam ma kon sakon | Celebrate the workers of Lavana. | |
| May 27–30 | River festival | ບຸນຊ່ວງເຮືອ;Bunsuangheu | Holiday with Lavanan Folk origins, which celebrates water and its importance to Lavana and its society. | |
| June 3 | Day of the Republic | ວັນປະຕິວັດ;Vanpativad | Celebrate the establishment of the People's Republic of Lavana in 1960. | |
| July 12 | Day of the Revolution | ວັນປະຕິວັດ;van pativad | Commemorate the start of the Lavanan Civil War. | |
| September 19 | People's Day | ມື້ປະຊາຊົນ;mupasason | Celebrate the people and culture of Lavana | |
| October 3 | Independence Day | ວັນເອກະລາດ;van ekalad | Celebrate the independence of Lavana, and the end to colonization. | |
| November 25 | End of Civil Struggle Day | ສິ້ນສຸດວັນຕໍ່ສູ້ພົນລະເຮືອນ;sinsud van tosu phonla heuon | Celebrate the end of the Lavanan Civil War in 1961. | |
| December 31 | New Year's Eve | ປີ ໃໝ່ ລາວ;pi mai lav | Day before the Euclean new year. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Proposed party election changes in Lavana, and what it means for the country". Coius Monitor. 7 December 2021. Retrieved 14 March 2022. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "November 7" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ "Abnormal military movements reported in Lavana, possible coup?". Foreign Affairs of the World. 6 March 2022. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ "Lavanan Government releases new casualty figures following coup". Coius Monitor. 14 March 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ↑ "phak pheu cha kamchad khon thola nyod" [Party to be rid of traitors]. Paper of the Lavanan Worker. 13 March 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ↑ "Keomany announces new constitutional changes". Coius Monitor. 13 March 2022. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ "Exclusive interview with Lavanan Premier Laina Keomany". Coius Monitor. 10 April 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ↑ Nazarivna, Mariya (1 October 2022). "Deadly blast in Lavana threatens stability in the region". Free Press. Retrieved 25 October 2022.
- ↑ "Hacyinian diplomats meet with Lavanan Premier". Coian Monitor. 2 October 2022. Retrieved 25 October 2022.