Tofino: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (97 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| native_name_lang = | | native_name_lang = | ||
| settlement_type = Capital City | | settlement_type = Capital City | ||
| image_skyline = | | image_skyline = Tofino Collage Updated 2021.png | ||
| image_alt = | | image_alt = | ||
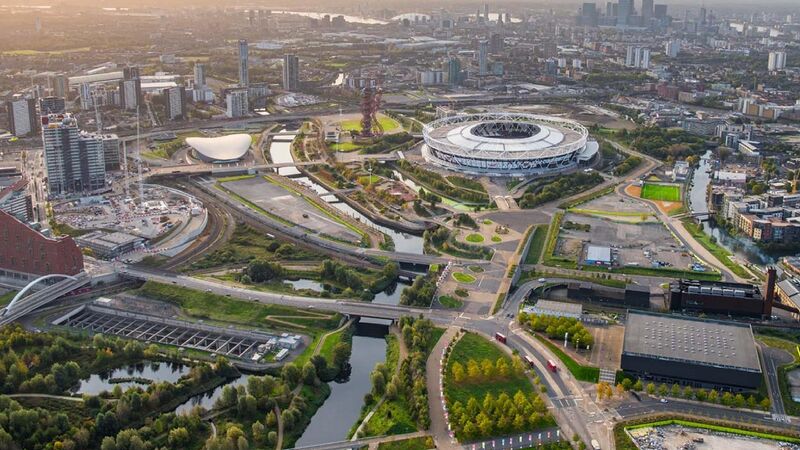
| image_caption = | | image_caption = Clockwise from top left: Downtown skyline with [[Zian Bank Tower]] dominating the skyline; Kingston District and SealBank Arena with the mountains in the background; [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]]; the [[Supreme Court of Zamastan]]; the [[Headquarters of the Coalition of Crown Albatross|Headquarters building]] of the [[Coalition of Crown Albatross]]; ; Downtown Tofino, including the [[New Peace Tower]] | ||
| image_flag = | | image_flag = | ||
| flag_alt = | | flag_alt = | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| nickname = Glass and Pine City | | nickname = Glass and Pine City | ||
| motto = | | motto = | ||
| image_map = | | image_map = TofinoLocationInZamastan.png | ||
| map_alt = | | map_alt = | ||
| map_caption = Tofino's location within Zamastan | | map_caption = Tofino's location within Zamastan | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| government_footnotes = | | government_footnotes = | ||
| leader_party = [[Green Liberal Party (Zamastan)|GLP]] | | leader_party = [[Green Liberal Party (Zamastan)|GLP]] | ||
| leader_title = Mayor | | leader_title = [[Mayor of Tofino|Mayor]] | ||
| leader_name = Bryan Donaldson | | leader_name = [[Sophie Webb-Lancaster]] | ||
| leader_party2 = [[Green Liberal Party (Zamastan)|GLP]] | |||
| leader_title2 = Deputy-Mayor | |||
| leader_name2 = [[Bryan Donaldson]] | |||
| unit_pref = <!-- or UK --> | | unit_pref = <!-- or UK --> | ||
<!-- ALL fields with measurements have automatic unit conversion --> | <!-- ALL fields with measurements have automatic unit conversion --> | ||
| Line 98: | Line 101: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Tofino''' is the capital | '''Tofino''' is the [[wikipedia:Capital city|capital]] and largest city in [[Zamastan]]. With a population of roughly 22.9 million people within its city limits and an additional 11 million in the immediate surrounding cities, it's often ranked as the [[List of cities proper by population (Iearth)|second-largest metropolitan area]] in the [[Coalition of Crown Albatross]] after the [[Yuan]]eze capital of [[Shanghan]], as well as one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities. It is a coastal seaport city, located on the lower side of [[Horseshoe Bay (body of water)|Horseshoe Bay]]. Founded as a [[Skith]]an colony by [[Percy Armillio]] in 1711, the city's indigenous history spans back over 10,000 years as native Zamah St'ani [[Catica First Nations]] (specifically that of the [[Catica First Nations#List of tribes|Kelownan peoples]]) settled along the coastal area of what would become modern-day Tofino, namely in the [[Delk, Tofino|Delk neighborhood]]. With its boundaries marked by the [[Zian River]] to the north, [[Belcaara Inlet]] to the south, and [[Hapson Harbor]] and [[Porrier River]] to the east, Tofino is the largest entity of the [[Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area]], which also includes the city of [[Arinals]]. The metropolitan area has a population of over 51 million people. | ||
Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the [[Tofino | Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the [[Tofino Film Festival]] which hosts films from all over the C.C.A., the [[Tofino Intuition and Ideas Conference|TIIC]] which is a media organization conference dedicated to scientific, cultural, and academic topics. The city is home to multiple sports teams, including the [[Tofino Whitecaps (football team)|Whitecaps]] ([[Zamastan Football League|ZFL]]), [[Tofino United FC|TUFC]] ([[Zamastan Soccer League|ZSL]]), [[Tofino Mariners (basketball team)|Mariners]] ([[Zamastan Basketball Association|ZBA]]), and [[Tofino Seals (baseball team)|Seals]] ([[Zamastan Baseball League|ZBL]]). Tofino is home to the [[Headquarters of the Coalition of Crown Albatross|headquarters building]] of the Coalition of Crown Albatross, meaning that delegates all across [[Iearth|the world]] meet in General Assembly and Security Council matters. The [[Secretary-General of the C.C.A.|CCA General-Secretary]] likewise has their office in Tofino. | ||
The government and military headquarters of Zamastan operate in and around Tofino, with the [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]] (legislative), [[Zian Presidential Mansion]] (executive, [[President of Zamastan|President]]), and the [[Zamastanian Armed Forces]] all located within the city. Tofino is home to many national monuments and museums, primarily situated on or around [[Gaviria Park]]. The city hosts many foreign embassies as well as the headquarters and campuses of many international organizations, trade unions, non-profit, lobbying groups, and professional associations. | The government and military headquarters of Zamastan operate in and around Tofino, with the [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]] (legislative), [[Zian Presidential Mansion]] (executive, [[President of Zamastan|President]]), the [[Supreme Court of Zamastan]] (judicial), and the [[Zamastanian Armed Forces]] all located within the city. Tofino is home to many national monuments and museums, primarily situated on or around [[Gaviria Park]]. The city hosts many foreign embassies as well as the headquarters and campuses of many international organizations, trade unions, non-profit, lobbying groups, and professional associations. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 109: | Line 112: | ||
===Settlement=== | ===Settlement=== | ||
[[ | [[Adula]]n explorers became acquainted with the area of the future Tofino when [[Skith]]an explorer [[Percy Armillio]] explored the coast of present-day Gaviria Park and parts of Coal Inlet in 1711. The Gold Rush of 1739 brought over 25,000 men, mainly from central and eastern Adulan regions such as modern-day [[Quetana]], [[Mulfulira]], and [[Emmiria]], to nearby [[Arinals]] (founded March 29, 1737) on the Zian River, on their way to the Vallium Canyon, bypassing what would become Tofino. | ||
Religious institutions brought by Skithan settlers, such as the catholic faith of the [[Church of | Religious institutions brought by Skithan settlers, such as the catholic faith of the [[Catholic Church of Zamastan]] and the protestant [[Church of Zian]] became prominent in the Tofino area. [[King Almarez II]] sent broad amounts of supplies and additional workers - many of them slaves - to the colony to build up the infrastructure and start expanding further into the continent. | ||
===[[Zamastan War of Independence|Revolution of 1802-1804]]=== | ===[[Zamastan War of Independence|Revolution of 1802-1804]]=== | ||
| Line 129: | Line 132: | ||
Hapson's decision to conduct the assault on the Governor's Mansion in the middle of the night paid off for the NLF, as they were met with relatively light resistance from Governor Pisano's bodyguards, all of whom were armed and told to be ready for war to break out but were not anticipating the first target to be Governor Pisano. Some were half-asleep as Hapson and his men made their way from hallway to hallway, room to room in search of Pisano; the guards were taken out with very light losses to Hapson's forces with one two of his men sustaining moderate but not life-threatening injuries. Once the NLF team reached Pisano's living quarters and broke the door down after hearing movement inside, they encountered an almost trembling Governor who had managed to arm himself after hearing the commotion throughout the residence. He froze for a moment as he eyed the dozen or so men who stood in his doorway, all with their weapons aimed squarely at him. He made a last-ditch effort to raise his weapon and fire but was gunned down and killed before he was able to fire a single round in their direction. | Hapson's decision to conduct the assault on the Governor's Mansion in the middle of the night paid off for the NLF, as they were met with relatively light resistance from Governor Pisano's bodyguards, all of whom were armed and told to be ready for war to break out but were not anticipating the first target to be Governor Pisano. Some were half-asleep as Hapson and his men made their way from hallway to hallway, room to room in search of Pisano; the guards were taken out with very light losses to Hapson's forces with one two of his men sustaining moderate but not life-threatening injuries. Once the NLF team reached Pisano's living quarters and broke the door down after hearing movement inside, they encountered an almost trembling Governor who had managed to arm himself after hearing the commotion throughout the residence. He froze for a moment as he eyed the dozen or so men who stood in his doorway, all with their weapons aimed squarely at him. He made a last-ditch effort to raise his weapon and fire but was gunned down and killed before he was able to fire a single round in their direction. | ||
Hapson and his men had completed their first major objective; removing the only Skith politician in power in Zamastan and giving their cause the momentum that it needed going forward. Three weeks later, the King of Skith ordered a halt on all shipments and settlement travel to and from the island colonies, and the Free State of Zamah St'an was established on October 28th, 1804 with Tomias Hapson as the de-facto President, Avi Taures as the Chief of Trade and Commerce, and an abolitionist named [[Henry Tiller]] as the General of Armed Forces. | Hapson and his men had completed their first major objective; removing the only Skith politician in power in Zamastan and giving their cause the momentum that it needed going forward. Three weeks later, the King of Skith ordered a halt on all shipments and settlement travel to and from the island colonies, and the Free State of Zamah St'an was established on October 28th, 1804 with Tomias Hapson as the de-facto President, Avi Taures as the Chief of Trade and Commerce, and an abolitionist named [[Henry Tiller]] as the General of Armed Forces. | ||
===Growth and | ===Growth and development=== | ||
An improved shipping port of Tofino was incorporated on April 6, 1866, the same year that the first transnational train station was established. The [[Great Tofino Fire]] on June 13, 1866, razed the entire city. The [[Tofino Fire Department]] was established that year and the city quickly rebuilt. Tofino's population grew from a settlement of 40,000 people in 1861 to over 220,000 by the turn of the century and 1,000,000 by 1911. | An improved shipping port of Tofino was incorporated on April 6, 1866, the same year that the first transnational train station was established. The [[Great Tofino Fire]] on June 13, 1866, razed the entire city. The [[Tofino Fire Department]] was established that year and the city quickly rebuilt. Tofino's population grew from a settlement of 40,000 people in 1861 to over 220,000 by the turn of the century and 1,000,000 by 1911. | ||
| Line 142: | Line 143: | ||
===[[1919 Tofino Earthquake]]=== | ===[[1919 Tofino Earthquake]]=== | ||
At 7:12 am on January 12, 1919, a major earthquake struck Tofino and western Zamastan. As buildings collapsed from the shaking, ruptured gas lines ignited fires that spread across the city and burned out of control for several days. With water mains out of service, the [[ | At 7:12 am on January 12, 1919, a major earthquake struck Tofino and western Zamastan. As buildings collapsed from the shaking, ruptured gas lines ignited fires that spread across the city and burned out of control for several days. With water mains out of service, the [[Zamastanian Armed Forces]] attempted to contain the inferno by dynamiting blocks of buildings to create firebreaks. More than three-quarters of the city lay in ruins, including almost all of the downtown core. Contemporary accounts reported that 1,498 people lost their lives, though modern estimates put the number around 50,000. More than half of the city's population of 1,200,000 was left homeless. Refugees settled temporarily in makeshift tent villages in what is now Gaviria Park, on the beaches, and elsewhere. Many fled permanently to [[Tirzah]]. | ||
===Twentieth | ===Twentieth century=== | ||
The dominance of the economy by big business was accompanied by an often militant labor movement. The rise of industrial tensions throughout the district led to Zamastan's first general strike in 1920, at the Folsted coal mines on Tofino. Following a lull in the 1920s, the strike wave peaked in 1935 when unemployed men flooded the city to protest conditions in the relief camps run by the military in remote areas throughout the administrative district. After two tense months of daily and disruptive protesting, the relief camp strikers decided to take their grievances to the federal government and embarked on the On-to-Tofino Trek, but their protest was put down by force. The workers were arrested near [[Jade Harbor]] and interned in work camps for the duration of the decade. | The dominance of the economy by big business was accompanied by an often militant labor movement. The rise of industrial tensions throughout the district led to Zamastan's first general strike in 1920, at the Folsted coal mines on Tofino. Following a lull in the 1920s, the strike wave peaked in 1935 when unemployed men flooded the city to protest conditions in the relief camps run by the military in remote areas throughout the administrative district. After two tense months of daily and disruptive protesting, the relief camp strikers decided to take their grievances to the federal government and embarked on the On-to-Tofino Trek, but their protest was put down by force. The workers were arrested near [[Jade Harbor]] and interned in work camps for the duration of the decade. | ||
Other social movements, such as the first-wave feminist, moral reform, and temperance movements were also instrumental in Tofino's development. [[Elain Ellen Denmer]], a Tofino suffragist and prohibitionist, became the first woman elected to a administrative district's legislature in Zamastan in 1918. Zamastan's first drug law came about following an inquiry conducted by the federal Secretary of Labor and future President [[Tyler Kordia]]. Kordia was sent to investigate damages claims resulting from a riot when the | Other social movements, such as the first-wave feminist, moral reform, and temperance movements were also instrumental in Tofino's development. [[Elain Ellen Denmer]], a Tofino suffragist and prohibitionist, became the first woman elected to a administrative district's legislature in Zamastan in 1918. Zamastan's first drug law came about following an inquiry conducted by the federal Secretary of Labor and future President [[Tyler Kordia]]. Kordia was sent to investigate damages claims resulting from a riot when the Euronia Exclusion League led a rampage through Yuanville and Quetanatown. Two of the claimants were opium manufacturers, and after further investigation, Kordia found that white women were reportedly frequenting opium dens as well as Gladysynthian men. A federal law banning the manufacture, sale, and importation of opium for non-medicinal purposes was soon passed based on these revelations. These riots, and the formation of the Euronia Exclusion League, also act as signs of a growing fear and mistrust towards the Gladysynthians living in Tofino and throughout Zian. These fears were exacerbated by the [[1945 Danaska Conflict|First Danaska War]], leading to the eventual internment or deportation of all Gladysynthian-Zamastanians living in the city and the district. After the war, these men and women were not allowed to return to cities like Tofino causing areas, like the aforementioned Laeraltown, to cease to be ethnically diverse areas as the communities never revived. | ||
Amalgamation with [[Tirzah]] and [[Arinals]] gave the city its final boundaries not long before it became the largest metropolis in the country. As of January 1, 1949, the population of the enlarged Tofino was 3,228,193. | Amalgamation with [[Tirzah]] and [[Arinals]] gave the city its final boundaries not long before it became the largest metropolis in the country. As of January 1, 1949, the population of the enlarged Tofino was 3,228,193. | ||
| Line 153: | Line 154: | ||
On September 29th, 1972, President [[Marvin Gaviria]] was [[Assassination of Marvin Gaviria|assassinated while delivering a speech]] outside on [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|the steps of Congressional Hall]]. | On September 29th, 1972, President [[Marvin Gaviria]] was [[Assassination of Marvin Gaviria|assassinated while delivering a speech]] outside on [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|the steps of Congressional Hall]]. | ||
===21st | ===21st century=== | ||
In the later half of the 2010 decade, Tofino suffered a string of terror attacks, including the [[ | The [[New Peace Tower]], constructed in 2004 to commemorate 200 years of Zamastanian independence, was the tallest structure in the city at the time of completion. As of 2019, it is currently the third tallest structure in the city, surpassed by [[Forrester Tower]] and [[Zian Bank Tower]]. | ||
In the later half of the 2010 decade, saw both prosperity and hardship. While the economy grew significantly due to new investments and a lower crime rate, Tofino suffered a string of terror attacks, including the [[October 2017 Tofino Attacks|2017 attacks]] which claimed over 430 lives, and the city was the epicenter of the [["PoverTea" Protests]] of 2019, which largely centered around discontent of [[President of Zamastan|President]] [[Anya Bishop]]'s administration. On November 2nd, several protestors and police officers were killed during the riots in Tofino, resulting in a [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]] motion to remove Bishop from office. | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
Located on the Tofino Peninsula, Tofino lies between Vallium Inlet to the north and the [[Zian River]] to the | [[File:1823 development plan Tofino.jpg|thumb|right|A 19th century map of planned developments in Tofino]] | ||
Located on the Tofino Peninsula, Tofino lies between Vallium Inlet to the north and the [[Zian River]] to the north. [[Horseshoe Bay (body of water)|Horseshoe Bay]], to the west, leads out to the [[Olympic Ocean]]. The city has an area of 114 km2 (44 sq mi), including both flat and hilly ground. Tofino has one of the largest urban parks in the [[Coalition of Crown Albatross]], [[Gaviria Park]], which covers 404.9 hectares (1,001 acres). The [[Zian Mountains]] dominate the cityscape, and on a clear day, scenic vistas include [[Grouse Mountain]] and the snow-capped volcano Mount Greening to the southeast, Delk Island in Horseshoe Bay to the west and southwest, and Bowen Island to the northwest. | |||
====Ecology==== | ====Ecology==== | ||
The vegetation in the Tofino area was originally temperate rain forest, consisting of conifers with scattered pockets of maple and alder, and large areas of swampland (even in upland areas, due to poor drainage). The conifers were a typical coastal Zian mix of Douglas fir, Western red cedar, and Western Hemlock. The area is thought to have had the largest trees of these species on the Zian Coast. The largest trees in Tofino's old-growth forest were in the Kingston area, where the first logging occurred, and on the southern slopes of Gills Creek and French Bay, especially around Jericho Beach. The forest in Gaviria Park was logged between the 1860s and 1890s, and evidence of old-fashioned logging techniques such as springboard notches can still be seen there. | The vegetation in the Tofino area was originally temperate rain forest, consisting of conifers with scattered pockets of maple and alder, and large areas of swampland (even in upland areas, due to poor drainage). The conifers were a typical coastal Zian mix of Douglas fir, Western red cedar, and Western Hemlock. The area is thought to have had the largest trees of these species on the Zian Coast. The largest trees in Tofino's old-growth forest were in the Kingston area, where the first logging occurred, and on the southern slopes of Gills Creek and French Bay, especially around Jericho Beach. The forest in Gaviria Park was logged between the 1860s and 1890s, and evidence of old-fashioned logging techniques such as springboard notches can still be seen there. | ||
Many plants and trees growing throughout Tofino and the Western Mainland were imported from other parts of the continent and from points across the | Many plants and trees growing throughout Tofino and the Western Mainland were imported from other parts of the continent and from points across the Olympic Ocean. Examples include the monkey puzzle tree, the Maximusian Maple, and various flowering exotics, such as magnolias, azaleas, and rhododendrons. Some species imported from harsher climates in Northern Adula or [[Nortua]] have grown to immense sizes. The native Douglas Maple can also attain a tremendous size. Many of the city's streets are lined with flowering varieties of Yuan cherry trees donated from the government of [[Yuan]]. These flower for several weeks in early spring each year, an occasion celebrated by the Tofino Cherry Blossom Festival. Other streets are lined with flowering chestnut, horse chestnut, and other decorative shade trees. | ||
====Climate==== | ====Climate==== | ||
| Line 169: | Line 173: | ||
Tofino is also one of the wettest Zamastanian cities. However, precipitation varies throughout the metropolitan area. Annual precipitation as measured at [[Tofino International Airport]] on the south side of the city averages 1,189 mm (46.8 in), compared with 1,588 mm (62.5 in) in the downtown area and 2,044 mm (80.5 in) in North Tofino. The daily maximum averages 22 °C (72 °F) in July and August, with highs sometimes reaching 30 °C (86 °F). | Tofino is also one of the wettest Zamastanian cities. However, precipitation varies throughout the metropolitan area. Annual precipitation as measured at [[Tofino International Airport]] on the south side of the city averages 1,189 mm (46.8 in), compared with 1,588 mm (62.5 in) in the downtown area and 2,044 mm (80.5 in) in North Tofino. The daily maximum averages 22 °C (72 °F) in July and August, with highs sometimes reaching 30 °C (86 °F). | ||
==Cityscape | ===Cityscape=== | ||
As of 2011, Tofino is the most densely populated city in Zamastan. Urban planning in Tofino is characterized by high-rise residential and mixed-use development in urban centers, as an alternative to sprawl. As part of the larger Metro Tofino region, it is influenced by the policy direction of livability as illustrated in Metro Tofino's Regional Growth Strategy. | As of 2011, Tofino is the most densely populated city in Zamastan. Urban planning in Tofino is characterized by high-rise residential and mixed-use development in urban centers, as an alternative to sprawl. As part of the larger Metro Tofino region, it is influenced by the policy direction of livability as illustrated in Metro Tofino's Regional Growth Strategy. | ||
Tofino has been ranked one of the most livable cities in [[ | Tofino has been ranked one of the most livable cities in the [[Coalition of Crown Albatross]] for more than a decade. As of 2010, Tofino has been ranked as having one of the highest quality of living of any city in the C.C.A.. In contrast, according to [[The Tofino Times]], Tofino had the sixth-most overpriced real estate market in the world and was second-highest in [[Euronia]] after [[Tirzah]] in 2007. Tofino has also been ranked among Zamastan's most expensive cities in which to live. Sales in February 2016 were 56.3% higher than the 10-year average for the month. The Tofino Times has also ranked Tofino as the tenth-cleanest city in the C.C.A.. | ||
Tofino's characteristic approach to urban planning originated in the late 1950s, when city planners began to encourage the building of high-rise residential towers in Tofino's West End, subject to strict requirements for setbacks and open space to protect sight lines and preserve green space. The success of these dense but livable neighborhoods led to the redevelopment of urban industrial sites, such as North False Creek and Coal Harbor, beginning in the mid-1980s. The result is a compact urban core that has gained international recognition for its "high amenity and 'livable' development". In 2006, the city launched a planning initiative entitled EcoDensity, with the stated goal of exploring ways in which "density, design, and land use can contribute to environmental sustainability, affordability, and livability". | Tofino's characteristic approach to urban planning originated in the late 1950s, when city planners began to encourage the building of high-rise residential towers in Tofino's West End, subject to strict requirements for setbacks and open space to protect sight lines and preserve green space. The success of these dense but livable neighborhoods led to the redevelopment of urban industrial sites, such as North False Creek and Coal Harbor, beginning in the mid-1980s. The result is a compact urban core that has gained international recognition for its "high amenity and 'livable' development". In 2006, the city launched a planning initiative entitled EcoDensity, with the stated goal of exploring ways in which "density, design, and land use can contribute to environmental sustainability, affordability, and livability". | ||
[[File: | ====Architecture==== | ||
[[File: | ''See also: [[List of tallest buildings in Tofino]], [[List of tallest buildings (CCA)]]'' | ||
<center> | |||
<gallery class="center" widths="200" heights="150"> | |||
File:Bruxels_April_2012-4.jpg|The [[Zian Presidential Mansion]] is the official residence of the [[President of Zamastan]]. | |||
File:British_Columbia_Parliament_Buildings_-_panoramio.jpg|[[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]] is the home of the Zamastanian legislature. The bi-lateral departments of the [[Congress Chamber (Zamastan)|Congress Chamber]] and [[The Senate (Zamastan)|the Senate]] convene in this building. | |||
File:Canton_CTF_Finance_Center_(2016-08-22).jpg|[[Zian Bank Tower]], the tallest tower in Tofino and Zamastan, as well as the fourth-tallest building in the world. | |||
File:GZIFC.jpg|[[Forrester Tower]], the twin tower of Zian Bank and which houses the HQ for [[ZSuites Incorporated|ZSuites and Forrester]]. | |||
File:NewPeaceTowerTofino.jpg|New Peace Tower. | |||
File:International_Commerce_Centre_201008.jpg|[[One Trinity Center]], the second tallest tower in Tofino and Zamastan, as well as the fifth tallest building in the world. | |||
File:Tokyo-Midtown-Tower-05.jpg|M. Gaviria Building, Headquarters of the [[Zamastanian Intelligence Service|Z.I.S.]] | |||
File:CCA_Headquarters_Tofino.jpg|[[Headquarters of the Coalition of Crown Albatross]] | |||
</gallery> | |||
</center> | |||
Tofino's skyline, with its many skyscrapers, is universally recognized, and the city has been home to several of [[List of tallest buildings (CCA)|the tallest buildings in the world]]. As of 2021, Tofino had 6,455 high-rise buildings, the third most in the world after [[Gangkou]] and [[Shanghan]]. There are several modern buildings in the downtown area. A collection of Edwardian buildings in the city's old downtown core were, in their day, the tallest commercial buildings in the 1910s. These were, in succession, the [[Carter-Cotton Building]] (former home of [[The Tofino Times]] newspaper), the [[Mannax Building]] (1907) and the [[Sun Tower (Zamastan)|Sun Tower]] (1911), the former two at Cambie and Hastings Streets and the latter at Beatty and Pender Streets. The [[New Peace Tower]], constructed in 1904 to commemorate 100 years of Zamastanian independence, was the tallest structure in the world at the time of completion. As of 2019, it is currently the seventh tallest structure in the city. The [[One Trinity Center]] was the tallest building upon completion in 1989, but was surpassed by the [[Zian Bank Tower]] in 2012. | |||
The character of Tofino's large residential districts is often defined by the elegant brownstone rowhouses and townhouses and shabby tenements that were built during a period of rapid expansion from 1870 to 1930. In contrast, Tofino also has neighborhoods that are less densely populated and feature free-standing dwellings. In neighborhoods such as Delk, Belles, and Hapson Heights, large single-family homes are common in various architectural styles such as Tudor Revival and Victorian. | |||
Stone and brick became the city's building materials of choice after the construction of wood-frame houses was limited in the aftermath of the [[1919 Tofino Earthquake]]. A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the roof-mounted wooden water tower. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could break municipal water pipes. Garden apartments became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, such as Cascades. | |||
====Districts and neighborhoods==== | |||
''Main article: [[Neighborhoods in Tofino]]'' | |||
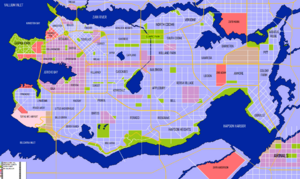
[[File:TofinoMapDistrictsUpdated.png|thumb|right|A district map of Tofino]] | |||
Tofino has 63 specialized districts. The majority are residential priority neighborhoods, with others classified for industrial, environmental, and government purposes. 55 are incorporated, including 2 directly government affiliated (Congressional Park and [[Embassy Row (Zamastan)|Embassy Row]]), and another being [[Gaviria Park]]. The 55 incorporated districts are; | |||
{{div col|colwidth=12em}} | |||
*[[Gaviria Park]] | |||
*Congressional Park | |||
*[[Embassy Row (Zamastan)|Embassy Row]] | |||
*[[Armitage, Tofino|Armitage (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Jericho Basin, Tofino|Jericho Basin (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Kitsilano, Tofino|Kitsilano (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Collingwood, Tofino|Collingwood (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Donaldson, Tofino|Donaldson (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Odessa, Tofino|Odessa (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Delk, Tofino|Delk (Downtown)]] | |||
*[[Kingston, Tofino|Kingston]] | |||
*[[French Bay, Tofino|French Bay]] | |||
*[[Belles, Tofino|Belles]] | |||
*[[Fraser, Tofino|Fraser]] | |||
*[[Point Grey, Tofino|Point Grey]] | |||
*[[Douglass, Tofino|Douglass]] | |||
*[[Surrey, Tofino|Surrey]] | |||
*[[Oakridge, Tofino|Oakridge]] | |||
*Melali | |||
*Sunset | |||
*Gills Creek | |||
*[[Holland Park, Tofino|Holland Park]] | |||
*Cascades | |||
*Killarney | |||
*Hemlock Heights | |||
*[[North Coome, Tofino|North Coome]] | |||
*[[South Coome, Tofino|South Coome]] | |||
*Hapson Heights | |||
*Kerrisdale | |||
*Mackay | |||
*Lynntown | |||
*Belcarra | |||
*Derby Ranch | |||
*Little Anchorhead | |||
*Peace Arch | |||
*Tynehead | |||
*Capilano | |||
*Jayna | |||
*Arbutus Ridge | |||
*Colony Farm | |||
*Anmore | |||
*[[Pitt, Tofino|Pitt]] | |||
*Barnston | |||
*Prara | |||
*Verodine | |||
*Birtos | |||
*Feracci | |||
*Rersa Village | |||
*[[Vanresa, Tofino|Vanresa]] | |||
*[[Leidon, Tofino|Leidon]] | |||
*[[Bell, Tofino|Bell]] | |||
*[[Gibiville, Tofino|Gibiville]] | |||
*[[Guilbrook, Tofino|Guilbrook]] | |||
*[[Rosgrave, Tofino|Rosgrave]] | |||
*[[Applebury, Tofino|Applebury]] | |||
{{div col end}} | |||
As the diplomatic center of Zamastan, several foreign governments have embassies located in the city. Most are located in '''[[Embassy Row (Zamastan)]]''', a district neighborhood dedicated to ambassador residences and offices. | |||
====Parks==== | |||
The City of Tofino has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the Zamastanian Federal Park Service, the Zian Provincial Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the Tofino Department of Parks and Recreation. Most notable is [[Gaviria Park]]. | |||
= | {{div col|colwidth=12em}} | ||
*[[Gaviria Park]] | |||
*Washing Meadows | |||
*The Bottleneck | |||
*Archie Byrne Park | |||
*Maple Fields | |||
*Reuben Lane Park | |||
*Lewis Ellis Park | |||
*Kellen Park | |||
*Mooney Park | |||
*Paul Chandler Park | |||
*Glenn Park | |||
*Caleb Duncan Park | |||
*Alaina Hicks Park | |||
*Cook Park | |||
*Goodname Park | |||
*Higgins Park | |||
*Madisyn Peterson Park | |||
*Aaren Park | |||
*Franky Warner Park | |||
*Chelsea Hopkins Park | |||
*Hugo Botelho Park | |||
*Barnes Park | |||
*Revolutionary Gardens | |||
*Megan Booth Park | |||
{{div col end}} | |||
==== | ====Military Installations==== | ||
There are multiple military instillations in and around Tofino, including [[Zamastanian Naval Forces|ZNB Tofino]], [[Zamastanian Army|ZAB Adam]], and three [[Zamastanian Air Force|air force]] bases; AFB Anderson, AFB Mann, and at [[Tofino International Airport]] with a contingent of aircraft. | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
The metropolitan area referred to as Greater Tofino, with more than | The metropolitan area referred to as Greater Tofino, with more than 22.4 million residents, is the most populous metropolitan area in the country, with its inclusion of [[Arinals]] across the bay. Tofino has been called a "city of neighborhoods". Each neighborhood in Tofino has a distinct character and ethnic mix. People of [[Yuan]]eze, [[Quetana]]n, and [[Skith]]an origins were historically the largest ethnic groups in the city, and elements of Skithan society and culture are still visible in some areas, particularly South Kingston and Donaldson. Germans are the next-largest European ethnic group in Tofino and were a leading force in the city's society and economy until the rise of anti-Gladysynthian sentiment with the outbreak of the [[1945 Danaska Conflict|First Danaska War]]. Today, east-[[Euronia]] and [[Drambenburg]] are the largest visible ethnic group in the city, with a diverse Yuan-speaking community, and several dialects, including [[Beleroskov]] and [[Jaginistan]]. Neighborhoods with distinct ethnic commercial areas include the [[Emmiria]]town, Yuan Market, Little [[Cadair]], [[Gladysynthia]]town, and [[Lissatha]]ville. | ||
The wider metro area of Tofino, known as the [[Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area]], is home to more than 55 million people, making it among the most populated areas in the world. The neighboring city of [[Arinals]] is the second-largest city in Zamastan and is located across Hapson Harbor and by the city's southern mainland connection. The city of [[Tirzah]] is classified as a suburb of Tofino, and is known as one of the wealthiest residential areas in the C.C.A.. Several billionaires, actors, politicians, and other celebrities have their residences or vacation homes here. | |||
===Race and ethnicity=== | |||
The city's population in 2020 was 44% White (33.3% non-Hispanic White), 25.5% Black (23% non-Hispanic Black), 0.7% [[Catica First Nations|First Nations]], and 12.7% [[Ausiana]]n. Hispanics or Latinos of any race represented 28.6% of the population, while [[Ausiana]]ns constituted the fastest-growing segment of the city's population between 2010 and 2020; the non-Hispanic White population declined three percent, the smallest recorded decline in decades; and for the first time since the [[Parabocan War]], the number of Black people declined over a decade. Throughout its history, Tofino has been a major port of entry for immigrants into Zamastan. More than 20 million [[Nortua]]n and [[Adula]]n immigrants were received between 1892 and 1924. | |||
Approximately 37% of the city's population is foreign born, and more than half of all children are born to mothers who are immigrants as of 2013. In Tofino, no single country or region of origin dominates. The ten largest sources of foreign-born individuals in the city as of 2021 were [[Janapa]], [[Ossinia]], [[East Chanchajilla]], [[Yuan]], [[Haduastan]], [[Qolaysia]], [[Emmiria]], [[Saint Croix and Bens]], [[Kyti]], and [[Constantio]], while the [[Barangadesh]]i-born immigrant population has become one of the fastest growing in the city, counting over 94,000 by 2021. | |||
===Religion=== | |||
The Tofino area is the 7th-most religious metropolis in Zamastan. Largely a result of Eastern Euronian missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion as of 2014. [[Church of Zian|Protestantism]] is the largest Christian denomination (33%), followed by [[wikipedia:Roman catholic|Verdusan Catholicism]] (23%), and other Christians (3%). Evangelical Protestantism is the largest branch of Protestantism in the city (9%), followed by Mainline Protestantism (8%), while the converse is usually true for other cities and metropolitan areas. In Evangelicalism, Baptists are the largest group; in Mainline Protestantism, Reformed Protestants are the largest. The majority of historically Black churches are affiliated with the Baptist Convention and Progressive Baptist Convention. Orthodox Christians (mainstream and independent) were the largest Central Adulan Christian groups. | |||
Judaism, with approximately 1.1 million adherents, more than half of whom live in Donaldson, is the second largest religion. The ethnoreligious population makes up 10.4% of the city and its religious demographic makes up 8%. The largest Jewish denominations are Orthodox, Haredi, and Conservative Judaism. Reform Jewish communities are prevalent through the area. Islam ranks the third largest religion in Tofino, with estimates ranging between 600,000 and 1,000,000 observers, including 7% of the city's public school children. These three largest groups are followed by Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Zoroastrianism, and a variety of other religions, as well as atheism. In 2014, 24% of Tofino residents self-identified with no organized religious affiliation; a little over 3% of Tofino residents were atheist. | |||
===Sexual orientation and gender identity=== | |||
[[File:Pride_March_Tofino_2019.jpg|thumb|right|The Tofino Pride March in 2019]] | |||
The Tofino metropolitan area is home to about 970,000 self-identifying gay and bisexual people, the largest in Zamastan and one of the world's largest. Same-sex marriages were legalized on June 4, 1979, three years before the national legalization in 1982. The annual Tofino Pride March (or gay pride parade) is one of the largest pride parade in the world, attracting tens of thousands of participants and millions of sidewalk spectators each June. | |||
==Education== | |||
===Primary and secondary education=== | |||
The Tofino Public Schools system, managed by the Tofino Department of Education, is the largest public school system in Zamastan, serving about 2.3 million students in more than 3,400 separate primary and secondary schools. The city's public school system includes eighteen specialized high schools to serve academically and artistically gifted students. The city government pays the Tirzah Public Schools to educate a very small, detached section of the city. The Tofino Charter School Center assists the setup of new charter schools. There are approximately 1,150 additional privately run secular and religious schools in the city. | |||
===Higher education and research=== | |||
More than 1,200,000 students are enrolled in Tofino's more than 130 higher education institutions, the highest number of any city in the world, with more than half a million in the Tofino Public Universities and Colleges (TPUC) system alone as of 2020, including both degree and professional programs. Tofino has, on average, the best higher education institutions of any global city. The public TPUC system is one of the largest universities in the nation, comprising 28 institutions across all districts: senior colleges, community colleges, and other graduate/professional schools. The public Provincial University of Zian (PUZ) system includes campuses in Tofino, including: Downstate Health Sciences University, Fashion Institute of Technology, Maritime College, and the College of Optometry. | |||
Tofino is home to such notable private universities as [[Kingston University]], [[Hapson University]], [[University of Tofino]], [[Tofino Institute of Technology]], [[Abell University]], and [[Hevala University]]; several of these universities are ranked among the top universities in the world. The city also hosts other smaller private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions, such as: [[St. Peter's University (Tofino)|St. Peter's University]], [[Delk College]], [[Armitage College]], The [[College of Mount Qira]], [[Aikman School of Design]], The [[Mayne School]], [[Robinson Institute]], [[Tofino Film Academy]], and Lynntown College. | |||
Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. Tofino has the most postgraduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in Zamastan. In 2020, there were 43,523 licensed physicians were practicing in Tofino. Major biomedical research institutions include [[Fraser Cancer Center]], [[Oakridge University]], TPUC Downstate Medical Center, Coome College of Medicine, Grouse Mountain School of Medicine, and Anmore Medical College. | |||
==Human Resources== | |||
===Public health=== | |||
The Tofino Health and Hospitals Organization (HHO) operates the public hospitals and clinics in Tofino. A public benefit corporation with Z$8.7 billion in annual revenues, HHO is the largest municipal healthcare system in the country serving 1.9 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents. HHO was created in 1969 by the Zian Provincial Legislature as a public benefit corporation. HHO operates 11 acute care hospitals, five nursing homes, six diagnostic and treatment centers, and more than 70 community-based primary care sites, serving primarily the poor and working class. HHO's Health Plan is one of Zian area's largest providers of government-sponsored health insurance and is the plan of choice for nearly half million Tofino citizens. HHO's facilities annually provide millions of Tofino citizens services interpreted in more than 190 languages. The most well-known hospital in the HHO system is [[Karrisdale Hospital]], the oldest public hospital in Zamastan. Karrisdale is the designated hospital for treatment of the President of Zamastan and other world leaders if they become sick or injured while in Tofino. | |||
===Public safety=== | |||
The [[Fire Department of Tofino]] (FDT), provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the districts. The FDT is the largest municipal fire department in the country and the second largest in the world. The FDT employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed EMTs and paramedics. The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to Tofino. In addition to responding to building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to high-rise structures, the FDT also responds to fires that occur in the Tofino Subway. Secluded bridges and tunnels, as well as large parks and wooded areas that can give rise to brush fires, also present challenges. | |||
The | The [[Tofino Metropolitan Police Department]] (TMPD) has been the largest police force in Zamastan by a significant margin, with more than 55,000 sworn officers. | ||
Crime in Tofino is largely concentrated in areas associated with poverty, drug abuse, and gangs. A 2010 study found that 5% of city blocks accounted for over one-quarter of the city's total crime. The more affluent neighborhoods of Northwest Tofino are typically safe, especially in areas with concentrations of government operations, such as Downtown Tofino, Ironville, Embassy Row, and Jade Quarter, but reports of violent crime increase in poorer neighborhoods generally concentrated in the eastern portion of the city. Approximately 60,000 residents are ex-convicts. In 2012, Tofino's annual murder count had dropped to 88, the lowest total since 1961. The murder rate has since risen from that historic low, though it remains close to half the rate of the early 2000s. Tofino was once described as the "murder capital" of Zamastan during the early 1990s. The number of murders peaked in 1991 at 479, but the level of violence then began to decline significantly. | |||
Crime in Tofino | |||
Organized crime has long been associated with Tofino, with the [[Duvall syndicate]], one of the world's largest international criminal organizations known most prominently for drug smuggling, having significant influence in the city's black market, which is among the world's most lucrative. Additionally, other syndicates like the [[Zitassan Mafia]], [[SHADOW]], and [[San Beausoleil Mafia]] are active in the Zamastanian criminal underworld. | |||
In | ==Government and politics== | ||
===Government=== | |||
Tofino has been a metropolitan municipality with a mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1828. In Tofino, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services. | |||
The [[Mayor of Tofino|Mayor]] and council members are elected to four-year terms. The [[Tofino City Council|City Council]] is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a three consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break. | |||
===Politics=== | |||
The current mayor of Tofino is [[Sophie Webb-Lancaster]], a member of the [[Green Liberal Party (Zamastan)|GLP]] elected on September 22nd, 2021. She replaced [[Bryan Donaldson]], also a member of the [[Green Liberal Party (Zamastan)|GLP]] who was elected on September 22nd, 2017, but declined to run for a second term. | |||
==Economy== | |||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
===Festivals=== | ===Festivals=== | ||
Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the [[Tofino | Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the [[Tofino Film Festival|Tofino Film Festival]] which hosts films from all over the C.C.A., the [[Tofino Intuition and Ideas Conference]] which is a media organization conference dedicated to scientific, cultural, and academic topics. | ||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
Tofino is home to many restaurants with hundreds of examples of global varieties of food. Zamastanian dishes such as steam-smoked fish (notably salmon and trout). Seafood is the most well known form of food in Tofino due to its proximity to the ocean and isolation thanks to the mountains. Signature sushi roll is done in many ways, but the one consistent ingredient is grilled savory and chewy salmon skin. Busy Tofinoites are often particular about their coffee, and love pour-overs and flavored espresso drinks. There are many cozy independent shops to be found who take their coffee very seriously. Local recommendations are to try soy or almond milk to replace traditional milk and cream at almost any place you find. spot prawn are pink creatures are large, sweet shrimp fished in the waters surrounding Tofino in the month of May. Most fine restaurants in Tofino serve fresh prawns when available. | Tofino is home to many restaurants with hundreds of examples of global varieties of food. Zamastanian dishes such as steam-smoked fish (notably salmon and trout). Seafood is the most well known form of food in Tofino due to its proximity to the ocean and isolation thanks to the mountains. Signature sushi roll is done in many ways, but the one consistent ingredient is grilled savory and chewy salmon skin. Busy Tofinoites are often particular about their coffee, and love pour-overs and flavored espresso drinks. There are many cozy independent shops to be found who take their coffee very seriously. Local recommendations are to try soy or almond milk to replace traditional milk and cream at almost any place you find. spot prawn are pink creatures are large, sweet shrimp fished in the waters surrounding Tofino in the month of May. Most fine restaurants in Tofino serve fresh prawns when available. | ||
===Landmarks=== | ===Landmarks=== | ||
[[Gaviria Park]] is a | [[Gaviria Park]] is a landscaped urban park in Tofino. It is located near the [[Congressional Hall (Zamastan)|Congressional Hall]] grounds, the [[Zian Presidential Mansion]], and is between the downtown neighborhood of Point Gray, Kingston, and the [[Horseshoe Bay (body of water)|Horseshoe Bay]]. The term Gaviria Park commonly includes areas that are also officially part of neighboring Congressional Park to the east, as it continues a uniformed park display alongside unique and iconic architectural displays such as Congressional Hall and the Presidential Mansion. Named after [[President of Zamastan|President]] [[Marvin Gaviria]] in 1974, the park contains and borders a number of museums, art galleries, cultural institutions, and various memorials, sculptures, and statues. Much of the park remains as densely forested as it was in the late 1800s, with about a half million trees, some of which stand as tall as 76 metres (249 ft) and are hundreds of years old. Thousands of trees were lost (and many replanted) after three major windstorms that took place in the past 100 years. Significant effort was put into constructing the near three century old [[Tofino Seawall]], which can draw thousands of people to the park in the summer. The park also features forest trails, beaches, lakes, children's play areas, and the [[Tofino Zoo and Aquarium]], among many other attractions. The park receives approximately 24 million visitors each year. | ||
The [[Zamastan National Archives]] houses thousands of documents important to Zamastanian history, including the the [[Constitution of Zamastan]]. Located in three buildings along the corridor of [[Gaviria Park]], the library has a collection of over 147 million books, manuscripts, and other materials. | |||
The [[Zamastan Archives]] houses thousands of documents important to Zamastanian history, including the the [[Constitution of Zamastan]]. Located in three buildings | |||
===Libraries and museums=== | ===Libraries and museums=== | ||
The [[Tofino Art | The [[Tofino Art Museum]] has a permanent collection of nearly 10,000 items. However, little or none of the permanent collection is ever on view. Downtown is also home to the [[Contemporary Art Gallery (Tofino)]], which showcases temporary exhibitions by up-and-coming Tofino artists. | ||
In the Kingston district are the [[Tofino Maritime Museum]], the [[Tauren Wells Space Center]], and the [[Tofino Civic Museum]], the largest civic museum in Zamastan. The [[Tofino Museum of Anthropology]] at [[University of Tofino]] is a leading museum of [[Catica First Nations]] culture, specifically that of the [[Kelownan peoples]]. A more interactive museum is Science World at the head of | In the Kingston district are the [[Tofino Maritime Museum]], the [[Tauren Wells Space Center]], and the [[Tofino Civic Museum]], the largest civic museum in Zamastan. The [[Tofino Museum of Anthropology]] at [[University of Tofino]] is a leading museum of [[Catica First Nations]] culture, specifically that of the [[Kelownan peoples]]. A more interactive museum is Science World at the head of Jericho Bay. The city also features a diverse collection of Public Art. The most visited museum in the city is the [[Zamastan Museum of Natural History]], and other notable museums and galleries are: the [[Zamastan Museum of Adulan Art]]; the [[National Museum of Zamastanian History]]; the [[Museum of the Catica First Nations]]; The [[Zamastan Gallery of Art]] features works of Zamastanian, [[Adula]]n, [[Ausiana]]n, [[Nortua]]n, and [[Euronia]]n art. There are many private art museums in the city, which house major collections and exhibits open to the public such as the [[Zamastan Museum of Women in the Arts]]. | ||
===Zoo=== | ===Zoo=== | ||
The [[Tofino Zoo]] is the largest zoo in Zamastan and one of the largest in the [[ | The [[Tofino Zoo and Aquarium]] is the largest zoo in Zamastan and one of the largest in the [[Coalition of Crown Albatross]], holding over 4,000 species of animals. | ||
===Music and nightlife=== | ===Music and nightlife=== | ||
[[File:1_times_square_night_2013.jpg|thumb|right|Olivar Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment center, and neighborhood in Collingwood downtown district.]] | |||
Musical contributions from Tofino include performers of classical, folk and popular music. The [[Tofino Symphony Orchestra]] is the professional orchestra based in the city. The [[Tofino Opera]] is a major opera company in the city, and City Opera of Tofino is the city's professional chamber opera company. The city is home to a number of Zamastanian composers including Barton Sharman, James Polluck, and Madison Wareka. | Musical contributions from Tofino include performers of classical, folk and popular music. The [[Tofino Symphony Orchestra]] is the professional orchestra based in the city. The [[Tofino Opera]] is a major opera company in the city, and City Opera of Tofino is the city's professional chamber opera company. The city is home to a number of Zamastanian composers including Barton Sharman, James Polluck, and Madison Wareka. | ||
Tofino has a vibrant nightlife scene, whether it be food and dining, or bars and nightclubs. The Kingston Entertainment District has the city's highest concentration of bars and nightclubs with closing times of 3 am, in addition to various after-hours clubs open until late morning on weekends. The street can attract large crowds on weekends and is closed to traffic on such nights. Donaldson is also a popular area for nightlife with many upscale restaurants and nightclubs. | Tofino has a vibrant nightlife scene, whether it be food and dining, or bars and nightclubs. Olivar Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment center, and neighborhood in the Collingwood downtown district along Olivar Street and Velmara Boulevard. Brightly lit by numerous billboards and advertisements, it stretches from West 13th to West 21st Streets, and is sometimes referred to as "the Crossroads of the World" and "the heart of the Capital". Olivar Square is one of the world's most visited tourist attractions, drawing an estimated 50 million visitors annually. Approximately 330,000 people pass through Olivar Square daily, many of them tourists, while over 460,000 pedestrians walk through Olivar Square on its busiest days. The Kingston Entertainment District has the city's highest concentration of bars and nightclubs with closing times of 3 am, in addition to various after-hours clubs open until late morning on weekends. The street can attract large crowds on weekends and is closed to traffic on such nights. Donaldson is also a popular area for nightlife with many upscale restaurants and nightclubs. | ||
==Sporting== | ===Sporting=== | ||
The mild climate of the city and proximity to ocean, mountains, rivers and lakes make the area a popular destination for outdoor recreation. Tofino has over 1,298 hectares (3,210 acres) of parks, of which, [[Gaviria Park]], at 404 hectares (1,000 acres), is the largest. The city has several large beaches, many adjacent to one another, extending from the shoreline of Gaviria Park around False Creek to the south side of French Bay, from Chinook Hill to the Government Endowment Lands, (which also has beaches that are not part of the city proper). The 18 kilometres (11 mi) of beaches include Second and Third Beaches in Gaviria Park, French Bay (First Beach), Sunset, Chinook Hill Beach, Jericho, Rausch, Meyer Banks, Meyer Banks Extension, Meyer Banks West, and Tannson Beach. There is also a freshwater beach at Trout Lake in Kordia Park. The coastline provides for many types of water sport, and the city is a popular destination for boating enthusiasts. | The mild climate of the city and proximity to ocean, mountains, rivers and lakes make the area a popular destination for outdoor recreation. Tofino has over 1,298 hectares (3,210 acres) of parks, of which, [[Gaviria Park]], at 404 hectares (1,000 acres), is the largest. The city has several large beaches, many adjacent to one another, extending from the shoreline of Gaviria Park around False Creek to the south side of French Bay, from Chinook Hill to the Government Endowment Lands, (which also has beaches that are not part of the city proper). The 18 kilometres (11 mi) of beaches include Second and Third Beaches in Gaviria Park, French Bay (First Beach), Sunset, Chinook Hill Beach, Jericho, Rausch, Meyer Banks, Meyer Banks Extension, Meyer Banks West, and Tannson Beach. There is also a freshwater beach at Trout Lake in Kordia Park. The coastline provides for many types of water sport, and the city is a popular destination for boating enthusiasts. | ||
{{Wide image|Olympic Park, Tofino, April 2004 (2).jpg|800px|Aerial view of the [[Olympic Park, Tofino|Olympic Park]] in April 2004 ahead of the [[2004 Summer Olympic Games (Iearth)|2004 Summer Olympics]]}} | |||
Within a 20- to 30-minute drive from downtown Tofino are the North Shore Mountains, with three ski areas: Egret Mountain, Grouse Mountain, and Mount Killiam. Mountain bikers have created world-renowned trails across the North Shore. The Blackfoot River, Abotsford Creek and Phelan River, also on the North Shore, provide opportunities to whitewater enthusiasts during periods of rain and spring melt, though the canyons of those rivers are more utilized for hiking and swimming than whitewater. | Within a 20- to 30-minute drive from downtown Tofino are the North Shore Mountains, with three ski areas: Egret Mountain, Grouse Mountain, and Mount Killiam. Mountain bikers have created world-renowned trails across the North Shore. The Blackfoot River, Abotsford Creek and Phelan River, also on the North Shore, provide opportunities to whitewater enthusiasts during periods of rain and spring melt, though the canyons of those rivers are more utilized for hiking and swimming than whitewater. | ||
Running races include the Tofino Sun Run (a 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) race) every April; the Tofino Marathon, held every May; and the | Running races include the Tofino Sun Run (a 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) race) every April; the Tofino Marathon, held every May; and the Elsuit Tofino Half-Marathon held every June. The Grouse Grind is a 2.9-kilometre (1.8 mi) climb up Grouse Mountain open throughout the summer and fall months, including the annual Grouse Grind Mountain Run. Hiking trails include the Stella-Chinook Trail, an arduous 42-kilometre-long (26 mi) hike from West Tofino's Tapico Bay to Deep Cove in the District of North Tofino. Tofino is also home to notable cycling races. | ||
Tofino hosts teams from all of the Big 5 in Zamastan; the [[Zamastan Football League|ZFL]] ([[Tofino Whitecaps (football team)|Tofino Whitecaps]]), [[Zamastan Baseball League]] ([[Tofino Seals (baseball team)|Tofino Seals]]), [[Zamastan Soccer League]] ([[Tofino United FC|Tofino United FC]]), [[Zamastan Hockey League]] ([[Tofino Pelicans (hockey team)|Tofino Pelicans]]), and [[Zamastan Basketball Association]] ([[Tofino Mariners (basketball team)|Tofino Mariners]]). The Football [[Teal Cup (Sporting Championship)|Teal Cup]] is held in Tofino every year as the final championship game in the league. | |||
Tofino was the host city for the [[1958 Summer Olympic Games (Iearth)|1958]] and [[2004 Summer Olympic Games (Iearth)|2004 Summer]] [[Olympic Games (Iearth)|Olympics]] (and made a [[Tofino bid for the 2026 Summer Olympics|bid]] for the [[2026 Summer Olympic Games (Iearth)|2026 Games]]), the [[1993 Tofino World Cup|1993]] [[World Cup (Iearth)|World Cup]], and the 2000, 2004, 2005, and 2017 [[Euonia Games (international multi-sport event)|Euronia Games]]. | |||
Additional venues that have multiple or non-permanent tenants include [[Suchet Barthél Stadium]]. | |||
===Current professional teams=== | ====Current professional teams==== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:95%;" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:95%;" | ||
!scope="col" style="width:120px;"|Professional Team | !scope="col" style="width:120px;"|Professional Team | ||
| Line 249: | Line 401: | ||
!class="sortable"|Sport | !class="sortable"|Sport | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Tofino Whitecaps ( | | [[Tofino Whitecaps (football team)|Tofino Whitecaps]] || [[Zamastan Football League]] || [[wikipedia:American football|Football]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Tofino Seals ( | | [[Tofino Seals (baseball team)|Tofino Seals]] || [[Zamastan Baseball League]] || [[wikipedia:Baseball|Baseball]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Tofino | | [[Tofino United FC|Tofino United FC]] || [[Zamastan Soccer League]] || [[wikipedia:Association football|Soccer]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Tofino Pelicans ( | | [[Tofino Pelicans (hockey team)|Tofino Pelicans]] || [[Zamastan Hockey League]] || [[wikipedia:Ice hockey|Hockey]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Tofino Mariners ( | | [[Tofino Mariners (basketball team)|Tofino Mariners]] || [[Zamastan Basketball Association]] || [[wikipedia:Basketball|Basketball]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
<center> | |||
<gallery class="center" widths="200" heights="150"> | |||
File:State_of_Origin_Game_II_2018.jpg|[[Orris Stadium]], [[Tofino United FC|Tofino United FC]] <br><small>[[Zamastan Soccer League|ZSL]]</small> | |||
File:Cowboys_Stadium_full_view.jpg|[[Blackwater Energy Stadium]], [[Tofino Whitecaps (football team)|Whitecaps]] <br><small>[[Zamastan Football League|ZFL]]</small> | |||
File:ATT_Sunset_Panorama.jpg|[[Trainrail Park]], [[Tofino Seals (baseball team)|Seals]] <br><small>[[Zamastan Baseball League|ZBL]]</small> | |||
File:Montreal-CH-CentreBell.jpg|[[Pegassi Center]], [[Tofino Pelicans (hockey team)|Pelicans]] <br><small>[[Zamastan Hockey League|ZHL]]</small> | |||
File:Rupp_Arena_-_UCLA_v._UK_on_12-03-16.jpg|[[Siore Arena]], [[Tofino Mariners (basketball team)|Mariners]] <br><small>[[Zamastan Basketball Association|ZBA]]</small> | |||
</gallery> | |||
</center> | |||
==Transportation== | |||
===Rapid Transport=== | |||
Mass transit in Tofino, most of which runs 24 hours a day, accounts for one in every four users of mass transit in Zamastan, and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in the [[Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area]]. | |||
===Rail=== | |||
[[File:TofinoSubwayStationPlatform41.jpg|thumb|right|A train arriving at a station in the [[Tofino Subway System]]]] | |||
The [[Tofino Subway System]] is the largest rapid transit system in the world when measured by stations in operation, with 364, and by length of routes. Nearly all of Tofino's subway system is open 24 hours a day, in contrast to the overnight shutdown common to systems in most cities, including [[Cardiff]], [[Ponamu]], [[Lerbin]], [[Shanghan]], [[Vongane]], and [[Skithiana]]. The Tofino Subway is also the busiest metropolitan rail transit system in the world, with 1.56 billion passenger rides in 2015, while [[William Castovia Central Terminal]], also referred to as "Tofino Central Station", is the world's largest railway station by number of train platforms. | |||
===Buses=== | |||
The [[Tofino Bus Terminal]], the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 6,800 buses and 200,000 commuters daily. | |||
===Air=== | |||
===Ferries=== | |||
===Taxis and trams=== | |||
===Streets and highways=== | |||
====River crossings==== | |||
'''Zian River''' | |||
*[[Kingston Bridge]]; [[Kingston, Tofino|Kingston]] - [[Tirzah]] | |||
*[[Fraser Bridge]]; [[Belles, Tofino|Belles]] - [[Tirzah]] | |||
*[[Brentwood Bridge]]; [[North Coome, Tofino|North Coome]] - [[Tirzah]] | |||
*[[Mannal Bridge]]; [[North Coome, Tofino|North Coome]] - [[Tirzah]] | |||
*[[Annes Bridge]]; [[Verodine, Tofino|Verodine]] - [[Ashwood]] | |||
*[[Akaitcho Bridge]]; [[Verodine, Tofino|Verodine]] - [[Cannock]] | |||
*[[Collough Bridge]]; [[Verodine, Tofino|Verodine]] - [[Cannock]] | |||
*[[Thistlerock Bridge]]; [[Pitt, Tofino|Pitt]] - [[Cannock]] | |||
*[[Muir Bridge]]; [[Arbutus Ridge, Tofino|Arbutus Ridge]] - [[Cannock]] | |||
*[[Theite Bridge]]; [[Arbutus Ridge, Tofino|Arbutus Ridge]] - [[Cannock]] | |||
'''Jericho Bay''' | |||
*[[Garden Bridge (Tofino)|Garden Bridge]]; [[Donaldson, Tofino|Donaldson]] - [[Delk, Tofino|Delk]] | |||
*[[Calder Tunnel]]; [[Jericho Basin, Tofino|Jericho Basin]] - [[Delk, Tofino|Delk]] | |||
'''Belcarra Inlet''' | |||
*[[Graham Bridge]]; [[Derby Ranch, Tofino|Derby Ranch]] - [[Seaforth]] | |||
*[[Manning Bridge]]; [[Belcarra, Tofino|Belcarra]] - [[Seaforth]] | |||
*[[Orkney Bridge]]; [[Feracci, Tofino|Feracci]] - [[Nalton]] | |||
*[[Tomias Hapson Bridge]]; [[Hapson Heights, Tofino|Hapson Heights]] - [[Nalton]] | |||
'''Gibi Creek''' | |||
*[[Iskana-Porrier Bridge]]; [[Gibiville, Tofino|Gibiville]] - [[Arinals]] | |||
*[[Pickett Bridge]]; [[Colony Farm, Tofino|Colony Farm]] - [[Arinals]] | |||
*[[Thoole Bridge]]; [[Arbutus Ridge, Tofino|Arbutus Ridge]] - [[Arinals]] | |||
===Cycling network=== | |||
==Environment== | |||
===Environmental impact reduction=== | |||
===Water purity and availability=== | |||
===Air quality=== | |||
==Notable people== | |||
{{Template:Zamastan}} | |||
[[Category: Cities]] [[Category: Places]] [[Category: Zamastan]] [[Category:Cities in Zamastan]] | [[Category: Cities]] [[Category: Places]] [[Category: Zamastan]] [[Category:Cities in Zamastan]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:38, 18 September 2024
Tofino | |
|---|---|
Capital City | |
 Clockwise from top left: Downtown skyline with Zian Bank Tower dominating the skyline; Kingston District and SealBank Arena with the mountains in the background; Congressional Hall; the Supreme Court of Zamastan; the Headquarters building of the Coalition of Crown Albatross; ; Downtown Tofino, including the New Peace Tower | |
| Etymology: Native Catican: Sea Meets Mountain | |
| Nickname(s): Glass and Pine City | |
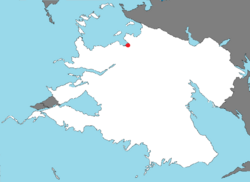 Tofino's location within Zamastan | |
| Country | Zamastan |
| Administrative District (Province) | Zian |
| Founded | April 28, 1711 |
| Founded by | Percy Armillio |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Sophie Webb-Lancaster (GLP) |
| • Deputy-Mayor | Bryan Donaldson |
| Area | |
| • Urban | 876.5 km2 (338.40 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,878.5 km2 (1,111.40 sq mi) |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Capital City | 22,870,000 (1st) |
| Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area (51,483,000) | |
| Time zone | UTC+7 |
| Website | tofinocity.gov.za |
Tofino is the capital and largest city in Zamastan. With a population of roughly 22.9 million people within its city limits and an additional 11 million in the immediate surrounding cities, it's often ranked as the second-largest metropolitan area in the Coalition of Crown Albatross after the Yuaneze capital of Shanghan, as well as one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities. It is a coastal seaport city, located on the lower side of Horseshoe Bay. Founded as a Skithan colony by Percy Armillio in 1711, the city's indigenous history spans back over 10,000 years as native Zamah St'ani Catica First Nations (specifically that of the Kelownan peoples) settled along the coastal area of what would become modern-day Tofino, namely in the Delk neighborhood. With its boundaries marked by the Zian River to the north, Belcaara Inlet to the south, and Hapson Harbor and Porrier River to the east, Tofino is the largest entity of the Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area, which also includes the city of Arinals. The metropolitan area has a population of over 51 million people.
Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the Tofino Film Festival which hosts films from all over the C.C.A., the TIIC which is a media organization conference dedicated to scientific, cultural, and academic topics. The city is home to multiple sports teams, including the Whitecaps (ZFL), TUFC (ZSL), Mariners (ZBA), and Seals (ZBL). Tofino is home to the headquarters building of the Coalition of Crown Albatross, meaning that delegates all across the world meet in General Assembly and Security Council matters. The CCA General-Secretary likewise has their office in Tofino.
The government and military headquarters of Zamastan operate in and around Tofino, with the Congressional Hall (legislative), Zian Presidential Mansion (executive, President), the Supreme Court of Zamastan (judicial), and the Zamastanian Armed Forces all located within the city. Tofino is home to many national monuments and museums, primarily situated on or around Gaviria Park. The city hosts many foreign embassies as well as the headquarters and campuses of many international organizations, trade unions, non-profit, lobbying groups, and professional associations.
History
Before 1700's
Archaeological records indicate that Catica First Nations people were already living in the "Tofino" area from 8,000 to 10,000 years ago. The city is located in the traditional and presently unceded territories of the Kelowna, Nuuchahnulth, and Castoni tribes. They had villages in various parts of present-day Tofino, such as Gaviria Park and near the mouth of the Zian River.
Settlement
Adulan explorers became acquainted with the area of the future Tofino when Skithan explorer Percy Armillio explored the coast of present-day Gaviria Park and parts of Coal Inlet in 1711. The Gold Rush of 1739 brought over 25,000 men, mainly from central and eastern Adulan regions such as modern-day Quetana, Mulfulira, and Emmiria, to nearby Arinals (founded March 29, 1737) on the Zian River, on their way to the Vallium Canyon, bypassing what would become Tofino.
Religious institutions brought by Skithan settlers, such as the catholic faith of the Catholic Church of Zamastan and the protestant Church of Zian became prominent in the Tofino area. King Almarez II sent broad amounts of supplies and additional workers - many of them slaves - to the colony to build up the infrastructure and start expanding further into the continent.
Revolution of 1802-1804
Battle of Tofino (1802)
On July 17th, 1802, a slave named Tomias Hapson and a Skithan hand master named Avi Taures, who had developed friendships with the slaves he watched over, raided a munitions depot in the primary settlement of Tofino. After a battle that lasted for several hours, over 300 Skithan soldiers and settlers were killed, and the slave army took over the port. Tomias Hapson and Avi Taures recruited several thousand slaves, along with abolitionist white and native colonists, and began a purge in the city to kill all slave owners and Skithan military and colonial personnel.
Purge of Tofino (1802-1803)
For nearly 11 months, the rebels went on a hunt for colonialists who remained loyal to the crown, and on October 2nd, 1803, a mob killed the mayor and his family while they attempted to reach a departing ship in the port of Maple Bay.
The next week as news reached Skith, King Almarez had issued an order for Hapson and Taures to be executed by any capable man on the island and announced that a reward of over 50,000 shinnels would be given to anyone able to complete the task. He was well aware of the favorable treatment Taures had been giving to the slave laborers on the colony and had also heard rumors about the makeshift army he was assembling in preparation for a rebellion against the Skith crown. In response to this, the King decided to ship approximately 5,000 more Skithan Army soldiers to the colony with the sole mission of suppressing this rebellion should it come to fruition. At the same time, Tomias Hapson was continuing his campaign to rally up supporters for his cause as tension in Zamah St'an rose to a boiling point.
Sacking of the Governor's Residence (1804)
On September 3rd, 1804, the Zamastan War of Independence officially marked its turning point with Hapson and a division of about 50 of his loyal soldiers (a diverse group consisting of native Zamah St'an and slaves as well as national soldiers who shared Taures' ideals) initiating a surprise midnight attack on the Governor's Mansion in the capital of Tofino. Chico Pisano, who was appointed by King Almaraz as his replacement as Governor of the colony, had recently taken up residence there. Hapson and Taures's men, who had come to be known as the National Liberation Front, surrounded the building and strategically made their way towards Pisano's living quarters after breaking their way into the massive residence. Having been provided with substantial weaponry via the many Skithan soldiers who had defected to the NLF, Taures's group of guerilla fighters were surprisingly well-equipped for the operation and even more importantly, most had intense passion for their cause. Not only were the Skithan fighters motivated by the moral disagreements they had with the occupation of Zamastan, but also because it was widely known that soldiers for the Kingdom were not treated much differently than mere peasants back in their homeland. Once they had outlived their usefulness in times of war, they were given lowly jobs back in Skith and given little to no recognition or compensation for risking their lives in the name of their country. Many believed they would be better off assisting Hapson and Taures in their cause and earning the colony its independence, which in turn would create a place where they could create a more desirable society for themselves.

Hapson's decision to conduct the assault on the Governor's Mansion in the middle of the night paid off for the NLF, as they were met with relatively light resistance from Governor Pisano's bodyguards, all of whom were armed and told to be ready for war to break out but were not anticipating the first target to be Governor Pisano. Some were half-asleep as Hapson and his men made their way from hallway to hallway, room to room in search of Pisano; the guards were taken out with very light losses to Hapson's forces with one two of his men sustaining moderate but not life-threatening injuries. Once the NLF team reached Pisano's living quarters and broke the door down after hearing movement inside, they encountered an almost trembling Governor who had managed to arm himself after hearing the commotion throughout the residence. He froze for a moment as he eyed the dozen or so men who stood in his doorway, all with their weapons aimed squarely at him. He made a last-ditch effort to raise his weapon and fire but was gunned down and killed before he was able to fire a single round in their direction.
Hapson and his men had completed their first major objective; removing the only Skith politician in power in Zamastan and giving their cause the momentum that it needed going forward. Three weeks later, the King of Skith ordered a halt on all shipments and settlement travel to and from the island colonies, and the Free State of Zamah St'an was established on October 28th, 1804 with Tomias Hapson as the de-facto President, Avi Taures as the Chief of Trade and Commerce, and an abolitionist named Henry Tiller as the General of Armed Forces.
Growth and development
An improved shipping port of Tofino was incorporated on April 6, 1866, the same year that the first transnational train station was established. The Great Tofino Fire on June 13, 1866, razed the entire city. The Tofino Fire Department was established that year and the city quickly rebuilt. Tofino's population grew from a settlement of 40,000 people in 1861 to over 220,000 by the turn of the century and 1,000,000 by 1911.
Tofino merchants outfitted prospectors bound for the Zian Gold Rush in 1898. One of those merchants, Charles Pattington, had opened the first Pattington's store at Gorba and Samuelson Streets in 1892 and, along with Spencer's and the Hudson's Bay department stores, formed the core of the city's retail sector for decades.
The economy of early Tofino was dominated by large companies such as the ZPR, which fueled economic activity and led to the rapid development of the new city; in fact, the ZPR was the main real estate owner and housing developer in the city. While some manufacturing did develop, including the establishment of the Zian Sugar Refinery by Mark Yeunn Rogers in 1890, natural resources became the basis for Tofino's economy. The resource sector was initially based on logging and later on exports moving through the seaport, where commercial traffic constituted the largest economic sector in Tofino by the 1930s.
1919 Tofino Earthquake
At 7:12 am on January 12, 1919, a major earthquake struck Tofino and western Zamastan. As buildings collapsed from the shaking, ruptured gas lines ignited fires that spread across the city and burned out of control for several days. With water mains out of service, the Zamastanian Armed Forces attempted to contain the inferno by dynamiting blocks of buildings to create firebreaks. More than three-quarters of the city lay in ruins, including almost all of the downtown core. Contemporary accounts reported that 1,498 people lost their lives, though modern estimates put the number around 50,000. More than half of the city's population of 1,200,000 was left homeless. Refugees settled temporarily in makeshift tent villages in what is now Gaviria Park, on the beaches, and elsewhere. Many fled permanently to Tirzah.
Twentieth century
The dominance of the economy by big business was accompanied by an often militant labor movement. The rise of industrial tensions throughout the district led to Zamastan's first general strike in 1920, at the Folsted coal mines on Tofino. Following a lull in the 1920s, the strike wave peaked in 1935 when unemployed men flooded the city to protest conditions in the relief camps run by the military in remote areas throughout the administrative district. After two tense months of daily and disruptive protesting, the relief camp strikers decided to take their grievances to the federal government and embarked on the On-to-Tofino Trek, but their protest was put down by force. The workers were arrested near Jade Harbor and interned in work camps for the duration of the decade.
Other social movements, such as the first-wave feminist, moral reform, and temperance movements were also instrumental in Tofino's development. Elain Ellen Denmer, a Tofino suffragist and prohibitionist, became the first woman elected to a administrative district's legislature in Zamastan in 1918. Zamastan's first drug law came about following an inquiry conducted by the federal Secretary of Labor and future President Tyler Kordia. Kordia was sent to investigate damages claims resulting from a riot when the Euronia Exclusion League led a rampage through Yuanville and Quetanatown. Two of the claimants were opium manufacturers, and after further investigation, Kordia found that white women were reportedly frequenting opium dens as well as Gladysynthian men. A federal law banning the manufacture, sale, and importation of opium for non-medicinal purposes was soon passed based on these revelations. These riots, and the formation of the Euronia Exclusion League, also act as signs of a growing fear and mistrust towards the Gladysynthians living in Tofino and throughout Zian. These fears were exacerbated by the First Danaska War, leading to the eventual internment or deportation of all Gladysynthian-Zamastanians living in the city and the district. After the war, these men and women were not allowed to return to cities like Tofino causing areas, like the aforementioned Laeraltown, to cease to be ethnically diverse areas as the communities never revived.
Amalgamation with Tirzah and Arinals gave the city its final boundaries not long before it became the largest metropolis in the country. As of January 1, 1949, the population of the enlarged Tofino was 3,228,193.
On September 29th, 1972, President Marvin Gaviria was assassinated while delivering a speech outside on the steps of Congressional Hall.
21st century
The New Peace Tower, constructed in 2004 to commemorate 200 years of Zamastanian independence, was the tallest structure in the city at the time of completion. As of 2019, it is currently the third tallest structure in the city, surpassed by Forrester Tower and Zian Bank Tower.
In the later half of the 2010 decade, saw both prosperity and hardship. While the economy grew significantly due to new investments and a lower crime rate, Tofino suffered a string of terror attacks, including the 2017 attacks which claimed over 430 lives, and the city was the epicenter of the "PoverTea" Protests of 2019, which largely centered around discontent of President Anya Bishop's administration. On November 2nd, several protestors and police officers were killed during the riots in Tofino, resulting in a Congressional Hall motion to remove Bishop from office.
Geography
Located on the Tofino Peninsula, Tofino lies between Vallium Inlet to the north and the Zian River to the north. Horseshoe Bay, to the west, leads out to the Olympic Ocean. The city has an area of 114 km2 (44 sq mi), including both flat and hilly ground. Tofino has one of the largest urban parks in the Coalition of Crown Albatross, Gaviria Park, which covers 404.9 hectares (1,001 acres). The Zian Mountains dominate the cityscape, and on a clear day, scenic vistas include Grouse Mountain and the snow-capped volcano Mount Greening to the southeast, Delk Island in Horseshoe Bay to the west and southwest, and Bowen Island to the northwest.
Ecology
The vegetation in the Tofino area was originally temperate rain forest, consisting of conifers with scattered pockets of maple and alder, and large areas of swampland (even in upland areas, due to poor drainage). The conifers were a typical coastal Zian mix of Douglas fir, Western red cedar, and Western Hemlock. The area is thought to have had the largest trees of these species on the Zian Coast. The largest trees in Tofino's old-growth forest were in the Kingston area, where the first logging occurred, and on the southern slopes of Gills Creek and French Bay, especially around Jericho Beach. The forest in Gaviria Park was logged between the 1860s and 1890s, and evidence of old-fashioned logging techniques such as springboard notches can still be seen there.
Many plants and trees growing throughout Tofino and the Western Mainland were imported from other parts of the continent and from points across the Olympic Ocean. Examples include the monkey puzzle tree, the Maximusian Maple, and various flowering exotics, such as magnolias, azaleas, and rhododendrons. Some species imported from harsher climates in Northern Adula or Nortua have grown to immense sizes. The native Douglas Maple can also attain a tremendous size. Many of the city's streets are lined with flowering varieties of Yuan cherry trees donated from the government of Yuan. These flower for several weeks in early spring each year, an occasion celebrated by the Tofino Cherry Blossom Festival. Other streets are lined with flowering chestnut, horse chestnut, and other decorative shade trees.
Climate
Tofino is one of Zamastan's warmest cities in the winter. Tofino's climate is temperate by Zamastanian standards and is classified as oceanic or marine west coast, bordering on a warm summer Mediterranean Climate. While during summer months the inland temperatures are significantly higher, Tofino has the coolest summer average high of all major Zamastanian metropolitan areas. The summer months are typically dry, with an average of only one in five days during July and August receiving precipitation. In contrast, there is some precipitation during nearly half the days from November through March.
Tofino is also one of the wettest Zamastanian cities. However, precipitation varies throughout the metropolitan area. Annual precipitation as measured at Tofino International Airport on the south side of the city averages 1,189 mm (46.8 in), compared with 1,588 mm (62.5 in) in the downtown area and 2,044 mm (80.5 in) in North Tofino. The daily maximum averages 22 °C (72 °F) in July and August, with highs sometimes reaching 30 °C (86 °F).
Cityscape
As of 2011, Tofino is the most densely populated city in Zamastan. Urban planning in Tofino is characterized by high-rise residential and mixed-use development in urban centers, as an alternative to sprawl. As part of the larger Metro Tofino region, it is influenced by the policy direction of livability as illustrated in Metro Tofino's Regional Growth Strategy.
Tofino has been ranked one of the most livable cities in the Coalition of Crown Albatross for more than a decade. As of 2010, Tofino has been ranked as having one of the highest quality of living of any city in the C.C.A.. In contrast, according to The Tofino Times, Tofino had the sixth-most overpriced real estate market in the world and was second-highest in Euronia after Tirzah in 2007. Tofino has also been ranked among Zamastan's most expensive cities in which to live. Sales in February 2016 were 56.3% higher than the 10-year average for the month. The Tofino Times has also ranked Tofino as the tenth-cleanest city in the C.C.A..
Tofino's characteristic approach to urban planning originated in the late 1950s, when city planners began to encourage the building of high-rise residential towers in Tofino's West End, subject to strict requirements for setbacks and open space to protect sight lines and preserve green space. The success of these dense but livable neighborhoods led to the redevelopment of urban industrial sites, such as North False Creek and Coal Harbor, beginning in the mid-1980s. The result is a compact urban core that has gained international recognition for its "high amenity and 'livable' development". In 2006, the city launched a planning initiative entitled EcoDensity, with the stated goal of exploring ways in which "density, design, and land use can contribute to environmental sustainability, affordability, and livability".
Architecture
See also: List of tallest buildings in Tofino, List of tallest buildings (CCA)
The Zian Presidential Mansion is the official residence of the President of Zamastan.
Congressional Hall is the home of the Zamastanian legislature. The bi-lateral departments of the Congress Chamber and the Senate convene in this building.
Zian Bank Tower, the tallest tower in Tofino and Zamastan, as well as the fourth-tallest building in the world.
Forrester Tower, the twin tower of Zian Bank and which houses the HQ for ZSuites and Forrester.
One Trinity Center, the second tallest tower in Tofino and Zamastan, as well as the fifth tallest building in the world.
M. Gaviria Building, Headquarters of the Z.I.S.
Tofino's skyline, with its many skyscrapers, is universally recognized, and the city has been home to several of the tallest buildings in the world. As of 2021, Tofino had 6,455 high-rise buildings, the third most in the world after Gangkou and Shanghan. There are several modern buildings in the downtown area. A collection of Edwardian buildings in the city's old downtown core were, in their day, the tallest commercial buildings in the 1910s. These were, in succession, the Carter-Cotton Building (former home of The Tofino Times newspaper), the Mannax Building (1907) and the Sun Tower (1911), the former two at Cambie and Hastings Streets and the latter at Beatty and Pender Streets. The New Peace Tower, constructed in 1904 to commemorate 100 years of Zamastanian independence, was the tallest structure in the world at the time of completion. As of 2019, it is currently the seventh tallest structure in the city. The One Trinity Center was the tallest building upon completion in 1989, but was surpassed by the Zian Bank Tower in 2012.
The character of Tofino's large residential districts is often defined by the elegant brownstone rowhouses and townhouses and shabby tenements that were built during a period of rapid expansion from 1870 to 1930. In contrast, Tofino also has neighborhoods that are less densely populated and feature free-standing dwellings. In neighborhoods such as Delk, Belles, and Hapson Heights, large single-family homes are common in various architectural styles such as Tudor Revival and Victorian.
Stone and brick became the city's building materials of choice after the construction of wood-frame houses was limited in the aftermath of the 1919 Tofino Earthquake. A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the roof-mounted wooden water tower. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could break municipal water pipes. Garden apartments became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, such as Cascades.
Districts and neighborhoods
Main article: Neighborhoods in Tofino
Tofino has 63 specialized districts. The majority are residential priority neighborhoods, with others classified for industrial, environmental, and government purposes. 55 are incorporated, including 2 directly government affiliated (Congressional Park and Embassy Row), and another being Gaviria Park. The 55 incorporated districts are;
- Gaviria Park
- Congressional Park
- Embassy Row
- Armitage (Downtown)
- Jericho Basin (Downtown)
- Kitsilano (Downtown)
- Collingwood (Downtown)
- Donaldson (Downtown)
- Odessa (Downtown)
- Delk (Downtown)
- Kingston
- French Bay
- Belles
- Fraser
- Point Grey
- Douglass
- Surrey
- Oakridge
- Melali
- Sunset
- Gills Creek
- Holland Park
- Cascades
- Killarney
- Hemlock Heights
- North Coome
- South Coome
- Hapson Heights
- Kerrisdale
- Mackay
- Lynntown
- Belcarra
- Derby Ranch
- Little Anchorhead
- Peace Arch
- Tynehead
- Capilano
- Jayna
- Arbutus Ridge
- Colony Farm
- Anmore
- Pitt
- Barnston
- Prara
- Verodine
- Birtos
- Feracci
- Rersa Village
- Vanresa
- Leidon
- Bell
- Gibiville
- Guilbrook
- Rosgrave
- Applebury
As the diplomatic center of Zamastan, several foreign governments have embassies located in the city. Most are located in Embassy Row (Zamastan), a district neighborhood dedicated to ambassador residences and offices.
Parks
The City of Tofino has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the Zamastanian Federal Park Service, the Zian Provincial Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation, and the Tofino Department of Parks and Recreation. Most notable is Gaviria Park.
- Gaviria Park
- Washing Meadows
- The Bottleneck
- Archie Byrne Park
- Maple Fields
- Reuben Lane Park
- Lewis Ellis Park
- Kellen Park
- Mooney Park
- Paul Chandler Park
- Glenn Park
- Caleb Duncan Park
- Alaina Hicks Park
- Cook Park
- Goodname Park
- Higgins Park
- Madisyn Peterson Park
- Aaren Park
- Franky Warner Park
- Chelsea Hopkins Park
- Hugo Botelho Park
- Barnes Park
- Revolutionary Gardens
- Megan Booth Park
Military Installations
There are multiple military instillations in and around Tofino, including ZNB Tofino, ZAB Adam, and three air force bases; AFB Anderson, AFB Mann, and at Tofino International Airport with a contingent of aircraft.
Demographics
The metropolitan area referred to as Greater Tofino, with more than 22.4 million residents, is the most populous metropolitan area in the country, with its inclusion of Arinals across the bay. Tofino has been called a "city of neighborhoods". Each neighborhood in Tofino has a distinct character and ethnic mix. People of Yuaneze, Quetanan, and Skithan origins were historically the largest ethnic groups in the city, and elements of Skithan society and culture are still visible in some areas, particularly South Kingston and Donaldson. Germans are the next-largest European ethnic group in Tofino and were a leading force in the city's society and economy until the rise of anti-Gladysynthian sentiment with the outbreak of the First Danaska War. Today, east-Euronia and Drambenburg are the largest visible ethnic group in the city, with a diverse Yuan-speaking community, and several dialects, including Beleroskov and Jaginistan. Neighborhoods with distinct ethnic commercial areas include the Emmiriatown, Yuan Market, Little Cadair, Gladysynthiatown, and Lissathaville.
The wider metro area of Tofino, known as the Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area, is home to more than 55 million people, making it among the most populated areas in the world. The neighboring city of Arinals is the second-largest city in Zamastan and is located across Hapson Harbor and by the city's southern mainland connection. The city of Tirzah is classified as a suburb of Tofino, and is known as one of the wealthiest residential areas in the C.C.A.. Several billionaires, actors, politicians, and other celebrities have their residences or vacation homes here.
Race and ethnicity
The city's population in 2020 was 44% White (33.3% non-Hispanic White), 25.5% Black (23% non-Hispanic Black), 0.7% First Nations, and 12.7% Ausianan. Hispanics or Latinos of any race represented 28.6% of the population, while Ausianans constituted the fastest-growing segment of the city's population between 2010 and 2020; the non-Hispanic White population declined three percent, the smallest recorded decline in decades; and for the first time since the Parabocan War, the number of Black people declined over a decade. Throughout its history, Tofino has been a major port of entry for immigrants into Zamastan. More than 20 million Nortuan and Adulan immigrants were received between 1892 and 1924.
Approximately 37% of the city's population is foreign born, and more than half of all children are born to mothers who are immigrants as of 2013. In Tofino, no single country or region of origin dominates. The ten largest sources of foreign-born individuals in the city as of 2021 were Janapa, Ossinia, East Chanchajilla, Yuan, Haduastan, Qolaysia, Emmiria, Saint Croix and Bens, Kyti, and Constantio, while the Barangadeshi-born immigrant population has become one of the fastest growing in the city, counting over 94,000 by 2021.
Religion
The Tofino area is the 7th-most religious metropolis in Zamastan. Largely a result of Eastern Euronian missionary work and colonialism, Christianity is the largest religion as of 2014. Protestantism is the largest Christian denomination (33%), followed by Verdusan Catholicism (23%), and other Christians (3%). Evangelical Protestantism is the largest branch of Protestantism in the city (9%), followed by Mainline Protestantism (8%), while the converse is usually true for other cities and metropolitan areas. In Evangelicalism, Baptists are the largest group; in Mainline Protestantism, Reformed Protestants are the largest. The majority of historically Black churches are affiliated with the Baptist Convention and Progressive Baptist Convention. Orthodox Christians (mainstream and independent) were the largest Central Adulan Christian groups.
Judaism, with approximately 1.1 million adherents, more than half of whom live in Donaldson, is the second largest religion. The ethnoreligious population makes up 10.4% of the city and its religious demographic makes up 8%. The largest Jewish denominations are Orthodox, Haredi, and Conservative Judaism. Reform Jewish communities are prevalent through the area. Islam ranks the third largest religion in Tofino, with estimates ranging between 600,000 and 1,000,000 observers, including 7% of the city's public school children. These three largest groups are followed by Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Zoroastrianism, and a variety of other religions, as well as atheism. In 2014, 24% of Tofino residents self-identified with no organized religious affiliation; a little over 3% of Tofino residents were atheist.
Sexual orientation and gender identity
The Tofino metropolitan area is home to about 970,000 self-identifying gay and bisexual people, the largest in Zamastan and one of the world's largest. Same-sex marriages were legalized on June 4, 1979, three years before the national legalization in 1982. The annual Tofino Pride March (or gay pride parade) is one of the largest pride parade in the world, attracting tens of thousands of participants and millions of sidewalk spectators each June.
Education
Primary and secondary education
The Tofino Public Schools system, managed by the Tofino Department of Education, is the largest public school system in Zamastan, serving about 2.3 million students in more than 3,400 separate primary and secondary schools. The city's public school system includes eighteen specialized high schools to serve academically and artistically gifted students. The city government pays the Tirzah Public Schools to educate a very small, detached section of the city. The Tofino Charter School Center assists the setup of new charter schools. There are approximately 1,150 additional privately run secular and religious schools in the city.
Higher education and research
More than 1,200,000 students are enrolled in Tofino's more than 130 higher education institutions, the highest number of any city in the world, with more than half a million in the Tofino Public Universities and Colleges (TPUC) system alone as of 2020, including both degree and professional programs. Tofino has, on average, the best higher education institutions of any global city. The public TPUC system is one of the largest universities in the nation, comprising 28 institutions across all districts: senior colleges, community colleges, and other graduate/professional schools. The public Provincial University of Zian (PUZ) system includes campuses in Tofino, including: Downstate Health Sciences University, Fashion Institute of Technology, Maritime College, and the College of Optometry.
Tofino is home to such notable private universities as Kingston University, Hapson University, University of Tofino, Tofino Institute of Technology, Abell University, and Hevala University; several of these universities are ranked among the top universities in the world. The city also hosts other smaller private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions, such as: St. Peter's University, Delk College, Armitage College, The College of Mount Qira, Aikman School of Design, The Mayne School, Robinson Institute, Tofino Film Academy, and Lynntown College.
Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. Tofino has the most postgraduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in Zamastan. In 2020, there were 43,523 licensed physicians were practicing in Tofino. Major biomedical research institutions include Fraser Cancer Center, Oakridge University, TPUC Downstate Medical Center, Coome College of Medicine, Grouse Mountain School of Medicine, and Anmore Medical College.
Human Resources
Public health
The Tofino Health and Hospitals Organization (HHO) operates the public hospitals and clinics in Tofino. A public benefit corporation with Z$8.7 billion in annual revenues, HHO is the largest municipal healthcare system in the country serving 1.9 million patients, including more than 475,000 uninsured city residents. HHO was created in 1969 by the Zian Provincial Legislature as a public benefit corporation. HHO operates 11 acute care hospitals, five nursing homes, six diagnostic and treatment centers, and more than 70 community-based primary care sites, serving primarily the poor and working class. HHO's Health Plan is one of Zian area's largest providers of government-sponsored health insurance and is the plan of choice for nearly half million Tofino citizens. HHO's facilities annually provide millions of Tofino citizens services interpreted in more than 190 languages. The most well-known hospital in the HHO system is Karrisdale Hospital, the oldest public hospital in Zamastan. Karrisdale is the designated hospital for treatment of the President of Zamastan and other world leaders if they become sick or injured while in Tofino.
Public safety
The Fire Department of Tofino (FDT), provides fire protection, technical rescue, primary response to biological, chemical, and radioactive hazards, and emergency medical services for the districts. The FDT is the largest municipal fire department in the country and the second largest in the world. The FDT employs approximately 11,080 uniformed firefighters and more than 3,300 uniformed EMTs and paramedics. The fire department faces multifaceted firefighting challenges in many ways unique to Tofino. In addition to responding to building types that range from wood-frame single family homes to high-rise structures, the FDT also responds to fires that occur in the Tofino Subway. Secluded bridges and tunnels, as well as large parks and wooded areas that can give rise to brush fires, also present challenges.
The Tofino Metropolitan Police Department (TMPD) has been the largest police force in Zamastan by a significant margin, with more than 55,000 sworn officers.
Crime in Tofino is largely concentrated in areas associated with poverty, drug abuse, and gangs. A 2010 study found that 5% of city blocks accounted for over one-quarter of the city's total crime. The more affluent neighborhoods of Northwest Tofino are typically safe, especially in areas with concentrations of government operations, such as Downtown Tofino, Ironville, Embassy Row, and Jade Quarter, but reports of violent crime increase in poorer neighborhoods generally concentrated in the eastern portion of the city. Approximately 60,000 residents are ex-convicts. In 2012, Tofino's annual murder count had dropped to 88, the lowest total since 1961. The murder rate has since risen from that historic low, though it remains close to half the rate of the early 2000s. Tofino was once described as the "murder capital" of Zamastan during the early 1990s. The number of murders peaked in 1991 at 479, but the level of violence then began to decline significantly.
Organized crime has long been associated with Tofino, with the Duvall syndicate, one of the world's largest international criminal organizations known most prominently for drug smuggling, having significant influence in the city's black market, which is among the world's most lucrative. Additionally, other syndicates like the Zitassan Mafia, SHADOW, and San Beausoleil Mafia are active in the Zamastanian criminal underworld.
Government and politics
Government
Tofino has been a metropolitan municipality with a mayor–council form of government since its consolidation in 1828. In Tofino, the city government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services.
The Mayor and council members are elected to four-year terms. The City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each term for the mayor and council members lasts four years and has a three consecutive-term limit, which is reset after a four-year break.
Politics
The current mayor of Tofino is Sophie Webb-Lancaster, a member of the GLP elected on September 22nd, 2021. She replaced Bryan Donaldson, also a member of the GLP who was elected on September 22nd, 2017, but declined to run for a second term.
Economy
Culture
Festivals
Tofino is the site of many important and culturally significant conferences, festivals, and other events, including the Tofino Film Festival which hosts films from all over the C.C.A., the Tofino Intuition and Ideas Conference which is a media organization conference dedicated to scientific, cultural, and academic topics.
Cuisine
Tofino is home to many restaurants with hundreds of examples of global varieties of food. Zamastanian dishes such as steam-smoked fish (notably salmon and trout). Seafood is the most well known form of food in Tofino due to its proximity to the ocean and isolation thanks to the mountains. Signature sushi roll is done in many ways, but the one consistent ingredient is grilled savory and chewy salmon skin. Busy Tofinoites are often particular about their coffee, and love pour-overs and flavored espresso drinks. There are many cozy independent shops to be found who take their coffee very seriously. Local recommendations are to try soy or almond milk to replace traditional milk and cream at almost any place you find. spot prawn are pink creatures are large, sweet shrimp fished in the waters surrounding Tofino in the month of May. Most fine restaurants in Tofino serve fresh prawns when available.
Landmarks
Gaviria Park is a landscaped urban park in Tofino. It is located near the Congressional Hall grounds, the Zian Presidential Mansion, and is between the downtown neighborhood of Point Gray, Kingston, and the Horseshoe Bay. The term Gaviria Park commonly includes areas that are also officially part of neighboring Congressional Park to the east, as it continues a uniformed park display alongside unique and iconic architectural displays such as Congressional Hall and the Presidential Mansion. Named after President Marvin Gaviria in 1974, the park contains and borders a number of museums, art galleries, cultural institutions, and various memorials, sculptures, and statues. Much of the park remains as densely forested as it was in the late 1800s, with about a half million trees, some of which stand as tall as 76 metres (249 ft) and are hundreds of years old. Thousands of trees were lost (and many replanted) after three major windstorms that took place in the past 100 years. Significant effort was put into constructing the near three century old Tofino Seawall, which can draw thousands of people to the park in the summer. The park also features forest trails, beaches, lakes, children's play areas, and the Tofino Zoo and Aquarium, among many other attractions. The park receives approximately 24 million visitors each year.
The Zamastan National Archives houses thousands of documents important to Zamastanian history, including the the Constitution of Zamastan. Located in three buildings along the corridor of Gaviria Park, the library has a collection of over 147 million books, manuscripts, and other materials.
Libraries and museums
The Tofino Art Museum has a permanent collection of nearly 10,000 items. However, little or none of the permanent collection is ever on view. Downtown is also home to the Contemporary Art Gallery (Tofino), which showcases temporary exhibitions by up-and-coming Tofino artists.
In the Kingston district are the Tofino Maritime Museum, the Tauren Wells Space Center, and the Tofino Civic Museum, the largest civic museum in Zamastan. The Tofino Museum of Anthropology at University of Tofino is a leading museum of Catica First Nations culture, specifically that of the Kelownan peoples. A more interactive museum is Science World at the head of Jericho Bay. The city also features a diverse collection of Public Art. The most visited museum in the city is the Zamastan Museum of Natural History, and other notable museums and galleries are: the Zamastan Museum of Adulan Art; the National Museum of Zamastanian History; the Museum of the Catica First Nations; The Zamastan Gallery of Art features works of Zamastanian, Adulan, Ausianan, Nortuan, and Euronian art. There are many private art museums in the city, which house major collections and exhibits open to the public such as the Zamastan Museum of Women in the Arts.
Zoo
The Tofino Zoo and Aquarium is the largest zoo in Zamastan and one of the largest in the Coalition of Crown Albatross, holding over 4,000 species of animals.
Music and nightlife
Musical contributions from Tofino include performers of classical, folk and popular music. The Tofino Symphony Orchestra is the professional orchestra based in the city. The Tofino Opera is a major opera company in the city, and City Opera of Tofino is the city's professional chamber opera company. The city is home to a number of Zamastanian composers including Barton Sharman, James Polluck, and Madison Wareka.
Tofino has a vibrant nightlife scene, whether it be food and dining, or bars and nightclubs. Olivar Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment center, and neighborhood in the Collingwood downtown district along Olivar Street and Velmara Boulevard. Brightly lit by numerous billboards and advertisements, it stretches from West 13th to West 21st Streets, and is sometimes referred to as "the Crossroads of the World" and "the heart of the Capital". Olivar Square is one of the world's most visited tourist attractions, drawing an estimated 50 million visitors annually. Approximately 330,000 people pass through Olivar Square daily, many of them tourists, while over 460,000 pedestrians walk through Olivar Square on its busiest days. The Kingston Entertainment District has the city's highest concentration of bars and nightclubs with closing times of 3 am, in addition to various after-hours clubs open until late morning on weekends. The street can attract large crowds on weekends and is closed to traffic on such nights. Donaldson is also a popular area for nightlife with many upscale restaurants and nightclubs.
Sporting
The mild climate of the city and proximity to ocean, mountains, rivers and lakes make the area a popular destination for outdoor recreation. Tofino has over 1,298 hectares (3,210 acres) of parks, of which, Gaviria Park, at 404 hectares (1,000 acres), is the largest. The city has several large beaches, many adjacent to one another, extending from the shoreline of Gaviria Park around False Creek to the south side of French Bay, from Chinook Hill to the Government Endowment Lands, (which also has beaches that are not part of the city proper). The 18 kilometres (11 mi) of beaches include Second and Third Beaches in Gaviria Park, French Bay (First Beach), Sunset, Chinook Hill Beach, Jericho, Rausch, Meyer Banks, Meyer Banks Extension, Meyer Banks West, and Tannson Beach. There is also a freshwater beach at Trout Lake in Kordia Park. The coastline provides for many types of water sport, and the city is a popular destination for boating enthusiasts.
Within a 20- to 30-minute drive from downtown Tofino are the North Shore Mountains, with three ski areas: Egret Mountain, Grouse Mountain, and Mount Killiam. Mountain bikers have created world-renowned trails across the North Shore. The Blackfoot River, Abotsford Creek and Phelan River, also on the North Shore, provide opportunities to whitewater enthusiasts during periods of rain and spring melt, though the canyons of those rivers are more utilized for hiking and swimming than whitewater.
Running races include the Tofino Sun Run (a 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) race) every April; the Tofino Marathon, held every May; and the Elsuit Tofino Half-Marathon held every June. The Grouse Grind is a 2.9-kilometre (1.8 mi) climb up Grouse Mountain open throughout the summer and fall months, including the annual Grouse Grind Mountain Run. Hiking trails include the Stella-Chinook Trail, an arduous 42-kilometre-long (26 mi) hike from West Tofino's Tapico Bay to Deep Cove in the District of North Tofino. Tofino is also home to notable cycling races.
Tofino hosts teams from all of the Big 5 in Zamastan; the ZFL (Tofino Whitecaps), Zamastan Baseball League (Tofino Seals), Zamastan Soccer League (Tofino United FC), Zamastan Hockey League (Tofino Pelicans), and Zamastan Basketball Association (Tofino Mariners). The Football Teal Cup is held in Tofino every year as the final championship game in the league.
Tofino was the host city for the 1958 and 2004 Summer Olympics (and made a bid for the 2026 Games), the 1993 World Cup, and the 2000, 2004, 2005, and 2017 Euronia Games.
Additional venues that have multiple or non-permanent tenants include Suchet Barthél Stadium.
Current professional teams
Transportation
Rapid Transport
Mass transit in Tofino, most of which runs 24 hours a day, accounts for one in every four users of mass transit in Zamastan, and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in the Tofino-Arinals Metropolitan Area.
Rail

The Tofino Subway System is the largest rapid transit system in the world when measured by stations in operation, with 364, and by length of routes. Nearly all of Tofino's subway system is open 24 hours a day, in contrast to the overnight shutdown common to systems in most cities, including Cardiff, Ponamu, Lerbin, Shanghan, Vongane, and Skithiana. The Tofino Subway is also the busiest metropolitan rail transit system in the world, with 1.56 billion passenger rides in 2015, while William Castovia Central Terminal, also referred to as "Tofino Central Station", is the world's largest railway station by number of train platforms.
Buses
The Tofino Bus Terminal, the main intercity bus terminal of the city, serves 6,800 buses and 200,000 commuters daily.
Air
Ferries
Taxis and trams
Streets and highways
River crossings
Zian River
- Kingston Bridge; Kingston - Tirzah
- Fraser Bridge; Belles - Tirzah
- Brentwood Bridge; North Coome - Tirzah
- Mannal Bridge; North Coome - Tirzah
- Annes Bridge; Verodine - Ashwood
- Akaitcho Bridge; Verodine - Cannock
- Collough Bridge; Verodine - Cannock
- Thistlerock Bridge; Pitt - Cannock
- Muir Bridge; Arbutus Ridge - Cannock
- Theite Bridge; Arbutus Ridge - Cannock
Jericho Bay
Belcarra Inlet
- Graham Bridge; Derby Ranch - Seaforth
- Manning Bridge; Belcarra - Seaforth
- Orkney Bridge; Feracci - Nalton
- Tomias Hapson Bridge; Hapson Heights - Nalton
Gibi Creek
- Iskana-Porrier Bridge; Gibiville - Arinals
- Pickett Bridge; Colony Farm - Arinals
- Thoole Bridge; Arbutus Ridge - Arinals