Amilagro
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Federated Socialist States of Sukong 綠國聯赤邦 (Sukong) Lòu Kě Lìen Chǐeak Pàoung | |
|---|---|
| Motto: “一同,咱們強。︁” Together, we are strong. | |
| Anthem: "TBA" "When That Day Comes" | |
| Party anthem: "TBA" "Socialism Is Good" | |
 Sukong (green) on a globe | |
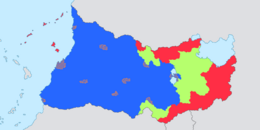 Land divisions in Sukong:
Federal territory
Unincorporated states
Ethnic states
City states | |
| Location | Northwestern Olivacia, east of the Sunadic Ocean |
| Capital and | Ca Luo |
| Official languages | Sukong |
| Ethnic groups (2023) | TBA |
| Religion (2023) | TBA |
| Demonym(s) | Sukong |
| Government | Federal Marxist-Leninist one-party parliamentary socialist republic |
| Legislature | People's Federal Council |
| Independence | |
• Colonisation | 1786 |
| 7 May 1938 - 14 August 1943 | |
• Market reform | 8 June 1975 |
| Area | |
• | 822,167 km2 (317,440 sq mi) (not ranked) |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | |
• 2023 census | 338,732,804 |
• Density | 412/km2 (1,067.1/sq mi) (not ranked) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | 37.2 medium (not ranked) |
| HDI (2023) | high (not ranked) |
| Currency | Sukong Yen (¥) (SKY) |
| Time zone | UTC+4, +5 |
| Date format | yyyy年mm月dd日 |
| Driving side | left |
| Internet TLD | .sk |
Sukong(IPA:/ˈsʊ.kɒŋ/), officialy the Federated Socialist States of Sukong (Amilagran: 綠國 (Lòu Kě) IPA:/lou˧˩kɤ˧˩˦/, 綠國聯赤邦 (Lòu Kě Lìen Chǐeak Pàoung) IPA:/lou˧˩kɤ˧˩˦lien˧˩t͡ɕʰiøk̚˧˩˦pɒuŋ˧˩/) is a country in northwestern Olivacia. Sukong covers a land area of 822,167km2 (317,440 sq mi), with a population of 288,580,617 inhabitants, ammounting to a population densitsy of 351 inhabitants per km2 (909.1/sq mi), it is one of the most densely populated nations in Anteria, and the largest confucianist majority country, with over [TBA]% of the population identifying as confucianist. The majority of the population (about 60%) live in the western part of the country, near the coast of the Sunadic ocean.
Sukong is a federal Marxist-Leninist one-party parliamentary socialist republic, with an elected legislature. It has TBA states, of which all have their own legislature, leader, and constitution. There are three unincorporated territory, called [TBA], which doesn't have it's own constitution or leader. Sukong's capital, TBA, is the largest city in the country and among the largest in Olivacia. Sukong shares land borders with Horokoshi in the south, and Zartona in the southeast, as well as a maritime border with Riamo in the northwest.
Etymology
According to the [TBA] Common Dictionary, the name "Sukong" is derived from the north-western city of Shiu Kung (熊公), whose name means "Bear Duke" in Sukong. The Riamese sailors had arrived to the city in about [TBA], when Shiu Kung was still an independent city state. Overtime, especially during the Riamese colonisation of Sukong, the name was butchered to its current form, Sukong.
Louke (Lòu Kě, 綠國, IPA:[lou˧˩kɤ˧˩˦], is the native name for Sukong, used in all of the language's dialects. It is mentioned in the Constitution of Sukong, as well as many historical sources. The name means "Green Country", refering to the nation's lush rainforests. Its use only became common shortly before the 1938 Socialist Revolution.
[TBA names in other languages native to Sukong]
History
Geography
Climate
The climate of Sukong comprises of a wide range of weather conditions across a large land area and varied topography, however most of the country is tropical. The Köppen climate classification system divides the country into five main climatic zones: equatorial, monsoon, tropical savanna, semi-arid, and subtropical. The variation in the country's climatic conditions produces many microclimates, ranging from equatorial rainforests in the south, tropical savannas in north-eastern Sukong, and laurel forests in the eastern mountains.
Biodiversity and conservation
Enviroment
Politics
Sukong is a one-party state governed by the Federal Communist Party (FCP) (Sukong: 聯赤黨, Lìen Chhǐek Täng, LCT), which self-declares as Marxist-Leninist. Along with Montilla and the USWR, this makes Sukong one of the few countries in Anteria governed by a communist party. Despite the government's declarations, many economists and politologists have disagreed with this, saying that the country, whilst governed by a communist party, has a mixed-market economy, therefore it shouldn't be defined as truly communist.
Sukong officially describes itself, most notably in the constitution, as a "Socialist state governed by a people's democratically elected dictatorship, based on an alliance of peasants, workers, and the unfortunate, united by their desire for true equality and the promise of the end to the oppressive leadership of the bourgeoisie.", as well as a "people's democracy", however, the government claims the right to censor what it considers "anti-revolutionary speech and rhethoric", although censorship has been decreasingly less common.
Federal Communist Party
Government
Administrative subdivisions
Judicial system and law enforcement
Sociopolitical issues and human rights
Foreign relations
Public views of government
The most well-known political issues in Sukong are the changes to the economical structure of the populace, a growing divide between the rich and the poor, and government corruption. Despite these problems, the majority of Sukongs hold a positive view towards the government. Independent international studies conducted in Sukong by the Adrian Nowý School of Advanced International Studies (ANSAIS) in Králowec show that on average, 92% of the respondents were satisfied with the Sukong government. The study attributed this to the government's efficiency, attentiveness and responsiveness, as well as the extensive welfare state, which the study claimed had a 93% satisfaction rate.
Military
Economy
Resources
Transport
Research
Tourism
Demographics
Population
Urbanisation
Largest urban areas
Migration
Religion
Spread of Buddhism
Native religious beliefs
Health
Education
Languages
Culture
Cinema
Music
Literature
Architecture
Art
Cuisine
Sports
See also
Notes
External links

