Nuragara Province: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (-typos) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
The '''Nuragara Province''', otherwise known officially as the Nuragara Capital Province, is the most populous of the [[Mahanan]] provinces. It is bordered by the [[Nyandak Province|Nyandak]] and [[Thubten Province|Thubten]] provinces to the west, the [[Paranani Province]] to the south and the [[Sadheshi Province]] to the east. Nuragara has a population of an estimated 9.2 million as of 2020. | The '''Nuragara Province''', otherwise known officially as the Nuragara Capital Province, is the most populous of the [[Mahanan]] provinces. It is bordered by the [[Nyandak Province|Nyandak]] and [[Thubten Province|Thubten]] provinces to the west, the [[Paranani Province]] to the south and the [[Sadheshi Province]] to the east. Nuragara has a population of an estimated 9.2 million as of 2020. | ||
Nuragara is densely populated, containing both the capital city of [[Jutpandi]] | Nuragara is densely populated, containing both the capital city of [[Jutpandi]] and the large metropolitan city of [[Battagara]]. The geography of Nuragara is diverse, being amongst the largest provinces of Mahana, so it ranges from valleys in the south, along the footsteps of the [[Samripe Mountain Range|Samripes]], to lush forests in the central regions. | ||
A lot of Nuragara's population lives within the two major urban areas of [[Jutpandi]] and [[Battagara]], with the cities having a combined population of around 2,474,000. The rest of the diaspora is located around other large urban towns and villages. The two major cities of the province started as merchant and market cities, acting as holding points for the [[Pearl Road]] over a millennium ago. The important town of {{wp|Lumbini}} is located only 20 miles south of the border of the province however it was included in the historic borders of the province. | == Geography == | ||
The Nuragara province is bordered by the [[Nyandak Province|Nyandak]] and [[Thubten Province|Thubten]] provinces to the west, the [[Paranani Province]] to the south and the [[Sadheshi Province]] to the east. It is an average-sized province, around X km2 (X sq mi). | |||
A lot of Nuragara's population lives within the two major urban areas of [[Jutpandi]] and [[Battagara]], with the cities having a combined population of around 2,474,000. The rest of the diaspora is located around other large urban towns and villages. The two major cities of the province started as merchant and market cities, acting as holding points for the [[Pearl Road]] over a millennium ago. The important town of {{wp|Lumbini}} is located only 20 miles south of the border of the province, however it was included in the historic borders of the province. | |||
Within the north-eastern most points of the province, the most western points of the Sheshtri National Park lie. As well as this, a majority of the eastern portion of the province contains the [[Samripe Mountain Range]], with the peak of [[X92]] (7,445 m) within the borders. As well as this, the western and south-western portions of the province contain parts of the [[Careleon Plateau]], making the province one of the most geographically diverse. | Within the north-eastern most points of the province, the most western points of the Sheshtri National Park lie. As well as this, a majority of the eastern portion of the province contains the [[Samripe Mountain Range]], with the peak of [[X92]] (7,445 m) within the borders. As well as this, the western and south-western portions of the province contain parts of the [[Careleon Plateau]], making the province one of the most geographically diverse. | ||
The central and most populated parts of the region | The central and most populated parts of the region are temperate, stuck in between two climate extremes. The area of temperate land in the Nuragara Province particularly is of note due to its rarity, defined by the bedrock of Jurassic limestone that creates a type of grassland habitat. | ||
==History== | |||
Nuragara came into existence as a historic Kṣētra (Region) of the Kingdom of Mahana in the early 11th century. The first known reference to Nuragara was in 1004, as Nuruvāddaṭā, deriving from the name of the capital city at the time, [[Vaddkewatta]]. The suffix -nura is the genitive plural of the Old [[Mahanan]] word for | == History == | ||
Nuragara came into existence as a historic Kṣētra (Region) of the Kingdom of Mahana in the early 11th century. The first known reference to Nuragara was in 1004, as Nuruvāddaṭā, deriving from the name of the capital city at the time, [[Vaddkewatta]]. The suffix -nura is the genitive plural of the Old [[Mahanan]] word for “those that care for, watch, guard, protect, or defend.” It was also at this time that the Nuragara Province was the most important region of the [[Nadal Empire]]. Since unification the province has continued to exist, despite ideas during the 1950s to split the province in two between [[Jutpandi]] and [[Battagara]]. | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
==Transport== | ==Transport== | ||
| Line 79: | Line 84: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
{{Eurth}} | |||
[[Category:Mahana]] | [[Category:Mahana]] | ||
{{Region icon Eurth}} | |||
{{Country icon Mahana}} | |||
Latest revision as of 17:40, 10 April 2024
Nuragara Province | |
|---|---|
Capital Province of Mahana | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Jutpandi |
| Government | |
| • State Governor | Palash Piya (MC) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 8,334,230 |
| Demonym | Nuragaran |
| Time zone | UTC+8 |
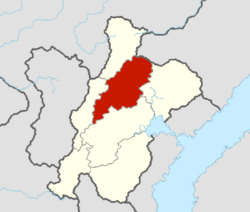
The Nuragara Province, otherwise known officially as the Nuragara Capital Province, is the most populous of the Mahanan provinces. It is bordered by the Nyandak and Thubten provinces to the west, the Paranani Province to the south and the Sadheshi Province to the east. Nuragara has a population of an estimated 9.2 million as of 2020.
Nuragara is densely populated, containing both the capital city of Jutpandi and the large metropolitan city of Battagara. The geography of Nuragara is diverse, being amongst the largest provinces of Mahana, so it ranges from valleys in the south, along the footsteps of the Samripes, to lush forests in the central regions.
Geography
The Nuragara province is bordered by the Nyandak and Thubten provinces to the west, the Paranani Province to the south and the Sadheshi Province to the east. It is an average-sized province, around X km2 (X sq mi).
A lot of Nuragara's population lives within the two major urban areas of Jutpandi and Battagara, with the cities having a combined population of around 2,474,000. The rest of the diaspora is located around other large urban towns and villages. The two major cities of the province started as merchant and market cities, acting as holding points for the Pearl Road over a millennium ago. The important town of Lumbini is located only 20 miles south of the border of the province, however it was included in the historic borders of the province.
Within the north-eastern most points of the province, the most western points of the Sheshtri National Park lie. As well as this, a majority of the eastern portion of the province contains the Samripe Mountain Range, with the peak of X92 (7,445 m) within the borders. As well as this, the western and south-western portions of the province contain parts of the Careleon Plateau, making the province one of the most geographically diverse.
The central and most populated parts of the region are temperate, stuck in between two climate extremes. The area of temperate land in the Nuragara Province particularly is of note due to its rarity, defined by the bedrock of Jurassic limestone that creates a type of grassland habitat.
History
Nuragara came into existence as a historic Kṣētra (Region) of the Kingdom of Mahana in the early 11th century. The first known reference to Nuragara was in 1004, as Nuruvāddaṭā, deriving from the name of the capital city at the time, Vaddkewatta. The suffix -nura is the genitive plural of the Old Mahanan word for “those that care for, watch, guard, protect, or defend.” It was also at this time that the Nuragara Province was the most important region of the Nadal Empire. Since unification the province has continued to exist, despite ideas during the 1950s to split the province in two between Jutpandi and Battagara.
Economy
Transport
Demographics
Culture
Cuisine
Language
References
