Satavia: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (40 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = Satavian Federation | |conventional_long_name = Satavian Federation | ||
|native_name = ''{{wpl|Afrikaans_language|Asteriaans}} | |native_name = ''Satawiese Federasie'' ({{wpl|Afrikaans_language|Asteriaans}})<br> ''Satavisch Federatie'' ({{wpl|Dutch_language|Hennish}}) | ||
|common_name = Satavia | |common_name = Satavia | ||
|image_flag = Flag of Satavia.png | |image_flag = Flag of Satavia.png | ||
|alt_flag = Flag of Satavia | |alt_flag = Flag of Satavia | ||
|national_motto = | |national_motto = | ||
|national_anthem = <br> [[File: | |national_anthem = "[[I Heard My Country Calling]]"<br>[[File:ModernMediaPlayer 2;39.png|250px|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o6ZvylOSy5A]] | ||
|image_coat = Coat of Arms of Satavia.png | |image_coat = Coat of Arms of Satavia.png | ||
|symbol_type = Coat of arms | |symbol_type = Coat of arms | ||
|image_map | |image_map={{Switcher|[[File:SataviaAsterias.png|250px|upright=1.15|frameless]]|Satavia in the Asterias|[[File:Map of Satavia (FCS) - all labels.png|250px|upright=1.15|frameless]]|Map of Satavia|default=1}} | ||
|alt_map = | |alt_map = | ||
|map_caption = | |map_caption= | ||
|image_map2 = | |image_map2 = | ||
|alt_map2 = | |alt_map2 = | ||
|map_caption2 = | |map_caption2 = | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|ethnic_groups = | |ethnic_groups = | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |ethnic_groups_year = | ||
|demonym = Satavian | |demonym = [[Satavians|Satavian]] | ||
|government_type = {{wpl|Federal}} {{wpl|Parliament| | |government_type = {{wpl|Federal}} {{wpl|Parliament|parliamentary}} {{wpl|Republic|constitutional republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = [[President of Satavia]] | |leader_title1 = [[President of Satavia|President]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Jago Elliot]] | |leader_name1 = [[Jago Elliot]] | ||
|leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of Satavia]] | |leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of Satavia|Prime Minister]] | ||
|leader_name2 = [[Arthur Warwick]] | |leader_name2 = [[Arthur Warwick]] | ||
|legislature = [[Parliament of Satavia]] | |legislature = [[Parliament of Satavia]] | ||
|upper_house = [[ | |upper_house = [[Senate of Satavia|Senate]] | ||
|lower_house = [[House of Representatives]] | |lower_house = [[House of Representatives of Satavia|House of Representatives]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = Independence from [[Estmere]] | |sovereignty_type = Independence from [[Estmere]] | ||
|established_event1 = [[Dominion of Satavia|Federation]] | |established_event1 = [[Dominion of Satavia|Federation]] and [[Constitution of Satavia|Constitution]] | ||
|established_date1 = 1 October 1816 | |established_date1 = 1 October 1816 | ||
|established_event2 = [[ | |established_event2 = [[Satavia Act]] | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 23 September 1936 | ||
|established_event3 = [[Satavia | |established_event3 =[[Constitution of Satavia|Current constitution]] | ||
|established_date3 = | |established_date3 =17 December 1976 | ||
|established_event4 = | |established_event4 = | ||
|established_date4 = | |established_date4 = | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|established_event6 = | |established_event6 = | ||
|established_date6 = | |established_date6 = | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = 600,105 | ||
|population_estimate = | |population_estimate = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = 24,581,912 | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year =2022 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 =40.96 | ||
|GDP_nominal = $ | |GDP_nominal = $479 billion | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |GDP_nominal_year = 2022 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $19,500 | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $19,500 | ||
|GDP_PPP = $ | |GDP_PPP = $719 billion | ||
|GDP_PPP_year = | |GDP_PPP_year = 2022 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = $29,250 | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $29,250 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = | |Gini =37.9 | ||
|Gini_change = | |Gini_change =increase | ||
|Gini_year = | |Gini_year =2022 | ||
|HDI = | |HDI =0.838 | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = 2022 | ||
|HDI_change = decrease | |HDI_change = decrease | ||
|currency = | |currency =[[Satavian guilder]] | ||
|currency_code = SVG | |currency_code = SVG | ||
|time_zone = | |time_zone =[[Satavian Standard Time]] | ||
|utc_offset = + 11 | |utc_offset = + 11 | ||
|date_format = dd.mm.yyyy | |date_format = dd.mm.yyyy | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
}} | }} | ||
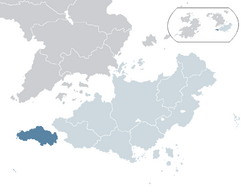
'''Satavia''', officially the '''Satavian Federation''', is an {{wpl | '''Satavia''', officially the '''Satavian Federation''', is an {{wpl|island country}} in western [[Asteria Inferior]] comprising the island of Satavia and several outlying islands. Satavia shares a {{wpl|maritime border}} with [[Nuvania]] across the [[Van Horn Strait]]. Satavia is the smallest country in Asteria Inferior by land area and third smallest by population but maintains the highest GDP per capita and living standards on the continent. Satavia is a {{wpl|federal}} {{wpl|parliamentary}} {{wpl|constitutional republic}}, consisting of six provinces, two territories and one {{wpl|dependent territory}} in {{wpl|free association}} with Satavia, the [[Patrick Islands]].{{Refn|group="N"|Satavia maintains the islands are in free association; the position taken by the [[Community of Nations]] is that the islands are a non-self-governing dependency.}} Satavia's capital, largest city and primary economic centre is [[Port Hope]], whilst other major cities include [[Burnaby]], [[Fort Dent]], [[Northport]], [[Port Arthur]] and [[Victoriaburg]]. | ||
The first human habitation of the island began some 38,000 years ago, and they are the ancestors of modern {{wpl|indigenous|Indigenous Satavians}}. Despite the advancements of neighbouring indigenous peoples in Asteria Inferior, native groups within Satavia remained relatively primitive, avoiding contact with other tribal groups such as those in Nuvania, whilst living in general harmony with one another. Satavia is believed to have been first discovered sometime in 1512 by [[Johannes van Twiller]], however, it was [[Álvaro de Mascarenhas]] who first recorded the existence of the landmass in 1533, believing it to be an extension of the Asterian mainland. [[Jan van Breybach]] was the first to correctly identify Satavia as a separate island, landing at Sandy Cove in 1541, claiming the land for [[Hennehouwe]] and establishing the city that would eventually become Port Hope as the capital of the [[Dolphin Bay Colony]]. | |||
Hennish colonisation continued for the next two hundred years, albeit at a slower pace than in neighbouring Nuvania. [[Victoriaburg|Fort Zilverzee]] was founded in 1611 at the site of modern-day [[Victoriaburg]], whilst further north the Hennish established the [[Krokodillenrivier Kolonie]] with its capital in [[Kaapburg]], which would later become part of [[Port Arthur]]. The last of the Hennish colonies, the [[Orange Colony|Oranjekolonie]] was established in 1712. Following the Hennish defeat in the [[War of 1747]], Hennehouwe ceded the Satavian Colonies and Nuvania to [[Estmere]]. Following Estmere's acquisition of Satavia, immigration to the island increased and Estmerish settlers soon began to outnumber the local Hennish. As the [[Dolphin Bay Colony]] expanded, new colonies were carved out in accordance; [[Colony of Maria|Maria]] in 1750, the [[East River Colony]] in 1753 and [[New Borland]] in 1790. Meanwhile, the western side of Satavia evolved separately; the [[Longwood Colony]] was founded in 1764, [[Breeze River Colony]] in 1768, [[Queen's Colony]] in 1770 and the [[Arundel River Colony]] in 1775. [[User:Norcandy/Sandbox/Pienaar's Revolt|Following a major revolt on the frontier of the Dolphin Bay colony]] and several other minor revolts, primarily by the {{wpl|Afrikaner|Asteriaaners}}, the descendants of the original Hennish settlers, Estmere began preparations to grant the colonies responsible government. In 1798, several minor Western colonies united to become the [[Western Confederation]]. In 1813, the [[Crocodile River Colony]] joined to become [[Western Satavia]] and participated in the [[Federation of Satavia|Federation Talks of 1812-1815]], but ultimately withdrew after their concerns that power would be concentrated in the east of the country. In 1816, responsible government and {{wpl|dominion}} status was conferred upon Satavia when five colonies federated to become provinces within Satavia (Western Satavia continued to remain independent of Satavia until 1838). Satavia remained a dominion for the next 120 years and was the last of Estmere's dominions to declare independence when the aftermath of the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]] saw the Estmerish monarchy abolished and the last of Satavia's legal links to Estmere ended. Satavia was occupied by Nuvania during the Great War and after its [[Defence of Port Hope|rapid surrender following the capture of Port Hope]], Satavian forces fought a long and gruelling guerrilla campaign for the duration of the war. | |||
In 1939, three years following the proclamation of the [[Union of Satavia]], members of the [[Satavian Army|Army]] launched a [[February Coup|coup d'état]] that overthrew the democratically elected government and ended over 120 years of stable democratic rule. The [[National Party (Satavia)|National Dictatorship]] would rule Satavia for nearly four decades before its removal by members of the [[Hope Province|Hope Province Provincial Guard]] in [[1976 Satavian coup d'état|September 1976]]. | |||
Since the restoration of democracy in 1976, Satavia has seen relative economic prosperity, but in recent years rising {{wpl|cost of living}}, increasing {{wpl|income inequality}} and {{wpl|government debt|rising national debt}} have created divides within the country. Satavia also continues to deal with its complex history, including the near-wipeout of the indigenous population and subsequent issues stemming from the theft of native land and indigenous rights during a period known as the [[Great Shame]]. Satavia is a member of [[ASTCOM]], the [[Community of Nations]], [[Embrosphere]], [[International Council for Democracy]], [[Organization of Asterian Nations]] and is an associate member of the [[North Vehemens Organization]]. | |||
Satavia | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The name ''Satavia'' is derived from the {{wpl|Chibcha}} personal name ''Sátiva''. Chibcha-speaking peoples lived around the area where Jan van Breybach first landed at Sandy Cove, and in 1658, Markus Winkelhock wrote that the name was given to Jan van Breybach during his first meeting with indigenous people and incorrectly assumed to be the name of the island.<ref name="De Asterische Kolonies">{{cite book| last1 = Winkelhock | first1 = Markus | title = De Asterische Kolonies | location = s'Holle | publisher = | date = 1658}}</ref> The name ''Satavia'' was seldom used to refer to the island until the 1760s;<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 1/5">{{Cite book |last=Elliot |first=Jago |author1-link=Jago Elliot |title=SATAVIA, Volume I: Before the Storm |year=2018 |publisher= |location= |isbn= |url= }}</ref> before that date, the island as a whole was usually simply referred to by the separate colonies, or as a part of the ''Hennish Asterias'' and later ''Estmerish Asterias''. By 1800, however, the island and the colonies located on the island were usually collectively referred to as ''Estmerish Satavia'' or simply ''Satavia''.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 1/5"/> When the Western Confederation joined together with the Crocodile River Colony in 1813 they became known as Western Satavia; the federation of the other five colonies in 1816 saw the eastern half become known as the Dominion of Satavia. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{main|History of Satavia}} | {{main|History of Satavia}} | ||
===Prehistory=== | ===Prehistory=== | ||
Human habitation of | Human habitation of Satavia began some 38,000 years ago.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 1/5"/><ref name="The Satavian Natives">{{Cite book |last=Daniël |first=Mackenzie |author1-link= |title=The Natives: Satavia's indigenous population |year=1981 |publisher= Birdstone Press|location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Satavia's indigenous population was primarily comprised of three groups; {{wpl|Arawak}}, {{wpl|Caribe}} and {{wpl|Chibcha}} peoples, with the Caribe and Chibcha being by far the most numerous.<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/> Satavia's indigenous population remained primitive despite the advancements of the native populations of other neighbouring Asterian nations, primarily due to their isolation by the Van Horn Strait.<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/><ref name="Advancements of Indigenous peoples">{{Cite journal |last=Lewisham |first=Mary |author1-link= |title=Advancements of the Arawak, Caribe and Chibcha|year=1974 |publisher= United Publishing Corporation (UPC)|location=Port Hope |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Many pre-historic sites, such as those of the Arawak in the [[Orange Province]], were destroyed during the genocide of Satavia's indigenous people in a period now known as the Great Shame.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 1/5"/><ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5">{{Cite book |last=Elliot |first=Jago |author1-link=Jago Elliot |title=SATAVIA, Volume III: 1747 to 1936|year=2020 |publisher= |location= |isbn= |url= }}</ref> As a result, and coupled with the natural hostility that existed between the colonists and natives, there is little remaining historical evidence of indigenous practices in Satavia.<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/><ref name="Advancements of Indigenous peoples"/> However, it is known from contemporary accounts by Hennish settlers that, unlike in neighbouring Nuvania, all of the indigenous groups were {{wpl|hunter-gatherers}}.<ref name="De Asterische Kolonies"/> Satavia's last {{wpl|uncontacted peoples}}, located deep within the [[Central Territory|Central Territories]] was contacted in 1924.<ref name="Chibcha people contacted in CT">{{cite news| last = Clarke | first = Caleb | title = Rogue Chibcha peoples contacted in CT; isolated due to health concerns | pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=12 July 1924 | url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/archive/128982412132}}</ref> Despite reports of uncontacted tribal people living within the Central Territory surfacing as late as 2020,<ref name="Savages living in the CT">{{cite news| last = De Ruyter | first = Carlos | title = Pictured: "Uncontacted peoples" living like savages in the Central Territory | pages = | newspaper = The Daily Mail | location = Northport | date=23 February 2020 | url = https://www.dailymail.co.sv/news/19981921193}}</ref> the existence of further uncontacted tribes has been ruled out as unlikely partly due to Satavia's rapid deforestation and urbanisation leaving no significant free land that has been uncharted by modern civilisation.<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/> Just 181,271 people (or 0.74%) of Satavia's population identified as descendants of Indigenous Asterians in the 2022 census, whilst just under 5% of people identified as creole.<ref name="2022 Satavian census">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date= 25 October 2022 |title=Satavian Federal Census 2022 |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 18 July 2023}}</ref> | ||
===Euclean exploration and colonisation=== | |||
{{main|Hennish Satavia}} | |||
[[File:King George Sound 1833.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Crew of Gaullican ship ''La Zélée'' making contact with natives nearby modern-day Port Arthur, 1593]] | |||
It is widely accepted that the first recorded sighting of Satavia was by [[Johannes van Twiller]] in 1512; however, Van Twiller incorrectly identified Satavia as an extension to the Asterian landmass and as such failed to record the existence of the island.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 1/5"/> [[Álvaro de Mascarenhas]] first recorded the existence of Satavia, but too believed it to be an extension of the Asterian landmass.<ref name="Álvaro de Mascarenhas biography">{{Cite book |last=Gomes dos Santos Aveiro |first=João |author1-link= |title=Álvaro de Mascarenhas: The Life and Adventures of the Greatest Explorer of them All|year=2014 |publisher= |location=Precea |isbn= |url= }}</ref> It was Jan van Breybach who first landed at [[Port Hope|Sandy Cove]] in 1541 and would later confirm his suspicion that Satavia was an island and not an extension of Asteria Inferior.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5">{{Cite book |last=Elliot |first=Jago |author1-link=Jago Elliot |title=SATAVIA, Volume II: The Hennish|year=2019 |publisher= |location= |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Whilst in the service of the [[Asterian Company]] (AK), Van Breybach began the first efforts to settle and colonise Satavia. In 1560, Van Breybach established a new settlement north of Sandy Cove at [[Bendburg]] and six years later at [[Sikostad]] on the banks of [[Lake Kapivlei]].<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5"/> Sikostad was the sight of the [[Sikostad Massacre]] in 1567, where an unknown group of indigenous Satavians attacked the city, massacring much of the local population - including Jan van Breybach.<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/><ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5"/><ref name="Native Danger">{{Cite book |last=Verwoerd |first=Hendrik |author1-link= |title=Native Danger|year=2007 |publisher= University Press |location=Port Hope |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Following the massacre, the Hennish carried out brutal reprisals across the modern-day [[Hope Province]] that saw the beginning of the [[Great Native Wars]], a low-level conflict invariably described as a genocide<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/><ref name="Advancements of Indigenous peoples"/><ref name="Native Danger"/> or as a frontier war.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5"/> In 1611, the Hennish government sent a fleet of ships to the Asterias in order to settle on the western side of the island, arriving at [[Fort Zilverzee]] (modern-day Victoriaburg). The new port city aimed to provide a stop-over for vessels heading from [[Coius]] and [[Sublustria]] on their way to the Asterias; and in 1673, a combination of Hennish settlers and [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] {{wpl|hugenots}} arrived in Satavia settled at the mouth of the [[Crocodile River]], establishing the city of Kaapburg; which would eventually become part of [[Port Arthur]].<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5"/> The final Hennish colony to be established, the [[Oranjekolonie]], was settled in 1712. Hennish exploration was relatively limited; mainly keeping to the coastal areas, except in the Dolphin Bay Colony where colonists settled up to the [[East River]] and further North were limited to the boundaries of the [[River Pelham]].<ref name="Hennish in the Asterias">{{Cite book |last=Peereboom |first=Thijs |author1-link= |title=De Hennish in Asteria|year=1973 |publisher= |location=s'Holle |isbn= |url= }}</ref> | |||
Whilst there were several opportunities to establish colonies further inland, or on Satavia's southern coast, these were mostly ruled out for two primary reasons; the ferocity of native tribes around [[Lake Taxaroga]] and the [[Rogue River]],<ref name="The Satavian Natives"/><ref name="Native Danger"/> and the prioritisation of the colonisation of Nuvania by the Hennish government.<ref name="Colonisation of Nuvania">{{Cite book |last=Bishorst |first=Lodewijk |author1-link= |title=Colonising Nuvania: The Great Unknown|year=1988 |publisher= Die Vrystaat Publishing Group |location=Pietersburg |isbn= |url= }}</ref> | |||
=== | [[File:Satavia in 1771.png|thumb|right|250px|The Satavian colonies in 1771, on the eve of Pienaar's Revolt]] | ||
Following the Estmerish defeat during the [[Estmero-Hennish War of 1747]], the Satavian colonies were ceded to Estmere. The Estmerish acquisition of the colonies saw the launch of a population boom that was coupled with huge territorial growth along the coast of the whole island; new colonies sprang up, many of them launched by various {{wpl|private companies}} such as the [[Longwood Colonial Company]].<ref name="The Longwood Company">{{Cite book |last=Hope |first=Richard |author1-link= |title=The Longwood Company: A complete history|year=1979 |publisher= Birdstone Press |location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> As settler numbers increased, new colonies on the eastern coast were carved out of the Dolphin Bay colony; [[Colony of Maria|Maria]] in 1750, the [[East River Colony]] in 1753 and the [[New Borland|New Territories]] in 1759.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/> Meanwhile, the western areas of Satavia experienced equal population growth; the Crocodile River Colony experienced huge growth and soon eclipsed Fort Zilverzee in both population and territory, whilst other colonies such as the [[Breeze River Colony]] were established in 1768 and [[Queen's Colony]] in 1770. By 1770, the Satavian colonies had expanded rapidly, and the number of Estmerish settlers soon began to match the Hennish settlers. It was around this time that the Hennish settlers began identifying as {{wpl|afrikaners|Asteriaaners}} for the first time.<ref name="The Asteriaaners">{{Cite book |last=Malan |first=D. F. |author1-link= |title=The Asteriaaners: The Hennish on the wrong continent|year=2000 |publisher= Birdstone Press |location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> In 1771, the [[User:Norcandy/Sandbox/Pienaar's Revolt|first and most significant major revolt]] launched by Asteriaaners began on the frontier of the Dolphin Bay Colony began following the death of an Estmerish Magistrate at the hands of a group of Asteriaaner farmers.<ref name="Pienaar's Revolt">{{Cite book |last=Snow |first=Dan |author1-link= |title=Pienaar's Revolt|year=2016 |publisher= Birdstone Press |location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> The revolt, which was primarily centred around the rights of the Asteriaaners, resistance to Estmerish anti-slavery laws, competing land claims with new Estmerish settlers and resistance to taxation without representation set in motion the [[Federation of Satavia|Federation of the Satavian colonies]] and {{wpl|home rule}}.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="The Asteriaaners"/><ref name="Pienaar's Revolt"/> Despite Estmere's violent suppression of the revolt, Estmere soon began offering concessions shortly afterwards. The [[Arundel River Colony]] was established in 1775, four years following the revolt, and was populated almost exclusively by Asteriaaners, many of whom had left the Dolphin Bay Colony following the fallout of the revolt.<ref name="The Asteriaaners"/><ref name="Pienaar's Revolt"/> In 1790, the New Territories were divided between Maria and a new {{wpl|penal colony}}, [[New Borland]] was formed. Meanwhile, in 1798, the Estmerish government ended the charters given to the private companies who had set up colonies on Satavia's west coast, and several were merged to form the [[Western Confederation]].<ref name="Second Empire book">{{Cite book |last=Thomas |first=William |author1-link= |title=The Second Empire|year=1973 |publisher= Birdstone Press |location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Serious suggestions of a united federation of colonies was first considered in the early 1800s, but faced stiff resistance - particularly from the leaders of the Orange Colony, Arundel and the three western colonies - who were fearful that a new, singular colony would have its power centred in the now predominantly-Estmerish Dolphin Bay colony.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/> Representatives from the western colonies arrived in Morwall in 1808 with the hopes of securing a deal with Estmere that would allow for responsible government without the prerequisite of forming a united federation of colonies.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/> This was, however, denied by the government of [[Richard Lascelles, Earl of Allerton|Lord Allerton]] who were insistent that home rule could only be achieved if the Satavian colonies federated.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/> The Estmerish government had been swayed by [[Theodore Howard]], the pro-federation [[User:Norcandy/Sandbox/Governor of the Hope Province|Govervor of the Dolphin Bay Colony]], that it was not only economically sensible but administratively easier to unite the colonies into one singular administrative unit.<ref name="Federation Journal">{{Cite journal |last=O'Hanrahanrahan |first=Peter |author1-link= |title=Federation of Satavia as a case study for advanced engineering|year=2012 |publisher= United Publishing Corporation (UPC)|location=Port Hope |isbn= |url= }}</ref> | |||
===Federation and nation building=== | |||
{{main|Federation of Satavia|Great Shame|Satavia during the Great War}} | |||
[[File:Satavia in 1816.png|thumb|right|250px|The Satavian colonies in 1816, following Federation]] | |||
By 1811, the concept of a united Satavia had become increasingly popular, particularly as neighbouring Nuvania was granted home rule and dominion status that year.<ref name="Federation Journal"/> Nonetheless, there remained significant opposition to federation; notably, in the Western Colonies. The Asteriaaner colonies were fearful of dominance by the much larger Dolphin Bay Colony, a fear that was confirmed when it was decided in 1813 that Sandy Cove - the capital of the Dolphin Bay Colony, and largest city in Estmerish Satavia, would become the capital of the new unified colony.<ref name="Federation Journal"/><ref name="1816-2000 complete census data">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date=21 August 2000|title=Complete Census Data & Records (1816-2000) |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 11 July 2023}}</ref> Furthermore, there were Estmerish concerns that several different colonies threatened to deepen the ethnic divide between Asteriaaners and the Estmerish.<ref name="Federation Journal"/> In 1814, newly-formed Western Satavia withdrew from the Federation Talks. | |||
[[File:Opening of the first parliament.jpg|thumb|left|250px|''The Grand Opening'' depicts the opening of the first [[Parliament of Satavia|Satavian Parliament]] in 1816]] | |||
Satavia's first election, the [[1816 Satavian general election|1816 general election]] was held across the five colonies involved in Federation over three weeks from 13 July to 2 August 1816.<ref name="Federation Journal"/> The voter role was not consistent across the colonies; in the Dolphin Bay Province (with the most liberal voter restrictions) all men over the age of 25 under a {{wpl|property qualification}}, whereas the Orange Province (the most restrictive) had a male-only, whites-only, {{wpl|Calvanism|Kasperist}}, property-qualified and an age restriction of 27.<ref name="Satavian Voting Restrictions">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date=25 June 2020|title=Voting Limitations & Restrictions in Satavia|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 11 July 2023}}</ref> [[Richard Somerset]] would be elected the first Prime Minister of Satavia in the election. On 3 September 1816, the [[Parliament of Estmere|Estermish Parlament]] passed the [[Satavia Act, 1816]] which lay out the provisions for Satavia to attain responsible government.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="Federation Journal"/> Additionally, the colonial councils of the five colonies (which had attained representative government in 1800) passed their own versions of the act.<ref name="Federation Journal"/> On 1 October 1816 the act entered effect, as did the [[Constitution of Satavia]]. Upon its passage, Satavia became a federation consisting of five provinces ([[Arundel]], [[Dolphin Bay Province|Dolphin Bay]], [[Pioneerstaat|Maria]], [[New Borland]] and the [[Orange Province]]) and one territory ([[Central and Western Territories]]).<ref name="Federation Journal"/> Western Satavia attained self-governance in 1819, but not dominion status. By 1833, the comparative economic prosperity of the Dominion of Satavia led to further calls to join the dominion.<ref name="West Satavia calls to join Dominion">{{cite news| last = Carter | first = Daniel | title = West Satavia Colony considers joining Dominion of Satavia; Hillingdon approves| pages = | newspaper = Economic Review | location = Morwall | date=28 August 1833 | url = https://www.economicreview.es/archive/news/leads/f98qhf2389fh894}}</ref> The Dominion government, lead by [[Patrick Conway]], was in favour of accepting Western Satavia into the federation, and drafted several proposals, all of which were rejected by the Western Satavian government.<ref name="Federation Journal"/><ref name="Western Freestate Fact File">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Administrative_Divisions |date=14 October 2013|title=Western Freestate: Fact File|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 13 December 2022}}</ref> However, talks continued throughout the 1830s. In 1838, Satavia was affected by the [[Great Drought of 1837-38|Great Drought]], which impacted Western Satavia's agriculture-based economy significantly.<ref name="Drought Cripples Economy; money talks in Morwall">{{cite news| last = Beckham | first = David | title = Drought Cripples Economy; money talks in Morwall| pages = | newspaper = The West Satavian | location = Port Arthur | date=5 July 1838| url = https://www.thefreestate.co.sv/archive/news/12f98h9289f81_f1891}}</ref> The government of Western Satavia requested financial compensation from Estmere; however, as Estmerish government policy had remained a preference for the unification of the island of Satavia as part of their wider colonial consolidation efforts to improve governance, the government of [[List of prime ministers of Estmere|Lord Hillingdon]] instead proposed a modified version of Conway's sixth and final ascension proposal.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="Federation Journal"/> Despite being fiercely debated within both Satavia and Western Satavia, it was ultimately accepted by both sides. Western Satavia, which would become the [[Western Freestate]], was given special status within Satavia and had vastly more control over its internal affairs than the other provinces.<ref name="Western Freestate Fact File"/> An updated passage of the Satavia Act promulgated in [[Satavia Act, 1838|1838]] and saw Western Satavia join the Dominion of Satavia. In [[1855 Satavian general election|1855]], [[Johan van Vallier]] became Prime Minister of Satavia; and the following few decades would become known as the [[Satavian Boom]] as huge immigration to Satavia from Estmere, other parts of the Estmerish colonial empire and Euclea (particularly [[Caldia]] and [[Piraea]]) brought massive economic growth.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="Second Empire book"/><ref name="Satavian Boom">{{Cite book |last=Sexton |first=Jonathon |author1-link= |title=Business is Booming - Satavia examined|year=1986 |publisher= United Publishing Corporation (UPC) |location=Port Hope |isbn= |url= }}</ref> However, this period of growth also coincided with the [[Great Shame]], during which the vast majority - an estimated 95% - of Satavia's indigenous population was systematically exterminated.<ref name="Native Danger"/><ref name="Satavian Boom"/><ref name="Genocide: A Complete History">{{Cite book |last=Dupuis |first=Ludovic |author1-link= |title=Genocide: A Complete History|year=2017 |publisher= Association École |location=Verlois |isbn= |url= }}</ref><ref name="The Great Shame">{{Cite book |last=O'Driscoll |first=Brian |author1-link= |title=The Great Shame examined|year=2005 |publisher= United Publishing Corporation (UPC) |location=Port Hope |isbn= |url= }}</ref> Van Vallier, a member of the right-wing [[Dominion Party (Satavia)|Dominion Party]] also sought to increase Satavian autonomy whilst remaining within the Estmerish Empire, frequently coming into conflict with the Liberal government of the Satavian-born [[Richard Hope, Earl of Longwood]].<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/> | |||
[[File:The Royal Navy during the Second World War A4606.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Royal Satavian Navy sailors aboard ''[[HMSS Satavia]]'' in the [[Arucian Sea]], 1933]] | |||
[[File:HMAS Sydney 4 inch guns SLV H98.105 3249.jpg|thumb|right|250px|''HMSS Danger Cove'' in combat off the coast of [[North Kabu|Kabu]], 1931]] | |||
*Nuvanian independence | |||
*Viceroyalty of Asterias | |||
*Great War (big) - at home and abroad - contribution | |||
*Nuvanian forces leave, Satavian forces re-occupy the country. a few skrimishes (Battle of Laingsdorp in c. 1934) | |||
Following the conclusion of the Great War, the political atmosphere in Estmere remained volatile.<ref name="Estmere Aflame: The Impact of the Great War">{{Cite book |last=White |first=Callum |author1-link= |title=Estmere Aflame: The Impact of the Great War|year=2004 |publisher= Birdstone Press |location=Morwall |isbn= |url= }}</ref> The Estmerish government announced two referendums to be held in 1936; one on the status of [[Borland (Kylaris)|Borland]] but the other on the future of the Estmerish monarchy.<ref name="Estmere govt referendums">{{cite news| last = Ricciardo | first = Daniel | title = Estmerish Govt. announces referendums on fate of Borland, Monarchy | pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=16 January 1936 | url= https://www.hopepost.co.sv/archive/18676779}}</ref> The abolition of the monarchy, which at that time seemed inevitable, would complicate the relationship between Satavia and Estmere, and consequently Limes - who was a passionate advocate of full independence from Estmere, even before the Great War - informed the Estmerish government sometime in March 1936 of Satavia's intention to achieve independence.<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="Estmere Aflame: The Impact of the Great War"/> Negotiations began in April 1936 and an agreement was soon reached amicably in June. The Satavian government drafted the [[Satavia Act, 1936|Satavia Act 1936 (Dom.)]] which passed through both houses with relatively little opposition.<ref name="Satavia Act, 1936">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Politics |date= 12 January 2000 |title=Satavia Act, 1936 at legislation.gov.sv |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 14 June 2021}}</ref> The Governor-General, Sydney Warwick, initially refused to grant royal assent, waiting instead for the Parliament of Estmere to pass an almost identical piece of legislation, the [[Satavia Act, 1936|Satavia Act 1936 (Kin.)]]. [[Wolfgar E.R. Godfredson]], in his capacity as [[President of Estmere|Chairman of the Transitional Authority]] provided assent on the | |||
*Independence etc. monarchy existence - discussion with lil | |||
=== | ===National party dictatorship=== | ||
Satavia | {{main|National Party (Satavia)}} | ||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
[[File:Vietnam | ===Return to democracy (1976-present)=== | ||
{{main|Satavian Crisis}} | |||
[[File:New Zealand soldier with an Australian M113 in South Vietnam during 1968.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Satavian soldier of the [[Satavian Army|2nd Battalion, Western Regiment]] at the confluence of the [[Satavia#Geography|Crocodile]] and [[Satavia#Geography|Hex]] rivers during the [[Satavian Crisis]] (1977)]] [[File:General Westmoreland visits 161st Field Battery, Royal New Zealand Artillery at Nui Dat.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Rizealand|General McPherson]] ([[Rizealand]]) meeting with Satavian Army commanders in the Orange Mountains, 1977]] | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
*formatting | |||
==Geography== | |||
===Biodiversity=== | |||
* cool plants | |||
* a few trees still kicking around (satavian environmental terrorism™) | |||
* dolphins | |||
* rheas cougars CAPPY etc | |||
* rivers (incl. river pelham, thanks estmere, rogue river - epic name, and vooneeaboo - even greater name, thanks savages | |||
* kapivlei (capybara pond, north of sikostad, incredible) - pond with capybaras | |||
* more dolphins | |||
* some other dolphins | |||
===Climate=== | |||
*pretty hot | |||
*sometimes wet | |||
*sometimes dry | |||
*depends on where you live | |||
*crazy !notafrikaners with guns shooting savages | |||
*politically mild and right-wing | |||
==Government and politics== | |||
==Government | |||
{{main|Parliament of Satavia}} | {{main|Parliament of Satavia}} | ||
{{Multiple image | |||
| caption_align = center | |||
| total_width = 340 | |||
| image1 = David Cameron official.jpg | |||
| caption1 = [[Jago Elliot]],<br>[[President of Satavia]] | |||
| image2 = John Key February 2015.jpg | |||
| caption2 = [[Arthur Warwick]],<br>[[Prime Minister of Satavia]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Sidebar | {{Sidebar | ||
| name = Parliament of Satavia | | name = Parliament of Satavia | ||
| Line 149: | Line 227: | ||
| content1 = | | content1 = | ||
'''House of Representatives''' | '''House of Representatives''' | ||
[[File:House of | [[File:House of Reps.svg|250px|center]] | ||
'''Government''' | '''Government'''{{legend|#0E7BE8|Conservative & Country Party: 61 seats}}{{legend|#C92216|United Party: 37 seats}}'''Opposition'''{{legend|#FFC508|Liberal Party: 47 seats}}'''Other Opposition'''{{legend|#19E0C9|Satavia First: 4 seats}}{{legend|#FF483B|Labour & Social Democratic Party: 3 seats}} | ||
'''Senate''' | |||
''' | [[File:Parliament satavia.svg|250px|center]] | ||
[[File: | '''Government'''{{legend|#0E7BE8|Conservative & Country Party: 46 seats}}{{legend|#C92216|United Party: 19 seats}}'''Opposition'''{{legend|#FFC508|Liberal Party: 26 seats}}'''Other Opposition'''{{legend|#19E0C9|Satavia First: 4 seats}}{{legend|#FF483B|Labour & Social Democratic Party: 1 seats}} | ||
'''Government''' | |||
}} | }} | ||
Satavia | Satavia is a federal parliamentary constitutional republic. Satavia's constitution, ratified in 1816, is one of the world's oldest.<ref name="Constitution of Satavia: A History">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 21 June 2016 |title=Constitution of Satavia: A History |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 16 January 2023}}</ref> Additionally, Satavia is one of the world's oldest federations, in which power is separated between the federal government and the provincial or territorial governments.<ref name="Constitution of Satavia: A History"/> The Satavian system of government is heavily influenced by that of Estmere's and follows the {{wpl|Westminster System|Northabbey system}} closely. Following federation in 1816, Satavia had a [[House of Representatives of Satavia|House of Representatives]] and a [[House of Peers of Satavia|House of Peers]], much like Estmere. The House of Peers was unelected, containing only appointed politicians that included a mixture of primarily-Estmerish peers and Satavian-born commoners.<ref name="Satavian Parliament">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 11 January 2007 |title=Inside the Parliament of Satavia |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 16 June 2020}}</ref> The House of Peers was only replaced by the [[Senate of Satavia|Senate]] in 1939. Members in the House of Representatives, of which there are 152 available seats, are elected through {{wpl|single-member constituencies}} (usually called electoral divisions) using the {{wpl|first-past-the-post system}}.<ref name="Elections in Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 14 August 2005 |title=Elections in Satavia |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 12 April 2013}}</ref> Meanwhile, in the Senate, citizens vote for a party. The total popular vote in a province or territory for each party is then allocated into seats using a modified version of the {{wpl|D'Hondt method}}.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> Each province and territory is allotted 12 senators, regardless of total population, for a total of 96 available Senate seats.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> Voting is mandatory on the federal level and has been since 1976, with some exceptions. Mandatory voting on a provincial level is also now in place across the country; it was introduced first in the Hope Province in 1882, Western Freestate in 1896,{{Refn|group="N"|Whilst universal suffrage had been established by 1976, mandatory voting in the Western Freestate excluded ethnically Bahian people until 1983, ethnically Coian people until 1985 and indigenous people until 2007<ref name="Satavian Voting Restrictions"/>}} Maria (now the Pioneerstaat) and New Borland in 1918, whilst Arundel and the Orange Province introduced identical legislation in 1922 introducing compulsory voting.{{Refn|group="N"|Arundel and the Orange Province both placed limitations on female and indigenous mandatory voting; females were required to vote from 1982 and indigenous people from 2007<ref name="Satavian Voting Restrictions"/>}} Mandatory voting is enforced across all age limits, and exceptions are only granted to Satavians living overseas, who are still entitled to vote if they can provide their last known address.<ref name="Satavian Voting Restrictions"/> A [[Satavian guilder|G]]1,000 (approximately {{wpl|Euro|€}}100) fine is levied for a first offence, increasing up to G2,500 (approximately €300) for a repeat offence. As a result, Satavian electoral turnout is amongst the highest in the world, usually resting at approximately 90%.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/><ref name="Help! I didn't vote!">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 19 September 2022|title=Help! I didn't vote! |work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 20 September 2022}}</ref> | ||
[[Elections in Satavia]] occur sporadically. On a federal level, four types of election exist as defined in the Satavian constitution.<ref name="Constitution of Satavia: A History"/> They all elect members to the House of Representatives and Senate, the terms of which for members are both four years; elections must be called at least three years, 364 days following a previous election. However, a procedure known as [[Electoral pushback]] exists in which, with the approval of the [[High Court of Satavia]], an election may be delayed by up to 270 days past the date it should have been held.<ref name="Electoral pushback">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 17 October 2020|title=How electoral pushback works|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 27 June 2021}}</ref> This is most commonly used on a provincial level, where provincial elections may be "pushbacked" to come into sync with another election, helping to reduce costs, improve voter turnout and increase efficiency.<ref name="Electoral pushback"/> Electoral pushback is a procedure unique to Satavia.<ref name="Electoral pushback"/> Federal elections occur when the Prime Minister asks the President to dissolve both the House of Representatives and the Senate, meaning all seats in both houses are up for election.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> General elections occur when the Prime Minister asks for the President to dismiss the House of Representatives only, whilst the Senate remains in place.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> Similarly, a Senate election sees only the Senate dismissed, whilst the House of Representatives remains to continue their terms. {{wpl|By-elections}} occur when a member of the House of Representatives resigns, dies or becomes incapacitated and is removed from his seat. An election is held only in that division, and their successor replaces them until the next election.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> In contrast to this, when a member of the Senate is no longer willing or able to carry out their term, they are replaced by another member of their party (except for the National Capital District, where the seat remains vacant until the next election).<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/><ref name="NCD Elections">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date=8 March 2018|title=Elections in the NCD|work=NCD Government |access-date= 23 September 2022}}</ref> In the extremely unlikely event that the Senator is an independent, it is constitutionally unclear as to what would occur,<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> but it is expected that their seat would remain vacant until the next election.<ref name="Elections in Satavia"/> | |||
The | The [[President of Satavia]] is the {{wpl|non-executive}} {{wpl|ceremonial}} {{wpl|head of state}} of Satavia.<ref name="President of Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 12 January 2017|title=About the President|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 18 November 2019}}</ref> The position has existed since 1939, when [[Marinus de Klerk]] was selected as Satavia's first president. The longest-serving president is [[Apollonas Georgallis]], who served from 1961-1974, whilst the longest-serving elected president is [[Philip Fairfax]], who served from 2002-2013. The President is always a member of the Senate and is usually, but not necessarily, the leader of the party with the most representation.<ref name="President of Satavia"/> The position of President is modelled on the historical position of [[Governor-General of Satavia]], who was from 1816 to 1936 the [[Estmere|Estmerish Monarch]]'s {{wpl|viceregal}} representative in Satavia.<ref name="President of Satavia"/> As a result, despite being a nominally ceremonial position, the President can appoint governments (but requires the assent of the Senate), as well as call elections.<ref name="President of Satavia"/> This has caused controversy in the past, most notably in 1996 when incumbent Liberal Prime Minister, [[John Barrett]], requested the President of Satavia, [[Damian de Jager]] dissolved both houses and called for a federal election. However, De Jager, a member of the Conservative & Country party, refused his request and instead dissolved only the House of Representatives in a general election. De Jager did not want to risk losing the majority the Conservative & Country party held in the Senate, so refused to dissolve it.<ref name="De Jager affair">{{cite news| last = Telea | first = Mark | title = De Jager affair explained | pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=21 June 1996 | url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/archive/343242344337}}</ref> The [[De Jager affair]] would lead to the [[Presidential (Responsibilities & Duties) Act 1999]] as well as a constitutional amendment in 2013. The President's authority is represented in the provinces by a Governor, and in the territories by an Administrator. | ||
The [[ | The [[Prime Minister of Satavia]] is the {{wpl|head of government}} and {{wpl|executive}} of Satavia.<ref name="Prime Minister of Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Government_and_politics |date= 16 December 2012|title=About the Prime Minister|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 23 February 2023}}</ref> The position of Prime Minister has been continuously held since October 1, 1816. The first holder, Richard Somerset, served just under 13 years across two separate terms. Originally, the Prime Minister could come from either house; most Prime Ministers originally served as either {{wpl|commoners}} or {{wpl|peers}} in the [[House of Peers of Satavia|House of Peers]].<ref name="House of Peers of Satavia">{{cite book| last1 = Verstappen | first1 = Max | title = Inside the Satavian House of Peers | location = Port Hope | publisher = United Publishing Corporation (UPC)| date = 1957}}</ref> [[Arthur O'Connell]] was the first Prime Minister to be a member of the lower house, the House of Representatives, whilst his successor, [[Henry King-Stewart]] was the final Prime Minister who served as a member of the upper house. From 1936 until 1939, the Prime Minister was both the head of state and government of the [[Union of Satavia]]. | ||
Although traditionally regarded as Asteria Inferior's most economically and politically stable nation,<ref name="SATAVIA (History) 3/5"/><ref name="SATAVIA (History) 2/5"/><ref name="Elections in Satavia"/><ref name="Ask the Eucloids">{{cite news| last = Murphy | first = Cillian | title = Ask the Eucloids: Asteria Inferior | pages = | newspaper = Die Vrystaat | location = Pietersburg | date=5 July 2013 | url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/archive/343242344337}}</ref> Satavia experienced two coups d'état and one attempted coup d'état within 38 years (the first, the [[February Coup]] of 1939, the [[1976 Satavian coup d'état]] and an attempted coup d'état during the [[Admiral's Rebellion]] of 1946).<ref name="The art of the Coup d'état">{{cite book| last1 = Athanasiou | first1 = Jasper | title = The art of the coup d'état - how to launch a coup | location = Port Hope | publisher = United Publishing Corporation (UPC)| date = 2009}}</ref> They remain the only coups d'état in Satavian history. | |||
Satavian politics is generally regarded as operating within a {{wpl|two-party system|loose two-party system}}.<ref name="Satavian Politics">{{cite book| last1 = De Ruyter | first1 = Felix | title = A Boy's Game: Satavian politics | location = Port Hope | publisher = United Publishing Corporation | date = 2013}}</ref> Satavia's two major political parties are the [[Conservative & Country Party]], who are generally regarded as {{wpl|centre-right}} to {{wpl|right-wing}}, and the [[Liberal Party (Satavia)|Liberal party]], regarded as {{wpl|centre-left}} to {{wpl|left-wing}}. The {{wpl|centrist}}, Western Freestate-based [[United Party of Satavia|United party]] are usually considered as Satavia's {{wpl|third party}} and have been instrumental in allowing the Conservative & Country party to form governments in the past.<ref name="Satavian Politics"/> Other active major political parties include [[Satavia First]] and the [[Labour & Social Democratic Party of Satavia|Labour & Social Democratic party]]. Satavia has 42 registered federal political parties, of which only five have representation, and 729 registered provincial political parties (including affiliates of major federal political parties).<ref name="Satavian Politics"/><ref name="Political parties in Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date= 3 August 2023 |title=Registry of political parties|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 3 August 2023}}</ref> | |||
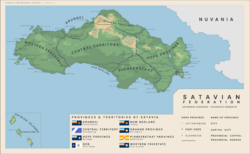
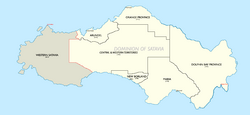
===Provinces and territories=== | |||
{{main|Provinces and territories of Satavia}} | |||
Satavia has six provinces - [[Arundel]] (AR), the [[Hope Province]] (HP), [[New Borland]] (NB), the [[Orange Province]] (OP), the [[Pioneerstaat]] (PS) and the [[Western Freestate]] (WF) - and two territories - the [[Central Territory]] (CT) and the [[Port Hope|National Capital District]] (NCD). Additionally, the [[Patrick Islands]] (PI) is a {{wpl|state in free association}} with Satavia. No legal distinction exists between the provinces and territories, all of which have their own elected legislatures and leaders. In the provinces, the governor is the representative of the president and a mostly {{wpl|ceremonial}} position, although is tasked with providing assent to acts of provincial legislation, whilst the premier is the leader of a provincial government.<ref name="Federal System">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date= 21 June 2014 |title=Satavia's federal system explained|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 1 August 2023}}</ref> In the territories, the governor's official title is "Administrator", whilst the premier's title is "Chief Minister". Despite having no legal distinction, a practical difference between the provinces and territories is that the Premier of the province can recommend to the president a successor for the position of governor, whereas the territorial administrators are chosen unilaterally by the federal government with little to no input from the territories.<ref name="Federal System"/> This is a system inherited from the colonial period, where the governor represented the [[Governor-General of Satavia|governor-general]], who in turn represented the [[Crown of Estmere]].<ref name="Federal System"/><ref name="Satavia's whacky system">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Demographics |date= 7 October 2001 |title=Today I Learned: How Satavia chooses its Governors|work=Jerry Seinfeld via Blogspot |access-date= 3 February 2007}}</ref> | |||
=== | Except for the National Capital District, the provinces and territories retain full control over most areas of governance, including public services and {{wpl|emergency services}} with each province and territory operating its own [[List of law enforcement agencies in Satavia|law enforcement agencies]].<ref name="Federal System"/> Despite the provinces and territories mostly possessing {{wpl|plenary legislative power}}, the federal government may unilaterally revoke provincial legislation as provided under the Satavian constitution.<ref name="Constitution of Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Constitution_of_Satavia |date= 1 October 1816 |title=Constitution of Satavia|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 11 September 2009}}</ref> The federal government has {{wpl|overriding supremacy}} over the provincial governments, as settled in the 1995 [[High Court of Satavia|High Court]] case, ''[[Federation v The Hope Province|Satavian Federation vs Hope Province]]''.<ref name="Federal System"/><ref name="Federation v Hope">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Federation_v_The_Hope_Province |date= 12 June 2020 |title=Court Documents: 1995/36 - "Federation v Hope Province"|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 17 June 2021}}</ref> | ||
Satavia | |||
====Provinces==== | ====Provinces==== | ||
{ | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | ||
|+ style="text-align:center;background:#BFD7FF" |Provinces of Satavia | |||
|- | |||
! class="unsortable" |[[List of Satavian flags#States and territories|Flag]] | |||
! scope="col" width="110" |Province | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |Postal | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |{{wpl|ISO 3166|ISO}} | |||
![[List of Satavian capital cities|Capital]] | |||
!Population<br />(Sep 2022) | |||
!Area (km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
!Population Density (/km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
!No. of Reps. in [[House of Representatives of Satavia|Parliament]] | |||
![[Satavia#Administrative Divisions|Governor]] | |||
! colspan="2" |[[Satavia#Administrative Divisions|Premier]]<br />(Party) | |||
!Provincial Government | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Westerse Vrystaat.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Arundel]]'''|| AR || SV-AR || style="text-align:left" |[[Henschhoek]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|2522192}}|| style="text-align:right" | 27,956 | |||
|90.22 | |||
|16 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Willem de Ruyter]] | |||
| style="background-color: #1f7ae0" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[François Roigard]]<br>([[Conservative & Country Party|C&C]]) | |||
|[[Government of Arundel]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Hope Province.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Hope Province]]'''|| HP || SV-HP || style="text-align:left" |[[Burnaby]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|6694196}}|| style="text-align:right" | 141,622 | |||
|47.27 | |||
|42 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Johan de Vilock]] | |||
| style="background-color: #e29a1d" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Walter Mackenzie]] ([[Liberal Party (Satavia)|Liberal]]) | |||
|[[Government of the Hope Province]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of New Borland.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[New Borland]]'''|| NB || SV-NB || style="text-align:left" |[[Talbot]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|403,156}}|| style="text-align:right" | 10,788 | |||
|37.37 | |||
|2 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Philip Crawley]] | |||
| style="background-color: #e29a1d" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Eliza Smuts]]<br>([[Liberal Party (Satavia)|Liberal]]) | |||
|[[Government of New Borland]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Orange Province.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Orange Province]]'''|| OP || SV-OP || style="text-align:left" |[[Northport]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|3,102,850}}|| style="text-align:right" | 47,172 | |||
|65.78 | |||
|19 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Daniël Schoeman]] | |||
| style="background-color: #1f7ae0" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Jannie de Jager]]<br>([[Conservative & Country Party|C&C]]) | |||
|[[Government of the Orange Province]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Pioneerstat Province.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Pioneerstaat]]'''|| PS || SV-PS || style="text-align:left" |[[Bloemstad]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|2,701,421}}|| style="text-align:right" | 83,902 | |||
|32.20 | |||
|17 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Harold Key]] | |||
| style="background-color: #e29a1d" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Callum White]]<br>([[Liberal Party (Satavia)|Liberal]]) | |||
|[[Government of the Pioneerstaat]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Western Freestate.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Western Freestate]]'''|| WF || SV-WF || style="text-align:left" |[[Port Arthur]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|6,503,294}}|| style="text-align:right" | 99,829 | |||
|65.14 | |||
|37 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Christopher de Beer]] | |||
| style="background-color: #1f7ae0" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Theo Goodwin]]<br>([[Conservative & Country Party|C&C]]) | |||
|[[Government of the Western Freestate]] | |||
|} | |||
====Territories==== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | |||
|+ style="text-align:center;background:#BFD7FF" |Territories of Satavia | |||
|- | |||
! class="unsortable" |[[List of Satavian flags#States and territories|Flag]] | |||
! scope="col" width="160" |Territory | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |Postal | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |{{wpl|ISO 3166|ISO}} | |||
![[List of Satavian capital cities|Capital]] | |||
!Population<br />(Sep 2022) | |||
!Area (km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
!Population Density (/km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
!No. of Reps. in [[House of Representatives of Satavia|Parliament]] | |||
![[Satavia#Administrative Divisions|Administrator]] | |||
! colspan="2" |[[Satavia#Administrative Divisions|Chief Minister]]<br />(Party) | |||
!Territorial Government | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Central Territory.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Central Territory]]'''|| CT || SV-CT || style="text-align:left" |[[Hondeburg]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|204,198}}|| style="text-align:right" | 186,620 | |||
|1.09 | |||
|1 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[James Pienaar]] | |||
| style="background-color: #1f7ae0" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Louis Plummer]]<br>([[Conservative & Country Party|C&C]]) | |||
|[[CT Government]] | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the National Capital District.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Port Hope|National Capital District]]'''|| NCD || SV-NCD || style="text-align:left" |[[Port Hope]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|2,421,671}}|| style="text-align:right" | 336 | |||
|7,207.35 | |||
|18 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Craig Marshall]] | |||
| style="background-color: #e29a1d" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Martin Verschoor]]<br>([[Liberal Party (Satavia)|Liberal]]) | |||
|[[NCD Government]] | |||
|} | |||
====Associated states==== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | |||
|+ style="text-align:center;background:#BFD7FF" |Associated states of Satavia | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
! class="unsortable" |[[List of Satavian flags#States and territories|Flag]] | |||
! scope="col" width="160" |Associated State | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |Postal | |||
! scope="col" width="030" |{{wpl|ISO 3166|ISO}} | |||
![[Patrick's Town|Capital]] | |||
!Population<br />(Mar 2008) | |||
!Area (km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
!Population Density (/km<sup>2</sup>) | |||
![[Patrick Islands|High Chief]] | |||
! colspan="2" |[[Prime Minister of Naua Roa|Prime Minister]]<br />(Party) | |||
!Government | |||
|- style="text-align:center" | |||
|{{flagicon image|Flag of the Patrick Islands.png|size=100px}}|| style="text-align:left" |'''[[Patrick Islands|Patrick Islands/Naua Roa]]'''|| PI || SV-PI || style="text-align:left" |[[Patrick's Town]]|| style="text-align:right" |{{nts|28,934}}|| style="text-align:right" | 1,882 | |||
|15.37 | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Kara Na Paoa]] | |||
| style="background-color: #83d8de" | | |||
| style="text-align:left" |[[Dara Niuꞌa]]<br>([[Patrick Islands|Paiga Naua Roa]]) | |||
|[[High Council of Naua Roa|Government of Naua Roa]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== | ===Foreign relations=== | ||
{{main| | {{main|Foreign relations of Satavia}} | ||
[[File:Malta Attard San Anton Palace BW 2011-10-09 10-06-16.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Embassy of Satavia, Montecara]]]] | |||
Largely due to Satavia's large military and economic prosperity, it is often considered a {{wpl|regional power}} within Asteria Inferior.<ref name="Asterian Powers">{{Cite book |last=Hakkinen |first=Mika |author1-link= |title=Powers of the World: The Asterias|year=2005 |publisher=Association École |location= Verlois|isbn= |url= }}</ref> Satavia has maintained close relations with its former colonial overlords, [[Estmere]] and [[Hennehouwe]], whilst also pursuing an aggressive foreign policy in regards to socialist states, particularly Chistovodia.<ref name="Foreign Policy">{{Cite book |last=Snell |first=Arthur |author1-link= |title=A Colossal C**k up!|year=2023 |publisher=Birdstone Press |location=Morwall|isbn= |url= }}</ref> Satavia also keeps a close relationship with Rizealand, which provided strong material support during the Satavian Crisis. Since 1981, Satavia has been an associate member of the North Vehemens Organization and keeps an increasingly pro-[[Camden]] and pro-[[AFR|Assunçã]] foreign policy outlook.<ref name="Foreign Policy"/> | |||
Satavia's first diplomatic mission was established in 1824, by the government of the newly-formed Dominion of Satavia in Morwall.<ref name="Foreign Policy"/> Although the original building has since been destroyed, the embassy remains situated at its original location in Central Morwall. Similarly, the first diplomatic mission established in Satavia was the Estmerish High Commission (now embassy), located in Port Hope.<ref name="Foreign Policy"/> Satavia is host to 154 diplomatic missions from 77 countries, with the majority of missions located in Port Hope and Victoriaburg. | |||
Satavia's closest relations are with its neighbour Nuvania.<ref name="Foreign Policy"/> Satavia opened a High Commission in Pietersburg in 1840, whilst Nuvania opened a High Commission the following year, in Port Hope.<ref name="Foreign Policy"/> Satavia and Nuvania, under the terms of the [[Van Horn Agreement]], maintain a {{wpl|free travel agreement}} with one another. Nuvania also remains Satavia's largest trade partner in both {{wpl|exports}} and {{wpl|imports}}. | |||
Satavia was a founding member of [[ASTCOM]], and is additionally a member of the [[Community of Nations]], [[Embrosphere]], [[International Council for Democracy]], [[Organization of Asterian Nations]] and is an associate member of the [[North Vehemens Organization]]. | |||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
{{main|Satavian Armed Forces}} | {{main|Satavian Armed Forces}} | ||
{{Multiple image | |||
| perrow=2 | |||
| total_width=400 | |||
| caption_align = center | |||
| image1 = ANZAC Day service at the National War Memorial - Flickr - NZ Defence Force (20).jpg | |||
| caption1 = {{wpl|Private}} of the [[Satavian Army]] wearing the {{wpl|service dress uniform}} with the distinctive {{wpl|campaign hat|"lemon squeezer" campaign hat}} | |||
| image2 = Satavian Air Force F-16.jpg | |||
| caption2 = {{wpl|General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon}} of the [[Satavian Air Force]] operating at [[Daga Roa Naval Base]] in July 2018 | |||
| image3 = Operação "Poseidon 2021" (51475998419).jpg | |||
| caption3 = [[SNV Johan van Vallier]] (formerly {{wpl|HMS Ocean|ENS Dragon}}), a {{wpl|helicopter carrier}} and {{wpl|flagship}} of the [[Satavian Naval Service]] | |||
| image4 = HMAS Anzac Aug 2007.jpg | |||
| caption4 = [[SNV Macquarie]] in August 2013. Macquarie is the fifth of the eight ship {{wpl|ANZAC-class|Talbot-class}} of {{wpl|frigates}} operated by the Satavian Naval Service | |||
}} | |||
[[ | The [[Satavian Armed Forces]] (SAF) is comprised of the [[Satavian Army]] (including the [[Satavian Coast Guard]]), [[Satavian Air Force]] and [[Satavian Naval Service]] (which includes the [[Satavian Naval Service|Fleet Air Arm]]). The SAF is under the authority of the [[Cabinet of Satavia|Department of Defence]] and under the direct oversight of the [[Cabinet of Satavia|Secretary of State for Defence]], who as of 2023 is [[Julian Murphy]].<ref name="DOD">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavian_Armed_Forces |date= 13 February 2006 |title=About us: the Department of Defence|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 18 August 2016}}</ref> The {{wpl|Commander-in-Chief}} of the SAF is the President of Satavia. The [[Satavian Armed Forces|Chief of the Defence Staff]] and [[Satavian Armed Forces|Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff]] are the military leaders of the SAF, and the position can only be held once, for three years. It is rotated between the three services as stipulated under the {{wpl|military|Tri-Service Agreement}}.<ref name="DOD"/> The current Chief of the Defence Staff is General [[Jack Turcan]] (Army), whilst the Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff is Rear Admiral [[William McLaughlin]] (Naval Service).<ref name="Defence Staff">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavian_Armed_Forces |date= 12 October 2022 |title=The Defence Staff|work=Armed Forces of Satavia |access-date= 15 January 2024}}</ref> | ||
All citizens | The Satavian Army is relatively large, numbering some 86,230 active personnel, including 9,500 {{wpl|conscripts}} completing their {{wpl|national service}} requirements<ref name="Defence Staff"/>. All citizens are required, with some exceptions - including, but not limited to, overseas residence or education and other essential employment - to complete one year of national service, either in the Armed Forces or in one of several other organisations.<ref name="National Service">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavian_Armed_Forces |date= 1 March 2015 |title=National Service in Satavia - what you need to know|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 7 May 2023}}</ref> Additionally, each province operates its own Provincial Guard, under the control and supervision of the Governor of each respective province.<ref name="Provincial Guard">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavian_Armed_Forces |date= 24 January 2001 |title=SAF: What is the Provincial Guard?|work=Government of Satavia |access-date= 7 May 2023}}</ref> The Provincial Guard Forces are predominantly a {{wpl|reserve force}} that are usually activated at times of national emergencies or natural disasters.{{citation needed}} The size and power of the Provincial Guards has decreased drastically since the return to democracy in 1976.<ref name="What happened to the Provincial Guard?">{{cite news| last = DeAngelo| first = Bailey | title = What has happened to the Provincial Guard?| pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=25 July 2006| url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/feature/satavia/21812898921}}</ref> The largest provincial guard is the [[Hope Province Provincial Guard]], which numbers some 2,500 men. Arundel became the first province to abolish its provincial guard, doing so in 2017.<ref name="Arundel Provinical Guard">{{cite news| last = Santa| first = Diego | title = Arundel finally abolishes Provincial Guard; cites cost| pages = | newspaper = The Henschhoek Examiner | location = Henschhoek | date=24 October 2020 | url = https://www.henschhoekexaminer.co.sv/ar/military/arundel_abolishes_provinci_guard}}</ref> Meanwhile, the Satavian Air Force - by far the smallest of the three forces - primarily operates {{wpl|helicopters}}, {{wpl|helicopter gunships}} and {{wpl|transport}} aircraft.<ref name="Inside the Air Force">{{Cite book |last=Hamilton |first=Lewis |author1-link= |title=Inside the Air Forces of the World |year=2022 |publisher=Birdstone Press |location= Morwall|isbn= |url= }}</ref> The Air Force, does however, continue to operate 18 {{wpl|F-16 fighter jets}}, purchased in 1989. The Satavian Naval Service is the largest of the three services.<ref name="Satavian Navy">{{Cite book |last=Vettel |first=Sebastian |author1-link= |title=The Satavian Naval Service: First In, Last Out|year=2004 |publisher=Die Vrystaat Publishing Group |location= Pietersburg|isbn= |url= }}</ref> The Naval Service is generally classed as a largely {{wpl|green-water navy}}, with some {{wpl|blue-water navy|blue-water}} capabilities.<ref name="Blue water navies">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Military |date= 14 August 2021 |title=Navies of the World|work=Navywatch.org|access-date= 18 February 2023}}</ref> As a result of Satavia's strategic location at the mouth of the Arucian, in addition to its unhindered access to the Vehemens and Glacial oceans (enhanced by forward operating bases such as [[Daga Roa Naval Base]]), the Naval Service is central to [[Satavian Armed Forces|Defence Plan 2030]], which aims to convert Satavia's navy into a fully-fledged blue-water navy.<ref name="Defence Plan 2030">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Military |date= 21 October 2020 |title=Defence Plan 2030 |work=Armed Forces of Satavia |access-date= 22 October 2020}}</ref> This, in part, is intended to help counter the influence of [[Chistovodia]] in the Arucian.<ref name="Satavia aims to battle socialists">{{cite news| last = Underwood| first = Frank | title = Defence Plan aims to tackle Chistovodia, other socialists| pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=24 October 2020 | url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/news/satavia/218982189128921}}</ref> As part of the programme, Satavia acquired ''{{wpl|HMS Ocean|ENS Dragon}}'', a small {{wpl|helicopter carrier}} in 2017 from Estmere, renaming the ship ''[[SNV Johan van Vallier]]''.<ref name="Satavia Acquires ENS Dragon">{{cite news| last = Underwood | first = Frank | title = DOD coughs up €84 million for ENS Dragon sale | pages = | newspaper = The Hope Post | location = Port Hope | date=17 January 2017 | url = https://www.hopepost.co.sv/news/satavia/12891824981248124}}</ref> Additionally, the Satavian Naval Service operates four {{wpl|Heroine-class|Darling-class diesel-electric submarines}}, launched from 2003 to 2004. The Naval Service also operates four older frigates and destroyer escorts, purchased from Estmere in 1984, as well as eight modern {{wpl|ANZAC-class|Talbot-class}} produced in [[Werania]] on behalf of Satavia from 1998 to 2007. The Naval Service also operates four {{wpl|offshore patrol vessels}} and 22 {{wpl|patrol boats}}. The Fleet Air Arm is operated in cooperation with the Satavian Air Force.<ref name="Naval Watch">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Military |date= 24 February 2023 |title=Satavian Navy: information |work=navaltracker.es |access-date= 1 August 2023}}</ref> | ||
From 2017-2018, the Satavian Armed Forces' total budget was approximately G172 billion, or 4.3% of GDP, placing Satavia amongst the highest proportional spenders in the Asterias. Satavia is an associate member of the North Vehemens Organizations, and maintains close military associations with Estmere, Nuvania and Rizealand.<ref name="DOD"/><ref name="NVO allies">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia#Military |date= 31 October 2007 |title=Our Allies: Major NVO partners |work=North Vehemens Organization |access-date= 6 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
==Economy== | |||
===Agriculture=== | |||
[[File:Cow (Fleckvieh breed) Oeschinensee Slaunger 2009-07-07.jpg|thumb|right|250px|This is Bobetta. Bobetta is a cow. Bobetta is from the Hope Province, but she doesn't know that.]] | |||
[[File:Argentinean asado.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Bobetta later that evening. She doesn't look like she is feeling too well.]] | |||
*sheep | |||
*cattle - biggest meat producer? | |||
*wine in the far south | |||
=== | ===Energy=== | ||
*hmm imported energy (thx daddy nuvania) | |||
*coal is cool | |||
*organic oil | |||
*no green energy (that's for euclean hippies) | |||
===Mineral resources=== | |||
*major copper exporter | |||
*plenty of iron | |||
*gold | |||
*lithium | |||
*iodine (wtf is it?? nobody knows but we got it (its under the rainforest where those endangered species live, but we don't care)) | |||
===Services=== | |||
*we do this a lot (somebody explain) | |||
*finance Barrett Bank | |||
*Port Arthur Banking Corporation (PABC) big bank boys | |||
*Asterian Standard Bank (ASB) | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
*nice beeches | |||
*popular because its safe | |||
*easy access | |||
*good hotels | |||
*people are not so nice so don't annoy them | |||
===Transportation=== | |||
*roads | |||
*railway | |||
*higways (interprovincial) | |||
*busses | |||
*trains | |||
*ships | |||
*planes (lots of planes) | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
The | The 2022 Satavian Federal Census recorded the resident Satavian population at 24,581,912 people, giving Satavia a population density of 40.96/km2, which is below average for [[Asteria Inferior]].<ref name="SIB Factbook">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Estmere#Military |date= 28 December 2022 |title=SIB Factbook: Satavia |work=Government of Estmere |access-date= 7 August 2023}}</ref> As an urbanised country, Satavia's population is predominantly located within its cities, whilst the country's interior, particularly in the Central Territory, is extremely sparsely populated.<ref name="2022 Satavian census"/><ref name="SIB Factbook"/> Satavia's life expectancy of 76.5 years is the highest in Asteria Inferior,<ref name="SIB Factbook"/> a fact often attributed to high living standards and the availability of healthcare across the country.<ref name="Healthcare in Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia |date= 17 June 2015 |title=Healthcare in Satavia |work=Satavian Federal Healthcare Bureau|access-date= 7 August 2023}}</ref> Satavia has a {{wpl|fertility rate}} of 1.97, and has been decreasing since the 1980s.<ref name="SIB Factbook"/> | ||
{{Largest cities | {{Largest cities | ||
| name = Largest cities of Satavia | | name = Largest cities of Satavia | ||
| class = blue | | class = light blue | ||
| country = Satavia | | country = Satavia | ||
| kind = | | kind = urban areas | ||
| stat_ref = | | stat_ref = 2022 Satavian Federal Census<ref name="2022 Satavian census"/> | ||
| list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> | | list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> | ||
| div_name = Province | | div_name = Province/Territory | ||
| div_link = | | div_link = | ||
| city_1 = Port Hope | | city_1 = Port Hope | ||
| div_1 = National Capital District | | div_1 = National Capital District | ||
| pop_1 = 2,421,671 | | pop_1 = 2,421,671 | ||
| img_1 = | | img_1 = Sydney Opera House, botanic gardens 1.jpg | ||
| city_2 = Burnaby | div_2 = Hope Province | pop_2 = | | city_2 = Burnaby | div_2 = Hope Province | pop_2 = 1,822,105 | img_2 = Sunsets of Brisbane, Queensland, September 2021, 01.jpg | ||
| city_3 = Victoriaburg| div_3 = | | city_3 = Victoriaburg| div_3 = Western Freestate | pop_3 = 1,322,981 | img_3 = Aerial view of Townsville.jpg | ||
| city_4 = | | city_4 = Port Arthur| div_4 = Western Freestate| pop_4 = 1,003,192| img_4 =Cairns view of CBD 3.jpg | ||
| city_5 = | | city_5 = Bloemstad | div_5 = Pioneerstaat | pop_5 = 843,128 | ||
| city_6 = | | city_6 = Fort Kinnon | div_6 = Western Freestate | pop_6 = 841,299 | ||
| city_7 = | | city_7 = Northport | div_7 = Orange Province| pop_7 = 715,163 | ||
| city_8 = | | city_8 = Konningstad | div_8 = Hope Province| pop_8 = 701,221 | ||
| city_9 = | | city_9 = Henschhoek | div_9 = Arundel | pop_9 = 633,195 | ||
| city_10 = | | city_10 = Fort Dent | div_10 = Hope Province| pop_10 =633,126 | ||
| city_11 = Markethaven| div_11 = Hope Province| pop_11 =593,724 | |||
| city_12 = Cape James| div_12 = Hope Province| pop_12 =571,193 | |||
| city_13 = Windstad| div_13 = Orange Province| pop_13 =501,234 | |||
| city_14 = Kingsleigh| div_14 = Western Freestate| pop_14 =422,496 | |||
| city_15 = Fort Mackenzie| div_15 = Western Freestate| pop_15 =403,329 | |||
| city_16 = Waterkloof| div_16 = Arundel| pop_16 =378,777 | |||
| city_17 = Macquarie| div_17 = Hope Province| pop_17 =361,292 | |||
| city_18 = Westhasen| div_18 = Orange Province| pop_18 =201,241 | |||
| city_19 = Vorsterburg| div_19 = Western Freestate| pop_19 =133,282 | |||
| city_20 = Danger Cove| div_20 = Western Freestate| pop_20 =101,151 | |||
}} | }} | ||
===Ancestry and immigration=== | ===Ancestry and immigration=== | ||
From 1541 until 1747, the vast majority of the settlers arriving in Satavia came from modern-day Hennehouwe.<ref name="1816-2000 complete census data"/><ref name="Ancestry in Satavia">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia |date= 22 February 2021 |title=Ancestry of modern Satavians |work=Government of Satavia|access-date= 7 August 2023}}</ref>, including Hennish and Petois people, in addition to a significant number of Gaullican {{wpl|Hugenots}} fleeing religious persecution.<ref name="Hugenots">{{Cite book |last=Sinatra |first=Frank |author1-link= |title=History of the Hugenots |year=1981 |publisher=Birdstone Press |location= Morwall|isbn= |url= }}</ref> Mass migration began after the Estmerish acquisition of the Satavian colonies, which saw a huge influx of predominantly Estmerish people.<ref name="1816-2000 complete census data"/><ref name="Ancestry in Satavia"/> Furthermore, significant immigration from [[Caldia]] occurred towards the mid-19th century, as well as large-scale immigration from Bahia, most notably [[Garambura]] and [[Rwizikuru]], [[Dezevau]] and [[Satria]]. Satavia also became a popular destination for [[Piraea|Piraeans]] before and after the Great War, with the vast majority settling in Victoriaburg, a city which now boasts the largest Piraean population outside of Piraea, and has led to its nickname ''[[Victoriaburg|Little Alikianos]]''.<ref name="1816-2000 complete census data"/><ref name="Ancestry in Satavia"/><ref name="Victoriaburg Fact File">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia |date= 16 July 2017 |title=Victoriaburg in Brief |work=Visit Satavia|access-date= 15 December 2023}}</ref> | |||
The Satavian Federal Statistics Office collects data on race, ethnicity, ancestry and religion in addition to other categories including spoken languages, making it one of the most sweeping and in-depth census reports in the world.<ref name="2022 Satavian census"/><ref name="About the census">{{cite web|url=https://iiwiki.us/wiki/Satavia |date= 14 April 2019 |title=About Us: What is the Census?|work=Government of Satavia|access-date= 7 June 2019}}</ref> At the 2022 census, Satavians who were {{wpl|white (race)|white}} comprised 81.34% of the population, whilst {{wpl|black (race)|black Satavians}} made up 10.89%, {{wpl|mixed race|Creoles}} 4.82%, whilst the remaining 2.95% were other racial groups. Most notably, only 0.74% of the population self-identified as {{wpl|indigenous american|Indigenous Asterian}}, a decrease of 0.53% from 2012. The vast majority of Creoles also said they identified more with their Euclean ancestry rather than their Indigenous ancestry. | |||
Satavians were also asked to identify most strongly with one or two ancestries. The following most commonly nominated ancestries were: | |||
{{div col}} | {{div col}} | ||
* [[Estmere|Estmerish]] ( | *[[Estmere|Estmerish]] (37.61%) | ||
* [[Hennehouwe|Hennish]] ( | *[[Hennehouwe|Hennish]] (29.01%) | ||
* [[Rwizikuru|Rwizikuran]] ( | *[[Rwizikuru|Rwizikuran]] (6.75%) | ||
* [[ | *[[Piraea|Piraean]] (5.75%) | ||
* [[ | *[[Garambura|Garamburan]] (4.08%) | ||
*[[Caldia|Caldian]] (3.31%) | |||
* [[ | *[[Gaullica|Gaullican]] (1.86%) | ||
* [[ | *{{wpl|Indigenous|Indigenous Asterian}} (0.74%) | ||
* | *[[Borland|Borish]] (0.51%) | ||
* [[ | |||
{{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
Additionally, 3.52% of Satavians identified as being of "Other Eastern Euclean ancestry", whilst a further 1.94% identified as being of "Other Western Euclean ancestry". Just under 1% of respondents identified as being of other, unlisted heritage. Since 1541, Satavia has seen net migration into the country except for a brief period from 1972 until 1978, during the collapse of the National Party dictatorship and the beginning of the Satavian Crisis. | |||
===Language=== | ===Language=== | ||
{{bar box | {{bar box | ||
| float = right | | float = right | ||
| title = | | title = Proficiency in languages in Satavia | ||
| titlebar = #ddd | | titlebar = #ddd | ||
| left1 = Language | | left1 = Language | ||
| right1 = Percent | | right1 = Percent | ||
| caption = | | caption = Percentage of Satavians who identified as "proficient" in a language (2022) | ||
| width = 315px | | width = 315px | ||
| bars = | | bars = | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp|English language|Estmerish}}|# | {{bar percent|{{wp|English language|Estmerish}}|#4fab5b|91.01}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp|Afrikaans language|Asteriaans}}|# | {{bar percent|{{wp|Afrikaans language|Asteriaans}}|#faec28|83.79}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp|Dutch language|Hennish}}|# | {{bar percent|{{wp|French language|Gaullican}}|#e60000|29.13}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp| | {{bar percent|{{wp|Dutch language|Hennish}}|#ffa200|20.27}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp| | {{bar percent|{{wp|German language|Weranian}}|#811cc9|6.84}} | ||
{{bar percent|{{wp|Greek language|Piraean}}|#4eccb7|3.21}} | |||
}} | |||
{{Pie chart | |||
| thumb = right | |||
| caption = First languages in Satavia (2022) | |||
| other = | |||
| label1 = {{wpl|English|Estmerish}} | |||
| value1 = 51.55 | |||
| color1 = Green | |||
| label2 = {{wpl|Afrikaans|Asteriaans}} | |||
| value2 = 42.42 | |||
| color2 = Yellow | |||
| label3 = {{wpl|Dutch language|Hennish}} | |||
| value3 = 4.79 | |||
| color3 = Orange | |||
| label4 = {{wpl|Greek language|Piraean}} | |||
| value4 = 0.35 | |||
| color4 = Blue | |||
| label5 = Others | |||
| value5 = 0.89 | |||
| color5 = Red | |||
}} | }} | ||
Satavia has only one official language at a federal level, {{wpl|English language|Estmerish}}. However, both {{wpl|Afrikaans language|Asteriaans}} and {{wpl|Dutch language|Hennish}} are recognised national languages. {{wpl|South African English|Satavian Estmerish}} is the primary variety of Estmerish spoken in Satavia, and is most closely related (and often confused with) {{wpl|South African English|Nuvanian Estmerish}}. Satavian spelling is mostly consistent with {{wpl|British English|Standard Estmerish}}, whilst pronunciations deviate significantly, even within Satavia. Asteriaans is an official language in all the provinces and territories, whilst Hennish is only an official language in the Hope Province. {{wpl|Dutch language|Hope Hennish}} is the official dialect of Hennish, and is spoken as a {{wpl|first language}} by over 1.1 million Satavians. | |||
Additionally, over 91% of Satavians stated they could "speak and understand" Estmerish "proficiently", whilst 83% said the same for Asteriaans. In {{wpl|government schools}}, children must take compulsory Estmerish lessons until the age of 16 (which is the age that children are legally able to {{wpl|drop out}}). Additionally, in all provinces and territories except the Hope Province, children must also take compulsory Asteriaans classes until the age of 16. In the Hope Province, where possible, pupils can choose between Asteriaans or Hennish. Alongside Estmerish and Asteriaans, school children are encouraged to take a third language, usually {{wpl|French|Gaullican}} or {{wpl| German |Weranian}}. Consequently, the vast majority (86%) of Satavians identified as speaking two or more languages fluently, whilst some 34% claimed they were able to speak three or more languages fluently. | |||
Whilst there are no regulations in place on a federal level in the large private education sector, 93% of privately-educated Satavians identified as {{wpl|bilingual}} (predominantly in Estmerish and Asteriaans), whilst 47% identified as {{wpl|trilingual}}, well above the national average. | |||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
{{Pie chart | {{Pie chart | ||
| thumb = right | | thumb = right | ||
| caption = Religious identification in Satavia ( | | caption = Religious identification in Satavia (2022) | ||
| other = | | other = | ||
| label1 = {{wpl| | | label1 = {{wpl|Protestant|Amendist}} | ||
| value1 = | | value1 = 80.36 | ||
| color1 = Blue | | color1 = Blue | ||
| label2 = {{wpl|Irreligious}} | | label2 = {{wpl|Irreligious}} | ||
| value2 = | | value2 = 12.16 | ||
| color2 = | | color2 = Grey | ||
| label3 = [[ | | label3 = [[Episemialist Church|Episemialist]] | ||
| value3 = | | value3 = 4.09 | ||
| color3 = Purple | | color3 = Purple | ||
| label4 = [[ | | label4 = [[Solarian Catholic Church|Catholic]] | ||
| value4 = | | value4 = 1.86 | ||
| color4 = | | color4 = Yellow | ||
| label5 = | | label5 = {{wpl|Atudism|Atudite}} | ||
| value5 = | | value5 = 0.34 | ||
| color5 = Red | | color5 = Red | ||
| label6 = Others | |||
| value6 = 1.19 | |||
| color6 = Green | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{wpl|Calvanism|Kasperism}} is the {{wpl|state religion}} of Satavia. Specifically, the [[Satavian Reformed Church]] is the state church and has been endorsed since its creation in 1824. Kasperist settlers played a crucial role in the colonisation of Satavia, and as a result, many of their descendants remain Kasperist. Kasperism is Satavia's largest branch of {{wpl|Protestant|Amendism}}, with some 85% of all [[Sotirianity|Sotirian]]s in Satavia belonging to the Satavian Reformed Church, whilst 79.91% of all Satavians identified as Kasperist. Kasperist following is highest amongst Asteriaans and Hennish-speaking people. Despite its position as Satavia's state religion, since the introduction of the [[Religion (Freedom, Worship & State) Act 1986]] by the [[Kokkinakis ministry|government of]] [[Leander Kokkinakis]] (himself an Episemialist), the state has effectively been separated from the church. However, Kasperism plays a major role in influencing politics and this is perhaps best demonstrated in that the Conservative & Country party's official religious denomination is Kasperism. | |||
{{wpl|Church of England|Embrian Communionists}} represent Satavia's second largest Amendist religion. The vast majority, some 90% of Embrian Communioniststs, are primarily Estmerish-speaking whites or ethnically Bahian. Meanwhile, the [[Episemialist Church|Episemialist Church]] is Satavia's second largest religion and second largest Sotirian religion following Ammendism. Satavia's Episemialists are almost exclusively members of the Piraean diaspora, centred in the city of Victoriaburg, which itself has the largest Episemialist following in Satavia. | |||
Other Sotirian religions, including [[Solarian Catholic Church|Solarian Catholicism]] exist in the minority, in addition to [[Atudism|Atudites]], [[Irfan|Irfanics]] and other religious groups. | |||
{{wpl|Irreligion}} has, in the past twenty years, risen significantly in Satavia. In the 2002 census, only 3.1% of Satavians identified as irreligious, {{wpl|atheist}} or {{wpl|agnostic}}, whilst twenty years later that had risen to 12.16%. Although church attendance remains high, it has declined from its previous highs during the 20th century. Satavia ranks relatively highly in {{wpl|religious freedom indexes}}. | |||
===Health=== | ===Health=== | ||
*everyone is healthy | |||
*except for some people ig | |||
*free healthcare in some places | |||
*not in others | |||
*federal health cover scheme (thx kokkinakis) | |||
*free ambulance (thx som1) | |||
*smoking kills | |||
===Education=== | |||
*state school aren't epic | |||
*private schools are good though :) and that's what matters beecause who cares about the poor | |||
==Culture== | |||
*jungles | |||
*crazy asteriaaners | |||
*shooting guns | |||
*putting shrimp on the braai | |||
*having a beer | |||
*watching sports | |||
*basically everyone's a redneck ({{wpl|rooinek}}???) | |||
== | ===Arts=== | ||
== | *nice painting | ||
*nice grafiti | |||
*idk something interesting here about jungle painters and paintings that may or may not depict people slaughtering defenceless natives | |||
*books (picnic at hanging rock :skull:) | |||
*opera, that's why we built the expensive opera house | |||
===Media and entertainment=== | ===Media and entertainment=== | ||
{{main|Cinema of Satavia|Television in Satavia|Media of Satavia|Music of Satavia|Pioneer folk music}} | |||
{{multiple image|perrow=2|total_width=250 | |||
| image1 = 1928.png | |||
| image2 = A Secret theatrical release poster.png | |||
| footer = {{wpl|Theatrical release posters}} of ''[[1928]]'' and ''[[A Secret]]'', two of Satavia's most culturally significant films | |||
}} | |||
The Satavian domestic film industry is a major producer of Estmerish-language films and television. Most notably, {{wpl|Paramount Global|Mountpara}} is a Satavian-based multinational entertainment conglomerate, which includes {{wpl|Paramount Pictures|Mountpara Pictures}} film studio, which is the second-oldest film studio in the {{wpl|new world}}. The first full-length feature film in Asteria Inferior, ''[[The Rainforest Rambler]]'' was filmed in Satavia in 1907 and released later that year. The Satavian film industry suffered during National Party rule, although propaganda films such as ''[[Our Brave Country]]'' (1970) were nonetheless popular. Following the end of the National Party dictatorship in 1976, Satavian film production prospered in a period known as the [[Casey Street Hurricane]]. Notable "Hurricane" films included the international {{wpl|blockbusters}} ''[[The Last Plane out of Victoriaburg's Almost Gone]]'' (1977) and the {{wpl|Mad Max|Manic Mark film series}}. Additionally, war films and films that examined Satavia's national culture and identity were paticularly popular and characteristic of the period, and included ''[[Cool Carting]]'' (1978), ''[[King's Rock]]'' (1979), ''{{wpl|Knight Rider|Day Rider}}'' (1983), ''[[1928]]'' (1985) and ''[[Satavian 'Till I Die]]'' (1986). Other notable Satavian films released since include ''[[A Secret]]'' (1999), the seventh highest grossing film of all time, ''[[Pienaar]]'' (2021), ''[[The Fallen (film)|The Fallen]]'' (2021) and ''[[The Depression Club]]'' (2023). Satavia is also a major outlet for Asteriaans-language productions, including popular {{wpl|television serials}} ''[[Vertel my Nou!]]'', ''{{wpl|modern family|'n Moderne Familie}}'' and ''[[Naelloper]]''. | |||
{{wpl| | Satavia has a government-funded {{wpl|national broadcaster}}, the [[Satavian Broadcasting Corporation]]. Additionally, Satavia has four private commercial television networks (three broadcast in Estmerish, one in Asteriaans), multiple {{wpl|pay-TV services}} and numerous public radio and local television networks. Satavia has five major national newspapers - ''[[The Hope Post]]'', ''[[The Satavian]]'', ''[[Daily Mail]]'', ''[[The Freestate]]'' and the ''[[Satavian Economic Review]]''. Additionally, hundreds of provincial and city-based newspapers exist, most notably the ''[[Northport Koerant]]'', ''[[Bloemstad Burger]]'' and the ''[[Arundel Herald]]''. Additionally, there is limited Hope Hennish broadcasting, with the ''[[Bendburgerkrant]]'' being the most notable and largest by circulation. | ||
{{wpl| | {{wpl|Bush ballad|Pioneer poems}} are perhaps the most quintessentially Satavian form of {{wpl|folk music}}. {{wpl|Banjo Paterson|Barton de Groot}} and {{wpl|Henry Lawson|Chilly Limes}} are regarded as the most famous pioneer poets, whose work in the late 19th century helped shape the {{wpl|national character|national character of Satavia}}. '{{wpl|Waltzing Matidla}}', '[[Die Wandelaar]]' and '[[En de Rooinek zong God Bescherme de Koning]]' are the most famous examples of pioneer poems. Modern Satavian music culture has been shaped by immigration from Euclea as well as Bahia and Coius. Well-known Satavian bands include {{wpl|Cold Chisel|Hot Hammer}} (most well known for their anti-war {{wpl|pub-rock}} song {{wpl|Khe Sanh|Hwababoo}}), {{wpl|AC/DC|DC/AC}}, {{wpl|Men at Work|Hard at Work}}, {{wpl|Empire of the Sun (band)|Kingdom of the Moon}}, {{wpl|Bee Gees|D-Notice}}, {{wpl|Overtone (musical group)|Undertone}} and {{wpl|OneRepublic|TwoKingdoms}}. Satavian singers include {{wpl|Johnny Clegg|Jack Kloppie}}, {{wpl|Sia|Kate Furler}}, {{wpl|Troye Sivan|Piraeus Hasapis}}, {{wpl|Gotye|André de Jager}}, {{wpl|Vance Joy|Free Reya}}, {{wpl|Dean Lewis|Cardinal}}, {{wpl|Sufjan Stevens|Scott Jackson}}, {{wpl|Brooke Fraser|Ella D'Angelis}} and {{wpl|Kylie Minogue|Louise Theron}}. | ||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
*estmere but mix it with hennish, piraean + !south africa and !anzac foods and there you go | |||
*pavlolva just for fun | |||
*braai (shrimp on bbq, yumm) | |||
*beef | |||
*wine | |||
===Symbols=== | |||
*dolphin (obv) | |||
*rhea | |||
*guns | |||
*dolphins | |||
*the flag | |||
*national personification (might use britannia in the 1900s because estmere wanted to be different and used zeelandia but we'll see) | |||
*dolphin | |||
===Sports and recreation=== | |||
[[File:2022 NRLGF stadium.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Stadium Satavia]] during the [[Super League (rugby union)|Super League 2022 Grand Final]]]] | |||
{{wpl|Rugby union}} is often considered the national sport of Satavia and its most popular sport, followed by {{wpl|Cricket}} and {{wpl|Association football (soccer)}}. Other sports popular in Satavia include {{wpl|athletics}}, {{wpl|swimming}}, {{wpl|surfing}}, {{wpl|golf}}, {{wpl|boxing}}, {{wpl|judo}}, {{wpl|cycling}}, {{wpl|sailing}}, {{wpl|field hockey}} and {{wpl|netball}}. In recent years, {{wpl|baseball}} and {{wpl|softball}} have become increasingly popular (largely thanks to the rapid expansion of the [[Arucian Baseball League|ABL]] and [[Arucian Softball League|ASL]] outside of the Arucian), and [[Zadany]] has become more popular at the expense of {{wpl|Polo}}. | |||
Rugby union is Satavia's most popular sport. Satavia's national team, the [[Satavia national rugby union team|Dolphins]], are the third-most successful team in [[Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|Rugby World Cup]] history, having won the tournament on two separate occasions; in [[1985 Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|1985]] and [[1997 Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|1997]]. Satavia hosted the most recent edition in [[2021 Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|2021]], and finished as runners-up. In women's rugby union, Satavia is also highly accomplished, having won the [[Women's Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|Women's Rugby World Cup]] in [[2011 Women's Rugby World Cup (Kylaris)|2011]], which was also hosted by Satavia. The Satavian national team participates in the [[Asterias Cup (rugby union)|Asterias Cup]] every year, which it has won ten times, in comparison to Nuvania's eleven titles. Additionally, Nuvania and Satavia contest the [[Kitchener Cup]] every year as part of a three-match test series. Satavia's top-tier rugby league is the [[Super League (rugby union)|Super League]], which features teams from the Arucian, Nuvania, Satavia and Sublustria. The [[Blues (rugby union)|Blues]], based in Port Hope, is the joint most successful side, having won five titles, matched only by the [[Super League (rugby union)|Crocodiles]]. Satavian teams have won the Super League ten times, compared to Nuvania's eight. Super League teams pick players from within Satavia's premier domestic league, the [[National Rugby Championship]] (NRC). Many Super League teams are affiliated with NRC teams; for instance, the Blues are the Super League wing of [[Port Hope|Port Hope RFC]], the Asterias' oldest rugby club. The [[Provincial Rugby League]] (PRL) is usually Satavia's most-watched domestic sporting event which sees players return from their clubs to play in an inter-provincial league. The Hope Province is the most successful province, winning 46 titles whilst the Western Freestate is the only other province to have won, winning on 39 occasions. Rugby union is by far Satavia's most played and watched sport, whilst Satavia's impact on the sport beyond the country is undeniable; {{wpl|Rugby union|Asterian rules}}, in contrast to {{wpl|Rugby union|Euclean rules}}, formed the basis for the early rules of internationally codified rugby union, whilst Satavian diaspora abroad created clubs that still operate within the top leagues of their respective countries - for instance, [[Morwall Asteriaans]] continue to play in the [[ERU Championship]] in Estmere. | |||
Cricket is Satavia's second most popular sport by both participants and spectators. Satavia's international cricket team is highly accomplished, and Satavia is widely regarded as one of the greatest cricketing nations, having won the [[KCC Cricket World Cup]] three times, as well as most recently in [[2022 KCC Cricket World Cup|2022]]. Satavia's domestic cricket league, the [[Provincial Cricket League]] (PCL) is operated on a Trans-Van Horn basis and includes eight Satavian teams (one representing each province and territory) and eight Nuvanian teams (one representing each province). Whilst the most successful team is the [[Pietersburg|Kaap Province]], who have won seven titles, the [[Hope Province]] is the second most successful team, and most successful Satavian team with five titles. | |||
Association football (soccer) is Satavia's third most popular sport. Satavia's national team, [[Satavia national football team|The Cougars]], has seen limited success with their best result of a Round of 16 finish coming at the [[1983 IFF Coupe du Monde]], jointly hosted by Satavia and Nuvania. The women's team, however, has seen greater success; achieving a best result of fourth at the [[2021 IFF Coupe du monde|2021 IFF Feminine Coupe du Monde]]. The [[Top 12]] is Satavia's domestic soccer league, and since its inception in 1868 has been dominated by the [[Springbank Lions]], the only team never to have been relegated from the tournament. | |||
Satavia is widely accomplished in athletics. In boxing, [[Joel Tristan]] is widely regarded as one of the greatest {{wpl|welterweight}} boxers of all time, whilst Satavia is equally accomplished in women's boxing, taking two golds from a possible five at the [[2022 Summer Invictus Games]]. [[Daniël du Toit]] is the current [[2022 Summer Invictus Games|Invictus champion]] in {{wpl|pole-vaulting}}, and additionally holds the world pole-vaulting record. In {{wpl|tennis}}, [[Jannie Duquesne]] is Satavia's most successful tennis player, being the only player to achieve {{wpl|grand slam of tennis|two calendar year grand slams}}, coming in 1973 and 1975. Satavia's highest-ranked player currently is [[Chase Kruger]], who is ranked sixth in the world. In {{wpl|Swimming}}, [[Rynold Verdoorn]] is the world and Invictus 200m backstroke champion. Satavia hosted the [[2002 Summer Invictus Games]] in Port Hope. In {{wpl|surfing}}, Satavia is extremely competitive and a popular destination - currently hosting a stop on the WSL Tour, [[Cloudfall]], as well as a popular big wave destination at [[Toebreaker]] (both in the Western Freestate). Current {{wpl|World Surf League|World Surf League Championship}} surfers include three-time and incumbent world champion [[Indhi Scott]], as well as other surfers such as [[Peter Strauss]] and [[John John Alvares]]. [[Georgios Poulos]], a nine time world surfing champion, is widely regarded as one of the greatest surfers of all time. | |||
Satavia has produced four {{wpl|Formula 1|GP1}} world champions; [[Max Scheckter]] in 1963, [[Pieter Fendersen]] in 1979, [[Jackie Hendrickse]] in 1999, 2000 and 2003 and most recently [[Blaze Cook]] in 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016. Additionally, Satavia hosted the [[Satavian Grand Prix]] at the since-demolished [[Breybach International Circuit]] from 1961 until 1994, and has hosted the grand prix at the [[Cape James Circuit]] since 2002. In [[SailGP]], the Satavian SailGP team are the only team to have won the championship, doing so every year since its inception in 2019. | |||
==See also== | |||
{{Portal|Kylaris|redlinks=y}} | |||
*[[List of sovereign states and dependent territories (Kylaris)|List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Kylaris]] | |||
==Notes== | |||
{{reflist|group=N}} | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Satavia]] | [[Category:Satavia]] | ||
[[Category:Kylaris]] | [[Category:Kylaris]] | ||
[[Category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | [[Category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:08, 10 March 2024
Satavian Federation | |
|---|---|
| Capital and largest city | Port Hope |
| Official languages | Estmerish |
| Recognised national languages | Asteriaans Hennish |
| Demonym(s) | Satavian |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic |
| Jago Elliot | |
| Arthur Warwick | |
| Legislature | Parliament of Satavia |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from Estmere | |
• Federation and Constitution | 1 October 1816 |
| 23 September 1936 | |
| 17 December 1976 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 600,105 km2 (231,702 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 24,581,912 |
• Density | 40.96/km2 (106.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $719 billion |
• Per capita | $29,250 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $479 billion |
• Per capita | $19,500 |
| Gini (2022) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high |
| Currency | Satavian guilder (SVG) |
| Time zone | UTC+ 11 (Satavian Standard Time) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +51 |
| Internet TLD | .sv |
Satavia, officially the Satavian Federation, is an island country in western Asteria Inferior comprising the island of Satavia and several outlying islands. Satavia shares a maritime border with Nuvania across the Van Horn Strait. Satavia is the smallest country in Asteria Inferior by land area and third smallest by population but maintains the highest GDP per capita and living standards on the continent. Satavia is a federal parliamentary constitutional republic, consisting of six provinces, two territories and one dependent territory in free association with Satavia, the Patrick Islands.[N 1] Satavia's capital, largest city and primary economic centre is Port Hope, whilst other major cities include Burnaby, Fort Dent, Northport, Port Arthur and Victoriaburg.
The first human habitation of the island began some 38,000 years ago, and they are the ancestors of modern Indigenous Satavians. Despite the advancements of neighbouring indigenous peoples in Asteria Inferior, native groups within Satavia remained relatively primitive, avoiding contact with other tribal groups such as those in Nuvania, whilst living in general harmony with one another. Satavia is believed to have been first discovered sometime in 1512 by Johannes van Twiller, however, it was Álvaro de Mascarenhas who first recorded the existence of the landmass in 1533, believing it to be an extension of the Asterian mainland. Jan van Breybach was the first to correctly identify Satavia as a separate island, landing at Sandy Cove in 1541, claiming the land for Hennehouwe and establishing the city that would eventually become Port Hope as the capital of the Dolphin Bay Colony.
Hennish colonisation continued for the next two hundred years, albeit at a slower pace than in neighbouring Nuvania. Fort Zilverzee was founded in 1611 at the site of modern-day Victoriaburg, whilst further north the Hennish established the Krokodillenrivier Kolonie with its capital in Kaapburg, which would later become part of Port Arthur. The last of the Hennish colonies, the Oranjekolonie was established in 1712. Following the Hennish defeat in the War of 1747, Hennehouwe ceded the Satavian Colonies and Nuvania to Estmere. Following Estmere's acquisition of Satavia, immigration to the island increased and Estmerish settlers soon began to outnumber the local Hennish. As the Dolphin Bay Colony expanded, new colonies were carved out in accordance; Maria in 1750, the East River Colony in 1753 and New Borland in 1790. Meanwhile, the western side of Satavia evolved separately; the Longwood Colony was founded in 1764, Breeze River Colony in 1768, Queen's Colony in 1770 and the Arundel River Colony in 1775. Following a major revolt on the frontier of the Dolphin Bay colony and several other minor revolts, primarily by the Asteriaaners, the descendants of the original Hennish settlers, Estmere began preparations to grant the colonies responsible government. In 1798, several minor Western colonies united to become the Western Confederation. In 1813, the Crocodile River Colony joined to become Western Satavia and participated in the Federation Talks of 1812-1815, but ultimately withdrew after their concerns that power would be concentrated in the east of the country. In 1816, responsible government and dominion status was conferred upon Satavia when five colonies federated to become provinces within Satavia (Western Satavia continued to remain independent of Satavia until 1838). Satavia remained a dominion for the next 120 years and was the last of Estmere's dominions to declare independence when the aftermath of the Great War saw the Estmerish monarchy abolished and the last of Satavia's legal links to Estmere ended. Satavia was occupied by Nuvania during the Great War and after its rapid surrender following the capture of Port Hope, Satavian forces fought a long and gruelling guerrilla campaign for the duration of the war.
In 1939, three years following the proclamation of the Union of Satavia, members of the Army launched a coup d'état that overthrew the democratically elected government and ended over 120 years of stable democratic rule. The National Dictatorship would rule Satavia for nearly four decades before its removal by members of the Hope Province Provincial Guard in September 1976.
Since the restoration of democracy in 1976, Satavia has seen relative economic prosperity, but in recent years rising cost of living, increasing income inequality and rising national debt have created divides within the country. Satavia also continues to deal with its complex history, including the near-wipeout of the indigenous population and subsequent issues stemming from the theft of native land and indigenous rights during a period known as the Great Shame. Satavia is a member of ASTCOM, the Community of Nations, Embrosphere, International Council for Democracy, Organization of Asterian Nations and is an associate member of the North Vehemens Organization.
Etymology
The name Satavia is derived from the Chibcha personal name Sátiva. Chibcha-speaking peoples lived around the area where Jan van Breybach first landed at Sandy Cove, and in 1658, Markus Winkelhock wrote that the name was given to Jan van Breybach during his first meeting with indigenous people and incorrectly assumed to be the name of the island.[1] The name Satavia was seldom used to refer to the island until the 1760s;[2] before that date, the island as a whole was usually simply referred to by the separate colonies, or as a part of the Hennish Asterias and later Estmerish Asterias. By 1800, however, the island and the colonies located on the island were usually collectively referred to as Estmerish Satavia or simply Satavia.[2] When the Western Confederation joined together with the Crocodile River Colony in 1813 they became known as Western Satavia; the federation of the other five colonies in 1816 saw the eastern half become known as the Dominion of Satavia.
History
Prehistory
Human habitation of Satavia began some 38,000 years ago.[2][3] Satavia's indigenous population was primarily comprised of three groups; Arawak, Caribe and Chibcha peoples, with the Caribe and Chibcha being by far the most numerous.[3] Satavia's indigenous population remained primitive despite the advancements of the native populations of other neighbouring Asterian nations, primarily due to their isolation by the Van Horn Strait.[3][4] Many pre-historic sites, such as those of the Arawak in the Orange Province, were destroyed during the genocide of Satavia's indigenous people in a period now known as the Great Shame.[2][5] As a result, and coupled with the natural hostility that existed between the colonists and natives, there is little remaining historical evidence of indigenous practices in Satavia.[3][4] However, it is known from contemporary accounts by Hennish settlers that, unlike in neighbouring Nuvania, all of the indigenous groups were hunter-gatherers.[1] Satavia's last uncontacted peoples, located deep within the Central Territories was contacted in 1924.[6] Despite reports of uncontacted tribal people living within the Central Territory surfacing as late as 2020,[7] the existence of further uncontacted tribes has been ruled out as unlikely partly due to Satavia's rapid deforestation and urbanisation leaving no significant free land that has been uncharted by modern civilisation.[3] Just 181,271 people (or 0.74%) of Satavia's population identified as descendants of Indigenous Asterians in the 2022 census, whilst just under 5% of people identified as creole.[8]
Euclean exploration and colonisation
It is widely accepted that the first recorded sighting of Satavia was by Johannes van Twiller in 1512; however, Van Twiller incorrectly identified Satavia as an extension to the Asterian landmass and as such failed to record the existence of the island.[2] Álvaro de Mascarenhas first recorded the existence of Satavia, but too believed it to be an extension of the Asterian landmass.[9] It was Jan van Breybach who first landed at Sandy Cove in 1541 and would later confirm his suspicion that Satavia was an island and not an extension of Asteria Inferior.[10] Whilst in the service of the Asterian Company (AK), Van Breybach began the first efforts to settle and colonise Satavia. In 1560, Van Breybach established a new settlement north of Sandy Cove at Bendburg and six years later at Sikostad on the banks of Lake Kapivlei.[10] Sikostad was the sight of the Sikostad Massacre in 1567, where an unknown group of indigenous Satavians attacked the city, massacring much of the local population - including Jan van Breybach.[3][10][11] Following the massacre, the Hennish carried out brutal reprisals across the modern-day Hope Province that saw the beginning of the Great Native Wars, a low-level conflict invariably described as a genocide[3][4][11] or as a frontier war.[10] In 1611, the Hennish government sent a fleet of ships to the Asterias in order to settle on the western side of the island, arriving at Fort Zilverzee (modern-day Victoriaburg). The new port city aimed to provide a stop-over for vessels heading from Coius and Sublustria on their way to the Asterias; and in 1673, a combination of Hennish settlers and Gaullican hugenots arrived in Satavia settled at the mouth of the Crocodile River, establishing the city of Kaapburg; which would eventually become part of Port Arthur.[10] The final Hennish colony to be established, the Oranjekolonie, was settled in 1712. Hennish exploration was relatively limited; mainly keeping to the coastal areas, except in the Dolphin Bay Colony where colonists settled up to the East River and further North were limited to the boundaries of the River Pelham.[12] Whilst there were several opportunities to establish colonies further inland, or on Satavia's southern coast, these were mostly ruled out for two primary reasons; the ferocity of native tribes around Lake Taxaroga and the Rogue River,[3][11] and the prioritisation of the colonisation of Nuvania by the Hennish government.[13]
Following the Estmerish defeat during the Estmero-Hennish War of 1747, the Satavian colonies were ceded to Estmere. The Estmerish acquisition of the colonies saw the launch of a population boom that was coupled with huge territorial growth along the coast of the whole island; new colonies sprang up, many of them launched by various private companies such as the Longwood Colonial Company.[14] As settler numbers increased, new colonies on the eastern coast were carved out of the Dolphin Bay colony; Maria in 1750, the East River Colony in 1753 and the New Territories in 1759.[5] Meanwhile, the western areas of Satavia experienced equal population growth; the Crocodile River Colony experienced huge growth and soon eclipsed Fort Zilverzee in both population and territory, whilst other colonies such as the Breeze River Colony were established in 1768 and Queen's Colony in 1770. By 1770, the Satavian colonies had expanded rapidly, and the number of Estmerish settlers soon began to match the Hennish settlers. It was around this time that the Hennish settlers began identifying as Asteriaaners for the first time.[15] In 1771, the first and most significant major revolt launched by Asteriaaners began on the frontier of the Dolphin Bay Colony began following the death of an Estmerish Magistrate at the hands of a group of Asteriaaner farmers.[16] The revolt, which was primarily centred around the rights of the Asteriaaners, resistance to Estmerish anti-slavery laws, competing land claims with new Estmerish settlers and resistance to taxation without representation set in motion the Federation of the Satavian colonies and home rule.[5][15][16] Despite Estmere's violent suppression of the revolt, Estmere soon began offering concessions shortly afterwards. The Arundel River Colony was established in 1775, four years following the revolt, and was populated almost exclusively by Asteriaaners, many of whom had left the Dolphin Bay Colony following the fallout of the revolt.[15][16] In 1790, the New Territories were divided between Maria and a new penal colony, New Borland was formed. Meanwhile, in 1798, the Estmerish government ended the charters given to the private companies who had set up colonies on Satavia's west coast, and several were merged to form the Western Confederation.[17] Serious suggestions of a united federation of colonies was first considered in the early 1800s, but faced stiff resistance - particularly from the leaders of the Orange Colony, Arundel and the three western colonies - who were fearful that a new, singular colony would have its power centred in the now predominantly-Estmerish Dolphin Bay colony.[5] Representatives from the western colonies arrived in Morwall in 1808 with the hopes of securing a deal with Estmere that would allow for responsible government without the prerequisite of forming a united federation of colonies.[5] This was, however, denied by the government of Lord Allerton who were insistent that home rule could only be achieved if the Satavian colonies federated.[5] The Estmerish government had been swayed by Theodore Howard, the pro-federation Govervor of the Dolphin Bay Colony, that it was not only economically sensible but administratively easier to unite the colonies into one singular administrative unit.[18]
Federation and nation building
By 1811, the concept of a united Satavia had become increasingly popular, particularly as neighbouring Nuvania was granted home rule and dominion status that year.[18] Nonetheless, there remained significant opposition to federation; notably, in the Western Colonies. The Asteriaaner colonies were fearful of dominance by the much larger Dolphin Bay Colony, a fear that was confirmed when it was decided in 1813 that Sandy Cove - the capital of the Dolphin Bay Colony, and largest city in Estmerish Satavia, would become the capital of the new unified colony.[18][19] Furthermore, there were Estmerish concerns that several different colonies threatened to deepen the ethnic divide between Asteriaaners and the Estmerish.[18] In 1814, newly-formed Western Satavia withdrew from the Federation Talks.

Satavia's first election, the 1816 general election was held across the five colonies involved in Federation over three weeks from 13 July to 2 August 1816.[18] The voter role was not consistent across the colonies; in the Dolphin Bay Province (with the most liberal voter restrictions) all men over the age of 25 under a property qualification, whereas the Orange Province (the most restrictive) had a male-only, whites-only, Kasperist, property-qualified and an age restriction of 27.[20] Richard Somerset would be elected the first Prime Minister of Satavia in the election. On 3 September 1816, the Estermish Parlament passed the Satavia Act, 1816 which lay out the provisions for Satavia to attain responsible government.[5][18] Additionally, the colonial councils of the five colonies (which had attained representative government in 1800) passed their own versions of the act.[18] On 1 October 1816 the act entered effect, as did the Constitution of Satavia. Upon its passage, Satavia became a federation consisting of five provinces (Arundel, Dolphin Bay, Maria, New Borland and the Orange Province) and one territory (Central and Western Territories).[18] Western Satavia attained self-governance in 1819, but not dominion status. By 1833, the comparative economic prosperity of the Dominion of Satavia led to further calls to join the dominion.[21] The Dominion government, lead by Patrick Conway, was in favour of accepting Western Satavia into the federation, and drafted several proposals, all of which were rejected by the Western Satavian government.[18][22] However, talks continued throughout the 1830s. In 1838, Satavia was affected by the Great Drought, which impacted Western Satavia's agriculture-based economy significantly.[23] The government of Western Satavia requested financial compensation from Estmere; however, as Estmerish government policy had remained a preference for the unification of the island of Satavia as part of their wider colonial consolidation efforts to improve governance, the government of Lord Hillingdon instead proposed a modified version of Conway's sixth and final ascension proposal.[5][18] Despite being fiercely debated within both Satavia and Western Satavia, it was ultimately accepted by both sides. Western Satavia, which would become the Western Freestate, was given special status within Satavia and had vastly more control over its internal affairs than the other provinces.[22] An updated passage of the Satavia Act promulgated in 1838 and saw Western Satavia join the Dominion of Satavia. In 1855, Johan van Vallier became Prime Minister of Satavia; and the following few decades would become known as the Satavian Boom as huge immigration to Satavia from Estmere, other parts of the Estmerish colonial empire and Euclea (particularly Caldia and Piraea) brought massive economic growth.[5][17][24] However, this period of growth also coincided with the Great Shame, during which the vast majority - an estimated 95% - of Satavia's indigenous population was systematically exterminated.[11][24][25][26] Van Vallier, a member of the right-wing Dominion Party also sought to increase Satavian autonomy whilst remaining within the Estmerish Empire, frequently coming into conflict with the Liberal government of the Satavian-born Richard Hope, Earl of Longwood.[5]

- Nuvanian independence
- Viceroyalty of Asterias
- Great War (big) - at home and abroad - contribution
- Nuvanian forces leave, Satavian forces re-occupy the country. a few skrimishes (Battle of Laingsdorp in c. 1934)
Following the conclusion of the Great War, the political atmosphere in Estmere remained volatile.[27] The Estmerish government announced two referendums to be held in 1936; one on the status of Borland but the other on the future of the Estmerish monarchy.[28] The abolition of the monarchy, which at that time seemed inevitable, would complicate the relationship between Satavia and Estmere, and consequently Limes - who was a passionate advocate of full independence from Estmere, even before the Great War - informed the Estmerish government sometime in March 1936 of Satavia's intention to achieve independence.[5][27] Negotiations began in April 1936 and an agreement was soon reached amicably in June. The Satavian government drafted the Satavia Act 1936 (Dom.) which passed through both houses with relatively little opposition.[29] The Governor-General, Sydney Warwick, initially refused to grant royal assent, waiting instead for the Parliament of Estmere to pass an almost identical piece of legislation, the Satavia Act 1936 (Kin.). Wolfgar E.R. Godfredson, in his capacity as Chairman of the Transitional Authority provided assent on the
- Independence etc. monarchy existence - discussion with lil
National party dictatorship
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
Return to democracy (1976-present)

- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
- formatting
Geography
Biodiversity
- cool plants
- a few trees still kicking around (satavian environmental terrorism™)
- dolphins
- rheas cougars CAPPY etc
- rivers (incl. river pelham, thanks estmere, rogue river - epic name, and vooneeaboo - even greater name, thanks savages
- kapivlei (capybara pond, north of sikostad, incredible) - pond with capybaras
- more dolphins
- some other dolphins
Climate
- pretty hot
- sometimes wet
- sometimes dry
- depends on where you live
- crazy !notafrikaners with guns shooting savages
- politically mild and right-wing
Government and politics
|
House of Representatives Government Conservative & Country Party: 61 seats United Party: 37 seats Opposition Liberal Party: 47 seats Other Opposition Satavia First: 4 seats Labour & Social Democratic Party: 3 seats
Senate Government Conservative & Country Party: 46 seats United Party: 19 seats Opposition Liberal Party: 26 seats Other Opposition Satavia First: 4 seats Labour & Social Democratic Party: 1 seats |
Satavia is a federal parliamentary constitutional republic. Satavia's constitution, ratified in 1816, is one of the world's oldest.[30] Additionally, Satavia is one of the world's oldest federations, in which power is separated between the federal government and the provincial or territorial governments.[30] The Satavian system of government is heavily influenced by that of Estmere's and follows the Northabbey system closely. Following federation in 1816, Satavia had a House of Representatives and a House of Peers, much like Estmere. The House of Peers was unelected, containing only appointed politicians that included a mixture of primarily-Estmerish peers and Satavian-born commoners.[31] The House of Peers was only replaced by the Senate in 1939. Members in the House of Representatives, of which there are 152 available seats, are elected through single-member constituencies (usually called electoral divisions) using the first-past-the-post system.[32] Meanwhile, in the Senate, citizens vote for a party. The total popular vote in a province or territory for each party is then allocated into seats using a modified version of the D'Hondt method.[32] Each province and territory is allotted 12 senators, regardless of total population, for a total of 96 available Senate seats.[32] Voting is mandatory on the federal level and has been since 1976, with some exceptions. Mandatory voting on a provincial level is also now in place across the country; it was introduced first in the Hope Province in 1882, Western Freestate in 1896,[N 2] Maria (now the Pioneerstaat) and New Borland in 1918, whilst Arundel and the Orange Province introduced identical legislation in 1922 introducing compulsory voting.[N 3] Mandatory voting is enforced across all age limits, and exceptions are only granted to Satavians living overseas, who are still entitled to vote if they can provide their last known address.[20] A G1,000 (approximately €100) fine is levied for a first offence, increasing up to G2,500 (approximately €300) for a repeat offence. As a result, Satavian electoral turnout is amongst the highest in the world, usually resting at approximately 90%.[32][33]
Elections in Satavia occur sporadically. On a federal level, four types of election exist as defined in the Satavian constitution.[30] They all elect members to the House of Representatives and Senate, the terms of which for members are both four years; elections must be called at least three years, 364 days following a previous election. However, a procedure known as Electoral pushback exists in which, with the approval of the High Court of Satavia, an election may be delayed by up to 270 days past the date it should have been held.[34] This is most commonly used on a provincial level, where provincial elections may be "pushbacked" to come into sync with another election, helping to reduce costs, improve voter turnout and increase efficiency.[34] Electoral pushback is a procedure unique to Satavia.[34] Federal elections occur when the Prime Minister asks the President to dissolve both the House of Representatives and the Senate, meaning all seats in both houses are up for election.[32] General elections occur when the Prime Minister asks for the President to dismiss the House of Representatives only, whilst the Senate remains in place.[32] Similarly, a Senate election sees only the Senate dismissed, whilst the House of Representatives remains to continue their terms. By-elections occur when a member of the House of Representatives resigns, dies or becomes incapacitated and is removed from his seat. An election is held only in that division, and their successor replaces them until the next election.[32] In contrast to this, when a member of the Senate is no longer willing or able to carry out their term, they are replaced by another member of their party (except for the National Capital District, where the seat remains vacant until the next election).[32][35] In the extremely unlikely event that the Senator is an independent, it is constitutionally unclear as to what would occur,[32] but it is expected that their seat would remain vacant until the next election.[32]
The President of Satavia is the non-executive ceremonial head of state of Satavia.[36] The position has existed since 1939, when Marinus de Klerk was selected as Satavia's first president. The longest-serving president is Apollonas Georgallis, who served from 1961-1974, whilst the longest-serving elected president is Philip Fairfax, who served from 2002-2013. The President is always a member of the Senate and is usually, but not necessarily, the leader of the party with the most representation.[36] The position of President is modelled on the historical position of Governor-General of Satavia, who was from 1816 to 1936 the Estmerish Monarch's viceregal representative in Satavia.[36] As a result, despite being a nominally ceremonial position, the President can appoint governments (but requires the assent of the Senate), as well as call elections.[36] This has caused controversy in the past, most notably in 1996 when incumbent Liberal Prime Minister, John Barrett, requested the President of Satavia, Damian de Jager dissolved both houses and called for a federal election. However, De Jager, a member of the Conservative & Country party, refused his request and instead dissolved only the House of Representatives in a general election. De Jager did not want to risk losing the majority the Conservative & Country party held in the Senate, so refused to dissolve it.[37] The De Jager affair would lead to the Presidential (Responsibilities & Duties) Act 1999 as well as a constitutional amendment in 2013. The President's authority is represented in the provinces by a Governor, and in the territories by an Administrator.
The Prime Minister of Satavia is the head of government and executive of Satavia.[38] The position of Prime Minister has been continuously held since October 1, 1816. The first holder, Richard Somerset, served just under 13 years across two separate terms. Originally, the Prime Minister could come from either house; most Prime Ministers originally served as either commoners or peers in the House of Peers.[39] Arthur O'Connell was the first Prime Minister to be a member of the lower house, the House of Representatives, whilst his successor, Henry King-Stewart was the final Prime Minister who served as a member of the upper house. From 1936 until 1939, the Prime Minister was both the head of state and government of the Union of Satavia.
Although traditionally regarded as Asteria Inferior's most economically and politically stable nation,[5][10][32][40] Satavia experienced two coups d'état and one attempted coup d'état within 38 years (the first, the February Coup of 1939, the 1976 Satavian coup d'état and an attempted coup d'état during the Admiral's Rebellion of 1946).[41] They remain the only coups d'état in Satavian history.
Satavian politics is generally regarded as operating within a loose two-party system.[42] Satavia's two major political parties are the Conservative & Country Party, who are generally regarded as centre-right to right-wing, and the Liberal party, regarded as centre-left to left-wing. The centrist, Western Freestate-based United party are usually considered as Satavia's third party and have been instrumental in allowing the Conservative & Country party to form governments in the past.[42] Other active major political parties include Satavia First and the Labour & Social Democratic party. Satavia has 42 registered federal political parties, of which only five have representation, and 729 registered provincial political parties (including affiliates of major federal political parties).[42][43]
Provinces and territories
Satavia has six provinces - Arundel (AR), the Hope Province (HP), New Borland (NB), the Orange Province (OP), the Pioneerstaat (PS) and the Western Freestate (WF) - and two territories - the Central Territory (CT) and the National Capital District (NCD). Additionally, the Patrick Islands (PI) is a state in free association with Satavia. No legal distinction exists between the provinces and territories, all of which have their own elected legislatures and leaders. In the provinces, the governor is the representative of the president and a mostly ceremonial position, although is tasked with providing assent to acts of provincial legislation, whilst the premier is the leader of a provincial government.[44] In the territories, the governor's official title is "Administrator", whilst the premier's title is "Chief Minister". Despite having no legal distinction, a practical difference between the provinces and territories is that the Premier of the province can recommend to the president a successor for the position of governor, whereas the territorial administrators are chosen unilaterally by the federal government with little to no input from the territories.[44] This is a system inherited from the colonial period, where the governor represented the governor-general, who in turn represented the Crown of Estmere.[44][45]
Except for the National Capital District, the provinces and territories retain full control over most areas of governance, including public services and emergency services with each province and territory operating its own law enforcement agencies.[44] Despite the provinces and territories mostly possessing plenary legislative power, the federal government may unilaterally revoke provincial legislation as provided under the Satavian constitution.[46] The federal government has overriding supremacy over the provincial governments, as settled in the 1995 High Court case, Satavian Federation vs Hope Province.[44][47]
Provinces
| Flag | Province | Postal | ISO | Capital | Population (Sep 2022) |
Area (km2) | Population Density (/km2) | No. of Reps. in Parliament | Governor | Premier (Party) |
Provincial Government | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Arundel | AR | SV-AR | Henschhoek | 2,522,192 | 27,956 | 90.22 | 16 | Willem de Ruyter | François Roigard (C&C) |
Government of Arundel | |
 |
Hope Province | HP | SV-HP | Burnaby | 6,694,196 | 141,622 | 47.27 | 42 | Johan de Vilock | Walter Mackenzie (Liberal) | Government of the Hope Province | |
 |
New Borland | NB | SV-NB | Talbot | 403,156 | 10,788 | 37.37 | 2 | Philip Crawley | Eliza Smuts (Liberal) |
Government of New Borland | |
 |
Orange Province | OP | SV-OP | Northport | 3,102,850 | 47,172 | 65.78 | 19 | Daniël Schoeman | Jannie de Jager (C&C) |
Government of the Orange Province | |
 |
Pioneerstaat | PS | SV-PS | Bloemstad | 2,701,421 | 83,902 | 32.20 | 17 | Harold Key | Callum White (Liberal) |
Government of the Pioneerstaat | |
 |
Western Freestate | WF | SV-WF | Port Arthur | 6,503,294 | 99,829 | 65.14 | 37 | Christopher de Beer | Theo Goodwin (C&C) |
Government of the Western Freestate | |
Territories
| Flag | Territory | Postal | ISO | Capital | Population (Sep 2022) |
Area (km2) | Population Density (/km2) | No. of Reps. in Parliament | Administrator | Chief Minister (Party) |
Territorial Government | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Central Territory | CT | SV-CT | Hondeburg | 204,198 | 186,620 | 1.09 | 1 | James Pienaar | Louis Plummer (C&C) |
CT Government | |
 |
National Capital District | NCD | SV-NCD | Port Hope | 2,421,671 | 336 | 7,207.35 | 18 | Craig Marshall | Martin Verschoor (Liberal) |
NCD Government | |
Associated states
| Flag | Associated State | Postal | ISO | Capital | Population (Mar 2008) |
Area (km2) | Population Density (/km2) | High Chief | Prime Minister (Party) |
Government | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Patrick Islands/Naua Roa | PI | SV-PI | Patrick's Town | 28,934 | 1,882 | 15.37 | Kara Na Paoa | Dara Niuꞌa (Paiga Naua Roa) |
Government of Naua Roa | |
Foreign relations
Largely due to Satavia's large military and economic prosperity, it is often considered a regional power within Asteria Inferior.[48] Satavia has maintained close relations with its former colonial overlords, Estmere and Hennehouwe, whilst also pursuing an aggressive foreign policy in regards to socialist states, particularly Chistovodia.[49] Satavia also keeps a close relationship with Rizealand, which provided strong material support during the Satavian Crisis. Since 1981, Satavia has been an associate member of the North Vehemens Organization and keeps an increasingly pro-Camden and pro-Assunçã foreign policy outlook.[49]
Satavia's first diplomatic mission was established in 1824, by the government of the newly-formed Dominion of Satavia in Morwall.[49] Although the original building has since been destroyed, the embassy remains situated at its original location in Central Morwall. Similarly, the first diplomatic mission established in Satavia was the Estmerish High Commission (now embassy), located in Port Hope.[49] Satavia is host to 154 diplomatic missions from 77 countries, with the majority of missions located in Port Hope and Victoriaburg.
Satavia's closest relations are with its neighbour Nuvania.[49] Satavia opened a High Commission in Pietersburg in 1840, whilst Nuvania opened a High Commission the following year, in Port Hope.[49] Satavia and Nuvania, under the terms of the Van Horn Agreement, maintain a free travel agreement with one another. Nuvania also remains Satavia's largest trade partner in both exports and imports.
Satavia was a founding member of ASTCOM, and is additionally a member of the Community of Nations, Embrosphere, International Council for Democracy, Organization of Asterian Nations and is an associate member of the North Vehemens Organization.
Military
The Satavian Armed Forces (SAF) is comprised of the Satavian Army (including the Satavian Coast Guard), Satavian Air Force and Satavian Naval Service (which includes the Fleet Air Arm). The SAF is under the authority of the Department of Defence and under the direct oversight of the Secretary of State for Defence, who as of 2023 is Julian Murphy.[50] The Commander-in-Chief of the SAF is the President of Satavia. The Chief of the Defence Staff and Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff are the military leaders of the SAF, and the position can only be held once, for three years. It is rotated between the three services as stipulated under the Tri-Service Agreement.[50] The current Chief of the Defence Staff is General Jack Turcan (Army), whilst the Vice-Chief of the Defence Staff is Rear Admiral William McLaughlin (Naval Service).[51]
The Satavian Army is relatively large, numbering some 86,230 active personnel, including 9,500 conscripts completing their national service requirements[51]. All citizens are required, with some exceptions - including, but not limited to, overseas residence or education and other essential employment - to complete one year of national service, either in the Armed Forces or in one of several other organisations.[52] Additionally, each province operates its own Provincial Guard, under the control and supervision of the Governor of each respective province.[53] The Provincial Guard Forces are predominantly a reserve force that are usually activated at times of national emergencies or natural disasters.[citation needed] The size and power of the Provincial Guards has decreased drastically since the return to democracy in 1976.[54] The largest provincial guard is the Hope Province Provincial Guard, which numbers some 2,500 men. Arundel became the first province to abolish its provincial guard, doing so in 2017.[55] Meanwhile, the Satavian Air Force - by far the smallest of the three forces - primarily operates helicopters, helicopter gunships and transport aircraft.[56] The Air Force, does however, continue to operate 18 F-16 fighter jets, purchased in 1989. The Satavian Naval Service is the largest of the three services.[57] The Naval Service is generally classed as a largely green-water navy, with some blue-water capabilities.[58] As a result of Satavia's strategic location at the mouth of the Arucian, in addition to its unhindered access to the Vehemens and Glacial oceans (enhanced by forward operating bases such as Daga Roa Naval Base), the Naval Service is central to Defence Plan 2030, which aims to convert Satavia's navy into a fully-fledged blue-water navy.[59] This, in part, is intended to help counter the influence of Chistovodia in the Arucian.[60] As part of the programme, Satavia acquired ENS Dragon, a small helicopter carrier in 2017 from Estmere, renaming the ship SNV Johan van Vallier.[61] Additionally, the Satavian Naval Service operates four Darling-class diesel-electric submarines, launched from 2003 to 2004. The Naval Service also operates four older frigates and destroyer escorts, purchased from Estmere in 1984, as well as eight modern Talbot-class produced in Werania on behalf of Satavia from 1998 to 2007. The Naval Service also operates four offshore patrol vessels and 22 patrol boats. The Fleet Air Arm is operated in cooperation with the Satavian Air Force.[62]
From 2017-2018, the Satavian Armed Forces' total budget was approximately G172 billion, or 4.3% of GDP, placing Satavia amongst the highest proportional spenders in the Asterias. Satavia is an associate member of the North Vehemens Organizations, and maintains close military associations with Estmere, Nuvania and Rizealand.[50][63]
Economy
Agriculture
- sheep
- cattle - biggest meat producer?
- wine in the far south
Energy
- hmm imported energy (thx daddy nuvania)
- coal is cool
- organic oil
- no green energy (that's for euclean hippies)
Mineral resources
- major copper exporter
- plenty of iron
- gold
- lithium
- iodine (wtf is it?? nobody knows but we got it (its under the rainforest where those endangered species live, but we don't care))
Services
- we do this a lot (somebody explain)
- finance Barrett Bank
- Port Arthur Banking Corporation (PABC) big bank boys
- Asterian Standard Bank (ASB)
Tourism
- nice beeches
- popular because its safe
- easy access
- good hotels
- people are not so nice so don't annoy them
Transportation
- roads
- railway
- higways (interprovincial)
- busses
- trains
- ships
- planes (lots of planes)
Demographics
The 2022 Satavian Federal Census recorded the resident Satavian population at 24,581,912 people, giving Satavia a population density of 40.96/km2, which is below average for Asteria Inferior.[64] As an urbanised country, Satavia's population is predominantly located within its cities, whilst the country's interior, particularly in the Central Territory, is extremely sparsely populated.[8][64] Satavia's life expectancy of 76.5 years is the highest in Asteria Inferior,[64] a fact often attributed to high living standards and the availability of healthcare across the country.[65] Satavia has a fertility rate of 1.97, and has been decreasing since the 1980s.[64]
| Rank | Province/Territory | Pop. | Rank | Province/Territory | Pop. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Port Hope  Burnaby |
1 | Port Hope | National Capital District | 2,421,671 | 11 | Markethaven | Hope Province | 593,724 |  Victoriaburg  Port Arthur |
| 2 | Burnaby | Hope Province | 1,822,105 | 12 | Cape James | Hope Province | 571,193 | ||
| 3 | Victoriaburg | Western Freestate | 1,322,981 | 13 | Windstad | Orange Province | 501,234 | ||
| 4 | Port Arthur | Western Freestate | 1,003,192 | 14 | Kingsleigh | Western Freestate | 422,496 | ||
| 5 | Bloemstad | Pioneerstaat | 843,128 | 15 | Fort Mackenzie | Western Freestate | 403,329 | ||
| 6 | Fort Kinnon | Western Freestate | 841,299 | 16 | Waterkloof | Arundel | 378,777 | ||
| 7 | Northport | Orange Province | 715,163 | 17 | Macquarie | Hope Province | 361,292 | ||
| 8 | Konningstad | Hope Province | 701,221 | 18 | Westhasen | Orange Province | 201,241 | ||
| 9 | Henschhoek | Arundel | 633,195 | 19 | Vorsterburg | Western Freestate | 133,282 | ||
| 10 | Fort Dent | Hope Province | 633,126 | 20 | Danger Cove | Western Freestate | 101,151 | ||
Ancestry and immigration
From 1541 until 1747, the vast majority of the settlers arriving in Satavia came from modern-day Hennehouwe.[19][66], including Hennish and Petois people, in addition to a significant number of Gaullican Hugenots fleeing religious persecution.[67] Mass migration began after the Estmerish acquisition of the Satavian colonies, which saw a huge influx of predominantly Estmerish people.[19][66] Furthermore, significant immigration from Caldia occurred towards the mid-19th century, as well as large-scale immigration from Bahia, most notably Garambura and Rwizikuru, Dezevau and Satria. Satavia also became a popular destination for Piraeans before and after the Great War, with the vast majority settling in Victoriaburg, a city which now boasts the largest Piraean population outside of Piraea, and has led to its nickname Little Alikianos.[19][66][68]
The Satavian Federal Statistics Office collects data on race, ethnicity, ancestry and religion in addition to other categories including spoken languages, making it one of the most sweeping and in-depth census reports in the world.[8][69] At the 2022 census, Satavians who were white comprised 81.34% of the population, whilst black Satavians made up 10.89%, Creoles 4.82%, whilst the remaining 2.95% were other racial groups. Most notably, only 0.74% of the population self-identified as Indigenous Asterian, a decrease of 0.53% from 2012. The vast majority of Creoles also said they identified more with their Euclean ancestry rather than their Indigenous ancestry.
Satavians were also asked to identify most strongly with one or two ancestries. The following most commonly nominated ancestries were:
- Estmerish (37.61%)
- Hennish (29.01%)
- Rwizikuran (6.75%)
- Piraean (5.75%)
- Garamburan (4.08%)
- Caldian (3.31%)
- Gaullican (1.86%)
- Indigenous Asterian (0.74%)
- Borish (0.51%)
Additionally, 3.52% of Satavians identified as being of "Other Eastern Euclean ancestry", whilst a further 1.94% identified as being of "Other Western Euclean ancestry". Just under 1% of respondents identified as being of other, unlisted heritage. Since 1541, Satavia has seen net migration into the country except for a brief period from 1972 until 1978, during the collapse of the National Party dictatorship and the beginning of the Satavian Crisis.
Language
First languages in Satavia (2022)
Satavia has only one official language at a federal level, Estmerish. However, both Asteriaans and Hennish are recognised national languages. Satavian Estmerish is the primary variety of Estmerish spoken in Satavia, and is most closely related (and often confused with) Nuvanian Estmerish. Satavian spelling is mostly consistent with Standard Estmerish, whilst pronunciations deviate significantly, even within Satavia. Asteriaans is an official language in all the provinces and territories, whilst Hennish is only an official language in the Hope Province. Hope Hennish is the official dialect of Hennish, and is spoken as a first language by over 1.1 million Satavians.
Additionally, over 91% of Satavians stated they could "speak and understand" Estmerish "proficiently", whilst 83% said the same for Asteriaans. In government schools, children must take compulsory Estmerish lessons until the age of 16 (which is the age that children are legally able to drop out). Additionally, in all provinces and territories except the Hope Province, children must also take compulsory Asteriaans classes until the age of 16. In the Hope Province, where possible, pupils can choose between Asteriaans or Hennish. Alongside Estmerish and Asteriaans, school children are encouraged to take a third language, usually Gaullican or Weranian. Consequently, the vast majority (86%) of Satavians identified as speaking two or more languages fluently, whilst some 34% claimed they were able to speak three or more languages fluently.
Whilst there are no regulations in place on a federal level in the large private education sector, 93% of privately-educated Satavians identified as bilingual (predominantly in Estmerish and Asteriaans), whilst 47% identified as trilingual, well above the national average.
Religion
Religious identification in Satavia (2022)
Kasperism is the state religion of Satavia. Specifically, the Satavian Reformed Church is the state church and has been endorsed since its creation in 1824. Kasperist settlers played a crucial role in the colonisation of Satavia, and as a result, many of their descendants remain Kasperist. Kasperism is Satavia's largest branch of Amendism, with some 85% of all Sotirians in Satavia belonging to the Satavian Reformed Church, whilst 79.91% of all Satavians identified as Kasperist. Kasperist following is highest amongst Asteriaans and Hennish-speaking people. Despite its position as Satavia's state religion, since the introduction of the Religion (Freedom, Worship & State) Act 1986 by the government of Leander Kokkinakis (himself an Episemialist), the state has effectively been separated from the church. However, Kasperism plays a major role in influencing politics and this is perhaps best demonstrated in that the Conservative & Country party's official religious denomination is Kasperism.
Embrian Communionists represent Satavia's second largest Amendist religion. The vast majority, some 90% of Embrian Communioniststs, are primarily Estmerish-speaking whites or ethnically Bahian. Meanwhile, the Episemialist Church is Satavia's second largest religion and second largest Sotirian religion following Ammendism. Satavia's Episemialists are almost exclusively members of the Piraean diaspora, centred in the city of Victoriaburg, which itself has the largest Episemialist following in Satavia.
Other Sotirian religions, including Solarian Catholicism exist in the minority, in addition to Atudites, Irfanics and other religious groups.
Irreligion has, in the past twenty years, risen significantly in Satavia. In the 2002 census, only 3.1% of Satavians identified as irreligious, atheist or agnostic, whilst twenty years later that had risen to 12.16%. Although church attendance remains high, it has declined from its previous highs during the 20th century. Satavia ranks relatively highly in religious freedom indexes.
Health
- everyone is healthy
- except for some people ig
- free healthcare in some places
- not in others
- federal health cover scheme (thx kokkinakis)
- free ambulance (thx som1)
- smoking kills
Education
- state school aren't epic
- private schools are good though :) and that's what matters beecause who cares about the poor
Culture
- jungles
- crazy asteriaaners
- shooting guns
- putting shrimp on the braai
- having a beer
- watching sports
- basically everyone's a redneck (rooinek???)
Arts
- nice painting
- nice grafiti
- idk something interesting here about jungle painters and paintings that may or may not depict people slaughtering defenceless natives
- books (picnic at hanging rock :skull:)
- opera, that's why we built the expensive opera house
Media and entertainment
The Satavian domestic film industry is a major producer of Estmerish-language films and television. Most notably, Mountpara is a Satavian-based multinational entertainment conglomerate, which includes Mountpara Pictures film studio, which is the second-oldest film studio in the new world. The first full-length feature film in Asteria Inferior, The Rainforest Rambler was filmed in Satavia in 1907 and released later that year. The Satavian film industry suffered during National Party rule, although propaganda films such as Our Brave Country (1970) were nonetheless popular. Following the end of the National Party dictatorship in 1976, Satavian film production prospered in a period known as the Casey Street Hurricane. Notable "Hurricane" films included the international blockbusters The Last Plane out of Victoriaburg's Almost Gone (1977) and the Manic Mark film series. Additionally, war films and films that examined Satavia's national culture and identity were paticularly popular and characteristic of the period, and included Cool Carting (1978), King's Rock (1979), Day Rider (1983), 1928 (1985) and Satavian 'Till I Die (1986). Other notable Satavian films released since include A Secret (1999), the seventh highest grossing film of all time, Pienaar (2021), The Fallen (2021) and The Depression Club (2023). Satavia is also a major outlet for Asteriaans-language productions, including popular television serials Vertel my Nou!, 'n Moderne Familie and Naelloper.
Satavia has a government-funded national broadcaster, the Satavian Broadcasting Corporation. Additionally, Satavia has four private commercial television networks (three broadcast in Estmerish, one in Asteriaans), multiple pay-TV services and numerous public radio and local television networks. Satavia has five major national newspapers - The Hope Post, The Satavian, Daily Mail, The Freestate and the Satavian Economic Review. Additionally, hundreds of provincial and city-based newspapers exist, most notably the Northport Koerant, Bloemstad Burger and the Arundel Herald. Additionally, there is limited Hope Hennish broadcasting, with the Bendburgerkrant being the most notable and largest by circulation.
Pioneer poems are perhaps the most quintessentially Satavian form of folk music. Barton de Groot and Chilly Limes are regarded as the most famous pioneer poets, whose work in the late 19th century helped shape the national character of Satavia. 'Waltzing Matidla', 'Die Wandelaar' and 'En de Rooinek zong God Bescherme de Koning' are the most famous examples of pioneer poems. Modern Satavian music culture has been shaped by immigration from Euclea as well as Bahia and Coius. Well-known Satavian bands include Hot Hammer (most well known for their anti-war pub-rock song Hwababoo), DC/AC, Hard at Work, Kingdom of the Moon, D-Notice, Undertone and TwoKingdoms. Satavian singers include Jack Kloppie, Kate Furler, Piraeus Hasapis, André de Jager, Free Reya, Cardinal, Scott Jackson, Ella D'Angelis and Louise Theron.
Cuisine
- estmere but mix it with hennish, piraean + !south africa and !anzac foods and there you go
- pavlolva just for fun
- braai (shrimp on bbq, yumm)
- beef
- wine
Symbols
- dolphin (obv)
- rhea
- guns
- dolphins
- the flag
- national personification (might use britannia in the 1900s because estmere wanted to be different and used zeelandia but we'll see)
- dolphin
Sports and recreation
Rugby union is often considered the national sport of Satavia and its most popular sport, followed by Cricket and Association football (soccer). Other sports popular in Satavia include athletics, swimming, surfing, golf, boxing, judo, cycling, sailing, field hockey and netball. In recent years, baseball and softball have become increasingly popular (largely thanks to the rapid expansion of the ABL and ASL outside of the Arucian), and Zadany has become more popular at the expense of Polo.
Rugby union is Satavia's most popular sport. Satavia's national team, the Dolphins, are the third-most successful team in Rugby World Cup history, having won the tournament on two separate occasions; in 1985 and 1997. Satavia hosted the most recent edition in 2021, and finished as runners-up. In women's rugby union, Satavia is also highly accomplished, having won the Women's Rugby World Cup in 2011, which was also hosted by Satavia. The Satavian national team participates in the Asterias Cup every year, which it has won ten times, in comparison to Nuvania's eleven titles. Additionally, Nuvania and Satavia contest the Kitchener Cup every year as part of a three-match test series. Satavia's top-tier rugby league is the Super League, which features teams from the Arucian, Nuvania, Satavia and Sublustria. The Blues, based in Port Hope, is the joint most successful side, having won five titles, matched only by the Crocodiles. Satavian teams have won the Super League ten times, compared to Nuvania's eight. Super League teams pick players from within Satavia's premier domestic league, the National Rugby Championship (NRC). Many Super League teams are affiliated with NRC teams; for instance, the Blues are the Super League wing of Port Hope RFC, the Asterias' oldest rugby club. The Provincial Rugby League (PRL) is usually Satavia's most-watched domestic sporting event which sees players return from their clubs to play in an inter-provincial league. The Hope Province is the most successful province, winning 46 titles whilst the Western Freestate is the only other province to have won, winning on 39 occasions. Rugby union is by far Satavia's most played and watched sport, whilst Satavia's impact on the sport beyond the country is undeniable; Asterian rules, in contrast to Euclean rules, formed the basis for the early rules of internationally codified rugby union, whilst Satavian diaspora abroad created clubs that still operate within the top leagues of their respective countries - for instance, Morwall Asteriaans continue to play in the ERU Championship in Estmere.
Cricket is Satavia's second most popular sport by both participants and spectators. Satavia's international cricket team is highly accomplished, and Satavia is widely regarded as one of the greatest cricketing nations, having won the KCC Cricket World Cup three times, as well as most recently in 2022. Satavia's domestic cricket league, the Provincial Cricket League (PCL) is operated on a Trans-Van Horn basis and includes eight Satavian teams (one representing each province and territory) and eight Nuvanian teams (one representing each province). Whilst the most successful team is the Kaap Province, who have won seven titles, the Hope Province is the second most successful team, and most successful Satavian team with five titles.
Association football (soccer) is Satavia's third most popular sport. Satavia's national team, The Cougars, has seen limited success with their best result of a Round of 16 finish coming at the 1983 IFF Coupe du Monde, jointly hosted by Satavia and Nuvania. The women's team, however, has seen greater success; achieving a best result of fourth at the 2021 IFF Feminine Coupe du Monde. The Top 12 is Satavia's domestic soccer league, and since its inception in 1868 has been dominated by the Springbank Lions, the only team never to have been relegated from the tournament.
Satavia is widely accomplished in athletics. In boxing, Joel Tristan is widely regarded as one of the greatest welterweight boxers of all time, whilst Satavia is equally accomplished in women's boxing, taking two golds from a possible five at the 2022 Summer Invictus Games. Daniël du Toit is the current Invictus champion in pole-vaulting, and additionally holds the world pole-vaulting record. In tennis, Jannie Duquesne is Satavia's most successful tennis player, being the only player to achieve two calendar year grand slams, coming in 1973 and 1975. Satavia's highest-ranked player currently is Chase Kruger, who is ranked sixth in the world. In Swimming, Rynold Verdoorn is the world and Invictus 200m backstroke champion. Satavia hosted the 2002 Summer Invictus Games in Port Hope. In surfing, Satavia is extremely competitive and a popular destination - currently hosting a stop on the WSL Tour, Cloudfall, as well as a popular big wave destination at Toebreaker (both in the Western Freestate). Current World Surf League Championship surfers include three-time and incumbent world champion Indhi Scott, as well as other surfers such as Peter Strauss and John John Alvares. Georgios Poulos, a nine time world surfing champion, is widely regarded as one of the greatest surfers of all time.
Satavia has produced four GP1 world champions; Max Scheckter in 1963, Pieter Fendersen in 1979, Jackie Hendrickse in 1999, 2000 and 2003 and most recently Blaze Cook in 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016. Additionally, Satavia hosted the Satavian Grand Prix at the since-demolished Breybach International Circuit from 1961 until 1994, and has hosted the grand prix at the Cape James Circuit since 2002. In SailGP, the Satavian SailGP team are the only team to have won the championship, doing so every year since its inception in 2019.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Satavia maintains the islands are in free association; the position taken by the Community of Nations is that the islands are a non-self-governing dependency.
- ↑ Whilst universal suffrage had been established by 1976, mandatory voting in the Western Freestate excluded ethnically Bahian people until 1983, ethnically Coian people until 1985 and indigenous people until 2007[20]
- ↑ Arundel and the Orange Province both placed limitations on female and indigenous mandatory voting; females were required to vote from 1982 and indigenous people from 2007[20]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Winkelhock, Markus (1658). De Asterische Kolonies. s'Holle.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Elliot, Jago (2018). SATAVIA, Volume I: Before the Storm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Daniël, Mackenzie (1981). The Natives: Satavia's indigenous population. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lewisham, Mary (1974). "Advancements of the Arawak, Caribe and Chibcha". Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 Elliot, Jago (2020). SATAVIA, Volume III: 1747 to 1936.
- ↑ Clarke, Caleb (12 July 1924). "Rogue Chibcha peoples contacted in CT; isolated due to health concerns". The Hope Post. Port Hope.
- ↑ De Ruyter, Carlos (23 February 2020). "Pictured: "Uncontacted peoples" living like savages in the Central Territory". The Daily Mail. Northport.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "Satavian Federal Census 2022". Government of Satavia. 25 October 2022. Retrieved 18 July 2023.
- ↑ Gomes dos Santos Aveiro, João (2014). Álvaro de Mascarenhas: The Life and Adventures of the Greatest Explorer of them All. Precea.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Elliot, Jago (2019). SATAVIA, Volume II: The Hennish.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Verwoerd, Hendrik (2007). Native Danger. Port Hope: University Press.
- ↑ Peereboom, Thijs (1973). De Hennish in Asteria. s'Holle.
- ↑ Bishorst, Lodewijk (1988). Colonising Nuvania: The Great Unknown. Pietersburg: Die Vrystaat Publishing Group.
- ↑ Hope, Richard (1979). The Longwood Company: A complete history. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Malan, D. F. (2000). The Asteriaaners: The Hennish on the wrong continent. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Snow, Dan (2016). Pienaar's Revolt. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Thomas, William (1973). The Second Empire. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 18.7 18.8 18.9 O'Hanrahanrahan, Peter (2012). "Federation of Satavia as a case study for advanced engineering". Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 "Complete Census Data & Records (1816-2000)". Government of Satavia. 21 August 2000. Retrieved 11 July 2023.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 "Voting Limitations & Restrictions in Satavia". Government of Satavia. 25 June 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2023.
- ↑ Carter, Daniel (28 August 1833). "West Satavia Colony considers joining Dominion of Satavia; Hillingdon approves". Economic Review. Morwall.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "Western Freestate: Fact File". Government of Satavia. 14 October 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2022.
- ↑ Beckham, David (5 July 1838). "Drought Cripples Economy; money talks in Morwall". The West Satavian. Port Arthur.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Sexton, Jonathon (1986). Business is Booming - Satavia examined. Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC).
- ↑ Dupuis, Ludovic (2017). Genocide: A Complete History. Verlois: Association École.
- ↑ O'Driscoll, Brian (2005). The Great Shame examined. Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC).
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 White, Callum (2004). Estmere Aflame: The Impact of the Great War. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ Ricciardo, Daniel (16 January 1936). "Estmerish Govt. announces referendums on fate of Borland, Monarchy". The Hope Post. Port Hope.
- ↑ "Satavia Act, 1936 at legislation.gov.sv". Government of Satavia. 12 January 2000. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 "Constitution of Satavia: A History". Government of Satavia. 21 June 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- ↑ "Inside the Parliament of Satavia". Government of Satavia. 11 January 2007. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- ↑ 32.00 32.01 32.02 32.03 32.04 32.05 32.06 32.07 32.08 32.09 32.10 "Elections in Satavia". Government of Satavia. 14 August 2005. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
- ↑ "Help! I didn't vote!". Government of Satavia. 19 September 2022. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 "How electoral pushback works". Government of Satavia. 17 October 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2021.
- ↑ "Elections in the NCD". NCD Government. 8 March 2018. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 "About the President". Government of Satavia. 12 January 2017. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ Telea, Mark (21 June 1996). "De Jager affair explained". The Hope Post. Port Hope.
- ↑ "About the Prime Minister". Government of Satavia. 16 December 2012. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Verstappen, Max (1957). Inside the Satavian House of Peers. Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC).
- ↑ Murphy, Cillian (5 July 2013). "Ask the Eucloids: Asteria Inferior". Die Vrystaat. Pietersburg.
- ↑ Athanasiou, Jasper (2009). The art of the coup d'état - how to launch a coup. Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation (UPC).
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 De Ruyter, Felix (2013). A Boy's Game: Satavian politics. Port Hope: United Publishing Corporation.
- ↑ "Registry of political parties". Government of Satavia. 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 44.4 "Satavia's federal system explained". Government of Satavia. 21 June 2014. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ↑ "Today I Learned: How Satavia chooses its Governors". Jerry Seinfeld via Blogspot. 7 October 2001. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ↑ "Constitution of Satavia". Government of Satavia. 1 October 1816. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ↑ "Court Documents: 1995/36 - "Federation v Hope Province"". Government of Satavia. 12 June 2020. Retrieved 17 June 2021.
- ↑ Hakkinen, Mika (2005). Powers of the World: The Asterias. Verlois: Association École.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 49.5 Snell, Arthur (2023). A Colossal C**k up!. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 "About us: the Department of Defence". Government of Satavia. 13 February 2006. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 "The Defence Staff". Armed Forces of Satavia. 12 October 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2024.
- ↑ "National Service in Satavia - what you need to know". Government of Satavia. 1 March 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ↑ "SAF: What is the Provincial Guard?". Government of Satavia. 24 January 2001. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ↑ DeAngelo, Bailey (25 July 2006). "What has happened to the Provincial Guard?". The Hope Post. Port Hope.
- ↑ Santa, Diego (24 October 2020). "Arundel finally abolishes Provincial Guard; cites cost". The Henschhoek Examiner. Henschhoek.
- ↑ Hamilton, Lewis (2022). Inside the Air Forces of the World. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ "Defence Plan 2030". Armed Forces of Satavia. 21 October 2020. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- ↑ Underwood, Frank (17 January 2017). "DOD coughs up €84 million for ENS Dragon sale". The Hope Post. Port Hope.
- ↑ "Our Allies: Major NVO partners". North Vehemens Organization. 31 October 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 64.2 64.3 "SIB Factbook: Satavia". Government of Estmere. 28 December 2022. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ↑ "Healthcare in Satavia". Satavian Federal Healthcare Bureau. 17 June 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 66.2 "Ancestry of modern Satavians". Government of Satavia. 22 February 2021. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ↑ Sinatra, Frank (1981). History of the Hugenots. Morwall: Birdstone Press.
- ↑ "Victoriaburg in Brief". Visit Satavia. 16 July 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
- ↑ "About Us: What is the Census?". Government of Satavia. 14 April 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.