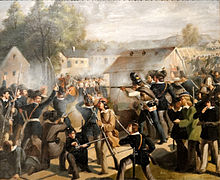Mascylla
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Crowned Republic of Mascylla Gekrönte Republik Maskillien (Hesurian) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Hier stehen Wir" "Here We Stand" | |
| Anthem: "Geeint in Blut und Schwur" "United in Blood and Oath" | |
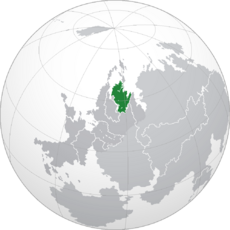 Location of Mascylla (dark green) in Berea (dark grey and green) | |
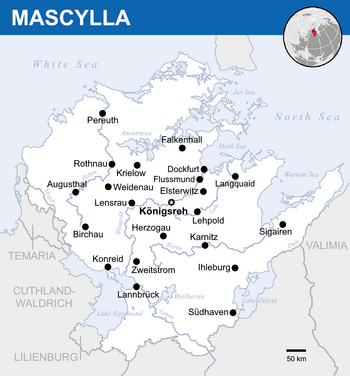 | |
| Capital | Königsreh |
| Largest city | Flussmund |
| Official languages | Hesurian |
| Recognised national languages | Cuthish, Waldish, Falian, Warnoan |
| Ethnic groups | 84.2% Mascyllary 10.5% other Telmerian 3.0% Black 2.3% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Mascyllary |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Queen | Dorothea I |
| Thomas Falkner | |
| Egon Weidmann | |
| Walther Steintz | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Reichssenat | |
| Reichsrat | |
| Establishment | |
• Congress of Rehnern | 20 December 1757 |
| 4 September 1789—29 March 1793 | |
• Treaty of Langquaid signed | 18 May 1793 |
• Coronation of Lukas I | 23 May 1793 |
| 10 May 1923—22 January 1924 | |
• Current constitution adopted | 24 January 1924 |
• Coronation of Maximilian I | 5 March 1924 |
| Area | |
• Total | 542,017.0 km2 (209,273.9 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 2.1% |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | |
• 2018 census | |
• Density | 90.4/km2 (234.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2017) | low |
| HDI (2016) | very high |
| Currency | Mascyllary Karning (MKN, Ӄ) |
| Date format | DD/MM/YYYY |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +47 |
| Internet TLD | .mc |
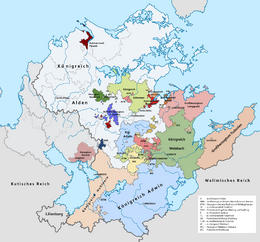
Mascylla (Hesurian: Maskillien), officially the Crowned Republic of Mascylla (Hesurian: Gekrönte Republik Maskillien) and rarely referred to as Mascillia, is a sovereign state on the Telmerian peninsula in northern Berea. It is bound to the west by Temaria, Lilienburg and Lake Sigismund, to the south by Cuthland-Waldrich and X, to the east by Valimia, and to the north by the North Sea and White Sea, with additional maritime borders with X to the north. Königsreh is the country's capital, and with Flussmund as the most populous city are the two main cultural and economic centres of Mascylla; other major cities and urban areas include Langquaid, Augusthal, Lannbrück, Dockfurt, Karnitz, Weidenau and Konreid. With a population of approximately 49 million inhabitants as of 2018 and a territorial area of 542,017 km2 (209,273.9 sq mi), Mascylla is both the second-most populous and second largest country in Telmeria.
Mascylla is a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy since its formal establishment in 1793. Current monarch since 2015 and the second female head of state in Mascylla's history is Dorothea I, while Thomas Falkner is elected head of government as Prime Minister since 2016. The constitution adopted in 1924 determines the separation of power is exercised by the country's Reichsrat and Reichssenat, the Kronenrat, formally by the ruling Monarch, and the High Court.
The area of what is now Mascylla was originally inhabited by a collection of Telmerian tribes, most notably the Therunders (Terunder), Falians (Fahlier), Aldens (Aldier) and Adhuins (Adhuiner) since classical antiquity. Following ill-fated attempts by the Cambran Empire to expand northward beyond modern-day Dulebia and its subsequent collapse in the aftermath of the Migration Period by 300 AD, the newly founded Albarian Kingdom annexed southern Mascylla while introducing Cambran innovations and customs to the region and developing a distinctive culture and language as the basis for modern Mascyllary culture. The presence of the Albarians prompted the slow creation of duchies and states from the Mascyllary tribes, and by 1000 AD most of Mascylla had been organized into a patchwork of petty kingdoms and duchies. Soon after, religious disputes and a prolonged series of dynastic disputes dominated Mascyllary politics in the Middle Ages, increasingly influenced by growing predecessors to the First Cuthish Empire.
After the Adwhinish Wars and War of Kalaphay Succession in 1569 and 1603 respectively, two nations had emerged as regional powers, Aldia and Adwhin, vying for hegemony over the remaining Mascyllary states, with Aldia rapidly rising with a colonial empire it had acquired from Cuthland in the 1700s. The hostilities between both nations began to grow and, following the gradual dwindling of power of the Cuthish Empire in the latter 18th century that left a power vacuum in Mascylla's central provinces, three consecutive wars of unification were fought in the 1740s, 1760s and 1770s respectively. The epitome of violence would be reached in the War of the Five Kings from 1789 to 1793, with Aldia, leading a confederacy of states against Adwhin and ultimately emerging victorious. The subsequent Treaty of Langquaid negotiated the unification of Mascylla into a nation state with a continuation of the Aldian monarchy at its helm. The collapse of Cuthland and its slow partition enabled Mascylla to vastly expand its Berean as well as Pamiran and Alvinian colonies. Moreover, Mascyllary culture and commerce flourished by the turn of the 19th century, and the Aldian colonial system expanded into a global colonial empire that was the second largest by the 1830s. However, with the rise of the Second Cuthish Empire under X and following the Second Cutho-Mascyllary War (1830–41), Mascylla was utterly defeated and forced to cede pre-1758 Cuthish territories in Mascylla as well as a portion of its colonial possessions. The ensuing antagonization by the Mascyllary populous and the mutual hateship between both countries that had developed over the last two hundred years was a decisive factor in the causing of the Great War (1910–16). As a major participant and ultimately victor of the war with its allies, it set the terms of peace, crippling Cuthland's military, economy and territorial extent, as well as reshaping the geopolitical order through the establishment of the Assembly of Nations in 1917. War-torn conservative Mascylla however succumbed to increasing calls for reform by the worker class, with the Mascyllary Revolution overthrowing the to this point de facto absolute monarchy and instituting a democratic republic with a constitutionally regulated monarch in 1924. An unprecedented economic boom in the 1920s and 1930s quickly recovered the damaged economy while solidifying the recently introduced democracy.
The enmities left by the Great War proved to be pivotal in the later course of the 20th century, when a re-organized Cuthland leading the Mageiros League and X rivaled the western democratic nations united by the BDTA after 1944. While Mascylla kept clinging onto its colonial possessions, the Melasian Crisis from 1941 to 1943 triggered the slow decolonization of its empire as well as the beginning of the Great Game (1944–1990). The 1960s and 1970s saw civil unrest and dissatisfaction with the country's policies, and additional terrorist movements and scandals further dragged Mascylla into a decade-long crisis, culminating into the July 20 1991 terrorist attacks. After numerous reconciliation attempts by the democratic and communist blocs and following the 1987 stock crash and financial crisis, the X collapsed, leaving Cuthland and Mascylla as the two remaining rivals of the former Great Game. Recent reapproachment with post-communist states beginning in the 1990s however kept diplomatic tensions between the two at bay.
Mascylla today retains its political, cultural and economic power amassed in the 19th and 20th centuries. As the 3rd largest economy by both nominal GDP and by PPP, Mascylla is a highly developed country. It additionally ranks highly in rankings of human development, education, political and personal freedom, healthcare, life expectancy and economic competitiveness. Generally considered to be one of the world's great powers, it is a permanent member state of the Assembly of Nations Security Council and recognized country possessing nuclear weapons. It is a member of the Assembly of Nations, BDTA, X.
Etymology
History
Prehistory
Telmerian tribes and antiquity
Middle Ages and Cuthish influence
Aldian and Adwhinish rivalry
Elbgau Confederacy and unification
Slow coordination
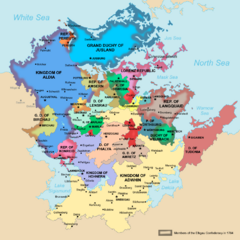
With the amplifying tension between Aldia and Adwhin following a row of conflicts in the mid-18th century that left the political dispute of Mascyllary nationalism unresolved, Albrecht II of Aldia envisioned a new political unit to coordinate customs, integrate the states' economies as well as boasting friedship among its members in order to efficiently tackle Adwhin together. The Congress of Rehnern in December 1757 concluded with the establishment of the Elbgau Confederacy, of which 12 states were initial members. Greatly upsetting Adwhin's plans of expanding its influence through dynastic ties in central Mascylla, it quickly orchestrated a move to deepen relations with its close neighbours such as the Kingdom of Holnia or Tudonia through the marriages of Princess Claudia of Merich-Karlsburg to the heir, Friedrich, of King Julian of Holnia and Prince Theodor to the daughter of Grand Duke Joseph of Tudonia. While unionists and nationalists saw the recent solidification of two large blocs as a victory and step towards unification, sovereign rulers repressing national beliefs were increasingly frustrated they would be eventually in the midst of a conflict between both sides; the fear of loosing significance or independence triggered a series of new inclusions to the Elbgau Confederacy which inadvertibly sped up Mascylla's unification. The additional creation of the Nordmaskillischer Zollverein (customs union) would further encroach on the division of Mascyllary states.
Nationalist actions and Revolutions of 1769
The results of the Congress of Rehnern in 1757 gave new motivation to the long existing movement of Mascyllary nationalism and single statehood. Various student movements and groups, most notably Junges Maskillien of the University of Tilchingen, sought to promote their belief of Mascylla's "right to be united", while heavily denouncing the Cuthish Empire's political and economic influence in Mascylla by the 1760s. While the states did not support nor represent the ideals of the growing movement, they allowed it to be distributed to the public without foreign intervention from authorities. However, numerous radicalizing groups attempted revolutions in Phalya in 1759 and Shwesia in 1765 respectively, to directly push for unification processes in broader politics, but also to establish representative government and in some cases the introduction of enlightened absolutism to its monarchies, in tandem with calls for reform and change in Cuthland and ALbeinland.
While the movement remained a fringe group of activists, their goal conincided with the political ambitions by both Aldia and Adwhin, who exploited their public popularity to bolster their vision of a united Mascylla under the leadership of their respective monarchies. Aldia emerged more sucessful with this approach however, when Aldish king Albrecht II promoted an influential leader of the movement in Aldia, Franz Kohlner, to the status of consultant to the government. While alienating the conservative members of the nobility and government, Albrecht amassed the support of the educated middle class, and following the institution of numerous reforms that brought Aldia towards a monarchy with enshrined enlightened aspects, it used its image as leverage and justification for its future leadership of Mascylla.
The social and politial discontent by reformists in other parts of Mascylla led to attempts by them to duplicate the success in Aldia. Subsequently, the July Revolutions of 1769 led to the occupation of military forts and the collapse of a number of small duchies reformed into representative democracies, the most notably of which the Republic of Konreid in 1769 and the Lorenz Republic in 1773. A council of representatives from the new states, members of the Elbgau Confederacy and other activists was assembled in Langquaid in September 1773 to draft a constitution for a unified Mascylla (Langquaider Reichsverfassung), later implemented as the charter of the Confederacy itself. In the south of the country, the revolutions were largely repressed by military force, and most of the movements were initially dissolved and exiled, with many of them fleeing north into Aldia.
War of the Five Kings and Mascyllary unification
The destabilizing effect of the attempted revolutions throughout the state further increased tension between the two coalitions led by Aldia and Adwhin. The economic integration of the two blocs additionally led to a sharp increase in economic prosperity and wealth, but on the cost of the Elbgau Confederacy needing natural resources and vital trade routes to continue its expanding economy, thus making a conflict due to the geopolitical and strategic importance of central Mascylla inevitable. The death of the aging Albrecht II and the ascension of his son and heir, Lukas I, who was vehemently in favor of national unification due to his father's efforts, was the turning point in Mascylla's history.
In March 1789, the Grand Duke of Phalya, Karl IV, suddenly died but leaving no apparent heir and the throne vacant. Aldia quickly suggested an Ahnern candidate, Lukas's brother Leopold, as Phalya's successor, but Adwhin recognizing the topographical importance of Phalya, aggressively objected and pushed for King Theodor's nephew, Prince Wilhelm, to succeed Karl IV. The issue quickly evolved into a diplomatic fiasco, and on 4 September 1789, Adwhin issued to resolve the conflict through war. While Adwhin quickly invaded Phalya, the Elbgau Confederacy was able muster a larger standing army under the command of Feldmarschall Wilhelm Stenreck, supported by a growing number of civil militias trained and equipped by Aldia. The conflict quickly escalated into a full-scale war and it became apparent the Elbgau Confederacy and its allies would emerge victorious. After numerous won battles in Eustria and Phalya over the course of two years, the Battle of Austerlitz in May 1790 was a decisive blow to the Adwhinish armies protecting the fortress of Auserburg, completely eradicating the bulk of its land army and capturing King Theodor himself. While Aldia continued to advance further south, Franz Kohlner and a trail of thousands of petty soldiers, peasants and activists, collectively known as the "Expedition of the Thousands" (Zug der Tausenden) marched onto and invaded Breisgau, Adwhin's seat of government.
Shortly thereafter, Adwhin capitulated without any peace terms and representatives of 32 Mascyllary states and free cities gathered in Langquaid to decide the political fate of Mascylla. Lukas I of Aldia was chosen to ascend the title of King of Mascyllla, the Elbgau Confederacy dissolved, and its member states as well as the defeated nations merged into a Mascyllary state. A rigorous debate erupted as to how the political system of Mascylla would actually be structured; a majority of states from the south who had a conservative view point advocated for an enlightened, but absolute monarchy, while the peasantry, middle class and a number of northern states favored a democratic republic with a monarch as its figure head. Fearing the southern states would disjoint and eventually rebel from Mascylla, Lukas I drafted a compromise betweeen the both parties, in which the monarch would have considerable power, but be advised and kept in check by elected members of government. While this compromise resolved the ongoing dispute of Mascylla's governance, Lukas had own personal aspirations as a leader of powrr and therefore detested being removed political powers. Franz Kohlner as an influential political figure first strongly opposed his proposal, but reluctantly agreed later on, burying the nation-wide hopes of a democracy for a century. The treaty itself was signed and ratified on 18 May 1793 after months of negotiation. Subsequently, Lukas I was officially coronated in Langquaid to the largest audience of nobility in Mascylla's history.
While the war itself was short, it left a devastating toll on the civilian population and southern economies who suffered from taxation and looting during the conflict. The government was largely composed of war veterans, such as Wilhelm Stenreck being elected as Mascylla's first Prime Minister, though former Adwhin and other southern states were deeply in debt, inpoverished and virtually politically unrepresented, culminating in a series of strikes and riots in 1795 which were quickly put down by Aldian military forces. However, Mascylla witnessed an unprecedented economic rise, and Lukas I massively grew in public popularity with the introduction of a new row of statutes that satisfied the expanding middle class of classical liberalists and nationalists who continued to rise in influence in national politics and commerce, while the country's separate monarchies were slowly replaced by constitutional systems.
Mascyllary Kingdom

The Mascyllary Kingdom was the brainchild of King Lukas I and his Prime Minister, Wilhelm Stenreck, upon its foundation in 1793. While the government of the new state was intended to establish the rule of the people under the supervised reign of a monarch, in reality both collaborated in splitting political duties and exchanging policy proposals and ideas, which as a matter of fact greatly bolstered Mascylla's political efficiency and rapid rise in international power. However, Lukas' impulsive actions were checked and regulated by Stenreck, who relied on more expertise in being a statesman and later constituted an intricate foreign policy that would ensure Mascylla's security as a unified nation while exercising its geopolitical ambitions, commonly known as his Ruhe, aber graulen policy ("Be calm, but growl" policy). While considerably unpopular due to his hardline domestic conservative policies, he signed into law universal healthcare and education, boasted the country's war-torn economy and was able to command enough respect in his government for him to largely shape Mascylla's political landscape throughout the first half of the 19th century.
With the deterioration of Stenreck's health by the 1820s, Lukas I assumed a more significant portion in the country's policymaking, while increasingly relying on the Reichsrat as an advistory body alone, which further alienated his former liberal and reformist allies in the elected components of government. When he finally died in 1832 however, his more ambitious and impulsive son, Lukas II, ascended the throne and redefined a large number of Stenreck's previous delicatly introduced policies. Aspiring to expand Mascylla's foreign and economic powers, he abandoned Stenreck's foreign policy, pursuing colonialist ambitions primarly in Pamira and Caphtora, which at this point were largely absent of Berean colonial presence. While at first unilaterally approaching Berean politics, his successors suffisticated the expansionist ideals of Lukas II, while embarking on approaching other powers it saw fit to combat its primary political enemy, the Cuthish Empire, that ultimately became a major factor leading to the Great War.
Cuthish Revolution and rise in power

Mascylla at first had a resentment towards intervening in other Telmerian conflicts concurrently with its unification, the most notable rejecting such ambition being Wilhelm Stenreck. Lukas I at first remained reluctant as to whether it should intervene in the Cuthish Revolution at first, but the bulk of representatives of parliament foremost denied any involvement with foreign wars if Mascylla's own countryside had not been rebuilt and its political unity settled. When the deposed Algar III of Cuthland however offered his restoration as Cuthland's monarch in exchange for a portion of its Berean and overseas territories, Lukas I pushed for a more prominent stance in Berean affairs, and with solidifying his rule and Mascylla's legitimacy especially in the country's south, he convinced Stenreck to overrule the Reichsrat and ratify the Ulich Agreement in February 1798, which saw the Mascyllary Kingdom entering the Cuthish Revolutionary War as its first military campaign and recognizing the Cuthish king's legitimacy in deposing its young democracy, which was widely seen as a threat to its just established monarchy.
While the war was at first successful with territorial gains in northern Cuthland for much of the conflict, Mascyllary cities such as Birchau and Vogtburg were sacked by Cuthish republican forces in 1799. Nevertheless, the republic was overthrown and the war concluded with the Cuthish monarchy's victory. The Treaty of Swithtun in 1800 saw Cuthland's third and last partition, with Mascylla annexing large territorial cessions by Cuthland, including the northern Cuthland regions and all of its remaining Alvinian and most of its northern Pamiran colonial possessions. The war elevated Mascylla to a great power in an instant and motivated imperialist politicians and nobility to argue for continuous colonial expansion and dominance of Telmerian politics, to the dismay of classical liberalists who advocated to consolidate Mascylla's pre-existing power and limit its interventionist attitude, in line with Stenreck's policies.
Second colonial empire and the Gründerjahre (1800—1840)
Over time, the political legitimacy of the monarchy and government had hardened and politicians began to experiment with numerous courses for domestic and foreign policy. With the worsening health of Stenreck, his power withered and was slowly taken over by more ambitious statesmen, supported by the too eager Lukas I who aspired to expand Mascylla's bulk of power in Berea and overseas in order to cement his legacy. His son, Crown Prince Lukas II staunchly rejected Stenreck's reserved approach to Telmeria and favorited to continue what he described to be a "continuous expansion of the Mascyllary nation" most notably in Pamira and Caphtora. Around this developing political objective, a group of conservative and monarchist politicians established the the first political party of Mascylla, the National Democrats, a predecessor to today's National Democratic Union, which dominated Mascyllary politics for well of the 19th century. The reign of Lukas II was shaped by the introduction of loyal statesmen who he thought to be able to project his political ambitions, restore the war-damaged economy and consolidate his father's legacy to bolster support for the monarchy.
The Mascyllary colonial empire, formerly under Aldish possession, developed from numerous attempts and stepstones: Caphtoran and Pamiran trade outposts and towns with little territorial extent and vaious Alvinian islands which had been explored and settled to establish plantations and mines. In the early 19th century, the colonies had almost no domestic political value and furthermore little economic importance; however, the accelerating growth of local populations (more than triple by 1850 than in 1810) soon challenged the weight of the metropole within the empire. Political interest also rose with an increased rivalry among Berean colonial powers over yet unclaimed territories which were further fueled by the aftermath of the Karsk Sea War and Conference of Aniarro in the 1820s, including the expansion of the Mascyllary colonial empire at the cost of collapsing Cuthland. A series of small-scale wars and skirmishes with other colonial powers, most notably Lavaria, and numerous colonial tribes and petty kingdoms in Caphtora and Pamira dempered romanticism and prestige of an emerging colonial power, but were quickly compensated through successful and expansive campaigns in Sfardia and Mavronesia, which gave rise to the largest Mascyllary colonial possession, Melasia, in 1830 and 1832 respectively.
Although exerting a large strain on Mascylla's home economy and political capital, it soon acquired enough resources in natural wealth and man labour to bolster its economy, which steadily grew by half in the next twenty years from 1830 to 1850. The emergence of the Second Industrial Revolution in the early 19th century also transformed Mascylla's economy to this point: the sharp increase in manufactured goods led to an explosion of the upper class' consumption and a larger gravance for raw resources, which enabled Mascylla to use its colonies as trade ports to buy and sell their goods while exerting influence on regions and territories with a wealth of resources desparatly needed in the metropole. In the following ten years, Mascylla rapidly grew to the second largest economy on the planet thanks to its expansive colonial system and trade agreements with native states abroad. The colonial empire had exceeded Mascylla's expectations and ambitions in catapulting the country to the status of a great power of Berea within thirty years.
Cutho-Mascyllary enmity and Neuzeit
After the partitions of Cuthland and the increasing agrivation of Cuthish and Mascyllary leaders greatly disturbed their relations in spite of a massive shift in power by the Cuthish collapse and rise of Mascylla, which was further deepened following Mascylla's aggressive foreign policy and expansion brought about by Lukas II and Friedrich Gäste. Stenreck and his political adversaries were deeply concerned about the abolition of the delicate policies set in place to ensure Mascyllary sovereignty which was now endangered. Ultimately, that proved to be true when Cuthland under the rule of X and the ensuing Ahlstead Wars signaled the now Second Cuthish Empire's stance on recovering its territories lost to mainly Dulebia and Mascylla. The resulting Second Cutho-Mascyllary War in September of 1839 was quickly decided as Cuthland scored a row of military victories, dispersing a Mascyllary army and encircling another one at Augusthal. The bulk of Mascylla's standing army was defeated in Vogtburg a month later and opened the opportunity to encircle and besiege Königsreh in spring of 1840. The hastily organized counter defences were however able to force the besieging army to disperse and capitulate after a crop failure and unrest in the Cuthish armies, but to no avail as Königsreh was forced to capitulate in summer and a provisional government willing to sign a treaty of surrender at Marienfelde.

As a result of the negotiations, and formally declared by the Treaty of Alderport, Mascylla was forced to pay reparations and indemnities of 4 billion karnings and cede Elpsland and Dorsace to Cuthland, as well as a number of colonies primarly in Alvinia.
The war left Mascylla, its political administration and military deeply humiliated, which was previously considered to be one of the most well equipped and organized Beream armies. Reluctance over accepting the conclusion, revanchism and already significant popularity of an expansionist Mascylla further aggravated the Cuthish–Mascyllary enmity and became a key factor in Mascylla's foreign policy going from 1842 onward. Therefore, Mascylla underwhent a dramatic transformation from an isolated and humiliated power, to the centre of a system of Berean alliances intended to counter the growing influence and friendship of Cuthland and the Dulebian Empire by the turn to the 20th century. It established the Otimo Acordo with Lavaria in 1900 and four years later normalized and eased tensions with Albeinland through the Albo-Mascyllary Alliance.
The Neuzeit (lit.: 'new age') was a product of the renewed strength and prosperity from its alliances and continued peace in the late 19th century. Due to prolonged economic growth, relative peace and cultural, political and scientific innovation by its populous, Mascylla reinstituted a state of wealth and being a Berean leader in not only military, but also societal and commerce affairs. Simultaneously, the invention and introduction of popular amusements brought about by scientists and innovative artists, most notably the cinema and art styles of Impressionism and Art Nouveau, aided in Mascylla preserving its place as a centre of arts and expression. Additionally, events such as the Universalausstellung of 1891 hosted in Königsreh was an opportunity for the country to present its most recent scientific discoveries, inventions and research. These and other developments, often sponsored by the government itself, were attempts at constituting the bulk of a soft power for the Mascyllary state in solidifying its influence not only in its colonial empire and political power, but also culture and technology. Nervertheless, Mascylla remained deeply divided on terms of ideology, foreign policy, regionalism, economic growth and distribution, and the classes, which became a more frequently addressed subject with the introduction of the worker class emancipating in the political process by the Proletarian Party under Georg Schmidt in the 1890s and the increasing polarisition of the debate on women's suffrage, the bourgeoisie and the political legitimacy of the monarchies.
Great War and Revolution of 1923
Great War (1911-1916)

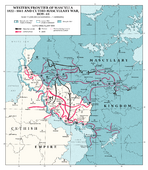
Mascylla did not expect war when the Great War came about, as Prime Minister Paul Martinsen began attempts of reconciliation and political détente with the Lindenau Accord in 1904, albeit with fierce resistance from a majority of the Reichsrat and King Ludwig I himself, who opted to resort to warfare if necessary as soon as possible. While Mascylla remained divided as to whether to anticipate a war with Cuthland or begin negotiations to ease relations, it became very active in international affairs with politically intervening in the Third Dulebo-Gurkhan War in 1899-1902 and the X, to the dismay of Martinsen who witnessed a counteracting movement in foreign policymaking while undermining the government's policies.
When the X triggered a complex network of alliances and treaties, it drew every Berean power, including Mascylla, into conflict within the first few weeks. Whiel Mascylla was militarly superior in 1911, Cuthland was more efficient and effective at organizing its armies and planning a decisive strike on Mascylla's western defences in Aldia. In September of 1911, Cuthish forces under the command of X swiftly defeated the armies garrisoned at Saarow and Geißdorf, which prompted the Mascyllary Kingdom to hastily muster their defences without prior tactical decisioning. Therefore, the Cuthish was able to penetrate Mascyllary defences at their border and sweep into the Fanian Plain, quickly gaining military control over important industrial regions in Mascylla, in hopes of forcing a quick defeat on Mascylla. While the campaign was very successful within the first four months in curbing combat opportunities of Mascylla such as in the First Battle of Augusthal in late 1911 and the Battle of Winden in 1912, the decisive Battle of Lückwalde proved the Mascyllary forces under Friedrich von Gabig and Ehrhard von Belau could resist the Cuthish advance and save the capital from a siege. Following that and Mascylla fully mobilized, the Northern Front began to solidify with the emergence of trench warfare and increasing war-weariness. The less intense fighting along the southern frontier to Valimia and Cuthland also became static in late 1913. In 1915 to 1916 however, after the assassination of Paul Martinsen by a Cuthish nationalist, the utilization of the tank and improved war tactics were finally able to penetrate the stalemate of the front, and swift but often intense fightings caused tromendous casualties and costly victories. The Mascyllary were able to push beyond its borders and well into Cuthland near Kingsham and Alderport by spring of 1916, before the Cuthish signed an instrument of armistice on 29 May 1916 and Mascylla ended effective fighting three days later.
Interwar period

The Armala Coalition posed their terms to primarly Cuthland in the Treaty of Lehpold, hosted by Mascylla, in 1916-17, in which they intended and forced Cuthland to pay huge sums of war reparations, demilitarize heavily and abolish its monarchy. Mascylla had the prevailent say in the treatment of Cuthland in the negotiations, and opted to treat it harshly. It regained the territories of Elpsland and Dorsace lost in the Second Cutho-Mascyllary War, received reparations in form of war material, financial assets and industrial goods, and occupied Cuthland's Lake Sigismund region, while carving up Cuthland's northern territories into the independent state of Temaria under Mascyllary supervision, as well as Lilienburg in the east. Mascylla also received the Mandate of Alvinia from the remains of the Cuthish colonial empire as well as the Mandate of X of the former Gurkhan Empire. The treaty layed out the framework of a genuine Berean peace under the established Assembly of Nations in 1917. Mascylla continued to remain active in foreign affairs though, such as intervening in the Cuthish Civil War or establishing an elaborate system of alliances with the newly founded Berean states, called the Kleinbund.
The conclusion of the war was propagated as an enourmous success and evidence of Mascylla's position as a world power, but came at the cost of entirely devastated rural and industrial regions in Aldia and Folnery and enourmous civilian and military casualties. The war effort left the war-torn economy crippled, and was only sustainably supported by the taxation of its empire and Cuthish war reparations. Only by the 1920 did Mascylla's economy begin to recover from the war, but at the expense of the worker class who were further exploited to retrieve the country's economic growth. Civil strife for reform and the re-introduction of the welfare state cancelled due to financial issues in 1918 further undermined Mascylla's stability and heated up debates for a political transformation.
Revolution of 1923

The revolution was ultimately brought about by previous criticism towards the conservative policies of monarchism and nationalism, calls for reform mainly by the politicized worker class as well as the bankcruptcy of the government, the war devastation increasingly attributed to the aristocracy itself and recent political instability in Cuthland spilling over into Mascylla. The boiling point came when in March 1923 soldiers and military personnel resisted and eventually revolted against the amounting pressure by the government to restore civil order and much of the destruction of western Aldia despite lacking funding and resources. The garrisons of Augusthal and Weidenau mutineered on 12 March and inspired their civil counterparts in the police and worker councils to protest as well. The government shortly after constituted its resignation and states its loss of confidence in the monarchy on 8 May, which quickly collapsed when the Mascyllary Supreme Command under Ehrhart von Belau and Karl Georg von Pritnitz announced its neutrality on 13 May. Ludwig I and most of his subordinate nobility abdicated on 15 May and attempted seeking exile in Rovina, but was apprehended on crossing the border, transported to Königsreh and publicly executed in front of the Reichsrat building simultaneously with the proclamation of the May Republic by Leo Baeck on 23 May 1923.
A hastily assembled council of representatives from the SDP and sovereign worker councils led by the GAV is gathered in Königsreh the following day on May 24 in order to seek recognition by the Assembly of Nations and international community. Negotiations with the desparatly needed Reichswehr for their military support and political influence in the upper class culminated in the Zeschtemann-Gabig Pact on 2 June, which granted the Supreme Command to partake in a set of political decisions albeit limited, under a constitutional monarchy but in exchange for supporting the social democrats of the provisional government. The Freikorps, independent but Reichswehr-loyal soldier councils, intervened in the revolution and successfully pushed back the growing movements of far-left socialists under Werhner Pehring and Emil Hiebert having already established short-lived attempts at carving out soviet republics such as the Proletarian Republic of Mascylla. The eventual crushing of the insurgencies and solidification of the government as a compromise between the conservative military and liberal social democrats ended the revolution when the first election of the Reichsrat was held and the first government under Peter Zeschtemann was inaugurated on 26 January 1924.
Crowned Republic (1924—present)
Post-revolution period and Brüllende Zwanziger

After the Great War and preceding revolution, the Mascyllary populated saw politics as tiresome and instead favored private freedoms and lifestyle granted by the introduced democratic system. New cultural innovations and suffistication of the cinema, dance, music styles and most notably alcoholic consumption as well as the introduction of a cultural dynamism and common lifestyle defined the era for Mascylla. The stimulation of economic growth resulting from the readiness and ability of the worker class to consume led to drastic increase in the country's economy previously unseen: within the 1920s the economy grew by more than a fourth of its original size; the ecomomic prosperity witnessed is famously referred to as the Brüllende Zwanziger or Roaring Twenties. Corraborating economic policy reforms and co-operation with Lavaria and Albeinland solidifed the young democracy's legitimacy at large. Mascylla internationally rose as a economic powerhouse and political power thanks to its heavy say in the Assembly of Nations and foreign post-war affairs.
The slow crumbling of Mascylla's colonial empire became more evident with the post-war taxation and exploitation of its colonies while neglecting their development, domestic rights or political autonomy. Growing voices in the successor states to the previously defeated Central Alliance in the Great War called for an end of colonialism which were temporarily balanced with Mascylla's and other Berean empires' importance in the organization. Internally, the excessive consumption of beverages evolved into a national debate and was outlawed nationally from 1925 to 1931 until being revoked under public pressure. The development of organized crime also coincided with the economic prosperity of Mascylla and trafficking of alcoholic products. Furthermore, the question as to whether Mascylla should continue its approach of a major power to the world or rather stipulate a state of isolationism polarised the political landscape of the young democracy, and formed the basis of two blocs of political parties opting for continued imperialism (Weltblock) or domestic preference (Heimatblock).
Melasian Crisis (1941—43) and decolonization

The economic prosperity enjoyed by Mascylla in the decade following the Mascyllary Revolution eased tensions within the colonial realm temporarily, but were resumed quickly following the gradual end of extraordinary commerical growth in the metropole by 1935, to the neglect of colonial territories heavily depending on foreign export and a stable common market. Among those, Melasia grew increasingly self-righteous, and with a nationalist spirit and identity acquired in the war efforts of the colonial empire in the Great War and post-war Mascyllary military. The staunchly conservative policies of the colonial administration largely retrieved from the Mascyllary Kingdom after the war were unable to implement reforms that would weaken segregational laws and racial inequality in its empire, which directly helped mitigate the popularity of and association with Mascylla's rule.
The 1941 revolt and subsequent Melasian Crisis in Melasia was the culmination of these tensions and issues, and was further agitated by Cuthland developing it into a proxy war between both nations. Despite the combined effort of the Mascyllary military and supporting economic wealth, its actions were ill-fated in that the gruesome guerilla warfare of Melasia's native population and deployments of Mascyllary soldiers costly in war material and human loss were ineffective in successfully regaining control over all of Melasia. Cuthland's direct intervention in the conflict through border skirmishes and preparations for a large-scale offensive pushed the Assembly of Nations to seek negotiating a truce and subsequent peace treaty in 1943 in the face of rapidly rising tensions, which forced Mascylla to withdraw and grant Melasia its independence and Cuthland border territories in the west and south of Mascylla. The inhabitants of Melasia supporting Mascylla were massively forced to flee and pursue immigration to Mascylla, sparking a fiery political and civil debate.
The crisis was a devastating blow to Mascylla's prestige as a world power and humiliation of its prowess. The majority of the Assembly of Nations approved Melasia's sovereignty and called for the begin of decolonization of Berea's colonial empires. Under pressure from the AN and the signing of a new coalition government under Ernest Rähner in 1946, Mascylla presented its plan to disband its colonial holdings in three stages beginning in 1950, 1960 and lastly in 1970. The brutality witnessed in the Melasian Crisis transformed the public perception of colonialism and Mascylla's moral conscience, and dealt a heavy blow to the country's view of its "ethic superiority". The awareness brought about by the war not only affected society and cultural views, but also foreign policy and the military, who introduced or consolidated the usage of aircraft carriers, strategic bombers and researched means of asymmetric warfare, having learned from its tactical mistakes and issues faced.
Great Game (1944—1989)

While the Treaty of Königsreh of 1943 resolved the initial disputes and tensions of the Melasian Crisis through compromisional negotiations, in reality it further deepened the enmities between Berea's leading powers in the status quo of the Great War and its direct aftermath. Owed to reactionary policies after the crisis, Mascylla, along with its closest allies Lavaria and Albeinland established the Berean Defence Treaty Association in 1944 in response to Cuthland's Mageiros League founded two years later rapidly rising in influence with the accession of independent Melasia to the alliance. A third party emerged from the communist states of the east dominated by the X, and the world's geopolitics became divided on the ideological and political lines of authoritarianism, western democracies and socialism. The ensuing Great Game was therefore the dominant factor of international politics and ultimately that of Mascylla. An unprecedented economic boom succeeded that of the 1920s, but with increased stability and continuous wealth brought to the Mascyllary economy, state and new middle class; the rise of mass-consumerism and awakened interest in politics can be attributed to that era.
The prioritized development of nuclear weaponry as a method of counter-balancing the powers of the other blocs respectively culminated in the 1963 Ace test of Albeinland's and Mascylla's Operation Whitehorse, the first nuclear weapons test in history. The introduction of mutually assured destruction to the larger conflict significantly contributed to the prolonged peace between the sides, albeit under the existential threat of nuclear warfare, which became a major point of debate by a counterculture movement developing from other criticism on society and politics in the early 1960s. Criticism on Mascyllary politics have temporarily been publicly discredited and persecuted in fear of the ideologies of the respective blocs settling in the country, which has lead to a significant ailing of its democratic values, to the dismay and concern of much of its youth and citizenry.


The 1967 oil crisis was a major shift in the Great War, marking the end of authoritarian rule in Melasia, civil unrest in Cuthland and the downfall of the Mageiros League as one of the world's three major blocs. While Mascylla initially survived the economic recession, it showed symptoms of the onset of resulting stagflation beginninng in the late 1960s and ending a decade later. Efforts to contain economic damage and lower stubbornly high unemployment rates after the crisis have been extensive, but often miscalculated or not sustainably conceptualized. After a period of civil and public outcry and unrest due to political scandals and the economic turnout from 1968—1977, Mascylla was weakened in political willpower and strength, but regained much of its prestige by Charlotte Mayn's administration in the 1980s. The development of ICBMs and initiation of a more aggressive foreign policy called Rückdrängen (meaning 'push back') disturbed the détente of the Great Game and temporarily re-heated tensions between the powers, but with a more close association with the X. The launch of X triggered the Space Race, by which a collaborative effort by Mascylla and Dulebia succeeded in first landing humans on the Moon in 1981. The subsequent years experienced renewed ease in tensions and with the collapse of the X, abpruptly triggering the 1987 financial crash, the Great Game is generally considered to have ended in 1989. The weakened socialist world and Cuthland's allies paved the way for a brief era of Mascyllary and BDTA global unipolarity.
Civil dissatisfaction and reform period (1966—1981)
Between 1966 and 1981, Mascylla was witness to tromendous social and political change, civil upheaval and general instability fueled by political scandals, intrigue and economic stagnation suffered from the 1967 financial crisis and increased foreign competition. Beginning in March 1966, controversial education reforms implemented by incumbent Prime Minister Ulrich Werner on the matter of university and school curriculum regulations and payment for access to these institutions prompted thousands of students to protest in opposition to the law, but quickly expanded beyond its original intention and encompassed an umbrella movement of various political ideologies, sub-cultures and countercultures. The demonstrations grew in size, while it had adopted characteristics and intentions of other demands by the public, such as civil rights for colored citizens and the acceptance of homosexuals (commonly referred to as the Sexual Revolution), and feminists. On 13 June 1966 the movement merged into the activist organization Außerstaatlich-Völkische Opposition (ASVO) with Benno Gruhner and Eduard Malch as its figureheads. The student protests of 1966-68 dominated national media attention and polarized the political debate, considerably by the government itself who sought to discredit and weaken the movement under suspiction of them being sponsored and motivated by third foreign parties. Major episodes of riots and protests in Mascylla's cities continued to escalate, and the shooting of student Alexander Schmitt by Königsreh police forces on 11 September 1966 infuriated the members of the ASVO and seeking retaliation against the government, now having declared the ASVO as a "communist cell".
Under amounting pressure on the government by the ASVO and spreading general strikes of workers demanding higher wages, the government issued a state of emergency while envoking to use its military. On 28 February, 1968, media agencies were informed and revealed the short-coming Kornbach affair to the public, accusing Ulrich Werner to have rigged the choosing of the Highest Judge of the High Court to oppose further support to the movement and legal change. Twenty co-perpretators were sentenced and jailed, and Werner forced to resign by his own party (the NDU) and after loosing a vote of no-confidence to the Reichsrat. The succession of liberal Konrad Dierck as Prime Minister and implementation of new reforms eased tensions and led to the ASVO being fully disolved in 1969. However, other points not met were still rigorously defended and demonstrated with protests and riots throughout the country, and political instability in the aftermath shock of the scandal remained apparent until the 1980s. Trust had been completely lost in the government, and mediocre achievements in supplementing change and reforms meagerly advanced Dierck's administration. Furthermore, the assassination of the ASVO's leaders a year later continuously disrupted the social order briefly returned after Werner's resignation.
A splinter group of the ASVO, the Revolutionary Garrison founded in 1970, continued to brutally oppose the Mascyllary state, and conducted a series of terrorist attacks, kidnappings and hijackings in light of forcefully establishing communism in Mascylla. Various politicians and public figures fell victim to or were injured by the RG, and its crimes, leaders being sentenced and motivations captivated the nation. The developments of the 1960s and 1970s thoroughly split the Social Democratic Party and essentially deprived its function as a government party while the NDU had to reconcile with the Kornbach scandal and the Centre Party suffered internal fighting. Its economic downturn, social insurgency and weakened administration were largely resolved however with the election of Charlotte Mayn of the SDP by a landslide in 1981, noted for her cunning political maneuvering and skill, economic reforms and keen charismatic appearance, which by many is considered to have "brought back the people's optimism and willpower."
Contemporary history


The turning point came when in 1991 Königsreh was struck by a series of terrorist attacks of the Revolutionary Garrison on July 20, 1991. The attack left 504 people dead and devastated the functions of the government in a constitutional crisis after which members of the Reichsrat and state parliaments of Eustria and Folnery had been killed, while the collapse of the Martinsen Center gravely damaged Königsreh inner city. The proclaimed state of emergency gave away to the largest man hunt in history, lasting nine years in total, in pursuit of the attack's perpretators. While the emergency right retained by the government had been revoked in its aftermath and after the death of Pascal Schneidmühl, the initial mastermind of the attacks, by Mascyllary special forces in Pereuth in 2002, it constituted a keen sense of threat by society itself as well as controversial efforts to counter-act terrorism through mass surveillance and advanced rights of the national DSA intelligence agency to access law enforcement information. Numerous allegations of human rights abuses have also been brought forward and repeatedly investigated by Reichsrat committees in 2003, 2004 and 2012 respectively.
In the wake of the Great Game, the BDTA remained the world's sole powerful political bloc. Political stability and economic sturdiness established by Mayn's administration was continued after the election of Michael Meilke, and further rose in prominence with the aftermath of the financial crisis of 1987 and solidification of economic liberalism of the country in the 1990s. However, underlying social issues such as stoic unemployment rates and uneven local economic development plagued the sense of confidence in the government which had struggled to emerge from the crisis period of the 1960s and 1970s. Efforts to bridge the gap of trust in Mascylla's future after the conclusion of the 20th century have been introduced, such as expanded healthcare services, a suffisticated space program of the Raumfähre and continued international diplomatic interventionism.
The assassination of Michael Meilke on March 19, 2000, left the country in a profound state of shock, still recovering from the July 20 attacks. The disillusionment of Mascyllary invulnerability transformed domestic and foreign policy, and evolved as a vocal point of dispute by the nation's right and left politics, while also coinciding with the official end of the Mascyllary colonial empire with the release of X into independence in 199X. Furthermore, the new rise of Cuthland-Waldrich as a second-coming emerging world power and stregthened political players in Pamira, namely Kodesh and Nanzhou, challenged the privileged position of the BDTA. Reconciling foreign policies were introduced with Prime Minister Konrad Folln to combat that issue, but preserved its dominant attitude in international affairs, such as military supporting parties in the X beginning in X in opposition to Cuthland and introducing sanctions against Dulebia with continued allegations of election fraud and autocratic governance of Alexey Volodin in 2010. The recent decade saw a significant revival of interest in international politics and preservation of Mascyllary importance in Telmeria and by a broader perspective, Berea.
Geography
Topography and hydrography
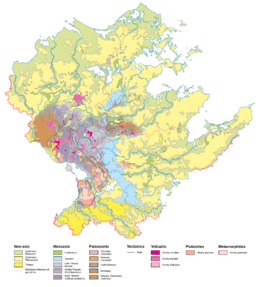
Geology
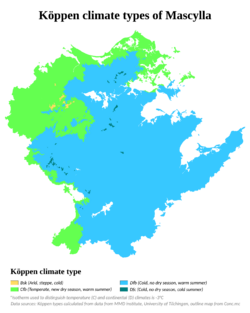
Climate
| Climate data for Königsreh (Schönhoch), normals 1975–present, extremes 1950–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.5 (59.9) |
17.0 (62.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
28.9 (84.0) |
32.4 (90.3) |
34.9 (94.8) |
35.1 (95.2) |
37.4 (99.3) |
32.8 (91.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
14.0 (57.2) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.9 (44.4) |
8.7 (47.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
5.7 (42.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
2.3 (36.1) |
5.3 (41.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
14.1 (57.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
16.6 (61.9) |
9.4 (48.9) |
6.6 (43.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.7 (30.7) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
1.1 (34.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.4 (50.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
1.2 (34.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.5 (−8.5) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−4 (25) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.3 (37.9) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.9 (37.2) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−20.2 (−4.4) |
−22.5 (−8.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 47.3 (1.86) |
40.5 (1.59) |
39.7 (1.56) |
36.0 (1.42) |
58.8 (2.31) |
70.1 (2.76) |
62.1 (2.44) |
59.2 (2.33) |
86.9 (3.42) |
31.3 (1.23) |
26.9 (1.06) |
38.0 (1.50) |
596.8 (23.50) |
| Average snowy days | 13 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 66 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 61.7 | 77.6 | 119.4 | 165.6 | 228.1 | 236.9 | 240.3 | 216.2 | 160.8 | 119.4 | 63.5 | 57.3 | 1,746.8 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Source: MMD and MaskData | |||||||||||||
Biodiversity and environment
Politics
Government