Freice
Country of Freice[a] Tehua Faiose'va (Freician) 並外民国 (Hoterallian) Namiminkoku | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Ati Faio'se, ma seia ka likoa (Freician) My Freice, gallant and free | |
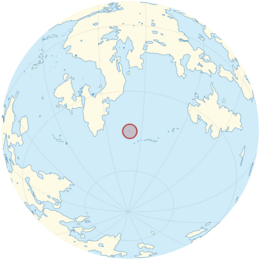 Location of Freice in the Kaldaz Ocean | |
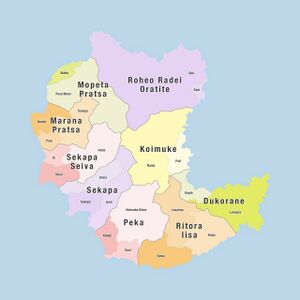
 Map of Freice | |
| Status | Country of Riamo |
| Capital and largest village | Sekapa |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion (2021) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Freician |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary democracy under a federal monarchial republic |
• Monarch | Diana II |
| Ailu Apoka Semeia | |
| Kana Tenqel | |
| Legislature | General Kiuva |
| Country of Riamo | |
• Self-government | 1 February 1969 |
• Country status | 1 March 1980 |
• Recognition of independence in foreign relations | 28 November 1992 |
| Area | |
• Total | 121.3 km2 (46.8 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• 2021 census | 14,158 (not ranked) |
• Density | 117/km2 (303.0/sq mi) (not ranked) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 32.7 million ACU |
• Per capita | 2,312 ACU |
| Currency | Hoterallian gena (HTG) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:00 |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +451 |
| Internet TLD | .fe |
a Traders are permitted to denominate their capital in Anáhuaca pesos if they import/export at least 40% of their stock to/from Anáhuac. | |
Freice (Freician: Faio’se, faʊseɪ; Hoterallian 並外民, Namimin), also known as the Country of Freice (Freician: Tehua Faiose’va, tɛhʌɑ faʊseɪvɑː; Hoterallian: 並外民国, Namiminkoku) is an island country in the Kaldaz Ocean. Freice’s capital and most populated village is Sekapa, located on the western side of the island. The island comprises a land area of 121 km2 (47 sq mi), and the highest point is Mopeta Nogeia, at 342 m (1,122 ft) in elevation. At the 2021 census, the population was 14,158.
Freice was first inhabited by Kaldaic people, who settled on the island around the first millennium. The population of the island, called the Faio, from which the island’s native name comes, had established a stable and comparatively complex system of government by the time of contact with colonial powers in the eighteenth century.[1] The Riamese were the first to visit the island in 1742. The island was formally annexed in 1759. Between 1911 and 1931, the island was occupied by Hoterallia following the Great War, before being returned to Riamo. The island’s colonial past remains evident in the large populations of Riamese and Hoterallians and in the prevalence of their respective languages among the population.[2]
In 1969, Freice was granted self-government as an autonomous state of Riamo. In 1980, it was granted further powers and redesignated as a country within the Riamese Federation. Freicians are Riamese citizens and Diana II is Freice’s head of state as Queen of the Riamese.[3] Today, over half of the approximately 32,000 Freicians live outside of Freice, mostly in Riamo and Anáhuac.[4]
Etymology
In the Freician language, the island is called Faio'se (literally "place of the Faio"). The Faio people were the nomadic people who first settled on the island at the beginning of the first milennium, their name coming from Fase uahi (old Freician for "first settler"). Today, Freicians are called "Faiose'io", meaning "a person from the place of the Faio", although some people continue to use the name Faio in relation to modern Freicians.
The exonym "Freice" is a corruption of the Freician name. The name was first recorded in the anonymously-written Travels to the Islands of the Kaldaz, first published in 1743.[5] The Riamese initially called the island "Windy Island" in reference to the weather at the time of the first contact. The word Freice was adopted as the official Common Language name in 1761.[6]
History
Early history
Humans are believed to have first arrived on the island around the time of the first millenium, landing via the Pohnpenesian islands.[7] Life on the island prior to colonisation operated under a system comparable to feudalism, in which an agrarian population worked under the stewardship of a noble class (the talitai'ama). The island was governed by a succession of rulers (called the Nekuo'lu) from the Maoateuamava Dynasty, with the semi-mythical Kitatahaia establishing dominion over the island around 1229.
The first scholarly writing on the early settlers is found in the Luge Tunaranegato Binima (widely considered as Freice's first constitution) in the 13th century. The first mention of the Faio people is mentioned here, although it is assumed that the word had been in common usage long before this. The Faio people are the primary ancestors of the majority of native Freicians today. The Faio economy was dominated byfarming and fishing, with very little contact outside of the island.[8]
Riamese Colonization
The Riamese first made contact with the island in 1742 when the RRS Wilmington landed at what is now Sekapa. A small military garrison was established with the agreement of the local rulers, providing the Riamese with a strategic position in the Kaldaz.[9] The Riamese maintained only limited contact with the native inhabitants, preferring to avoid direct interactions. The annexation of the island was not considered at first due to the small size and cordial relations with its government.[10]
Beginning in the late 1740s, discontent emerged amongst the nobles over the increasing influence of the Riamese over the island's politics. Attempts to placate this with bribes enjoyed some success for a decade, until a revolt broke out in 1759. The Riamese garrison quelled the rebellion and, believing it to have been initiated by the Nekuo'lu, promptly overthrew the indigenous government and instituted a military occupation of the island. Shortly thereafter, Riamo formally annexed the island.[11]
Slavery was never instituted on the island, although forced labour was commonplace, with thousands of Freicians forcibly taken and employed in construction projects, conscripted into the Riamese army, or sent to other Riamese colonies to work for little-to-no pay.[12] A number of forts were constructed using such labour, most of which have since been demolished. An official investigation into the effects of this practice was undertaken by the Riamese federal government in 2006, which led to a formal apology given to the people of Freice in 2007.[13]
The Riamese actively suppressed indigenous culture. A number of prominent towns and villages were renamed, with Sekapa being renamed to Wilmington after the first landing.[13] Ethnic Freicians were prohibited from certain occupations, many of which were reserved for high-ranking Riamese naval officers and their associates.
Beginning in the early 1900s, a number of political movements emerged, seeking economic and political reform. Whilst few openly argued for independence, being a potentially capital crime, pro-independence movements began to gain traction as underground resistance against Riamese colonialism quickly grew.
Hoterallian occupation
During the Great War, Riamo and Hoterallia entered into the war on opposing sides. The Hoterallian navy was tasked with eliminating Riamese naval presence in the Southern Sundaic and Northern Kaldaz, precipitating an invasion of Freice by June 1910. A landing at Wilmington-West Freice by Hoterallian marines quickly followed by the storming of the Riamese garrison on the island.[14][15]
Following the conclusion of the Great War, the Treaty of Tsuwan divided Riamese imperial territories amongst the victors, with Freice transferred to Hoterallia as a colonial mandate. Under the treaty, Freice was partially demilitarised, and Hoterallia agreed not to fully assimilate the island into its empire.[16]
The Hoterallian occupation is divided into two periods: the transitional phase and the permanent phase. The transitional phase saw the consolidation of Hoterallian rule. It was divided into five districts, each of which reported to a rear admiral at the navy headquarters in the newly-renamed Sekapa. The island's legal system was administered under Hoterallian law.[17] The permanent phase saw a transition from naval to civilian administration, with a Freician Elected Authority established to govern the islands under the authority of the Navy Ministry.[18] A governor was established, elected by Freicians and appointed by the Hoterallians, reporting to the Director of the Supreme Authority.
The Hoterallians sought cooperation from Freician leaders, promoting cultural and linguistic nationalism to win their favour and to undermine allegiance to the Riamese. Freician was taught in schools and native practices, largely suppressed by the Riamese, were once more introduced.[19] This was coupled with the exploitation of Freice's natural resources and the suppression of Freician independence movements - often by force.
By the late 1920s, with the mandate coming to an end, the Hoterallians sought to encourage opposition to a handover to Riamo with a propaganda campaign. This campaign presented the Riamese as authoritarian colonisers who sought to destroy Freice's traditional way of life.[20] Nonetheless, on 18th July 1931, sovereignty was transferred to Riamo.
Resumed Riamese sovereignty
The island was returned to Riamo in 1931. A series of political and legal reforms transformed the governance of the island in response to the levels of self-government afforded to the island under Hoterallian occupation. In 1932, native Freicians entered into the island's civil service for the first time, with the Freice Language Order 1938 permitting the use of Freician in schools.[21]
In 1950, a new Assembly of Delegates was established to provide representation for native Freicians. This body had only an advisory role, but beginning in 1958, could pass non-binding resolutions which increasingly carried weight with the colonial authorities.[21]
Starting in 1965, the federal government began discussions on the political future of Freice. The lack of economic development and domestic political institutions rendered independence an impossibility, with discussions focussed on the level of autonomy the island should receive. In 1967, a draft paper was issued which proposed a locally-elected assembly and an island government with responsibility for certain domestic policy areas.[22]
Self-government
The Government of Freice Act 1969 came into force on 1 February 1969, granting Freice the right to self-government and changing its status from a colony to an autonomous state. Under the act, a constituent assembly would be established with a remit for establishing a new constitution. Sema T. Anamia, a prominent lawyer and advocate for self-determination, was elected president of the assembly on that date and worked to establish a new constitution, which came into force on 1 January 1972.[23] He continued to serve as president of the Assembly of Delegates (head of government) until his resignation in 1983. Freice's sole airport is named in his honour.
From 1971, Freice began to cement close political and economic relations with Hoterallia. The Taiyō Initiatives, named after Hoterallian representative in Freice Taiyō Yamashita, constituted part of Hoterallia's attempts to expand its economic power, with investment in Freice to harness markets in which it could sell goods and services. A number of projects were established with Hoterallian assistance, including the construction of a new hospital and the laying of new roads.
The 1970s and 1980s were characterised by attempts to reverse colonial policies on Freician culture. In 1974, the Freician language was mandated as the primary language for teaching in school.[24] In 1976, the first official representation in Guri was set up to serve as the island's first diplomatic mission.[25] Brief flirtations with independence never led to any serious attempt to separate, primarily due to continued economic underdevelopment and a reliance on aid from Riamo and Hoterallia.
In 1980, Freice became a Country of the Riamese Federation, granting it further self-governance to the point of near-independence. In 1987, Freice signed its first international agreement when the government of Katesu Fapera signed the first of a number of Special Cooperation Agreements with Hoterallia.[26] Emerging from these agreements was the establishment of a number of Hoterallian businesses, including textiles, electronics, and telecommunications.
In November 1992, the Riamese government formally recognised Freice's independence in foreign affairs. Under the Government of Freice (Foreign Relations) Act, Freice was permitted to enter into international treaties and be regarded as an independent state under international law when so requested by the island's government. As of 2023, the Freician government has entered into diplomatic relations with 12 states (including Riamo).
Recent history
The 21st century has seen increased focus on combating HIV/AIDS in Freice. Government policies, which included monitoring and education on good sexual health, successfully reduced the number of cases from 11.1% of the population to 2.9 between 1999 and 2005.[27] This focus wained in the 2010s as economic stagnation prompted a shift in focus, although beginning with the election of Kana Tenqel in 2023, the Freician government has renewed its attention on the health crisis.[28]
Aniara Neileka was elected as the first female leader of Freice in June 2021. Under her brief leadership, she led Freice to become an independent member of the Saltstil Pact, the island previously being represented by Riamo. In July 2022, she was deposed by a coup d'état led by the left-wing Common Wealth Party. The new government, which established a de facto single party state, fell after only a few months due to internal divisions, prompting an interim government to take over leadership.[29][30]
2022 saw significant constitutional changes on a scale not seen since the 1970s. In January, a new parliamentary body was elected. In June of that year, Freice adopted a new constitution, creating a new broadly presidential political system. Aniara returned to government to serve a full term, leaving office in 2022.[31]
The Freician Issue
In March 2023, Freice became embroiled in an international crisis when the Riamese federal government declared its opposition to medical aid from from Anáhuac and Hoterallia, offered to help combat Freice's HIV/AIDS crisis. On 24 March 2023, the Riamese foreign ministry announced in Twatter a meeting with the Anáhuaca ambassador over the issue.[32] The Freician government reacted negatively, condemning the move for politicising a health crisis and undermining Freice's right to self-government.[33]
The crisis prompted a rise in internet searches about Freice, with the island's international profile raised significantly. The crisis has also led to renewed calls for Freician independence. Polling conducted by Portington University on 1 April 2023 found that 49% of respondents supported independence, tied with those opposing it.[34] Faio'se Ekaitaki'e ka Orpasa'e, a pro-independence Freician political party, has openly stated that the federal government's actions "proves that Freice can only be free when it unlocks itself from the handcuffs of continued union."[35]
Geography
Freice is an island nation in the Kaldaz Ocean, 936 km (582 mi) from the nearest point on mainland Olivacia. It is located in the south-centre of the Olivacian plate, and so is geologically considered part of the continent. It is located at latitude 92°E and longtitude 52°S. The island is approximately 47 km (29 miles) in length and 26 km (16 miles) wide, covering an area of 121.3 km2 (46.8 sq mi) in the general shape of the letter 'L'.[36]
The island's geography is divided between hilly terrain in the north-east of the island, and flat plateaus and west and south. There, the terrain is generally flat and fertile, and which is where the vast majority of the population resides and economic activity takes place. The north-west of the island is dominated by the Eastern Highlands, which includes the Oratite Hills.[37] The area surrounding the range constitutes a National Nature Reserve and is protected by law.[38]
There are a number of small rocks off the coast, which are nature reserves and host to a number of birds and sea species.[36] All are located within five miles off the shore. This includes Far Rock (Freician: Tora Matakita), located off the coast of Roheo Radei Oratite, which was historically considered a holy site.[39]
Freice is home to a large variety of flora and fauna, with around 19 mammal species, 10 amphibian species, 8 reptile species, and around 150 species of fish native to the island and its surrounding waters.[40] Historically, Freice was host to a number of endemic bird species and subspecies, but these have since become extinct following decades of hunting and land clearance from the 1820s to the 1960s.[41]
Climate
Freice has an oceanic climate (Koppen: Cfb), characterised by relatively frequent rainfall and a narrow temperature range. The highest recorded temperature in Freice (36.3 °C) was in Sekapa on 3 January 2010. Average temperatures range between 15 and 20 °C (59 and 68 °F) in summer, and between 2 and 10 °C (41 and 50 °F) in July, with the climate broadly characterised as cool, wet, and windy.[42] Snow is rare, recorded only in the highland hills in the island’s northeast, usually once every few decades.
| Climate data for Freice | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 36.3 (97.3) |
34.6 (94.3) |
33.6 (92.5) |
25.5 (77.9) |
20.2 (68.4) |
15.1 (59.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19 (66) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.1 (84.4) |
31.3 (88.3) |
35.1 (95.2) |
36.3 (97.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 19.9 (67.8) |
19.4 (66.9) |
17.9 (64.2) |
15.1 (59.2) |
12.5 (54.5) |
9.8 (49.6) |
9.5 (49.1) |
10.8 (51.4) |
12.7 (54.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
16.3 (61.3) |
18.2 (64.8) |
14.8 (58.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.1 (50.2) |
8.8 (47.8) |
6.6 (43.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
2.7 (36.9) |
2.4 (36.3) |
2.8 (37.0) |
4.1 (39.4) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.2 (45.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
3.2 (37.8) |
1.6 (34.9) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
0.0 (32.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 41.7 (1.64) |
35.8 (1.41) |
35.0 (1.38) |
40.6 (1.60) |
37.2 (1.46) |
44.0 (1.73) |
42.5 (1.67) |
61.0 (2.40) |
52.6 (2.07) |
50.8 (2.00) |
48.7 (1.92) |
51.0 (2.01) |
540.9 (21.30) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 8.5 | 8.1 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 11.0 | 11.4 | 13.1 | 14.3 | 14.7 | 14.0 | 12.5 | 10.7 | 138.7 |
| Average afternoon realative humidity (%) | 51 | 52 | 52 | 56 | 58 | 64 | 61 | 56 | 53 | 51 | 53 | 49 | 55 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 257.3 | 226.0 | 210.8 | 177.0 | 148.8 | 132.0 | 151.9 | 179.8 | 195.0 | 232.5 | 234.0 | 248.0 | 2,393.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 59 | 62 | 57 | 59 | 53 | 49 | 53 | 58 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 53 | 56 |
| Source: Riamse Meteorological Office[42] | |||||||||||||
Politics and foreign relations
Freice is a self-governing nation under the sovereignty of the Riamese Federation. The island has full internal self-governance, with Riamo formally responsible for its defence and foreign relations.[3] It operates as a parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy[b]. The Riamese Monarch is head of state, represented locally by the Representative of the Sovereign, and executive authority vested in the Government of Freice.
The most recent constitution was adopted in 2022 (The Constitution Act 2022). Under the constitution, the head of government is the Keomoru’lu (“Overseer”), who is appointed as the nominee of the party gathering the most votes.[43] A Cabinet of Ministers is nominated by the Keomoru’lu and appointed by the Representative of the Sovereign. The legislature - the General Kiuva - consists of 21 members elected by the electors of each district constituency. The Keomoru’lu, when they are not an elected member, is permitted to sit as an ex officio member with the same rights and privileges as other members.[44]
The current Representative of the Sovereign is Ailu Apoka Semeia (since 2 March 2023).[45] The current Keomoru’lu is Kana Tenqel (since 20 January 2023), who is the leader of Mulo Uahi ma pa Kiuoa.[46]
Relationship with Riamo
Freice’s relationship with Riamo is governed by the Government of Freice Act 1979 (GFA).[3] Freice is designated under the Act as a “Country for which the Government in Right of the Federation is responsible.”[47] It is autonomous and self-governing with its own independent legal, administrative and fiscal systems. The Riamese government has ultimate responsibility for the ‘good government’ of Freice; international representation; ensuring the island meets its international obligations; and defence.
Previously, foreign relations were fully deferred to the Riamese government. However, since the 1980s, Freice has developed its own foreign policy independent of Riamo. The island maintains representations in Guri, Orajioe, and San Jorge Xayacatlán, and has established diplomatic relations with twelve sovereign states and a number of non-sovereign territories. In 2021, it became an independent member of the Saltstil Pact, having previously been represented by Riamo.[48]
As per its right to self-government, Freice’s participation in the federal political system is limited. Freice sends three non-voting delegates to the Riamese Senate, and is able to opt-in to a number of federal services and initiatives, whilst the majority Federation Law does not apply in Freice without the consent of the Freician government. This system, known as the “Give and Take System”, was devised by the Riamese government and sees Freice cease to participate in federal politics in areas where it has autonomy.[49]
Freice does not maintain an independent military force, with RRAF Yaqia in the southeast of the island providing principal defence. A Tactical Response Unit of the Royal Freice Police Service was established in 2023, replacing a previous paramilitary unit.[50]
Administrative divisions
Administrative divisions Freice formerly consisted of three regions comprising 25 villages. The Freician government abolished these in 2022, replacing them with 9 new smaller divisions called “districts” (Freician: riseki):[51]
- Dukorane
- Koimuke
- Marana Pratsa
- Mopeta Pratsa
- Peka
- Ritora Iisa
- Roheo Radei Oratite
- Sekapa (not to be confused with Sekapa, which is the main town in the district)
- Sekapa Seiva
Districts are further divided into towns, which are groupings of smaller villages and larger settlements. They are: Alui, Aolo, Areia, Ataia, Fana Mano, Hamia, Kalapi, Kapia, Koimuke Seiva, Lemana, Levaima, Matta, Maui, Nania, Pulo, Puti, Sani, Savaga, Sekapa, Soni, Tuhea, Ui and Yaqia.[52]
The districts have various administrative functions, such as waste collection and leisure and recreation.[53] Each district is governed by a District Administrative Council, which is elected by the eligible voters resident in the district. The Atika’lu is the head of the district government.
Population
Demographics
As of April 2021, Freice had a population of 14,158 inhabitants. The majority of residents (75.02%) are ethnic Freicians, a Kaldaic ethnic group descended from the nomadic Faio people. Minorities include Hoterallians at 12.32%, Riamese at 8.59%, Anahuense at 2.21% and Pohnpenesians at 1.12% (figures from the 2001 census).[54]
89% of the population is Freician, while 11% are non-Freician. Of the non-Freician population, the majority are citizens of Riamo, Hoterallia, and Anahuac.[54] From 2015, a number of Gavrillian and Pohnpenesian workers were brought in as labour due to insufficient manpower amongst the population. The vast majority of these workers had left the island by 2019.[55][56]
Languages
Freice has three official languages: Freician, Common, and Hoterallian.[43] Freician is a Kaldaic language closely related to Pohnpenesian. Due to colonisation by both Riamese and Hoterallian forces, it has borrowed a number of terms from the Common and Hoterallian languages, with the former significantly influencing Freicians’ grammar.[57]
The Freician language is spoken by the vast majority of islanders, and is recognised in Freice’s constitution as the island’s “national language”. Whilst the Common Language was, historically, a lingua franca amongst different ethnic groups, the promotion of the Freician language since self-government and immigration requirements have resulted in both Riamese and Hoterallian communities having proficiency.[58] The Common Language has been an official language since colonisation, but is largely limited to government and commerce. The Hoterallian language was recognised as an official language in 2023; however, with some exceptions, the language is largely spoken between Hoterallians.[59]
Estimates claim the number of people who speak Freician worldwide to be around 30,000.[57] Radio and Television Freice transmits Freician-language programming, with specialist providers offering some services in Freician in Riamo, Anahuac, and Hoterallia.
Religion
The Riamese Orthodox Church is the largest religion in Freice, with adherents comprising about 76% of the population.[54] The Constitution of Freice guarantees freedom of religion, including the practice and changing of religion, and prohibits the government from promoting one religion over others.[43] Other Christian groups include the Silvadian Catholic and Methodist communities, which represents much of the remaining Christian population. There are also small groups of Seventh-Day Adventists and Christadelphians.
The Gaoist religion is the largest minority religion in Freice, with practitioners constituting around 10% of the population.[54] Gaoists are predominantly resident in Sekapa, where most Hoterallians live. In recent years, a number of Gaoists and Orthodox Christians have united to form interfaith congregations, combining certain religious practices and worshipping together.[60]
The introduction of Christianity to the island largely ended traditional religion and the worship of other deities. However, there have been many attempts at reviving traditional religion to varying degrees of success.[61]
Health
Life expectancy of the people of Freice in 2019 was 68 years for men and 72 years for women.[62] Historically, infant mortality was high due to a lack of infrastructure and limited knowledge of good medical practice. However, since the 1980s infant mortality has been reduced from 37 to 20 per 1,000 live births.[63]
Kaineki Tumatuga General Hospital in Sekapa is the only hospital in Freice, and is the primary provider of medical services.[64] A number of villages and towns host medical centres staffed by both qualified practitioners and volunteers, offering consultations and limited medical provision.[63]
Since the 1980s, the most significant health problems in Freice are related to HIV/AIDS. Freice faces a generalized epidemic, with approximately 3 percent of adults aged 15 to 49 infected.[65] In the 21st century, this rate has declined and stabilised, reducing from an historic high of 11.1% in 1998. A renewed focus on combating the virus in the 2020s has prompted an international response, with medical aid coming from Riamo, Hoterallia, and Anahuac. HIV prevalence is higher in rural areas than in urban areas, arising from a greater prevalence of prostitution and limited knowledge of safe-sex practices.[66]
Education
Education in Freice is free and compulsory between the ages of 4 and 17. The Ministry of Public Health, Education, and Social Services oversees education on the island, with the primary agency being the Commission on Education Standards and Testing.[67]
Freicians enjoy a relatively high level of education when considering its income level and development, with a 97.9% literacy rate.[68]
Each district has at least one primary school, with boarding schools more common in isolated areas where transportation links are more limited.[68] Previously, a majority of schools were operated by the Riamese Orthodox Church, but most of these have since fallen under the operation of the national government.
Historically, Freicians were taught in the Common Language first, with the Freician language being taught from the age of 10. However, since the 1970s, the Freician language has been given precedence, with the Common Language now taught only from grade 3.[24]
There are two tertiary institutions on the island: University School of Medicine, Sekapa (Kekarem), and the Freice Institute of Science, Technology, and Engineering (FISTE).[69] The majority of students study abroad, predominantly in Riamo and Anahuac.
Culturally, scholarship is held in high esteem. The body of academic knowledge created by Freicians has been collected and preserved at the Institute of Education and Learning in Sekapa. This includes all doctoral and master’s dissertations written by any ethnic Freician in any country, as well as all scholarly works published by or about Freicians. Since 2012, these have been made publicly available at no cost.
Economy
The economy is strongly affected by the island’s geography. Freice is isolated from most foreign markets, lacks in modern infrastructure, has very few natural resources, and has little capacity for manufacturing. Consequently, most income comes from tourism, which makes up approximately 71.2% of the country’s GDP. Foreign aid, largely from Riamo but also from Hoterallia, also makes up a significant part of the island’s budget.[52]
Freice forms part of the Federal Customs Area (FCA), with unfettered trade to and from Riamo and a common tariff on imports. Suggestions of a new agreement, particularly one that gives Freice control over import tariffs, have been raised on several occasions.[70] As part of this, Freice is a party to a number of free trade agreements negotiated by the Riamese federal government.
Despite this, a significant part of Freice’s export market is in Anahuac (26.6%) and Hoterallia (18.3%).[71] Because of this, Freice enjoys a strong economic relationship with the two states. Previously, the Anahuaca peso was the official currency, but its use was problematic due to its limited purchasing power, the Hoterallian peso replaced it in 2023.[72]
The island is a member of the Oriental Trade Alliance (OTA) within the Saltstil Pact, which provides for a reduction of quotas and tariffs amongst member states and simplifies processes for the movement of goods, services, and people across the Oriental Trade Area.[73][74]
The Comprehensive Action Plan for a 21st Century Freice (CAP) is a government initiative created to develop Freice’s economy and reduce the island’s dependence on foreign aid and tourism. The plan sets national priorities for social and economic development, including the modernisation and expansion of infrastructure, the promotion of the private sector, and the construction of a number of new commercial centres.[75] The Chamber of Commerce and Trade of Freice, a not-for-profit organisation of Freician businesses, is a major participant in the CAP.[76]
Transport
Transport services in Freice are limited, although recent efforts have been made to modernise and expand roads as part of the CAP initiative. The A1 is the main road on the island, starting at Matta in the northwest and progressing along the island's western, southern, and eastern coasts to Alui in the northeast. The A2 crosses the country east-to-west, linking Sekapa to Nania. The Sekapa Tramway is the only railroad on the island, opened in January 2023 following the redevelopment of the old railway opened in 1901.[77]
A number of roads are unpaved, with the limited number of paved roads causing congestion to be an issue at certain peak times in major urban areas.
The only airport on the island is Sema T. Anamia International Airport in Sekapa. Passenger services is provided by Freice Airlines, the flag carrier airline for Freice. Flights operate four days a week to Hernández de Córdoba International Airport, with chartered flights available for Guri and Orajioe.[78]
The Ialegita Nelige Marina provides sea access. In recent years, the marina has been modernised in recent years, including expansion and the improvement of roads linking it to the A1. The marina is an important import/export hub, as well as the home of a limited number of civil vessels.[79]
Culture
Media
Radio and Television Freice (Freician: Faiose'i Lerika ka Paasukase) is the national broadcaster of the island, owned by and operated through the Ministry of Finance, Infrastructure, and Sustainable Development. FLP broadcasts domestic programs as well as certain programs from Anáhuac, Riamo, and Hoterallia, and also provides radio and limited internet services.[80] There are also a small number of private commercial radio stations, which also carry some programming from Riamese and Anáhuaca stations.
Mulo'i Puineta (Freician: Island's Bulletin) is the main newspaper on the island, published in Sekapa. Previously a weekly newspaper published on Friday, it became a triweekly paper in 2023, publishing on Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday.[81]
Talitai'ama
The Talitai'ama is the traditional nobility of Freice. Before colonisation the Talitai'ama constituted the highest class below the monarch, possessing significant power in government and owning the majority of the land. Noble titles were abolished by the Riamese in 1759 on the island's annexation, but continued to play an informal role into the present day. In 2023, following a referendum, the Talitai'ama were formally restored and recognised by the Freician government, allowing members to use their titles in a formal capacity.[82]
Whilst the constitution explicitly prohibits any member of the Talitai'ama from occupying a position of authority by right of their title, members do weild immense power in their local communities.[83] Despite concerns about the impact on the island's democratic system, the Talitai'ama are widely considered to be an important part of the national culture, with many seeking redress for problems through the nobles rather than through elected government.[83]
Arts
Arts and crafts play an important role in Freician culture. Predominant among this is boat building, a practice long associated with the island's seafaring culture. This includes both boats and seafaring accessories, including ornately-decorated oars. The giving of nautical crafts, most commonly a small boat, is a common sign of appreciation or affection, usually given to confirm or affirm a friendship.[84] During the royal visit of Prince and Princess Arthur of Riamo in 2022, a number of such crafts were offered as a show of loyalty.[85]
Most Freicians have some experience in crafting these objects, with a significant informal economy operating around the buying and selling of these items. The Freice National Arts Centre, located in Sekapa, includes an extensive display of arts and crafts, which is an important tourist attraction.
See also
References
- ↑ Jules Strachan, 'Uncovering pre-colonial histories in Freice', Riamese Journal of Anthropological Studies, 18, no.11 (2019), pp.113-129
- ↑ Sailama Vaitami, 'Living history: Dual legacies of colonisation in Freice', Journal of Kaldaic and Southern Olivacian History, 26, no.5 (2021), pp.19-40
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Freice and the Federation". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ↑ "Support for Freicians overseas". Government of Freice. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ [Anonymous], Travels to the Islands of the Kaldaz [1743], p.2
- ↑ John Aitken, 'First contacts: Riamese trading with indigenous Kaldaic peoples in the mid eighteenth century', Journal of Kaldaic and Southern Olivacian History, 25, no.7 (2020), pp.88-102
- ↑ Sofia Botín, 'Tracing roots in Olivacian history', Journal of Kaldaic and Southern Olivacian History, 15, no.3 (2010), pp.88-124
- ↑ Sofia Botín, 'Economic practices aong the early Freicians', Journal of Kaldaic and Southern Olivacian History, 17, no.1 (2012), pp.22-41
- ↑ Christian Cassey, Imperialism and Riamese Politics, 1700-1825 (Guri: Hache Educational Press, 1999), p.67. ISBN 881-4-3192-325-4
- ↑ Ibid., p.73
- ↑ Makama Hutiua, 'Early colonial government and the survival of traditional practices', Friends of Freice Journal, 4, no.1 (2014), pp.7-16
- ↑ Cassey, Imperialism and Riamese Politics, p.77
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Federal government apologies to Freice over colonial practices" Riamo News Archived 18 May 2019. Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ Ibid., p.310
- ↑ Siotefe Koela (1998) "The Seige of Wilmington", Friends of Freice Journal 18(2), pp.28-39
- ↑ Rameia, R.E. (2019) A History of the Hoterallian Government in Freice (Portington: Portington Press), p.75
- ↑ "Hoterallia And Freice: An Island Where The Phoenix Once Landed." Minami no Taiyō. Retrieved December 11, 2018.
- ↑ "The History of The Imperial Hoterallian Navy: Freician's Naval Authority" Hojo Daily. 10 October 2007. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- ↑ Rameia, R.E. (2011) 'The role of Freician nationalism in the Hoterallian Government (1911-1915)', Journal of Kaldaic History, 9(3), pp.111-129
- ↑ Yoshihiro, Kondō. "The Hoterallian Propaganda On Freice." Hojo Daily. 16 January 2010. 4 March 2017.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Makama Hutiua (2008) "The advent of civil rights in post-handover Freice", Friends of Freice Journal 29(3), pp.8-14
- ↑ "Freice - the Jewel of the Kaldaz". 18 March 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ↑ "Freice constitution at 40". Riamo News. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Freician government to make indigenous tongue sole official language". The Gazette. Archived 2 August 2009. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- ↑ "Representation in Guri celebrates 45 years". Government of Freice. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- ↑ "Special Cooperation Agreement". Hoterallia in Freice. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- ↑ "REPORT: HIV/AIDS response in the Country of Freice". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ↑ "Freice government creates HIV body". Riamo News. Retrieved 26 March 2023.
- ↑ "Human rights groups condemn Freice constitution change". Riamo News. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ↑ "Freice's new government passes controversial constitutional law". The Gazette. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ↑ "Kana sweeps to office; MURO collapses". Kaposa Tama. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ↑ @RMFA (10 March 2022). "The Riamese Ministry of Foreign Affairs has scheduled an urgent talk with Anahuacan Authorities following the latest developments regarding #Freice. @RiamoSenate will be called to vote on the subject today, as this sudden move puts into question Freice's self-determination rights." - via Twatter.
- ↑ "'The Freician Issue' explained". Old Republic News. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ↑ "Freice Independence Survey (April 2023)". Portington University. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ "FEO: Federal government actions shows that independence is a must". Radio and Television Freice. Retrieved 3 April 2022.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Learn more about Freice". freice.fe. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ↑ "Protecting the natural environment". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ↑ "National Nature Reserve and Environmental Preservation Act, 1998" (PDF). Assembly of Delegates. Archived 7 August 2015. Retrieved January 3, 2018.
- ↑ "National Heritage Sites: Far Rock". Radio and Television Freice. 22 July 2022. Retrieved July 25, 2022.
- ↑ "Protecting Freice's Wildlife". Government of Freice. Retrieved 8 March 2019.
- ↑ Harman, Henry F. Riamo and Empire. p.231
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "Freice statistics". Riamese Meteorological Office. Retrieved 4 August 2019.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 Constitution Act 2022. Government of Freice. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
- ↑ "General Kiuva". Government of Freice. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ↑ "His Excellency The Representative of the Sovereign". Government of Freice. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ↑ "Cabinet of Ministers". Government of Freice. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ↑ "Government of Freice Act 1979" (PDF). Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Member state governments welcome accession of Freice". Saltstil Web Portal. Retrieved 27 June 2021.
- ↑ "How does the federal system work?". Riamo News. Retrieved 4 April 2022.
- ↑ "Tactical Response Unit". Royal Freice Police Service. Retrieved 14 April 2023.
- ↑ "Meeting passes local government reform". Radio and Television Freice.". Radio and Television Freice. Retrieved 24 March 2022.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "Freice". Global Factbook. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ↑ "District administration". Government of Freice. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 54.3 54.4 54.5 "Tesagena 2021 / Census 2021". Government of Freice. Retrieved 20 August 2021.
- ↑ "Controversy over migrant labour plan". Radio and Television Freice. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ↑ "Freice govt. says most migrant workers have left Freice following end of controversial policy". Riamo News. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Louis Manning, 'Speaking with a colonial tongue: The impact of Riamese colonisation on the Freician language', Journal of Kaldaic and Southern Olivacian History, 21, no.5 (2016), pp.104-142
- ↑ "Requirements for long-term stay". Government of Freice. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- ↑ "Frecia hace cambio de idioma". Noticias Imevisión. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
- ↑ "Interfaith dialogue". Riamese Orthodox Church in Freice. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ↑ "What links Kana, Christ, and anti-colonial activism?". Radio and Television Freice. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ↑ "Federal government announces Freice Health Action Plan". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 "Freice statistics". Federal Ministry of Health. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ "About us". Kaineki Tumatuga General Hospital. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ↑ "HIV/AIDS in Freice". Global Fund for HIV/AIDS Research. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ↑ "HIV/AIDS epidemic dashboard". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ↑ "Education services". Government of Freice. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 "Federal government commits to eliminating education access inequalities". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ↑ "Education services". Government of Freice. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ↑ "Freician assembly debates customs union exit". Glaze News. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ↑ "Trading". freice.fe. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ "Freice formally adopts gen". HHK. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "Oriental Trade Alliance in action". Saltstil Web Portal. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ↑ "Accession and Members of the Oriental Trade Alliance". Saltstil Web Portal. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ↑ "Comprehensive Action Plan for a 21st Century Freice". Government of Freice. Retrieved 8 May 2018.
- ↑ "Minister meets with Freice government for discussions on economic development". Riamese Federal Government. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ↑ "Freice Tramway officially opens". Railways Online. Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ↑ "Destinations". Sema T. Anamia International Airport. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- ↑ "About". Ialegita Nelige Marina. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ↑ "Services". Radio and Television Freice. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- ↑ "Mulo'i Puineta becomes tri-weekly". Mulo'i Puineta Online. Retrieved 12 April 2022.
- ↑ "Referendum sees victory for Kana-led initiatives". Riamo News. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 "Restoration of Freician nobility raises concerns about local democracy". Riamo News. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ↑ "Learn more about Freice". freice.fe. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ↑ "Prince Arthur receives warm welcome on first day of Freice visit". Riamo News. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
Notes
- ↑ Riamese federal legislation makes reference to the island as "the Country of Freice in the Riamese Federation." Prior to 2022, the Freician constitution declared the official name to be "Freice", but the Constitution Act 2022 now gives "Freice" and "Country of Freice" equal status.
- ↑ The official terminology used by the Freician government is "monarchical republic". This term relates to the nature of republicanism in Riamo, which is a rejection not of monarchical authority, but of the rule of nobility at the expense of the common people.
External links