Outline of Mascylla: Difference between revisions
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
====Free cities of Mascylla==== | ====Free cities of Mascylla==== | ||
[[File:Frankfurter Altstadt mit Skyline 2019 (100MP).jpg|270px|thumb|right|The historical centre of [[Köpenick]] with a partial view of the skyline of [[Königsreh]] in the background]] | |||
* [[Mascylla#Administrative divisions|Free cities of Mascylla]] (''Freie Städte'') | * [[Mascylla#Administrative divisions|Free cities of Mascylla]] (''Freie Städte'') | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 14 October 2020
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Mascylla.
Mascylla – sovereign country located on the northern extent of Telmeria. It is bordered by the White Sea to the north-west, the North Sea to the north-east, Lake Delcia to the south-east, X and Cuthland-Waldrich to the south, Lilienburg and Lake Sigismund to the south-west, Temaria to the west, and Valimia to the east. With a population of over 49 million and an area of more 338,000 square kilometres (130,000 sq mi), it is the most populous and largest country in Telmeria.
Mascylla was under the control of the Cuthish Empire for hundreds of years and more centuries being fragmented into smaller states. Efforts to resist the rising kingdom of Adwhin eventually led to the expulsion of the Elbgau Confederation led by Aldia from its sphere of influence in the mid-18th century, ensuing into a bitter war. It ended with a victory on behalf of the Confederation, unifying the region and becoming a nation-state in 1793.
Following its unification, Mascylla rose as a regional power and instituted a path towards international integrity. In the Great War, the Armala Coalition defended and won the fightings in Telmeria and Cardia, manifesting Lavaria, Mascylla and Albeinland as great powers and ultimately partners following the Treaty of Lehpold. Though the nation saw political stability throughout its history, the authoritarian monarchial system was overthrown during the revolution of 1923 and a more democratic government was introduced. In the second half of the 20th century Mascylla witnessed steady decolonization but diplomatic and economic growth, culminating in its leading role of Berean politics and representation.
General references
- Pronunciation: [məˈskɪlə] (English), [maˈskiːli̯ən] (Hesurian)
- Common Albish country name: Mascylla
- Official Albish country name: Crowned Republic of Mascylla
- Common endonym: Maskillien
- Official endonym: Gekrönte Republik Maskillien
- Adjectival: Mascylla, Mascyllary
- Demonym: Mascyllary
- Etymology: Name of Mascylla
- ISO country codes: MC, MAC
- ISO region codes: MC
- Internet country code top-level domain: .mc
Geography of Mascylla
- Mascylla is: a country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Berea
- Time zone: UTC+3
- Extreme points of Mascylla
- North: Dattheim at the White Sea
- South: Munstborn, at the X border
- West: Neukloster, at the Cuthish border
- East: Grächsitz, in north Tudona at the North Sea
- High: Schneespeer 2,597 m (8,520 ft)
- Low: Mascyllary coast 0 m
- Land boundaries: X km
 Temaria X km
Temaria X km Valimia X km
Valimia X km Cuthland-Waldrich X km
Cuthland-Waldrich X km Lilienburg 52 km
Lilienburg 52 km
- Maritime boundaries: X km
- X X km
- X X km
- Coastline: X km
- Population of Mascylla: 48,972,336 (as of 2018)
- Area of Mascylla: 338,424 km2
Topography of Mascylla
- Climate of Mascylla
- Geology of Mascylla
- National parks and protective areas of Mascylla
- Wildlife of Mascylla
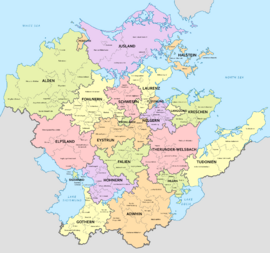
Administrative divisions of Mascylla
States of Mascylla
- States of Mascylla (Länder)
- Districts of Mascylla (Landkreise)
- Municipalities of Mascylla (Gemeinden)
- Districts of Mascylla (Landkreise)
Free cities of Mascylla
- Free cities of Mascylla (Freie Städte)
- Unified municipalities of Mascylla (Einheitsgemeinden)
- Major cities of Mascylla
- Capital city of Mascylla: Königsreh
- Flussmund - second commercial capital with Königsreh and largest city in Mascylla at more than 4 million inhabitants
- Langquaid - third largest city and information technology center for Telmeria
- Pereuth - largest commercial port facilities in Mascylla (jointly with Flussmund)
- Augusthal - infrastructure and transport hub for Mascylla, historical political centre
Demographics of Mascylla
Neighbouring states of Mascylla
Mainland Mascylla is bordered by:
The overseas territories of Mascylla also border: