Etruria: Difference between revisions
| (131 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = United Etrurian Federation | |conventional_long_name = United Etrurian Federation | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
|image_coat = EmblemofEtruria.png | |image_coat = EmblemofEtruria.png | ||
|alt_coat = | |alt_coat = | ||
|symbol_type = | |symbol_type = [[Coat of arms of Etruria|Coat of arms]] | ||
|national_motto = {{unbulleted list|[[ | |national_motto = {{unbulleted list|[[Deus, Libertas et Fraternitas]]||{{small|God, Liberty and Fraternity}}}} | ||
|national_anthem = {{unbulleted list|[[I figli di Romolo]]|{{small|Sons of Romulus}}}} | |national_anthem = {{unbulleted list|[[I figli di Romolo]]|{{small|Sons of Romulus}}}} | ||
|royal_anthem = | |royal_anthem = | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
|alt_map2 = | |alt_map2 = | ||
|map_caption2 = | |map_caption2 = | ||
|capital = [[ | |capital = [[Povelia]] | ||
|latd= | latm= | latNS = | |latd= | latm= | latNS = | ||
|longd= |longm= |longEW = | |longd= |longm= |longEW = | ||
|largest_city = [[ | |largest_city = [[Tyrrhenus]] | ||
|largest_settlement = | |largest_settlement = | ||
|largest_settlement_type = city | |largest_settlement_type = city | ||
|official_languages = {{wp|Italian}}<br>{{wp|Croatian language| | |official_languages = {{wp|Italian|Vespasian}}<br>{{wp|Croatian language|Novalian}}<br>{{wp|Slovene language|Carinthian}} | ||
|national_languages = | |national_languages = | ||
|regional_languages = | |regional_languages = | ||
|languages_type = | |languages_type = | ||
|languages = | |languages = | ||
|ethnic_groups = {{bulleted list| | |ethnic_groups = {{bulleted list|63.45% {{wp|Italians|Vespasian}}||14.03% {{wp|Croatians|Novalian}}||10.04% {{wp|Slovenes|Carinthian}}||4.18% {{wp|Serbs|Miruvian}}||3.51% {{wp|Greeks|Piraean}}||1.19% {{wp|French people|Gaullican}}|| 1.18% [[Marirana|Mariranian]]||1.09% [[Zorasan|Zorasani]]||1.06% {{wp|South Asian|Satrian}}}} | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2016 | |ethnic_groups_year = 2016 | ||
|religion = | |religion = [[Solarian Catholic Church|Solarian Catholicism]] ({{wp|State religion}}) | ||
|religion_year = 2016 | |religion_year = 2016 | ||
|demonym = Etrurian | |demonym = Etrurian | ||
| Line 58: | Line 57: | ||
|leader_name3 = [[Ivano Balić]] | |leader_name3 = [[Ivano Balić]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = [[History of Etruria|Formation]] | |sovereignty_type = [[History of Etruria|Formation]] | ||
|established_event1 = [[ | |established_event1 = [[Etrurian Revolution]] | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = 1783-1784 | ||
|established_event2 = [[ | |established_event2 = [[Declaration of the Republic of Heaven|Republic established]] | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 20 January 1784 | ||
|established_event3 = Monarchy restored | |established_event3 = Monarchy restored | ||
|established_date3 = 3 April 1810 | |established_date3 = 3 April 1810 | ||
| Line 82: | Line 81: | ||
|area_label2 = | |area_label2 = | ||
|area_dabodyalign = | |area_dabodyalign = | ||
|population_estimate = {{increase}} | |population_estimate = {{increase}} 68,389,868 | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = 2020 | ||
|population_census = 63,888,987 | |population_census = 63,888,987 | ||
|population_census_year = 2014 | |population_census_year = 2014 | ||
| Line 108: | Line 107: | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = | ||
|HDI_category = | |HDI_category = | ||
|currency = Etrurian florin | |currency = Etrurian florin (₣) | ||
|currency_code = | |currency_code = ETF | ||
|time_zone = | |time_zone = | ||
|utc_offset = | |utc_offset = | ||
| Line 118: | Line 117: | ||
|utc_offset_DST = | |utc_offset_DST = | ||
|drives_on = left | |drives_on = left | ||
|cctld = | |cctld = .et | ||
|iso3166code = | |iso3166code = | ||
|calling_code = | |calling_code = | ||
| Line 129: | Line 128: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Etruria''', officially the '''United Etrurian Federation''' or '''UEF''' ({{wp|Italian|Vespasian}}: Federazione Etruriana Unita; {{wp|Croatian|Novalian}}: Sjedinjene Etruriska Federacija; {{wp|Slovenian|Carinthian}}: Združena Etruriska Federacija) is a sovereign {{wp|parliamentary}} {{wp|federal republic}}, made up of | '''Etruria''', officially the '''United Etrurian Federation''' or '''UEF''' ({{wp|Italian|Vespasian}}: Federazione Etruriana Unita; {{wp|Croatian|Novalian}}: Sjedinjene Etruriska Federacija; {{wp|Slovenian|Carinthian}}: Združena Etruriska Federacija) is a sovereign {{wp|parliamentary}} {{wp|federal republic}}, made up of thirteen constituent states and two federal territories. Etruria also includes several islands [[List of islands of Etruria|several islands]], the largest being [[Aeolia]] and smaller archipelagos such as the [[Apocorona islands|Apocorona]]. Etruria is located in southern [[Euclea]]. It is is bordered (clockwise) by [[Amathia]] to the north-west, [[Gaullica]] to the north, [[Paretia]] to the east, to south, [[Juznavia]] to the south, and [[Piraea]] to the west. Etruria is home to 65.5 million people. The federal capital is [[Povelia]] and largest city is [[Tyrrhenus]]. | ||
Since classical times, its central geographic location in [[Euclea]] and the Mazdan and Solarian Seas, Etruria has historically been home to a myriad of peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient Vespasian tribes and Vespasic peoples dispersed throughout the Etrurian interior and insular Etruria, beginning from the classical era, [[Piraea|Pireans]], | Since classical times, its central geographic location in [[Euclea]] and between the Mazdan and Solarian Seas, Etruria has historically been home to a myriad of peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient Vespasian tribes and Vespasic peoples dispersed throughout the Etrurian interior and insular Etruria, beginning from the classical era, [[Piraea|Pireans]], Auratics and Atudite peoples established settlements in the south of Etruria, with Tyrrenii and inhabiting the centre and the north of Etruria respectively. The Vespasic tribe known as the Solarii formed the Solarian Tribunate in the 8th century BC, which eventually became a republic that conquered and assimilated its neighbours, including the powerful and wealthy Tyrenii. In the first century BC, the [[Solarian Empire]] emerged as the dominant power in the Solarian-Mazdan Basin and became the leading cultural, political and religious centre of [[Euclea|Euclean civilisation]]. The legacy of the Solarian Empire is widespread and can be observed in the global distribution of civilian law, republican governments, Sotirianism and the Solarian script. Its steady collapse in the 5th century AD corresponded with the arrival of {{wp|Slavs|Marolevic}} tribes from the west, who would go on to form the {{wp|Croatians|Novalian}} and {{wp|Slovenes|Carinthian}} peoples. | ||
These independent statelets often enjoyed a greater degree of democracy and wealth in comparison to the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Euclea at the time. By the 13th century, modern Etruria became dominated by three states, the [[Exalted Republic of Poveglia]], [[Grand Duchy of Carvagna]] and the [[Ecclesiastical State (Etruria)|Ecclesiastical State]]. | |||
The Renaissance | The Renaissance spread across Etruria from Povelia, bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration and art. Vespasian culture flourished at this time, producing famous scholars, artists and polymaths such as "Great people". The influence and commercial power of the maritime republics began to dominate the monarchies of the interior, culminating in the Povelian victory in the [[Etrurian Wars]] and becoming the dominant power in Etruria, leading to the [[Pax Poveliae]]. Povelian colonisation of the Asterias soon followed, introducing New World treasures to Etruria. The sudden rise of the [[Principality of Tyrrenhus]] in the south added pressure to Povelia. In the 18th century, Povelia’s decline began, hastened by the immense cost paid during the [[Ten Year’s War]]. This decline led to the [[Central Etrurian Wars]] and the [[Torazzi War]] between Povelia and Tyrrenhus, bankrupting and disrupting vast swathes of Etruria. The famine, debt and corruption led to the overthrow of the monarchy in Tyrrenhus, sparking the [[Etrurian Revolution]] (1783-1785) and the establishment of the [[Etrurian First Republic]], creating one of the earliest republics in history. The Republic would go on to unite Etruria and for the next fifteen years, engage in the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Wars]], spreading republican tradition and values across southern Euclea. The constant warfare, poor governance and state-terror would lead to the restoration of monarchy in 1810 and the [[United Kingdom of Etruria]]. | ||
From 1810 until 1880 would enjoy prosperity, growth and development. Etruria would establish one of the largest colonial empires, while federalism was greatly expanded and refined. However, debt, a poor economy and authoritarianism resulted in the [[1880 Revolution]] and the establishment of the [[Second Etrurian Republic]]. Etruria was a major participant in the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], from which it emerged victorious, however, poor territorial gains and political instability led to the emergence of the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] and the [[Solarian War]], which saw Etruria defeated. The [[Third Etrurian Republic]] emerged in the aftermath, rebuilding the country and establishing a fixed regime of civil rights and freedoms before being overthrown by the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military]] which established a Junta in wake of the [[Western Emergency]]. Democracy would be restored in 1983 with the current Fourth Republic. | From 1810 until 1880 would enjoy prosperity, growth and development. Etruria would establish one of the largest colonial empires, while federalism was greatly expanded and refined. However, debt, a poor economy and authoritarianism resulted in the [[1880 Revolution]] and the establishment of the [[Second Etrurian Republic]]. Etruria was a major participant in the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], from which it emerged victorious, however, poor territorial gains and political instability led to the emergence of the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] and the [[Solarian War]], which saw Etruria defeated. The [[Third Etrurian Republic]] emerged in the aftermath, rebuilding the country and establishing a fixed regime of civil rights and freedoms before being overthrown by the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military]] which established a Junta in wake of the [[Western Emergency]]. Democracy would be restored in 1983 with the current Fourth Republic, this was followed by numerous liberalising economic reforms that achieved high sustained economic growth and improvements to standards of living. Between the 1990s and 2010s, the country underwent political reforms in aim of Etruria joining the [[Euclean Community]]. A referendum held on EC membership in 2016 was defeated due to several major corruption scandals and the successful No-campaign being led by the right-wing [[Tribune Movement]], this ended all prospect of Etrurian membership of the EC. The loss of the referendum, coupled with the corruption scandals brought about the near collapse of the establishment parties in the [[2016 Etrurian general election|2016 election]] and a victory for the Tribune Movement, which formed the most right-wing government in Eastern Euclea since the Great War. | ||
Today, Etruria has a mixed market economy based around finance, industry and agriculture. It has the XX largest economy in [[Euclea]], and XX largest in the world. It is widely considered a {{wp|newly-industrialised economy}}, a {{wp|regional power}} and {{wp|middle power}}. It is a council member of the [[Community of Nations]], [[Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs|GIFA | Today, Etruria has a mixed market economy based around finance, industry and agriculture. It has the XX largest economy in [[Euclea]], and XX largest in the world. It is widely considered a {{wp|newly-industrialised economy}}, a {{wp|regional power}} and {{wp|middle power}}. It is a council member of the [[Community of Nations]], [[Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs|GIFA]] and the [[International Trade Organisation|ITO]]. | ||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
| Line 156: | Line 155: | ||
Between the 17th and the 11th centuries BC XX established contacts with Etruria and in the 8th and 7th centuries BC a number of XX colonies were established all along the coast of Vespasia and the southern part of the Aeolian Peninsula, that became known as XX. During this time, the Vespasii were rapidly growing in and around what would become Solaria, while north of them, the Vicalvii had cleared land around the seven-hills of Vicalvus. | Between the 17th and the 11th centuries BC XX established contacts with Etruria and in the 8th and 7th centuries BC a number of XX colonies were established all along the coast of Vespasia and the southern part of the Aeolian Peninsula, that became known as XX. During this time, the Vespasii were rapidly growing in and around what would become Solaria, while north of them, the Vicalvii had cleared land around the seven-hills of Vicalvus. | ||
=== Ancient Solaria and | === Ancient Solaria and Tyrrenhus === | ||
Solaria, a settlement on the coast of the Bay of Lasa Vecuvia conventionally founded in 757 BC, was ruled for a period of 239 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of Vespasii and Torian origin, later by Vicalvii kings. The tradition handed down seven kings: Romulus, Verus Tanis, Horius Antonius, Marcus Marcellius, Eugenius Prascus, Ceserius Tullius and Hadrianus Lutorius. In 511 BC, the Solarians expelled the last Vicalvii king from their city and established an oligarchic republic. | [[Solaria]], a settlement on the coast of the Bay of Lasa Vecuvia conventionally founded in 757 BC, was ruled for a period of 239 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of Vespasii and Torian origin, later by Vicalvii kings. The tradition handed down seven kings: Romulus, Verus Tanis, Horius Antonius, Marcus Marcellius, Eugenius Prascus, Ceserius Tullius and Hadrianus Lutorius. In 511 BC, the Solarians expelled the last Vicalvii king from their city and established an {{wp|oligarchic republic}}, supposedly upon the order of the [[Aventine Triad]], led by the sun gold [[Religio Solaris|Sol]]. | ||
To the north of Solaria, | To the north of Solaria, Tyrrenhus, a settlement built around the ford of the Metaia River rapidly grew under a series of successive kings, it dramatically expanded its territories to cover the entire Vicalvian Plain. Vicalvus' dominant position allowed it to influence Solaria until the expulsion of Hadrianus Lutorius. With the establishment of the [[Solarian Republic]], Vicalvus found a serious challenger to domination over southern [[Vespasia]]. The two cities would fight numerous wars known as the [[Wars of the Two Cities]], the wars ended in 256 BC when Tyrrenhus was defeated at the [[Battle of Salutaria]], resulting in the city's annexation by Solaria. Tyrennii culture would fuse with Solarian, creating the long-lasting Solarian culture that spread with the empire's growth. The Solarian Republic until the first century B.C. would expand to encompass all of modern day Etruria and western [[Auratia]], crossing the Solarian sea to establish colonies on the coasts of [[Tsabara]] and northern modern-day [[Zorasan]] in 89 BC. This expansion would instigate centuries-long conflicts with the [[Heavenly Dominion|Heavenly Dominions]]. | ||
[[File:Solarian EmpirePeak.png|250px|thumb|left|The [[Solarian Empire]] at its peak between 318 and 417 CE.]] | |||
In the wake of rebellion by [[Tarchon Parusna]] in the first century B.C. and a series of concurrent slave revolts, the Solarian Senate granted extraordinary powers to TBD, who with the assistance of allies within the senate, succeed in being granted the title of Emperor. Over the course of centuries, Solaria would expand and grow into a massive empire stretching from the western borders of [[Bahia]] to the southern reaches of [[Estmere]] and [[Swetania]], and engulfing the whole Solarian basin, in which the Tyrennii-Solarian and [[Piraea|Piraeo]] and many other cultures merged into a unique civilisation. The Solarian Peninsula was named Etruria was declared "Terra Saena" (Sacred Soil), granting special status compared to other imperial provinces. The long and triumphant reign of the first emperor, TBD, began a golden age of peace and prosperity. From its founding until the late 4th century CE, the Empire's leaders were relatively successful in maintaining a peaceful balance of power between the Emperor and Senate, while sporadic and isolated power struggles were recorded, this enabled to extend the period of prosperity. | |||
In the | In 395 CE, Mount Vecuvia erupted devastating much of the ancient city of Solaria, among the estimated 5,000 people killed was Emperor Diocletius. The Emperor's sudden death coupled with this as of yet declared successor sent the Empire spiralling into chaos, with numerous leading figures declaring themselves Emperor, sparking the [[Vecuvian Wars]]. The devastating localised and Empire-wide civil conflicts significantly weakened the central authority of the state, exacberating the strain of managing and protecting its vast territories. The near constant power-struggles between successive and short-reigning Emperors and the Senate hollowed out the central state, giving way to endemic corruption, poor provincial governance and economic malaise. This stagnation was coupled by ever growing threats, either from the [[Heavenly Dominion|Heavenly Dominions]] in northern Coius, to {{wp|Slavs|Marolevic}}, {{wp|Germanic tribes|Weranic}} tribal incursions from the Euclean west and north. Between 417-419 CE, the Heavenly Dominion launched a [[Solarian-Irfanic Wars|full-scale invasion]] of the Empire's holdings in northern Coius, evicting the Solarian Empire from the continent for the first time since 66 BCE. Between 419 and 426 CE, the Empire rapidly lost control of its western holdings to numerous migranting Marolevic tribes, while Weranic tribes to the north descended southward toward the province of [[Gaullica]]. In 424, the Empire essentially collapsed within its heartland, with numerous Senators establishing individual powerbases, while two years later, [[Claudius of Gaullica]] redeclared the Empire, laying the foundations of the [[Verliquoian Empire]]. Within Vespasia, the Empire's heartland fractured into numerous fiefdoms and statelets, which would remain the case until the expansion of the Verliquoian Empire decades later. | ||
The Solarian Empire was among the most powerful economic, cultural, political and military forces in the [[Kylaris|world]] of its time. It was one of the largest empires in world history. At its height under Velturius, it covered | The Solarian Empire was among the most powerful economic, cultural, political and military forces in the [[Kylaris|world]] of its time. It was one of the largest empires in world history. At its height under Velturius, it covered 3.4 million square kilometres. The Solarian legacy has deeply influenced the Euclean civilisation, shaping most of the modern world; among the many legacies of Solarian dominance are the widespread use of the Vespasic languages derived from the fusion of Tyrennii and Solarian, the numerical system, the modern {{wp|latin alphabet|Eastern alphabet}} and calendar, and the emergence of [[Sotirianity]] as a major world religion. | ||
=== Middle Ages === | |||
After the [[Fall of the Solarian Empire]] and the fragmentation of Etruria, the former heartland was dominated by small states ruled by former Solarian senators and other aristocratic elites. The western reaches of Etruria, would fall under the dominion of numerous {{wp|Slavs|Marolevic}} tribes, who would over the course of several decades fighting fierce internecine wars, culminating into the future Kingdoms of [[Kingdom of Carinthia|Carinthia]] and [[Kingdom of Novalia|Novalia]]. Efforts by the [[Empire of Arciluco]] to expand its dominion eastward to reclaim [[Solaria]] was repeatedly defeated by these Marolevic tribes, this in contrast to the [[Verliquoian Empire]], which succeeded in restoring imperial control over much of [[Vespasia]] between 432 and 449 CE. Verliquoian rule would go on uncontested for over two-hundred years, until in 665, the patricians of the city of [[Povelia]] successfully negotiated independence from the Empire, despite imperial rule ever being nominal or superficial. The patricians and merchants established the [[Exalted Republic of Povelia]] the following year, and would result in the establishment of Povelia as one of Euclea's great powers during the Renaissance and early modern period. During this time of Verliquoian dominance, the numerous provinces that later form the numerous comunes and city-states of Etruria were established to ease imperial administration, another notable development was the ever growing autonomy of the city of Solaria under the direct temporal rule of the [[Solarian Catholic Church|Papacy]]. | |||
[[File:Etruria1450.png|250px|thumbnail|right|Etrurian states in 1450.]] | [[File:Etruria1450.png|250px|thumbnail|right|Etrurian states in 1450.]] | ||
=== Early Modern === | === Early Modern === | ||
[ | [ | ||
[[File:Leutze, Emanuel — Storming of the Teocalli by Cortez and His Troops — 1848.jpg|250px|thumb|right|The sacking the city of Aztocheletynal by Di Mariran's soldiers in 1523.]] | [[File:Leutze, Emanuel — Storming of the Teocalli by Cortez and His Troops — 1848.jpg|250px|thumb|right|The sacking the city of Aztocheletynal by Di Mariran's soldiers in 1523.]] | ||
=== Revolutionary Etruria (1784–1810) === | |||
=== Revolutionary Etruria ( | |||
{{Main|Etrurian Revolution}} {{See also|Etrurian First Republic}} | {{Main|Etrurian Revolution}} {{See also|Etrurian First Republic}} | ||
[[File:BlessingoftheArmy.png|290px|thumb|right|Revolutionary Army soldiers being blessed by pro-Republican Etrurian cardinals in [[Solaria]] following the fall of the [[Ecclesiastical State (Kylaris)|Ecclesiastical State]] in 1789.]] | |||
[[File: | |||
=== Royal Restoration and 19th century (1810–1888) === | === Royal Restoration and 19th century (1810–1888) === | ||
{{Main|United Kingdom of Etruria}} | {{Main|United Kingdom of Etruria}} | ||
{{See also|Etrurian colonial empire}} | {{See also|Etrurian colonial empire}} | ||
[[File:EtrurianColonialEmpire1900.png|250px|thumb|right|The [[Etrurian colonial empire]] in 1900.]] | [[File:EtrurianColonialEmpire1900.png|250px|thumb|right|The [[Etrurian colonial empire]] in 1900.]] | ||
=== Second Republic (1888–1937) === | === Second Republic (1888–1937) === | ||
{{Main|Etrurian Second Republic}} | {{Main|Etrurian Second Republic}} | ||
=== National Solarian period (1937-1946) === | === National Solarian period (1937-1946) === | ||
{{Main|Solarian Republic of Etruria}} | {{Main|Solarian Republic of Etruria}} | ||
=== CN Mandate and Third Republic (1946-1960) === | |||
=== Third Republic (1946-1960) === | |||
{{Main|Etrurian Third Republic}} | {{Main|Etrurian Third Republic}} | ||
=== Military dictatorship (1960-1983) === | === Military dictatorship (1960-1983) === | ||
{{Main|Military dictatorship in Etruria}} | {{Main|Military dictatorship in Etruria|Western Emergency}} | ||
[[File:Massarosaw.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Etrurian soldiers greeting civilians following the bloodless coup of 1960.]] | [[File:Massarosaw.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Etrurian soldiers greeting civilians following the bloodless coup of 1960.]] | ||
=== Contemporary (1983-present) === | === Contemporary (1983-present) === | ||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
Etruria is located in | Etruria is located in [[Southern Euclea]]. To the north, Etruria borders [[Gaullica]] which is dominated by the Aventine Mountains which run northward, before declining southward along Etruria’s north-eastern border. This natural enclosure bounds the [[Eugenian Plain]] which dominates northern Etruria. The Aventine North is home to Etruria’s largest lakes, Lake Imperia and Lake Jovia. South of the plain and running from north-to-south is the Tarantine Mountains which stand as the spine of the Etruro-Piraean Peninsula. The Tarantines are divided from the Aventines by the Carinthian Gap, which is the far-western border of the Eugenian Plain. The Tarantines continue southward into [[Galenia]], Etruria’s only neighbour to the south. To the east is [[Auratia]] and the [[Bay of Povelia]], at the head of which is the [[Povelian Lagoon]], which contains marshland and hundreds of islands, and the island-city of the same [[Povelia|name]]. Etruria east of the Tarantines is marked by its hilly terrain and forests, while the areas west of the mountains are noted equally for their forests, fertile soil and rolling hills. To the west, Etruria borders [[Piraea]], while the [[Tarpeia|Federal Territory of Tarpeia]], also known as the Tarpeian Corridor (Corridoio Tarpeano), which separates Piraea from Galenia. Etruria also includes one large island, [[San Francesco]] and numerous smaller islands including the [[Apocorona Islands|Apocorona]], the [[Guardiani Islands|Guardiani]]. | ||
The country's total area is 548,549 km² (211,796 sq mi). Including the islands, Etruria has a coastline of 2,636 kilometres (1,637 miles) on the Solarian and Mazdan seas. | The country's total area is 548,549 km² (211,796 sq mi). Including the islands, Etruria has a coastline of 2,636 kilometres (1,637 miles) on the Solarian and Mazdan seas. | ||
The | The Tarantine Mountains form Etruria's backbone and the Aventines form most of its northern and eastern boundary, Etruria's highest point is located on Monte Tinia (4,810 m or 15,780 ft) in the northern reaches of the range. The Àdexe, Etruria's longest river (1,114 kilometres or 692 miles), flows from the Aventines on the north-western border with Guallica and crosses the Eugenian plain on its way to the Solarian Sea, where it enters the Bay of Povelia. The five largest lakes are, in order of diminishing size: Imperia (1,000 km2 or 386 sq mi), Jovia (212.51 km2 or 82 sq mi), San Paolo (145.9 km2 or 56 sq mi), San Pietro (124.29 km2 or 48 sq mi) and Balestra (113.55 km2 or 44 sq mi). | ||
The country is situated at the meeting point of the XXX Plate and the XXX Plate, leading to considerable seismic and volcanic activity. There are 17 volcanoes in Etruria, three of which are active: Vosca, Stalleria, Vesano and Veturius, which last erupted in 2015. | The country is situated at the meeting point of the XXX Plate and the XXX Plate, leading to considerable seismic and volcanic activity. There are 17 volcanoes in Etruria, three of which are active: Vosca, Stalleria, Vesano and Veturius, which last erupted in 2015. | ||
<gallery mode=packed heights= | <gallery mode=packed heights=200 style="font-size:88%;line-height:120%"> | ||
File:MontBlancFromENE.jpg|Monte Tinia is the highest peak in Euclea | File:MontBlancFromENE.jpg|Monte Tinia is the highest peak in Euclea | ||
File:Tuscany_(34445300666).jpg|Landscape of the Eugenian Plain | File:Tuscany_(34445300666).jpg|Landscape of the Eugenian Plain | ||
File:1_vernazza_2012.jpg|The village of San Andrea on the Costa d'Oro | File:1_vernazza_2012.jpg|The village of San Andrea on the Costa d'Oro | ||
File: | File:Canyon_of_Paklenica.jpg|Canyon in the Novalian region of the Tarantine mountains | ||
File:CaxadeLaguna.png|Marshy terrain of the Poveglian Lagoon | File:CaxadeLaguna.png|Marshy terrain of the Poveglian Lagoon | ||
File:Mt_Etna_and_Catania1.jpg|Mount Eita is the largest active volcano on Mainland Euclea. | File:Mt_Etna_and_Catania1.jpg|Mount Eita is the largest active volcano on Mainland Euclea. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=== Climate === | |||
Owing to Etruria’s geographical location and geography, there are three distinct climatic zones present: | |||
[[File:Tossa de Mar View.jpg|290px|thumb|right|The Solarian climate of the coast of San Francesco island.]] | |||
* The {{wp|Mediterranean climate|Solarian climate}}, characterised by warm/hot and dry summers, is dominant east of the Tarantine Mountains and coastal Etruria. | |||
**The First Solarian zone is associated to areas with hot summers. It is predominant across the coastal regions southern, central and eastern Vespasia and covering virtually all of inland central Vespasia up to the slopes of the Tarantine Mountains. Southern Vespasia and southern Novalia also fall under his climatic zone. These areas also tend to had cool or cold winters dependent upon air currents over northern Euclea. The major cities to fall under the First Zone include [[Solaria]], [[Tyrrenhus]], [[Stazzona]], [[Vilanja]], [[Centuripe]] and [[Bekovje]]. This climate also covers the entirety of the island of San Francesco. | |||
**The Second Solarian zone has warm rather than hot summers, and extends to additional cool-winter areas not typically associated with a Solarian climate, such as much of central and northern Novalia, all of [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]] and the interior of eastern Vespasia, along the border with [[Auratia]]. These areas also higher rainfall that the First Solarian Zone. Note areas with relatively high rainfall such as Galicia are not considered Mediterranean under local classifications but classed as oceanic. | |||
* The {{wp|Humid sub-tropical climate}}, characterised by warm humid summers and damp cold winters. This climatic zone covers the entirety of the Eugenian Plain an runs west-to-east, where hot humid air becomes trapped between the Aventines to the north, warm sea from the Solarian Sea to the south alongside the Tarantine Mountains. | |||
* The third climatic zone is the {{wp|Alpine climate|Aventine climate}}, characterised simply by the lack of trees owing to the deep cold. The Aventine Climate covers two distinct areas, the Aventine and Tarantine mountains, though during particularly cold winters, their climatic effects are known to descend into inland areas, notably Carinthia, northern [[Novalia]] and on some occasions, the Eugenian Plain of Vespasia. | |||
Average winter temperatures vary from 0 °C (32 °F) on the Alps to 12 °C (54 °F) in southern Novalia, so average summer temperatures range from 20 °C (68 °F) to over 25 °C (77 °F). Winters can vary widely across the country with lingering cold, foggy and snowy periods in the north and milder, sunnier conditions in the south. Summers can be hot and humid across the country, particularly in the south and central areas , while the northern interior can experience strong and recurrent thunderstorms throughout spring and autumn. These storms are also known to cause flashfloods and landslides in areas immediately south of the Aventine Mountains. | |||
=== Biodiversity === | |||
[[File:Wolf at Castello Belfort.jpg|290px|thumb|left|The {{wp|Italian wolf|Vespasian wolf}} once a common inhabitant of Etruria and a former cultural and mythological icon has come under protected status.]] | |||
Due to Etruria’s unique and varied geological features and climatic variances, it has one of the highest degrees of habitat and faunal diversity in Euclea. According to the International Committee for Nature, Etruria has over 50,000 species recorded in various biomes and habitats. Among these species include numerous endemic animal species such as the, {{wp|Sardinian long-eared bat|Francsiscan long-eared bat}}, {{wp|Italian newt|Vespasian newt}}, {{wp|Aeolian wall lizard|Guardiani wall lizard}} and the {{wp|brown cave salamander}}. Notable mammal species endemic to Etruria include the {{wp|Marsican brown bear}}, whose numbers have dwindled significantly due to hunting, the {{wp|Alpine ibex|Aventine ibex}}, the {{wp|Eurasian Lynx|Euclean lynx}} and the {{wp|Italian wolf|Vespasian wolf}}. Etruria is also home to 516 bird species and 56,213 invertebrate species, such as the endemic {{wp|Carniolan honey bee|Carinthian honey bee}}. Despite its diversity, Etruria has the seen the most dramatic and rapid decline in all Euclea, with over 1,200 species believed to have gone extinct since 1950, due to human development, pollution and destruction of natural habitats. Efforts to preserve wildlife through strengthening of laws regarding {{wp|national parks}} and wildlife sanctuaries have seen a steadying of the rate of decline. | |||
[[File:P anguinus2.jpg|290px|thumb|left|Etruria is home to the only known cave vertibrate, the {{wp|olm}}.]] | |||
[[File:Pinus halepensis forest, near Dubrovnik, Croatia - Stiller Beobachter.jpg|290px|thumb|right|A typical southern Etrurian forest near [[Supetar]] in [[Novalia]].]] | |||
Etruria's lengthy coastline and the commonality of deep and extensive cave systems has led Etruria to be home to several endemic aquatic cave species, such as the {{wp|Olm}}, the only known cave vertebrate. Etruria since the 1980s has established several Marine Life Sanctuaries, areas of sea protected by any human activity bar scientific research. The Bay of Povelia is known to be home to pods of {{wp|bottle nosed dolphins}}, {{wp|Sperm whale}}s (when migrating) and occasionally {{wp|humpback whale}}s, though this has been questioned by marine biologists. The {{wp|Mediterranean monk seal|Solarian monk seal}} was once one of the most common marine mammals to be spotted across Etruria’s coastlines, however, human activity and the stark increase in water pollutants and noise pollution has driven the monk seal away from the northern shores of Bay of Povelia, leaving the mammal mostly confined to the coasts of eastern [[Veratia]] and the islands of [[San Francesco]]. | |||
The flora of Etruria was estimated to comprise about 9,500 vascular plant species, though this figure has declined. Forests are also significantly present in the country, as they cover 10,490,000 hectares (104,899 km²) representing 19.12% of Etruria's land surface. This saw a significant decrease from 29.9% as of 1960, with a vast majority of this decline owed to {{wp|deforestation}} for agricultural use. Other habitat types include grasslands, wetlands, bogs, marshlands, scrub habitats, coastal and marine habitats. In terms of {{wp|phytogeography}}, Etruria is a part of the {{wp|Boreal Kingdom}} and is a part of the Central and Southern Euclea provinces of the Circumboreal Region and the Central province of the Solarian Region. Etruria is further divided between three ecoregions—Pannonian mixed forests, {{wp|Dinaric Mountains mixed forests|Western Tarantine mixed forests}} and {{wp|Illyrian deciduous forests|Etrurian deciduous forests}}. | |||
=== Environment === | |||
In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries, Etruria remains the host of significant environmental problems. It is among the lowest in Euclea for ecological sustainability and one of the lowest in the production of renewable energy. It consistently ranks as one of the worst in Euclea for environmental degradation, habitat destruction and air quality. Air pollution remains one of Etruria’s most pressing problems, especially in industrial regions, in the southern and northern Vespasia, as of 2020, Etruria ranked third in carbon emissions output in Euclea, Globally, Etruria is the sixth largest carbon dioxide producer. Extensive traffic and congestion in the largest metropolitan areas continue to cause severe environmental and health issues, while the continued use of coal-fired power plants and weak industrial carbon emissions regulations contribute to serious cases of smog. | |||
The | Unlike other Euclean countries, Etruria has fewer national parks, with the first only established in 1949. The belatedness of the national park movement permitted vast swathes of Etruria’s forested areas to be destroyed and numerous animal species to be forced int extinction or to become endangered. Deforestation, illegal building developments and poor land-management policies at the state and federal level, have led to significant erosion all over Etruria’s mountainous regions in the north and south, leading to numerous disasters such as the [[Montecorvino Mudslide]], [[Giassico Disaster]] and the [[San Girolamo Dam collapse]]. | ||
Many watercourses and coastal stretches have also been contaminated by industrial and agricultural activity, while because of rising water levels, [[Povelia]], the national capital, has been regularly flooded in recent years, with the problem increasing tenfold in the last six years. The repeated flooding of the national capital has led to renewed calls for the federal government to move elsewhere, while the rising waters in the Povelian Lagoon is also blamed on poorly designed canal networks, that have brought further water volumes into the tightly enclosed waterbody. Several areas of the Lagoon and the wider Povelian Bay have on occasions be sealed off due to industrial waste introducing toxic chemicals into the water. Waste from agricultural and industrial activity is not always disposed of by legal means, with historic cases of mafia groups being contracted to remove waste, and has led to permanent health effects on inhabitants of affected areas | |||
== Government and politics == | == Government and politics == | ||
| Line 326: | Line 280: | ||
| content1 = | | content1 = | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:StateCouncilEtruria2021.png|240px|right]] | ||
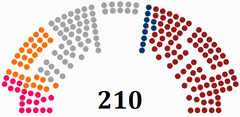
'''Government (194)'''<br>{{colorbox|#961c1c}} [[Tribune Movement]] ( | '''Government (194)'''<br>{{colorbox|#961c1c}} [[Tribune Movement]] (155)<br>'''People's Opposition (99)'''<br>{{colorbox|#f25c19}} [[Citizens' Alliance]] (48)<br>{{colorbox|#03386A}} [[Farmers and Workers Union]] (15)<br/>{{colorbox|#FF0000}} [[Popular Renewal (Etruria)|Popular Renewal]] (4)<br/> {{colorbox|#A2A5A5}} [[Independent (politics)|Independent]] (3) | ||
}} | |||
{{Sidebar | {{Sidebar | ||
| name = Etruria | | name = Etruria | ||
| Line 343: | Line 298: | ||
| content1 = | | content1 = | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Chamber of Representatives2022.png|240px|center]] | ||
'''Government ( | '''Government (373)'''<br>{{colorbox|#961c1c}} [[Tribune Movement]] (360)<br/> {{colorbox|#d71720}} [[Social Party of the Third Order]] (13)<br>'''Support (23)'''<br>{{colorbox|#03386a}} [[Farmers and Workers Union]] (23)<br>'''People's Opposition (206)'''<br>{{colorbox|#ff0066}} [[Social Democratic Party (Etruria)|Social Democratic Party]] (165)<br>{{colorbox|#f25c19}} [[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|Citizens' Alliance]] (26)<br> {{colorbox|#00b6a4}} [[Etruria plus Euclea]] (6)<br>{{colorbox|#006ab4}} [[Sotirian People's Force]] (4)<br>{{colorbox|#ff0000}} [[Popular Renewal (Etruria)|Popular Renewal]] (3) | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 351: | Line 306: | ||
'''Legislature:''' the legislative branch of Etruria is based on the adversarial model of parliament, as such the federal legislature is parliamentary. The [[Senate of Etruria|Senate]] is split into two houses: the [[State Council of Etruria|State Council]] and the [[Chamber of Representatives of Etruria|Chamber of Representatives]]. The Chamber of Representatives is the lower house and is the more powerful. The State Council is the upper house and although it can vote to amend proposed laws, the chamber can only vote to overrule its amendments should the state council reject the bill more than twice. Although the State Council can introduce bills, most important laws are introduced in the Chamber – and most of those are introduced by the government, which schedules the vast majority of parliamentary time in the Chamber. Parliamentary time is essential for bills to be passed into law, because they must pass through a number of readings before becoming law. Prior to introducing a bill, the government may run a public consultation to solicit feedback from the public and businesses, and often may have already introduced and discussed the policy in the president's State of the Union address, or in an election manifesto or party platform. | '''Legislature:''' the legislative branch of Etruria is based on the adversarial model of parliament, as such the federal legislature is parliamentary. The [[Senate of Etruria|Senate]] is split into two houses: the [[State Council of Etruria|State Council]] and the [[Chamber of Representatives of Etruria|Chamber of Representatives]]. The Chamber of Representatives is the lower house and is the more powerful. The State Council is the upper house and although it can vote to amend proposed laws, the chamber can only vote to overrule its amendments should the state council reject the bill more than twice. Although the State Council can introduce bills, most important laws are introduced in the Chamber – and most of those are introduced by the government, which schedules the vast majority of parliamentary time in the Chamber. Parliamentary time is essential for bills to be passed into law, because they must pass through a number of readings before becoming law. Prior to introducing a bill, the government may run a public consultation to solicit feedback from the public and businesses, and often may have already introduced and discussed the policy in the president's State of the Union address, or in an election manifesto or party platform. | ||
The Chamber has | The Chamber has 600 voting members, each representing a senatorial district for a five-year term without term limits. Chamber seats are apportioned on the basis of population, with [[Veratia]] providing 200 members and [[Il Dogado]] providing eight members. | ||
The State Council has | The State Council has 210 members - 150 are drawn from each state, which provide ten members and the remaining 60 are appointed by the government as non-partisan {{wp|crossbencher}}s in recognition of their contributions to national life. Both members drawn from the states and those appointed by the government hold their seats for single terms of ten years. The duty of the senate is to scrutinise all legislation, confirm appointments and ratify all international agreements. The State Council is able to table legislation over certain issues, these being; the constitution, limits of federal power, the separation between state and federal power, foreign policy and defence. | ||
'''Judiciary:''' | '''Judiciary:''' Etruria has a three-tier unitary {{wp|independent judiciary}} comprising the Court of Cassation, the Constitutional Court, 25 high courts, and a large number of trial courts. The court of cassation has original jurisdiction over cases involving fundamental rights and over disputes between states and the centre and has appellate jurisdiction over the high courts, while the constitutional court's mandate is limited to determining the constitutionality of federal and state law. It has the power to both strike down federal or state laws which contravene the constitution, and invalidate any government action it deems unconstitutional. | ||
==== Political parties ==== | ==== Political parties ==== | ||
{{Main|Politics of Etruria|List of political parties in Etruria}} | |||
From the restoration of democracy in 1984 after twenty-four years of [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military rule]] until 2016, the country operated a {{wp|two-party system}}, with power alternating between the {{wp|centre-left}} [[Social Democratic Party (Etruria)|Social Democratic Party]] and the {{wp|centre-right}} [[Etrurian Federalist Party]]. The SDP held government for a total of 18 years under three presidents, while the Federalists held power for a total of 14 years under four presidents, the last of whom served for only 35 days. The third largest party until 2016 was consistently the [[Farmers and Workers Union]], a {{wp|social conservative}} {{wp|agrarianism|agrarian}} party that competed for seats exclusively in [[Novalia]]. Until 2018, Etrurian governments were near exclusively formed out of coalitions between the major party and smaller allied parties. It was considered a tradition for the EFP to enter government with the FWU, while the SDP went into coalition with [[Sotirian Democracy]] until its merger with the EFP in 2002, and the [[Popular Liberal Party (Etruria)|Popular Liberal Party]] until its merger with the [[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|Citizens' Alliance]] in 2013. | |||
In 2016, the two-party system collapsed under the weight of three monumental events: the [[Etruria Euclean Community membership referendum, 2016|EC referendum]], the [[Miraviglia Scandal]] and the [[2016 Etrurian general election]]. The Miraviglia Scandal broke during the height of the EC referendum in the early Summer of 2016 and involved both major parties, though it struck the incumbent Federalist Party government under President [[Emiliano Reali]] particularly hard. The scandal had an adverse effect on the EC result, as many voters saw a No vote as a means of punishing the pro-EC Social Democrats and Federalists. The loss to the No campaign led by the [[Tribune Movement]] and widespread anger and resentment toward an establishment perceived to be {{wp|elitism|elitist}}, {{wp|corruption|corrupt}} and aloof fed into the rise of spoiler parties, especially the Tribune Movement and Citizens' Alliance. The subsequent snap election in August 2016 resulted in a landslide victory for the Tribune Movement, a far-right {{wp|neo-nationalist}} and {{wp|right-wing populism|right-wing populist}} party, which entered into coalition with the [[Farmers and Workers Union]] under President [[Francesco Carcaterra]]. The {{wp|liberalism|liberal}}-{{wp|centrism|centrist}} Citizens’ Alliance became the official party of opposition. The Federalists lost over 300 seats in total from both chambers of the [[Senate of Etruria|Senate]], while the Social Democrats lost over 200, sending the once dominating parties to third and fifth place respectively. | |||
In the most recent election in 2018, the new electoral law came into force. The Tribune Movement secured a second victory, gaining a {{wp|supramajority}} in the [[Chamber of Representatives (Etruria)|Chamber of Representatives]] and a two-thirds majority in the [[State Council of the Federation (Etruria)|State Council]] by itself, becoming the first party in Etruria since 1984 to form a single-party government. The Tribunes saw a net gain of 87 seats in the lower house and 28 in the upper house, the biggest increase of a sitting government in Etruria since 1984. The current political landscape since 2018 has come to be dominated by the Tribune Movement. | |||
Etruria’s federal system has allowed for the rise of state-exclusive political parties. Among the most prominent include [[Together for Carvagna]], [[Veratian National Party]], [[Chiastrine Democratic Party]] and much smaller minority parties such as, [[Piraean Liberty Party]], [[Carinthian and Novalian Party for Minorities]] and the [[Miruvian People’s Party]]. Etruria’s constitution prohibits political parties that promote or are dedicated to separatist causes. As of 2020, the Tribune Movement has majorities and governments in seven of the fifteen national states, followed by the Citizens who hold control over four states. | |||
Elections in Etruria are traditionally held every five years; however, the President holds the power to dissolve the Senate and call elections at will. The most recent election in 2018 was held two years after the election prior, being called at the height of the [[EC-Etruria Crisis]]. The next election is dated for 2023 but may be held earlier. Etruria’s elections from 1983 until 2000 utilised {{wp|first-past-the-post}}, before federal elections transitioned to {{wp|proportional representation}}. In 2017, the Tribune Movement government amended the federal electoral law introducing a new system that operations both FPTP and PR. The states are delegated the power to determine their electoral processes, with six of the seven Tribune Movement states reverting to FPTP from PR systems as of 2020. | |||
==== Constituent states ==== | ==== Constituent states ==== | ||
| Line 369: | Line 331: | ||
In order of population, the states are: | In order of population, the states are: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Map!!Name and flag!!Administrative centre!!Population!!Governor | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="18" |<center>{{Etruria labelled map}}</center> | |||
! colspan="5" |[[Administrative divisions of Etruria|States of Etruria]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Flag_of_Etrurian_Carinthia.png|30px]] [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]]||[[Praproče]]||5,448,369||[[Janez Hribar]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag_of_the_Republic_of_Pisa.svg|30px]] [[Dinara]] || [[San Alessandro]] ||5,248,480 || [[Augustina Faustini]] ([[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|CA]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag_of_the_Commune_of_Altidona.png|30px]] [[Altidona]] || [[Auronzo]] ||1,032,742 || [[Enrico Volpe]] ([[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|CA]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag of the Duchy of Chiastre.png|30px]] [[Chiastre]] || [[Carcoforo]] ||2,117,055|| [[Emmanuele Angrisani]] ([[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|CA]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag of Peravia.png|30px]] [[Peravia]] || [[Faulia]] || 7,925,386 || [[Alessandro Garavoglia]] ([[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|CA]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag of Cavarzere.png|30px]] [[Veratia]] || [[Carxeri]] || 9,352,687 || [[Giuliano Aurelio Vinci]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag of San Francesco.png|30px]] [[Aeolia]] || [[Porto di Sotirio]] ||1,128,553 || [[Luciano Giustiniani]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Flag of Andora.png|30px]] [[Andora]] || [[Accadia]] ||3,333,585 || [[Giorgio Maniero]] ([[Democratic Alternative for Etruria|DAE]]) | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:FlagofTorrazza.png|30px]] [[Torrazza]] ||[[Sagrado]]||3,956,111||[[Simone Parro]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:FlagofCavagna.png|30px]] [[Carvagna]] ||[[Stazzona]]||3,809,872||[[Annalisa Taddei]] ([[Citizens' Alliance (Etruria)|CA]]) | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Flag of Tyrrenhus State.png|30px]] [[Tyrrenhia]] ||[[Tyrrenhus]]||6,920,327||[[Pietro Andrea Ercolani]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Flag of Solaria.png|30px]] [[Solaria (State of Etruria)|Solaria]] || [[Solaria]] ||5,869,029||[[Vittore Amadeo Varro]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Flag_of_Navalia.png|30px]] [[Novalia]]||[[Vilanija]]||9,558,135|| [[Franjo Sarič]] ([[Farmers and Workers Union|FWU]]) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[File:Flag_of_Tarpeia.png|30px]] [[Tarpeia]]||[[Centuripe]]||1,700,655|| [[Nero Orlando]] ([[Tribune Movement|TM]]) | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="5" |[[Administrative divisions of Etruria|Federal Territories of Etruria]] | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[File:Flag of La Dogado.png|30px]] [[Il Dogado]] ||[[Povelia]]||988,882 ||[[Marco Antonio Cristofori]] ([[Democratic Alternative for Etruria|DAE]]) | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 415: | Line 379: | ||
* Concurrent List: includes subjects of common interest to both the Federal Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Federal as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Federal Government will prevail. | * Concurrent List: includes subjects of common interest to both the Federal Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Federal as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Federal Government will prevail. | ||
* Autonomous List: in effect replicates the constituent state list for the autonomous federal regions, with the concurrent list subordinated to ensure the constituent state's laws prevail over the AFR's. | * Autonomous List: in effect replicates the constituent state list for the autonomous federal regions, with the concurrent list subordinated to ensure the constituent state's laws prevail over the AFR's. | ||
=== Judiciary and law enforcement === | |||
{{Main|Judiciary of Etruria|Law enforcement in Etruria}} | |||
{{See also|Organised crime in Etruria}} | |||
The Etrurian judicial system is based on {{wp|Roman law|Solarian law}}, modified by the {{wp|Napoleonic code|Pantheonic code}} and later statutes. The [[Federal Court of Cassation (Etruria)|Federal Court of Cassation]] (''Corte Federale di Cassazione'') is the highest court in the country for both criminal and civil appeal cases. The [[Supreme Constitutional Court (Etruria)|Supreme Constitutional Court]] (''Corte Costituzionale Suprema'') rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution at both the federal and state level, should appeals be brought to the court from state-level supreme court rulings. In 2020, the [[Public Affairs Court (Etruria)|Public Affairs Court]] (''Corte Affari Pubblici'') was established to process all civil and criminal cases relating to {{wp|public administration}}, {{wp|worker's rights}} for {{wp|civil servants}}, {{wp|electoral law|federal electoral law}} and appeals relating to {{wp|public protest}}. | |||
[[File:Arma dei Carabinieri female officer.jpg|290px|thumb|left|A male and female member of the [[National Police Service (Etruria)|National Police Service]].]] | |||
From 1984 until 2017, law enforcement in Etruria was delegated to the states. Following the 2017 National Police Reform Act, all law enforcement in Etruria was federalised. Today, law enforcment is divided between the [[National Police Service (Etruria)|National Police Service]] (''Servizio di Polizia Nazionale''), which is the general law enforcement agency, and the [[Civil Security Service (Etruria)|Civil Sercurity Service]] (''Servizio di Sicurezza Civile''), which deals with federal crimes, combatting organised crime, financial and white collar crime. The National Police Service is divided into State Commands (''Commandi Stato''), Regional Commands (''Commandi Regionale''), Metropolitan Commands (''Comandi Metropolitano'') and Commune Commands (''Comandi Comune''). The National Police also has several subordinate agencies, the [[Federal Penitentiary Service (Etruria)|Federal Penitentiary Service]] (''Servizio Penitenziario Federale'') which manages the nation's prisons, the [[Auxiliary Community Police (Etruria)|Auxiliary Community Police]] (''Polizia di Comunità Ausiliaria''), which is dedicated to {{wp|community policing}} and acts as a reserve for the main police force in the event of natural disasters or major urban disturbances such as riots. The last two subordinate agencies are the [[Maritime and Customs Service]] (''Servizio Marittimo e Doganale''), which is dedicated to regulating and facilitating international trade, collecting import duties, and enforcing regulations, including trade and customs, and finally the [[Coast Guard (Etruria)|Coast Guard]]. | |||
Since their appearance in the late 18th century, Etrurian organised crime and criminal organisations have infiltrated the social and economic life of many regions in central and southern Etruria, the most notorious of which being the [[Tyrrenhian Mafia]], which would later expand into some foreign countries including [[Piraea]] and [[Marirana]]. Other organised crime groups include the [[Novalian Bratovštine]] and the [[Solarian Cricche]], while these organisations saw their power and influence peak during the 1950s and 1960s, they remained a significant presence in Etrurian life. Much of their crimes today are geared toward {{wp|gambling}}, {{wp|racketeering}}, {{wp|human trafficking}}, {{wp|drug trafficking}}, {{wp|arms trafficking}}, {{wp|prostitution}}, {{wp|construction}}, {{wp|tourism}} and {{wp|money laundering}}. From 1990 to 2010, Mafia recepits were estimated to have reached 10% of Etruria's GDP in worth. In 2018, the Etrurian government launched [[Operation Gladio]], the largest law enforcement operation in Etrurian history. The operation involved law enforcement agencies, the military and domestic intelligence service and resulted in the arrest of over 13,000 suspected Mafia members of various ranks and positions, the seizure of assets and property. While the operation was considered a "colossal success" and effectively crippled the mafia in Etruria, it did not go without criticism and condemnation, especially over its numerous reported abuses of legal rights, human rights and numerous cases of torture and {{wp|Death in custody|deaths in custody}}. | |||
==Foreign relations and military == | ==Foreign relations and military == | ||
{{Main|Foreign relations of Etruria}} | {{Main|Foreign relations of Etruria}} | ||
Etruria is a founding member of the [[Community of Nations]], [[International Council for Democracy]] and the [[Association of Solarian Nations]]. Etruria is also a member of the [[Atomic Energy Commission]], [[Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs|GIFA]] and the [[International Trade Organisation|ITO]], where it long offered strong support. Etruria is also a leading member of the [[Aurean Forum]], which aims to manage traffic and administration of the [[Aurean Straits]]. Following the establishment of the [[Etrurian Third Republic]] in 1948, Etrurian foreign policy was guided by the principle of "active neutrality", in which the country would remain neutral in relation to inter-bloc rivalries while engaging productively with nations and organisations alike. The [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|Military government]] throughout its 24-year rule mostly maintained the policy, though it was highly supportive of confronting socialism across Euclea and Coius, re-establishing its close relationship with [[Werania]] and [[Estmere]] for the first time since the [[Solarian War]]. The military dictatorship's pro-Eastern Euclea platform protected it serious criticism over its vagrant human rights abuses and authoritarianism. The EC became the strongest supporter for the democratic transition in 1984. Since the restoration of democracy in 1984, until the No-vote in the [[Etruria Euclean Community membership referendum, 2016|EC membership referendum in 2016]] successive governments sought to bring Etruria closer to the [[Euclean Community]], with the ultimate goal of securing membership. Etruria emerged as a vocal advocate for {{wp|human rights}}, {{wp|civil liberties}} and the protection of minorities across the world. | |||
[[File:Carcaterra-Hermansdotter.jpg|260px|thumb|right|President [[Francesco Carcaterra]] with EC High Commissioner [[Niina Hermansdohter]] in 2019.]] | |||
Despite successes in bringing Etruria closer to the EC, the defeat of the pro-membership campaign in the 2016 referendum and the electoral victory for the {{wp|right-wing populism|right-wing populist}} {{wp|neo-nationalism|neo-nationalist}} [[Tribune Movement]] resulted in a rapid souring of ties. Between 2016 and 2018, the EC was a vocal critic of the Tribune Movement's {{wp|democratic backsliding}}, culminating in the [[EC-Etruria Crisis]]. Etruria withdrew from the [[International Council for Democracy]] in 2018, claiming it was "built to promote liberal-leftism with near tyrannical means." The same period saw Etruria's government turn away from international institutions and multilateralism, claiming global bodies had infringed on national sovereignty. Conversely, under the Tribune Movement government, Etruria has placed greater emphasis on the [[Association of Solarian Nations]] and is currently planning on proposing a second body for the Solarian Sea states (Etruria, [[Montecara]] and [[Emessa]]), to include defence and economic ties. The outbreak of the [[Tsabaran Civil War]] and resurgence of [[Zorasan]] in late 2019 has seen a rapproachment between Etruria and the EC, led primarily by friendly governments in [[Estmere]] and [[Werania]]. Many observers have noted that the rapproachment can be credited to the Etrurian government seeing such a recovery of ties as key to "Etruria First." | |||
[[File:CarcaterraXiannan.jpg|260px|thumb|left|President Carcaterra with [[Xiaodong]]'s [[Yuan Xiannian]].]] | |||
One long term issue for Etrurian foreign policy has been its antagonistic relations with its smaller neighbours, specifically [[Piraea]] and [[Galenia]]. Both countries had been occupied historically by Etruria and most recently during the [[Solarian War]], this conflict saw numerous war crimes, such as the [[Etrurianisation of Piraea]], which some consider to be {{wp|genocide}}. Etruria's policy of {{wp|genocide denial}} both in politics and society has been a major thorn in its ties with these countries and was deepened with the 2018 National Dignity Act in Etruria, which prohibited any referencing of historic war crimes in schools and universities, both verbally and printed. [[Etrurian nationalism]] has also provoked crises if only brief, with its neighbours. | |||
Etruria is regardas as a {{wp|middle power}} by commentators, with it enjoying a high degree of military capabilities and significant {{wp|soft power}}, through language, cuisine, music and other cultural aspects. | |||
=== Military === | === Military === | ||
{{Main|Etrurian Defence Force}} | {{Main|Etrurian Defence Force}} | ||
The [[Etrurian | The [[Etrurian Army]], [[Etrurian Navy]], [[Etrurian Air Force]] and the [[Auxiliary Defence Force]] collectively form the [[Etrurian Defence Force]], under the Supreme Command (Commando Supremo), presided over by the President of Etruria. The armed forces is both voluntary and conscripted, as of 2016 the armed forces had 290,000 active personnel and 250,000 reserve, with a defence budget of $60.79 billion. Defence is managed by the [[Federal Ministry of National Security (Etruria)|Federal Ministry of National Defence]]. | ||
[[File:Esploratori.png|250px|thumbnail|left|An [[Etrurian Defence Force]] solider of the [[Esploratori]] in western Novalia.]] | [[File:Esploratori.png|250px|thumbnail|left|An [[Etrurian Defence Force]] solider of the [[Esploratori]] in western Novalia.]] | ||
The Etrurian Army's size is estimated at around 330,500 soldiers. In recent years, the Etrurian Army has played a sizeable role in international peacekeeping, and regularly takes a role in supporting law enforcement, search and rescue and disaster response. The [[Etrurian Navy]] primarily operates in the [[Solarian Sea|Solarian]], [[Mazdan Sea|Mazdan]] seas and the [[Gulf of Assionaire]], and conducts operations such as maritime patrol, search and rescue for the section of the Solarian and Mazdan seas under Etrurian sovereignty, as well as hydrographic measurements and research. The current position of the [[Etrurian Air Force]] is similar to that of the Navy, conducting aerial patrols, search and rescue and providing logistical support to international peacekeeping, while it has taken a leading role in transporting aid to disaster zones and conflicts. | |||
The final branch of the armed forces is the Auxiliary Defence Force, which is a popular militia that also serves as the country's gendarme in times of national emergency. The ADF is subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior during peace-time and in war-time, it is subordinate to the Supreme Command. As of 2016, the ADF had a strength of 55,000 active members and an estimated 255,000 reserve members. Since 2010, the ADF has also served as an emergency response force, assisting in the aftermaths of earthquakes. Most recently several ADF units were engaging in confronting several separatist movements in Carinthia and Marolev-ethnic armed groups, including the [[Battle of Starše]] in 2011. | The final branch of the armed forces is the Auxiliary Defence Force, which is a popular militia that also serves as the country's gendarme in times of national emergency. The ADF is subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior during peace-time and in war-time, it is subordinate to the Supreme Command. As of 2016, the ADF had a strength of 55,000 active members and an estimated 255,000 reserve members. Since 2010, the ADF has also served as an emergency response force, assisting in the aftermaths of earthquakes. Most recently several ADF units were engaging in confronting several separatist movements in Carinthia and Marolev-ethnic armed groups, including the [[Battle of Starše]] in 2011. | ||
The FMND previously oversaw the operations of Etruria's entire intelligence apparatus, until the [[Domestic Security Service (Etruria)|Domestic Security Service]] (Servizio di Sicurezza Domestico; SSD) was transferred to the [[Federal Ministry of Civil Security (Etruria)|Federal Ministry of Civil Security]] in 2018. Today, the FMND oversees the operations of the [[External Intelligence Service (Etruria)|External Intelligence Service]] (Servizio Intelligenza Esterno; SIE), which is tasked with providing the government with intelligence regarding foreign matters. The EIS also includes the [[Information Security Service (Etruria)|Information Security Service]] (Servizio Sicurezza Informazioni; SSI), which is tasked with providing {{wp|signals intelligence}} and {{wp|information assurance}} for the government and armed forces. The FMND also has some jursidication over the [[Strategic Intelligence Directorate (Etruria)|Strategic Intelligence Directorate]] (Direzione Intelligenza Strategica; DIS), which is the {{wp|military intelligence}} body for the armed forces. | |||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
{{Main|Economy of Etruria}} | {{Main|Economy of Etruria}} | ||
Etruria is the world's 18th largest economy as of 2019, with a nominal GDP of approximately $1.025 trillion, and the 15th largest economy with a GDP PPP of $1.850 trillion. Etruria has a {{wp|capitalist}} {{wp|mixed economy}}. The GDP per capita as of 2017 is $15,637 (nominal) and $33,747 (PPP). Etruria is classified as a {{wp|newly industrialised economy}} and has developed several highly competitive sectors, including its manufacturing, agriculture and tourist sectors. Its primary exports include {{wp|light goods}}, {{wp|home appliances|home}} and {{wp|electronic appliances}} and in recent decades, it has become a major producer of {{wp|locomotive}}s, {{wp|automobile}}s, {{wp|construction equipment}} and {{wp|aircraft}}. | |||
Etruria is the | Etruria’s economy is noted to have suffered a [[Lost Generation (Etruria)|Lost Generation]], with economists agreeing that Etruria is at least two-decades behind its wealthier neighbours in Eastern Euclea. The “lost decades” are blamed on the [[Solarian War]] (1943-1946) and the failure in post-war reconstruction, where {{wp|economic misgmanagement|incompetence}}, {{wp|corruption}} and {{wp|Bottleneck (production)|bottlenecks}} caused profound economic instability during the [[Etrurian Third Republic]] (1948-1960). Pro-market reforms during the Military government period (1960-1983) saw some limited success in confronting the structural flaws in the economy, enabling Etruria’s industrial output to reach pre-war levels and exceed them by 1978. Following the restoration of democracy in 1983, successive democratic governments instituted neoliberal reforms, producing sufficient dynamic growth to see Etruria become a developed economy by 2008 according to the [[International Trade Organisation]]. Etruria's economic growth averaged between 4.5-5% between 1985 and 2015, in recent years growth has increased to average 5.5% between 2015 and 2020. | ||
Etruria | |||
Today, Etruria’s economy remains mixed with the federal government regularly assisting national champions, such as [[Caviglia Aeronautica]], [[Nettuno-Accadia]], [[Casa]] and [[Valentino]]. Many economists also classify Etruria as {{wp|Corporatism#Neo-corporatism|neocorporatist}}, with significant degrees of {{wp|state-aid}} and a vibrant trade union movement aimed at promoting social enterprise and worker welfare. | |||
=== Industry === | === Industry === | ||
Industry accounts for 38% of Etruria’s GDP, and is the highest employer, with an estimated share of 43% of the national labour force. During the Military Dictatorship and subsequently, manufacturing has been the primary focus of government investment. This investment has supported the establishment of global brands in various sectors. | |||
[[File:Naples, Central station, gorgeous long-distance train.jpg|250px|thumbnail|right|Caviglia Rotaia's G10 high-speed train is a major product. ]] | [[File:Naples, Central station, gorgeous long-distance train.jpg|250px|thumbnail|right|Caviglia Rotaia's G10 high-speed train is a major product. ]] | ||
In 2018, Etruria produced an estimated 1.3 million {{wp|automobiles}} and {{wp|motorcycles}}, the Nth largest in the world. These vehicles are directed toward the domestic and Euclean markets, where they have proven highly competitive in the lower-price range. Etruria is also noted as a global producer of {{wp|locomotives}}, {{wp|bus}}es and {{wp|trams}}, where [[Caviglia Rotaia]] has become a global brand in the production of the former as well as high-speed trains for the developing Coian economies. | |||
During the 2000s and 2010s, [[Caviglia Aeronautica]] emerged as a growing producer of both military and civil aircraft. The company is lauded as a national champion and is the Nth largest producer of short-haul and regional-haul aircraft. The company is also the Nth largest producer in {{wp|private aircraft}}, including {{wp|helicopters}}. | |||
[[File:CA70 Passero.png|200px|thumbnail|left|The CA70 Passero military transport aircraft, developed by [[Caviglia Aeronautica]], the Nth largest producer of civil aircraft and Nth largest producer of military aircraft.]] | [[File:CA70 Passero.png|200px|thumbnail|left|The CA70 Passero military transport aircraft, developed by [[Caviglia Aeronautica]], the Nth largest producer of civil aircraft and Nth largest producer of military aircraft.]] | ||
Etruria has since developed a strong light goods and appliance industry, with noted brands such as [[Casa]] and [[Valentino]] becoming the Nth largest producers of {{wp|kitchen appliances}}, {{wp|electronic appliances}} and {{wp|home appliances}}. Casa is known to produce almost 88% of Etruria’s televisions and home entertainment systems purchased domestically. | |||
Etruria is also a praised shipbuilding, with its high capacity for oil tankers, freighters, cruise ships, ferries and personal yachts and mega yachts. [[Nettuno-Accadia]] is one of the largest shipbuilders in the world, is known to high quality vessels. | |||
Other areas in industry present in Etruria include mining, logging, steel producing and industrial chemicals. The Etrurian steel industry almost vanished during the 1960s, as the highly centralised industry dominated by Acciaio Etruriano became a {{wp|zombie company}}, owing to poor competitiveness and gross mismanagement. AE was privatised in 1988 and broken up into three smaller companies that have proven more dynamic in recent years. | |||
=== Tourism === | === Tourism === | ||
Etruria is the | Etruria is one of the most visited countries in the world, with an estimated 48.5 million visitors in 2014. Successive Etrurian governments have made use of the country’s natural environment, historic sites and cities to launch successful tourism campaigns. Etruria’s tourism industry is in part centred around the cities of [[Tyrrenhus]], [[Solaria]], [[Povelia]] and [[Stazzona]], while the interior and coasts of [[Novalia]] have since overtaken the cities as the most popular tourist destinations. | ||
[[File:Cavtat Croatia 2008-10-07.JPG|200px|thumbnail|right|The Novalian coast has become a popular destination for Euclean tourists during summertime. ]] | [[File:Cavtat Croatia 2008-10-07.JPG|200px|thumbnail|right|The Novalian coast has become a popular destination for Euclean tourists during summertime. ]] | ||
Tourism provides an estimated 14.5% of Etruria’s GDP ($ ) and employs 5.1% of the workforce ( xx workers) in 2018. | |||
=== Agriculture === | |||
Throughout much of its economic history, Etruria had been reliant on its agricultural sectors. It was not until the late 19th century, that industry had sufficiently replaced agriculture that its agrarian economic system was replaced. However, agriculture still plays a prominent role in Etruria’s economic output. Successive governments since the 1910s have implemented numerous measures and schemes to protect and support Etrurian farms. Since the 1960s, Etruria has actively impeded the emergence and growth of agribusinesses, protecting the small family-owned plots that have defined agriculture since the middle-ages. | |||
[[File:Vineyards in Tuscany quality image.jpg|250px|thumbnail|left|Vineyards of Carvagna produced much of the country's high quality wines. ]] | [[File:Vineyards in Tuscany quality image.jpg|250px|thumbnail|left|Vineyards of Carvagna produced much of the country's high quality wines. ]] | ||
As of 2018, there an estimated 1.95 million farms in Etruria, 47% being found in Vespasia (39% in the south and 61% in the north), 20% in Novalia and 33% in Carinthia. Over 90% of Etruria’s farms are small family-owned plots, averaging only 10 hectares in size. The number of farms has consistently decreased since the 1960s owing to rural-to-urban migration and cheaper imports from Coius or the Asterias. | |||
Etruria is one of the | Etruria is one of the largest producers of {{wp|wine}} in the world and a major producer of {{wp|chesse}}, {{wp|olive oils}} and horticulture. | ||
=== Infrastructure === | === Infrastructure === | ||
Until the early 20th century, Etruria’s infrastructure was among the weakest in Euclea for a major nation. For decades, Etruria had among the major nations, the shortest and most limited rail network. It was not until the 1920s that Etruria expanded its railways beyond three lines connecting the state and national capitals. During the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], the Etrurian government launched a major construction program, aimed at supporting its military requirements. This resulted in the creation of the acclaimed [[Autostrada of Etruria|Autostrade]] and {{wp|Strade Provinciali}} road network. The war also saw dramatic expansion of railroads, with 12,500km of track added between 1928 and 1934. The project is renown for its use of penal workers and women. | |||
Etruria has 998,365 km (620,355 mi) of serviceable roads, including 12,507 km (7,771 mi) of motorway. Both serviceable roads and motorways are state-owned and managed by [[Servizio Stradale Federale]], though several regions have seen private companies manage the road network. Etruria’s established road-network is praised for its high quality and connectivity, consistent criticisms regarding the poor quality of roads in mountainous and isolated areas have rarely been met. In 2019, the Etrurian government launched a multi-billion euclo project to modernise and expand roads and highways in these regions. | |||
Etruria | The national railway network, state-owned and operated by [[Amministrazione Ferroviaria Federale Etruria]], in 2019 totalled 18,888 km (11,736 mi) of which 16,213 km (10,074 mi) is electrified, and on which 5,100 locomotives and railcars run. Between 2000 and 2010, 5,900 km of railroad were upgraded to support {{wp|high-speed train}}s, and between 2010 and 2014, this was expanded 6,500 km. In 2014, the [[Linea Leopardo]] high-speed train network was launched. The Linea Leopardo travels the length of Etruria’s eastern coastline. In 2018, the [[Linea Leopardo II]] project was launched with the aim of establishing high-speed links between the major coastal cities and the interior to the west. Etruria has 11 rail border crossings through Aventine settings and elsewhere. Plans for increase the number of rail crossings into [[Gaullica]] and [[Auratia]] are currently underway. | ||
Etruria | Etruria has 18 international airports, with the primary hubs being [[Pietromontecorvino-Tyrrenhus International Airport|Pietromontecorvino]] in [[Tyrrenhus]], [[Francesco Cesare Candreva International Airport|Francesco Cesare Candreva]] near [[Povelia]], and [[Romolo Alessandri Solaria International Airport|Romolo Alessandri-Solaria]]. There are 106 regional airports as of 2018, with plans for the construction of sixty more regional level hubs by 2030. Etruria’s national carrier is [[Volaretruria]], which serves 82 destinations worldwide. | ||
[[File:Panorama di Genova (porto commerciale e porto antico).jpg|250px|thumb|left|One of the many container ports of Accadia. ]] | |||
Etruria operates 39 major seaports, the largest being [[Accadia]], which Etruria’s largest and the largest Euclean seaport on the Solarian Sea. Etruria operates a merchant fleet of 477 vessels, an increase of 13% as of 2019, compared to 2010. Etruria operates several ferry links, connecting regions and cities across Povelian Gulf, Insular Etruria and multi-national destinations, including [[Emessa]] and [[Auratia]]. | |||
=== Science and technology === | === Science and technology === | ||
Historically, Etruria has produced numerous scientists and inventors, with Etruria’s prominent role in the Euclean renaissance. Notable Etrurian scientists and engineers include, [[Leonardo Renanti]] (1511-1567) who pioneered astrology, [[Enrico Venti]] (1489-1539) who made vital discoveries about human anatomy. In more modern times, [[Alessandri de Vecchi]], who alongside [[Edmund Schultze]], developed vaccines for {{wp|anthrax}} and made breakthroughs in the study of {{wp|rabies}} during the 19th century. Novalian [[Stepan Staric]] played a key role in the development of the {{wp|telephone}} and [[Viktor Carraturo-Baric]] was vital in the development of {{wp|vulcanised rubber}}. | |||
[[File:Istituto del nuovo secolo.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The New Century Institute is a major recipient of government funding into research and development.]] | [[File:Istituto del nuovo secolo.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The New Century Institute is a major recipient of government funding into research and development.]] | ||
Today, Etruria is host to several major institutions and research groups that focus on engineering, energy, robotics and communications. The [[Innocenzo Dametto Institute]] is one of Euclea's leading research and development bodies, looking into cleaner energy production. The [[New Century Group]] is a state-backed series of R&D institutions dedicated to pioneering future technologies, primarily {{wp|Artificial Intelligence}}, {{wp|Quantum computing}}, {{wp|information technology}} and {{wp|robotics}}. As of 2018, the Etrurian government spent $23.5 billion on R&D, a 11% increase from 2016, ranking Etruria as one of the highest spenders on research and development. | Today, Etruria is host to several major institutions and research groups that focus on engineering, energy, robotics and communications. The [[Innocenzo Dametto Institute]] is one of Euclea's leading research and development bodies, looking into cleaner energy production. The [[New Century Group]] is a state-backed series of R&D institutions dedicated to pioneering future technologies, primarily {{wp|Artificial Intelligence}}, {{wp|Quantum computing}}, {{wp|information technology}} and {{wp|robotics}}. As of 2018, the Etrurian government spent $23.5 billion on R&D, a 11% increase from 2016, ranking Etruria as one of the highest spenders on research and development. | ||
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
{{Historical populations | |||
|type = sdsd | |||
|footnote = Source: Ufficio Federale di Statistica | |||
|1900|31475000 | |||
|1906|35500000 | |||
|1916|38021000 | |||
|1926|40148000 | |||
|1950|45800000 | |||
|1966|51213321 | |||
|1976|59336807 | |||
|1986|60982147 | |||
|1996|62250325 | |||
|2006|63871030 | |||
|2016|65596083 | |||
}} | |||
According to the 2014 census, Etruria had a population of 65.59 million - the [[Euclea#List of states and territories|4th largest]] in [[Euclea]] and [[List of sovereign states and dependent territories (Kylaris)|15th]] in the world. Etruria has a population density of 119.58/km2 (309.7/sq mi), relatively lower than the Euclean standard. Population in Etruria is distributed unevenly, with concentrations found along the coastlines, the [[Eugenian Plain]] and the [[Carinthian Plain]] in the north and north-west respectively. Etruria is the one of the few countries in East Euclea to meet the replacement rate of 2.1, with a {{wp|total fertility rate}} (TFR) of 2.4 as of 2018, as a result, Etruria's population is expected to exceed 70m by 2028 through mostly natural births instead of migration. The average age of Etruria is 32, among the lowest in Euclea. Etruria's birthrate compared to other Euclean countries has been subject to wide debate among statisticians, with many claiming income, standards of living and cultural values have played a role in maintaining the replacement rate. | |||
During the 1990s and 2000s, Etruria experienced a large wave of immigration from former colonies [[Satria]] (55%) and [[Badawiya]] (45%), by 2010 it was estimated that these migrants constituted 6.4% of the population. This number has since fallen as many migrants moved from Etruria to other countries in [[Eastern Euclea]]. | |||
Populations descdended from Etrurian colonists and immigrants can be found in [[Asteria Superior]] and [[Asteria Inferior]]. Beginning with the colonisation of [[Marirana]] in the late 15th century, significant numbers of colonists from [[Exalted Republic of Povelia|Povelia]] and other Etrurian city states would go on to settle in what is also now [[Belmonte]] and [[Imagua and the Assimas]]. An estimated 257,400 left metropolitan Etruria for the Asterias during the 16th century. This would rise to 560,000 in the 17th century and 333,000 in the early 18th century. Following the [[Etrurian Revolution]], migration to the Asterias would remain steady at 80,000 every decade between 1800 and 1830. The onset of the Industrial Revolution and urbanisation during the late 19th century saw Etrurian migration to the Asterias diminish. Another key diaspora can be found [[Caldia]], which has historically been a popular destination for political exiles and free-thinkers expelled due to their beliefs. Over 5,000 Etrurians settled in [[Caldia]] during the [[Etrurian Revolution Republic]] (1938-1946) and a further 55,000 during the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|Military Dictatorship]] (1960-1983). | |||
=== Ethnic groups === | === Ethnic groups === | ||
The constitution of the Etruria | {{Main|Ethnic groups in Etruria}} | ||
[[ | Etruria is a {{wp|multi-ethnic state|multinational}} and {{wp|multi-lingual state|multi-lingual}} nation. The Etrurian nation state since its formation during the [[Etrurian Revolution]] in the 1780s has recognised this constitutionally and culturally since. The 1983 Constitution differs from previous basic laws as it defines the multinational nature of Etruria as a "federal union of three nations and six peoples", this definition plays into the degree of recognition and rights afforded to the ethnic groups of Etruria. The same definition lends to Etruria being described as a {{wp|Plurinationalism|plurinational state}}. {{Wp|Regionalism}} within [[Vespasia]] has led to conflicts over the definition provided by the constitution. The identity of Etruria is widely based on the infusion of the territorial and ethnolinguistic idenities of its "three nations", insofar that the Etrurian identity is built from the overlap of the three dominant groups. The issue of national identity has been a long-term controversial topic in Etrurian society. | ||
[[File:EtruriaEthnicMap.png|290px|thumb|left|Map detailing the ethnic layout of Etruria per commune.]] | |||
The "Three Nations" (''Nazioni'') are [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]], [[Novalia]] and [[Vespasia]]. The definition of a nation is based upon the historical boundaries of the ethnolinguistic state prior to unification under the [[Etrurian First Republic]]. While Carinthia and Novalia can claim to be functional nationstates before 1784, however, this definition sparked the "Vespasian Debate", owing to Vespasia being a geographical term for the {{wp|Italian language|Vespasian-speaking}} region of Etruria, which prior to 1784 consisted of thirteen distinct [[Historic states of Etruria|city states and republics]]. The "Vespasian Debate" centres around whether the constitution should defined Etruria as a "Federal Union of sixteen nations and six peoples", owing to the lack of a Vespasian nationstate. | |||
{{Bar box | |||
|width = 280px | |||
|float = right | |||
|title = <small>Composition of Etruria by ethnicity (2016)</small> | |||
|titlebar = #ddd | |||
|bars = | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|Italians|Vespasian}}|#004023|63.45}} | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|Croatians|Novalian}}|#531c21|13.30}} | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|Slovenes|Carinthian}}|#324b6d|10.04}} | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|Serbians|Miruvian}}|#a64200|4.18}} | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|Greeks|Piraean}}|#ab8a07|3.51}} | |||
{{Bar percent|{{wp|French|Gaullican}}|#a2b7d5|1.19}} | |||
{{Bar percent|[[Marirana|Mariranian]]|#c24651|1.18}} | |||
{{Bar percent|[[Zorasan|Zorasani]]|#00a65b|1.09}} | |||
{{Bar percent|[[Satria|Satrian]]|#db9198|1.06}} | |||
|caption = <small>Source: Ufficio Federale di Statistica (UFS)</small> | |||
}} | |||
The "Six Peoples" (''Popoli'') refers to the largest and settled ethnic groups of Etruria; {{wp|Italians|Vespasians}}, {{wp|Croatians|Novalians}}, {{wp|Slovenes|Carinthians}}, {{wp|Serbians|Miruvians}}, {{wp|Greeks|Piraeans}} and {{wp|French people|Gaullicans}}. While being recognised as a People affords equal civil and political rights, in reality, Etruria has experienced discrimination along ethnic lines since its unification in 1786 and it was not until the 1984 Constitution, that either the Miruvians or Gaullicans were officially recognised as ethnic groups in Etruria. Despite official recognition, the Etrurian census provides the options of Etrurian, Vespasian, Carinthian or Novalian for identity, owing to the constitution's definition of an Etrurian citizen as a "person who resides, inhabits and identifies with the Federation of Etruria", as Piraeans, Gaullicans and Miruvians (though a stateless multi-national ethnic group) can identify with separate and distinct nationstates outside of Etruria, providing these options in the census would "contradict the constitutional definition of an Etrurian." | |||
According to the 2016 census, 87% of citizens idenify as Etrurian, 11% identified as their ethnicity (4% Vespasian, 4% Novalian and 3% Carinthian) and 2% idenitifed as "Other." The census showed that of the national population, 63.45% are {{wp|Italians|Vespasian}}, 13.30% {{wp|Croatians|Novalian}}, 10.04% {{wp|Slovenes|Carinthian}}, 4.18% {{wp|Serbians|Miruvian}}, 3.51% {{wp|Greeks|Piraean}}, 1.19% {{wp|French|Gaullican}}, 1.18% [[Marirana|Mariranian]], 1.09% [[Zorasan|Zorasani]], 1.06% [[Satria|Satrian]], 0.98% [[Tsabara|Tsabaran]] and 0.02 [[Savader]]. | |||
=== Lanugages === | |||
Etruria has three official languages {{wp|Italian language|Vespasian}}, {{wp|Croatian language|Novalian}} and {{wp|Slovenian language|Carinthian}}. All three languages and are used for the federal and state government's acts and laws, this is required constitutionally in all fifteen states regardless of ethnic makeup. This has been in place since the [[Etrurian First Republic]] as a means of fostering "unity and cohesion through the shared politic." Owing to the limited intermixing geographically of the three national ethnicities, everyday life is generally spoken in the respective "nation's" language. Regions where intermixing is prevalent, notably the Tarantine regions and the country's largest cities, Vespasian is most spoken in everyday and cultural life. Education across the country is conducted evenly in Vespasian, Novalian and Carinthian, this policy is mandated by the constitution and is known as "Tri-lingual Education". This has enabled the an overwhelming majority of Etrurians to speak the opposing languages from their mother tongue to an advanced degree by completion of secondary schooling. | |||
Exceptions to the TLE rule are found in certain states, notably [[Dinara]] and [[Peravia]], where communes in the far north boast sizeable {{wp|French people|Gaullican}} populations local schools teach the Gaullican language to Vespasian students over Novalian and Carinthian. The most prominent dialect of {{wp|French language|Gaullican}} spoken is {{wp|Franco-Provençal language|Gaullo-Aventine}} and is the dialect taught to Vespasian students. | |||
The Novalian language | The Etrurian constitution recognises a series of {{wp|regional languages}}, though the number has been reduced steadily since the 1888 constitution's universal recongition. The most widely spoken regional languages recognised include {{wp|Greek language|Piraean}}, {{wp|Serbian language|Miruvian}} (viewed as distinct to {{wp|Croatian language|Novalian}}) and {{wp|Franco-Provençal language|Gaullo-Aventine}}. The remaining regional languages are recognised dialects of {{wp|Italian language|Vespasian}}, the only Vespasian dialects to be recognised as regional languages are {{wp|Venetian language|Povelian}}, {{wp|Piedmontese language|Dinarian}} and {{wp|Neapolitan language|Solarian}}. With the exception of Miruvian and Piraean, regional languages may be used for state acts, laws, public signage and education, however the three national languages must also be present. | ||
=== Religion === | === Religion === | ||
In 2018, the proportion of Etrurians who identified themselves as Solarian Catholic Christians was 80.4%. Catholicism is the {{wp|state religion}} of Etruria, having been restored in 2022, for the first time since 1984. Catholicism has been the dominant religion in Etruria for over a millenia, when it was first introduced during the days of the [[Solarian Empire]]. Since its founding, Etruria has been the home of the [[Solarian Catholic Church|Holy See]] of the Catholic Church, based in the enclave of [[Tiberunum]] within the boundries of [[Solaria]]. Between 989 and 1787, the Church governed territory in southern Etruria through the [[Ecclesiastical State]] until its annexation by the [[Etrurian First Republic]] during the [[Etrurian Revolution]] and [[Etrurian Revolutionary Wars]]. The domination of the [[Pantheonisti]] faction during the revolution introduced a [[Pantheonist Republicanism|deeply religious form]] of {{wp|republicanism}}, which empowered and elevated Catholicism in all areas of life. During the Revolution, numerous non-Catholic Sotirian minorities were persecuted or expelled entirely from Etruria, including numerous [[Amendism|Amendist]] groups. The First Republic's near success in transforming Etruria into a religious homogenous nation would only be halted with the Republic's collapse during the [[Caltrini Restoration]]. The politically and constitutionally protected prominence of Catholicism would remain in place until the [[San Sepulchro Revolution]] of 1888 and the establishment of the [[Etrurian Second Republic]], which provided guarantees of religious freedom and equality. Between 1888 and 1938, there was a revival in non-Catholic religions, including a resurgence in Amendist churches and a more public display of faith by the country's {{wp|Orthodox Christianity|Episemalist churches}} in [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]] and [[Novalia]]. Political preference and cases of discrimination and repression, osentsibly returned under the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military government]] (1960-1984), which in some areas increased the predominance of Catholicism and the influence of the Church. Today, while not formally enshrined in law or policy, the Catholic Church still enjoys significant influence over government policy and in the everyday lives of Etrurian citizens. | |||
<gallery mode=packed heights=100 style="font-size:88%;line-height:120%"> | |||
[[File: | File:Duomo_-_Bergamo_-_panoramio.jpg|Auronzo Cathedral | ||
File:Florence_Duomo_from_Michelangelo_hill.jpg|Saint Jerome's Basilica in [[Stazzona]] | |||
File:Basilica_Venecia.jpg|Basilica of All Apostles in [[Povelia]] | |||
File:Milano,_Duomo,_2016-06_CN-03.jpg|Saint George over Solis Cathedral in [[Faulia]] | |||
File:NapoliSanFrancescoDaPaolaFacciata.jpg|Tiberunium Basilicia | |||
File:Zagreb_Cathedral_2020.jpg|Vilanja Cathedral | |||
</gallery> | |||
The largest non-Catholic Sotirian minority in Etruria is {{wp|Orthodox Christianity|Episemalism}}, which is practiced by 7.70% (4.9 million inhabitants) of the population. Episemalism is practiced near exclusively by {{wp|Serbians|Miruvians}} and {{wp|Greeks|Piraeans}} in the west of the country. The vast majority of Episemalists fall under the jurisdiction of the [[Ecumenical Patriarchate of Arciluco]], while a small minority belong to independent churches. Episemalists until the restoration of democracy in 1984, had long been one of the most repressed religious minorities in Etruria, where it was often viewed by government and society that Episemalism was a connotation for {{wp|Slavs|Marolevic}} nationalism and separatism. The Episemalists [[Bonfire of the Heresies|suffered in particular]] under the [[Etrurian First Republic]], who sought to either expell or convert its adherents. The revival under the Second Republic coincided with a warming of public opinion and an embrace of religious plurality. Repression returned under the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] (1938-1946) and the military dictatorship, with the former seeking to convert or expel the entire minority, while the latter sought to repress the Episemalist churches as part of its response to the [[Western Emergency]]. The restoration of democracy in 1984, once again guaranteed religious freedoms and since, the Episemalist Church in Etruria has noted a revival and more public display of its presence. | |||
Amendist churches constitute the smallest Sotirian minority, including an estimated 156,000 {{wp|Calvinism|Kasperists}}, 200,000 members of the [[United Reform Church of Etruria]], 100,000 members of individual Amendist churches. Etruria historically housed a small number of [[Witterites]], who arrived in Etruria following the 1888 Revolution, due to its liberal religious freedoms. However, the estimated 2,400 Witterites were ultimately killed during the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] and no community has since returned. The largest Amendist group in Etruria are the [[Cavernicoli]], who number 497,000 according to the 2014 census. The Cavernicoli originate as homegrown Amendist movement in northern [[Dinara]] state, who practiced their faith underground in secret. Collectively, the Amendist minority constitutes 1.49% of the national population. | |||
In 2014, 6.78% of the population identified as {{wp|atheism|atheist}} or {{wp|irreligious}}. It should be noted that Etruria records irreligion and atheism as the same on its official census and so no breakdown of this number is possible. This is an increase of 2.3% from the 2004 census. | |||
[[File:Cupola del duomo di firenze, vista, sinagoga 01.JPG|260px|thumb|right|The Stazzona Synagogue is the largest in Etruria.]] | |||
[[File:Rome Masjid.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The Grand Mazar of Tyrrenhus is the largest in southern Euclea by total land area.]] | |||
The largest non-Sotirian faith practiced in Etruria is [[Irfan]], where an estimated 2.70% (1,725,002 inhabitants) of the population identify as Irfani. Irfani have had a presence in Etruria as early as the 16th century, where many would settle primarily in [[Povelia]], owing to the city's lucerative trade with northern Coius. The vast majority of Irfani in Etruria originate from either [[Zorasan]], parts of [[Satria]] as migrants. 89% of the country's Irfani identify as XX and the remainder as XX. The next largest non-Sotirian minority is {{wp|Judaism|Atudism}}, which stands at 1.89% (1,207,501 adherants). According to some historical sources, the Atudites may have been present in Etruria as early as the 2nd Century CE, where many fled across the [[Solarian Sea]] following the brief take over of [[Adunis]] by the [[Second Heavenly Dominion]]. Atudites were recorded as enjoying significant freedom and prosperity in [[Povelia]], [[Accadia]], [[Solaria]] and [[Stazzona]] during the {{wp|renaissance}}. Etruria is estimated to have the largest population of Atudites outside [[Tsabara]]. The remaining identified faiths include [[Badi]], who represent 0.98% of the population and are drawn primarily from Badawiyan or Zorasani migrant communities, the smallest is recorded as [[Satyism|Satyists]], who constitute 0.76% of the population and is confined to migrant communities from [[Satria]]. | |||
=== Healthcare === | |||
The | Etruria has operated a {{wp|universal healthcare|universal public healthcare}} system since 1974, when the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military government]] established the [[Sistema Sanitario Federale]] (Federal Health System), which provides healthcare to all citizens. Healthcare is provided by a mixed public-private system and is reliant upon taxation and private insurance for funding. The SSF is organised federally by rhe [[Federal Ministry for Health and Social Services]], but the administration is devolved to the individual states. The state administrations are supported by federal funding, which is dispursed according to state populations, while private insurance is provided by a person's employer and optional schemes provided by private medical institutions. The Etrurian government funds universal cover for all citizens who's annual income falls below ₣50,000. In 2017, funding for individual public hospitals was boosted by the introduction of the Non-Emergency Fee (Tariffa non di Emergenza), in which patients who receive medical assistance for non life-threatening issues are required to pay a ₣90 fee. Significant reforms during the early 2010s saw major improvements to the quality of healthcare in Etruria, with the country enjoying one of the lowest rates of {{wp|infant mortality}} in Euclea. Etruria is also noted for its {{wp|palliative care}} system, {{wp|cosmetic surgery}} though not provided under the public health system is noted for its quality and affordability. Etruria is one of the few countries to introduce {{wp|mandatory vaccinations}}, which it did in 2008 to much controversy and opposition. | ||
Life expectancy in Etruria is 81 for males and 84 for females, placing the country Xth in the world for life expectancy. In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries, Etruria has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), as there are several health benefits of the {{wp|Mediterranean diet|Solarian diet}}. However, Etruria has one of the highest rates of daily smokers in Euclea, estimated at 43% in 2017, efforts to ban smoking indoors were blocked by the introduction of laws mandating separate and isolated smoking rooms. In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries also, Etruria ranks among one of the highest for the spread of {{wp|sexually transmitted diseases}}, while between 2000 and 2011, Etruria ranked as the highest for {{wp|HIV/AIDS}}. | |||
=== Education === | === Education === | ||
Etruria's education system is organised by the [[Federal Ministry for Education (Etruria)|Federal Ministry for Education]], but administration is devolved to the states. Etruria operates at least fifteen "Federal Institutes", academic institutions dedicated to the study of social sciences, medicine, engineering and economics. These institutions are utilised directly by the national government for policy making or national projects and are administered directly by the FME. Etruria has the highest concentration of {{wp|Parochial school}}s in Euclea, with an estimated 6,649 schools run or governed by the [[Solarian Catholic Church]]. | |||
Education in Etruria starts at the age of four or five (with the particular age chosen by the parents) for the 'Foundation' class ({{wp|Kindergarten}}) and six or seven years in the 1st class of primary school (Scuola Primaria). It is compulsory under federal law that children participate in one year of education before entering the 1st class at no later than 7 years of age. | |||
[[File:Archiginnasio ora blu Bologna.jpg|260px|thumb|left|The University of Saint Christopher in [[Stazzona]] is one of the oldest educational institutions in the world.]] | |||
At the end of the 6th class when students are 13, students take a compulsory exam that determines their degree of progress and is later referred to when determining their upper-secondary school. Students after 13 attend a general secondary school (scuola secondaria generale). They will attend this school during classes 7, 8, and 9, for a total of three years. Students then take another compulsory exam or in some cases more than one exams to determine the upper secondary level school they will attend. Some upper-secondary schools require exams in extra-circular activities, such as independent learning of languages, musical instruments or sports. Students either attend a Liceo, which prepares students for university education, or a technical school (scuola tecnica), which provides training in technical or vocational areas. Etrurian technical schools, dependent on their focus, can be directly tied to a {{wp|business}} or institution, to guarantee immediate employment or workplace experience. Both schools are completed through a final mandatory exam (Completamentol; Completion Exam), and may be followed by several forms of higher education, leading to {{wp|Licentiate (degree)|Diplomato}} or {{wp|Laurea}} (second cycle qualification) and eventually {{wp|Doctorate|dottorato}} (third cycle qualification). | |||
In Etruria, there are 540 university-level institutions for the pursuit of higher education as of 2018. There are 24 fully accredited traditional universities, 27 technical universities, 11 independent medical universities, 6 universities for the study of economics, 8 agricultural academies, 3 pedagogical universities, 18 theological academies, 5 maritime service universities and 4 national military academies. Also, there are a number of higher education institutions dedicated to the teaching of the arts—amongst these are the 19 academies of music. | |||
=== Functional urban areas === | === Functional urban areas === | ||
| Line 534: | Line 564: | ||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
=== Arts === | |||
[[File:Tarquinia Tomb of the Leopards.jpg|250px|thumb|left|Tomb of King Tarquinius is the oldest known fresco in Etruria.]] | |||
Art in Etruria across its history has played a key role in the development of {{wp|Western art|Euclean artwork}}, with one of the oldest frescoes in Euclea found in the [[Tomb of King Tarquinius]], which dates as far back as 930 BC. Ancient Etrurian artwork owes much of its infuence and characteristics to those found in [[Ancient Piraea]], however, Tyrrenhian and later Solarian art developed unique characteristics of their own. Most of Ancient Solaria's artwork was produced in the decoration of personal homes as the means of pursuing status among peers and often portrayed personal stories in extravagent ways. | |||
The emergence of panel paintings was pioneered by early Novalian painters, drawing on influence from neighboring [[Piraea]], who shared in the works of Episemalist iconography. This in turn led to the introduction of {{wp|Romanesque art|Solarianesque art}} during the early middle ages, where it grew in popularity across Vespasia. Artists in Vespasia began to explore improvements in realism and a focus on volume, producing many great artworks during the middle ages. | |||
[[File:Vasari, Giorgiodel Sarto, Andrea - Holy Family - Google Art Project.jpg|280px|thumb|right|The Family (1540-41) by [[Giovanni Aldrovandini]] in the [[Galleria della Laguna]].]] | |||
[[File:The_Taking_of_Christ-Caravaggio_(c.1602).jpg|280px|thumb|right|The Kiss of Betrayal (1602-1603) by [[Giulio Venti]] in the [[Galleria Federale]] is the leading example of {{wp|Italian Baroque|Vespasian Baroque}}.]] | |||
The golden age of Etrurian painting and sculpture came during the [[Etrurian renaissance|renaissance]] (1320-1635), driven by the patronage of Etruria's ruling elites, including the Solarian Catholic Church and outside influences. The renaissance produced numerous artists and scultpures, who's work played significant roles in the development of modern Euclean arts and the freedom of artistic expression and innovation. Leading Etrurian artists of the renaissance including [[Andrea Farese]], [[Giovanni Aldrovandini]], [[Tiziano della Vadera]], [[Andrija Vareši]] and [[Ivan Antonevic]] revolutionised painting through innovative uses of {{wp|perspective (graphical)|perspective}}, proportion and a refinement of the use of human anatomy, which in turn greatly refined portraiture and landscape works. With the innovations of proportion and understanding of human anatomy, Etrurian sculpture works became integral fixtures of the renaissance. Many great sculpture artists were hired by leading patrician families or rulers to honour ancestors or heroic figures, while the Church played a prominent role in Etruria through its patronage of artists in the production of statues of Saints and holy figures. | |||
The succession of the Renaissance period by {{wp|Italian Baroque|Vespasian Baroque}} saw further transitions into different expressions by artists, which dominated the 17th century. This in turn was replaced by the emergence of {{wp|Rococ art}}, which played a significant role in the evolution of landscape artists specifically, who's use of plastic paints enabled the creation of numerous masterpieces depicting various Etrurian locales and cities. Etrurian art would decline during the late 18th century owing to the upheveal of the [[Etrurian Revolution]], where many established painters and sculpture arists were persecuted for their historic service to monarchs or leading patrician families. Following the revolution, {{wp|Romanticism}} spread to Etruria in the 19th century, where many artists embraced the style to critique or lament the struggles of the revolutionary period. The most prominent Etrurian romantic artist was the [[Povelia|Povelian]] [[Ugo Desiderato]], who produced numerous scenes depicting the glory of the [[Exalted Republic of Povelia]] prior to its downfall during the Revolution. However, the romantic period saw the leading artistic hubs move away from Etruira to northern Euclea. | |||
The early 20th century saw Etruria give way to the {{wp|futurism|futurist movement}}, and Etruria's resurgence as a leading light in painting and sculpture. Futurism grew in popularity during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], due to its expressive use of colours to depict violence, machinery and modernity. The movement was patronised by the [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] as a means of expressive propaganda, this connection to the [[National Solarianism|National Solarianist regime]] and [[Solarian War]] saw the descrediting of futurism and its ultimate demise across Etruria and Euclea. | |||
=== Literature and philosophy === | |||
The first recorded instance of literature in Etruria is a stage play performed in [[Tyrrenhus]] in 669 BC, references to this play were recorded by later Ancient Solarian historians. The Tyrrhenian oral tradition was adopted by the Ancient Solarians following the establishment of the [[Solarian Republic]] in 356 BC, where the speeches and thoughts of prominent patricians were documented in great detail, this in turn consolidated the foundation of Solarian literature. The literature of Ancient Solaria remains highly influential today, owed to the preservation of works by the likes of Tinian, Aitan, Arminius and Sacerio. Among the most treasured works of Ancient Solaria are the preserved transcripts of speeches made by the leaders of the Solarian Republic, especially Sacerio, who's thoughts and monologues on {{wp|classical republicanism}} would prove pivotal in the [[Etrurian Revolution]] in the late 18th century. Ancient Solaria was also famous for its poetry, drama and mythical epics. Ancient Solarian writers, much like their successors during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, through their work also constitute philosophers of equal measure. | |||
[[File:Portrait de Dante.jpg|260px|thumb|left|[[Aurelio Adriano Cioni]] is considered to be Etruria's most acclaimed poet, the founder of modern Vespasian and one of [[Carvagna]]'s greatest rulers.]] | |||
Going into the middle ages and renaissance, Etruria's most prominent poets, especially in [[Vespasia]] would commonly serve in prominent political positions. This celebration of literary talent through public office would play a pivotal role in some of Etruria's leading poetry, story telling and essay production. As such, many Vespasian works from those two periods would take on loftier tones, while many stories and poems took on the form of {{wp|allegory|allegories}}. The renaissance period saw numerous Vespasian political leaders take inspiration from their Ancient Solarian ancestors, in documenting their inner thoughts, oratory and ideals, be it on love, religion or politics. This is best exemplified by the works of [[Francesco Cesare Candreva]], when serving as [[Doge of Povelia]], produced [[The City]], is one of the most famous essays on political science and modern philosophy. Carinthia and Novalia drew inspiration from both the [[West Euclea|Marolevic west]] and the Vespasian east, with emphasis on virtues and principles. Novalia's [[Pavle Babić]] produced the poem [[Izgubljena Zora]], considered to be one of the best poems on chivalry. Carinthia's [[Ivan Tavčar]] in 1563, wrote [[Marija je Dostavila]], one of Etruria's most translated and re-published stories, and acclaimed for its prose and religious themes. | |||
The 17th and early-to-mid 18th centuries saw Etrurian literature dominated by recurring themes of Sotirian values, providence and interpretations of [[Etrurian mythology]]. [[Giovanni Pio Renaldi]]'s [[La Bestia]] is considered to be the most read fairytale book in Etruria, with its numerous short-stories focusing on individual mythical beats and beings. The role of Sotirian themes came as a backlash against the [[Amendist Wars|Amendist movement]] in northern Euclea, these produced numerous poems, stories and essays. The works by [[Dante Fattoruso]]'s works on [[Solarian Catholic Church|Solarian Catholicism]] would go on to be integral sources for the development of [[Etrurian Republicanism]] in the lead up to the [[Etrurian Revolution]]. | |||
Etrurian literature was thrown into chaos with the Etrurian Revolution, the lead up saw the emergence of themes regarding {{wp|liberty}}, {{wp|justice}}, {{wp|democracy}} and {{wp|dignity}}. The overthrow of the Vespasian states during the [[Etrurian First Republic]] dispatched numerous poets and writers across [[Euclea]], many of whom fled persecution over their patronage to aristocrats and patrician families. Those who remained pioneered new literary themes, celebrating or defining the [[Republic of Heaven]] ideal of the revolution. The Revolution is also acclaimed as Etruria's philosophical golden age, with [[Antonio Gennaro Volci]]'s [[Il Carillon della Repubblica]] was praised by revolutionary leader [[Francesco Caciarelli]] as the epitome of Etrurian republicanism and by many writers since. [[Prežihov Rusjan]]'s [[Božja Podoba]] (1786) is widely considered to be one of the most articulate arguments against {{wp|slavery}} and is cited by the First Republic in its decree abolishing slavery and the slave trade in Etruria. | |||
The 19th and early 20th centuries for Etrurian literature was dominated by the celebrations of {{wp|industrial revolution|industry}}, {{wp|science}} and modernity. While some writers decried the destruction of nature in pursuit of industrial progress, a vast majority of Etruria's writers welcomed the change, with poems and stories advocating the mill and factory as measures of humanity's progress. The same periods saw a resurrection of Revolutionary-era literary themes in the preceding years to the [[San Sepulchro Revolution]] of 1888 and the second and final overthrow of monarchy in Etruria. {{wp|Romanticism}} played its role during the latter stages of the 19th century, with images portrayed in prose of a new and united Etruria destined for global prosperity. The previous celebrations of modernity and industry ultimately gave way to the emergence of {{wp|futurism}}, which in turn sought the celebration of youth, violence, speed and the machine. Etrurian literature of the 20th century, especially in the 1950s and 1960s was defined by the popularity of {{wp|dystopia|dystopian fiction}}, a cultural reaction to the devastation and conditions of Etruria during and after the [[Solarian War]]. | |||
=== Cinema === | |||
Etrurian film first emerged in the late 1900s, with two companies dominating the industry: [[Fauglia Cinematografica]] and [[Serenità Cines]], with both producing anticipated {{wp|silent films}} throughout the 1910s. During the 1920s, a further eight companies emerged, producing quality films, which were soon exported out of Etruria. Cinema was later used by both the [[Etrurian Second Republic]] and [[Etrurian Revolutionary Republic]] to produce wartime propaganda during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]] and [[Solarian War]] respectively, this would be repeated in a different manner under the [[Military Dictatorship in Etruria|Military dictatorship]] during the 1960s and 1970s. | |||
=== | Etrurian cinema declined rapidly in the post-solarian war period, where mass destitution and economic devastation hindered the capital or means for production of feature length products. It was not until the late 1950s, that Etrurian cinema made an artistic comeback. In 1960, the [[CineTyrrenio]] studios were launched, unleashing an entirely new genre of films produced and directed by Etrurians, under the influence of the military government. During the 1960s and 1970s, {{wp|Sword-and-sandal|Pepla}} films emerged, centred around the [[Piraeo-Solarian]] period, and usually following Ancient Solarian heroes or epics. Many of these films were extravagent with their set designs and costumes and became immensely popular in Etruria and beyond. Other genres to emerge during this time was [[Serafici]] (Seraphic), historic epics based around the lives of [[Solarian Catholic Church|Solarian Catholic Saints]], another was [[Dogi e Commercianti]] (Doges and Merchants), which often constituted comedies or romantic tragedies set during the Etrurian renaissance. Etrurian cinema during the 1960s and 1970s was noted for its "escapism", diverting attention away from the poor condition of Etruria in the post-war period and the violence of the [[Western Emergency]]. [[Marirana|Mariranian]] {{wp|Spaghetti westerns|Spaghetti easterns}} became immensely popular in Etruria during the 1960s and 1970s, leading to a short period of Etruria imitations being produced, though they failed to make significant impact. | ||
[[File:La grande guerra.jpg|280px|thumb|left|The Great War (1961) was at that time the most expensive Etrurian film made and followed the true story of twin brothers fighting in Auratia against [[Gaullica]].]] | |||
Etrurian cinema also provoked controversy during the same period with the genre of [[Epiche Eroiche]] (Heroic Epics), where films were produced as a cinematic series covering Etruria's battles during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]] and the [[Solarian War]], usually with the Etrurian characters in question facing suicidal odds, only to survive through bravery, pluck and determination. The 1968 film [[Outcry]] was widely condemned as {{wp|historical revisionism}}, by portraying Etrurian soldiers during the [[Solarian War]] fighting to defend [[Piraea|Piraean nuns]] from Piraean partisans who sought to attack their nunery. With the restoration of democracy in 1983, Etrurian film transitioned toward more international and away from nationalistic genres. The [[Povelia Film Festival]] has been an annual fixture since its establishment in 1949. | |||
=== Media === | |||
{{Main|Media in Etruria}} | |||
In 1925, [[ARE|Ammisitrazione Radiotelevisione Etruriana]] was founded and is Etruria's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation. It operates television and radio stations across the entirety of Etruria, specifically serving local, regional, state and national audiences and is funded directly by the Etrurian government and through advertisment, which abolished the historic {{wp|license fee}} in 2009. [[ARE News]] is the nation's most popular provider for daily broadcast news and information. Other major providers in Etrurian media include [[Orrizonte TV]], which competes with ARE at the national and regional level, other competative providers include [[NNT]], which operates at the [[Novalia|Novalian regional level]] and [[Zora do Sumraka]], which serves [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthian]] regional audiences. | |||
[[Newspapers in Etruria|Newspaper readership]] in Etruria differs per region, where preferances for national or regional papers fluctuates. In the [[Vespasia|Vespasian states]] of Etruria, the overwhelming preferance is for national level papers, including the centrist [[Il Popolo]], right-wing [[Telegrafo Solariano]] and the independent [[Nuovo Percorso]]. Readers in [[Novalia]] and [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]] are shown to be major consumers of regional or local newspapers, many of which are sister publications of national papers. During the 1990s and early 2000s, {{wp|Tabloid journalism|tabloid newspapers}} grew in popularity, with [[La Stella]] briefly overtaking the established national papers as the most circulated. However, a series of scandals indicating extensive falsifications and its use as a political tool to descredit politicians eventually led to the downfall of La Stella and tabloid journalism in Etruria. | |||
The media sector in Etruria is decentralised between [[Tyrrenhus]], [[Solaria]] and [[Fauglia]], where national newspapers and television and radio are largely based. While, [[Praproče]] and [[Dubovica]] dominate the media sectors of [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]] and [[Novalia]] respectively. The Etrurian publishing industry, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies at the local and national levels produce an estimated $12.5 billion for the Etrurian economy each year. Etruria is also home to some of the oldest continuously serving publishing houses in [[Euclea]], with [[San Dionigi Editore]] (1603) and [[Stefano Barbarigo Editore]] (1611) still in business. | |||
=== Music === | |||
Ever since [[Ancient Solaria]], music has played a prominent role in Etrurian culture. From {{wp|folk music}}, including the iconic {{wp|tarantella}} to {{wp|opera}}, {{wp|classical music}}, Etruria has been a hotbed for innovations in instruments and genres of music, with the {{wp|violin}} and {{wp|piano}} being invented in Etruria and the musical forms of the symphony, concerto, and sonata, tracing their roots back to innovations of Baroque-era Vespasian music. Famous Etrurian composers from the renaissance include {{wp|Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina|Valaseno}}, {{wp|Claudio Monteverdi|Montecorvino}} and {{wp|Gesualdo|Karelo}}, who introduced acclaimed {{wp|magridals}} and innovated {{wp|polyphony}}. | |||
[[File:La Fenice Opera House from the stage.jpg|290px|thumb|left|La Leone operahouse in [[Povelia]].]] | |||
In music, Etruria is most famous for the creation of {{wp|opera}}, where it began as a popular form of theatre, shared by all classes. The origins of opera are believed to be northern Vespasia, primarily [[Povelia]] and [[Faulia]] during the early 17th century. No major works from the earliest period of opera have survived, though later works and pieces produced in the 19th century remain popular and stand as some of the most famous ever written. Many works by {{wp|Rossini|Gioachino}}, {{wp|Bellini|Ercolani}}, {{wp|Verdi|Vitiello}} and {{wp|Puccini|Bonera}} are perfomed in operahouses worldwide. Etruria operates the highest number of opera houses in the world, with the [[La Leone]] in [[Povelia]], the [[Ducato Giorgio]] in [[Faulia]] and [[Papa Pio X opera house|Papa Pio X]] in [[Tyrrenhus]] being the most popular establishments in Etruria. La Leone and the Ducato Giorgio are considered to be among the best in the world for operatic perfomances. While considered to be a classical form, operas remain among the most popular music forms in Etruria, enjoyed across all age groups and socio-economic classes. | |||
[[File:Giacomo Puccini pianoforte.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Girolamo Enrico Bonera is considered to be Etruria's greatest producer of operas and dance melodies.]] | |||
During the 1950s, Etrurian music genres were dominated by {{wp|swing music|swing}} and {{wp|schlager music}}, imported from [[Werania]]. {{wp|Caterina Valente|Sophia Valentino}} became a Euclean chart topper during this decade with her take on popular swing and schlager music. During the 1960s and 1970s, the policies of the [[Military dictatorship in Etruria|military government]] stemmed the spread of popular genres like {{wp|progressive rock}} and {{wp|free jazz}}, though they became widely embraced genres in the underground cultural scene. The policies of the dictatorship however did lead to the emergence of {{wp|turbo folk}} in the early 1980s, which initially began among the {{wp|Serbian people|Miruvian}} minority, before being emulated by the {{wp|Croatians|Novalians}} and {{wp|Slovenes|Carinthians}}, turbo folk in the latter two languages also became popular among {{wp|Italians|Vespasians}}, leading to turbo folk being considered the "genre of democratisation." The late 1980s saw musical innovations in {{wp|electronic music|electronic}} and {{wp|dance music|dance}} music, introducing the sub-genres of {{wp|Italodance|Etrurodance}} and {{wp|Italohouse|EtruroHouse}}; known for their futuristic sounds and prominent use of synthesisers and drum machines. Etrurodance and Etrurohouse faded by the early 2000s, though have seen a revival in the 2010s. The leading artists of Etrurian electronic music include {{wp|Eiffel 65|Inferno 12}}, {{wp|Benny Benassi|Leo Scipio}}, {{wp|Gigi D'Agostino|Mario D'Santis}} and the Novalian due {{wp|Colonia (music group)|Castra}}. | |||
=== Cuisine === | === Cuisine === | ||
Etrurian cuisine is greatly defined by its multiethnic nature, with its food drawing influences from the climate, geography and three major cultures. The role of its [[Solarian Sea|Solarian roots]] is found its extensive use of fish and seafood dishes, and its inspirations from the land in the form of cuisines from [[Novalia]] and [[Carinthia]] have helped develop a great variety of dishes and divisions of its cuisine. Over the centuries, the distinct cuisines of Etruria's cultures have merged to create a unique "Etrurian fusion" of popular Central Euclean recipes with those of the [[Vespasia|Vespasian region]]. There are four divisions of Etrurian cuisine: | |||
[[File:VespasianGoulash.png|280px|thumb|right|Vespasian Goulash is a popular national dish, including the ingredients and recipes of all three nations.]] | |||
* '''Vespasian''': Defined as the Solarian diet, Vespasian cuisine is centred around {{wp|pasta}}, alongside herb enriched sauces, though with distinct regional differences. | |||
* '''Carinthian-Hinterland''': The stews, thick soups and meath dishes of Carinthia and inland Novalia, such as {{wp|Matevž}} and {{wp|goulash}}. | |||
* '''Novalian''': Heavily inspired by its Solarian roots, with a primary focus on seafood dishes, such as the fish stew {{wp|Brudet}}, salted or grilled sardines (slana riba), usually served with salad. | |||
* '''Etrurian Fusion''': Etrurian Fusion refers to numerous dishes that draw influences from the above divisions. The most prominent of Etrurian Fusion is [[Vespasian Goulash]], which includes the use of tomato, onion & garlic Marinara sauce, alongside macaroni pasta and grounded beef. | |||
=== Sport === | === Sport === | ||
The most popular sport in Etruria is a {{wp|football}}, varieties of which have been played in regions of Etruria since Solarian times, however it was not until the late 19th century that football came to dominate Etrurian sports. [[S.S Solaria]] is the oldest team in Etruria, being founded in 1894. Etruria's [[Lega A (Etruria)|Lega A]] is the nation's premier league division and one of the most watched in Euclea, with [[S.S San Marco]] and [[A.S Tyrrenhus]] among the most successful football clubs in the world. The [[Etruria national football team|national team]] also stands as one of the best in the world, recently coming third in the [[2019 IFF Coupe du monde]]. Etruria had historically won the Coupe du Monde in XXXX, XXXX, XXXX and XXXX. | |||
[[File:Tifosi curva nord lazio.jpg|280px|thumb|left|Fans [[A.S Tyrrenhus]] during a derby with [[S.S Palestrina]] in 2018.]] | |||
[[File:Roma - panoramio (87).jpg|270px|thumb|right|The [[Foro degli Eroi]] in [[Tyrrenhus]] hosts the [[Etrurian Open (tennis)|Etrurian Open]] tennis tournament.]] | |||
{{wp|Tennis}}, {{wp|basketball}}, {{wp|volleyball}} and {{wp|futsal}} are other popular sports enjoyed by Etrurians. The country has hosted the [[Etrurian Open (tennis)|Etrurian Open]] tennis tournament since 1956,and since grown in viewership and prestige since the 1990s. The country's rising sports in popularity are {{wp|motorcycle racing}} and {{wp|formula one}}, the annual [[Accadia Grand Prix]] held at the [[Sergio Virzì Ippodromo]] elevated Etrurian motor racing to global audiences. {{wp|Rugby}} first emerged as a sport in Etruria during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]], when it was introduced by [[Estmere|Estmerish]] soldiers during the 1920s, since rugby has become a popular sport, particularly in southern Vespasia. The [[Etruria national rugby team|national rugby team]] has competed internationally since 1950 and is considered a tier-one rugby team. {{wp|Cycle sport|Bicycle racing}} is a popular and familiar sport, especially in [[Carinthia (Etruria)|Carinthia]] and [[Novalia]], the [[Ogled Koroške]] hosted in Carinthia is an annual fixture in international bicycle racing and has grown in prominence owing to the natural beauty of the designated racing route through the country's foothills. | |||
Owing to the mountainous terrain of Etruria and the [[Aventine Mountains]], {{wp|Skiing}} is considered to be a national sport, {{wp|Alpine skiing|Aventine skiing}} is the third most practiced sport, and the country is a popular international skiing destination, known for its ski resorts in both the Aventines and Tarantine mountains. Etruria has among the most extensive and high quality skiing facilities in the world, with Etrurian skiers regularly achieving good results at the [[Winter Invictus Games]], and the skiing world cup and championships. | |||
Etruria is the birthplace of the modern {{wp|Olympic Games|Invictus Games}}, hosting the first games in [[1898 Summer Invictus Games|1898]], then in [[1998 Summer Invictus Games|1998]] and most recently in [[2010 Summer Invictus Games|2010]]. Etruria has hosted the games the second most times, after [[Gaullica]]. The country has also hosted the {{wp|Winter Olympic games|Winter Invictus Games}} twice, in [[1920 Winter Invictus Games|1920]] and [[1956 Winter Invictus Games|1956]]. | |||
=== Public holidays === | === Public holidays === | ||
| Line 564: | Line 654: | ||
|1 May||{{wp|International Workers' Day}}||''Festa del Lavoro'' (or ''Festa dei Lavoratori'')|| | |1 May||{{wp|International Workers' Day}}||''Festa del Lavoro'' (or ''Festa dei Lavoratori'')|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |20 July||[[Festa per la Nascita della Reppublica|Birth of the Republic Day]]||''Festa per la Nascita della Reppublica''||Anniversiary of the founding of the [[Etrurian First Republic]] in 1784. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|15 August||{{wp|Ferragosto}}/{{wp|Assumption of Mary|Assumption Da}}||''Ferragosto'' or ''Assunzione''|| | |15 August||{{wp|Ferragosto}}/{{wp|Assumption of Mary|Assumption Da}}||''Ferragosto'' or ''Assunzione''|| | ||
| Line 578: | Line 666: | ||
|25 December||{{wp|Christmas Day}}||''Natale''|| | |25 December||{{wp|Christmas Day}}||''Natale''|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
|26 December||{{wp|Saint Stephen's | |26 December||{{wp|Saint Stephen's Day}}||''Santo Stefano''|| | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 584: | Line 672: | ||
[[Category:Etruria]] | [[Category:Etruria]] | ||
[[Category:Kylaris]] | [[Category:Kylaris]] | ||
[[Category:Countries (Kylaris)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 11 March 2024
United Etrurian Federation
3 other official names
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Motto:
| |||||||
Anthem:
| |||||||
 Location of Etruria (in light green), within Euclea (light grey) | |||||||
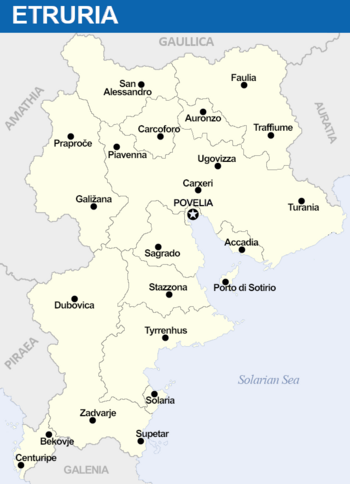 | |||||||
| Capital | Povelia | ||||||
| Largest city | Tyrrhenus | ||||||
| Official languages | Vespasian Novalian Carinthian | ||||||
| Ethnic groups (2016) |
| ||||||
| Religion (2016) | Solarian Catholicism (State religion) | ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Etrurian | ||||||
| Government | Constitutional parliamentary federal republic | ||||||
| Francesco Carcaterra | |||||||
| Vittoria Vasari | |||||||
| Ivano Balić | |||||||
| Legislature | Senate of the Federation | ||||||
| State Council | |||||||
| Chamber of Representatives | |||||||
| Formation | |||||||
| 1783-1784 | |||||||
| 20 January 1784 | |||||||
• Monarchy restored | 3 April 1810 | ||||||
| 10 May 1888 | |||||||
• Treaty of Kesselbourg | 12 February 1935 | ||||||
• Current constitution | 1 July 1983 | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
• | 548,549 km2 (211,796 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 2020 estimate | |||||||
• 2014 census | 63,888,987 | ||||||
• Density | 119.58/km2 (309.7/sq mi) | ||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate | ||||||
• Total | |||||||
• Per capita | |||||||
| Gini | 46.9 high | ||||||
| HDI | 0.843 very high | ||||||
| Currency | Etrurian florin (₣) (ETF) | ||||||
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy | ||||||
| Driving side | left | ||||||
| Internet TLD | .et | ||||||
Etruria, officially the United Etrurian Federation or UEF (Vespasian: Federazione Etruriana Unita; Novalian: Sjedinjene Etruriska Federacija; Carinthian: Združena Etruriska Federacija) is a sovereign parliamentary federal republic, made up of thirteen constituent states and two federal territories. Etruria also includes several islands several islands, the largest being Aeolia and smaller archipelagos such as the Apocorona. Etruria is located in southern Euclea. It is is bordered (clockwise) by Amathia to the north-west, Gaullica to the north, Paretia to the east, to south, Juznavia to the south, and Piraea to the west. Etruria is home to 65.5 million people. The federal capital is Povelia and largest city is Tyrrhenus.
Since classical times, its central geographic location in Euclea and between the Mazdan and Solarian Seas, Etruria has historically been home to a myriad of peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient Vespasian tribes and Vespasic peoples dispersed throughout the Etrurian interior and insular Etruria, beginning from the classical era, Pireans, Auratics and Atudite peoples established settlements in the south of Etruria, with Tyrrenii and inhabiting the centre and the north of Etruria respectively. The Vespasic tribe known as the Solarii formed the Solarian Tribunate in the 8th century BC, which eventually became a republic that conquered and assimilated its neighbours, including the powerful and wealthy Tyrenii. In the first century BC, the Solarian Empire emerged as the dominant power in the Solarian-Mazdan Basin and became the leading cultural, political and religious centre of Euclean civilisation. The legacy of the Solarian Empire is widespread and can be observed in the global distribution of civilian law, republican governments, Sotirianism and the Solarian script. Its steady collapse in the 5th century AD corresponded with the arrival of Marolevic tribes from the west, who would go on to form the Novalian and Carinthian peoples.
These independent statelets often enjoyed a greater degree of democracy and wealth in comparison to the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Euclea at the time. By the 13th century, modern Etruria became dominated by three states, the Exalted Republic of Poveglia, Grand Duchy of Carvagna and the Ecclesiastical State.
The Renaissance spread across Etruria from Povelia, bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration and art. Vespasian culture flourished at this time, producing famous scholars, artists and polymaths such as "Great people". The influence and commercial power of the maritime republics began to dominate the monarchies of the interior, culminating in the Povelian victory in the Etrurian Wars and becoming the dominant power in Etruria, leading to the Pax Poveliae. Povelian colonisation of the Asterias soon followed, introducing New World treasures to Etruria. The sudden rise of the Principality of Tyrrenhus in the south added pressure to Povelia. In the 18th century, Povelia’s decline began, hastened by the immense cost paid during the Ten Year’s War. This decline led to the Central Etrurian Wars and the Torazzi War between Povelia and Tyrrenhus, bankrupting and disrupting vast swathes of Etruria. The famine, debt and corruption led to the overthrow of the monarchy in Tyrrenhus, sparking the Etrurian Revolution (1783-1785) and the establishment of the Etrurian First Republic, creating one of the earliest republics in history. The Republic would go on to unite Etruria and for the next fifteen years, engage in the Etrurian Revolutionary Wars, spreading republican tradition and values across southern Euclea. The constant warfare, poor governance and state-terror would lead to the restoration of monarchy in 1810 and the United Kingdom of Etruria.
From 1810 until 1880 would enjoy prosperity, growth and development. Etruria would establish one of the largest colonial empires, while federalism was greatly expanded and refined. However, debt, a poor economy and authoritarianism resulted in the 1880 Revolution and the establishment of the Second Etrurian Republic. Etruria was a major participant in the Great War, from which it emerged victorious, however, poor territorial gains and political instability led to the emergence of the Etrurian Revolutionary Republic and the Solarian War, which saw Etruria defeated. The Third Etrurian Republic emerged in the aftermath, rebuilding the country and establishing a fixed regime of civil rights and freedoms before being overthrown by the military which established a Junta in wake of the Western Emergency. Democracy would be restored in 1983 with the current Fourth Republic, this was followed by numerous liberalising economic reforms that achieved high sustained economic growth and improvements to standards of living. Between the 1990s and 2010s, the country underwent political reforms in aim of Etruria joining the Euclean Community. A referendum held on EC membership in 2016 was defeated due to several major corruption scandals and the successful No-campaign being led by the right-wing Tribune Movement, this ended all prospect of Etrurian membership of the EC. The loss of the referendum, coupled with the corruption scandals brought about the near collapse of the establishment parties in the 2016 election and a victory for the Tribune Movement, which formed the most right-wing government in Eastern Euclea since the Great War.
Today, Etruria has a mixed market economy based around finance, industry and agriculture. It has the XX largest economy in Euclea, and XX largest in the world. It is widely considered a newly-industrialised economy, a regional power and middle power. It is a council member of the Community of Nations, GIFA and the ITO.
Etymology
The assumptions on the etymology of the name "Etruria" are very numerous and the corpus of the solutions proposed by historians and linguists is very wide. Many historians note that the Etrurian mountain range that extends across northern Etruria and rising up east of Sea/Lake X then southwards along the border with Sardenya were prominent features of Vespasic faiths in ancient history. Etruria in ancient Vespasic (Etrúra) meant "Sacred Rock" and since the Aventine mountains meet the Etrurians roughly in the central region of the north and push south towards the X Sea, many historians surmise that as the Vespasic tribes expanded, they considered the Aventines and the Etrurians to be one and the same and extended the name Etrúra to the rest of the country. As Vespasic developed into latin, Etrúra evolved into Etruria and the name has remained in use since.
The term Transetruria or Transetrurian was only introduced in the 19th century to refer to Vespasia and its territories in Carinthia and Novalia and remained in use within officialdom, eventually being adopted as the official title of the federation in 1921, as a means of unifying the three constituent states.
History
Pre-history
Excavations throughout Etruria revealed a hominid presence dating back to the Palaeolithic period, some 210,000 years ago, modern Humans appeared about 48,000 years ago. Much of the pre-history presence is concentrated around the Poveglian Basin in the north and the Alluvian plains in southern Etruria.
The Ancient peoples of pre-Solarian Etruria– such as the Torians, the Vepasii (from which the Solarians emerged), Vicalvii, Otians, Samanians, Sorines, the Guallics, the Suratii, and many others. Other peoples were identified as the primarily mountainous, Novarians, Carumnii and the southern and coastal focused Aeoluii.
Between the 17th and the 11th centuries BC XX established contacts with Etruria and in the 8th and 7th centuries BC a number of XX colonies were established all along the coast of Vespasia and the southern part of the Aeolian Peninsula, that became known as XX. During this time, the Vespasii were rapidly growing in and around what would become Solaria, while north of them, the Vicalvii had cleared land around the seven-hills of Vicalvus.
Ancient Solaria and Tyrrenhus
Solaria, a settlement on the coast of the Bay of Lasa Vecuvia conventionally founded in 757 BC, was ruled for a period of 239 years by a monarchical system, initially with sovereigns of Vespasii and Torian origin, later by Vicalvii kings. The tradition handed down seven kings: Romulus, Verus Tanis, Horius Antonius, Marcus Marcellius, Eugenius Prascus, Ceserius Tullius and Hadrianus Lutorius. In 511 BC, the Solarians expelled the last Vicalvii king from their city and established an oligarchic republic, supposedly upon the order of the Aventine Triad, led by the sun gold Sol.
To the north of Solaria, Tyrrenhus, a settlement built around the ford of the Metaia River rapidly grew under a series of successive kings, it dramatically expanded its territories to cover the entire Vicalvian Plain. Vicalvus' dominant position allowed it to influence Solaria until the expulsion of Hadrianus Lutorius. With the establishment of the Solarian Republic, Vicalvus found a serious challenger to domination over southern Vespasia. The two cities would fight numerous wars known as the Wars of the Two Cities, the wars ended in 256 BC when Tyrrenhus was defeated at the Battle of Salutaria, resulting in the city's annexation by Solaria. Tyrennii culture would fuse with Solarian, creating the long-lasting Solarian culture that spread with the empire's growth. The Solarian Republic until the first century B.C. would expand to encompass all of modern day Etruria and western Auratia, crossing the Solarian sea to establish colonies on the coasts of Tsabara and northern modern-day Zorasan in 89 BC. This expansion would instigate centuries-long conflicts with the Heavenly Dominions.

In the wake of rebellion by Tarchon Parusna in the first century B.C. and a series of concurrent slave revolts, the Solarian Senate granted extraordinary powers to TBD, who with the assistance of allies within the senate, succeed in being granted the title of Emperor. Over the course of centuries, Solaria would expand and grow into a massive empire stretching from the western borders of Bahia to the southern reaches of Estmere and Swetania, and engulfing the whole Solarian basin, in which the Tyrennii-Solarian and Piraeo and many other cultures merged into a unique civilisation. The Solarian Peninsula was named Etruria was declared "Terra Saena" (Sacred Soil), granting special status compared to other imperial provinces. The long and triumphant reign of the first emperor, TBD, began a golden age of peace and prosperity. From its founding until the late 4th century CE, the Empire's leaders were relatively successful in maintaining a peaceful balance of power between the Emperor and Senate, while sporadic and isolated power struggles were recorded, this enabled to extend the period of prosperity.
In 395 CE, Mount Vecuvia erupted devastating much of the ancient city of Solaria, among the estimated 5,000 people killed was Emperor Diocletius. The Emperor's sudden death coupled with this as of yet declared successor sent the Empire spiralling into chaos, with numerous leading figures declaring themselves Emperor, sparking the Vecuvian Wars. The devastating localised and Empire-wide civil conflicts significantly weakened the central authority of the state, exacberating the strain of managing and protecting its vast territories. The near constant power-struggles between successive and short-reigning Emperors and the Senate hollowed out the central state, giving way to endemic corruption, poor provincial governance and economic malaise. This stagnation was coupled by ever growing threats, either from the Heavenly Dominions in northern Coius, to Marolevic, Weranic tribal incursions from the Euclean west and north. Between 417-419 CE, the Heavenly Dominion launched a full-scale invasion of the Empire's holdings in northern Coius, evicting the Solarian Empire from the continent for the first time since 66 BCE. Between 419 and 426 CE, the Empire rapidly lost control of its western holdings to numerous migranting Marolevic tribes, while Weranic tribes to the north descended southward toward the province of Gaullica. In 424, the Empire essentially collapsed within its heartland, with numerous Senators establishing individual powerbases, while two years later, Claudius of Gaullica redeclared the Empire, laying the foundations of the Verliquoian Empire. Within Vespasia, the Empire's heartland fractured into numerous fiefdoms and statelets, which would remain the case until the expansion of the Verliquoian Empire decades later.
The Solarian Empire was among the most powerful economic, cultural, political and military forces in the world of its time. It was one of the largest empires in world history. At its height under Velturius, it covered 3.4 million square kilometres. The Solarian legacy has deeply influenced the Euclean civilisation, shaping most of the modern world; among the many legacies of Solarian dominance are the widespread use of the Vespasic languages derived from the fusion of Tyrennii and Solarian, the numerical system, the modern Eastern alphabet and calendar, and the emergence of Sotirianity as a major world religion.
Middle Ages
After the Fall of the Solarian Empire and the fragmentation of Etruria, the former heartland was dominated by small states ruled by former Solarian senators and other aristocratic elites. The western reaches of Etruria, would fall under the dominion of numerous Marolevic tribes, who would over the course of several decades fighting fierce internecine wars, culminating into the future Kingdoms of Carinthia and Novalia. Efforts by the Empire of Arciluco to expand its dominion eastward to reclaim Solaria was repeatedly defeated by these Marolevic tribes, this in contrast to the Verliquoian Empire, which succeeded in restoring imperial control over much of Vespasia between 432 and 449 CE. Verliquoian rule would go on uncontested for over two-hundred years, until in 665, the patricians of the city of Povelia successfully negotiated independence from the Empire, despite imperial rule ever being nominal or superficial. The patricians and merchants established the Exalted Republic of Povelia the following year, and would result in the establishment of Povelia as one of Euclea's great powers during the Renaissance and early modern period. During this time of Verliquoian dominance, the numerous provinces that later form the numerous comunes and city-states of Etruria were established to ease imperial administration, another notable development was the ever growing autonomy of the city of Solaria under the direct temporal rule of the Papacy.
Early Modern
[
Revolutionary Etruria (1784–1810)

Royal Restoration and 19th century (1810–1888)

Second Republic (1888–1937)
National Solarian period (1937-1946)
CN Mandate and Third Republic (1946-1960)
Military dictatorship (1960-1983)
Contemporary (1983-present)
Geography
Etruria is located in Southern Euclea. To the north, Etruria borders Gaullica which is dominated by the Aventine Mountains which run northward, before declining southward along Etruria’s north-eastern border. This natural enclosure bounds the Eugenian Plain which dominates northern Etruria. The Aventine North is home to Etruria’s largest lakes, Lake Imperia and Lake Jovia. South of the plain and running from north-to-south is the Tarantine Mountains which stand as the spine of the Etruro-Piraean Peninsula. The Tarantines are divided from the Aventines by the Carinthian Gap, which is the far-western border of the Eugenian Plain. The Tarantines continue southward into Galenia, Etruria’s only neighbour to the south. To the east is Auratia and the Bay of Povelia, at the head of which is the Povelian Lagoon, which contains marshland and hundreds of islands, and the island-city of the same name. Etruria east of the Tarantines is marked by its hilly terrain and forests, while the areas west of the mountains are noted equally for their forests, fertile soil and rolling hills. To the west, Etruria borders Piraea, while the Federal Territory of Tarpeia, also known as the Tarpeian Corridor (Corridoio Tarpeano), which separates Piraea from Galenia. Etruria also includes one large island, San Francesco and numerous smaller islands including the Apocorona, the Guardiani.
The country's total area is 548,549 km² (211,796 sq mi). Including the islands, Etruria has a coastline of 2,636 kilometres (1,637 miles) on the Solarian and Mazdan seas.
The Tarantine Mountains form Etruria's backbone and the Aventines form most of its northern and eastern boundary, Etruria's highest point is located on Monte Tinia (4,810 m or 15,780 ft) in the northern reaches of the range. The Àdexe, Etruria's longest river (1,114 kilometres or 692 miles), flows from the Aventines on the north-western border with Guallica and crosses the Eugenian plain on its way to the Solarian Sea, where it enters the Bay of Povelia. The five largest lakes are, in order of diminishing size: Imperia (1,000 km2 or 386 sq mi), Jovia (212.51 km2 or 82 sq mi), San Paolo (145.9 km2 or 56 sq mi), San Pietro (124.29 km2 or 48 sq mi) and Balestra (113.55 km2 or 44 sq mi).
The country is situated at the meeting point of the XXX Plate and the XXX Plate, leading to considerable seismic and volcanic activity. There are 17 volcanoes in Etruria, three of which are active: Vosca, Stalleria, Vesano and Veturius, which last erupted in 2015.
Climate
Owing to Etruria’s geographical location and geography, there are three distinct climatic zones present:
- The Solarian climate, characterised by warm/hot and dry summers, is dominant east of the Tarantine Mountains and coastal Etruria.
- The First Solarian zone is associated to areas with hot summers. It is predominant across the coastal regions southern, central and eastern Vespasia and covering virtually all of inland central Vespasia up to the slopes of the Tarantine Mountains. Southern Vespasia and southern Novalia also fall under his climatic zone. These areas also tend to had cool or cold winters dependent upon air currents over northern Euclea. The major cities to fall under the First Zone include Solaria, Tyrrenhus, Stazzona, Vilanja, Centuripe and Bekovje. This climate also covers the entirety of the island of San Francesco.
- The Second Solarian zone has warm rather than hot summers, and extends to additional cool-winter areas not typically associated with a Solarian climate, such as much of central and northern Novalia, all of Carinthia and the interior of eastern Vespasia, along the border with Auratia. These areas also higher rainfall that the First Solarian Zone. Note areas with relatively high rainfall such as Galicia are not considered Mediterranean under local classifications but classed as oceanic.
- The Humid sub-tropical climate, characterised by warm humid summers and damp cold winters. This climatic zone covers the entirety of the Eugenian Plain an runs west-to-east, where hot humid air becomes trapped between the Aventines to the north, warm sea from the Solarian Sea to the south alongside the Tarantine Mountains.
- The third climatic zone is the Aventine climate, characterised simply by the lack of trees owing to the deep cold. The Aventine Climate covers two distinct areas, the Aventine and Tarantine mountains, though during particularly cold winters, their climatic effects are known to descend into inland areas, notably Carinthia, northern Novalia and on some occasions, the Eugenian Plain of Vespasia.
Average winter temperatures vary from 0 °C (32 °F) on the Alps to 12 °C (54 °F) in southern Novalia, so average summer temperatures range from 20 °C (68 °F) to over 25 °C (77 °F). Winters can vary widely across the country with lingering cold, foggy and snowy periods in the north and milder, sunnier conditions in the south. Summers can be hot and humid across the country, particularly in the south and central areas , while the northern interior can experience strong and recurrent thunderstorms throughout spring and autumn. These storms are also known to cause flashfloods and landslides in areas immediately south of the Aventine Mountains.
Biodiversity

Due to Etruria’s unique and varied geological features and climatic variances, it has one of the highest degrees of habitat and faunal diversity in Euclea. According to the International Committee for Nature, Etruria has over 50,000 species recorded in various biomes and habitats. Among these species include numerous endemic animal species such as the, Francsiscan long-eared bat, Vespasian newt, Guardiani wall lizard and the brown cave salamander. Notable mammal species endemic to Etruria include the Marsican brown bear, whose numbers have dwindled significantly due to hunting, the Aventine ibex, the Euclean lynx and the Vespasian wolf. Etruria is also home to 516 bird species and 56,213 invertebrate species, such as the endemic Carinthian honey bee. Despite its diversity, Etruria has the seen the most dramatic and rapid decline in all Euclea, with over 1,200 species believed to have gone extinct since 1950, due to human development, pollution and destruction of natural habitats. Efforts to preserve wildlife through strengthening of laws regarding national parks and wildlife sanctuaries have seen a steadying of the rate of decline.

Etruria's lengthy coastline and the commonality of deep and extensive cave systems has led Etruria to be home to several endemic aquatic cave species, such as the Olm, the only known cave vertebrate. Etruria since the 1980s has established several Marine Life Sanctuaries, areas of sea protected by any human activity bar scientific research. The Bay of Povelia is known to be home to pods of bottle nosed dolphins, Sperm whales (when migrating) and occasionally humpback whales, though this has been questioned by marine biologists. The Solarian monk seal was once one of the most common marine mammals to be spotted across Etruria’s coastlines, however, human activity and the stark increase in water pollutants and noise pollution has driven the monk seal away from the northern shores of Bay of Povelia, leaving the mammal mostly confined to the coasts of eastern Veratia and the islands of San Francesco. The flora of Etruria was estimated to comprise about 9,500 vascular plant species, though this figure has declined. Forests are also significantly present in the country, as they cover 10,490,000 hectares (104,899 km²) representing 19.12% of Etruria's land surface. This saw a significant decrease from 29.9% as of 1960, with a vast majority of this decline owed to deforestation for agricultural use. Other habitat types include grasslands, wetlands, bogs, marshlands, scrub habitats, coastal and marine habitats. In terms of phytogeography, Etruria is a part of the Boreal Kingdom and is a part of the Central and Southern Euclea provinces of the Circumboreal Region and the Central province of the Solarian Region. Etruria is further divided between three ecoregions—Pannonian mixed forests, Western Tarantine mixed forests and Etrurian deciduous forests.
Environment
In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries, Etruria remains the host of significant environmental problems. It is among the lowest in Euclea for ecological sustainability and one of the lowest in the production of renewable energy. It consistently ranks as one of the worst in Euclea for environmental degradation, habitat destruction and air quality. Air pollution remains one of Etruria’s most pressing problems, especially in industrial regions, in the southern and northern Vespasia, as of 2020, Etruria ranked third in carbon emissions output in Euclea, Globally, Etruria is the sixth largest carbon dioxide producer. Extensive traffic and congestion in the largest metropolitan areas continue to cause severe environmental and health issues, while the continued use of coal-fired power plants and weak industrial carbon emissions regulations contribute to serious cases of smog.
Unlike other Euclean countries, Etruria has fewer national parks, with the first only established in 1949. The belatedness of the national park movement permitted vast swathes of Etruria’s forested areas to be destroyed and numerous animal species to be forced int extinction or to become endangered. Deforestation, illegal building developments and poor land-management policies at the state and federal level, have led to significant erosion all over Etruria’s mountainous regions in the north and south, leading to numerous disasters such as the Montecorvino Mudslide, Giassico Disaster and the San Girolamo Dam collapse.
Many watercourses and coastal stretches have also been contaminated by industrial and agricultural activity, while because of rising water levels, Povelia, the national capital, has been regularly flooded in recent years, with the problem increasing tenfold in the last six years. The repeated flooding of the national capital has led to renewed calls for the federal government to move elsewhere, while the rising waters in the Povelian Lagoon is also blamed on poorly designed canal networks, that have brought further water volumes into the tightly enclosed waterbody. Several areas of the Lagoon and the wider Povelian Bay have on occasions be sealed off due to industrial waste introducing toxic chemicals into the water. Waste from agricultural and industrial activity is not always disposed of by legal means, with historic cases of mafia groups being contracted to remove waste, and has led to permanent health effects on inhabitants of affected areas
Government and politics
Etruria is a federal parliamentary republic governed under the 1983 Constitution, recently amended in 2017, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. Unlike other presidential republics the President is both head of state and head of government and depends for his tenure on the confidence of Parliament. It is a constitutional federal republic and representative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law".
Federalism in Etruria defines the power distribution between the federal government and the constituent states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances, which however have never been considered overly strong. The Constitution of Etruria, which came into effect on 1 July 1983, states in its preamble that Etruria is "a sovereign, Solarian Catholic democratic republic and union of three states". Etruria's form of government, traditionally described as "quasi-federal" with a strong centre and weak constituent states, has grown increasingly federal since the late 1980s as a result of political agitation at the constituent level. However, since 2016, the level of separation between federal and state has significantly declined.
Branches of government
Executive: The President of Etruria is the head of state and head of government and is supported by the party or political alliance holding the majority of seats in the lower house of the senate. The executive branch of the Etrurian government consists of the president, the vice president, and the Federal Cabinet—this being the executive committee—headed by the president. The president is mandated to select his deputy and his Federal Cabinet, however the cabinet must receive the confidence of the state council to be confirmed. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of one of the houses of congress. In the Etrurian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature; the president and his council are directly responsible to the lower house of the congress (the chamber of representatives).
The president and the cabinet may be removed by the senate by a motion of no confidence. There are no term limits for the presidency.
 |
|
Government (194) Tribune Movement (155) People's Opposition (99) Citizens' Alliance (48) Farmers and Workers Union (15) Popular Renewal (4) Independent (3) |
 |
|
Government (373) Tribune Movement (360) Social Party of the Third Order (13) Support (23) Farmers and Workers Union (23) People's Opposition (206) Social Democratic Party (165) Citizens' Alliance (26) Etruria plus Euclea (6) Sotirian People's Force (4) Popular Renewal (3) |
Legislature: the legislative branch of Etruria is based on the adversarial model of parliament, as such the federal legislature is parliamentary. The Senate is split into two houses: the State Council and the Chamber of Representatives. The Chamber of Representatives is the lower house and is the more powerful. The State Council is the upper house and although it can vote to amend proposed laws, the chamber can only vote to overrule its amendments should the state council reject the bill more than twice. Although the State Council can introduce bills, most important laws are introduced in the Chamber – and most of those are introduced by the government, which schedules the vast majority of parliamentary time in the Chamber. Parliamentary time is essential for bills to be passed into law, because they must pass through a number of readings before becoming law. Prior to introducing a bill, the government may run a public consultation to solicit feedback from the public and businesses, and often may have already introduced and discussed the policy in the president's State of the Union address, or in an election manifesto or party platform.
The Chamber has 600 voting members, each representing a senatorial district for a five-year term without term limits. Chamber seats are apportioned on the basis of population, with Veratia providing 200 members and Il Dogado providing eight members.
The State Council has 210 members - 150 are drawn from each state, which provide ten members and the remaining 60 are appointed by the government as non-partisan crossbenchers in recognition of their contributions to national life. Both members drawn from the states and those appointed by the government hold their seats for single terms of ten years. The duty of the senate is to scrutinise all legislation, confirm appointments and ratify all international agreements. The State Council is able to table legislation over certain issues, these being; the constitution, limits of federal power, the separation between state and federal power, foreign policy and defence.
Judiciary: Etruria has a three-tier unitary independent judiciary comprising the Court of Cassation, the Constitutional Court, 25 high courts, and a large number of trial courts. The court of cassation has original jurisdiction over cases involving fundamental rights and over disputes between states and the centre and has appellate jurisdiction over the high courts, while the constitutional court's mandate is limited to determining the constitutionality of federal and state law. It has the power to both strike down federal or state laws which contravene the constitution, and invalidate any government action it deems unconstitutional.
Political parties
From the restoration of democracy in 1984 after twenty-four years of military rule until 2016, the country operated a two-party system, with power alternating between the centre-left Social Democratic Party and the centre-right Etrurian Federalist Party. The SDP held government for a total of 18 years under three presidents, while the Federalists held power for a total of 14 years under four presidents, the last of whom served for only 35 days. The third largest party until 2016 was consistently the Farmers and Workers Union, a social conservative agrarian party that competed for seats exclusively in Novalia. Until 2018, Etrurian governments were near exclusively formed out of coalitions between the major party and smaller allied parties. It was considered a tradition for the EFP to enter government with the FWU, while the SDP went into coalition with Sotirian Democracy until its merger with the EFP in 2002, and the Popular Liberal Party until its merger with the Citizens' Alliance in 2013.
In 2016, the two-party system collapsed under the weight of three monumental events: the EC referendum, the Miraviglia Scandal and the 2016 Etrurian general election. The Miraviglia Scandal broke during the height of the EC referendum in the early Summer of 2016 and involved both major parties, though it struck the incumbent Federalist Party government under President Emiliano Reali particularly hard. The scandal had an adverse effect on the EC result, as many voters saw a No vote as a means of punishing the pro-EC Social Democrats and Federalists. The loss to the No campaign led by the Tribune Movement and widespread anger and resentment toward an establishment perceived to be elitist, corrupt and aloof fed into the rise of spoiler parties, especially the Tribune Movement and Citizens' Alliance. The subsequent snap election in August 2016 resulted in a landslide victory for the Tribune Movement, a far-right neo-nationalist and right-wing populist party, which entered into coalition with the Farmers and Workers Union under President Francesco Carcaterra. The liberal-centrist Citizens’ Alliance became the official party of opposition. The Federalists lost over 300 seats in total from both chambers of the Senate, while the Social Democrats lost over 200, sending the once dominating parties to third and fifth place respectively.
In the most recent election in 2018, the new electoral law came into force. The Tribune Movement secured a second victory, gaining a supramajority in the Chamber of Representatives and a two-thirds majority in the State Council by itself, becoming the first party in Etruria since 1984 to form a single-party government. The Tribunes saw a net gain of 87 seats in the lower house and 28 in the upper house, the biggest increase of a sitting government in Etruria since 1984. The current political landscape since 2018 has come to be dominated by the Tribune Movement.
Etruria’s federal system has allowed for the rise of state-exclusive political parties. Among the most prominent include Together for Carvagna, Veratian National Party, Chiastrine Democratic Party and much smaller minority parties such as, Piraean Liberty Party, Carinthian and Novalian Party for Minorities and the Miruvian People’s Party. Etruria’s constitution prohibits political parties that promote or are dedicated to separatist causes. As of 2020, the Tribune Movement has majorities and governments in seven of the fifteen national states, followed by the Citizens who hold control over four states.
Elections in Etruria are traditionally held every five years; however, the President holds the power to dissolve the Senate and call elections at will. The most recent election in 2018 was held two years after the election prior, being called at the height of the EC-Etruria Crisis. The next election is dated for 2023 but may be held earlier. Etruria’s elections from 1983 until 2000 utilised first-past-the-post, before federal elections transitioned to proportional representation. In 2017, the Tribune Movement government amended the federal electoral law introducing a new system that operations both FPTP and PR. The states are delegated the power to determine their electoral processes, with six of the seven Tribune Movement states reverting to FPTP from PR systems as of 2020.
Constituent states
Internally, the Etrurian Federation is divided into three constituent republics and five Autonomous Federal Regions; four under Vespasia and one under Novalia. The federal capital is Poveglia. All states, as well as the Autonomous Federal Regions, have elected legislatures and governments, both patterned on the national model. Both the constituent states and autonomous regions are divided further into Regions (Regione) and then into Communes (Communi).
In order of population, the states are:
| Map | Name and flag | Administrative centre | Population | Governor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States of Etruria | |||||
| Praproče | 5,448,369 | Janez Hribar (TM) | |||
| San Alessandro | 5,248,480 | Augustina Faustini (CA) | |||
| Auronzo | 1,032,742 | Enrico Volpe (CA) | |||
| Carcoforo | 2,117,055 | Emmanuele Angrisani (CA) | |||
| Faulia | 7,925,386 | Alessandro Garavoglia (CA) | |||
| Carxeri | 9,352,687 | Giuliano Aurelio Vinci (TM) | |||
| Porto di Sotirio | 1,128,553 | Luciano Giustiniani (TM) | |||
| Accadia | 3,333,585 | Giorgio Maniero (DAE) | |||
| Sagrado | 3,956,111 | Simone Parro (TM) | |||
| Stazzona | 3,809,872 | Annalisa Taddei (CA) | |||
| Tyrrenhus | 6,920,327 | Pietro Andrea Ercolani (TM) | |||
| Solaria | 5,869,029 | Vittore Amadeo Varro (TM) | |||
| Vilanija | 9,558,135 | Franjo Sarič (FWU) | |||
| Centuripe | 1,700,655 | Nero Orlando (TM) | |||
| Federal Territories of Etruria | |||||
| Povelia | 988,882 | Marco Antonio Cristofori (DAE) | |||
The 1983 Constitution and more specifically the 1986 Convention Amendment laid out more clearly the federal system of Etruria, openly stating that the Federal Government is the governing authority of a federal union of three states and five autonomous regions.
The government of Etruria is based on a 3 tiered system, in which the Constitution of Etruria delineates the subjects on which each tier of government has executive powers. The Constitution originally provided for a two-tier system of government, the Federal Government (also known as the Union-Authority), representing the nation. Later, a third tier was added in the form of Municipalities. In the current arrangement, Article 15 of the constitution delimits the subjects of each level of governmental jurisdiction, dividing them into three lists:
- National List: includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, law enforcement, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. The Federal Government alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the National List.
- Constituent State List: contains subjects of State and local importance such as trade, commerce, agriculture and irrigation. The State Governments alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the State List.
- Concurrent List: includes subjects of common interest to both the Federal Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Federal as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Federal Government will prevail.
- Autonomous List: in effect replicates the constituent state list for the autonomous federal regions, with the concurrent list subordinated to ensure the constituent state's laws prevail over the AFR's.
Judiciary and law enforcement
The Etrurian judicial system is based on Solarian law, modified by the Pantheonic code and later statutes. The Federal Court of Cassation (Corte Federale di Cassazione) is the highest court in the country for both criminal and civil appeal cases. The Supreme Constitutional Court (Corte Costituzionale Suprema) rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution at both the federal and state level, should appeals be brought to the court from state-level supreme court rulings. In 2020, the Public Affairs Court (Corte Affari Pubblici) was established to process all civil and criminal cases relating to public administration, worker's rights for civil servants, federal electoral law and appeals relating to public protest.

From 1984 until 2017, law enforcement in Etruria was delegated to the states. Following the 2017 National Police Reform Act, all law enforcement in Etruria was federalised. Today, law enforcment is divided between the National Police Service (Servizio di Polizia Nazionale), which is the general law enforcement agency, and the Civil Sercurity Service (Servizio di Sicurezza Civile), which deals with federal crimes, combatting organised crime, financial and white collar crime. The National Police Service is divided into State Commands (Commandi Stato), Regional Commands (Commandi Regionale), Metropolitan Commands (Comandi Metropolitano) and Commune Commands (Comandi Comune). The National Police also has several subordinate agencies, the Federal Penitentiary Service (Servizio Penitenziario Federale) which manages the nation's prisons, the Auxiliary Community Police (Polizia di Comunità Ausiliaria), which is dedicated to community policing and acts as a reserve for the main police force in the event of natural disasters or major urban disturbances such as riots. The last two subordinate agencies are the Maritime and Customs Service (Servizio Marittimo e Doganale), which is dedicated to regulating and facilitating international trade, collecting import duties, and enforcing regulations, including trade and customs, and finally the Coast Guard.
Since their appearance in the late 18th century, Etrurian organised crime and criminal organisations have infiltrated the social and economic life of many regions in central and southern Etruria, the most notorious of which being the Tyrrenhian Mafia, which would later expand into some foreign countries including Piraea and Marirana. Other organised crime groups include the Novalian Bratovštine and the Solarian Cricche, while these organisations saw their power and influence peak during the 1950s and 1960s, they remained a significant presence in Etrurian life. Much of their crimes today are geared toward gambling, racketeering, human trafficking, drug trafficking, arms trafficking, prostitution, construction, tourism and money laundering. From 1990 to 2010, Mafia recepits were estimated to have reached 10% of Etruria's GDP in worth. In 2018, the Etrurian government launched Operation Gladio, the largest law enforcement operation in Etrurian history. The operation involved law enforcement agencies, the military and domestic intelligence service and resulted in the arrest of over 13,000 suspected Mafia members of various ranks and positions, the seizure of assets and property. While the operation was considered a "colossal success" and effectively crippled the mafia in Etruria, it did not go without criticism and condemnation, especially over its numerous reported abuses of legal rights, human rights and numerous cases of torture and deaths in custody.
Foreign relations and military
Etruria is a founding member of the Community of Nations, International Council for Democracy and the Association of Solarian Nations. Etruria is also a member of the Atomic Energy Commission, GIFA and the ITO, where it long offered strong support. Etruria is also a leading member of the Aurean Forum, which aims to manage traffic and administration of the Aurean Straits. Following the establishment of the Etrurian Third Republic in 1948, Etrurian foreign policy was guided by the principle of "active neutrality", in which the country would remain neutral in relation to inter-bloc rivalries while engaging productively with nations and organisations alike. The Military government throughout its 24-year rule mostly maintained the policy, though it was highly supportive of confronting socialism across Euclea and Coius, re-establishing its close relationship with Werania and Estmere for the first time since the Solarian War. The military dictatorship's pro-Eastern Euclea platform protected it serious criticism over its vagrant human rights abuses and authoritarianism. The EC became the strongest supporter for the democratic transition in 1984. Since the restoration of democracy in 1984, until the No-vote in the EC membership referendum in 2016 successive governments sought to bring Etruria closer to the Euclean Community, with the ultimate goal of securing membership. Etruria emerged as a vocal advocate for human rights, civil liberties and the protection of minorities across the world.
Despite successes in bringing Etruria closer to the EC, the defeat of the pro-membership campaign in the 2016 referendum and the electoral victory for the right-wing populist neo-nationalist Tribune Movement resulted in a rapid souring of ties. Between 2016 and 2018, the EC was a vocal critic of the Tribune Movement's democratic backsliding, culminating in the EC-Etruria Crisis. Etruria withdrew from the International Council for Democracy in 2018, claiming it was "built to promote liberal-leftism with near tyrannical means." The same period saw Etruria's government turn away from international institutions and multilateralism, claiming global bodies had infringed on national sovereignty. Conversely, under the Tribune Movement government, Etruria has placed greater emphasis on the Association of Solarian Nations and is currently planning on proposing a second body for the Solarian Sea states (Etruria, Montecara and Emessa), to include defence and economic ties. The outbreak of the Tsabaran Civil War and resurgence of Zorasan in late 2019 has seen a rapproachment between Etruria and the EC, led primarily by friendly governments in Estmere and Werania. Many observers have noted that the rapproachment can be credited to the Etrurian government seeing such a recovery of ties as key to "Etruria First."
One long term issue for Etrurian foreign policy has been its antagonistic relations with its smaller neighbours, specifically Piraea and Galenia. Both countries had been occupied historically by Etruria and most recently during the Solarian War, this conflict saw numerous war crimes, such as the Etrurianisation of Piraea, which some consider to be genocide. Etruria's policy of genocide denial both in politics and society has been a major thorn in its ties with these countries and was deepened with the 2018 National Dignity Act in Etruria, which prohibited any referencing of historic war crimes in schools and universities, both verbally and printed. Etrurian nationalism has also provoked crises if only brief, with its neighbours.
Etruria is regardas as a middle power by commentators, with it enjoying a high degree of military capabilities and significant soft power, through language, cuisine, music and other cultural aspects.
Military
The Etrurian Army, Etrurian Navy, Etrurian Air Force and the Auxiliary Defence Force collectively form the Etrurian Defence Force, under the Supreme Command (Commando Supremo), presided over by the President of Etruria. The armed forces is both voluntary and conscripted, as of 2016 the armed forces had 290,000 active personnel and 250,000 reserve, with a defence budget of $60.79 billion. Defence is managed by the Federal Ministry of National Defence.
The Etrurian Army's size is estimated at around 330,500 soldiers. In recent years, the Etrurian Army has played a sizeable role in international peacekeeping, and regularly takes a role in supporting law enforcement, search and rescue and disaster response. The Etrurian Navy primarily operates in the Solarian, Mazdan seas and the Gulf of Assionaire, and conducts operations such as maritime patrol, search and rescue for the section of the Solarian and Mazdan seas under Etrurian sovereignty, as well as hydrographic measurements and research. The current position of the Etrurian Air Force is similar to that of the Navy, conducting aerial patrols, search and rescue and providing logistical support to international peacekeeping, while it has taken a leading role in transporting aid to disaster zones and conflicts.
The final branch of the armed forces is the Auxiliary Defence Force, which is a popular militia that also serves as the country's gendarme in times of national emergency. The ADF is subordinate to the Ministry of the Interior during peace-time and in war-time, it is subordinate to the Supreme Command. As of 2016, the ADF had a strength of 55,000 active members and an estimated 255,000 reserve members. Since 2010, the ADF has also served as an emergency response force, assisting in the aftermaths of earthquakes. Most recently several ADF units were engaging in confronting several separatist movements in Carinthia and Marolev-ethnic armed groups, including the Battle of Starše in 2011.
The FMND previously oversaw the operations of Etruria's entire intelligence apparatus, until the Domestic Security Service (Servizio di Sicurezza Domestico; SSD) was transferred to the Federal Ministry of Civil Security in 2018. Today, the FMND oversees the operations of the External Intelligence Service (Servizio Intelligenza Esterno; SIE), which is tasked with providing the government with intelligence regarding foreign matters. The EIS also includes the Information Security Service (Servizio Sicurezza Informazioni; SSI), which is tasked with providing signals intelligence and information assurance for the government and armed forces. The FMND also has some jursidication over the Strategic Intelligence Directorate (Direzione Intelligenza Strategica; DIS), which is the military intelligence body for the armed forces.
Economy
Etruria is the world's 18th largest economy as of 2019, with a nominal GDP of approximately $1.025 trillion, and the 15th largest economy with a GDP PPP of $1.850 trillion. Etruria has a capitalist mixed economy. The GDP per capita as of 2017 is $15,637 (nominal) and $33,747 (PPP). Etruria is classified as a newly industrialised economy and has developed several highly competitive sectors, including its manufacturing, agriculture and tourist sectors. Its primary exports include light goods, home and electronic appliances and in recent decades, it has become a major producer of locomotives, automobiles, construction equipment and aircraft.
Etruria’s economy is noted to have suffered a Lost Generation, with economists agreeing that Etruria is at least two-decades behind its wealthier neighbours in Eastern Euclea. The “lost decades” are blamed on the Solarian War (1943-1946) and the failure in post-war reconstruction, where incompetence, corruption and bottlenecks caused profound economic instability during the Etrurian Third Republic (1948-1960). Pro-market reforms during the Military government period (1960-1983) saw some limited success in confronting the structural flaws in the economy, enabling Etruria’s industrial output to reach pre-war levels and exceed them by 1978. Following the restoration of democracy in 1983, successive democratic governments instituted neoliberal reforms, producing sufficient dynamic growth to see Etruria become a developed economy by 2008 according to the International Trade Organisation. Etruria's economic growth averaged between 4.5-5% between 1985 and 2015, in recent years growth has increased to average 5.5% between 2015 and 2020.
Today, Etruria’s economy remains mixed with the federal government regularly assisting national champions, such as Caviglia Aeronautica, Nettuno-Accadia, Casa and Valentino. Many economists also classify Etruria as neocorporatist, with significant degrees of state-aid and a vibrant trade union movement aimed at promoting social enterprise and worker welfare.
Industry
Industry accounts for 38% of Etruria’s GDP, and is the highest employer, with an estimated share of 43% of the national labour force. During the Military Dictatorship and subsequently, manufacturing has been the primary focus of government investment. This investment has supported the establishment of global brands in various sectors.
In 2018, Etruria produced an estimated 1.3 million automobiles and motorcycles, the Nth largest in the world. These vehicles are directed toward the domestic and Euclean markets, where they have proven highly competitive in the lower-price range. Etruria is also noted as a global producer of locomotives, buses and trams, where Caviglia Rotaia has become a global brand in the production of the former as well as high-speed trains for the developing Coian economies.
During the 2000s and 2010s, Caviglia Aeronautica emerged as a growing producer of both military and civil aircraft. The company is lauded as a national champion and is the Nth largest producer of short-haul and regional-haul aircraft. The company is also the Nth largest producer in private aircraft, including helicopters.

Etruria has since developed a strong light goods and appliance industry, with noted brands such as Casa and Valentino becoming the Nth largest producers of kitchen appliances, electronic appliances and home appliances. Casa is known to produce almost 88% of Etruria’s televisions and home entertainment systems purchased domestically.
Etruria is also a praised shipbuilding, with its high capacity for oil tankers, freighters, cruise ships, ferries and personal yachts and mega yachts. Nettuno-Accadia is one of the largest shipbuilders in the world, is known to high quality vessels.
Other areas in industry present in Etruria include mining, logging, steel producing and industrial chemicals. The Etrurian steel industry almost vanished during the 1960s, as the highly centralised industry dominated by Acciaio Etruriano became a zombie company, owing to poor competitiveness and gross mismanagement. AE was privatised in 1988 and broken up into three smaller companies that have proven more dynamic in recent years.
Tourism
Etruria is one of the most visited countries in the world, with an estimated 48.5 million visitors in 2014. Successive Etrurian governments have made use of the country’s natural environment, historic sites and cities to launch successful tourism campaigns. Etruria’s tourism industry is in part centred around the cities of Tyrrenhus, Solaria, Povelia and Stazzona, while the interior and coasts of Novalia have since overtaken the cities as the most popular tourist destinations.
Tourism provides an estimated 14.5% of Etruria’s GDP ($ ) and employs 5.1% of the workforce ( xx workers) in 2018.
Agriculture
Throughout much of its economic history, Etruria had been reliant on its agricultural sectors. It was not until the late 19th century, that industry had sufficiently replaced agriculture that its agrarian economic system was replaced. However, agriculture still plays a prominent role in Etruria’s economic output. Successive governments since the 1910s have implemented numerous measures and schemes to protect and support Etrurian farms. Since the 1960s, Etruria has actively impeded the emergence and growth of agribusinesses, protecting the small family-owned plots that have defined agriculture since the middle-ages.
As of 2018, there an estimated 1.95 million farms in Etruria, 47% being found in Vespasia (39% in the south and 61% in the north), 20% in Novalia and 33% in Carinthia. Over 90% of Etruria’s farms are small family-owned plots, averaging only 10 hectares in size. The number of farms has consistently decreased since the 1960s owing to rural-to-urban migration and cheaper imports from Coius or the Asterias.
Etruria is one of the largest producers of wine in the world and a major producer of chesse, olive oils and horticulture.
Infrastructure
Until the early 20th century, Etruria’s infrastructure was among the weakest in Euclea for a major nation. For decades, Etruria had among the major nations, the shortest and most limited rail network. It was not until the 1920s that Etruria expanded its railways beyond three lines connecting the state and national capitals. During the Great War, the Etrurian government launched a major construction program, aimed at supporting its military requirements. This resulted in the creation of the acclaimed Autostrade and Strade Provinciali road network. The war also saw dramatic expansion of railroads, with 12,500km of track added between 1928 and 1934. The project is renown for its use of penal workers and women.
Etruria has 998,365 km (620,355 mi) of serviceable roads, including 12,507 km (7,771 mi) of motorway. Both serviceable roads and motorways are state-owned and managed by Servizio Stradale Federale, though several regions have seen private companies manage the road network. Etruria’s established road-network is praised for its high quality and connectivity, consistent criticisms regarding the poor quality of roads in mountainous and isolated areas have rarely been met. In 2019, the Etrurian government launched a multi-billion euclo project to modernise and expand roads and highways in these regions.
The national railway network, state-owned and operated by Amministrazione Ferroviaria Federale Etruria, in 2019 totalled 18,888 km (11,736 mi) of which 16,213 km (10,074 mi) is electrified, and on which 5,100 locomotives and railcars run. Between 2000 and 2010, 5,900 km of railroad were upgraded to support high-speed trains, and between 2010 and 2014, this was expanded 6,500 km. In 2014, the Linea Leopardo high-speed train network was launched. The Linea Leopardo travels the length of Etruria’s eastern coastline. In 2018, the Linea Leopardo II project was launched with the aim of establishing high-speed links between the major coastal cities and the interior to the west. Etruria has 11 rail border crossings through Aventine settings and elsewhere. Plans for increase the number of rail crossings into Gaullica and Auratia are currently underway.
Etruria has 18 international airports, with the primary hubs being Pietromontecorvino in Tyrrenhus, Francesco Cesare Candreva near Povelia, and Romolo Alessandri-Solaria. There are 106 regional airports as of 2018, with plans for the construction of sixty more regional level hubs by 2030. Etruria’s national carrier is Volaretruria, which serves 82 destinations worldwide.
Etruria operates 39 major seaports, the largest being Accadia, which Etruria’s largest and the largest Euclean seaport on the Solarian Sea. Etruria operates a merchant fleet of 477 vessels, an increase of 13% as of 2019, compared to 2010. Etruria operates several ferry links, connecting regions and cities across Povelian Gulf, Insular Etruria and multi-national destinations, including Emessa and Auratia.
Science and technology
Historically, Etruria has produced numerous scientists and inventors, with Etruria’s prominent role in the Euclean renaissance. Notable Etrurian scientists and engineers include, Leonardo Renanti (1511-1567) who pioneered astrology, Enrico Venti (1489-1539) who made vital discoveries about human anatomy. In more modern times, Alessandri de Vecchi, who alongside Edmund Schultze, developed vaccines for anthrax and made breakthroughs in the study of rabies during the 19th century. Novalian Stepan Staric played a key role in the development of the telephone and Viktor Carraturo-Baric was vital in the development of vulcanised rubber.
Today, Etruria is host to several major institutions and research groups that focus on engineering, energy, robotics and communications. The Innocenzo Dametto Institute is one of Euclea's leading research and development bodies, looking into cleaner energy production. The New Century Group is a state-backed series of R&D institutions dedicated to pioneering future technologies, primarily Artificial Intelligence, Quantum computing, information technology and robotics. As of 2018, the Etrurian government spent $23.5 billion on R&D, a 11% increase from 2016, ranking Etruria as one of the highest spenders on research and development.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1900 | 31,475,000 | — |
| 1906 | 35,500,000 | +12.8% |
| 1916 | 38,021,000 | +7.1% |
| 1926 | 40,148,000 | +5.6% |
| 1950 | 45,800,000 | +14.1% |
| 1966 | 51,213,321 | +11.8% |
| 1976 | 59,336,807 | +15.9% |
| 1986 | 60,982,147 | +2.8% |
| 1996 | 62,250,325 | +2.1% |
| 2006 | 63,871,030 | +2.6% |
| 2016 | 65,596,083 | +2.7% |
| Source: Ufficio Federale di Statistica | ||
According to the 2014 census, Etruria had a population of 65.59 million - the 4th largest in Euclea and 15th in the world. Etruria has a population density of 119.58/km2 (309.7/sq mi), relatively lower than the Euclean standard. Population in Etruria is distributed unevenly, with concentrations found along the coastlines, the Eugenian Plain and the Carinthian Plain in the north and north-west respectively. Etruria is the one of the few countries in East Euclea to meet the replacement rate of 2.1, with a total fertility rate (TFR) of 2.4 as of 2018, as a result, Etruria's population is expected to exceed 70m by 2028 through mostly natural births instead of migration. The average age of Etruria is 32, among the lowest in Euclea. Etruria's birthrate compared to other Euclean countries has been subject to wide debate among statisticians, with many claiming income, standards of living and cultural values have played a role in maintaining the replacement rate.
During the 1990s and 2000s, Etruria experienced a large wave of immigration from former colonies Satria (55%) and Badawiya (45%), by 2010 it was estimated that these migrants constituted 6.4% of the population. This number has since fallen as many migrants moved from Etruria to other countries in Eastern Euclea.
Populations descdended from Etrurian colonists and immigrants can be found in Asteria Superior and Asteria Inferior. Beginning with the colonisation of Marirana in the late 15th century, significant numbers of colonists from Povelia and other Etrurian city states would go on to settle in what is also now Belmonte and Imagua and the Assimas. An estimated 257,400 left metropolitan Etruria for the Asterias during the 16th century. This would rise to 560,000 in the 17th century and 333,000 in the early 18th century. Following the Etrurian Revolution, migration to the Asterias would remain steady at 80,000 every decade between 1800 and 1830. The onset of the Industrial Revolution and urbanisation during the late 19th century saw Etrurian migration to the Asterias diminish. Another key diaspora can be found Caldia, which has historically been a popular destination for political exiles and free-thinkers expelled due to their beliefs. Over 5,000 Etrurians settled in Caldia during the Etrurian Revolution Republic (1938-1946) and a further 55,000 during the Military Dictatorship (1960-1983).
Ethnic groups
Etruria is a multinational and multi-lingual nation. The Etrurian nation state since its formation during the Etrurian Revolution in the 1780s has recognised this constitutionally and culturally since. The 1983 Constitution differs from previous basic laws as it defines the multinational nature of Etruria as a "federal union of three nations and six peoples", this definition plays into the degree of recognition and rights afforded to the ethnic groups of Etruria. The same definition lends to Etruria being described as a plurinational state. Regionalism within Vespasia has led to conflicts over the definition provided by the constitution. The identity of Etruria is widely based on the infusion of the territorial and ethnolinguistic idenities of its "three nations", insofar that the Etrurian identity is built from the overlap of the three dominant groups. The issue of national identity has been a long-term controversial topic in Etrurian society.
The "Three Nations" (Nazioni) are Carinthia, Novalia and Vespasia. The definition of a nation is based upon the historical boundaries of the ethnolinguistic state prior to unification under the Etrurian First Republic. While Carinthia and Novalia can claim to be functional nationstates before 1784, however, this definition sparked the "Vespasian Debate", owing to Vespasia being a geographical term for the Vespasian-speaking region of Etruria, which prior to 1784 consisted of thirteen distinct city states and republics. The "Vespasian Debate" centres around whether the constitution should defined Etruria as a "Federal Union of sixteen nations and six peoples", owing to the lack of a Vespasian nationstate.
The "Six Peoples" (Popoli) refers to the largest and settled ethnic groups of Etruria; Vespasians, Novalians, Carinthians, Miruvians, Piraeans and Gaullicans. While being recognised as a People affords equal civil and political rights, in reality, Etruria has experienced discrimination along ethnic lines since its unification in 1786 and it was not until the 1984 Constitution, that either the Miruvians or Gaullicans were officially recognised as ethnic groups in Etruria. Despite official recognition, the Etrurian census provides the options of Etrurian, Vespasian, Carinthian or Novalian for identity, owing to the constitution's definition of an Etrurian citizen as a "person who resides, inhabits and identifies with the Federation of Etruria", as Piraeans, Gaullicans and Miruvians (though a stateless multi-national ethnic group) can identify with separate and distinct nationstates outside of Etruria, providing these options in the census would "contradict the constitutional definition of an Etrurian."
According to the 2016 census, 87% of citizens idenify as Etrurian, 11% identified as their ethnicity (4% Vespasian, 4% Novalian and 3% Carinthian) and 2% idenitifed as "Other." The census showed that of the national population, 63.45% are Vespasian, 13.30% Novalian, 10.04% Carinthian, 4.18% Miruvian, 3.51% Piraean, 1.19% Gaullican, 1.18% Mariranian, 1.09% Zorasani, 1.06% Satrian, 0.98% Tsabaran and 0.02 Savader.
Lanugages
Etruria has three official languages Vespasian, Novalian and Carinthian. All three languages and are used for the federal and state government's acts and laws, this is required constitutionally in all fifteen states regardless of ethnic makeup. This has been in place since the Etrurian First Republic as a means of fostering "unity and cohesion through the shared politic." Owing to the limited intermixing geographically of the three national ethnicities, everyday life is generally spoken in the respective "nation's" language. Regions where intermixing is prevalent, notably the Tarantine regions and the country's largest cities, Vespasian is most spoken in everyday and cultural life. Education across the country is conducted evenly in Vespasian, Novalian and Carinthian, this policy is mandated by the constitution and is known as "Tri-lingual Education". This has enabled the an overwhelming majority of Etrurians to speak the opposing languages from their mother tongue to an advanced degree by completion of secondary schooling.
Exceptions to the TLE rule are found in certain states, notably Dinara and Peravia, where communes in the far north boast sizeable Gaullican populations local schools teach the Gaullican language to Vespasian students over Novalian and Carinthian. The most prominent dialect of Gaullican spoken is Gaullo-Aventine and is the dialect taught to Vespasian students.
The Etrurian constitution recognises a series of regional languages, though the number has been reduced steadily since the 1888 constitution's universal recongition. The most widely spoken regional languages recognised include Piraean, Miruvian (viewed as distinct to Novalian) and Gaullo-Aventine. The remaining regional languages are recognised dialects of Vespasian, the only Vespasian dialects to be recognised as regional languages are Povelian, Dinarian and Solarian. With the exception of Miruvian and Piraean, regional languages may be used for state acts, laws, public signage and education, however the three national languages must also be present.
Religion
In 2018, the proportion of Etrurians who identified themselves as Solarian Catholic Christians was 80.4%. Catholicism is the state religion of Etruria, having been restored in 2022, for the first time since 1984. Catholicism has been the dominant religion in Etruria for over a millenia, when it was first introduced during the days of the Solarian Empire. Since its founding, Etruria has been the home of the Holy See of the Catholic Church, based in the enclave of Tiberunum within the boundries of Solaria. Between 989 and 1787, the Church governed territory in southern Etruria through the Ecclesiastical State until its annexation by the Etrurian First Republic during the Etrurian Revolution and Etrurian Revolutionary Wars. The domination of the Pantheonisti faction during the revolution introduced a deeply religious form of republicanism, which empowered and elevated Catholicism in all areas of life. During the Revolution, numerous non-Catholic Sotirian minorities were persecuted or expelled entirely from Etruria, including numerous Amendist groups. The First Republic's near success in transforming Etruria into a religious homogenous nation would only be halted with the Republic's collapse during the Caltrini Restoration. The politically and constitutionally protected prominence of Catholicism would remain in place until the San Sepulchro Revolution of 1888 and the establishment of the Etrurian Second Republic, which provided guarantees of religious freedom and equality. Between 1888 and 1938, there was a revival in non-Catholic religions, including a resurgence in Amendist churches and a more public display of faith by the country's Episemalist churches in Carinthia and Novalia. Political preference and cases of discrimination and repression, osentsibly returned under the military government (1960-1984), which in some areas increased the predominance of Catholicism and the influence of the Church. Today, while not formally enshrined in law or policy, the Catholic Church still enjoys significant influence over government policy and in the everyday lives of Etrurian citizens.
Saint Jerome's Basilica in Stazzona
Basilica of All Apostles in Povelia
Saint George over Solis Cathedral in Faulia
The largest non-Catholic Sotirian minority in Etruria is Episemalism, which is practiced by 7.70% (4.9 million inhabitants) of the population. Episemalism is practiced near exclusively by Miruvians and Piraeans in the west of the country. The vast majority of Episemalists fall under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Arciluco, while a small minority belong to independent churches. Episemalists until the restoration of democracy in 1984, had long been one of the most repressed religious minorities in Etruria, where it was often viewed by government and society that Episemalism was a connotation for Marolevic nationalism and separatism. The Episemalists suffered in particular under the Etrurian First Republic, who sought to either expell or convert its adherents. The revival under the Second Republic coincided with a warming of public opinion and an embrace of religious plurality. Repression returned under the Etrurian Revolutionary Republic (1938-1946) and the military dictatorship, with the former seeking to convert or expel the entire minority, while the latter sought to repress the Episemalist churches as part of its response to the Western Emergency. The restoration of democracy in 1984, once again guaranteed religious freedoms and since, the Episemalist Church in Etruria has noted a revival and more public display of its presence.
Amendist churches constitute the smallest Sotirian minority, including an estimated 156,000 Kasperists, 200,000 members of the United Reform Church of Etruria, 100,000 members of individual Amendist churches. Etruria historically housed a small number of Witterites, who arrived in Etruria following the 1888 Revolution, due to its liberal religious freedoms. However, the estimated 2,400 Witterites were ultimately killed during the Etrurian Revolutionary Republic and no community has since returned. The largest Amendist group in Etruria are the Cavernicoli, who number 497,000 according to the 2014 census. The Cavernicoli originate as homegrown Amendist movement in northern Dinara state, who practiced their faith underground in secret. Collectively, the Amendist minority constitutes 1.49% of the national population.
In 2014, 6.78% of the population identified as atheist or irreligious. It should be noted that Etruria records irreligion and atheism as the same on its official census and so no breakdown of this number is possible. This is an increase of 2.3% from the 2004 census.
The largest non-Sotirian faith practiced in Etruria is Irfan, where an estimated 2.70% (1,725,002 inhabitants) of the population identify as Irfani. Irfani have had a presence in Etruria as early as the 16th century, where many would settle primarily in Povelia, owing to the city's lucerative trade with northern Coius. The vast majority of Irfani in Etruria originate from either Zorasan, parts of Satria as migrants. 89% of the country's Irfani identify as XX and the remainder as XX. The next largest non-Sotirian minority is Atudism, which stands at 1.89% (1,207,501 adherants). According to some historical sources, the Atudites may have been present in Etruria as early as the 2nd Century CE, where many fled across the Solarian Sea following the brief take over of Adunis by the Second Heavenly Dominion. Atudites were recorded as enjoying significant freedom and prosperity in Povelia, Accadia, Solaria and Stazzona during the renaissance. Etruria is estimated to have the largest population of Atudites outside Tsabara. The remaining identified faiths include Badi, who represent 0.98% of the population and are drawn primarily from Badawiyan or Zorasani migrant communities, the smallest is recorded as Satyists, who constitute 0.76% of the population and is confined to migrant communities from Satria.
Healthcare
Etruria has operated a universal public healthcare system since 1974, when the military government established the Sistema Sanitario Federale (Federal Health System), which provides healthcare to all citizens. Healthcare is provided by a mixed public-private system and is reliant upon taxation and private insurance for funding. The SSF is organised federally by rhe Federal Ministry for Health and Social Services, but the administration is devolved to the individual states. The state administrations are supported by federal funding, which is dispursed according to state populations, while private insurance is provided by a person's employer and optional schemes provided by private medical institutions. The Etrurian government funds universal cover for all citizens who's annual income falls below ₣50,000. In 2017, funding for individual public hospitals was boosted by the introduction of the Non-Emergency Fee (Tariffa non di Emergenza), in which patients who receive medical assistance for non life-threatening issues are required to pay a ₣90 fee. Significant reforms during the early 2010s saw major improvements to the quality of healthcare in Etruria, with the country enjoying one of the lowest rates of infant mortality in Euclea. Etruria is also noted for its palliative care system, cosmetic surgery though not provided under the public health system is noted for its quality and affordability. Etruria is one of the few countries to introduce mandatory vaccinations, which it did in 2008 to much controversy and opposition.
Life expectancy in Etruria is 81 for males and 84 for females, placing the country Xth in the world for life expectancy. In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries, Etruria has a relatively low rate of adult obesity (below 10%), as there are several health benefits of the Solarian diet. However, Etruria has one of the highest rates of daily smokers in Euclea, estimated at 43% in 2017, efforts to ban smoking indoors were blocked by the introduction of laws mandating separate and isolated smoking rooms. In comparison to other Eastern Euclean countries also, Etruria ranks among one of the highest for the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, while between 2000 and 2011, Etruria ranked as the highest for HIV/AIDS.
Education
Etruria's education system is organised by the Federal Ministry for Education, but administration is devolved to the states. Etruria operates at least fifteen "Federal Institutes", academic institutions dedicated to the study of social sciences, medicine, engineering and economics. These institutions are utilised directly by the national government for policy making or national projects and are administered directly by the FME. Etruria has the highest concentration of Parochial schools in Euclea, with an estimated 6,649 schools run or governed by the Solarian Catholic Church.
Education in Etruria starts at the age of four or five (with the particular age chosen by the parents) for the 'Foundation' class (Kindergarten) and six or seven years in the 1st class of primary school (Scuola Primaria). It is compulsory under federal law that children participate in one year of education before entering the 1st class at no later than 7 years of age.

At the end of the 6th class when students are 13, students take a compulsory exam that determines their degree of progress and is later referred to when determining their upper-secondary school. Students after 13 attend a general secondary school (scuola secondaria generale). They will attend this school during classes 7, 8, and 9, for a total of three years. Students then take another compulsory exam or in some cases more than one exams to determine the upper secondary level school they will attend. Some upper-secondary schools require exams in extra-circular activities, such as independent learning of languages, musical instruments or sports. Students either attend a Liceo, which prepares students for university education, or a technical school (scuola tecnica), which provides training in technical or vocational areas. Etrurian technical schools, dependent on their focus, can be directly tied to a business or institution, to guarantee immediate employment or workplace experience. Both schools are completed through a final mandatory exam (Completamentol; Completion Exam), and may be followed by several forms of higher education, leading to Diplomato or Laurea (second cycle qualification) and eventually dottorato (third cycle qualification).
In Etruria, there are 540 university-level institutions for the pursuit of higher education as of 2018. There are 24 fully accredited traditional universities, 27 technical universities, 11 independent medical universities, 6 universities for the study of economics, 8 agricultural academies, 3 pedagogical universities, 18 theological academies, 5 maritime service universities and 4 national military academies. Also, there are a number of higher education institutions dedicated to the teaching of the arts—amongst these are the 19 academies of music.
Functional urban areas
| Rank | Region | Pop. | Rank | Region | Pop. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tyrrhenus  Solaria |
1 | Tyrrhenus | Palestrina | 5,981,640 | 11 | Poveglia | Àdexe | 823,997 |  San Alessandro  Fauglia |
| 2 | Solaria | Aventina | 5,573,217 | 12 | Stazzona | Carvagna | 710,343 | ||
| 3 | San Alessandro | Lamuria | 3,772,475 | 13 | Galižana | Štinjan | 694,683 | ||
| 4 | Fauglia | Dinara | 2,403,919 | 14 | Piavenna | Ossuccio | 614,111 | ||
| 5 | Accadia | San Pietro | 1,998,187 | 15 | Centuripe | Tarpeia | 500,735 | ||
| 6 | Dubovica | Krivaja | 1,431,383 | 16 | Sagrado | Torrazza | 499,324 | ||
| 7 | Turania | Moresco | 1,392,003 | 17 | Castello Nero | Valle di Conti | 494,007 | ||
| 8 | San Francesco | Meloria Superiore | 1,376,113 | 18 | Bekovje | Kopriva | 470,561 | ||
| 9 | Praproče | Kapitala | 994,537 | 19 | Auronzo | Valle dei lupi | 379,886 | ||
| 10 | Auronzo | Falerone Inferiore | 969,897 | 20 | Ugovizza | Gniva | 371,990 | ||
Culture
Arts
Art in Etruria across its history has played a key role in the development of Euclean artwork, with one of the oldest frescoes in Euclea found in the Tomb of King Tarquinius, which dates as far back as 930 BC. Ancient Etrurian artwork owes much of its infuence and characteristics to those found in Ancient Piraea, however, Tyrrenhian and later Solarian art developed unique characteristics of their own. Most of Ancient Solaria's artwork was produced in the decoration of personal homes as the means of pursuing status among peers and often portrayed personal stories in extravagent ways.
The emergence of panel paintings was pioneered by early Novalian painters, drawing on influence from neighboring Piraea, who shared in the works of Episemalist iconography. This in turn led to the introduction of Solarianesque art during the early middle ages, where it grew in popularity across Vespasia. Artists in Vespasia began to explore improvements in realism and a focus on volume, producing many great artworks during the middle ages.

The golden age of Etrurian painting and sculpture came during the renaissance (1320-1635), driven by the patronage of Etruria's ruling elites, including the Solarian Catholic Church and outside influences. The renaissance produced numerous artists and scultpures, who's work played significant roles in the development of modern Euclean arts and the freedom of artistic expression and innovation. Leading Etrurian artists of the renaissance including Andrea Farese, Giovanni Aldrovandini, Tiziano della Vadera, Andrija Vareši and Ivan Antonevic revolutionised painting through innovative uses of perspective, proportion and a refinement of the use of human anatomy, which in turn greatly refined portraiture and landscape works. With the innovations of proportion and understanding of human anatomy, Etrurian sculpture works became integral fixtures of the renaissance. Many great sculpture artists were hired by leading patrician families or rulers to honour ancestors or heroic figures, while the Church played a prominent role in Etruria through its patronage of artists in the production of statues of Saints and holy figures.
The succession of the Renaissance period by Vespasian Baroque saw further transitions into different expressions by artists, which dominated the 17th century. This in turn was replaced by the emergence of Rococ art, which played a significant role in the evolution of landscape artists specifically, who's use of plastic paints enabled the creation of numerous masterpieces depicting various Etrurian locales and cities. Etrurian art would decline during the late 18th century owing to the upheveal of the Etrurian Revolution, where many established painters and sculpture arists were persecuted for their historic service to monarchs or leading patrician families. Following the revolution, Romanticism spread to Etruria in the 19th century, where many artists embraced the style to critique or lament the struggles of the revolutionary period. The most prominent Etrurian romantic artist was the Povelian Ugo Desiderato, who produced numerous scenes depicting the glory of the Exalted Republic of Povelia prior to its downfall during the Revolution. However, the romantic period saw the leading artistic hubs move away from Etruira to northern Euclea.
The early 20th century saw Etruria give way to the futurist movement, and Etruria's resurgence as a leading light in painting and sculpture. Futurism grew in popularity during the Great War, due to its expressive use of colours to depict violence, machinery and modernity. The movement was patronised by the Etrurian Revolutionary Republic as a means of expressive propaganda, this connection to the National Solarianist regime and Solarian War saw the descrediting of futurism and its ultimate demise across Etruria and Euclea.
Literature and philosophy
The first recorded instance of literature in Etruria is a stage play performed in Tyrrenhus in 669 BC, references to this play were recorded by later Ancient Solarian historians. The Tyrrhenian oral tradition was adopted by the Ancient Solarians following the establishment of the Solarian Republic in 356 BC, where the speeches and thoughts of prominent patricians were documented in great detail, this in turn consolidated the foundation of Solarian literature. The literature of Ancient Solaria remains highly influential today, owed to the preservation of works by the likes of Tinian, Aitan, Arminius and Sacerio. Among the most treasured works of Ancient Solaria are the preserved transcripts of speeches made by the leaders of the Solarian Republic, especially Sacerio, who's thoughts and monologues on classical republicanism would prove pivotal in the Etrurian Revolution in the late 18th century. Ancient Solaria was also famous for its poetry, drama and mythical epics. Ancient Solarian writers, much like their successors during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, through their work also constitute philosophers of equal measure.

Going into the middle ages and renaissance, Etruria's most prominent poets, especially in Vespasia would commonly serve in prominent political positions. This celebration of literary talent through public office would play a pivotal role in some of Etruria's leading poetry, story telling and essay production. As such, many Vespasian works from those two periods would take on loftier tones, while many stories and poems took on the form of allegories. The renaissance period saw numerous Vespasian political leaders take inspiration from their Ancient Solarian ancestors, in documenting their inner thoughts, oratory and ideals, be it on love, religion or politics. This is best exemplified by the works of Francesco Cesare Candreva, when serving as Doge of Povelia, produced The City, is one of the most famous essays on political science and modern philosophy. Carinthia and Novalia drew inspiration from both the Marolevic west and the Vespasian east, with emphasis on virtues and principles. Novalia's Pavle Babić produced the poem Izgubljena Zora, considered to be one of the best poems on chivalry. Carinthia's Ivan Tavčar in 1563, wrote Marija je Dostavila, one of Etruria's most translated and re-published stories, and acclaimed for its prose and religious themes.
The 17th and early-to-mid 18th centuries saw Etrurian literature dominated by recurring themes of Sotirian values, providence and interpretations of Etrurian mythology. Giovanni Pio Renaldi's La Bestia is considered to be the most read fairytale book in Etruria, with its numerous short-stories focusing on individual mythical beats and beings. The role of Sotirian themes came as a backlash against the Amendist movement in northern Euclea, these produced numerous poems, stories and essays. The works by Dante Fattoruso's works on Solarian Catholicism would go on to be integral sources for the development of Etrurian Republicanism in the lead up to the Etrurian Revolution.
Etrurian literature was thrown into chaos with the Etrurian Revolution, the lead up saw the emergence of themes regarding liberty, justice, democracy and dignity. The overthrow of the Vespasian states during the Etrurian First Republic dispatched numerous poets and writers across Euclea, many of whom fled persecution over their patronage to aristocrats and patrician families. Those who remained pioneered new literary themes, celebrating or defining the Republic of Heaven ideal of the revolution. The Revolution is also acclaimed as Etruria's philosophical golden age, with Antonio Gennaro Volci's Il Carillon della Repubblica was praised by revolutionary leader Francesco Caciarelli as the epitome of Etrurian republicanism and by many writers since. Prežihov Rusjan's Božja Podoba (1786) is widely considered to be one of the most articulate arguments against slavery and is cited by the First Republic in its decree abolishing slavery and the slave trade in Etruria.
The 19th and early 20th centuries for Etrurian literature was dominated by the celebrations of industry, science and modernity. While some writers decried the destruction of nature in pursuit of industrial progress, a vast majority of Etruria's writers welcomed the change, with poems and stories advocating the mill and factory as measures of humanity's progress. The same periods saw a resurrection of Revolutionary-era literary themes in the preceding years to the San Sepulchro Revolution of 1888 and the second and final overthrow of monarchy in Etruria. Romanticism played its role during the latter stages of the 19th century, with images portrayed in prose of a new and united Etruria destined for global prosperity. The previous celebrations of modernity and industry ultimately gave way to the emergence of futurism, which in turn sought the celebration of youth, violence, speed and the machine. Etrurian literature of the 20th century, especially in the 1950s and 1960s was defined by the popularity of dystopian fiction, a cultural reaction to the devastation and conditions of Etruria during and after the Solarian War.
Cinema
Etrurian film first emerged in the late 1900s, with two companies dominating the industry: Fauglia Cinematografica and Serenità Cines, with both producing anticipated silent films throughout the 1910s. During the 1920s, a further eight companies emerged, producing quality films, which were soon exported out of Etruria. Cinema was later used by both the Etrurian Second Republic and Etrurian Revolutionary Republic to produce wartime propaganda during the Great War and Solarian War respectively, this would be repeated in a different manner under the Military dictatorship during the 1960s and 1970s.
Etrurian cinema declined rapidly in the post-solarian war period, where mass destitution and economic devastation hindered the capital or means for production of feature length products. It was not until the late 1950s, that Etrurian cinema made an artistic comeback. In 1960, the CineTyrrenio studios were launched, unleashing an entirely new genre of films produced and directed by Etrurians, under the influence of the military government. During the 1960s and 1970s, Pepla films emerged, centred around the Piraeo-Solarian period, and usually following Ancient Solarian heroes or epics. Many of these films were extravagent with their set designs and costumes and became immensely popular in Etruria and beyond. Other genres to emerge during this time was Serafici (Seraphic), historic epics based around the lives of Solarian Catholic Saints, another was Dogi e Commercianti (Doges and Merchants), which often constituted comedies or romantic tragedies set during the Etrurian renaissance. Etrurian cinema during the 1960s and 1970s was noted for its "escapism", diverting attention away from the poor condition of Etruria in the post-war period and the violence of the Western Emergency. Mariranian Spaghetti easterns became immensely popular in Etruria during the 1960s and 1970s, leading to a short period of Etruria imitations being produced, though they failed to make significant impact.

Etrurian cinema also provoked controversy during the same period with the genre of Epiche Eroiche (Heroic Epics), where films were produced as a cinematic series covering Etruria's battles during the Great War and the Solarian War, usually with the Etrurian characters in question facing suicidal odds, only to survive through bravery, pluck and determination. The 1968 film Outcry was widely condemned as historical revisionism, by portraying Etrurian soldiers during the Solarian War fighting to defend Piraean nuns from Piraean partisans who sought to attack their nunery. With the restoration of democracy in 1983, Etrurian film transitioned toward more international and away from nationalistic genres. The Povelia Film Festival has been an annual fixture since its establishment in 1949.
Media
In 1925, Ammisitrazione Radiotelevisione Etruriana was founded and is Etruria's publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation. It operates television and radio stations across the entirety of Etruria, specifically serving local, regional, state and national audiences and is funded directly by the Etrurian government and through advertisment, which abolished the historic license fee in 2009. ARE News is the nation's most popular provider for daily broadcast news and information. Other major providers in Etrurian media include Orrizonte TV, which competes with ARE at the national and regional level, other competative providers include NNT, which operates at the Novalian regional level and Zora do Sumraka, which serves Carinthian regional audiences.
Newspaper readership in Etruria differs per region, where preferances for national or regional papers fluctuates. In the Vespasian states of Etruria, the overwhelming preferance is for national level papers, including the centrist Il Popolo, right-wing Telegrafo Solariano and the independent Nuovo Percorso. Readers in Novalia and Carinthia are shown to be major consumers of regional or local newspapers, many of which are sister publications of national papers. During the 1990s and early 2000s, tabloid newspapers grew in popularity, with La Stella briefly overtaking the established national papers as the most circulated. However, a series of scandals indicating extensive falsifications and its use as a political tool to descredit politicians eventually led to the downfall of La Stella and tabloid journalism in Etruria.
The media sector in Etruria is decentralised between Tyrrenhus, Solaria and Fauglia, where national newspapers and television and radio are largely based. While, Praproče and Dubovica dominate the media sectors of Carinthia and Novalia respectively. The Etrurian publishing industry, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies at the local and national levels produce an estimated $12.5 billion for the Etrurian economy each year. Etruria is also home to some of the oldest continuously serving publishing houses in Euclea, with San Dionigi Editore (1603) and Stefano Barbarigo Editore (1611) still in business.
Music
Ever since Ancient Solaria, music has played a prominent role in Etrurian culture. From folk music, including the iconic tarantella to opera, classical music, Etruria has been a hotbed for innovations in instruments and genres of music, with the violin and piano being invented in Etruria and the musical forms of the symphony, concerto, and sonata, tracing their roots back to innovations of Baroque-era Vespasian music. Famous Etrurian composers from the renaissance include Valaseno, Montecorvino and Karelo, who introduced acclaimed magridals and innovated polyphony.

In music, Etruria is most famous for the creation of opera, where it began as a popular form of theatre, shared by all classes. The origins of opera are believed to be northern Vespasia, primarily Povelia and Faulia during the early 17th century. No major works from the earliest period of opera have survived, though later works and pieces produced in the 19th century remain popular and stand as some of the most famous ever written. Many works by Gioachino, Ercolani, Vitiello and Bonera are perfomed in operahouses worldwide. Etruria operates the highest number of opera houses in the world, with the La Leone in Povelia, the Ducato Giorgio in Faulia and Papa Pio X in Tyrrenhus being the most popular establishments in Etruria. La Leone and the Ducato Giorgio are considered to be among the best in the world for operatic perfomances. While considered to be a classical form, operas remain among the most popular music forms in Etruria, enjoyed across all age groups and socio-economic classes.
During the 1950s, Etrurian music genres were dominated by swing and schlager music, imported from Werania. Sophia Valentino became a Euclean chart topper during this decade with her take on popular swing and schlager music. During the 1960s and 1970s, the policies of the military government stemmed the spread of popular genres like progressive rock and free jazz, though they became widely embraced genres in the underground cultural scene. The policies of the dictatorship however did lead to the emergence of turbo folk in the early 1980s, which initially began among the Miruvian minority, before being emulated by the Novalians and Carinthians, turbo folk in the latter two languages also became popular among Vespasians, leading to turbo folk being considered the "genre of democratisation." The late 1980s saw musical innovations in electronic and dance music, introducing the sub-genres of Etrurodance and EtruroHouse; known for their futuristic sounds and prominent use of synthesisers and drum machines. Etrurodance and Etrurohouse faded by the early 2000s, though have seen a revival in the 2010s. The leading artists of Etrurian electronic music include Inferno 12, Leo Scipio, Mario D'Santis and the Novalian due Castra.
Cuisine
Etrurian cuisine is greatly defined by its multiethnic nature, with its food drawing influences from the climate, geography and three major cultures. The role of its Solarian roots is found its extensive use of fish and seafood dishes, and its inspirations from the land in the form of cuisines from Novalia and Carinthia have helped develop a great variety of dishes and divisions of its cuisine. Over the centuries, the distinct cuisines of Etruria's cultures have merged to create a unique "Etrurian fusion" of popular Central Euclean recipes with those of the Vespasian region. There are four divisions of Etrurian cuisine:
- Vespasian: Defined as the Solarian diet, Vespasian cuisine is centred around pasta, alongside herb enriched sauces, though with distinct regional differences.
- Carinthian-Hinterland: The stews, thick soups and meath dishes of Carinthia and inland Novalia, such as Matevž and goulash.
- Novalian: Heavily inspired by its Solarian roots, with a primary focus on seafood dishes, such as the fish stew Brudet, salted or grilled sardines (slana riba), usually served with salad.
- Etrurian Fusion: Etrurian Fusion refers to numerous dishes that draw influences from the above divisions. The most prominent of Etrurian Fusion is Vespasian Goulash, which includes the use of tomato, onion & garlic Marinara sauce, alongside macaroni pasta and grounded beef.
Sport
The most popular sport in Etruria is a football, varieties of which have been played in regions of Etruria since Solarian times, however it was not until the late 19th century that football came to dominate Etrurian sports. S.S Solaria is the oldest team in Etruria, being founded in 1894. Etruria's Lega A is the nation's premier league division and one of the most watched in Euclea, with S.S San Marco and A.S Tyrrenhus among the most successful football clubs in the world. The national team also stands as one of the best in the world, recently coming third in the 2019 IFF Coupe du monde. Etruria had historically won the Coupe du Monde in XXXX, XXXX, XXXX and XXXX.
Tennis, basketball, volleyball and futsal are other popular sports enjoyed by Etrurians. The country has hosted the Etrurian Open tennis tournament since 1956,and since grown in viewership and prestige since the 1990s. The country's rising sports in popularity are motorcycle racing and formula one, the annual Accadia Grand Prix held at the Sergio Virzì Ippodromo elevated Etrurian motor racing to global audiences. Rugby first emerged as a sport in Etruria during the Great War, when it was introduced by Estmerish soldiers during the 1920s, since rugby has become a popular sport, particularly in southern Vespasia. The national rugby team has competed internationally since 1950 and is considered a tier-one rugby team. Bicycle racing is a popular and familiar sport, especially in Carinthia and Novalia, the Ogled Koroške hosted in Carinthia is an annual fixture in international bicycle racing and has grown in prominence owing to the natural beauty of the designated racing route through the country's foothills.
Owing to the mountainous terrain of Etruria and the Aventine Mountains, Skiing is considered to be a national sport, Aventine skiing is the third most practiced sport, and the country is a popular international skiing destination, known for its ski resorts in both the Aventines and Tarantine mountains. Etruria has among the most extensive and high quality skiing facilities in the world, with Etrurian skiers regularly achieving good results at the Winter Invictus Games, and the skiing world cup and championships.
Etruria is the birthplace of the modern Invictus Games, hosting the first games in 1898, then in 1998 and most recently in 2010. Etruria has hosted the games the second most times, after Gaullica. The country has also hosted the Winter Invictus Games twice, in 1920 and 1956.
Public holidays
Citizens of Etruria enjoy a large number of public holidays, officially known as Federal Holidays. The origins of the holidays are varied; some are cultural holidays, steeped in Eturian history, while a majority are derived from the Solarian tradition, and others are derived from the country's modern history. There are currently 19 official public holidays, all of which are non-working day
| Date | Estmerish name | Official Etrurian name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day | Capodanno | |
| 6 January | Epiphany | Epifania | |
| 10 February | Rivodutri Victory | Vittoria Rivodutri | Final battle of the Great War, resulting in a victory over Gaullica |
| A Sunday in spring | Easter | Pasqua | |
| Monday after Easter | Easter Monday | Lunedì dell'Angelo, Lunedì in Albis or more commonly Pasquetta | |
| 1 May | International Workers' Day | Festa del Lavoro (or Festa dei Lavoratori) | |
| 20 July | Birth of the Republic Day | Festa per la Nascita della Reppublica | Anniversiary of the founding of the Etrurian First Republic in 1784. |
| 15 August | Ferragosto/Assumption Da | Ferragosto or Assunzione | |
| 1 November | All Saints' Day | Tutti i santi (or Ognissanti) | |
| 26 November | Sons of Romulus Day | Figli di Giorno Romolo | Celebration of the Etrurian Armed Forces |
| 8 December | Immaculate Conception | Immacolata Concezione (or just Immacolata) | |
| 25 December | Christmas Day | Natale | |
| 26 December | Saint Stephen's Day | Santo Stefano |