Shangea: Difference between revisions
old>Xiaodong No edit summary |
m (1 revision imported) |
Revision as of 16:56, 11 March 2019
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong 晓东吉祥共和国 Xiǎodōng Jíxiáng Gònghéguó | |
|---|---|
| Motto: 吉祥我国多么光芒万丈! How bright is our Auspicious Nation! | |
| Anthem: 但愿吾天上我的祖国兴盛千代 Dàn yuàn wú tiānshàng wǒde zǔguó xīngshèng qiāndài | |
 Location of Xiaodong in Borea | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Rongzhuo |
| Official languages | Xiaodongese |
| Recognised regional languages | Duljunese |
| Ethnic groups (2013) | Xiaodongese (91.8%) Duljunese (6.2%) Other (2%) |
| Religion | Taojiao |
| Demonym(s) | Xiaodongese |
| Government | Unitary National Principlist dominant-party state |
| Yuan Xiannian | |
| Xi Yao-tong | |
| Xu Bangguo | |
| Lu Yanling | |
| Legislature | State Presidium |
| Establishment | |
| 1866 | |
| 20 September 1936 | |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 138,360,000 |
• 2013 census | 136,563,356 |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | $1,201,787 million |
• Per capita | $8,685 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $402,426 million |
• Per capita | $2,906 |
| Gini | 36.8 medium |
| HDI | 0.744 high |
| Currency | Renjin (RJN) |
| Date format | yyy-mm-dd |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +893 |
| ISO 3166 code | XI |
| Internet TLD | .xi |
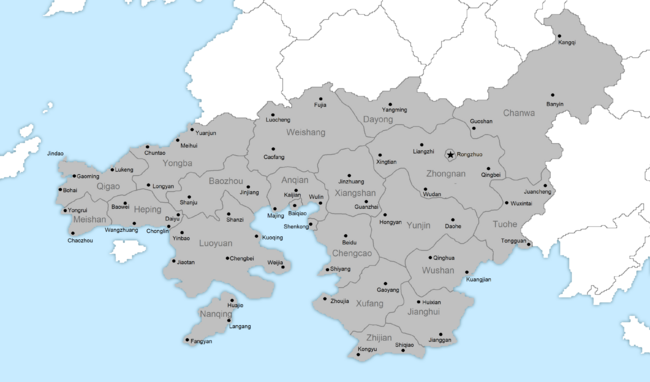
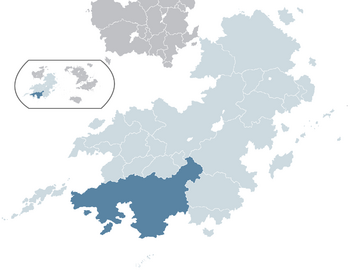
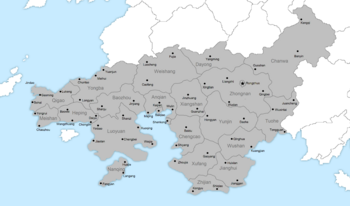
The Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong (晓东吉祥共和国; Xiǎodōng Jíxiáng Gònghéguó) more commonly known as Xiaodong (晓东; Xiǎodōng) is a nation in Borea, Esquarium bordering Min to the south, Tinza to the north and in the east having maritime borders with Senria. It has a population of 138,360,000 with a nominal GDP of $402,426 million, with its capital and largest city being Rongzhuo located on the north eastern coast.
The home of the Xiaodongese people, Xiaodong was first united by the Jianzhao Emperor in 200 BEC under the Xiang dynasty which ruled Xiaodong from 200 BCE to its collapse in 500 CE - during the rule of the Xiang dynasty Confucianism and Taoism became prevalent. Following the Xiang for 100 years Xiaodong was politically unstable in the period known as the "War of Four Kingdoms" as rival warlords and nobles fought for control. In 731 Xiaodong was united again under the Tao dynasty that introduced Buddhism and Kamism whilst overseeing the high point of Xiaodongese literature and art. However, in 1415 the Tao dynasty was usurped by the Jiao clan who created the Jiao dynasty, which fused Buddhism, Taoism and Confucianism together to create Taojiao. Although initially wealthy, by the 1600's the Jiao dynasty was being torn apart by civil war and uprisings, most disastrously the Red Orchid Rebellion in 1656. In 1680 the dynasty finally collapsed, resulting in a Senrian warlord to conquer Xiaodong and create the Toki Sougunate. However, the Toki's attempts to promote Senrian culture led to the development of Xiaodongese nationalism. In 1866 military officers staged the Baiqiao Revolution which overthrew the Toki Shogunate, achieved de facto independence from Tuthina and the enthronement of the Xiyong Emperor who created the Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire (a semi-constitutional monarchy) and oversaw a period of economic modernisation and semi-constitutional rule. Between 1875-1888 Xiaodong conquered and annexed the Duljunese Kingdom to the west, and subjugated neighbouring Tinzhan, turning it into a puppet state. In 1911 Xiaodong underwent the Constitutional Revolution which led to the creation the first Xiaodongese constitutional revolution.
During the 1920's the Xiaodongese state became more totalitarian which heightened under the Zhanxun Emperor leading to in 1927 Xiaodong invading Senria starting the Senrian-Xiaodongese War. The war resulted in a Xiaodongese defeat and internal rebellion with the creation of the State of Xiaodong and the start of the Xiaodongese Civil War. These military failures led to in 1936 the Xiaodongese government to be overthrown in the Corrective Revolution by a group of young military officers who created the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong, an ostensibly democratic republic, but in practice a dominant party "guided democracy" under the Xiaodong Regeneration Society headed by Lu Keqian who enacted many far reaching political, economic and social reforms. In 1988 Xiaodong transitioned into a multi-party democracy and after 1984 began to marketise its economy, although the Xiaodong Regeneration Society has maintained a monopoly on political power. This political hegemony was challenged in 2017 leading to the beginning of "Normalisation under Yuan Xiannian.
Xiaodong is currently a parliamentary republic, with its ceremonial head of state being Chairperson of the legislative branch of the government, the State Presidium, and the head of government being the First Minister of the executive branch of government, the Council of Ministers. Since the 1980's Xiaodong has undertaken substantial political reforms to democratise the country although corruption has remained.
Xiaodong’s economy has been described as being in a system of state capitalism in which bureaucrats and corporations known as Caihongs are the cornerstones of the economy. Although part of the Xiaodongese economy are state owned, it has under gone substantial neoliberalisation with most state owned corporations being privatised. Major Xiaodongese exports include coal, rice, bauxite and coffee. Xiaodong is a member of the Monic Union, and maintains relations with most other nations, both democratic and dictatorial, having especially close relations with Ankoren. Xiaodong's cultural influence, growing economy, interventionist foreign policy and possession of nuclear weapons makes it a middle power on the world stage and a regional power in eastern Borea.
Etymology
The name "Xiaodong" derives from the Xiaodongese pronunciation of the characters that make up Xiaodong's name, 晓东. Its name in fuhao is Xiǎodōng (/ɕiɑu tʊŋ/). The characters of 晓东 translate to "Dawning East". The characters were first used to describe Xiaodong by the Tao dynasty, and were during the Toki Sougunate recognised as the name of the country by Xiaodongese nationalists, and was adopted as the name of the country following the Baiqiao Revolution. It is sometimes transliterated in the Latin alphabet as "Shiaodong".
The current name of Xiaodong, the "Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong" (晓东吉祥共和国; Xiǎodōng Jíxiáng Gònghéguó) was adopted following the Corrective Revolution in 1936.
History
Ancient Xiaodong
The first human life in modern day Xiaodong is recorded to date back to the 6th millennium BC with early Neolithic sites with human remains having been unearthed through archaeology. The first humans in modern day Xiaodong are commonly referred to by anthropologists as "proto-Xiaodongese" having immigrated from Lahudica, originally settling in the southern coastal regions before moving into the more mountainous north during the neolithic period. The proto-Xiaodongese at this point shared similarities with Monic people from Koyro and Tuthina, with the more modern "Xiaodongese" people largely being a mix of the proto-Xiaodongese people's.

The proto-Xiaodongese people's had infrequent contact with Koy tribes. In the north of the country much of the population was nomadic whilst in the south proto-Xiaodongese people began to adopt more agricultural lifestyles. Most proto-Xiaodongese resided in along the Miaoshen river, with migration to more mountainous regions of the country being slow as the population concentrated in the southern coastal regions. Early agriculture was primarily focused around the growing of rice and the rearing of livestock. Proto-Xiaodongese people had begun to form small city states around 3000BC with the beginning of the Xiaodongese bronze age, in which semi-cohesive cultural attitudes and trends began to emerge. It was during the creation of these city states that basic political units based around kings and feudal lords began to arise alongside the concept of families. Xiaodong was ruled for a time by various tribes such as the Xitain, Donghu, Banpo and Caotang.
The Great Monic Migration resulted in marauding tribes to Monicnise ancient Xiaodong, displacing the local language and resulting in the development of the Xiaodongese language. The migration which took place between 2000-1000 BCE and resulted in a the societal shift to nomadic communities. This started to end around 1000 BCE when pastoral lifestyles began to develop, with farmers utilising intensive dry-field and paddy-field agriculture around 900 BCE.
In 850 BCE the Miaoshen river civilisation developed, which was considered the first recognisably Xiadongese society began to emerge. The Miaoshen river civilisation saw the Syodongmun script begin to be used by Xiaodongese elites and adapted to fit the Xiaodongese language, whilst society became dominated by large land owning families began to create proto-states, with a distinctive land owning class emerging. The Miaoshen river civilisation developed into the ancient kingdoms of Shan and Xiao, although very little is known about these kingdoms.
Xiang dynasty (300BCE-500CE)
The first unified Xiaodongese state was formed around 300 BCE by the legendary Jianzhao Emperor, who created the Empire of Great Xiang (大向帝国; Dà Xiàng Dì Guó). Traditional Xiaodongese canon states that the Jianzhao Emperor was the son of Heaven who successfully united petty kingdoms which he named the "tianxia" (天下; "under heaven"). The existence of the Jianzhao Emperor has been hard to verify with most archaeologists saying the founding of the Xiang dynasty as traditionally told is a myth, with some archaeologists saying that Xiang dynasty was more likely to be founded in 200 BCE. It is known that at the same time of the Xiang dynasty's existence several other smaller kingdoms and that the Xiang emperors retroactively justified the rise of the Xiang as they had taken the "Mandate of Heaven" (天命). The original capital of the Xiang dynasty was recorded to be Fuzhou (复州; Fùzhōu) which is near modern day city of Lunkeng.
Under the Xiang a feudal system was implemented, with the well-field system (井田制度; jǐngtián zhìdù) being its central feature. Society was divided between aristocratic clans that supported a centralised government around the Emperor. The mid-Xiang period (50 BCE - 300 CE) saw a tight centralisation of power by Xiaodongese Emperors, who moved the capital to Rongzhuo (容㒂; Róngzhuó) around 0 CE.
Four Kingdoms (500-731)
- four clans continually rule
- division and civil war
- glorious emperor unites Xiaodong
Tao dynasty (731-1415)
- Empire of Great Tao - 大陶帝国 - Dà Táo Dì Guó
- longest serving dynasty
- ruled by strong emperors inspired by legalism, before said emperor is assassinated by his brother who promotes neo-confucianism
- glorious defeat of Senria by legalist emperor
- buddhism and Kamism arrives
- lots of art and culture
- wars with Senria
- dynasty gets poor
- weak boy emperor is couped by one family who are the power behind the throne - the Jiao family
Jiao dynasty (1415-1667)
- Empire of Great Jiao - 大皎帝国 - Dà Jiǎo Dì Guó
- clan head becomes emperor
- Jiao are decadent people who squander Xiaodong's riches
- creates Taojiao - mix of Buddhism and confucianism
- almost wins war with Senria before a peasant uprising ruins everything
- oh shit Christianity's arrived, starts repressing it
- goes into decline
Toki Sougunate (1667-1868)
- Toki Shogunate - 土岐 幕府时代 (Tǔqí Mùfǔ Shídài)
- Senrian mercenary takes over
- implements Senrian like government system
- hated by most Xiaodongese
- overthrown, but develops Xiaodongese nationalism as a result of existing
- from a neutral perspective quite good rulers overseeing technological development and a capitalist economy
Heavenly Empire (1868-1933)

- Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire - 大天晓东帝国 (Dà Tiān Xiǎodōng Dìguó)
- Baiqiao Revolution
- becomes empire - bullies literally all its neighbours
- Constitutional Revolution
- nicks Sakata from Senria
- Senrian-Xiaodongese War
- Xiaodong loses war
Civil War (1933-1936)
- Commies declare independent state
- Government corrupt and incompetent
- Collapse of empire
- Corrective Revolution
Auspicious Republic (1936-present)
Following the creation of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong (晓东吉祥共和国; Xiǎodōng Jíxiáng Gònghéguó) the new government was faced with economic, political and social collapse. The first priorities of the new government was to crush communist forces in the civil war and stabilise the economic situation. In the short term the government moved in against the communist revolutionaries in Kuoqing and reintegrate Duljun into Xiaodong. Whilst the civil war was ended by the regime relatively quickly (having already gone in favour of the government since the summer of 1936), the Second Duljunese-Xiaodongese War lasted until 1940 before Duljun became part of Xiaodong again. In foreign relations the new regime quickly abandoned the Treaty of Keishi with Senria, but managed to establish separate peace with Tuthina. Domestically the new regime quickly enshrined itself as a

dominant -party state with the 1935 Constitution prescribing that Lu Keqian's ideology, National Principlism, was to be the ideology of the state. Politically Xiaodong was declared a democratic republic but under a "guided democracy" in which the Xiaodong Regeneration Society monopolised political power. Rongzhuo after two years as acting as the provisional capital was declared the permanent capital. Although opposition to the regime was muted at the time, the new government continued its predecessors censorship and poor human rights record, creating a new secret police known as the Public Security Secretariat (more commonly known as the Shujichu, named after the phonetic Xiaodongese term for secretariat) and setting up a network of "re-education centres". However, the restrained repression exercised by Lu and his economic development and social policies has often cast the early republic as being a "benevolent dictatorship" or a "post-totalitarian" regime.
Economic reconstruction and social reforms were steadily passed during the 1930's. As the new regime was adamant that Xiaodong undergo modernisation, the government under Lu Keqian established free education for all, a rudimentary healthcare system, nominal gender equality and a more codified legal system. Most dramatic was the economic reforms pursued by Minister of Finances Ma Renzhong which dismantled feudalism supporting land reform and encouraging rapid industrial development. Despite a concentrated effort by Senria to sabotage re-industrialisation (Operation Red Pheasant) by 1940 Xiaodong had record economic growth setting off the so-called "Decade of Development".
In 1945 Lu died, being succeeded as First Minister by Ma Renzhong. Ma at first governed in a tandemocracy with State Chairman Yu Changshao, but an attempted coup d'état in 1946 led to Ma to assert the power of the Regeneration Society against that of the military, leading to Xiaodong to become a bureaucratic authoritarian regime that's policies were essentially pragmatic rather than ideological. During the back-to-back rule of Ma, Li Zhaozheng and Lu Fangliang Xiaodong oversaw rapid economic development and the emergence of new cultural and social movements in the country, with Xiaodongese cinema and new media especially blossoming. In the wake of the Great Republican Uprising in neighbouring Tuthina Xiaodong was able to assert itself as a regional power under the "Three Fundamentals" whilst tensions with Senria increased, especially following the assassination of Senrian Prime Minister Kitamura Tokiyasu.
By the early 1970's however the Xiaodongese economy had started to decline due to high inflation and mismanagement of state resources. The new First Minister Sun Yuting increased repression internally as well as being confronted with the Coastal Crisis in 1975 after the Senrian government under Takahata Takesi attempted to force Xiaodong to pay for Treaty of Keishi reparations in a show of gunboat diplomacy. In 1977 a series of syndicalist strike action by the Xiaodongese Labour Union of Free Workers' led to the Kuoqing Massacre, the most blood repression under the Auspicious Republic.
In 1984 Sun was assassinated by a Senrian Tokkeitai agent, being succeeded by Qian Xingwen. Confronted with a failing economy Qian approved of several shock therapy packages that liberalised the Xiaodongese economy, privatising state assets, deregulating industry, removing price controls and opening the country to foreign investment. The shock therapy program resulted in economic growth but poverty ad unemployment to grow; this alongside lack of political reform led to the Orchid Revolution in 1988 which saw thousands protest against the regime and demand economic and political reform. As a result Qian and his Second Minister Li Jingyao allowed for multi-party democracy and devolution to the provinces of Duljun and East Thianchin. However the victory of a separatist party in Duljun following these reforms led to a declaration by Duljunese of independence which was rejected by the Xiaodongese government. Subsequently a military revolt in the province led to the start of the Duljunese War which lasted from 1988-1997. The war resulted in over 150,000 people to be killed and 300,000 to be displaced, with both sides being accused of ethnic cleansing and genocide. The war was eventually won by Xiaodong in 1997 under the leadership of Yang Zhengming and Han Guanzheng when the separatist capital of Caofang surrendered to Xiaodongese forces.
The 1990's also saw increased tension with Senria - under Qian Operation Calm Waters saw Senrian ships bombed with limpet mines, which resulted in Senria under hardline Prime Minister Haruka Kiyosi to order the 1987 bombing of the Mausoleum of Lu Keqian which killed 87 Xiaodongese people. Xiaodong retaliated in 1990 by releasing sarin gas on the Keisi Metro which killed 54 and severely wounded 62 people. This in turn led Senria in 1994 on the 60th Anniversary of the Corrective Revolution to bomb both the State Presidium and the parade that day in Rongzhuo commemorating the revolution. 73 people on parade and 54 state presidium delegates were killed in the attack. These actions led to pressure from Tuthina as well as reformists led by First Minister Han to begin détente with Senria - by 2004 Senria under the similarly reformist Izumi Sigesato and Xiaodong agreed to restart official relations for the first time since 1936. During this time, Xiaodong also became integrated into the Tengkong system and in 2004 became a member state of the Esquarian Union.
During the 2000's under First Minister Yuan Xiannian there has been massive economic growth with Xiaodong becoming a middle income country as part of the governments "Xiaodong 34" strategy. Between the mid-2000's to early 2010's there was also a blossoming of new cultural activities, especially in music and cinema as well as iaodong cooperating with other countries to a greater extent, despite controversy erupting over a perceived right-wing shift by the Yuan government especially surrounding issues such as genocide denial. In 2008 Xiaodong had its first successful nuclear test when it successfully launched and detonated a five kiloton nuclear weapon.
Proposed constitutional reforms in 2014 were met with protests which resulted in a sharp decline in the popularity of the government, who lost their majority in the 2016 general election. After allegations of rigging the 2017 election and being met with subsequent protests the government led a crackdown and started "Normalisation" that aims to reassert the Regeneration Society's power. Since then Yuan Xiannian has been said to be the most powerful man in Xiaodong since Lu Keqian.
Government and Politics
Xiaodong is officially a unitary parliamentary republic with its supreme law being the Constitution of Xiaodong the current version being published in 1987. The legislative branch consists of the unicameral State Presidium (国家常务委员会) which is led by a Chairperson (主席) who serves as head of state and elected by the Presidium for a single seven year term. The executive branch is centred around the Council of Ministers (晓东部长会议) which is led and appointed by a First Minister (首席部長) who functions as the head of government. Xiaodong maintains a three tier judiciary, with higher, prefectureral and municipal courts. The Chairperson of the State Presidium on the advice of the Minister of Justice can form a Supreme Judicial Yuan (最高司法院) that serves as the highest appellate court in certain cases. All judges, civil servants and politicians are picked from the Examination Secretariat - prior to 1994 the Examination Secretariat was the de facto organ used to advance the careers of judges, civil servants and politicians, although since 1994 its influence has declined. The current Chairperson of the Presidium is Yuan Xiannian and First Minister is Xi Yao-tong.
Since 1936 Xiaodong has been a dominant-party state under the Xiaodong Regeneration Society (晓东再生会) via its political front the National Regeneration Bloc, which established the current governmental system after the Corrective Revolution. From 1936-1988 the Xiaodong Regeneration Society ruled Xiaodong as a de facto one-party state but after pursuing some democratic reforms legalised opposition parties. The Xiaodong Regeneration Society continue to maintain control over the state apparatus, media and economy meaning opposition is weak, although anti-government forces have become more prominent in recent years with the State Presidium no longer being a complete rubber stamping body as it was in the past. The Xiaodong Regeneration Society adhere to a nationalist, statist ideology known as National Principlism (国家主体主义) that seeks to uphold a centralised form of authoritarian democracy. Elections for the State Presidium are held every five years, although critics maintain they are neither free nor fair. Political apathy is high due to government corruption, authoritarianism and a weak opposition. Unlike in most countries, ideological differences are not the main divides in Xiaodongese politics, which is based much more on guanxi networks between politicians.
In 2017 after an election that was allegedly rigged a series of protests resulted in the government of Yuan Xiannian and Xi Yao-tong to launch a crackdown on protesters and the declaration of a state of emergency. International observers state this state of emergency, named "Normalisation" (正规化; zhèngguī huà) has turned Xiaodong into a de facto police state.
Government
Xiaodong's has no official separation of powers as defined by the Constitution. Officially the executive and legislative branch is headed by the Chairman of the State Presidium who oversees the legislative process and appoints the First Minister, who forms the main core of the executive (the Council of Ministers). Supreme legislative organ is the State Presidium whereas the Supreme Judicial Yuan functions as the highest body within the judicial branch.
The relationship between the Chairperson and the First Minister is often disputed. According to convention the Chairperson plays a mostly ceremonial role outside of appointing the First Minister, overseeing the passing of legislation, acting as commander-in-chief of the armed forces and chairing legislative sessions. The Chairperson is elected in an indirect election by the State Presidium. Meanwhile the First Minister officially acts as the head of government appointing and leading the executive (the Council of Ministers) which heads several government departments (eg. Ministry of International Relations, Ministry of Finances, etc) with their being 28 departments overall. Whilst the First Minister is appointed by the Chairperson, they must commanded the confidence of the State Presidium. Whilst the Constitution implies that the First Ministers' power outstrips that of the Chairperson, political convention since 1983 means that the Chairperson shares power with the First Minister in what has been described as an overall collective leadership between the Chairperson and the Council of Ministers. Currently due to the overwhelming dominance of the Xiaodong Regeneration Society within government the Chairman of the XRS, former First Minister and current State Chairperson Yuan Xiannian also holds considerable power First Minister Xi Yao-tong to the point that Yuan has been described as the de facto leader of Xiaodong.
Legislature
| File:Xiaodong State Presidium.png |
|
Government (319) Xiaodong Regeneration Society (319) Official Opposition (78) Association for Promoting Democracy (78) Crossbench (46) Independents (46) Other Opposition (120) Movement for National Principlism (75) Independents (45) |
The main legislative body of Xiaodong is the unicameral State Presidium which consists of 563 elected representatives (known as Presidium Delegates). The State Presidium is chaired by the Chairperson who oversees legislative sessions in a manner similar to a speaker. As the Chairman is often performing duties as head of state, day-to-day legislative affairs are handled by the Presiding Officer of the State Presidium of Xiaodong who is the de facto speaker. Since 1992 there has been an official opposition (官方反对党) whose duty it is to scrutinise the government, with the People's Party having dominated the role since 1991. Critics maintain that the official opposition merely exist to give the government an air of legitimacy, although it has been noted that the opposition has grown more assertive in recent years. In 2008, a bipartisan presidial commission recommended the creation of presidial committees to better scrutinise government policy, although no such moves to formally establish committees have been attempted yet.
Any presidium delegate has the right to propose draft laws to the presidium, which must pass a simple majority vote to become formally part of the law. Despite this most successful draft laws have come from the government benches which has always maintained a legislative majority. The presidium has the right to amend the constitution if the government has a supermajority (two thirds of the total seats) or can declare a referendum on a proposed constitutional amendment if it possesses a simple majority (half of total seats). This has never been a constitution written in. Currently within the State Presidium the ruling Regeneration Society maintain a majority of 319 seats. The opposition consists of the far-right Association for Promoting Democracy with 78 seats, the socialist Movement for National Principlism with 75 seats and 91 independents.
Since the start of Normalisation, the United Democratic Appeal for Xiaodong, a coalition of various pro-democracy parties who have 137 seats, have refused to take their seats in the State Presidium due to the alleged rigging of the 2017 election. In 2018 the coalition and its parties were deregistered by the electoral commission and its seats in the State Presidium redistributed to other parties. Another party that won 54 seats in the 2017 election, the populist, radical democratic Alliance for Democracy in Xiaodong like the UDA had a policy of abstentionism before being banned as a political party in January and its seats declared vacant - a month later, the New Frontier Party (the political front for the salvationist religious group the Righteous Harmony Movement) was also banned and its seats invalidated.
Elections
General elections are held every five years in Xiaodong for the State Presidium, mayors, prefectual congresses and local municipal governments, although the State Presidium can be dissolved at the request of the State Chairman at any time. Citizens over the age of 21 who are not in prison or deemed mentally ill are entitled to vote, with universal suffrage having been adopted in 1963. Voting for representatives in the State Presidium and prefectual congresses is performed via a mixed member majoritarian system - 115 are elected by first-past-the-post and 100 via single non-transferable vote. Within the State Presidium members are elected in either multi-member districts that all send back five members or one member districts to the state presidium. Mayors and members of local municipal governments are elected on a first-past the-post basis. Since 2011 electronic voting has been introduced and widely used in Xiaodong. The last general election in Xiaodong saw a 78.3% turnout, but was allegedly conducted with massive electoral fraud to favour the ruling ZSH. Elections that fail to produce a 50% turnout are invalid under Xiaodongese law.
Judiciary
Xiaodongese law has since 1936 been based on legalist traditions alongside civil law from Teutonia. Previously Xiaodong maintained a strong Confucianist judicial system based on the belief that the maintenance of tradition would be more effective in maintaining social order, but since the rise of Legalist philosophy since the 1930's the law has become more codified. Nevertheless, the rule of law in Xiaodong is subject to the will of the state which is seen as above the law. Xiaodongese law stipulates one is only guilty if they confess their crime, ingraining torture into the legal system.
The highest judicial authority in Xiaodong is the State Presidium which officially delegates responsibility of such authority to the Minister of Justice. The Minister of Justice can advise the State Presidium to convene the Supreme Judicial Yuan to serve as the highest appeal court if the Minister of Justice deems a case to be applicable to the Yuan, although often requests to convene the body are rejected by the Ministry of Justice.
Subdivisions
Xiaodong is divided into 16 prefectures (省), each with their own regional government head by a chief minister (首席部長) with a prefectural presidium located in a prefectual capital. Prefectures are further divided into 113 counties and finally townships, with cities being a series of merged townships forming a municipality rather than a county. There are 22 municipalities.
There are three special autonomous regions in Xiaodong - Duljun, East Thianchin and Darma. Thianchin and Darma were given devolution in 1988 and Dulju 2002. Under devolution, each SAR has its own regional presidium and governor (省长) - although individual prefectures in the SAR's have less autonomy over tax, health, and public services, the SAR's as a whole has devolved power over areas such as environment, public services, transport, agriculture, housing, aspects of law and order and economic development.
The capital, Rongzhuo, is considered its own administrative unit
| # | Prefecture (省) | Administrative centre | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Darma (德沃爾) | Trishuli (新花园) | 10,826,470 |
| 2 | Shenqu (神曲) | Minqin (民勤) | 3,325,400 |
| 3 | Duljun (山国) | Hejintao (和进套) | 15,266,392 |
| 4 | Fenjiazhi (风家值) | Caofang (操放) | 3,245,900 |
| 5 | Chuqian (处钱) | Zhinning (只能宁) | 3,325,400 |
| 6 | Dongtou (懂头) | Ningjin (宁晋) | 5,145,600 |
| 7 | Jiebu (姐不) | Shenkong (神空) | 9,456,300 |
| 8 | Chenghu (珹湖) | Renpou (人剖) | 3,188,800 |
| 9 | Langang (兰港) | Lunkeng (沦坈) | 5,151,200 |
| 10 | Rongzhuo (容㒂) | Rongzhuo (容㒂) | 22,028,482 |
| 11 | Taixin (台新) | Hongbu (红不) | 3,145,600 |
| 12 | Niushangzi (扭伤自) | Yinbaolei (崟堡垒) | 3,565,400 |
| 13 | Xibuguo (西部过) | Kuoqing (阔请) | 10,317,900 |
| 14 | Gaoming (高铭) | Zhonghe (中和) | 5,123,300 |
| 15 | Huayuan (话元) | Baiqiao (白壳) | 12,257,156 |
| 16 | Thianchin (天津) | Heping (和平) | 6,021,700 |
| 17 | Qingbei (清被) | Guoshan (过山) | 4,243,200 |
| 18 | Meifucun (没付村) | Guojing (过境)) | 3,334,300 |
| 19 | Qihongtang (其红糖) | Xiagang (下刚) | 5,145,600 |
| 20 | Zhongdong (中东) | Jinjiang (进疆) | 3,245,900 |
Armed forces and intelligence
The armed forces of Xiaodong is known as the Xiaodongese Defence Forces, which is split into an army, navy and airforce. The Xiaodongese Armed Forces currently has around 1,050,750 troops overall (585,500 active, 225,000 in reserve and 240,250 paramilitary groups), making it overall ahead of the Vajorrian Federal Defence Force but behind the Royal Lyonese Forces in terms of manpower. The Chairperson of the State Preisidum is the commander-in-chief of the Xiaodongese Armed Forces, which answers to the Council of Ministers via Ministry of Defence and Military Planning (MoDMP). Military affairs are primarily handled by the Joint Defence Council, a forum of military commanders who are subordinate to the MoDMP. The military in Xiaodong have since 1953 not taken a role in politics, as under single-party rule the top ranks in the military were occupied by party officials. Since democratisation the military have been kept subordinate to the civilian government. The coast guard and gendarmerie forces take on military functions - however, they are responsible to the Ministry of Internal Affairs rather than the MoDMP. The main intelligence unit, the Public Security Secretariat (Shujichu), also is officially part of the military structure however they report directly to the First Minister's Office. In recent years, there has been a push to merge the Xiaodongese army together into one cohesive joint command - currently there is intense rivalry between the Shujichu and the military divisions under the MoDMP. Xiaodong currently spends 3.9% ($21,325,710,315) of its budget on the military. Since 1935 as per agreements made in the Treaty of Shenkong, Xiaodong has renounced the right to wage an offensive war in eastern Borea and Lahudica.
The Xiaodongese Defence Forces were preceded by the Heavenly Xiaodongese Army, which was the first modern army in Xiaodong. Following the abolition of the Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire, the former Heavenly Xiaodongese Army was renamed and consolidated into the Xiaodongese Defence Army, which underwent modernisation in the 1930's. In the 1970's the defence forces underwent modernisation again purchasing weapons from Ankoren and Teutonia, and since 2008 have undergone a further stage of modernisation and restructuring to be a more professional, efficient force. Xiaodong has committed to the development of its navy and airforce, which have been substantially modernised and expanded since 2008. The Xiaodongese navy in particular has undergone a transition from a brown water to green-water navy.

Xiaodong has a history of possessing weapons of mass destruction. During the 1930's it was known that Xiaodong had started to develop a stockpile of chemical weapons in the form of mustard gas, and during the 1950's started a biological warfare research programme. Xiaodong has resisted attempts to sign treaties that ban chemical weapons, and has been accused of possessing chemical and biological weapons such as sarin, nerve and mustard gas - however this has not been proven as of 2015. Xiaodong has admitted that it possess facilities that produce chemical and biological weapons, but asserts that they have been inactive since the mid-1990's. Under First Minister Sun Yuting following the Coastal Crisis Xiaodong started to develop a nuclear weapons programme which was mired in development until the mid-2000's (during which Xiaodong maintained strategic ambiguity over possession of nuclear weapons). The first successful nuclear test was conducted in 2008 and since then Xiaodong has expanded its program massively, developing intermediate-range ballistic missiles in 2015. Xiaodong maintains an arsenal of 40-80 nuclear warheads with a sea and land based delivery system. Xiaodong as of 2017 has conducted 5 tests and has a no-first use policy over nuclear weapons.
Conscription - known as "Patriotic Civic Service" (爱国公民勤务; Àiguó gōngmín qínwù) is currently enforced for all citizens between the ages of 18-21 for a period of 24 months. It was introduced in 1869 for all male citizens for a 28 month period with conscientious objection not being recognised by the government, with only those deemed "unfit for service" being exempted. The government mandated that women also be included in conscription in 1938. In 1988 the government reformed the conscription law decreasing the time of service to 24 months and offering alternate service in a non-combatant role on medical grounds, and university students given the opportunity to opt to serve for 12 months in either an combatant or non-combatant role. "Draft evasion" is punished harshly in Xiaodong.
Human Rights
Human rights in Xiaodong continue to be a controversial domestically and abroad, with human right monitoring organisations such as the Esquarian Human Rights Monitor, Guardians of Liberty and Global Assessment of Human Rights as of 2017 ranking Xiaodong as unfree. The EHRM stated "Xiaodong has become the site of disastrous attacks on liberty after the ruling Xiaodong Regeneration Society rigged an election to retain power, crushed protesters with military force, jailed opposition, stamped out free speech and a free media, resurrected the thought-dead censorship laws and surveillance system and endorsed police brutality and torture. The culture of child labour and a lack of worker safety laws remains untouched".
The Xiaodongese constitution gives the state the ability to repress civil liberties if it wishes. Capital punishment is legal in Xiaodong and is commonly used, whilst many political dissidents have allegedly undergone "forced disappearance" under the rule of Yuan Xiannian. Human rights bodies have accused the state of torture, censorship, widespread racism and violations of various freedoms. Much of this has heightened during the "Normalisation" process.
Foreign relations
Xiaodong's foreign policy objectives up until 1988 were formalised in the "Three Fundamentals" - the isolation of Senria from international affairs, the maintenance of Xiaodong as a regional power in eastern Borea, and the reclamation of "lost territories" (land ceded to Tinza, Narmada and Min in the 1930's). In more recent years Xiaodong has also emphasised free trade issues.
Xiaodong has since 1936 when it pledged to no longer wage offensive war in the Borea-Lahudica - however, it has been involved in violent confrontations with Senria over the years. Xiaodong is famous internationally for using "panda diplomacy", using giant pandas as diplomatic gifts to other countries. Panda diplomacy stretches back to the Xiang dynasty when Xiaodong sent pandas to the Senrian and Tuthinian emperors. Xiaodong is a member of the International Forum for Developing States, Monic Union, Organisation of Esquarian Nations and Tengkong System. It was previously a member of the Esquarian Union.
Xiaodong's closest relations are with the Nautasian Union (and its predecessor state Ankoren) and Tuthina, although the nature of these close relations differ. In regards to Ankoren, following the Corrective Revolution when Lu Keqian met Nurcan Taylan in 1936 both countries began to foster close political and economic ties as both countries were ruled by one-party governments intent on regional hegemony. Close cooperation between both governments became more prominent under Sun Yuting and Hakim Ali Ghaddar, and have since Evren Volkan and Yuan Xiannian held office seen a dramatic revival with the onset of the Ankoren-Caliphate conflict seeing Xiaodong support Ankoreni interventions in Nautasia. The government of Xi Yao-tong has furthered this policy, signing significant trade deals with Ankoren in 2016 and 2017, whilst Xiaodong publicly supported a vote for unification in the 2017 Ankoreni-Irvadi referendum. Ankoren meanwhile has provided military cooperation with Xiaodong, most prominently during the Third Duljunese-Xiaodongese War. The extremely close and friendly relations between Xiaodong and the Nautasian Union has been called the Estanban-Rongzhuo Axis.
There is close economic and political ties between Tuthina and Xiaodong, but relations between the two countries are complex and fraught with differences. Since the 1935 Treaty of Shenkong Tuthina and Xiaodong have attempted to maintain cordial relations. During the 1940's-1980's relations were cool with trade being frequent but Xiaodong often being highly critical and mistrustful of the Tuthinian government, even considerign supporting republican forces during the Great Republican Uprising. Since the 1980's Xiaodong has sought to maintain good relations with Tuthina, which improved in the 1990's. Tuthina as per the Treaty of Shenkong currently maintains a naval base at the Shenkong harbour having been continually leashed to Tuthina since 1935. Xiaodong is also one of the largest purchasers of Tuthinan goods and by and large sides with Tuthina in international disputes, being a major advocate of economic integration in the region. However, there have been difficulties within the relationship - many Xiaodongese officials maintain that Tuthina acts as an imperialist power, with the poor state of Xiaodongese-Senrian relations being of concern to Tuthinian policy makers whilst Xiaodong has since the 1850's refused to be a member of the Tengkong system.
Xiaodong is well known for having poor relations with Senria. Xiaodongese-Senrian relations have long been contentious - the Zhengzhi War under the Xiang dynasty, Yufang war under the Tao dynasty and Chuanjin war under the Jiao dynasty were all fought with Senria. The Toki Sougunate led to anti-Senrian sentiment to become an integral part of Xiaodongese nationalism. However modern Senrian-Xiaodongese relations have been shaped by the events leading up to and following the Senria-Xiaodongese War and co-current Senrian Genocide which resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Keisi which demanded reparations from Xiaodong and forced it to admit sole responsibility for the war. Since 1936 Xiaodong has refused to abide by the treaty nor admit to committing a "policy of genocide". This has led to both governments to sponsor internal instability in their respective countries - Senria sponsoring or supporting Operation Red Pheasant, the assassination of Sun Yuting, 1987 Lu Mausoleum bombing, 1994 State Presidium bombing ad support for the Duljunese in the second and third Duljunese-Xiaodongese War, Xiaodong sponsoring the attempted assassination of Imahara Katurou, the assassination of Kitamura Tokiyasu, Operation Calm Waters and the 1990 Keisi Metro sarin attack with both nations participating in the Coastal Crisis. Diplomatic relations started in 2004 due to pressure from Tuthina and the moderate personalities of Senrian Prime Minister Izumi Sigesato and First Minister Han Guanzheng - however under Yuan Xiannian relations have began to become tense again.
Xiaodong has varied relations with other nations. Relations between Tinza and Xiaodong have been complicated by a variety of factors. Like with Senria, there still exists significant controversy regarding Xiaodong's imperialist actions in the 1900's whilst Xiodong also claims sovereignty over the region of Lhogrong (known as Beijiang in Xiaodong) which has complicated relations. Xiaodong has similar issues with Min and the west Thianchin region. Xiaodong also has poor relations with Narmada especially since the assumption of power of syndicalists in the 1980's. Tensions between the two have largely revolved around territorial disputes, which escalated in the 2017 during the Huashan conflict.
Meanwhile, Xiaodongese relations with Luziyca has fluctuated - in 2003 Xiaodong joined the Esquarian Union which saw relations improve dramatically between the two nations, although relations seriously deteriorated in 2004 when the Xiaodongese government refused to end transitional controls regarding freedom of movement in the EU, despite large amounts of Xiaodongese leaving Xiaodong to work in other EU countries. Since the election of a Liberal government in Luziyca relations have worsened. Xiaodong has a working trade relationship with Namor with Xiaodongese officials expressing an interest in increased investment in the country in recent years. Xiaodong has moved in a similar direction with Evroseia which has become one of the biggest investors in Xiaodong.
Crime and law enforcement
Geography
Xiaodong's geography is mainly divided between the mountains, hills, plateaus and plains. The northern Duljun is dominated by the Huashan mountain range, with its highest point being located in the Wuxintai prefecture at Mount Shaowei at 2,678 meters. Further south in the Qiaoguo and Liaojing regions the country is dominated by plains and basins. Around 18% of the country is forested, mainly in the central provinces straddling the more mountainous north and the flatter south.
Xiaodong is commonly considered to be a hilly and mountainous country, with only the coastal regions retaining flat land in the form of plains. As a consequence of this, over half the population reside on the coast whilst the more mountainous north remains much more sparsely populated. The south-eastern coast contains the majority of Xiaodong's arable land. Several rivers run through Xiaodong, the longest of which is the Zhuchao River which passes from the city of Henjintao to the southern coast. Several smaller rivers run from the mountainous regions to the coast, with Xiaodong as a result having a well connected water network.
Biodiversity
Climate
Economy
Xiaodong maintains a nominal GDP of $167,318 million, with its average growth rate being 7% since 2000. The main sectors of the Xiaodongese economy are coal, textile, chemical, machinery, iron, and steel.
Xiaodong's economy is driven by a mixture of state owned enterprises (SOE's) and private businesses within the framework of a mixed economy, with SOE's and industrial conglomerates (known as Caihongs) dominating the economy over independent ventures. The close nature between the state and corporations has meant that economists have frequently stated that Xiaodong possesses a corpratist economy, with the state dominating the allocation of capital through indicative planning. This corpratist model which sees both corporate and state bureaucrats being the primary drivers of the economy has resulted in Xiaodongs economy to be called a state-sponsored capitalism. As of 2018 as much of a third of the Xiaodongese economy remains under state ownership, compared to over two-thirds during the 1970's.
Xiaodong is a newly industrialised country with a rapidly expanding industrial sector. The main sectors of Xiaodong's economy is based around heavy industry, mining and agriculture. Bauxite and iron are amongst the most widely mined metals with Xiaodong whilst coal remains the single largest export. Prior to the move to an industrial economy Xiaodong's main export was rice, which continue to be some of the biggest industries within Xiaodong. Since the mid-2000's heavy industry and the production of metals and ships have become two of Xiaodong's largest industries with consumer goods being the largest economic sector.
In 2016 Xiaodong received $98,600 million in foreign direct investment. The government has tried to court more FDI but Normalisation has led to total receipts of FDI to diminish. Xiaodong has $288,428,880,000 in external debt (which is 24% as a percentage of GDP) and $473,504,078,000 in public debt (which is 39.4% as a percentage of GDP).
With a Gini rating of 36.8, wealth inequality remains a serious problem in Xiaodong. According to an independent study conducted in November 2015 over 36% of the nations wealth is concentrated in the top 10% of income earners in comparison to the lowest 10% only receiving 4%. Poverty is also a serious problem in Xiaodong with an estimated 20% of the population living below the international poverty line, and many more working in low paid jobs. The Xiaodongese government has refused to impose a minimum wage, stating it would hurt Xiaodong's competitive nature oversea's, although a recommended "basic wage" exists, albeit unenforced.
Economic history
Following the Corrective Revolution the Xiaodongese government committed to industrialisation and the creation of a modern economy. To achieve massive and rapid industrialisation the state implemented import substitution industrialisation, central planning and the nationalisation of the Caihongs. Over time restrictions on capital flow, foreign investment and financial transactions were implemented as were protectionist policies. The architect of this economic policy was Ma Renzhong who aimed to lead Xiaodong through a "decade of development". During the 1940's-50's economic planning and centralised control was used to industrialise and modernise the Xiaodongese economy - whilst economic growth was achieved by the 1970's this had devolved into high inflation as growth faltered.
Economic failure in the early 1980's led to state officials to abandon import substitution industrialisation and support a form of export-oriented industrialisation. Financial Minister Mao Zhongchen under the direction of neoliberal economist Wang Datong oversaw several shock therapy packages that saw the privatisation of state assets, deregulation especially of the labour market, increased investment into coal as a national resource, the dismantling of tariffs and liberalising other sectors of the economy. Between 1986-2005 Xiaodong maintained a fixed exchange rate with the Luziycan lira until a currency crisis forced Xiaodong to devalue the Renjin. Since then Xiaodong has experienced rising inflation alongside economic growth. In order to lower the price of exports the Xiaodongese government currently follow a policy of forced devaluation of the Renjin keeping its exchange rate (according to critics artificially) low. Alongside the value of the Renjin being kept low interest rates also are held down by the Xiaodongese Reserve Bank. Between 2005-2017 Xiaodong was placed under the New Economic Policy which regulated domestic markets, liberalised the financial sector, utilising economic planning and placing more emphasis on corpratisation rather than privatisation. A stock market crash in 2016 followed by a recession in 2017 has led to further economic reform in Xiaodong with the government committing to market-based structural reform.
Agriculture
Whilst the importance of agriculture has consistently declined in Xiaodong since the move to an industrial economy in the 1940's, it still remains a integral component of the economy. The main corps grown in Xiaodong are rice, soybeans sugarbeets, opium and jasmine tea. Farming in Xiaodong is concentrated in the Fenjiazhi, Chuqianand Zhongdong prefectures, all of which are located in Central Xiaodong.
Xiaodongese agriculture has traditionally been very labour intensive, with the growing of rice and tea traditionally being seen as a cultural tradition. There has been famines in Xiaodongese history although with the development of modern agricultural technology Xiaodong has not suffered a famine since 1855. Since the 1950's most farms in Xiaodong are large scale commercial operations with traditional Xiaodongese farms becoming rarer.
Xiaodong maintains extremely protectionist policies regarding its agricultural industry which is heavily subsidised, with foreign agricultural goods subject to high tariffs. The government has been hesitant to liberalise the agricultural sector out of fear of being a net food importer.
Currency
The official currency of Xiaodong is the Renjin (金). Various forms of the Renjin have existed over the centuries being until 1987 backed by the gold standard. In 1987 the Xiaodongese government under Sun Yuting decreed that the Renjin should no longer be backed by gold, and instead maintain a fixed exchange rate to the Luziycan lira. This was maintained until 2005 when Xiaodong underwent a currency crisis when investors feared that the Xiaodongese government could no longer support the Renjin's exchange rate with foreign capital. As a result of the currency crisis the Xiaodongese government abandoned the fixed exchange rate devaluing the Renjin, which has subsequently been floated by the Xiaodongese Reserve Bank. The Renjin is currently a fiat currency, with one Renjin being worth $0.29 of the universal standard dollar.
Since 2017 the Renjin's value has decreased rapidly with inflation reaching a high of 450% in March 2017 before being reduced to 380% in August. The Xiaodongese Reserve Bank has talked of replacing the Renjin with a new currency to help fight inflation.
The Xiaodongese Reserve Bank is the central bank of Xiaodong and reserves the sole right to issue banknotes and coins. It is run by a Governor who are appointed by the Council of Ministers with advice from the Reserve Banks bored of directors. The Reserve Bank has recently seen its powers curbed - in particular its ability to print money to cover deficits - as part of the government's economic reform strategy.
Energy
The majority of Xiaodongese electricity (70.5%) is generated from coal, with 9.2% coming from natural gas, 8.7% from hydroelectric power, 6.1% from oil and 5.2 from nuclear power. Xiaodongese authorities have in recent years sought to expand the hydroelectric industry at the expense of traditional fossil fuels, although with 85.8% of Xiaodongese electricity being generated by fossil fuels it is still dependent on such sources. The Xiaodongese government expects electricity consumption to increase by an average 3.8-5.1% from 2015-2020.
Xiaodong has one of the largest proven coal reserves in the world, with around 77,833 million tonnes being proven to exist in 2014, with the majority of coal being mined in the Jiebu, Langang, Fenjiazhi, Chuqian, Xibuguo and Zhongdong prefectures with smaller reserves found in the Shenqu and Wuxintai prefectures. A large proportion of Xiaodongese industry is focused on the production and export of Xiaodongese coal reserves - in 2014 it was recorded that 485 million tonnes of coal was mined in Xiaodong. All coal mining in Xiaodong is supervised by the Xiaodongese Mining Confederation.
In 2015 it was recorded that Xiaodong has around 18,500,000,000 m³ of proven natural gas reserves but only 46,500 bbl of proven oil reserves. Both natural resources are under the ownership of the state-owned Xiaodongese Petroleum and Gas, although in recent years the Xiaodongese government has committed to a partial privatisation and allow Ankoreni energy companies to extract Xiaodongese gas.
Xiaodong under Sun Yuting during the 1970's actively pursued nuclear energy, constructing four nuclear power stations and pouring billions in nuclear research. However the 1988 Yuxiang nuclear disaster where nuclear waste in a storage tank overheated and exploded with the force of 50 tonnes of TNT releasing 10 MCi of radioactivity led to concerns over Xiaodong's nuclear program, leading to two power stations to be closed down and for the government to invest back into fossil fuels. In 2007 the government under Yuan Xiannian announced massive investments into hydroelectric power with the Jiangshi Dam (one of the largest hydroelectric dams on the plament) being built between 2007-2015.
Industry
Xiaodong has since the 1950's built a sizeable industrial base with the main industries being shipbuilding and metal-products. Xiaodongese industry is overwhelmingly focused towards heavy industry although since the mid-1970's light industry has developed at a fast rate. Since then, Xiaodong's industry is primarily based on the prodction of iron and steel, as well machinery and shipbuilding. Industry employs around 32.54% of the total workforce.
The fastest growing industrial sector in Xiaodong is the manufacture of machinery and consumer goods, with the development of both being accelerated by recent moves to liberalise the Xiaodongese labour market. The majority of heavy industry in Xiaodong is state-owned by companies such as the Xiaodongese Mining Confederation, the National Bureau for Industrial Development and Rongzhuo Steelworks although in recent years there has been a move to privatise most industry.
Textiles is a growing industrial sector in Xiaodong, especially that relating to silk and wool products. This has followed a general trend for the increased manufacture of consumer goods such as televisions, household appliances and electronic goods. However light industry is still dwarfed by the heavy industrial sector.
Science and Technology
Investment in scientific research has increased in recent years within Xiaodong. Historically Xiaodong has made some scientific advancements especially under the Xiang and Tao dynasties (in particular the development of gun powder and papermaking) but in the 20th century imported a large portion of modern technology. Xiaodongese investment into scientific research increased during the late 1960's and early 1970's when the government created the National Association for Scientific and Technological Research, pairing industrial and scientific institutions and launching a nuclear research committee with the intention of nuclear proliferation. The Nuclear Research Committee was dissolved in 1986 when the government began investing in other scientific research instead. These include the Xiaodongese Space Research Committee, which aims to launch a Xiaodongese man into space by 2050.
Xiaodong's most famous living scientist is Lin Yuhong who alongside Senrian scientist Katou Makoto in Tuthina has made groundbreaking research in cancer treatment.
Services
The service sector in Xiaodong - which includes banking, finance and tourism - is the fastest growing economic sector in the country, although industry still takes precedence over it.
Xiaodong since the 1980's has sought to rapidly expand its banking and financial services sector first through privatisations and then deregulation. The major domestic banks in Xiaodong (Shenkong Investment Bank, Xiaodongese Bank of Commerce and Zhongdong Industrial Bank) maintain a policy of encouraging customers to buy stocks via loans, with the banks buying stocks back to stimulate further demand. These three banks also heavily invest in government bonds in return for the guarantee of the government investing in and subsequently paying back for key sectors of the economy that banks provide loans for. This model of banking has come under strain since 2016 when a stock crisis caused the banking sector to be nationalised by the government.
Tourism is an increasingly important industry for Xiaodong, receiving 9.7 million tourists in 2016. The industry has developed since the liberalisation of visa controls in the 1960's, with historical Xiaodongese sites and its natural geography being some of the main reasons tourists are attracted to Xiaodong. The majority of tourists in Xiaodong come from countries in the Commonwealth of Sovereign States such as Tuthina, Min, Senria and Tinza. Several countries such as Tuthina, Ankoren, Phikam and Koyro have visa-free access to Xiaodong. A large part of Xiaodongese tourism is domestic tourism, as Xiaodong's expansive public transport system allows for relatively trouble free travel within the country. However Xiaodong is recent years has attempted to attract more international tourists by launching tourism campaigns in Borea, Nordania and Velkia. Most tourists in Xiaodong travel to Rongzhuo, Baiqiao and Henjintao.
With the growth of a consumerist culture retail in Xiaodong is growing at a much faster rate. The largest retail outlets in Xiaodong is Shenzhen Malls and the Silk Market. Xiaodong has come under criticism for poor standards in regards to protection of intellectual property with counterfeit goods commonly on sale in the country.
Transportation
Xiaodong has a developed system of transportation via rail, road, marine shipping and air travel. In recent years the government has invested in its infrastructure to modernise it. Currently Xiaodong maintains several highways and motorways which have been expanded as car travel has become more common. Xiaodong's automobile industry has expanded in recent years as car ownership has increased. Whilst Xiaodong does produce cars domestically they are often lambasted for their poor quality, leading to a large amount of automobiles to be imported from Senria. Bicycles whilst there total use has been declining are still widely used in Xiaodong, with 9% of all trips in the country done via bicycle.
Bus servicing in Xiaodong is deregulated to prefectures and municipalities, with some bus servicing being privatised and others owned by local government. As such bus routes in Xiaodong vary from prefecture to prefecture, with some rural routes being unavailable by bus. Bus servicing in large cities however continue to be a widely used and convenient way to travel.
Xiaodong has a total of 58 airports, with 10 of those being international airports. The largest international airport in Xiaodong is the Lu Keqian International Airport, located in Rongzhuo. Other major airports include Baiqiao Nanbian, Xiyong International Shenkong Airport, Sun Yuting Aiport Kuoqing and Henjintao-Tongguan. The main airline in Xiaodong is Xiaodongese State Airways, a nationalised airline that caters for both domestic and international flights. There are however several smaller private airlines that operate in Xiaodong.
Rail transport is well developed in Xiaodong, with major cities and other urban centres including those in neighbouring countries being connected by rail. The majority of rail services provided by the government-owned Xiaodongese State Railways who divide their services into regional rail, inter-city rail, and rapid transit. Some high-speed lines are operated by a compendium of private train companies as are some international lines. Railways are some of the most used transport in Xiaodong with an average 380 million passengers carried in rail transport per year.
Xiaodong maintains several ports, the largest being located in Rongzhuo and Baiqiao. Xiaoferry regularly runs maritime ferries from Baiqiao to Sakata in Senria.
Demographics
The last Xiaodongese census in 2013 recorded 136,563,356 people living in Xiaodong, with the population estimated to be 138,360,000 in 2018. Around 68% of Xiaodongese people live in urban areas, with the largest cities being Rongzhuo with over 12 million people and Baiqiao with 9 million people. 29.18% of the population is between the ages of 0-19, 31.48% 20-39, 24.8% 40-59, 12.93% 60-79 and 1.61% over the age of 80.
In 1978 First Minister Sun Yuting announced the government would implement a two-child policy to stem population growth. The policy remained in effect until 1994 when the government announced the aims of the family planning policy was complete. Since then population growth has been at a steady rate as the government has encouraged larger families.
Education
Education in Xiaodong is divided into primary, secondary and tertiary education. Educational facilities are managed by the Ministry of Education who also set the National Curriculum which guarantees nationwide educational topics. Private schools are exempt from the National Curriculum, but must have their own standards approved by the Ministry of Education and Scientific Research.
In 1869 all boys in urban areas were mandated to go into compulsory education, which was extended to girls in urban areas in the 1920's. Following the Corrective Revolution the government implemented a system of universal primary education with literacy rates rising substantially across the country thereafter. All education was controlled by the Ministry of Education and funded through state assets until 1986 when the government allowed private schools to be established. The same year subsidies for tertiary education were removed. As of 2015 literacy rates amongst those over 18 stand at 96.5% with most illiteracy being concentrated in rural area.
Education is compulsory up until the age of 18. Prior to education most children attend kindergartens (which are privately run) which lasts from the years of 3 to 5. At five children are enrolled into primary schools, which they attend for five and a half days. Lessons are divided into 45 minute blocks with most schools starting around 8:45AM and ending at 5:30PM. At a primary level students start by learning Xiaodongese, mathematics, science and physical education. Around the third year history, geography and art are introduced, whilst in the fourth year music and civic studies are taught as well. For the first two years pupils are in classes of mixed ability. They are then streamlined in the third year into different sets based on ability, and are subject to being promoted or relegated to a higher or lower set based on academic performance. Students remain in primary education until the age of 11 where they sit National Standardised Primary Examinations. Students must pass in Xiaodongese, mathematics and science before entering Middle School.
Middle school lasts from the age of 11 to 14. Drama, information technology, design technology, and religious studies are introduced as subjects. Science is also divided into chemistry, biology, and physics whilst students are required to learn another language (with common options being Literary Tuthinan, Koy or Ankoreni). Middle school is structured similarly to primary school, with students being streamlined by the second year and lessons consisting of 45 minute blocks. The end of Middle School sees students take National Standardised Secondary Examinations where students are expected to pass in the 4 core subjects. From the age of 14 to 18 students are enrolled into lower high school where they take the 4 core subjects alongside physical education and information technology as well as two social sciences and either design technology or one of the arts. National Standardised Tertiary Exams are taken at the age of 16 were students must pass the core subjects to enter Upper High school. From there students can either enter vocational schools that specialise in technologies or arts, or standard schools that teach the remaining subjects alongside new ones such as politics, sociology, geology etc. Students are expected to pick four subjects including one core to study over a period of two years before taking National Specialised Examinations in those subjects. From there students are then given the option to enter higher education or the job market.
The Xiaodongese education system has been criticised for the pressure it places on students which have been accused of dehumanising them. It has also been criticised for being highly centralised. As such in recent years the government has passed through several reforms to decentralise decisions to schools and to put less focus of rigorous testing and more on practical application then simply theory, although these reforms have been criticised as being too conservative and simply tinkering around the edges.
Xiaodong's tertiary education sector is state owned but requires students to pay fees. Xiaodongese student tuition fees are lower then they are in commonwealth countries; however the GDP per capita of Xiaodongese citizens is lower, meaning students from poorer backgrounds still face difficulties in entering higher education. Student loans are given by the government. In recent years attaining tertiary educational qualifications has been more imperative to Xiaodongese students leading to universities to become more competitive. This has resulted in a rise in cheating as well as suicide due to pressure to academically succeed.
Xiaodongese students enter university not only if they pass entrance exams but also based on recommendations from previous teachers/employers as well as their past academic performance. Around 69.6% of Xiaodongese citizens under 25 attended university with 63.4% holding a qualification. In recent years the Xiaodongese government has declared its intent to subsidise a portion of student university fees to promote better education. The most sought out university courses in Xiaodong are the engineering and technology courses, which also demand the highest university fees.
Xiaodongese universities have been criticised for poor marking in regards to plagiarism and the selling of "fake degrees", with over 100,000 bachelor degrees, masters and PhD dissertations being proven to be plagiarised in 2008. The Xiaodongese Ministry of Education and Scientific Research stated the situation regarding plagiarised degrees was "simply unforgivable" and has launched an investigation into the matter.
Ethnic groups
Ethnic composition of Xiaodong (2013 census)
Xiaodong is commonly understood as ethnically diverse society with the dominant ethnic group being Xiaodongese. According to the 2013 census 58.4% of citizens were identified as ethnically Xiaodongese, 13.2% Duljunese, 8.8% Tiancinese, 5.3% Gashengi, 4.2% Ba, 3.7% Ho Ne, 1.5% Pala, 0.8% Tinzan and 4.1% of other ethnic groups.
The Xiaodongese people are a Monic people who are unified by their speaking of the Xiaodongese language, being descended from a mix of Monic people's from Senria and Namor. The largest non-Xiaodongese ethnic group are the Duljunese people who mainly reside in Duljun - whilst also a Monic people, the Duljunese people speak a different language, known as Duljunese and traditionally lead nomadic lifestyle. The third largest group is the Tiancinese who are mainly concentrated in East Thianchin alongside the Ho Ne people, whilst the Ba people reside in central Xiaodong speaking the Ba language. The Gashengi people live in the autonomous republic in the south.
Xiaodong prior to the 1940's had a large minority of Senrian people, who were the second largest ethnic group making up over 10% of the population. Senrians however were banished from Xiaodong following several population swaps between Xiaodong and Senria that has been described as "ethnic cleansing". Today the Senrian population is said be under 10,000 people and "fast declining".
Since the Baiqiao Revolution ethnic minorities in Xiaodong have undergone "Xiaodongisation" with the Xiaodongese government promoting a more ethnically homogeneous Xiaodong whilst promoting the rights of the Xiaodongese majority. This has led to ethnic tensions with Tiancinese and Ho Ne people (who traditionally dominated commercial life in Xiaodong) and Duljunese people (who are geographically concentrated in a traditionally autonomous area). Under the Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire the Xiaodongese government undertook policies most historians state constitute an ethnic cleansing with ethnic displacement being carried out in the 1930's and 1940's. The third Xiaodongese-Duljunese War led to both Xiaodongese and Duljunese minority communities in Duljun to undergo what some have described as genocide; since the end of the war ethnic tensions have cooled, although they remain tense.
Healthcare
Health in Xiaodong is provided through either two state-owned insurance companies or private provided overseen by the Ministry of Pubic Safety, headed by Wen Ruihuan. Healthcare insurance is optional with healthcare providers being more expensive the better quality their care. State hospitals are under the direct jurisdiction of the Ministry of Public Safety who also allocate the health budget which also accounts for and partially subsidises private hospitals. The average life expectancy is 69 years - for men it is 67, women 72. State-insurance programs subsidise healthcare on a means-tested basis. Poorer households have up to 50% of their healthcare costs paid by the government whilst households on higher incomes have as little as 6% of their healthcare covered by the government.
Healthcare came under semi-government control in 1966, having previously been primarily disturbed through private insurance schemes or through traditional methods. Since the mid-1960's healthcare had continued to be expanded, although critics maintain that it is underfunded. Standards between urban and rural healthcare have been very pronounced. Rural areas often face a lack of hospitals and consistently have less funds allocated towards them compared to urban centres, which co-currently have higher levels of life expectancy. Within rural areas Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B are common despite recent attempts to lessen their spread. Pollution in the form of poor air quality means that tuberculoses is the most pressing health problem within urban areas. Smoking both of tobacco and opium remains popular in Xiaodong. Whilst the state does offer subsidised insurance programmes for the majority of health problems, it does not so for most eye and dental care.
Language
The official language of Xiaodong is Xiaodongese. In the south of the country the Qiaoguo dialect is spoken, whilst in the north the language speak the Rongzhuo dialect. Various ancient dynasties attempted to assimilate the northern and southern Xiaodongese people's through language policies that removed Koy influences replacing them with purely Xiaodongese ones. The Xiaodongese dialect has more exaggerated tones and characteristic rhotic vowels. In 1938 in an effort to boost literacy rates the Xiaodongese government created fuhao, a romanisation system based on the Latin alphabet. Within East Thianchin, Tianchinese people speak a unique dialect known as East Tianchinese. East Tianchinese whilst having some similarities with Xiaodongese still displays many differences and is sometimes considered to be a different language. It is not romanisated by fuhao but by another romanisation, pe̍h-ōe-jī.
The Duljunese people, who historically ruled large parts of Xiaodong, speak their own language, Duljunese, which has its an unique script and is unrelated to Xiaodongese. Duljunese is spoken mostly in Duljun where most Duljunese people reside.
Largest cities
Template:XiaodongCities The largest cities in Xiaodong tend to be located in coastal regions, particularly in southern Xiaodong where the majority of the population live in cities. The largest city in Xiaodong is the capital Rongzhuo, which is one of the largest cities in the world. Rongzhuo has consistently been the largest city in Xiaodong since the Toki Sougunate. Baiqiao has traditionally been the second largest city, followed by either Shenkong or Kuoqing.
Religion
Reigious affliation of Xiaodong (2013 census)
Xiaodong is one of the most religiously diverse countries in Esquarium. Traditionally Xiaodongese culture has had a spirit of religious pluralism and strongly syncretic, with most Xiaodongese people believing in a range of spiritual and religious beliefs.
Generally the largest spiritual belief is the shamanistic Taojiao. Taojiao is a complex series of beliefs that put forward a polytheistic, animist view of the world wherein gods in the heavens are the spirits of ancestors who have surpassed reincarnation, and that to reach heaven one must lead a dutiful life, with an emphasis on ancestor worship. Taojiao is heavily based on Xiaodongese mythology and has over time adopted neo-Confucianism as a core tenant of its belief system. Taojiao became more codified under the Heavanly Empire but is a relatively heterogeneous series of beliefs. According to the last Xiaodongese census in 2013, 35.9% of Xiaodongese follow Taojiao although due to its syncretic nation the amount of people who participate in Taojiao rituals is likely to be much higher.
The second largest religion in Xiaodong is Khaturvism, with 28.3% of Xiaodongese recorded as following the faith. Khaturvism came to Xiaodong during the 1200's and has since retained a substantial presence in western Xiaodong, especially on the Min-Xiaodongese border. The most prominent form of Khaturvism practiced in Xiaodong is Nikayambulan which was in 1563 delcared alongside Confucianism and Taojiao as one of the "three thoughts of harmony". The second most practiced form of Khaturvism is Nikayanghuta which is followed by 5.6%, predominately amongst Tiancinese people.
Salvationist Sects are the third largest religion in Xiaodong with 15.3% of the population adhering to them. Salvationist sects always have been prominent in Xiaodong but their influence has fluctuated, reaching their peak with the 1860 Re Orchid Rebellion when the Red Orchid sect took over large swathes of the country. Since the 1980's salvationist sects have risen in popularity again.
Ba folk religion has traditionally been prominent amongst the Ba people with 3.2% of the population professig belief in it. 4.5% of the population define themselves as having no religious beliefs and 2.2% follow Kamism.
The majority of the Duljunese population follow Duljunese Shamanism, which is 9.1% of the overall population.
Culture
Xiaodongese culture has undergone substantial changes throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries but has mostly maintained thousand-year old cultural practices. Xiaodongese culture is fairly conservative with traditional Taojiao ideals of hierarchy, harmony, family, collectivism and respect to elders being mostly unchanged despite attempts to modernise them in recent years. Whilst industrialisation saw aspects of Xiaodongese culture (such as feudalism) seriously undermined, other aspects have remained dominant. Since the rise of consumerism and the growth of civil society of the 1990's Xiaodongese culture and society have started to more seriously examine the socially conservative aspects of Xiaodongese culture, in particular its social Darwinism.
Traditionally calligraphy, poetry, literature, painting and Xiaodongese opera have been the most respected parts of Xiaodongese culture. The abolition of cultural controls, growth of consumerism and foreign influences has meant that in recent years Xiadong's music, television and film industries have expanded rapidly overtaking traditional cultural bastions as the main indicators of Xiaodongese popular culture.
Animation
Modern animation was brought to Xiaodong in 1907 when a short cartoon by Luziycan animator Tomas Visnovsky was shown in Xiaodongese cinemas, with the first Xiaodongese animated short being made in 1923 by Xiaodongese filmaker Deng Zixiang. Early Xiaodongese animation was under strict censorship and used as propaganda in the Senrian-Xiaodongese War. It was not until 1947 with the creation of the animated film, The Jade Kingdom, did Xiaodong get its first feature length animate film. Early Xiaodongese animation was very much based on western styles fused with Xiaodongese traditional artistic elements, especially in the realm of character design.
The 1964 animated film The Girl and her deer (女孩和她的鹿; Nǚhái hé tā de lù) was considered to be influential in the development of Xiaodongese animation; it's animation style departed from western norms, emphasising water colours and the quality of animation rather than movements, and drew much more heavily on traditional Xiaodongese art and was for the time critically acclaimed. Many animated films drew upon the The Girl and Her Deer during the 1960's-1970's and it is for that reason that those decades have sometimes been considered the "golden era of Xiaodongese animation" - as Xiaodongese animation drew upon classical Xiaodongese literature and more abstract, creative settings it was able to more easily escape the censorship rules imposed on other areas of Xiaodongese art in the 1970's. Xiaodngese animation was translated into Luziycan and Pavon amongst others.
Architecture
Architecture in Xiaodong is inspired primarily by that in Tuthina, Senria and Koyro and up until the late 19th century remained largely unchanged for centuries. Traditional Xiaodongese architecture emphasises bilateral symmetry, horizontal emphasis and layouts rooted in Xiaodongese superstition with buildings being made out of brick and stone within a wooden framework. For ventilation enclosed courtyards, pavilions and "sky wells" are common in ancient Xiaodongese architecture.
Commoner architecture (i.e non imperial) traditionally is built in simple styles and low rung, with the height of a building traditionally denoting its inhabitants closeness to the heavens and thus their social rank. Imperial architecture in Xiaodong is distinguished by its use of blue roof tiles, again signifying the heavens as well as being the colour of the Emperor. Guardian lions are an integral part of Xiaodongese imperial architecture.
Starting in the 1870's Xiaodong began to embrace western architectural styles, predominantly those of a neo-classical style (such as the Rongzhuo opera house) although traditional styles continued to be built. Following the Corrective Revolution and during the 1940's art deco styles in Xiaodongese architecture - especially in Baiqiao and Kuoqing - became much more prevalent. Art deco came under heavy criticism from conservatives as traditional styles fell out of fashion, but continued to be built due to a liberalised construction market.
Housing concerns during the 1950's led the government to slash funding for art deco and promote cheaper, functional styles instead most prominently brutalist architecture. Although opposed by many the relatively cheap nature of brutalist architecture meant it continued to be widely built in metropolitan centres well into the early 2000's, when neo-futurism became more prominent with reinforced concrete being phased out in favour of steel and glass.
Art
Xiaodongese art has generally been consistent in style and tone from the Tao dynasty to the present day, having assimilated foreign techniques and concepts into traditional styles. Xiaodongese art is usually used to describe Xiaodongese paintings, pottery, and sculpture. Modern art is greatly frowned upon in Xiaodong, with classical Xiaodongese art still being overwhelmingly dominant in Xiaodong.
Xiaodongese painting is usually done on paper and silk, which is often mounted either on hanging or hand scrolls. Traditionally rich households had paintings done on folding screens. Xiaodongese paintings are always drawn and coloured with brushes with styles often either being fine-brush with colour (工彩) or heavy brush (厚刷). Xiaodong's paintings are a wide array of nature, people and landscapes with the latter being the most highly sought by both domestic and foreign collectors. The mid 1200-1500's is considered to be the golden age of Xiaodongese art. Traditionally Xiaodongese paintings are drawn by a mixture of professional artists and their apprentices, although this practice has declined as art as become more commercialised.
Xiaodong also has a long history of pottery making, with porcelain being the main martial used in Xiaodong. Colbert is used mainly to produce blue flower (青花) pottery which was traditionally Xiaodongese largest cultural exports, having been mass produced since the mid-1500's. Blue flower pottery is believed to have been developed prior to the Tao dynasty, originating along the Taixin river. In the early 20th century intricate pottery fell out of favour for mass produced variants, but noticed a revival in the mid-1970's.
Early sculpture are mainly made from bronze and represent primarily human figures. During the Tao dynasty sculptures became larger usually made of stone and represented a wide array of subjects mainly for religious purposes - large sculptures were built at temples whilst smaller idols were for personal worship at home. Following the civil war sculptures continued to be used to deify figures whether they be religious or political, with metals other then bronze and gold being used for the first time. Democratisation and the lifting of cultural controls has still resulted in most sculptures to be done in orthodox styles with abstract sculptures being a rarity.
Cuisine

Xiaodong's food is primarily based around rice, vegetables and meats and is traditionally cooked so it possess a xianwei (鲜味) taste. Xiaodongese short grained rice is often steam-cooked and served with a variety of seafood alongside broth or soup. In most Xiaodongese dishes red yeast rice (红麴) is used to ensure a sweet taste and a reddish hue unique to Xiaodongese foods. Due to the countries coastal location, Xiaodongese dishes often also use fish-related ingredients and flavourings such as fish sauce and shrimp paste. Shark fins are also extensively used in Xiaodongese cuisine most notably in its shark fin soup, although recently there has been concerns that overfishing is resulting in a rapidly declining shark population. Xiaodongese food is usually eaten with chopsticks and spoons.
Xiaodongese cuisine can be divided into two groups. Furong (付容)cuisine from the northwest of Xiaodong uses sweet and spicy flavours with steaming and stir frying being commonly used with beef, duck, pork and slow-cooked soups being used more with less emphasis of sea food. In contrast Zhujian (住建)cuisine more widely eaten in the southeast mixes sweet and sour tastes and places much greater importance on seafood, fermented fish sauce and red yeast rice. Southern Xiaodong is also known internationally for dog meat. Immigration from Xiaodong to other parts of the world has resulted in Xiaodongese cuisine to be more widely eaten on an international scale.
Family and marriage
Xiaodongese views on family are heavily informed by the concept of filial piety. Filial piety is the term used to describe strains in Xiaodongese philosophy that emphasise the relationship between children and their parents with emphasis on how children should be respectful an obedient to children. Traditional Xiaodongese families are heavily patriarchal with the oldest male always being the head of the family and family inheritance (prior to 1940) being restricted to men. Prior to the 1970's due to demographic and economic strains it was traditional for three or four generations to live together in Xiaodong - however family planning in the 1970's led to a promotion of nuclear families.
Traditionally Xiaodongese marriages were complex affairs. A marriage would be arranged between two families by a matchmaker, with families expected to pay either a dowry or bride price (with the family of a higher rank paying less). Subsequently the spouse from the family of a higher rank would be expected to engage in polygyny or polyandry with the siblings of the lower ranking spouse, although men regardless of social rank were always allowed to keep concubines. Prior to marriage reform child marriage was not uncommon. Marriage reform in 1937 and 1952 saw the banning of concubinage, forced marriage and child marriage alongside severe restrictions on arranged marriages, dowries and bride prices. Economic pressures have also led to a decline in polygamous marriages, although such marriages are still existence in some parts of Xiaodong.
Film

Cinema was introduced to Xiaodong in 1902, with the first Xiaodongese film being "The Travels of Chen Huqiang" which was made in 1903. Early Xiaodongese cinema was heavily influenced and inspired by Xiaodongese opera which was then the dominant form of entertainment in Xiaodong. Film making in Xiaodong at the time was centred in Baiqiao and Kuoqing.
The first "talkies" in Xiaodong was made in 1928 during the Senrian-Xiaodongese War, and were primarily war and propaganda films intended to rally support for the war effort. The most famous was Leaving Home for Kitasuu which pioneered cinematic technique in Xiaodong in the realms of editing, lighting and sound design. Xiaodongese cinema suffered a decline in the early 1930's due to the after effects of the Senrian-Xiaodongese War and Corrective Revolution, but by the late 1930's and early 1940's with a relaxing of political repression Xiaodongese cinema entered its "Golden Age" of . Led by directors such as the Kang brothers and Guo Wenzhan the Golden Age saw films move beyond propaganda and embrace more realism and innovative cinematic techniques, with the most acclaimed films being Solitary Spring, Death on the East Sea River and Ms Jiang's Secret. During the 1950's the largest film studio - Jinhua Films - grew to have a virtual monopoly over the market leading to filmmakers to lose much of the innovation of the 1940's.
The late 1960's and early 1970's however saw the rise of low budget martial arts films explode in popularity, with the films of Li Changzhen (such as Legend of the Dragon) being especially successful. Between 1967-1975 Xiaodongese cinema entered a "second golden age" as martial arts films and romantic dramas became very popular, with independent studios driving both trends. The 1960's and 1970's golden age saw a tendenacy towards action and melodrama. The imposition of strict censorship in 1975 ended the second golden age, as martial arts films in particular coming under fire from authorities. The late 1970's to early 1980's saw Xiaodongese cinema churn out regular films but ones that were commonly seen as creatively stagnant and corporate in nature.
The social and economic changes of the 1980's led to another resurgence in Xiaodongese cinema, but unlike the melodrama of earlier years there was more emphasis towards neo-realism. Nevertheless, it was not until the release of Golden Rain in 2006 - a romantic drama film - that Xiaodongese cinema has seen a renaissance in recent years. Modern Xiaodongese cinema is often split between dramas and romances and action films, with a focus on realist acting and an increasing prevalence of both independent cinema and higher budget productions.
Holidays
| Holiday | Xiaodongese Fuhao |
Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Festival | 春节 Chūnjié |
Turn of the traditional lunisolar Xiaodongese calender | Celebrates the first day of every year in the Xiaodongese calender. |
| Lantern Festival | 元宵节 Yuánxiāojié |
15th day of the 1st month in the Xiaodongese calender | Celebrates the last day of the Spring Festival celebrations. |
| Restoration Day | 再生节 Zàishēngjié |
14th February | Celebrates the Baiqiao Revolution and the Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire. |
| Qingming Festival | 清明节 Qīngmíngjié |
15th day from the Spring Equinox | Visit, clean and honour ancestors. |
| Duanwu Festival | 端午节 Duānwǔjié |
5th day of the 5th lunar month | Commemorates fealty and filial piety, traditionally celebrated with dragon boat racing. |
| Ghost Festival | 盂兰盆 Yúlánpén |
5th night of the 7th lunar month | Make offerings to the dead and ancestors to ward them off from troubling the living. |
| National Day | 国庆节 Guóqìngjié |
20th-22th September | Celebrates the Great Revolution to Correct Xiaodong and the founding of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong. |
| Mid-Autumn Festival | 中秋节 Zhōngqiūjié |
15th day of the 8th lunar month | Celebrates the end of the autumn harvest. |
Literature
Xiaodongese literary tradition stretches back to the development of the Xiaodongese script around 2000BCE. The classical Xiaodongese canon is rooted in military strategy, geography, astrology and mythology. The Nine Texts (九个文本) - as series of philosophical, historical and literary texts integral to Taojiao - continue to be taught in the state-sponsored examinations for civil service. Other seminal Xiaodongese classics include Sijiu (a collection of Xiaodongese folklore) Journey to the Gods and The Blue Chamber.
Music
Xiaodong's music is diverse, having a mix of traditional and more modern influences. Traditionally, nanyin (南音) music has been dominant in Xiaodong, having light foreign influences due to Xiaodong's coastal location and was mainly preformed by amateur quguan groups who were often based around local temples. There are two main types of nanyin music - zhi (指) and qu (曲). Zhi is exclusively instrumental, being performed using gongche notation and can be up to thirty minutes in length (or divided into five pieces, or dei) whereas qu uses vocals and is far less conservative then zhi, having a much wider range of pieces. Nanyin is performed with a pipa, sanxian, xiao and erxian with singers using wooden flappers. In a "ten sounds" performance a suona and dizi is used.
Following the Baiqiao Revolution Xiaodongese music began to resemble that of music in Nordaniaand Conitia, with use of orchestrates especially wind and string instruments, which were combined with traditional Xiaodongese instruments. Xiaodongese musicians would travel to western countries such as Luziyca, Ainin, Vjaarland and Pavonistade,
bringing over western music and instruments which coincided with a general period of westernisation in Xiaodongese culture. Symphony orchestras became popular in the 1880's-1890's amongst the elite in Xiaodong. During the 1910's and early 1920's more modern forms of music became popular in Xiaodong, with Rongzhuo being known within the country for its vibrant jazz scene. Many musicians during the 1910's incorporated jazz elements in traditional music. When Xiaodongese society became more militarised during the 1920-30's brass instruments were used more as music reflected nationalist themes whilst jazz and popular music were shut down by the government.
Following the Corrective Revolution, the government promoted traditional nanyin music, but during the 1940's lifted restrictions on jazz and popular music, which underwent a revival in the 1950's-1960's. During the 1970's, music began to be put under stricter censorship with two forms of music being dominant - political music, which was promoted by the government and a modern form of Xiaodongese folk music. This "new folk" music often fused traditional Xiaodongese folk song melodies with a mix of traditional Xiaodongese and western instrumentation, and often took the form of ballads. The 1960's-1970's saw the introduction of electric guitars and electronic organs/synthesisers to be used in Xiadongese music. During the mid 1970's-1980's, Liu Zhou was recognised as the most pre-eminent Xiaodongese pop singer and became popular across the Monic world.
During the 1980's rock music became popular amongst the youth and was widely played and distributed on the black market, despite being frowned upon by the authorities. Nevertheless in 1984 the ban on rock music was successfully repealed and rock music in Xiaodong became extremely popular during the 1990's, especially heavy metal and after 1998 thrash metal. Punk music was also popular in the 1990's, with the first punk bands making a breakout in 1995.
Since the late 1990's the dominant popular music in Xiaodong has been "Xiao-pop", often similar to its western counterparts in its style, with its growth helped by its use in television, films and other elements of popular culture. Since the 1980's, "pop idols" have gained fame and popularity in Xiaodong.
Media
Xiaodong has several media sources with there being a semi-free press. The main daily newspaper in Xiaodong is the Xiaodong Observer (晓东观察报; Xiǎodōng guānchá bào) which is part of the state-owned Xiaodongese Broadcasting Network, and is considered to be pro-government and conservative. The other newspapers include the East Sea Daily (东海日報; Dōng Hǎi Rìbào), a privately owned paper that is more sensationalist and tabloid in nature than the Xiaodong Observer being known for its more populist and heavily nationalist editorials, the Xiaodong Evening Post (晓东晚報; Xiǎodōng Wǎnbào), a liberal centre-left paper that is anti-government and has a high circulation especially in southern Xiaodong, The Sun (太阳报; Tàiyáng Bào) an economic liberal paper focused on economic and business news and the Global Review (全球考察; Quánqiú Kǎochá) which was previously a pro-opposition paper but since 2014 has been owned by the same company that owns East Sea Daily, now re-orientated to be more right-wing populist and nationalist albeit more upmarket than the East Sea Daily.
Society
- Main page - Hokka system
Traditionally Xiaodongese society is highly stratified under the Hokka ( 種姓) system. The Hokka system, which forms an essential part of Taojiao teachings, stipulates that Xiaodongese society is roughly divided into several social classes, commonly seen as large families. At the top traditionally sit the shiren(士人; scholars and knights) and the guizu (贵族; nobles and artisans), followed by nongmin (农民; farm people) and finally shāng (商; understood to be traders). Prior to the 1960's a fifth class, didengren (低等人; roughly translates to subhuman) existed and was often used as a racial classification as well as a social one. Each social class saw themselves as an extended family, to the extent where family names are restricted to the social class one occupies. Each social class is expected to take a collectivist mindset that mandates that they help each other, whilst lower social classes are expected to support their superiors to retain a stable society. Within each social class gender parity is emphasised, although de facto sexism has always existed in Xiaodong.
The Hokka system was seriously undermined by Toki rule, which saw Senrians become a distinct dominant minority. Despite the industrialisation that took place after the Baiqiao Revolution, with which saw the rise of a new social class of industrial workers often straddling between the shāng and nongmin classes, the Baiqiao Revolution nevertheless saw the system greatly strengthened as the Hokka system was reinterpreted as integral to Xiaodongese culture. During the 1920-30's the system became more firmly entrenched as well as leading to discrimination to dramatically increase towards the didengren class in particular. Following the Corrective Revolution the Hokka system was formally abolished, with the influence of the guizu class declining in favour of the Tuhao (土豪; new money) class, which consists of a mix of shāng and shiren. Nevertheless the divides within Xiaodongese society and influence of the Hokka system remain albeit in a modified form with the traditional classes breaking down in favour of the Xin Hokka system which consists of the Tuhao, the zhongjian ren (中间人; middle people) and the buyi (布衣; commoners).
Sports
Xiaodong has maintained strong sporting traditions since the advent of dragon boat racing around 2,500 years ago. Currently the most popular sports in Xiaodong are martial arts followed by football and basketball. Badminton, ping pong, and swimming have also recently gained popularity in Xiaodong. Traditionally archery, horse racing, cuju and wrestling were the most practiced sports in Xiaodong. In modern Xiaodong, most citizens practice a form of tai chi or qigong.
Xiaodong has long been associated with martial arts, often grouped under the umbrella term Quanfa (拳法). Xiaodongese martial arts are divided into various sects (派; pài) with martial arts often being rooted and inspired by Xiaodongese philosophy. Xiaodongese martial arts generally place emphasis on acrobatics and kicking (such as high kick and flying kicks). Xiaodongese martial arts are encouraged today by all schools with thousands of training facilities and classes around the country.
Cuju was traditionally a popular sport in Xiaodong being the first mass sport in the country around the late Xiang dynasty. It continued to be practiced widely until the mid 1940's when football started to take its place, thanks partly to the advocacy the National Federation for Football (formed in 1918) gave to the sport. Currently football is by far the most popular sport in Xiaodong being divided into five leagues - the Premier league, the first league,
the second league, the third league, and the local leagues. The Premier league consists of the 16 best football clubs in Xiaodong, whilst the first league deals with the 25 next best teams. The second league also has 25 teams as does the third league. Teams advance to higher leagues if they are among the top four in the league at the end of the football season, whilst those at the bottom 4 places in the league are relegated to a lower league.
Other popular sports in Xiaodong include basketball which was introduced to Xiaodong in the 1960's and is managed by the National Basketball League, ping pong which is the largest amateur sport with Xiaodong producing famous ping pong players such as Li Jiangguo and badminton. The oldest sport in Xiaodong, dragon boat racing, is also still practiced with many watching the annual duanwu festival.
Television
Television is popular in Xiaodong, with the main three television stations - the state-owned Xiaodongese Broadcasting Network (XBN), the free to view Rongzhuo Broadcasting Corporation and the largest cable TV station, TV Xiaodong. Xiaodong has a wide range of television programming including children's television, animation, documentaries, music television, news, sport and movies. Television dramas are extremely popular in Xiaodong, especially those set in historical periods and fantasy romance.
There had been almost no television in Xiaodong prior to 1947 when the first Xuling Television set was created. There were only three television stations - the Central Xiaodong Television 1 (ZDX1), the Central Xiaodong Television 2 (ZDX2) and Xiaodongese Sports (XT). ZDX1 was exclusively broadcast in the Xiaodongese language and aired a broad variety of programming from children television shows, the news and adult dramas whilst the ZXD2 aired similar programming, albeit often programs with lower ratings. XT meanwhile primarily focused on sports programming.
Initially programming was primarily political, mostly taking the form of propaganda films praising the ruling regime - even in the nominally sports centred XT more time was dedicated to political programming. In 1949 the first children's programme - Little Xie Yuanhong - was created, and in 1950 television dramas and comedies were created. Programmes rarely exceeded 20 minutes, and typically television shows lasted for 12 episodes a series. All shows were under strict censorship laws, and so often avoided certain subjects such as politics (or only showed the positive aspects of Xiaodongese history) or religion. Television remained formulaic with most shows being contemporary in nature until the early 1960's, when the first science fiction and historical programmes started to be broadcast alongside documentaries. The XT channel was popular amongst Xiaodongese being less politicised and respected as a reliable and (comparably) uncensored channel for sporting interests. There was an upsurge in the popularity of television in the 1960's and 1970's as programming became more diverse. Initially people appearing on television were also under strict rules. Men were prohibited from wearing beards, and there were a limited number of clothes and haircuts non-political figures could wear on television. Make-up was strictly prohibited. These controls were relaxed during the 1980's, when the first colour televisions were introduced.
in 1985 the ZDX2 and XT were privatised and the state began to allow private networks to be set up. ZDX1 was renamed as the Xiaodongese Broadcasting Network (XBN) as private TV became popular. During the 1970's Xiaodongese drama shows began to become the dominant genre and during the 1990's there was a notable increase in production values and script quality.
Theatre and Dance

Traditional Xiaodongese opera has developed over centuries to combine music, vocal performance, mime, dance, and acrobatics within it. The earliest Xiaodongese theatrical performances during the early Xiang dynasty were based on "mask performance" (面具表演; miànjù biǎoyǎn) which were silent mime performances that were played in the royal court. Travelling performers would often act plays in villages that were based in folklore with dialogue spoken in verse, but these shows were for a long time seen as vulgar.
During the mid-Xiang dynasty zaju (雜劇) performances became popular, with the roles within performances started to be separated between the sheng (生; male characters) dan (旦; female characters) jing (净; painted face male often but not always in a supporting role) and chou (丑; male clown and always a minor or supporting character). By the Tao dynasty elements of acrobatics and dialogue began to be common in Xiaodongese theatre. Increasingly musical elements and singing was added to performances with the main instruments being used being jinghu's and yueqin's.
Under the Toki Sougunate elements of kabuki influenced Xiaodongese theatre, in particular a use of makeup over traditional masks and performances that often lasted full days. The Heavenly Xiaodongese Empire saw the height of Xiaodongese opera which began to exhibit plays based in history, mythology and contemporary life. Xiaodongese opera continued to be popular until the 1960's when the popularity of films started to surpass it. Since then there has been moves to change Xiaodongese opera (such as importing western theatrical techniques, shortening the length of plays and putting greater focus on contemporary plays) to mixed success. Template:XiaodongTopics