Bogmian language: Difference between revisions
m (→Alphabet) |
m (Zhousheng (Fjana) moved page Pustogorian Bogmian language to Bogmian language: Reworking of lore) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WIP}} | {{Region icon Anteria}}{{WIP}} | ||
{{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
| name = Bogmian<!-- language--> | | name = Bogmian<!-- language--> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| region = [[Kento-Poylash languages|Slavic Belt]] in [[Thuadia]] | | region = [[Kento-Poylash languages|Slavic Belt]] in [[Thuadia]] | ||
| ethnicity = Pustogorian Bogmians | | ethnicity = Pustogorian Bogmians | ||
| speakers = [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First_language L1]: 75,820 | | extinct = 1912 – 1940 in [[Bogmia]]<ref>Bogmian language in [[Bogmia]] developed into the [[Zhoushi language]] via the merger with Slavic Zhengian language, although some dialects are still linguistically close to the pure Bogmian spoken in the Tlhenget Mountain Range</ref> | ||
---- | |||
Still alive in Tlhenget: | |||
| speakers = | |||
| speakers2 = [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First_language L1]: 75,820<br>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_language L2]: 12,500<br>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Foreign_language FL]: 45,000 | |||
| familycolor = Indo-European | | familycolor = Indo-European | ||
| fam1 = [[Thuado-Thrismaran languages|Thuado-Thrismaran]] | | fam1 = [[Thuado-Thrismaran languages|Thuado-Thrismaran]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 51: | ||
| minority = {{Tree list}} | | minority = {{Tree list}} | ||
*{{flag|Qazhshava}} | *{{flag|Qazhshava}} | ||
** | **Northern Territory | ||
{{Tree list/end}} | {{Tree list/end}} | ||
| agency = | | agency = | ||
| Line 95: | Line 98: | ||
| notice = IPA | | notice = IPA | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Pustogorian Bogmian language''' (Bogmian: ''Pustogorská Bogmijština''), or simply referred to as '''Bogmian language''' (Bogmian: ''Bogmijština''), is a language spoken in the | The '''Pustogorian Bogmian language''' (Bogmian: ''Pustogorská Bogmijština''), or simply referred to as '''Bogmian language''' (Bogmian: ''Bogmijština''), or by its exile name referred to as the '''Pustogorian language''' or '''Pustogorian dialect''' (Bogmian: ''Pustogorština''), is a language spoken in the Pusté Gory ([[Haydag language|Haydag]]: ''Тлъенгетав Гаў'', [[wikipedia:English language|Common]]: ''Barren Mountains'' or ''Tlhenget Mountains'') area of the Northern Territory of [[Qazhshava]], which developed in a Bogmian community which fled [[Bogmia]] shortly after the [[Empire of Three Kings]] was formed. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{See also|Zhoushi language#History|label1=Zhoushi language history}} | {{See also|Zhoushi language#History|label1=Zhoushi language history}} | ||
The Bogmian language was the slavic language spoken in [[Bogmia]], but after the integration with the Slavic Zhengian, it developed into the present day form of the [[Zhoushi language]]. | The Bogmian language was the slavic language spoken in [[Bogmia]], but after the integration with the Slavic Zhengian, it developed into the present day form of the [[Zhoushi language]], which is still slavic, but with notable inclusion of some Zhengian grammatical aspects, such as [[wikipedia:Clusivity|fourth person denoting clusivity]] or large [[wikipedia:Austroasiatic languages|Prei-Phnom]] influence in phonology and vocabulary, as well as the development of a [[Zhoushi orthography|special alphabet]] lacking diacritics in favor of special characters. | ||
==Alphabet== | ==Alphabet== | ||
Although originally using the [[wikipedia:Coptic alphabet|Protopolyashi script]], Bogmian language in exile later developed an alphabet on its own. In an act of defiance, the Bogmians in exile developed a diacritic alphabet, which is in a strong contrast to the [[Zhoushi orthography#Zhoushi alphabet|Zhoushi grapheme script]]. This alphabet uses four [[wikipedia:Digraph (orthography)|digraphs]] (dj, dz, dž and tj) and three diacritic markers: [[wikipedia:Caron|caron]] for softening (Č, Ě, Ľ, Ň, Ř, Š and Ž), [[wikipedia:Circumflex|circumflex]] for phonetic shifts (Ĥ and Ô) and [[wikipedia:Acute accent|accute]] for [[wikipedia:Vowel length|vowel lenghtening]]) | {{See also|Common Marvinic orthography}} | ||
{| style="font-family:Arial Unicode MS; font-size:1. | Although originally using the [[wikipedia:Coptic alphabet|Protopolyashi script]], Bogmian language in exile later developed an alphabet on its own. In an act of defiance, the Bogmians in exile developed a diacritic alphabet, which is in a strong contrast to the [[Zhoushi orthography#Zhoushi alphabet|Zhoushi grapheme script]]. This alphabet uses four [[wikipedia:Digraph (orthography)|digraphs]] (dj, dz, dž and tj) and three diacritic markers: [[wikipedia:Caron|caron]] for softening (Č, Ě, Ľ, Ň, Ř, Š and Ž), [[wikipedia:Circumflex|circumflex]] for phonetic shifts (Ĥ and Ô) and [[wikipedia:Acute accent|accute]] for [[wikipedia:Vowel length|vowel lenghtening]] (Á, É, Í, Ó, Ú and Ý). | ||
{| style="<!--font-family:Arial Unicode MS;--> font-size:1.5<!--1.3-->em; border-color:black; border-width:1px; border-style:solid; border-collapse:collapse; background-color:#F8F8EF" | |||
| style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |A a | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |A a | ||
| style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |Á á | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |Á á | ||
| Line 198: | Line 202: | ||
|style="background:#FEE7E6"|k͡s ||ɨ ||ɨː ||z ||ʒ || | |style="background:#FEE7E6"|k͡s ||ɨ ||ɨː ||z ||ʒ || | ||
|} | |} | ||
The letter Ĥ was later introduced to distinguish the sound of /ɦ/ from foreign words from the sound /x/. Example of the usage may be the word ''ĥistorie'' (history), which is read as /ɦɪstorijɛ/. | |||
Historically, multiple variants were developed, including a [[wikipedia:Cyrillic script|govoric]] one: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|style="padding:0px"|<div style="width: 100%; height: 25em; overflow: auto;"> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: center; margin: 0 0 0 0" | |||
![[wikipedia:Coptic alphabet|Protopolyash]] !![[wikipedia:Cyrillic script|Govoric]] !![[wikipedia:Latin script|Latin]] !![[wikipedia:International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA Sound]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲁ ⲁ ||А а ||A a ||[[wikipedia:Open front unrounded vowel|a]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲁ ⲁ ||А́ а́ ||Á á ||[[wikipedia:Open front unrounded vowel|aː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲃ ⲃ ||Б б ||B b ||[[wikipedia:Voiced bilabial plosive|b]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲅ ⲅ ||Г г ||G g ||[[wikipedia:Voiced velar plosive|ɡ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲇ ⲇ ||Д д ||D d ||[[wikipedia:Voiced dental and alveolar plosives|d]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲆⲒ ⲇⲓ ||Дь дь ||Dj dj ||[[wikipedia:Voiced palatal plosive|ɟ]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲆⲌ ⲇⲍ ||Ѕ ѕ ||Dz dz ||[[wikipedia:Voiced alveolar affricate|d͡z]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲆϬ ⲇϭ ||Џ џ ||Dž dž ||[[wikipedia:Voiced postalveolar affricate|d͡ʒ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲉ ⲉ ||Е е ||E e ||[[wikipedia:Open-mid front unrounded vowel|ɛ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲉ ⲉ ||Е́ е́ ||É é ||[[wikipedia:Open-mid front unrounded vowel|ɛː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲓⲉ ⲓⲉ ||Ѣ ѣ ||Ě ě ||[[wikipedia:Palatalization (phonetics)|ʲ]][[wikipedia:Close-mid front unrounded vowel|e]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲍ ⲍ ||З з ||Z z ||[[wikipedia:Voiced alveolar fricative|z]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲓ ⲓ ||И и ||I i ||[[wikipedia:Close front unrounded vowel|i]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲓ ⲓ ||И́ и́ ||Í í ||[[wikipedia:Close front unrounded vowel|iː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲓ ⲓ ||Й й ||J j ||[[wikipedia:Voiced palatal approximant|j]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲒⲨ ⲓⲩ ||Ы ы ||Y y ||[[wikipedia:Close central unrounded vowel|ɨ]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲒⲨ ⲓⲩ ||Ы́ ы́ ||Ý ý ||[[wikipedia:Close central unrounded vowel|ɨː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲕ ⲕ ||К к ||K k ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless velar plosive|k]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲗ ⲗ ||Л л ||L l ||[[wikipedia:Voiced dental, alveolar and postalveolar lateral approximants|l]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲖⲒ ⲗⲓ ||Љ љ ||Ľ ľ ||[[wikipedia:Voiced palatal lateral approximant|ʎ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲙ ⲙ ||М м ||M m ||[[wikipedia:Voiced bilabial nasal|m]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲛ ⲛ ||Н н ||N n ||[[wikipedia:Voiced dental, alveolar and postalveolar nasals|n]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲚⲒ ⲛⲓ ||Њ њ ||Ň ň ||[[wikipedia:Voiced palatal nasal|ɲ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲟ ⲟ ||О о ||O o ||[[wikipedia:Open-mid back rounded vowel|ɔ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲟ ⲟ ||О́ о́ ||Ó ó ||[[wikipedia:Open-mid back rounded vowel|ɔː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲟ ⲟ ||Ө ө ||Ô ô ||[[wikipedia:Close back rounded vowel|u]]͡[[wikipedia:Close-mid back rounded vowel|o]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲡ ⲡ ||П п ||P p ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless bilabial plosive|p]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲣ ⲣ ||Р р ||R r ||[[wikipedia:Voiced dental, alveolar and postalveolar trills|r]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲢⲒ ⲣⲓ ||Ҏ ҏ ||Ř ř ||[[wikipedia:Voiced dental, alveolar and postalveolar trills#Voiced alveolar fricative trill|r̝]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲥ ⲥ ||С с ||S s ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless alveolar fricative|s]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲧ ⲧ ||Т т ||T t ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless dental and alveolar plosives|t]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲦⲒ ⲧⲓ ||Ть ть ||Tj tj ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless palatal plosive|c]] | |||
|- | |||
|ⲦⲤ ⲧⲥ ||Ц ц ||C c ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless alveolar affricate|t͡s]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲩ ⲩ ||У у ||U u ||[[wikipedia:Close back rounded vowel|u]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲩ ⲩ ||У́ у́ ||Ú ú ||[[wikipedia:Close back rounded vowel|uː]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲫ ⲫ ||Ф ф ||F f ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless labiodental fricative|f]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲭ ⲭ ||Х х ||H h ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless velar fricative|x]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ⲯ ⲯ ||В в ||V v ||[[wikipedia:Voiced labiodental fricative|v]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ϣ ϣ ||Ш ш ||Š š ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless postalveolar fricative|ʃ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ϩ ϩ ||Ґ ґ ||Ĥ ĥ ||[[wikipedia:Voiced glottal fricative|ɦ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ϫ ϫ ||Ч ч ||Č č ||[[wikipedia:Voiceless postalveolar affricate|t͡ʃ]] | |||
|- | |||
|Ϭ ϭ ||Ж ж ||Ž ž ||[[wikipedia:Voiced postalveolar fricative|ʒ]] | |||
|} | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
==Grammar== | |||
Unlike [[Zhoushi language|Zhoushi]], Pustogorian Bogmian preserved exclusively Slavic base, with little to no Zhengian influence. Example of this may be the lack of [[wikipedia:Clusivity|clusivity distinction]], still preserved [[wikipedia:Vowel length|vowel lenght]] and little to no [[Zhoushi grammar#Nouns|noun gender indifference]] (Only notable word is a loanword "Zombie"). | |||
{{Template:Anteria languages navbox}} | |||
{{Template:Mustelaria Navbox}} | {{Template:Mustelaria Navbox}} | ||
{{Template:Anteria info pages}} | {{Template:Anteria info pages}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:33, 29 April 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Bogmian | |
|---|---|
| Bogmijština | |
 Flag of the former Kingdom of Bogmia | |
| Pronunciation | /boɡmijʃcina/ |
| Region | Slavic Belt in Thuadia |
| Ethnicity | Pustogorian Bogmians |
| Extinct | 1912 – 1940 in Bogmia[1]
Still alive in Tlhenget: L1: 75,820 L2: 12,500 FL: 45,000 |
Thuado-Thrismaran
| |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | BG |
| ISO 639-2 | PBG |
| ISO 639-3 | PBG |
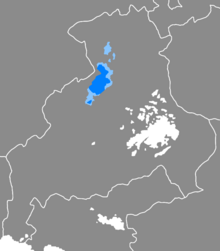 Distribution of the language
Absolute majority >30% of native speakers | |
The Pustogorian Bogmian language (Bogmian: Pustogorská Bogmijština), or simply referred to as Bogmian language (Bogmian: Bogmijština), or by its exile name referred to as the Pustogorian language or Pustogorian dialect (Bogmian: Pustogorština), is a language spoken in the Pusté Gory (Haydag: Тлъенгетав Гаў, Common: Barren Mountains or Tlhenget Mountains) area of the Northern Territory of Qazhshava, which developed in a Bogmian community which fled Bogmia shortly after the Empire of Three Kings was formed.
History
The Bogmian language was the slavic language spoken in Bogmia, but after the integration with the Slavic Zhengian, it developed into the present day form of the Zhoushi language, which is still slavic, but with notable inclusion of some Zhengian grammatical aspects, such as fourth person denoting clusivity or large Prei-Phnom influence in phonology and vocabulary, as well as the development of a special alphabet lacking diacritics in favor of special characters.
Alphabet
Although originally using the Protopolyashi script, Bogmian language in exile later developed an alphabet on its own. In an act of defiance, the Bogmians in exile developed a diacritic alphabet, which is in a strong contrast to the Zhoushi grapheme script. This alphabet uses four digraphs (dj, dz, dž and tj) and three diacritic markers: caron for softening (Č, Ě, Ľ, Ň, Ř, Š and Ž), circumflex for phonetic shifts (Ĥ and Ô) and accute for vowel lenghtening (Á, É, Í, Ó, Ú and Ý).
| A a | Á á | B b | C c | Č č | D d | Dj dj | Dz dz | Dž dž | E e |
| É é | Ě ě | F f | G g | H h | Ĥ ĥ | I i | Í í | J j | K k |
| L l | Ľ ľ | M m | N n | Ň ň | O o | Ó ó | Ô ô | P p | Q q |
| R r | Ř ř | S s | Š š | T t | Tj tj | U u | Ú ú | V v | Ƿ ƿ |
| X x | Y y | Ý ý | Z z | Ž ž |
| Order | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | — | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Majuscule | A | Á | B | C | Č | D | Dj | Dz | Dž | E | É | Ě | F | G | H | Ĥ | I | Í | J | K | L | Ľ | M |
| Minuscule | a | á | b | c | č | d | dj | dz | dž | e | é | ě | f | g | h | ĥ | i | í | j | k | l | ľ | m |
| IPA Sound | a | aː | b | t͡s | t͡ʃ | d | ɟ | d͡z | d͡ʒ | ɛ | ɛː | ʲe | f | g | x | ɦ | i | iː | j | k | l | ʎ | m |
| Order | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | |
| Majuscule | N | Ň | O | Ó | Ô | P | Q | R | Ř | S | Š | T | Tj | U | Ú | V | Ƿ | X | Y | Ý | Z | Ž | |
| Minuscule | n | ň | o | ó | ô | p | q | r | ř | s | š | t | tj | u | ú | v | ƿ | x | y | ý | z | ž | |
| IPA Sound | n | ɲ | ɔ | ɔː | u͡o | p | k͡v | r | r̝ | s | ʃ | t | c | u | uː | v | w | k͡s | ɨ | ɨː | z | ʒ |
The letter Ĥ was later introduced to distinguish the sound of /ɦ/ from foreign words from the sound /x/. Example of the usage may be the word ĥistorie (history), which is read as /ɦɪstorijɛ/.
Historically, multiple variants were developed, including a govoric one:
|
Grammar
Unlike Zhoushi, Pustogorian Bogmian preserved exclusively Slavic base, with little to no Zhengian influence. Example of this may be the lack of clusivity distinction, still preserved vowel lenght and little to no noun gender indifference (Only notable word is a loanword "Zombie").
- ↑ Bogmian language in Bogmia developed into the Zhoushi language via the merger with Slavic Zhengian language, although some dialects are still linguistically close to the pure Bogmian spoken in the Tlhenget Mountain Range