Saukania
Tokaura Kathunan Saukanian Alliance | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capitals | Dautan (religious) Khodan (summer capital) Kula (winter capital) |
| Type | Confederation of Tokaura states |
| Members | Acha Dathan Erya Ghulashan Khodan Kula Muridan Rhegan Sardash Sashan Tushan |
| Establishment | 1847 |
| Area | |
• | 1,116,863 km2 (431,223 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 27,214,000 |
• Density | 24.3/km2 (62.9/sq mi) |
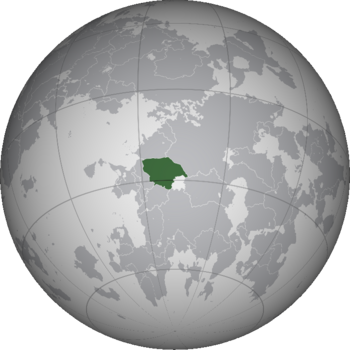
The Saukanian Alliance (Tokaura Kathunan), informally known by its toponym Saukania, or more rarely Tokaurasartha, is a confederation located in the Ghuran-Argan region of northwest Thrismari. The Alliance is comprised of eleven confederal entities known as ariyi, approximate to a city-state, united under the Dautan Oath.
Saukania has a total land area of 1,116,863 square kilometres (431,223 square miles) and a population of 47.4 million people. The climate of Saukania is continental arid and semi-arid, with limited annual precipitation. The majority of the population is concentrated in oases and along river valleys which are the primary source of irrigation and human habitation. The Alliance is landlocked, though it is bounded on its south-southeastern side by the inland Argan Sea. Saukania is bordered by Niater to its northeast, Sarocca to its northwest, Shirua to its south, and Talgiristan to its east-southeast.
The geography of Saukania includes large stretches of shrub-sandy and gravel desert in the centre and north of the territory, with grassy and shrub-steppe further south and along the foothills of the Ghuran Mountains, as well as around the Kulean Highlands. Saukania's rivers are among its most prominent and historically vital geographic landforms. Limited precipitation has forced dependence upon both Saukania's natural perennial rivers and irrigation canals sourced from its water. The three largest river valleys are the Sauka, the Apria, and the Kria.
Human habitation in Saukania began in the Palaeolithic, as early as 61,000 YBP. Farming communities were established in fertile valleys during the Neolithic. Complex archaeological and material cultures including the Sauka Valley Civilisation flourished in the region in the late bronze and early iron ages. Semi-nomadic pastoralists ancestral to the modern Saukanians became dominant in the country from the 1st millennium BC into the 1st AD, migrating out from an ethnocultural homeland in the upper Sauka valley, and founding a network of monarchical and republican states called ariyi (sing. ariye). These ancient polities were the early form of the modern Saukanian states.
The Alliance was founded in 1847 by the eleven largest and sovereign ariyi at Dautan, an important Saukanian religious site. Though alliances between ariyi were not a new concept, the Dautan Oath became the basis of the first alliance with a conscious and deliberative Saukanian character. Its formation has been attributed to the rise of powerful 19th century empires and their activities within Thrismari. The Dautan Oath preserves the sovereign and independent character of its constituent states in domestic affairs, while pledging to act as a unified body on the international theatre and in matters such as trade, defence, and diplomacy. The government of the Saukanian Alliance has been characterized as a hybrid of confederal and federal systems, with each member-state sending representatives to a council, which must act unanimously.
Modern Saukania possesses a still agriculture-heavy economy. Approximately half of the country is urban, though this number is steadily increasing. Exports include food, alcohol, and finished goods such as textiles. Saukanian carpets are a prominent cultural export. Tourism to Saukania forms a sizeable aspect of its economy, its largest cities possessing a staggering wealth of hospitality and service-oriented businesses. Archaeological sites are a major draw of tourism, being well-preserved due to a dry climate, as are natural geography sites including the Ghuran Mountains.
Saukanian-speaking peoples form the majority of the population, sharing an ethnocultural and ethnoreligious identity. The ariye constitutes an ethnic or sub-ethnic identity, with closely related ariyi grouped together in ethnocultural regions. Kulean and Khodanian are the two most widely spoken Saukanian dialects. Tradition is valued in Saukanian culture, and is the basis of a code of conduct and national self-expression known as Tokauratarya. Core concepts of Tokauratarya include hospitality for guests, retaliation against injury, sirauna (a masculine ideal analogous to the Latin virtus), and safeguarding the honour (kasauwe) of women.
Etymology
Modern Saukania ultimately derives its name from the Sauka, or Saukan, the largest river in the Alliance. The fertile plain of the Sauka valley has had disproportionate importance, wealth, population, and power relative to the rest of what constitutes modern Saukania. From the Bronze Age into the early Iron Age, it was the primary centre of the mysterious Sauka Valley Civilization, a culture unrelated to but directly preceding the settlement of the Tokauran people in the region. In the field of Saukanian history, the lands of the Sauka valley are referred to as Saukiana or "Saukania proper", to distinguish the river-bound region and historic civilization from the modern geopolitical toponym and exonym.
While the etymology of Saukania is Saukanian in origin, it has not served as the collective endonym for speakers of the Saukanian languages. The Saukanian-speakers call themselves and their language Tokaura. This common identity has been preserved for millennia, albeit with little political relevance. A number of Tokaura civilizations were established across what is present-day Saukania, of which the inhabitants of Saukiana were merely one of a number. The collective homeland of the Tokaura civilizations is known in Saukania as Tokaurasartha, though this is rarely employed as the country's exonym.
It is the historically disproportionate cultural influence and power of Saukiana that gave rise to the Saukanian exonym. It was popularised outside of Saukania by explorers, merchants, and diplomats that visited its city-states in the late 17th and early 18th century. Older exonyms for the country include Khodania, named for the oasis state of Khodan.
History
Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD)
Examination of prehistoric sites in Saukania has yielded an estimation of human habitation as far back as 61,000 years ago. With northern Thrismari a potential candidate for the origin of the human species, prehistoric Saukania may have been one of the first areas early man spread to in a southward peopling of the rest of the continent. Artefacts typical of the late Middle Palaeolithic, Upper Palaeolithic, and the Mesolithic have been discovered in Saukania. A number of sites yielded items from several eras, though the majority were confined to periods of (relatively) brief habitation in certain eras, before being abandoned. Changing climate and the somewhat cyclical expansion and retraction of the Western Thrismari Desert is likely to explain these differently situated habitation sites, and several sites were discovered in areas of modern Saukania which are sparsely inhabited if at all.
Permanent habitation and agriculture in prehistoric Saukania is not detectable until the beginning of the Neolithic around 11,000 years ago. As with prior eras, Saukania's climate and ecoregions were likely quite different than they are today, as a number of ancient Neolithic sites are located in what are presently fairly inhospitable regions of Saukania. Other presently inhospitable regions have yielded little-to-no evidence of prehistoric habitation. The agricultural development of Neolithic Saukania have been associated with a population termed Early Northern Thrismari Farmers or ENTF, a somewhat diverse yet related genetic grouping of people who gave rise to numerous successive archaeological cultures across the Neolithic period. Traces of hunter-gatherer populations have also been detected, potentially conserving older Mesolithic subsistence strategies before gradually being forced out or assimilated into the ENTF cultures. ENTF cultures over the Neolithic period include the Lower Laxad River Culture, the Sharp Angled Pottery Culture, the Keledan Culture, and the Mardan-Turana Cultural Complex.
Middle ages (6th - 16th centuries)
Early modern and modern Saukania (16th century - 1950)
The early modern period in Saukania began with the decline of the Golden Age of Wisdom (c. AD 1050-1475) marked by strong elite patronage of arts, philosophy, religion, and other aspects of culture aided by the wealth and prosperity brought from cross-continental trade along the Thrismari trade routes. The rise of new and powerful nomadic confederations is considered a primary reason for this decline, bringing an end to the relatively peaceful preceding period and motivating a shift in priorities among the elite of the oasis city-states. Expensive formal education and preparation of elite youths for prominent roles in academic and bureaucratic institutions were largely reduced in favour of remilitarising the social elite to meet the new external threats. One nomadic confederation, the Markashmir, began exacting tribute from various Saukanian cities in Kriana before eventually conquering it altogether between 1510 and 1520. Markashmir forces assailed many of the other vital river valleys, including the Saukanian Plain itself, primarily to raid demand tribute but in various occasions establishing direct rule over defeated oasis kingdoms.
Disruption of trade by these conflicts resulted in greater internecine warfare among the remaining city-states for territory and power. By 1580 the Markashmir confederation had reached the height of its power, controlling the valleys of Apriana, Khoson, Kriana, Tagesh, and Turuk, and exacting tribute from cities in the Saukanian Plain, Sadaha, and Markiana. A succession of dynastic civil wars between Markashmir princes saw the effective reduction of real control to the Kriana valley by 1620, with the remaining oasis cities newly independent and resurgent. In 1637, the Markashmir were eventually defeated by a rebellion of Krianian city-states, led by Khodan. Khodan subsequently established itself as the head of a Krianian federation and a local aristocratic family was elected to serve as its new royal line.
Contemporary Saukania (1950 - present)
Geography and climate
Saukania has an area of 1,116,863 square kilometres (431,223 sq mi), and is one of the largest countries in Thrismari by total land area. It is a dry and landlocked country, bordering Sarocca to the north, Shirua to the west and southwest, and Bezuria to the south. Though the country has no outlet to the sea, Saukania comprises approximately half of the coastline of the inland Argan Sea.
The country lies between longitudes 43° and 59°W and latitudes 22° and 32°S.
Physical geography and georegions
Saukania has a diverse physical environment. The relatively flat, desert topography that comprises the majority of Saukanian land area gives way in the south to grassland and shrub-steppe, and then to the forest-steppe foothills of the Ghuran Mountains and the montane grasslands and shrublands of the mountains proper.
The vast Western Thrismari Desert dominates the northern and central portion of Saukania. There are a few large ergs in the Saukanian region of the desert trending north, while much of the desert is comprised of desert pavement and bare rock.
In the south and south-west of the country is the Saukanian steppe, forming a wide U-shaped arc. Receiving more rainfall than the desert to the north, the steppe is comprised primarily of grass and shrub, with some forest steppe interspersed. This forest-steppe is more abundant along riparian zones formed by the rivers that descend from the Ghuran Mountains, and in the foothills of the mountains themselves. The elevation rises from the broadly flat surrounding landscape at the foothills and up to around 3500m at the mountain range itself. This area is known as the Saukanian uplands or highlands. Montane grass and shrublands replace the temperate steppe regions as the elevation increases.
Climate
Saukania is possessed primarily of an arid continental climate. Average rainfall is low, and the majority of the country is comprised of desert and steppe climate. The highlands to the southwest receive a larger amount of rainfall than the lowlands, owing to their high elevation, which comprised with snowmelt in the summer, provides the waterflow of Saukania's rivers. The steppe climate borders this highland zone, and has more grass and vegetation than areas further northeast.
Environmental issues
A fragile ecological area, Saukania faces a number of major environmental problems, such as land degradation in farmed areas and increased desertification. These issues are felt most keenly by the country's nomadic population, who face losing pasture land to encroaching dunes or harsher desert conditions which they need to graze their herds. Deforestation of Saukania's already limited supply of wooded areas is also a major concern.
Demographics
The population of Saukania was estimated at 27.2 million as of 2020 by the Saukanian Statistics Authority. While the Confederation's members hold synchronised decennial censuses for the sake of accuracy, reliable numbers are often hard to obtain in particular districts and among the nomadic and highland populations. A combination of refusals to divulge information, isolated and hard to access terrain, as well as the mobility of the nomadic groups, makes assessment of the more marginal Saukanian communities harder. Many highland communities are known to give false information in the form of inflated male counts and underreported females. In a 1980 census conducted by Khodan over the highland areas in its jurisdiction, one valley's reported population amounted to a gender imbalance of some 92% of inhabitants being male.
Nevertheless, estimates suggest approximately 5.7% of the population, around 1.55 million people, live a nomadic or semi-nomadic lifestyle. Of the remainder, approximately 41.2% were urban, and the remaining 53.1% live in rural areas. Saukania's urbanization rate has grown significantly in the last half century, as economic modernisation increases opportunity for rural inhabitants. The share of nomads has also declined as individuals or family units adopt semi-sedentary and fully sedentary lifestyles. Population growth in all segments of society is high, with an overall average of 1.67% annually. Fertility is the primary contributor to this growth, though it has slowed in recent decades. In 1960 the estimated TFR was 7.6 children per woman, which fell to 4.3 in 2010. Many Saukanians seek work in foreign countries, leading to a steady rate of emigration, though not enough to offset growth. Healthcare improvements and the lowering of the infant mortality rate have also contributed to longer lifespans and greater overall population.
Urbanization
Of the 41.2% of the population living in cities, just under half, or about 5 million, live in the four largest cities: Kula, Khodan, Acha, and Sardasar. Kula city alone (as distinguished from the wider city-state) boasts a population of 2.1 million. As noted, urbanization rate is increasing with the influx of rural populations into the cities for work and the drop in infant mortality. This urbanization is not without tension however. The ethnic diversity of the cities has always been higher than surrounding countryside, but has intensified in recent decades with the economic potential. Tensions between different Saukanian populations are ever-present, and incidents of violence not unknown. Increased urban development in the highlands has also fuelled tension and even conflict, as enlarged population centres increasingly come to reflect the more cosmopolitan and lowland-style system of government and overall culture, antagonising the surrounding highland peoples, particularly those with separate ethnic identities.
Ethnicity
TBA
Language
TBA
Religion
Major cities
Government and politics
The Saukanian Alliance is a confederation of eleven political units classed as city-states. It is governed by a Supreme Council made up of the leaders of Acha, Dathan, Erya, Ghulashan, Khodan, Kula, Muridan, Rhegan, Sardash, Sashan, and Tushan. The central budget of the Alliance is drawn from a percentage of the revenues of its constituent states. The states of Khodan and Kula together contribute 45% of the total budget of the Alliance.
Khodan and Kula serve as joint-capitals of the Alliance, as a recognition of their peer prestige and influence. Khodan is the designated summer capital, and Kula the designated winter capital. In addition, the site of Dautan is the ceremonial capital of the Alliance. Considered a sacred sanctuary in Saukanian tradition, it was the site of the signing of the Pact of Dautan, the Alliance's founding document. In modern times the site has been expanded and made a centre of the Alliance's administration. The dominance of Khodan and Kula within the Alliance is semi-formalised. Per tradition, the presidency of the Supreme Council is rotated between their leaders every five years, the junior partner holding the positions of vice-president and prime minister. The state of Acha, third-most powerful in the Alliance, traditionally holds a permanent vice-presidency and deputy prime ministership. All member-states are represented equally within the Supreme Council. In practice however, many of the smaller states are economically dependent upon the contributions of Acha, Khodan, and Kula to the central budget, as well as having traditional patron-client obligations with one of these three states.
The Alliance Council is a proportional-representative advisory body to the Supreme Council. Each city-state sends representatives proportional to its population of able-bodied men, i.e., their military potential.
The Alliance itself is a highly decentralised body. The city-states greatly value their autonomy and self-governance in matters of internal affairs. Foreign affairs such as trade, diplomacy, and war are powers ceded to the Alliance as a collective body as outlined in the Pact of Dautan. There is however no Alliance legislature or judiciary, as the Alliance has no power to impose any kind of common law among the member-states. The Pact of Dautan does, however, provide for an extradition treaty between the constituent polities, obligating the arrest and return of criminal suspects who have crossed a border.
Administrative divisions
Foreign relations
Military
The Confederation maintains a single armed force, staffed and supplied from all eleven constituent city-states. This force is known in English as the Confederate Army or the Saukanian Army. The Confederate Army has two primary service branches: the Confederate Army Ground Force, and the Confederate Army Air Force. Control of Saukania's waterways and influence over the Argan Sea is maintained by the Confederate Army Ground Force - Marine Corps.
Human rights
Culture
Saukanians share a cultural horizon, tracing common descent from the original proto-Saukanian population. Accordingly, they have much in common, including similar styles of dress, shared festivals and holidays, kindred musical and artistic traditions, and mutually intelligible social structures based on a hierarchical and reciprocal network of kinship-based civic units. Nevertheless, the Saukanian people are made up of several distinct and conscious ethnic groups of different sizes, each of which has developed its own culture in accordance with its social and geographical environment, and unique history in contact with neighbouring Saukanian and non-Saukanian peoples. A subcultural continuum is observable in most places in Saukania, where any one locality (village, valley, town, or city) is likely to share much in common with those in close proximity to itself, with this similarity decreasing over distance.
The overwhelming majority of sources on pre-modern Saukanian culture, in all periods, come from authorities outside of Saukania. Saukanologists compare these accounts with folk and oral traditions and more recent or second-hand accounts for an overall picture.
Social structure
Family and extended kinship networks are given utmost importance in Saukanian society. Noble families are at the top of the city-state social structure, mobilising loyalty with a semi-feudal patronage system through which they dispense rewards or grant favours to middle-class client families. These clients will in turn be the patron of families of lower social standing, and so the whole of the city-state is unified through these reciprocal and vertical relationships. Families are represented publicly by men and are governed patriarchally. Arranged marriages are common, especially among the elite and clients, for whom matrimony is an essential aspect of the patronage network. Despite this patronage network, familial self-sufficiency is greatly valued, and a family may lose face if it is unable to provide for itself. This dishonour falls primarily upon men, who are expected to provide the family with income. Though women have always, to some extent, participated in commercial labour, it is not seen as their responsibility to work for the family living.
In the aristocratic republican organisation of the city-states, wealth classes based typically on land size and income in the largely agrarian country play a pivotal role in politics and society. The city-states organise their democratic assemblies according to this ranking system, enfranchising those with a greater stake in the physical land over those with less or none. The traditional nobility is for the most part coterminous with the greatest wealth bracket, though not entirely. Some families of noble pedigree may fall in the census ranking, and lose out on the privilege of primary franchise, though not their right to sit in the various councils or assemblies reserved for the nobility. In the reverse, non-noble families may rise to the highest wealth bracket with all of its attendant privileges but remain excluded from all that is reserved for the nobility.
Honour
Honour is a vital aspect of Saukanian society. Honour belongs to the family, and has a symbiotic relationship with its members. That is to say, all members of a family benefit from the esteem in which their family is held, while the actions of any family member have the potential to benefit or harm this collective estimation. As an inevitable result of their greater social profile, overrepresented in the politics of their city-states, the aristocratic elite have the greatest concern for honour. Saukanian honour is in large part the quality of being left alone. In addition to estimation, it is also reputation in the sense of willingness to defend what is theirs, and respond with the culturally-determined proportionate severity to intruders, interlopers, and attackers. This is strongly connected to the ideology of personal justice in Saukania, and the law of blood for blood retaliation. A family that does not take appropriate compensation for the theft of property, the sexual assault or abduction of a woman, or a murder, collectively loses honour, since in their inaction they demonstrate an unwillingness or an inability to back up any previous reputation with action. These transgressive acts can result in blood feuds if the family of the perpetrator is uncooperative in finding a resolution, or if the victim's family is dissatisfied with any compensation proposal.
This aspect of honour is essentially male, and part of the wider male code of conduct. Responsibility for protecting the honour of the family from outside threats and for avenging it against successful attacks falls to men. As women are a direct means through which family honour can be harmed, an ideology of female protection through restriction of their movement prevails across Saukania. This is not a legal enforcement but a cultural one.
Clothing
Architecture and art
Music
Cuisine
Sport