Phaethon (Rocket): Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→Materials) |
||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
===Materials=== | ===Materials=== | ||
The rocket body is made of aluminium with some titanium reinforcement whereas the delta wing and tail are constructed of carbon composites. Ultralight aerospace-grade aluminium and carbon composites were chosen as thermal resistance is not needed for its mission profile; the rocket's mission and purpose is completed upon deployment. Phaethon may burn up upon re-entry. | The rocket body is made of aluminium with some titanium reinforcement whereas the delta wing and tail are constructed of carbon composites. Ultralight aerospace-grade aluminium and carbon composites were chosen as higher thermal resistance is not needed for its mission profile; the rocket's mission and purpose is completed upon deployment. Phaethon may burn up upon re-entry. | ||
The payload fairing was initially constructed of stainless steel cone but was later changed in favour of a graphene coated composite cone to further reduce mass. | |||
Titanium parts on Phaethon rockets consist of the vector-thrust nozzle and framework supports in the payload compartment. | |||
===Propulsion=== | ===Propulsion=== | ||
Revision as of 14:38, 14 November 2022
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Phaethon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Launch Vehicle (Air-launched to orbit) |
| Place of origin | Iverica |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2010-present |
| Used by | |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Suisa Special Projects Division, Astronomo Orbital Dynamics |
| Designed | 1999 |
| Manufacturer | Suisa Consildated Manufacturing |
| Produced | 2009-present |
| Variants | Phaethon XL |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 18,500 kg (40,800 lb) |
| Length | 16.9 m (55 ft) |
| Diameter | 1.27 m (50 in) |
| Wingspan | 6.7 m (22 ft) |
| Propellant | 3 stage; solid propellant, optional 4th stage monopropellant |
| Speed | exceeds 1,006.62 mph (1,620.00 km/h) (Supersonic+) |
Guidance system | Inertial Guidance System, GPS Receiver |
Launch platform | Fixed-wing aircraft Rotor-wing aircraft Ship-launched Vehicle-launched (mounted) |
| Transport | S-1011 Trestrell |
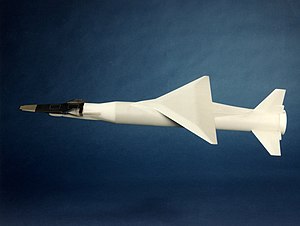
Phaethon is an air-launched launch vehicle developed by Suisa Special Project Devision and Astronomo Orbital Dynamics. It is currently operated by the Fuersas L'Aire and the Western Argis Aerospace Defence Command to launch Reconnaissance satellites. Phaethon was designed upon request of the Iverican Fuersas L'Aire; requiring a relatively expedient means of launching satellites on-demand to address Iverica's lack of larger rocket-launch capability.
Phaethon first flew in 2010 and remains active as of 2022. The vehicle consists of three solid propellant stages and an optional monopropellant fourth stage. Phaethon is released from its carrier aircraft at approximately 12,000 m (39,000 ft), and its first stage has a wing and a tail to provide lift and attitude control while in the atmosphere. Notably, the first stage does not have a thrust vector control (TVC) system.
The rocket can deploy small payloads of up to 443 kg (977 lb) into low Earth orbit though payloads have increased since the deployment of Phaethon XL. A variety of different satellites were developed since the success of its first launch. The rocket now also launches communications microsatellites and space-based radar microsatellites.
History
Design
Materials
The rocket body is made of aluminium with some titanium reinforcement whereas the delta wing and tail are constructed of carbon composites. Ultralight aerospace-grade aluminium and carbon composites were chosen as higher thermal resistance is not needed for its mission profile; the rocket's mission and purpose is completed upon deployment. Phaethon may burn up upon re-entry.
The payload fairing was initially constructed of stainless steel cone but was later changed in favour of a graphene coated composite cone to further reduce mass.
Titanium parts on Phaethon rockets consist of the vector-thrust nozzle and framework supports in the payload compartment.