Fravina: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|capital = [[Port de Sang]] | |capital = [[Port de Sang]] | ||
|largest_city = [[Port de Sang]] | |largest_city = [[Port de Sang]] | ||
|official_languages = [[Lysian]] | |official_languages = [[Lysia|Lysian]] | ||
|national_languages = [[Fravi Language|Fravi]] | |national_languages = [[Fravi Language|Fravi]] | ||
|regional_languages = | |regional_languages = | ||
|ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | |ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | ||
| 93.3% White | | 93.3% White | ||
| -- 84.6% White [[Lysia|Lysian]] | |||
| -- 8.7% Other white | |||
| 2.9% Indigenous | |||
| 1.5% Black | | 1.5% Black | ||
| 1.2% Mixed Race | | 1.2% Mixed Race | ||
| Line 37: | Line 34: | ||
|religion = {{unbulleted list | |religion = {{unbulleted list | ||
| 52.7% No Religion | | 52.7% No Religion | ||
| 38.9% Christian | | 38.9% Christian | ||
| -- 33.3% [[Catholic Church (Eurth)|Catholic]] | | -- 33.3% [[Catholic Church (Eurth)|Catholic]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 46: | ||
Fravi (adjective) | Fravi (adjective) | ||
|government_type = {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}} | |government_type = {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = [[President of Fravina|President]] and [[ | |leader_title1 = [[President of Fravina|President]] and [[Premier of Fravina|Premier]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Bernard Beaumont]] | |leader_name1 = [[Bernard Beaumont]] | ||
|leader_title2 = [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]] | |leader_title2 = [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]] | ||
| Line 73: | Line 68: | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = | ||
|population_census = 37,654,800 | |population_census = 37,654,800 | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = 2021 estimate | ||
|population_density_km2 = 485.87 | |population_density_km2 = 485.87 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = 781.93 | |population_density_sq_mi = 781.93 | ||
|GDP_nominal = 434,829,346,344 | |GDP_nominal = $434,829,346,344 | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |GDP_nominal_year = 2021 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = 11,547.78 | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $11,547.78 | ||
|HDI = <!--(Human Development Index; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 1--> | |HDI = <!--(Human Development Index; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 1--> | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = | ||
| Line 90: | Line 85: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Fravina''' (Lysian: ''Fravina''), officially the '''Republic of Fravina''' (Lysian: ''République de Fravina'') is a nation located on [[Argis]] on [[Eurth]], bordered by [[Velaheria]] to the southwest, [[Delamaria]] to the southeast, and the [[Adlantic Ocean]] to the east. Made up of 37.6 million Fravs, | '''Fravina''' (Lysian: ''Fravina''), officially the '''Republic of Fravina''' (Lysian: ''République de Fravina'') is a nation located on [[Argis]] on [[Eurth]], bordered by [[Sanarija]] to the north, [[Velaheria]] to the southwest, [[Delamaria]] to the southeast, and the [[Adlantic Ocean]] to the east. Made up of 37.6 million Fravs, its population is primarily of [[Lysia|Lysian]] heritage. Colonies first were founded in the late 1400s to 1500s, by Europan powers, which often came into conflict with the indigenous [[Frav Empire]]. | ||
Fravina is a {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}}, with three separate branches of government and a {{wp|Bicameralism|bicameral legislature}}, called the [[People's Council of Fravina]]. The nation's executive branch is headed by the [[President of Fravina|president]] and four [[Vice President of Fravina|vice presidents]], known as the [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]]. The [[Worker's Coalition of Fravina|socialists]] have maintained power in Fravina since 1948, with other parties forming a token opposition. Fravina's capital and largest city is [[Port de Sang]]. | Fravina is a {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}}, with three separate branches of government and a {{wp|Bicameralism|bicameral legislature}}, called the [[People's Council of Fravina]]. The nation's executive branch is headed by the [[President of Fravina|president]] and four [[Vice President of Fravina|vice presidents]], known as the [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]]. The [[Worker's Coalition of Fravina|socialists]] have maintained power in Fravina since 1948, with other parties forming a token opposition. Fravina's capital and largest city is [[Port de Sang]]. | ||
| Line 100: | Line 95: | ||
===Indigenous peoples and pre-colonial era=== | ===Indigenous peoples and pre-colonial era=== | ||
The earliest known complex civilization in Fravina was the [[Iritina]], who lived in the southern regions of modern-day Fravina. While much of Iritina history is lost, historians know that the Iritina civilization flourished around 800 | The earliest known complex civilization in Fravina was the [[Iritina]], who lived in the southern regions of modern-day Fravina. While much of Iritina history is lost, historians know that the Iritina civilization flourished around 800 BCE with a culture and language distinct from surrounding civilizations. By 869 BCE, the city of [[Dikasa]] conquered other Iritina cities and formed the [[Iritina Empire]]. | ||
By approximately 780 | By approximately 780 BCE, Iritina collapsed from unknown reasons. Historians speculate that it may have fell from the migrating [[Alonisin]] tribes from the west, civil war, natural disasters, or any combination of the three. After that, Fravina was mainly composed of three groups: the Iritina, Alonisin, and [[Diadi]]. The three were constantly in conflict with each other and with themselves over resources. Around 270 CE, some of the [[Idaha]] tribes from the south, in modern-day [[Delamaria]], migrated to Fravina. The Idaha and Iritina were constantly at war, which led to the extinction of the Iritina people around 800 AD. | ||
Around 1400, four [[Frav People|Fravi]] [[Four Cities|cities]] along the [[Orléans River]] formed an alliance. This alliance, called the [[Frav Empire]], was headed by the city of [[Tesina]], modern-day [[Port de Sang]]. By the way of several conquests, the Frav Empire grew to encompass the Alonisin and Diadi people by around 1500. | Around 1400, four [[Frav People|Fravi]] [[Four Cities|cities]] along the [[Orléans River]] formed an alliance. This alliance, called the [[Frav Empire]], was headed by the city of [[Tesina]], modern-day [[Port de Sang]]. By the way of several conquests, the Frav Empire grew to encompass the Alonisin and Diadi people by around 1500. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 104: | ||
When Fravina was first discovered by [[Europa (region)|Europan]] explorers it was named [[Lysian Columbia]] by the [[Lysia]]n explorer [[Louis Boneparte]]. | When Fravina was first discovered by [[Europa (region)|Europan]] explorers it was named [[Lysian Columbia]] by the [[Lysia]]n explorer [[Louis Boneparte]]. | ||
Early colonizers were often in conflict with the Frav Empire, but by 1695, the Frav Empire fell to Lysian forces led by Admiral [[Louis Orléans]]. Colonizers occupied the Four Cities, renaming them [[Port de Sang|Port de Orléans]], [[Belleville]], [[Beaufort]], and [[Cour de Valentine]]. The three colonies of Fravina ([[Prétredy]], [[Orléans]] and [[d'Olivier]]) were used as penal colonies by Lysia. | Early colonizers were often in conflict with the Frav Empire, but by 1695, the Frav Empire fell to Lysian forces led by Admiral [[Louis Orléans]]. Colonizers occupied the Four Cities, renaming them [[Port de Sang|Port de Orléans]], [[Belleville (Fravina)|Belleville]], [[Beaufort]], and [[Cour de Valentine]]. The three colonies of Fravina ([[Prétredy]], [[Orléans]] and [[d'Olivier]]) were used as penal colonies by Lysia. | ||
Many settlers were inticed by a number of economic speculative bubbles such as the fur trade, exotic plant trade as well as the construction boom in the late 18th century. Major exports of early colonies were flowers, fur, vegetables native to the new world as well as tobacco. | Many settlers were inticed by a number of economic speculative bubbles such as the fur trade, exotic plant trade as well as the construction boom in the late 18th century. Major exports of early colonies were flowers, fur, vegetables native to the new world as well as tobacco. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 115: | ||
===Civil Wars=== | ===Civil Wars=== | ||
The [[First Civil War of Fravina]] (1896-1902) between the [[Indigenous Confederacy]], [[Fravi Socialists (First Civil War)|Fravi Socialists]], and the [[First Republic of Fravina]]. Beginning with the [[Proclamation of Indigenous Independence]] in October 1896, the war grew to include the Socialists when | The [[First Civil War of Fravina]] (1896-1902) between the [[Indigenous Confederacy]], [[Fravi Socialists (First Civil War)|Fravi Socialists]], and the [[First Republic of Fravina]]. Beginning with the [[Proclamation of Indigenous Independence]] in October 1896, the war grew to include the Socialists when Premier [[Pierre Antier]] began persecuting the group in an attempt to stop the Socialists from expressing support for the Indigenous Confederacy. Despite initial losses, the Republic won the war in 1902. | ||
In the post-war period, Fravina struggled to rebuild, facing an economic depression. [[Lewis M. Nichols]], a popular colonel who served in the Civil War, gained control of the Fravi government in the [[1907 Fravi coup d'etat]]. Popular in the north, he moved the nation's capital from the southern [[Port de Sang|Port de Orléans]] to the [[Fort d'Olivier]] | In the post-war period, Fravina struggled to rebuild, facing an economic depression. [[Lewis M. Nichols]], a popular colonel who served in the Civil War, gained control of the Fravi government in the [[1907 Fravi coup d'etat]]. Popular in the north, he moved the nation's capital from the southern [[Port de Sang|Port de Orléans]] to the northern city of [[Fort d'Olivier]]. Following Nichols's death in 1938, southern Lieutenant Colonel [[Jacques de Mercy]] and northern Brigadier General [[Joseph Peretti]] came into conflict over succession, leading to the [[Second Civil War of Fravina]]. Those for De Mercy were colloquially referred to as the [[Roses (Fravina)|''Roses'']], and were mainly composed of socialists and so-called [[Green Liberals (Fravina)|Green Liberals]]. Those for Peretti were colloquially referred to as the [[Irises (Fravina)|''Irises'']], and were mainly composed of fascists and so-called [[Blue Liberals (Fravina)|Blue Liberals]]. | ||
The mainly industrial core of the southern regions vastly contributed to their victory | The mainly industrial core of the southern regions vastly contributed to their victory. The war ended in late August 1948 when the Roses, led by now [[Grand General of the Army (Fravina)|Grand General]] de Mercy, won the [[Siege of Fort d'Olivier]] and executed Peretti. | ||
===Contemporary Fravina=== | ===Contemporary Fravina=== | ||
The [[Fravina|Second Republic of Fravina]] was formed on 15 October 1948, with Grand General | The [[Fravina|Second Republic of Fravina]] was formed on 15 October 1948, with Grand General Jacques de Mercy ruling as the first president. The de Mercy government, as well as the subsequent [[Nicolas Martin (Fravina)|Martin]], [[Lucien LaClaire|LaClaire]], and [[Joël Fraise|Fraise]] governments, were filled with corruption and often failed to improve the standard of living for many Fravs. | ||
De Mercy ruled through martial law for much of his administration, up until 1955. Following him as [[President of Fravina|president]] was [[Grand Admiral of the Navy (Fravina)|Grand Admiral]] [[Nicolas Martin (Fravina)|Nicolas Martin]], who introduced free elections to the nation. However, much of this progress stagnated throughout the 1970s as [[Lucien LaClaire]] and [[Joel Woodville]] held power. | De Mercy ruled through martial law for much of his administration, up until 1955. Following him as [[President of Fravina|president]] was [[Grand Admiral of the Navy (Fravina)|Grand Admiral]] [[Nicolas Martin (Fravina)|Nicolas Martin]], who introduced free elections to the nation. However, much of this progress stagnated throughout the 1970s as [[Lucien LaClaire]] and [[Joel Woodville]] held power. | ||
The late 1980s and 1990s saw an increase in the standard of living in Fravina. Poverty, corruption, and decline were all on a decline during these decades. This success was largely accredited to the reforms of Presidents [[Marie Boche]] and [[Pierre Blanchet]]. | The late 1980s and 1990s saw an increase in the standard of living in Fravina. Poverty, corruption, and decline were all on a decline during these decades. This success was largely accredited to the reforms of Presidents [[Marie Boche]] and [[Pierre Blanchet]] under an agenda called [[Grand Republicanism (Fravina)|Grand Republicanism]]. | ||
President [[Jean-Michel Garnier]] oversaw the most corrupt administration since | President [[Jean-Michel Garnier]] oversaw the most corrupt administration since Jacques de Mercy, leading to internal schisms within the ruling [[Worker's Coalition of Fravina|Worker's Coalition]]. This led to the coalition's defeat in the 2010 election, when it and the [[United Liberal Coalition of Fravina|United Liberal Coalition]] won an equal number of seats in the People's Council. No government was formed from 2011-2016, with the [[Wing of Examination of Fravina|Wing of Examination]] of the [[People's Council of Fravina|People's Council]] acting as a caretaker government. | ||
Current President and [[ | Current President and [[Premier of Fravina|Premier]] [[Bernard Beaumont]] took power on 1 January 2016, after winning a thin majority in the [[Wing of Legislation of Fravina|Wing of Legislation]]. To avoid a repeat of the 2011-2016 term, the nation passed the [[Seventh Amendment to the Second Constitution of Fravina|Seventh Amendment]], allowing coalitions to be renegotiated following such a tie. If no new coalition was formed by 1 January, then a repeat election would take place on the following weekend. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 143: | Line 138: | ||
==Politics and Government== | ==Politics and Government== | ||
Fravina is a {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}} with three separate branches of government and a {{wp|Bicameralism|bicameral legislature}}, called the [[People's Council of Fravina]]. The nation's head of state is the [[President of Fravina|president]] and its four [[Vice President of Fravina|vice presidents]], known as the [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]]. The head of government is the [[ | Fravina is a {{wp|Semi-direct democracy|semi-direct}} {{wp|Democracy|democratic}} {{wp|federal republic}} with three separate branches of government and a {{wp|Bicameralism|bicameral legislature}}, called the [[People's Council of Fravina]]. The nation's head of state is the [[President of Fravina|president]] and its four [[Vice President of Fravina|vice presidents]], known as the [[Vice Presidential Council of Fravina|Vice Presidential Council]]. The head of government is the [[Premier of Fravina|Premier]], however the positions of President and Premier are traditionally held by the same person. The [[President of Fravina|president]] heads the [[Grand Committee of Fravina|Grand Committee]], which is made up of the most important positions in the [[Central Committee of Fravina|Central Committee]]. Fravina's judicial branch is made up of a series of courts, with the [[Grand Court of Fravina|Grand Court]] acting as the highest court of appeals in Fravina. | ||
===Political Divisions=== | ===Political Divisions=== | ||
Fravina is composed of 7 provinces. Every province is | Fravina is composed of 7 provinces. Every province is headed by an independently elected [[Premier Councillor (Fravina)|premier councillor]]. Every province is entitled to 10 examiners. The largest province by land area is [[Olivier]], and the smallest is [[Orléans]]. | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Flag !! Name !! Capital !! [[ | ! Flag !! Name !! Capital !! [[Premier Councillor (Fravina)|Premier Councillor]] !! Population | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Barbier Flag.png|150px]] || [[Barbier]] || [[Port de Barbier]] || [[Camille LaClaire]] || 8,291,100 | | [[File:Barbier-Flag.png|150px]] || [[Barbier]] || [[Port de Barbier]] || [[Camille LaClaire]] || 8,291,100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Mechis Flag.png|150px]] || [[Mechis]] || [[Domesis]] || [[Charles Halle]] || 1,941,100 | | [[File:Mechis-Flag.png|150px]] || [[Mechis]] || [[Domesis]] || [[Charles Halle]] || 1,941,100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Mont de Mercy Flag.png|150px]] || [[Mont de Mercy]] || [[Mercycourt]] || [[Paula Castaner]] || 4,150,200 | | [[File:Mont de Mercy Flag.png|150px]] || [[Mont de Mercy]] || [[Mercycourt]] || [[Paula Castaner]] || 4,150,200 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File: | | [[File:Olivier-Flag.png|150px]] || [[Olivier]] || [[Fort d'Olivier]] || [[Emmanuel Olivier]] || 1,395,100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Orléans Flag.png|150px]] || [[Orléans]] || [[Beaufort]] || [[André LaGarde]] || 12,742,050 | | [[File:Orléans Flag.png|150px]] || [[Orléans]] || [[Beaufort]] || [[André LaGarde]] || 12,742,050 | ||
| Line 168: | Line 163: | ||
=== Political Parties and Elections === | === Political Parties and Elections === | ||
[[File: | [[File:Bernard-Beaumont.png|thumb|right|Bernard Beaumont, President and Premier of Fravina since 1 January 2016]] | ||
Legislative elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, and examination elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, with only half the seats up for election. These elections determine the seats of the People's Council, of which the majority coalition of the Wing of Legislation forms the government. The only time Fravina failed to form a government was following the 2010 election, which led Fravina to be without an executive until after the 2015 election. | Legislative elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, and examination elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, with only half the seats up for election. These elections determine the seats of the People's Council, of which the majority coalition of the Wing of Legislation forms the government. The only time Fravina failed to form a government was following the 2010 election, which led Fravina to be without an executive until after the 2015 election. | ||
| Line 174: | Line 169: | ||
In Fravina, there are two major political coalitions. The [[Worker's Coalition of Fravia|Worker's Coalition]] is a leftist coalition composed of the [[Socialist Party of Fravina|Socialist Party]] and the [[Social Labour Party of Fravina|Social Labour Party]]. The [[United Liberal Coalition of Fravina|United Liberal Coalition]] is a centrist coalition of the [[Green Party of Fravina|Green Party]], the [[Blue Party of Fravina|Blue Party]], and the [[Free Capitalist Party of Fravina|Free Capitalist Party]]. The [[National People's Party of Fravina|National People's Party]] is the only recognized national party that is not part of any major coalition. | In Fravina, there are two major political coalitions. The [[Worker's Coalition of Fravia|Worker's Coalition]] is a leftist coalition composed of the [[Socialist Party of Fravina|Socialist Party]] and the [[Social Labour Party of Fravina|Social Labour Party]]. The [[United Liberal Coalition of Fravina|United Liberal Coalition]] is a centrist coalition of the [[Green Party of Fravina|Green Party]], the [[Blue Party of Fravina|Blue Party]], and the [[Free Capitalist Party of Fravina|Free Capitalist Party]]. The [[National People's Party of Fravina|National People's Party]] is the only recognized national party that is not part of any major coalition. | ||
Social Labour [[Bernard Beaumont]], elected in 2015, is serving as [[President of Fravina|President]] and [[ | Social Labour [[Bernard Beaumont]], elected in 2015, is serving as the current [[President of Fravina|President]] and [[Premier of Fravina]]. The four vice presidents are [[Adelie Grasse]], [[Glacier Homard]], [[Louise Rochefort]], and [[Valentine LaClaire]], with [[Jean-Luc Émissaire]] serving as [[Vice Premier of Fravina|Vice Premier]]. Leadership of the Wing of Examination is the [[General Examiner of Fravina|General Examiner]] Antoine Cartier. Leadership of the Wing of Legislation is the [[Speaker of the Legislation of Fravina|Speaker of the Legislation]] Ella Lambert. | ||
In the [[15th People's Council of Fravina]], the Wing of Legislation is controlled by the Worker's Coalition. The Wing of Examination has been without a majority since 1 January 2011, with a plurality controlled by the Worker's Coalition since 1 January 2016. | In the [[15th People's Council of Fravina]], the Wing of Legislation is controlled by the Worker's Coalition. The Wing of Examination has been without a majority since 1 January 2011, with a plurality controlled by the Worker's Coalition since 1 January 2016. | ||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
The [[Fravina | The [[Rose Forces of Fravina]] (''Forces Rose de Fravina'') are the military and paramilitary forces of Fravina, under the [[President of Fravina]] as Grand Chief. They consist of the [[Army of Fravina]] (''Armée de Fravina''), the [[Navy of Fravina]] (''Marine de Fravi''), and the [[Air Force of Fravina]] (''Force Aérienne de Fravina''). The Rose Forces are operated and maintained by the [[Department of Defense and War of Fravina|Department of Defense and War]]. The [[Civilian Army of Fravina|Civilian Army]] is an emergency police force in Fravina and is often mistaken as a part of the Rose Forces. The Civilian Army is operated by the [[Department of Safety and Stability of Fravina|Department of Safety and Stability]]. | ||
===Intelligence=== | |||
* [[Department of Documentation of Fravina|Department of Documentation]] — Civilian intelligence, foreign intelligence, intelligence gathering and analysis. | |||
* [[Ministry of Goats of Fravina|Ministry of Goats]] — Civilian intelligence, financial intelligence, special law enforcement. Reports to the [[Department of Safety and Stability of Fravina|Department of Safety and Stability]]. | |||
* [[Ministry of Internal Investigation of Fravina|Ministry of Internal Investigation]] — Civilian intelligence, criminal intelligence, counter domestic terrorism. Reports to the [[Department of Safety and Stability of Fravina|Department of Safety and Stability]]. | |||
* [[Ministry of Military Intelligence of Fravina|Ministry of Military Intelligence]] — Military intelligence. Reports to the [[Department of Defense and War of Fravina|Department of Defense and War]]. | |||
* [[Office for Worker Oversight of Fravina|Office for Worker Oversight]] — Worker intelligence, financial intelligence. Reports to the [[Ministry of Labour of Fravina|Ministry of Labour]] and [[Department of Industry of Fravina|Department of Industry]]. | |||
===Foreign Relations=== | ===Foreign Relations=== | ||
| Line 185: | Line 188: | ||
Fravina maintains good relations with many nations. It maintains a foreign policy largely interested in southeastern [[Argis]], with relations outside the region mostly maintained for its own safety and stability. | Fravina maintains good relations with many nations. It maintains a foreign policy largely interested in southeastern [[Argis]], with relations outside the region mostly maintained for its own safety and stability. | ||
Fravina is a member of the [[International Communist Economic Bloc]] and the [[Argic-Thalassan-Alharun Regional Association]]. | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| Line 207: | Line 212: | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
====Music and | ===Literature=== | ||
===Music=== | |||
Music has a long history in Fravina, stretching back to its colonial era under [[Lysia]]. For a large part of Fravi history, string quartets and quintets were popular among common people while [[Europa|Europan]] style orchestras and operas were more popular among the upper classes. | |||
When radios became common in Fravi households during the 1920s and 1930s, the government decided to broadcast stage musicals to keep the populace happy. When the [[Second Civil War of Fravina|Second Civil War]] broke out, both sides continued to broadcast stage musicals, as well as propagandistic songs, to raise morale. Jazz became a popular fixture on [[Fravi Roses|Rose]]-run radio, eventually becoming the predominant genre of music in Fravina. | |||
Jazz continues to be the most popular genre of music, while classical string quartets and quintets have made a return to popularity during the 1980s. Popular genres outside Fravina normally do not reach the same level of popularity inside Fravina. Genres such as rock and roll and electronic music only became popular in Fravi society during the 2010s. | |||
The government continues to broadcast stage musicals on radio and television, often drawing large numbers of viewers and listeners. | |||
===Live Theatre=== | |||
Besides television, live theatre is the most popular form of scripted entertainment in Fravina. Musical theatre remains especially popular in Fravina, especially in older generations. This is due mostly to live televisation of prominent theatre productions and the relatively cheap price of a theatre ticket compared to a cinema ticket. | |||
Fravina's biggest theatre district is located in [[Pont Noir]], [[Port de Sang]]. | |||
===Television and Cinema=== | |||
===Cuisine=== | |||
=== | ===Sports=== | ||
Fravina's most popular sport is table tennis, which is often played in doubles. Volleyball and basketball are also popular, but not to the extent of table tennis. Every school in Fravina is mandated to have a table tennis program, and table tennis matches attract the most viewers of any sport in Fravina. | |||
Due to the influence of football superstar [[Jules Pavard]] in the early 2010s, association football has risen to become a major sport in Fravina during international competitions, but continues to struggle in popularity outside of the national team. | |||
{{Eurth}} | {{Eurth}} | ||
{{Fravina}} | {{Fravina}} | ||
[[Category:Fravina]] | [[Category:Fravina]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 10 October 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Fravina République de Fravina | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Fort Comme Un Strong as One | |
| Anthem: "La Varsovienne" | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Port de Sang |
| Official languages | Lysian |
| Recognised national languages | Fravi |
| Ethnic groups (2019) |
|
| Religion (2019) | |
| Demonym(s) | Frav (singular)
Fravs (plural) Fravi (adjective) |
| Government | semi-direct democratic federal republic |
| Bernard Beaumont | |
| Adelie Grasse Glacier Homard Valentine LaClaire Louise Rochefort | |
| Jean-Luc Émissaire | |
| Legislature | People's Council |
| Wing of Examination | |
| Wing of Legislation | |
• Independence from Lysia | 8 July 1778 |
• Treaty of Labrador | 8 December 1809 |
• First Constitution of Fravina | 24 April 1810 |
• Second Constitution of Fravina | 16 June 1949 |
| Area | |
• Total | 48,156 sq mi (124,720 km2) |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate census | 37,654,800 |
• Density | 485.87/km2 (1,258.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | $434,829,346,344 |
• Per capita | $11,547.78 |
| Currency | aure (Ā) (AFV) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (UTC) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +48 |
| Internet TLD | .fv |
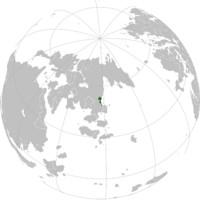
Fravina (Lysian: Fravina), officially the Republic of Fravina (Lysian: République de Fravina) is a nation located on Argis on Eurth, bordered by Sanarija to the north, Velaheria to the southwest, Delamaria to the southeast, and the Adlantic Ocean to the east. Made up of 37.6 million Fravs, its population is primarily of Lysian heritage. Colonies first were founded in the late 1400s to 1500s, by Europan powers, which often came into conflict with the indigenous Frav Empire.
Fravina is a semi-direct democratic federal republic, with three separate branches of government and a bicameral legislature, called the People's Council of Fravina. The nation's executive branch is headed by the president and four vice presidents, known as the Vice Presidential Council. The socialists have maintained power in Fravina since 1948, with other parties forming a token opposition. Fravina's capital and largest city is Port de Sang.
Etymology
Originally applied to a smaller portion of the current territory, the name Fravina comes from an endonym meaning "people of the river". The earliest linguistic evidence points to tribal origins of the name Fravina. It is derived by combining the indigenous Frav people and the Frav word ina meaning river. The actual river of this name refers to the Orléans River.
History
Indigenous peoples and pre-colonial era
The earliest known complex civilization in Fravina was the Iritina, who lived in the southern regions of modern-day Fravina. While much of Iritina history is lost, historians know that the Iritina civilization flourished around 800 BCE with a culture and language distinct from surrounding civilizations. By 869 BCE, the city of Dikasa conquered other Iritina cities and formed the Iritina Empire.
By approximately 780 BCE, Iritina collapsed from unknown reasons. Historians speculate that it may have fell from the migrating Alonisin tribes from the west, civil war, natural disasters, or any combination of the three. After that, Fravina was mainly composed of three groups: the Iritina, Alonisin, and Diadi. The three were constantly in conflict with each other and with themselves over resources. Around 270 CE, some of the Idaha tribes from the south, in modern-day Delamaria, migrated to Fravina. The Idaha and Iritina were constantly at war, which led to the extinction of the Iritina people around 800 AD.
Around 1400, four Fravi cities along the Orléans River formed an alliance. This alliance, called the Frav Empire, was headed by the city of Tesina, modern-day Port de Sang. By the way of several conquests, the Frav Empire grew to encompass the Alonisin and Diadi people by around 1500.
Lysian colonization
When Fravina was first discovered by Europan explorers it was named Lysian Columbia by the Lysian explorer Louis Boneparte.
Early colonizers were often in conflict with the Frav Empire, but by 1695, the Frav Empire fell to Lysian forces led by Admiral Louis Orléans. Colonizers occupied the Four Cities, renaming them Port de Orléans, Belleville, Beaufort, and Cour de Valentine. The three colonies of Fravina (Prétredy, Orléans and d'Olivier) were used as penal colonies by Lysia.
Many settlers were inticed by a number of economic speculative bubbles such as the fur trade, exotic plant trade as well as the construction boom in the late 18th century. Major exports of early colonies were flowers, fur, vegetables native to the new world as well as tobacco.
Lysian Columbia
The three colonies of Fravina declared independence from Lysia in 1778, and became a part of Lysian Columbia. Rising internal tensions caused the Oaktree Revolution against Columbia during the Delamarian War of 1804. The Oaktrees sought independence from Lysian Columbia, which was granted in 1809 by the Treaty of Labrador.
First Republic
The First Republic of Fravina had collected a large debt during the Delamarian War that it struggled to pay off. The debt continued to increase during the Fravina Shipping Crisis of 1833, the Native Fravi Rebellions, and the Fravina Labour Strikes of the 1880s. By the late 1800s, Fravina suffered from corruption.
Civil Wars
The First Civil War of Fravina (1896-1902) between the Indigenous Confederacy, Fravi Socialists, and the First Republic of Fravina. Beginning with the Proclamation of Indigenous Independence in October 1896, the war grew to include the Socialists when Premier Pierre Antier began persecuting the group in an attempt to stop the Socialists from expressing support for the Indigenous Confederacy. Despite initial losses, the Republic won the war in 1902.
In the post-war period, Fravina struggled to rebuild, facing an economic depression. Lewis M. Nichols, a popular colonel who served in the Civil War, gained control of the Fravi government in the 1907 Fravi coup d'etat. Popular in the north, he moved the nation's capital from the southern Port de Orléans to the northern city of Fort d'Olivier. Following Nichols's death in 1938, southern Lieutenant Colonel Jacques de Mercy and northern Brigadier General Joseph Peretti came into conflict over succession, leading to the Second Civil War of Fravina. Those for De Mercy were colloquially referred to as the Roses, and were mainly composed of socialists and so-called Green Liberals. Those for Peretti were colloquially referred to as the Irises, and were mainly composed of fascists and so-called Blue Liberals.
The mainly industrial core of the southern regions vastly contributed to their victory. The war ended in late August 1948 when the Roses, led by now Grand General de Mercy, won the Siege of Fort d'Olivier and executed Peretti.
Contemporary Fravina
The Second Republic of Fravina was formed on 15 October 1948, with Grand General Jacques de Mercy ruling as the first president. The de Mercy government, as well as the subsequent Martin, LaClaire, and Fraise governments, were filled with corruption and often failed to improve the standard of living for many Fravs.
De Mercy ruled through martial law for much of his administration, up until 1955. Following him as president was Grand Admiral Nicolas Martin, who introduced free elections to the nation. However, much of this progress stagnated throughout the 1970s as Lucien LaClaire and Joel Woodville held power.
The late 1980s and 1990s saw an increase in the standard of living in Fravina. Poverty, corruption, and decline were all on a decline during these decades. This success was largely accredited to the reforms of Presidents Marie Boche and Pierre Blanchet under an agenda called Grand Republicanism.
President Jean-Michel Garnier oversaw the most corrupt administration since Jacques de Mercy, leading to internal schisms within the ruling Worker's Coalition. This led to the coalition's defeat in the 2010 election, when it and the United Liberal Coalition won an equal number of seats in the People's Council. No government was formed from 2011-2016, with the Wing of Examination of the People's Council acting as a caretaker government.
Current President and Premier Bernard Beaumont took power on 1 January 2016, after winning a thin majority in the Wing of Legislation. To avoid a repeat of the 2011-2016 term, the nation passed the Seventh Amendment, allowing coalitions to be renegotiated following such a tie. If no new coalition was formed by 1 January, then a repeat election would take place on the following weekend.
Geography
Fravina is mostly hilly and mountainous in some parts.
Port de Sang is the capital and largest city. Other major cities are Fort d'Olivier, Port de Barbier, Belleville, and Beaufort.
Politics and Government
Fravina is a semi-direct democratic federal republic with three separate branches of government and a bicameral legislature, called the People's Council of Fravina. The nation's head of state is the president and its four vice presidents, known as the Vice Presidential Council. The head of government is the Premier, however the positions of President and Premier are traditionally held by the same person. The president heads the Grand Committee, which is made up of the most important positions in the Central Committee. Fravina's judicial branch is made up of a series of courts, with the Grand Court acting as the highest court of appeals in Fravina.
Political Divisions
Fravina is composed of 7 provinces. Every province is headed by an independently elected premier councillor. Every province is entitled to 10 examiners. The largest province by land area is Olivier, and the smallest is Orléans.
| Flag | Name | Capital | Premier Councillor | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Barbier | Port de Barbier | Camille LaClaire | 8,291,100 |
 |
Mechis | Domesis | Charles Halle | 1,941,100 |
 |
Mont de Mercy | Mercycourt | Paula Castaner | 4,150,200 |
 |
Olivier | Fort d'Olivier | Emmanuel Olivier | 1,395,100 |
 |
Orléans | Beaufort | André LaGarde | 12,742,050 |
 |
Prétredy | Nouveau-Séminaire | Jean Pearson | 4,862,000 |
 |
Romarin | Naufrage | Helene Capitaine | 4,273,250 |
Political Parties and Elections
Legislative elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, and examination elections are held every 5 years on the first weekend of December, with only half the seats up for election. These elections determine the seats of the People's Council, of which the majority coalition of the Wing of Legislation forms the government. The only time Fravina failed to form a government was following the 2010 election, which led Fravina to be without an executive until after the 2015 election.
In Fravina, there are two major political coalitions. The Worker's Coalition is a leftist coalition composed of the Socialist Party and the Social Labour Party. The United Liberal Coalition is a centrist coalition of the Green Party, the Blue Party, and the Free Capitalist Party. The National People's Party is the only recognized national party that is not part of any major coalition.
Social Labour Bernard Beaumont, elected in 2015, is serving as the current President and Premier of Fravina. The four vice presidents are Adelie Grasse, Glacier Homard, Louise Rochefort, and Valentine LaClaire, with Jean-Luc Émissaire serving as Vice Premier. Leadership of the Wing of Examination is the General Examiner Antoine Cartier. Leadership of the Wing of Legislation is the Speaker of the Legislation Ella Lambert.
In the 15th People's Council of Fravina, the Wing of Legislation is controlled by the Worker's Coalition. The Wing of Examination has been without a majority since 1 January 2011, with a plurality controlled by the Worker's Coalition since 1 January 2016.
Military
The Rose Forces of Fravina (Forces Rose de Fravina) are the military and paramilitary forces of Fravina, under the President of Fravina as Grand Chief. They consist of the Army of Fravina (Armée de Fravina), the Navy of Fravina (Marine de Fravi), and the Air Force of Fravina (Force Aérienne de Fravina). The Rose Forces are operated and maintained by the Department of Defense and War. The Civilian Army is an emergency police force in Fravina and is often mistaken as a part of the Rose Forces. The Civilian Army is operated by the Department of Safety and Stability.
Intelligence
- Department of Documentation — Civilian intelligence, foreign intelligence, intelligence gathering and analysis.
- Ministry of Goats — Civilian intelligence, financial intelligence, special law enforcement. Reports to the Department of Safety and Stability.
- Ministry of Internal Investigation — Civilian intelligence, criminal intelligence, counter domestic terrorism. Reports to the Department of Safety and Stability.
- Ministry of Military Intelligence — Military intelligence. Reports to the Department of Defense and War.
- Office for Worker Oversight — Worker intelligence, financial intelligence. Reports to the Ministry of Labour and Department of Industry.
Foreign Relations
Fravina maintains good relations with many nations. It maintains a foreign policy largely interested in southeastern Argis, with relations outside the region mostly maintained for its own safety and stability.
Fravina is a member of the International Communist Economic Bloc and the Argic-Thalassan-Alharun Regional Association.
Economy
Energy
Industry
Infrastructure
Transport
Demographics
Ethnic Groups
Education
As of 2017, Fravina has a simple literacy rate of 98.8% and a functional literacy rate of 93.3%
Religion
Culture
Literature
Music
Music has a long history in Fravina, stretching back to its colonial era under Lysia. For a large part of Fravi history, string quartets and quintets were popular among common people while Europan style orchestras and operas were more popular among the upper classes.
When radios became common in Fravi households during the 1920s and 1930s, the government decided to broadcast stage musicals to keep the populace happy. When the Second Civil War broke out, both sides continued to broadcast stage musicals, as well as propagandistic songs, to raise morale. Jazz became a popular fixture on Rose-run radio, eventually becoming the predominant genre of music in Fravina.
Jazz continues to be the most popular genre of music, while classical string quartets and quintets have made a return to popularity during the 1980s. Popular genres outside Fravina normally do not reach the same level of popularity inside Fravina. Genres such as rock and roll and electronic music only became popular in Fravi society during the 2010s.
The government continues to broadcast stage musicals on radio and television, often drawing large numbers of viewers and listeners.
Live Theatre
Besides television, live theatre is the most popular form of scripted entertainment in Fravina. Musical theatre remains especially popular in Fravina, especially in older generations. This is due mostly to live televisation of prominent theatre productions and the relatively cheap price of a theatre ticket compared to a cinema ticket.
Fravina's biggest theatre district is located in Pont Noir, Port de Sang.
Television and Cinema
Cuisine
Sports
Fravina's most popular sport is table tennis, which is often played in doubles. Volleyball and basketball are also popular, but not to the extent of table tennis. Every school in Fravina is mandated to have a table tennis program, and table tennis matches attract the most viewers of any sport in Fravina.
Due to the influence of football superstar Jules Pavard in the early 2010s, association football has risen to become a major sport in Fravina during international competitions, but continues to struggle in popularity outside of the national team.


