Vuswistan: Difference between revisions
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
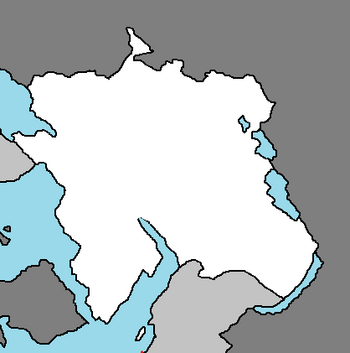
Vuswistan is located in Central [[Nortua]], on the coast of the [[Sotoa Sea]]. It borders [[Utobania]] and [[New Anea]] to the east, [[North Sotoa]] to the south, [[Syraranto]] via a maritime border to the west, and [[North Icadania]] by land to the west. | |||
The territory covers 156,594 square kilometres (121,851 square miles), consisting of 156,414 square kilometres (121,782 square miles) of land and 328 square kilometres (249 square miles) of water. Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Vinaric Alps with the highest point of the Vinara peak at 1,831 metres (6,007 feet) near the border with Utobania to the shore of the Sotoa Sea which makes up its entire southwest border. Insular Vuswistan consists of over a thousand islands and islets varying in size, 48 of which are permanently inhabited. The largest islands are Cres and Krk, each of them having an area of around 405 square kilometres (156 square miles). | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
Revision as of 21:27, 5 November 2020
Federation of Vuswistan | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
 | |
| Capital | Tyrnatini |
| Official languages | Utobanian |
| Government | |
| Panagiotakis Nicolalis | |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 29,743,000 |
| Currency | Resmian |
| Date format | mm-dd-yyyy |
The Federation of Vuswistan, most commonly known as Vuswistan, is a nation in the Coalition of Crown Albatross located on the continent of Nortua, bordered by North Sotoa, North Icadania, New Anea, and Utobania, with a small maritime border with Syraranto.
Vuswistan is a member state of several international organizations such as the Coalition of Crown Albatross and the Sotoan Basin Union.
History
Prehistory
The area known as Vuswistan today was inhabited throughout the prehistoric period. Fossils of Neanderthals dating to the middle Palaeolithic period have been unearthed in northern Vuswistan, with the most famous and the best presented site in V'rapina. Remnants of several Neolithic and Chalcolithic cultures were found in all regions of the country. The largest proportion of the sites is in the river valleys of northern Vuswistan, and the most significant cultures whose presence was discovered include Baden, Starčevo, and Vučedol cultures. The Iron Age left traces of the early Vustatt culture and the Vetène culture.
Antiquity
Much later, the region was settled by Utobanians and Sotoans, while the first Syrarantoan colonies were established on the hills of Kvar, Vorčula, and Vis. In 9 AD the territory of today's Vuswistan became part of the Utobanian Empire. Emperor Viocletian was native to the region, and he had a large palace built in Tyrnatini to which he retired after his abdication in AD 305.
During the 5th century, the last de jure Emperor Julius Upos ruled his small realm from the palace after fleeing Utobania to go into exile in 475. The period ends with Sotoan and Vuswistanian invasions in the first half of the 7th century and the destruction of almost all Utobanian towns. Utobanian survivors retreated to more favourable sites on the coast, islands and mountains. The city of Tyrnatini was founded by such survivors from Epidaurum.
Middle Ages
Constantio Empire
Modern Day
Geography
Vuswistan is located in Central Nortua, on the coast of the Sotoa Sea. It borders Utobania and New Anea to the east, North Sotoa to the south, Syraranto via a maritime border to the west, and North Icadania by land to the west.
The territory covers 156,594 square kilometres (121,851 square miles), consisting of 156,414 square kilometres (121,782 square miles) of land and 328 square kilometres (249 square miles) of water. Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Vinaric Alps with the highest point of the Vinara peak at 1,831 metres (6,007 feet) near the border with Utobania to the shore of the Sotoa Sea which makes up its entire southwest border. Insular Vuswistan consists of over a thousand islands and islets varying in size, 48 of which are permanently inhabited. The largest islands are Cres and Krk, each of them having an area of around 405 square kilometres (156 square miles).


