Federal Congress (Morrawia): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 448: | Line 448: | ||
[[Category:Anteria]] | [[Category:Anteria]] | ||
[[Category:Morrawia]] | [[Category:Morrawia]] | ||
[[Category:Government]] | |||
[[Category:Government institutions]] | |||
[[Category:Politics]] | [[Category:Politics]] | ||
[[Category:Politics of Morrawia]] | [[Category:Politics of Morrawia]] | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 28 August 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Federal Congress of the Republic of Morrawia Federální kongres Morawské republiky | |
|---|---|
| 48th Federal Congress | |
 Official seal of the Federal Congress of Morrawia | |
 Official logo of the Federal Congress of Morrawia | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate of the Republic House of Representative |
| History | |
| Founded | March 1, 1836 |
| Preceded by | National Assembly |
New session started | March 8, 2024 |
| Leadership | |
President of the Senate | |
President pro tempore | |
Senate Majority Leader | |
Speaker of the House | |
House Majority Leader | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 140 (Senate of the Republic) 741 (House of Representatives) |
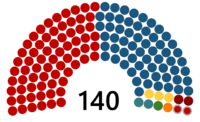 | |
Political groups | Majority (71)
Minority (69)
|
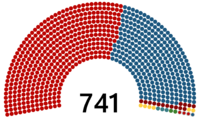 | |
Political groups | Majority (428)
Minority (313)
|
| Committees |
|
| Committees |
|
Joint committees |
|
Length of term | 4 years (House) and 6 years (Senate) |
| Authority | Legislative |
| Salary | ₮457,440 (ACU 114,360) |
| Elections | |
| Single Transferable Vote (Senate) | |
| Instant-runoff (House) | |
First election | March 3rd, 1836 (founding) |
First election | March 3rd, 1842 (all congressional seats filled) |
Last election | March 7th, 2024 (Senate) |
Last election | March 7th, 2024 (House) |
Next election | March 9th, 2026 (Senate) |
Next election | March 9th, 2028 (House) |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Capitol Building Republic of Morrawia | |
| Website | |
| federalcongress | |
| Constitution | |
| Morrawian Constitution, article II | |
The Federal Congress, or simply Congress, and officially Federal Congress of Morrawia, is the legislature of the federal government of the Republic of Morrawia. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the Morrawian House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Morrawian Senate of the Republic. It meets in the Capitol Building in Králowec, F.D. Morrawian Senators and Morrawian Representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Federal Congress has 881 voting members: 140 senators and 741 representatives. The Morrawian vice president, as President of the Senate, has a vote in the Senate only when casting a tie-breaking vote. The House of Representatives has one non-voting member.
Federal Congress convenes for a four-year term, commencing in March. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Days. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the four-year term of a Federal. The Reapportionment Act of 1995 established that there be 741 representatives, and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires that they be elected from single-member constituencies or districts. It is also required that the congressional districts be apportioned among states by population every ten years using the Morrawian census results, provided that each state has at least one congressional representative. Each senator is elected at-large in their state for a six-year term, with terms staggered, so every two years approximately one-third of the Senate is up for election. Each state, regardless of population or size, has seven senators, so currently, there are 140 senators for the 20 states.
Article Two of the Morrawian Constitution requires that members of the Federal Congress must be at least 18 years old for the House and at least 30 years old for the Senate of the Republic, be a citizen of the Morrawia for five years for the House and nine years for the Senate, and be an inhabitant of the state which they represent. Members in both chambers may stand for re-election an unlimited number of times, though they are limited by the national retirement age as per relevant legislation.
The Federal Congress was created by the Morrawian Constitution and first met in 1836, replacing the National Assembly in its legislative function. Although not legally mandated, in practice since the 19th century, Federal Congress members are typically affiliated with one of the two major parties, in contemporary period, that is the Liberal Party or the Republican Party, and and in fewer cases with third or other party or independents affiliated with no party. In the case of the latter, the lack of affiliation with a political party does not mean that such members are unable to caucus with members of the political parties. Members can also switch parties at any time, although this is quite uncommon.
Overview
Article Two of the Morrawian Constitution states, "All legislative powers herein granted shall be vested in a Federal Congress of the Republic of Morrawia, which shall consist of a Senate of the Republic and House of Representatives". The House and Senate are equal partners in the legislative process – legislation cannot be enacted without the consent of both chambers. The Constitution grants each chamber some unique powers. The Senate ratifies treaties and approves presidential appointments while the House initiates revenue-raising bills.
The House initiates impeachment cases, while the Senate decides impeachment cases. A two-thirds vote of the Senate is required before an impeached person can be removed from office.
The term Federal Congress can also refer to a particular meeting of the legislature. A Federal Congress covers four years. The current one, the 48th Federal Congress, began on March 8, 2024, and will end on March 8, 2028. Since the adoption of the Twenty-second Amendment to the Morrawian Constitution, the Federal Congress has started and ended at noon on the eight day of March of every even-numbered year. Members of the Senate are referred to as senators, members of the House of Representatives are referred to as representatives, congressmen, or congresswomen.
Scholar and representative Albert C. Aragonés asserted that the "historic mission of the Federal Congress has been to maintain freedom" and insisted it was a "driving force in Morrawian government" and a "remarkably resilient institution". Federal Congress is the "heart and soul of our democracy", according to this view, even though legislators rarely achieve the prestige or name recognition of presidents or highest judiciary justices. One wrote that "legislators remain ghosts in Morrawia's historical imagination". One analyst argues that it is not a solely reactive institution but has played an active role in shaping government policy and is extraordinarily sensitive to public pressure. Several academics described the Federal Congress:
"Federal Congress reflects us in all our strengths and all our weaknesses. It reflects our regional idiosyncrasies, our ethnic, religious, and racial diversity, our multitude of professions, and our shadings of opinion on everything from the value of war to the war over values. Federal Congress is the government's most representative body ... Federal Congress is essentially charged with reconciling our many points of view on the great public policy issues of the day".
Federal Congress is constantly changing and is constantly in flux. In recent times, the Morrawian South and West have gained House seats according to demographic changes recorded by the census and includes more women and minorities. While power balances among the different parts of government continue to change, the internal structure of the Federal Congress is important to understand along with its interactions with so-called intermediary institutions such as political parties, civic associations, interest groups, and the mass media.
The Federal Congress of the Republic of Morrawia serves two distinct purposes that overlap: local representation to the federal government of a congressional district by representatives and a state's at-large representation to the federal government by senators.
Most incumbents seek re-election, and their historical likelihood of winning subsequent elections exceeds 90 percent.
The historical records of the House of Representatives and the Senate of the Republic are maintained by the Center for Legislative Archives, which is a part of the National Archives & Records Administration.
Federal Congress is directly responsible for the governing of the Federal District, the current seat of the federal government, though since the passage of the Twenty-first Amendment to the Morrawian Constitution, this power has been greatly limited.
History
19th century
In the early years following its establishment, the Federal Congress was marked by significant political transformation and institutional development. The Federal Harmonization Act of 1845 aimed to foster cooperation among Morrawia’s diverse states, reflecting the delicate balance between federal authority and regional autonomy. This period was characterized by an expansion of congressional power, particularly as it began to assert itself in areas of national policy and economic regulation. Key figures such as Tristan Palacký, a prominent revolutionary leader and later a senior member of the Congress, played instrumental roles in shaping the legislative agenda, advocating for progressive reforms that aimed to consolidate the republic’s democratic institutions.
Throughout most of the 19th century, the Federal Congress was dominated by two major political parties: the Republican Unionists and the National Democrats. The Republican Unionists, who emerged from the revolutionary fervor of the early 19th century, were strong advocates for a centralized federal government and economic modernization. They were primarily supported by the industrialized center and northeast regions of Morrawia, which favored policies that promoted infrastructure development, industrial growth, and the abolition of slavery. In contrast, the National Democrats, representing the more agrarian northern, southern, and western regions, advocated for states' rights and a more decentralized federal structure. They were often at odds with the Republican Unionists, particularly over issues related to economic policy and slavery.
Several amendments over the years were passed regarding the Congress´s power. The 13th Amendment of 1859 provided the Federal Congress with clear authority to regulate various aspects of the economy and state governance, establishing legal boundaries between federal and state rights in these matters. The 15th Amendment of 1868 on the other hand expanded the representation of Králowec as a federal district, granting it representation equal to that of other states based on population, though its delegates remained non-voting members of the Federal Congress.
The mid-19th century saw increasing tension between the more industrialized center and northeast of the country and the agrarian regions in the north, south, and west. These differences became particularly pronounced over the issue of slavery, which nearly led to a civil war. The industrialized regions pushed for the abolition of slavery, aligning with broader global movements toward emancipation and modernization, while the agrarian states resisted, fearing economic collapse without slave labor. The crisis reached its peak in the late 1860s but was resolved through various compromises and later by the passage of the 16th and 17th Amendments to the Constitution in 1870 and 1871, respectively. The 16th Amendment prohibited slavery throughout Morrawia, while the 17th Amendment provided protections for voters, including former slaves, ensuring their participation in the democratic process.
The late 19th century, often referred to as the Morrawian Gilded Age (1870-1900), was marked by rapid economic growth and an influx of immigration that swelled the nation's population. During this period, the Federal Congress was dominated by a conservative faction within the National Democrats that prioritized economic expansion and the interests of burgeoning industrial capitalists. Lobbying activity intensified, particularly around issues such as trade tariffs and infrastructure development, leading to widespread public concern about the influence of special interest groups on the legislative process. This era also saw significant legislative efforts to regulate burgeoning industries and address the negative externalities of rapid economic growth, including environmental degradation and labor exploitation.
20th century
At the turn of the 20th century, Morrawia entered the Septennial of Reforms (1900-1907), a period marked by unprecedented cooperation within the Federal Congress. This era saw a series of sweeping reforms passed with broad bipartisan support, as presidents worked closely with congressional leaders to enact fundamental laws aimed at modernizing the nation’s political and social institutions. Key legislation during this period included the Universal Education Act of 1902, which established mandatory schooling for all children, and the Social Welfare Act of 1905, which laid the groundwork for a comprehensive social safety net, including unemployment benefits and health care subsidies. Also in 1905, 20th Amendment established universal suffrage for all women.
The beginnings of the Split Era, beginning already at the start of the new century, continued the momentum of the Septennial of Reforms but was marked by a more contentious political environment. While Congress remained a key driver of reform, internal divisions grew over issues such as labor rights, women’s suffrage, and economic regulation. Powerful Speakers of the House, such as Jan Hladík and Jan Bohatýr, emerged as central figures in this period, shaping the legislative agenda and navigating the complex dynamics of a rapidly evolving republic. The most important thing was however, from the beginning of the century, executive branch with the president on its top was assurping more and more power to shape legislative process, beginning the so-called Imperial presidency. However, grand legislation was still being passed despite changing politicla environment. The Federal Anti-Corruption Act of 1910 was a notable piece of legislation from this period, aimed at curbing the influence of special interest groups and restoring public trust in the legislative process.
NOT DONE YET
21st century
Women in the Federal Congress
Various social and structural barriers have prevented women from gaining seats in Congress. In the early 20th century, women's domestic roles and the inability to vote forestalled opportunities to run for and hold public office. The two party system and the lack of term limits favored incumbent white men, making the widow's succession – in which a woman temporarily took over a seat vacated by the death of her husband – the most common path to Congress for white women. In this age, the substantial icebreaker was usually the National Democratic Party, which frequently got women to be elected into the Federal Congress in a much higher rate, than any other party.
Women candidates began making substantial inroads in the the 30s and 40s and later in the 20th century, due in part to new political support mechanisms and public awareness of their underrepresentation in the Federal Congress. Recruitment and financial support for women candidates were rare until the second-wave feminism movement, when activists moved into electoral politics. Beginning in the 1970s, donors and political action committees like WP began recruiting, training and funding women candidates. Watershed political moments like the confirmation of Jiṙí Taclík and the series of Community rallies created momentum for women candidates, resulting in the biggest number of women elected in history and the election of members of The Pact, respectively.
Women of color faced additional challenges that made their ascension to the Federal Congress even more difficult. Wrób Lech laws, voter suppression and other forms of structural racism made it virtually impossible for women of color to reach Federal Congress prior to 1964. The passage of the Voting Rights Act that year, and the elimination of race-based immigration laws in the 1960s opened the possibility for Black, Latina and other non-white women candidates to run for Federal Congress.
Racially polarized voting, racial stereotypes and lack of institutional support still prevent women of color from reaching the Federal Congress as easily as white people. Senate elections, which require victories in statewide electorates, have been particularly difficult for women of color. Karolína Hangowá-Kollowá became the first woman of color to reach the Senate in 1987. The second, Alba Maria Carranza, won in 2006.
In 2024, Anna Raṡínowá became the first female President of the Senate of the Republic, which came with her role as the first female Vice President of Morrawia.
Role
Powers
Overview
Article Two of the Morrawian Constitution outlines the structure and powers of the Federal Congress. It details the election process, legislative procedures, and enumerates specific powers. Sections also limit congressional powers and outline state powers, some requiring congressional approval. The Necessary and Proper Clause grants Congress implied powers.
The Federal Congress has significant control over financial policy, including taxation, borrowing, and spending, though its influence has diminished with the growth of the welfare state and Keynesian economics. The Twenty-fourth Amendment expanded the Federal Congress's power to tax income without state apportionment.
Federal Congress plays a key role in national defense, including the power to declare war and maintain the military, though the executive branch has increasingly bypassed the Federal Congress in initiating military action. This shift has led to ongoing debates over the balance of power between the Federal Congress and the president regarding war decisions.
The body also has non-legislative powers, such as overseeing the executive branch through investigations and subpoenas. Critics argue that the Federal Congress has sometimes failed in its oversight duties, allowing the executive to gain more power, particularly in budgetary and legislative matters. Signing statements by presidents have further tilted power toward the executive, raising constitutional concerns.
The legislative branch has the exclusive power to remove federal officials through impeachment and can establish post offices, issue patents, create lower courts, and admit new states. However, there are concerns that the Federal Congress's power is being overshadowed by the growing authority of the presidency, particularly in managing financial crises.
Enumeration
The Constitution enumerates the powers of the Federal Congress in detail. In addition, other congressional powers have been granted, or confirmed, by constitutional amendments.
Generally militia forces are controlled by state governments, not the Federal Congress.
Implicit, commerce clause
Federal Congress also has implied powers deriving from the Constitution's various articles and clauses which permit the Federal Congress to "make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the Republic of Morrawia, or in any Ministry or Officer thereof". Broad interpretations of this article and of other clauses, the enumerated power to regulate commerce, in rulings such as Jakel v. Palacia, have effectively widened the scope of the Federal Congress's legislative authority far beyond that prescribed in the constitution.
Territorial government
Constitutional responsibility for the oversight of Králowec, F.D., the federal district and national capital, and the Morrawian territories of Adelaide Atoll, and Gorsko rests with the Federal Congress, except some Twenty-first Amendment to the Morrawian Constitution, devolving some of the powers to the local Králowec government. The republican form of government in territories is devolved by congressional statute to the respective territories including direct election of governors, the F.D. mayor and locally elective territorial legislatures.
Territory of Gorsko, at this time the only territory of Morrawia, elects a non-voting delegate to the Morrawian House of Representatives as they have throughout congressional history. They "possess the same powers as other members of the House, except that they may not vote when the House is meeting as the House of Representatives". They are assigned offices and allowances for staff, participate in debate, and appoint constituents to the four military service academies for the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Coast Guard.
The Liberal and Republican political parties nominate their presidential candidates at national conventions which include delegates from the the one major territory.
Checks and balances
The Constitution provides checks and balances among the three branches of the federal government. Its authors expected the greater power to lie with the Federal Congress as described in Article Two.
The Federal Congress's influence on the presidency has varied based on factors like leadership, political influence, war, and individual initiatives. The impeachment of Edward Soukup diminished presidential power for some time. However, the 20th and 21st centuries saw increased presidential power under leaders like Pawel Záworský and Karel Tusar. Despite laws like the Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974, the presidency remains more powerful today than in the 19th century. Executive branch officials often withhold sensitive information from the Federal Congress, leading to mutual distrust. The Federal Congress, slow and divided, is less suited for rapid decision-making, unlike the executive branch.
The Constitution grants the Federal Congress the power to remove executive or judicial officials through impeachment. The House of Representatives can impeach officials, while the Senate conducts the trial, requiring a two-thirds majority for conviction. A convicted official is removed from office and may be barred from future office. Two hundred fifty-one officials have been impeached, with 30 convicted. Four presidents have been impeached, two convicted, and one, Antonín Sád, resigned in 1931 after impeachment proceedings began.
The Senate checks executive power by confirming presidential appointments and ratifying treaties. Most nominees are confirmed, but rejections do occur. Treaties need a two-thirds Senate vote to be ratified, sometimes leading to presidential pressure on senators. The House plays no role in these processes except in filling a vice-presidential vacancy, requiring a majority vote in both chambers.
The 1836 Constitution established judicial review for the highest judiciary of the country, allowing courts to nullify unconstitutional laws, significantly limiting the Federal Congress's power. This power acts as a check on legislative authority, as seen in the 1857 Portoj decision, where the Court struck down a congressional act. The Court can also extend the Federal Congress's power through constitutional interpretation.
The Federal Congress's first investigation of the executive branch occurred in 1839 with St. Caroline's Defeat. Investigations help gather information for legislation, assess laws, and review qualifications and performance of officials. Committees can hold hearings, subpoena witnesses, and cite those who refuse to testify for contempt. Most hearings are public, with important ones widely reported. The Federal Congress generates vast amounts of information and publishes reports, maintaining irregularly updated databases in various formats.
Federal Congress also plays a role in presidential elections. Both Houses meet in joint session on the eighth day of March following a presidential election to count the votes, and they announcee the second round of elections, if no candidate wins a majority.
The main result of congressional activity is the creation of laws, most of which are contained in the Morrawian Code, arranged by subject matter alphabetically under several title headings to present the laws "in a concise and usable form".
Structure
Congress is split into two chambers – House and Senate – and manages the task of writing national legislation by dividing work into separate committees which specialize in different areas. Some members of Congress are elected by their peers to be officers of these committees. Further, Congress has ancillary organizations such as the Government Accountability Office and the Library of Congress to help provide it with information, and members of Congress have staff and offices to assist them as well. In addition, a vast industry of lobbyists helps members write legislation on behalf of diverse corporate and labor interests.
Committees
Specializations
The committee structure permits members of the Federal Congress to study a particular subject intensely. It is neither expected nor possible that a member be an expert on all subject areas before the Federal Congress. As time goes by, members develop expertise in particular subjects and their legal aspects. Committees investigate specialized subjects and advise the entire Federal Congress about choices and trade-offs. The choice of specialty may be influenced by the member's constituency, important regional issues, prior background and experience. Senators often choose a different specialty from that of the other senator from their state to prevent overlap. Some committees specialize in running the business of other committees and exert a some form of influence over all legislation, though generally congressional committees in Morrawia have mainly advisory function.
Power
Committees write legislation. While procedures, such as the House discharge petition process, can introduce bills to the House floor and effectively bypass committee input, they are exceedingly difficult to implement without committee action. Committees have only advisory and expertise power. Legislative, oversight, and internal administrative tasks are divided among over three hundred committees and subcommittees which gather information, evaluate alternatives, and identify problems. They propose solutions for consideration by the full chamber. In addition, they perform the function of oversight by monitoring the executive branch and investigating wrongdoing.
Officer
At the start of each four-year session, the House elects a speaker who does not normally preside over debates but serves as the majority party's leader. In the Senate, the vice president is the ex officio president of the Senate. In addition, the Senate elects an officer called the president pro tempore. Pro tempore means for the time being and this office is usually held by the most senior member of the Senate's majority party and customarily keeps this position until there is a change in party control. Accordingly, the Senate does not necessarily elect a new president pro tempore at the beginning of a new Congress. In the House and Senate, the actual presiding officer is generally a junior member of the majority party who is appointed so that new members become acquainted with the rules of the chamber.
Support services
National Library of the Federal Congress
The National Library of the Federal Congress was established by an act of Congress in 1840. It is primarily housed in three buildings on Capitol Hill, but also includes several other sites: the National Library Service for the Blind and Physically Handicapped in Králowec, F.D.. The National Audio-Visual Conservation Center in Kulpýṙ, Pallaine, a large book storage facility located in Fort Marat, Wallashia, and multiple overseas offices. The Library had mostly law books when it was burnt in 1866 in the Great Fire of Králowec, but the library's collections were restored and expanded when Federal Congress authorized the purchase of Jan Rýnský's private library. One of the library's missions is to serve the Federal Congress and its staff as well as the Morrawian public. It is one the largest library in the world with millions of items including books, films, maps, photographs, music, manuscripts, graphics, and materials in over 300 languages. It is the main national library of Morrawia.
Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service, part of the National Library of the Federal Congress, provides detailed, up-to-date and non-partisan research for senators, representatives, and their staff to help them carry out their official duties. It provides ideas for legislation, helps members analyze a bill, facilitates public hearings, makes reports, consults on matters such as parliamentary procedure, and helps the two chambers resolve disagreements. It has been called the "House's think tank" and has a staff of about 500 employees.
Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a federal agency which provides economic data to the Federal Congress.
It was created as an independent non-partisan agency by the Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974. It helps Congress estimate revenue inflows from taxes and helps the budgeting process. It makes projections about such matters as the national debt as well as likely costs of legislation. It prepares an annual Economic and Budget Outlook with a mid-year update and writes An Analysis of the President's Budgetary Proposals for the Senate's Appropriations Committee. The speaker of the House and the Senate's president pro tempore jointly appoint the CBO director for a four-year term.
Lobbying
Lobbyists represent diverse interests and often seek to influence congressional decisions to reflect their clients' needs. Lobby groups and their members sometimes write legislation and whip bills. In 2007, there were approximately 8,500 federal lobbyists in Králowec, F.D. They explain to legislators the goals of their organizations. Some lobbyists represent non-profit organizations and work pro bono for issues in which they are personally interested.
Police
The Morrawian Congressional Guard Department (MCGP) is a federal law enforcement agency with jurisdiction across Morrawia, tasked with safeguarding the Federal Congress both within the Federal District and across the nation, including its territories. Operating under the authority of the Congressional Security Board, the MCGP is unique as the only comprehensive federal law enforcement agency established by the legislative branch of the Morrawian federal government.
Partisanship versus bipartisanship
Federal Congress has alternated between periods of constructive cooperation and compromise between parties, known as bipartisanship or multipartisanship, and periods of deep political polarization and fierce infighting, known as partisanship. The period after the Great War was marked by partisanship, as is the case today. It is generally easier for committees to reach accord on issues when compromise is possible. Some political scientists speculate that a prolonged period marked by narrow majorities in both chambers of the Federal Congress has intensified partisanship in the last few decades, but that an alternation of control of the Federal Congress between Liberals and Republicans may lead to greater flexibility in policies, as well as pragmatism and civility within the institution.
Procedures
Sessions
A term of the Federal Congress is divided into four "sessions", one for each year. The Federal Congress has occasionally been called into an extra or special session. A new session commences on March 8 each year unless the Federal Congress decides differently. The Constitution requires the Federal Congress to meet at least once each year and forbids either house from meeting outside the Capitol without the consent of the other house.
Joint sessions
Joint sessions of the Federal Congress occur on special occasions that require a concurrent resolution from House and Senate. These sessions include certifying election results after a presidential election and the president's State of the Union address. The constitutionally mandated report, normally given as an annual speech, is modeled on previous Emperor´s Declaration, was written by most presidents after Soukup but personally delivered as a spoken oration beginning with Wáclaw Morawċík in 1906. Joint Sessions and Joint Meetings are traditionally presided over by the speaker of the House, except when counting presidential electoral results when the vice president (acting as the president of the Senate) presides.
Bills and resolutions
Ideas for legislation can come from members, lobbyists, state legislatures, constituents, legislative counsel, or executive agencies. Anyone can write a bill, but only members of Congress may introduce bills. Most bills are not written by Federal Congress members, but originate from the Executive branch. Interest groups often draft bills as well. The usual next step is for the proposal to be passed to a committee for review an advisory purposes. A proposal is usually in one of these forms:
Bills - Laws in the making. A House-originated bill begins with the letters "D.K." for "Dolní komora" or "lower chamber", followed by a number kept as it progresses.
Joint resolutions - There is little difference between a bill and a joint resolution since both are treated similarly. A joint resolution originating from the House, for example, begins "U.D.K." followed by its number.
Concurrent resolutions - They affect only the House and Senate and accordingly are not presented to the president. In the House, they begin with "S.U.D.K."
Simple resolutions - These concern only the House or only the Senate and begin with "J.U.D.K." or "J.U.H.K."
Representatives introduce a bill while the House is in session by placing it in the hopper on the Clerk's desk. It is assigned a number and referred to a committee which studies each bill intensely at this stage. Drafting statutes requires "great skill, knowledge, and experience" and sometimes take a year or more. Sometimes lobbyists write legislation and submit it to a member for introduction. Joint resolutions are the normal way to propose a constitutional amendment or declare war. On the other hand, concurrent resolutions (passed by both houses) and simple resolutions (passed by only one house) do not have the force of law but express the opinion of the Federal Congress or regulate procedure. Bills may be introduced by any member of either house. The Constitution states: "All bills for raising revenue shall originate in the House of Representatives". While the Senate cannot originate revenue and appropriation bills, it has the power to amend or reject them. Federal Congress has sought ways to establish appropriate spending levels.
Each chamber determines its own internal rules of operation unless specified in the Constitution or prescribed by law. In the House, a Rules & Administration Committee guides legislation; in the Senate, a Oversight, Accountability & Administration committee is in charge. Each branch has its own traditions. For example, the Senate relies heavily on the practice of getting "unanimous consent" for noncontroversial matters. House and Senate rules can be complex, sometimes requiring a hundred specific steps before a bill can become a law. Members sometimes turn to outside experts to learn about proper congressional procedures.
Each bill goes through several stages in each house including consideration by a committee and advice from the Supreme Audit Bureau. Most legislation is considered by standing committees which have jurisdiction over a particular subject such as Agriculture or Appropriations. The House has fifteen standing committees and the Senate has twenty-one. Standing committees meet at least once each month. Almost all standing committee meetings for transacting business must be open to the public unless the committee votes, publicly, to close the meeting. A committee might call for public hearings on important bills. Each committee is led by a chair who belongs to the majority party and a ranking member of the minority party. Witnesses and experts can present their case for or against a bill. Then, a bill may go to what is called a mark-up session, where committee members debate the bill's merits and may offer amendments or revisions. Committees may also amend the bill, but the full house holds the power to accept or reject committee amendments. After debate, the committee votes whether it wishes to report the measure to the full house. If amendments are extensive, sometimes a new bill with amendments built in will be submitted as a so-called clean bill with a new number. Both houses have procedures under which committees can be bypassed or overruled but they are rarely used. Generally, members who have been in the Federal Congress longer have greater seniority and therefore greater power.
A bill which reaches the floor of the full house can be simple or complex and begins with an enacting formula such as "Be it enacted by the Senate of the Republic and House of Representatives of the Republic of Morrawia in the Federal Congress assembled ..." Consideration of a bill requires, itself, a rule which is a simple resolution specifying the particulars of debate – time limits, possibility of further amendments, and such. Each side has equal time and members can yield to other members who wish to speak. Sometimes opponents seek to recommit a bill which means to change part of it. This is all happening in the three readings system in which the whole process operates. One additional reading to the so-called pre-reading time is then utilized in the second chamber. The house may debate and amend the bill. Generally, discussion requires a quorum, usually half of the total number of representatives, before discussion can begin, although there are exceptions. The precise procedures used by the House and Senate differ. A final vote on the bill follows.
Once a bill is approved by one house, it is sent to the other which may pass, reject, or amend it. For the bill to become law, both houses must agree to identical versions of the bill. If the second house amends the bill, then the differences between the two versions must be reconciled in a conference committee, an ad hoc committee that includes senators and representatives sometimes by using a reconciliation process to limit budget bills. Both houses use a budget enforcement mechanism informally known as pay-as-you-go or paygo which discourages members from considering acts that increase budget deficits. If both houses agree to the version reported by the conference committee, the bill passes, otherwise it fails.
The Constitution specifies that a majority of members (a quorum) be present before doing business in each house. The rules of each house assume that a quorum is present unless a quorum call demonstrates the contrary and debate often continues despite the lack of a majority.
Voting within the Federal Congress can take many forms, including systems using lights and bells and electronic voting. Both houses use voice voting to decide most matters in which members shout "aye" or "no" and the presiding officer announces the result. The Constitution requires a recorded vote if demanded by one-fifth of the members present or when voting to override a presidential veto. If the voice vote is unclear or if the matter is controversial, a recorded vote usually happens. The Senate uses roll-call voting, in which a clerk calls out the names of all the senators, each senator stating "aye" or "no" when their name is announced. In the Senate, the Vice President may cast the tie-breaking vote if present when the senators are equally divided.
The House reserves roll-call votes for the most formal matters, as a roll call of all 741 representatives takes quite some time. Normally, members vote by using an electronic device. In the case of a tie, the motion in question fails. Most votes in the House are done electronically, allowing members to vote yea or nay or present or open. Members insert a voting ID card and can change their votes during the last five minutes if they choose. In addition, paper ballots are used occasionally (yea indicated by green and nay by red). One member cannot cast a proxy vote for another. Congressional votes are recorded on an online database.
After passage by both houses, a bill is enrolled and sent to the president for approval. The president may sign it making it law or veto it, perhaps returning it to the Federal Congress with the president's objections. A vetoed bill can still become law if each house of Congress votes to override the veto with a two-thirds majority. Finally, the president may do nothing neither signing nor vetoing the bill and then the bill becomes law automatically after ten days (not counting Sundays) according to the Constitution. But if Congress is adjourned during this period, presidents may veto legislation passed at the end of a congressional session simply by ignoring it. The maneuver is known as a pocket veto, and cannot be overridden by the adjourned Federal Congress.
Public interaction
Advantage of incumbency
Citizens and representatives
Senators face reelection every six years, and representatives every four. Reelections encourage candidates to focus their publicity efforts at their home states or districts. Running for reelection can be a grueling process of distant travel and fund-raising which distracts senators and representatives from paying attention to governing, according to some critics. Although others respond that the process is necessary to keep members of the Federal Congress in touch with voters.
Incumbent members of the Federal Congress running for reelection have strong advantages over challengers. They raise more money because donors fund incumbents over challengers, perceiving the former as more likely to win, and donations are vital for winning elections. One critic compared election to the Federal Congress to receiving life tenure at a university. Another advantage for representatives is the practice of redistricting, though in recent years, several legislation severely restricted the practice. After each ten-year census, states are allocated representatives based on population, and officials in power can choose how to draw the congressional district boundaries to support candidates from their party with several limitations and guidelines. As a result, reelection rates of members of Congress hover around 90 percent, causing some critics to call them a privileged class. Academics such as National University of Králowec's Ṡtėpán Makád have proposed solutions to fix redistricting in Morrawia for good with mandatory non-partisan groups in every state as a part of Federal Election Commission. Senators and representatives enjoy free mailing privileges, called franking privileges. While these are not intended for electioneering, this rule is often skirted by borderline election-related mailings during campaigns.
Expensive campaigns
In 1971, the cost of running for Congress in Dalmate was ₮20,000 but costs have climbed. The biggest expense is television advertisements. Today's races cost more than a hundred thousand tollars for a House seat, and two hundred thousand or more for a Senate seat. Since fundraising is vital, "members of Congress are forced to spend ever-increasing hours raising money for their re-election".
In the 1970s the Constitutional Tribunal has been asked to determine whether the regulatory finance laws violated donors free speech. Some saw money as a good influence in politics since it "enables candidates to communicate with voters". In the split decision Free Morrawia v. FEC the court held 5–4 that the freedom of speech is not violated by the government when restricting independent expenditures for political campaigns by corporations, nonprofit organizations, labor unions, and other associations, thus supporting the New Campaign Reform Act of 1972. This is by many seen as one of the most consequential rulings in Morrawian history, which at least to certain extent kept large amounts of money out of politics, thus strengthening Morrawian democracy.
Elections are influenced by many variables. Some political scientists speculate there is a coattail effect (when a popular president or party position has the effect of reelecting incumbents who win by "riding on the president's coattails"), although there is some evidence that the coattail effect is irregular and possibly declining since the 1960s. Some districts are so heavily Liberal or Republican or other that they are called a safe seat. Any candidate winning the primary will almost always be elected, and these candidates do not need to spend money on advertising. But some races can be competitive when there is no incumbent. If a seat becomes vacant in an open district, then both parties may spend heavily on advertising in these races. In Pomaria in 1992, only four of twenty races for House seats were considered highly competitive.
Television and negative advertising
Since members of the Federal Congress must advertise heavily on television, this usually involves negative advertising, which smears an opponent's character without focusing on the issues. Negative advertising is seen as effective because "the messages tend to stick". These advertisements sour the public on the political process in general as most members of the Federal Congress seek to avoid blame. One wrong decision or one damaging television image can mean defeat at the next election, which leads to a culture of risk avoidance, a need to make policy decisions behind closed doors, and concentrating publicity efforts in the members' home districts.
Since at least 1960s, there has been mixed efforts to quell the effects of negative advertising with the majority of these attempts ending with the reading period in one of the chambers, due to fears of the freedom of speech violations. Some minor acts like the Campaign Management Act of 1985 were meant for limiting the disinformation wave against the opposing candidate, which has become increasingly popular in the decades prior. Most recent attempt was in 2020 with the ECO (Election Campaign Organization) Act was struck down by the Constitutional Tribunal for its vage and broad terms regarding mainly it´s provisions about personal attacks on non-campaigning individuals.
Perceptions
Prominent Founding Fathers, felt that elections were essential to liberty, that a bond between the people and the representatives was particularly essential, and that "frequent enough elections are unquestionably the only policy by which this dependence and sympathy can be effectually secured". In 2010, few Morrawians were familiar with leaders of the Federal Congress. The percentage of Morrawians eligible to vote who did, in fact, vote was 68% in 1960, but has been falling since, although there was a slight upward trend in the 2016 election. Public opinion polls asking people if they approve of the job the Federal Congress is doing have, in the last few decades, hovered around 31% with some variation. Scholar Julián Zelger suggested that the "size, messiness, virtues, and vices that make the Federal Congress so interesting also create enormous barriers to our understanding the institution ... Unlike the presidency, Federal Congress is difficult to conceptualize". Other scholars suggest that despite the criticism, "Federal Congress is a remarkably resilient institution ... its place in the political process is not threatened ... it is rich in resources" and that most members behave ethically. They contend that "Congress is easy to dislike and often difficult to defend" and this perception is exacerbated because many challengers running for Congress run against Congress, which is an "old form of Morrawian politics" that further undermines Federal Congress's reputation with the public.
An additional factor that confounds public perceptions of the Federal Congress is that congressional issues are becoming more technical and complex and require expertise in subjects such as science, engineering and economics. As a result, Congress often cedes authority to experts at the executive branch.
Since 2001, Congress has dropped ten points in the formal confidence poll with only twelve percent having "a great deal" or "quite a lot" of confidence in their legislators. Since 2011, the poll has reported Congress's approval rating among Morrawians at 16% or below three times. Public opinion of the Federal Congress plummeted further to 9% in October 2007 after parts of the Morrawians government deemed "nonessential government" were gutted and some even shut down as a part of austerity measures.
Smaller states and bigger states
When the Constitution was ratified in 1836, the ratio of the populations of large states to small states was roughly ten to one. The Sollandy Compromise gave every state, large and small, an equal vote in the Senate. Since each state has two senators, residents of smaller states have more clout in the Senate than residents of larger states. But since 1836, the population disparity between large and small states has grown. In 2010, for example, Elbennau had twenty-five times the population of Tawuii. Critics, such as constitutional scholar Florian Weinberg, have suggested that the population disparity works against residents of large states and causes a steady redistribution of resources from "large states to small states". Others argue that the Sollandy Compromise was deliberately intended by the Founding Fathers to construct the Senate so that each state had equal footing not based on population, and contend that the result works well on balance.
Members and constituents
A major role for members of the Federal Congress is providing services to constituents. Constituents request assistance with problems. Providing services helps members of the Federal Congress win votes and elections and can make a difference in close races. Congressional staff can help citizens navigate government bureaucracies. One academic described the complex intertwined relation between lawmakers and constituents as home style.
Motivation
One way to categorize lawmakers, according to former University of Tatrany political science professor Richard Fenský, is by their general motivation:
- Reelection: These are lawmakers who "never met a voter they didn't like" and provide excellent constituent services.
- Good public policy: Legislators who "burnish a reputation for policy expertise and leadership".
- Power in the chamber: Lawmakers who spend serious time along the "rail of the House floor or in the Senate cloakroom ministering to the needs of their colleagues". Famous legislator Honoré Mallate in the mid-19th century was described as an "issue entrepreneur" who looked for issues to serve his ambitions.
Privileges
Pay
Some critics complain congressional pay is high compared with a median Morrawian income. Others have countered that congressional pay is consistent with other branches of government. Another criticism is that members of the Federal Congress are insulated from the health care market due to their much better coverage. Others have criticized the wealth of members of the Federal Congress. In January 2014, it was reported that for the first time over one third of the members of the Congress were millionaires. Federal Congress has been criticized for trying to conceal pay raises by slipping them into a large bill at the last minute.
Members elected since 1979 are covered by the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS). Like other federal employees, congressional retirement is funded through taxes and participants' contributions. Members of Congress under FERS contribute 2.5% of their salary into the FERS retirement plan and pay 5.2% of their salary in Social Security taxes. And like federal employees, members contribute one-third of the cost of health insurance with the government covering the other two-thirds. The size of a congressional pension depends on the years of service and the average of the highest three years of their salary. By law, the starting amount of a member's retirement annuity may not exceed 80% of their final salary. In 2018, the average annual pension for retired senators and representatives under the Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS) was ₮154,491, while those who retired under FERS, or in combination with CSRS, was ₮95,480.
Members of Congress make fact-finding missions to learn about other countries and stay informed, but these outings can cause controversy if the trip is deemed excessive or unconnected with the task of governing. For example, The Imperial Street Journal reported in 2015 that lawmaker trips abroad at taxpayer expense had included spas, ₮1 800-per-night extra unused rooms, and shopping excursions. Some lawmakers responded that "traveling with spouses compensates for being away from them a lot in Králowec" and justify the trips as a way to meet officials in other nations.
Postage
The franking privilege allows members of the Federal Congress to send official mail to constituents at government expense. Though they are not permitted to send election materials, borderline material is often sent, especially in the run-up to an election by those in close races. Some academics consider free mailings as giving incumbents a big advantage over challengers.
Protection
Members of Congress enjoy parliamentary privilege, including freedom from arrest in all cases except for treason, felony, and breach of the peace, and freedom of speech in debate. This constitutionally derived immunity applies to members during sessions and when traveling to and from sessions. The term "arrest" has been interpreted broadly, and includes any detention or delay in the course of law enforcement, including court summons and subpoenas. The rules of the House strictly guard this privilege. A member may not waive the privilege on their own but must seek the permission of the whole house to do so. Senate rules are less strict and permit individual senators to waive the privilege as they choose.
The Constitution guarantees absolute freedom of debate in both houses, providing in the Constitution that "for any speech or debate in either House, they shall not be questioned in any other Place". Accordingly, a member of the Federal Congress may not be sued in court for slander because of remarks made in either house, although each house has its own rules restricting offensive speeches, and may punish members who transgress.
Obstructing the work of the Federal Congress is a crime under federal law and is known as contempt of the Federal Congress. Each member has the power to cite people for contempt but can only issue a contempt citation – the judicial system pursues the matter like a normal criminal case. If convicted in court of contempt of the Federal Congress, a person may be imprisoned for up to one year.