Ionio: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Tag: Manual revert |
||
| (87 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|other_symbol_type = <!--Use if a further symbol exists, e.g. hymn--> | |other_symbol_type = <!--Use if a further symbol exists, e.g. hymn--> | ||
|other_symbol = | |other_symbol = | ||
|image_map = <!--e.g. LocationCountry.svg--> | |image_map = <!--e.g. LocationCountry.svg--> Ionio Map City.png | ||
|loctext = <!--text description of location of country--> | |loctext = <!--text description of location of country--> | ||
|alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | |alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | |area = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | ||
|area_km2 = <!--Major area size (in square km)--> | |area_km2 = <!--Major area size (in square km)--> 314,212 | ||
|area_sq_mi = <!--Area in square mi (requires area_km2)--> 98,764 | |area_sq_mi = <!--Area in square mi (requires area_km2)--> 98,764 | ||
|area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | |area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
|area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | |area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | ||
|area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | |area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | ||
|population_estimate = | |population_estimate = 30,768,932 | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = 2022 | |population_estimate_year = 2022 | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 97.9 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = 271.03 | |population_density_sq_mi = 271.03 | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = | |GDP_nominal = 546,730,395,348 | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2022 | |GDP_nominal_year = 2022 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = 17,769 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = <!--(Gini measure of income inequality; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 100)--> | |Gini = <!--(Gini measure of income inequality; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 100)--> | ||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
|HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | |HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | ||
|currency = | |currency = Auro (𐠓) <!--Name/s of currency/ies used in country/territory--> | ||
|currency_code = IOL <!--ISO 4217 code/s for currency/ies (each usually three capital letters)--> | |currency_code = IOL <!--ISO 4217 code/s for currency/ies (each usually three capital letters)--> | ||
|time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> UTC - | |time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> UTC -05:00 | ||
|utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | |utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | ||
|time_zone_DST = <!--Link to DST (Daylight Saving Time) used, otherwise leave empty--> | |time_zone_DST = <!--Link to DST (Daylight Saving Time) used, otherwise leave empty--> | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
|electricity = <!--e.g. "230 V–50 Hz"--> | |electricity = <!--e.g. "230 V–50 Hz"--> | ||
|drives_on = Right <!--"right" or "left" (side of road)--> | |drives_on = Right <!--"right" or "left" (side of road)--> | ||
|cctld = <!--Internet country code top-level domain identifier (e.g. [[.br]], [[.de]], etc)--> . | |cctld = <!--Internet country code top-level domain identifier (e.g. [[.br]], [[.de]], etc)--> .ni | ||
|iso3166code = <!--ISO code only; no extra text. Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> ION | |iso3166code = <!--ISO code only; no extra text. Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> ION | ||
|calling_code = <!--e.g. [[+1]], [[+531]], [[+44]], etc--> +69 | |calling_code = <!--e.g. [[+1]], [[+531]], [[+44]], etc--> +69 | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Ionio''' ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:IPA/Italian [ˈjɔːnjo]]] <small>([[File:1200px-Speaker Icon.svg.png|17px]] [https://translate.google.com/?sl=it&tl=en&text=%CB%88j%C9%94%CB%90njo&op=translate listen italian])</small> ), officially the '''Federal Republic of Ionio''' ({{wp|Italian language|Cristinese}}: ''Repubblica federale di Ionio''), is a sovereign state in [[Aurelia]] on [[Eurth]]. Ionio bordered to the east by [[ | '''Ionio''' ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Help:IPA/Italian [ˈjɔːnjo]]] <small>([[File:1200px-Speaker Icon.svg.png|17px]] [https://translate.google.com/?sl=it&tl=en&text=%CB%88j%C9%94%CB%90njo&op=translate listen italian])</small> ), officially the '''Federal Republic of Ionio''' ({{wp|Italian language|Cristinese}}: ''Repubblica federale di Ionio''), is a sovereign state in [[Aurelia]] on [[Eurth]]. Ionio bordered to the nord by [[Advocatius]] and to the east by [[Heartfilia]] | ||
==Geography and environment== | ==Geography and environment== | ||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
===Geography and Climate=== | ===Geography and Climate=== | ||
[[File:Murge Castel del Monte.jpg|100px|thumb|right|Ionian hinterland]] | |||
TBA | TBA | ||
| Line 156: | Line 157: | ||
===Pre-colonial history=== | ===Pre-colonial history=== | ||
[[File:SantaAnaCave.JPG|200px|thumb| | [[File:SantaAnaCave.JPG|200px|thumb|left|Archaeological excavations of an ancient tomb dating back to the [[Tengrol Empire]].]] | ||
Little is known about the prehistoric Ionio. Some archaeological finds have shown human presence about 40,000 years BCE. It is assumed that these humans were hunter-gatherers and lived in small communities. | Little is known about the prehistoric Ionio. Some archaeological finds have shown human presence about 40,000 years BCE. It is assumed that these humans were hunter-gatherers and lived in small communities. | ||
| Line 164: | Line 165: | ||
===Colonial period=== | ===Colonial period=== | ||
[[File:Canaletto - De ingang van het Canal Grande bij de Punta della Dogana en de Santa Maria della Salute.jpg | [[File:Canaletto - De ingang van het Canal Grande bij de Punta della Dogana en de Santa Maria della Salute.jpg|thumb|right|The city of [[Sibari]] in 1630.]] | ||
In 700 [[Aroma]]n colonists (specifically, Arakhóran) arrived from the [[Aurelian Empire]] which in the present day corresponds to [[Kirvina]]. They founded the coastal trading cities of [[Sibarha]] (Σιβαρά), [[Tarassa]] (Ταραccα), and [[Miróia]] (Μιρόια). They maintained a presence as part of the [[Aurelian Empire]]'s eastern provinces. With the presence of the Aroman settlers were imported knowledge of mathematics, metalworking, architecture, science along with the breeding of cattle, pigs, horses and different plants for agriculture. | |||
By 1200s CE, their influence began to recede, and they were conquered by local tribes. These tribes founded the Kingdom of Ionio, a ‘melting pot’ state on their former location. With the formation of this kingdom begins a slow process of integration between the tribal cultures and the culture of the colonies of the Aurelian Empire. The period of maximum expansion of the kingdom dates back to about 1323 - 1443 where this kingdom had an intense economic and social activity. | |||
The duration of this reign lasted until 1500, when Ionio went through a period of rapid economic decline. Because of its mostly isolationist policy, this led to a collapse of civilization. The remaining city-states were weak and constantly at war with each other. These continuous struggles have provoked a weakening of the various city states becoming prey for future colonizers. | |||
In 1518 the first settlers from [[Gotneska]] arrived and founded the city of [[Torre dell' Orso]] and began to establish a colonial empire north of Ionio. In the city lies the tomb of the explorer [[James Clarke]] who died after discovering Ionio. During colonization, goutian culture such as rugby was imported, which would later evolve into {{wp|Gridiron football|Calcio a Griglia}}. | |||
In 1520 came the explorer mantellan [[Marco Caboto]] who landed on the coasts of Ionian but which were uninhabited. When he returned to his homeland I indicated the presence of uninhabited lands that can be colonized. Then an expedition for the colonization of these new lands started and on July 4, 1520 the first settlers arrived and the mantellan colonization of Ionio begins. | |||
The exploration began and the settlers met the indigenous peoples and the various city states that were at war with each other. Mantellan's army took advantage of this situation to gain as much ground as possible. The war with the local population took place until 1550 but in 1540 the expansionist aims of mantle were concentrated in the north of the Ionian and declared war on the colonial empire of Gotneska which lasted until 1550 with the peace treaty that sanctioned the victory of Mantella but had to respect the colonies of Gotneska that were present in the North Ionio. | |||
During this period the colonizers imposed the culture and religion of Mantellan. This process encountered many obstacles but during the seventeenth century the Cristinese language became the language that everyone spoke and the official religion was Christian Apostolic. The times of the various earlier cultures were converted into basilicas and churches. This process was sped up as the mantellan government sent experts in culture, architecture, scientists to Ionium to educate people about the new culture. The cities underwent a process of restructuring by adding Renaissance and Baroque elements. Although this process characterized the main culture of Ionian, the management of the colony by Mantellan and the various policies adopted by the various governors was increasing the discontent of the population. | |||
During the eighteenth century the ideas of the {{wp|Enlightenment}} arrived in Ionio and began to spread quickly among the high local population. The philosophy of the Enlightenment is considered the catalyst of the Ionian War of Independence as the population was unhappy with the new taxes that the governor [[Antonio De Santis]] had applied. | |||
===Revolution=== | ===Revolution=== | ||
[[File:Daniele Manin Repubblica di Venezia.jpg|200px|thumb| | [[File:Daniele Manin Repubblica di Venezia.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Proclamation of the Federal Republic of Ionio.]] | ||
Throughout the eighteenth century there was a popular discontent that involved all the beginnings of the population. The ideas of the Enlightenment had introduced new liberal and democratic concepts. | |||
With the outbreak of the [[Heartfilian Revolutionary War]] the Ionian populations saw an opportunity to declare independence and on July 10, 1760 [[Ionian Declaration of Independence]] was signed, starting war with the Mantellan forces. | |||
Mantellan's forces tried to control the situation but the revolutionaries had more local experience than Mantellan's army. The revolutionaries were aided by the [[Wampanoag Empire]] and [[Exarchate of Kirvina]] which led to a quick resolution of the conflict. In December 10 of 1764 there was the [[battle of Taranto]] which determined the defeat of the Mantellan army and the liberation of Ionian from the colonial period. | |||
December 13, 1764 is signed the [[Treaty of Rossano]] which sanctioned the end of the dominion of Mantellan as well as compensation for damages. In this period a provisional government was established which had the task of writing the new constitution and the formation of the new government. | |||
The formation of the constitution turned out to be complicated as the monarchists wanted to restore the monarchy of the Ionian kingdom while the republicans wanted a republic. After a long debate, a compromise was reached that is indicated in Article 4 allowing the states to adopt their form of government and forming the [[Kingdom of Sila]] while the other states adopted republican forms. | |||
On March 4, the birth of the Federal Republic of Ionio is proclaimed and March 10 the first elections are called in which the first [[Mario Bertinotti]] is elected as the first president, who was the general who led the revolutionaries to victory. Also in this period the [[San Foca Federal District]] was founded and the foundation of the city of [[San Foca]] then followed by the foundation of the coastal city of [[Torre Canne]]. | |||
===The age of reform and growth=== | |||
[[File:Election Day 1815 by John Lewis Krimmel.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Ionian political elections of 1784 in the city of Taranto]] | |||
With the Mario Bertinotti government began an intense phase of social but also economic reforms as well as a political transformation of Ionio that are guided on the ideas of the Enlightenment. Among the social reforms that Mario Bertinotti introduced was the free market concept and education reform that anadava to reduce the role of religion and put more emphasis on the sciences. At the same time they began a plan to rebuild merchant ports that had been partially destroyed by the War of Independence, and with the reforms on free allowed a reconstruction of ports and cities. | |||
In 1765 with the government-sponsored banking reform allowed the birth of the [[Banca Ionica]] founded by Antonio Colucci which then spawned a dynasty of entrepreneurs contemporarily there was the agraia reform that allowed the emancipation of peasants and consequently allowed economic development.In later times the first Ionian univerist institutions were founded as well as the first theater companies. New newspapers sprung up during this period and with a vibrant economy and culture allowed the foundations of Ionian post First Aurelian War to be laid. | |||
This period of great change saw the birth of the Conservative party, which defended traditional values, but in the elections of 1769 Mario Bertinotti's Democratic party won the election and continued the process of reforms that shaped modern Ionian society. As time went on, new technologies were introduced from the old world that allowed for an improvement in agricultural and manufacturing production, which in the late eighteenth century was also coming into being thanks to the freedom that the state guaranteed, making in the eyes of the Ionians their nation into a beacon of freedom on the Aurelian continent. | |||
The period from 1800 until 1810 is considered the period of crisis that then led to the outbreak of the [[First Aurelian War]] that was initiated by [[Kirvina]]. During this period the state faced several challenges including the modernization of the army and naval as well as a turbulent period that led in 1804 to the victory of Luca Bellini of the Pan Aurelian party That involved Ionio in joining the Kirvina coalition. | |||
===First Aurelian War=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Industrialisation=== | |||
TBA | |||
===The Roaring Years and Great Depression=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Second Aurelia War=== | |||
TBA | |||
===After the War and Economic Boom=== | |||
TBA | |||
===The Years of Lead (1969 - 1979)=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Economic and cultural revival=== | |||
=== | TBA | ||
* 90s Tangentopoli (Political corruption scandal) | |||
===21st century=== | |||
WIP | WIP | ||
* | * Ionian Lira (I₤) (1764 - 1999) | ||
* 8 September 2022 Ionio announces its position on the Zaxari v Côte de Fourrure Conflict crisis. The government of John Colucci announces sanctions against Côte de Fourrure and help with his neighbor friend Zaxar | |||
* Shfakien War | |||
* | |||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
| Line 200: | Line 254: | ||
{{main|Government of Ionio}} | {{main|Government of Ionio}} | ||
{{Multiple image|perrow=3||total_width=300 | |||
| header = Political figures of Ionio | |||
| direction = horizontal | |||
| align = left | |||
| caption_align = center | |||
| image1 = Silvio Berlusconi (2010) cropped.jpg | |||
| width1 = 132 | |||
| width2 = 115 | |||
| width3 = 115 | |||
| image2 = Matteo Salvini Viminale (cropped).jpg | |||
| image3 = Elisabetta Alberti Casellati cropped.jpg | |||
| caption1 = [[John Colucci]]<br />[[President of Ionio]] | |||
| caption2 = [[Alberto Salvini]]<br />[[Vice President of Ionio]] | |||
| caption3 = [[Elisabetta De Gregori]]<br />[[Speaker of the Senate of Ionio]] | |||
}} | |||
Ionio is a federal republic of 6 [[Ionio state|states]] and [[San Foca |federal district]]. It is a {{wp|federal republic}} and a {{wp|representative democracy}} "in which majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law." In the [[Ionian federalist system]], citizens are subjected to three levels of government: federal, state, and local. The government is regulated by a system of checks and balances defined by the [[Ionian Constitution]], which serves as the country's supreme legal document. The Constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The Constitution has been amended 28 times; the first ten amendments ([[Bill of Rights]]) and the [[Fourteenth Amendment]] form the central basis of Ioninan' individual rights. All laws and governmental procedures are subject to judicial review, and any law can be voided if the courts determine that it violates the Constitution. [[Constitutional Court of Ionio]] is the only top-level juridical body that has power to revise laws that are passed by states and the federal government. It is also responsible for settling conflicts of attribution between the powers of the federal government and the states and between the states themselves as well as judging the accusations brought against the president and verifying the admissibility of referendums. | |||
The federal government comprises three branches, all physically headquartered in [[San Foca]]: | |||
*{{wp|Legislative}} The bicameral Congress, made up of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies, makes federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment, by which it can remove sitting members of the federal government. | |||
*{{wp|Executive}} The president is the commander-in-chief of the military, can veto legislative bills before they become law (subject to congressional override), and appoints the members of the Cabinet (subject to Senate approval) and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies. | |||
*{{wp|Judicial}} The Supreme Court of Cassation is the highest court in Ionio for both criminal and civil appeal cases. Where a law now has an unclear interpretation, judges may request verification by the [[Constitutional Court of Ionio]] for appropriate verification of laws. | |||
The lower house, the Chamber of Deputies, has 300 voting members, each representing a congressional district for a five-year term. House seats are apportioned among the states by population. Each state then draws single-member districts to conform with the census apportionment. | |||
The upper house, the Senate, has 100 members with each state having two senators, elected at large to five-year terms. The Senate is unique among upper houses in being the most prestigious and powerful portion of the country's bicameral system; political scientists have frequently labeled it the "most powerful upper house" of any government. | |||
[[File:Princess Beatrice Elizabeth Mary of York 2018 (01).jpg|200px|thumb|right|Queen [[Rose II]]. Current Queen of the Kingdom of Sila ]] | |||
The president serves a five-year term and may be elected to the office no more than twice. The president is elected by direct vote taking into account the percentage of the votes that political parties and coalitions take. [[Constitutional Court of Ionio]] consists of fifteen judges, whose election is up to different bodies: five are chosen by Parliament, five by the President of the Republic and five by three colleges of which the most important magistrates are part. Their term of office is 6 years. | |||
Article 4 of the Ionian Constitution describes the formation of states and their forms of government that must be democratic and respect the current 28 amendments. Article 4 is remembered as the law of compromise between monarchists and republicans after the war of independence and to avoid a civil war that would last for many years. With this article was formed the state [[Kingdom of Sila]] which represents the heir to the ancient Kingdom of Ionium. Although members of the [[House of Cosenza]] have limited powers only within the [[Kingdom of Sila]] as the government is a constitutional monarchy, in the eyes of the federal government they are regarded as ordinary people although they are addressed in the formal style. | |||
===Law and criminal justice=== | ===Law and criminal justice=== | ||
| Line 236: | Line 322: | ||
The Federal Republic of Ionio is divided into 6 states and a federal district | The Federal Republic of Ionio is divided into 6 states and a federal district | ||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Name | !Name | ||
!Capital | !Capital | ||
!Population | !Population | ||
!Flag | |||
!Coat of Arms | !Coat of Arms | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[San Foca Federal District]] | |[[San Foca Federal District]] | ||
|[[San Foca]] | |[[San Foca]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:San Foca Federal District Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
| | |[[File:Coat of Arms of Veneto.png|center|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Republic of Taranto]] | |[[Republic of Taranto]] | ||
|[[Taranto]] | |[[Taranto]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:Republic of Taranto Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
| | |[[File:Coat of Arms of Apulia.svg|center|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Republic of Arachova]] | |||
|[[Republic of | |||
|[[Rossano]] | |[[Rossano]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:Republic of Arachova Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
| | |[[File:Coat of arms of Calabria.svg|center|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Republic of Salice]] | |[[Republic of Salice]] | ||
|[[Salice]] | |[[Salice]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:Republic of Salice Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
| | |[[File:CoA of Friuli-Venezia Giulia.svg|center|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Kingdom of Sila]] | |[[Kingdom of Sila]] | ||
|[[Cosenza]] | |[[Cosenza]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:Kingdom of Sila Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
| | |[[File:Valle d'Aosta-Stemma.svg|center|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Republic of Tropea]] | |[[Republic of Tropea]] | ||
|[[Tropea]] | |[[Tropea]] | ||
| | | | ||
|[[File:Republic of Tropea Flag.png|center|100px]] | |||
|[[File:Regione-Basilicata-Stemma.svg|center|100px]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Republic of Solarios]] | |||
|[[Galdurmar]] | |||
| | | | ||
| | |[[File:Republic of Soalrios Flag.png|center|100px]] | ||
|[[File:Vergina Sun WIPO.svg|center|100px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Demographics== | |||
TBA | |||
===Largest cities=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Immigration=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Languages=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Religion=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Education=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Health=== | |||
TBA | |||
===Holidays=== | |||
TBA | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| Line 294: | Line 411: | ||
TBA | TBA | ||
===Agriculture=== | |||
[[File:Vineyards in Tuscany quality image.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Vineyards in the Monterosso region, Republic of Tropea. The Ionian food industry is well known for the high quality and variety of its products.]] | |||
According to the last national agricultural census, there were 1.6 million farms in 2018 (−32.4% since 2010) covering 12.7 million hectares (63% of which are located in Northern Ionio). The vast majority (99%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), {{wp|grain}} fields take up 31%, {{wp|olive}} tree orchards 8.2%, {{wp|vineyards}} 5.4%, {{wp|citrus}} orchards 3.8%, {{wp|sugar beets}} 1.7%, and {{wp|horticulture}} 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%). | |||
Ionio is the world's top wine producer, and one of the leading in {{wp|olive oil}}, fruits ({{wp|apples}}, {{wp|olives}}, {{wp|grapes}}, {{wp|oranges}}, {{wp|lemons}}, {{wp|pears}}, {{wp|apricots}}, {{wp|hazelnuts}}, {{wp|peaches}}, {{wp|cherries}}, {{wp|plums}}, {{wp|strawberries}} and {{wp|Kiwifruit}}), and vegetables (especially {{wp|artichokes}} and {{wp|tomatoes}}). The most famous Ionian wines are probably the Monterossoo and the Leccese Barolo. Other famous wines are Sibari, Brindisi, Brunello di Montalto, Frascati, Montepulciano di Taranto, Morellino di Martina Franca, and the sparkling wines Aurora and Fasano. Quality goods in which Ionio specialises, particularly the already mentioned wines and regional cheeses, are often protected under the quality assurance labels DOC/DOP. This is considered important in order to avoid confusion with low-quality mass-produced ersatz products. | |||
===Mineral resources=== | |||
[[File:Colonnata, marble-quarry - panoramio - Frans-Banja Mulder (2).jpg|200px|thumb|right|Lumi quarry that produces the famous {{wp|Carrara marble|Lumi Marble}}.]] | |||
Mining activities in the Ionian are diverse but depend on location. The Sila mountain range contains coal deposits that were exploited during the industrial revolution for {{wp|coal}} production, and {{wp|iron ore}} gaiciments are present to a small extent. | |||
The main element of mining activity is {{wp|quartz}} and {{wp|silica}}. Important gaiciments of pure quartzite and are used to produce silica and then used in the production of microchips and solar panels while low-grade quartzite is used in the construction industry. | |||
There are small deposits of minerals such as {{wp|copper}}, {{wp|zinc}}, {{wp|graphite}} and are recorded considerable presence of {{wp|lead}} indicating the possibility of presence of {{wp|uranium}} and {{wp|thorium}}. | |||
In addition to the presence of minerals, the production of {{wp|marble}} is also notable, with {{wp|Carrara marble|Lumi Marble}} being cosdierated of a valuable variety and thus used throughout the world for the construction of buildings and in sculpture. | |||
===Oil industry and chemical industry=== | |||
[[File:ExxonMobil Baton Rouge.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Oil refinery in Taranto.]] | |||
The oil industry is highly developed, even though Ionio has very few oil fields. Most oil is imported from countries such as [[Fulgistan]] and TBA . Most refineries are located in coastal areas. The most famous is the Taranto refinery that manages to process more than 540,000 barrels per day. | |||
In the state of Tropea and Salice, there are few oil and natural gas deposits that are mined by the {{wp|Fracking|Hydraulic fracturing}}. | |||
===Industry=== | |||
[[File:ILVA - Unità produttiva di Taranto - Italy - 25 Dec. 2007.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Taranto steelworks in operation]] | |||
The industrial sector is very popular especially the metal industries, nuclear industry, war industry, shipbuilding and railway car. Since 1980 onwards is spreading the high technological industry (chips, computers and mobile phones). Widespread in the railway industry, oil refining and natural gas. In the nations has spread the processing of agricultural products. | |||
Ionio has an important manufacturing industry that is more concentrated in the north of the country. Thanks to the available resources, steel industries have developed that are mostly concentrated in Taranto. In Taranto there is the largest foundry in Ionio and therefore a fundamental hub in the industries that need iron and steel. Going down to the south and north, the model of small and medium-sized family-run industries prevails and in this case they produce textile material and luxury goods. | |||
In this sector is also considered the sector that is called The Ionian Style – especially in industrial design, furniture, cars – is characterized by the mixture of imagination and design rigor and is characterized by the use of materials considered waste, but at the same time innovative. Museums and awards are dedicated to Sicilian design, represented by companies, specialization schools and artists such as Gio Pontile, Enrico Sottsass and Bruno Mulinari, such as the Compasso d'Oro Award, the oldest and most prestigious design award in the world. The Fiorenza Fair, the largest South American exhibition center, annually hosts numerous international design exhibitions. | |||
Advanced and diversified, the Ioninan industry is particularly developed in the sectors of shipbuilding, household appliances, chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, agri-food and defense. In the automotive sector, which together with petrochemical and steel was the basis of the country's post-war industrialization. | |||
===High-tech industry=== | |||
[[File:2200missioncollegeblvd.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Blume Technology headquarters in Aurora]] | |||
With technological development and scientific research investment, it has enabled the development of the computer industry as well as the photovoltaic industry. Over the years the Ionian computer industry has developed intensively allowing the creation of large companies such as [[Blume Technology Corporation]] and ''[[Nakatomi Corportarion]]'' that produce not only microprocessors but also technological consumer goods. | |||
In addition to companies that produce hardware there are also companies that produce software such as [[Devotion]] that produce video games. Thanks to the university system, new software houses are continuously being born that continue to innovate the technological sector of Ionio. | |||
In addition to computer companies there are also pharmaceutical industries such as [[Schiroli Farmaceutici]] that produce pharmaceuticals as well as investing in the search for new medicines. In Ionio there are also companies that allow treatment using phage therapy with a collaboration with the universities of Ionio under a strict control of the Ministry of Health. | |||
The military industry is being driven by [[Ionian Military Industries]], [[Alenia Defense]] and [[Betona]] companies, which are investing in the development of modern weapons as well as modern security systems. | |||
===Banking=== | |||
[[File:Desert Financial Headquarters.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Headquarters of Banca di Tropea]] | |||
Ionio's banking sector is highly developed. The first banks were founded soon after the creation of Ionian due to the reforms that were undertaken. | |||
The city of San Foca is home to [[Ionio Stock Exchange]] a major financial center for stock trading while in the city of Taranto there is [[Ionio Mercantile Exchange]] which manages commodity futures exchange. The Ionio Stock Exchange is divided into two fundamental units. [[Ionio Industrial Average]] which deals with traditional industries and [[Automated Quotations Ionio Industrial Average]] where high-tech and next-generation industries are listed. | |||
Over the years, some States of Ionio have adopted tax relief laws that allow the registration of {{wp|Offshore company}}. | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
[[File:Alberobello BW 2016-10-16 13-43-03.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Trulli in Martina Franca]] | |||
Tourism is considered the key sector of Ionian economy. Thanks to an efficient transportation infrastructure, they allow for a constant handling of tourists throughout the year favored by the Mediterranean and sub-tropical climate. | |||
In Ionio there are many companies operating for the industrial sector especially the cruise company [[TSC Cruises]]. | |||
In Ionio there are also companies related to fun and amusement parks. The most famous company is Belmont Park which runs amusement parks and water parks, followed by [[Sette Bnadiere]] and [[Federico Fazzellini]]. | |||
In the republic of Tropea and the Republic of Solarios there is special interest in gambling tourism. | |||
The summer season is the most important because it manages a large amount of tourists who come from all over the world. During the winter season, winter tourism is widespread in the states of Sila and Arachova, although beach resorts in northern Ionio prevail because of its warm climate. The city [[Camigliatello Silano]] is famous for its ski slopes and various winter sports and for its policy against light pollution that allowed it to attract turisit to see Milky Way at night | |||
Thanks to the spectacular landscape many tourists come every year who visit Ionio and the number of tourists grows every year so much that there have been investment plans for the enhancement of infrastructure to manage the large amount of tourists. People mainly visit Ionio for its rich culture, cuisine, history, fashion, architecture and art although there is also tourism related to gambling. | |||
===Energy sector=== | |||
[[File:Entracque diga Chiotas1.jpg|200px|thumb|right|A hydroelectric power plant in the state of Sila]] | |||
Due to the deposits present and the import of coal, oil, and natural gas, it has enabled Ionian to produce electricity. But the primary ecological energy source remains hydropower because of the sila mountain range and its rivers. Geotemical and wind power have also enabled environmentally friendly development of energy production, but the primary contributing factor is solar panels, which have saved pollution from power plants | |||
Garbage collection also makes it possible to participate in electricity production with incinerators present in all states also due to the widespread diferentiated collection throughout the nation. | |||
''Insert nuclear section'' | |||
Ionio invests in the search for alternative energy sources including the production of {{wp|Biofuels}} as well as solutions for storing and reusing {{wp|Carbon capture and utilization|carbon dioxide}} | |||
==Infrastructure== | ==Infrastructure== | ||
===Highway=== | ===Highway and Road=== | ||
[[File:Tarvisio Exit East 2008 08.JPG|300px|thumb|left|A highway interchange near [[Carbonia]]]] | |||
The Ionian road network is very large and extensive, and its first construction riasle in the period when Aroman settlers founded the first towns. Things changed dramatically with the industrial revolution and the introduction of the first automobiles in 1910 until the first modern road network was built in 1916. | |||
This changed in 1956 when the volume of automobiles increased and plans began for the first national highway network, which was achieved in 1960 with the development of the Ionian Interstate. Until 1995, the interstate was state-owned with fuel tax funding but with computerization, the state-owned [[Interstate Ionica Corporation]] was created to manage the highway network and its construction and made the entire highway network tolled by adopting the {{wpl|Open road tolling}} system, consequently eliminating the fuel tax that was used to fund the highway. | |||
In addition to the highway there are national roads and local roads which are state-run but with delegation to the relevant administrations. There is a network of local and national and international bus transportation but they are reduced due to the strong competition of railways especially in national and international connections while at the local level they work very well as some bus companies are run by the railway companies. | |||
===Rail=== | ===Rail=== | ||
{{main|Rail transport in Ionio}} | |||
[[File:FS Trenitalia ETR400 15 (50832499597).jpg|300px|thumb|right|APT 400 while arriving at Tropea station]] | |||
Railway development dates back to the XXXX just after the [[First Aurelian War]]. In this period the first railway companies were born and in comity with the industrial revolution also began the rapid railway development of Ionio. In 1893, the Ionian federal government had to intervene to improve the railway situation, and eventually a law was passed that sanctioned the acquisition Rail infrastructure from private railway companies and the establishment of the state-owned [[Rete Ferroviaria Ionica]] company, which operates Rail infrastructure and asset management related to railways. | |||
This thing marks a profound change in railroad management but allowed for an increase in research and development by the railroad companies that turned first into the development of the Streamliner steam locomotives and finally in 1939 came the development of the progenitor of modern high-speed trains with ETV 0 that managed to reach 200 km/h using the 3KV DC electric transmission method. With this breakthrough came the electrification of the national railway until 1964 where they experimented with 25KV AC electric traction with ETV 100 that touched the maximum speed of 220 km/H | |||
The synergy between universities, private companies and public companies made it possible to develop the first Ionian high-speed railway in 1984 connecting San Foca with Taranto. The success of this venture made it possible to create the current rail network by improving the method of rail transportation and creating the backbone of the modern Ionian railway network. | |||
At present, the Ionian railway network is extensive especially in the south central part of the nation including the high-speed railway that connects the main cities.The rail tracks and infrastructure are managed by [[Rete Ferroviaria Ionica]] which is a state-owned corporation and acts as an impartial gidget in disputes between private railroad companies while ensuring the free railroad market. | |||
There are a total of 5 private ferroviaire companies that are the result of various mergers of old railway companies. The most important company is [[Ferrovia Ionica]] followed by [[Nuovo Trasporto Ferroviario]] and [[Solarios Railroad Corporation]]. Then there is [[Avanti Sila]], [[Ionita]] which are smaller railroad companies that focus heavily on regional services although they have expressed interest in domestic and international services. In recent years, the first experiments for high-speed rail transport for light freight have begun, finding great success. | |||
===Air=== | ===Air=== | ||
[[File:San Francisco International Airport at night.jpg|300px|thumb|left|[[San Foca International Airport]] overnight]] | |||
Air transportation became widespread in the 1950s and 1960s with the introduction of the first jet planes. Because of its artistic beauty and its central location in mainland Aurelia allowed Ionian to become a center of air transportation but things changed as early as 1964 with the introduction of the first high-speed trains and the gradual improvement of the railroad caused a collapse in domestic demand forcing Ionian air companies to focus more on the international market. | |||
Currently, the busiest airport in Ionian is [[San Foca International Airport]] followed by [[Rossano International Airport]] and [[Tropea International Airport]] which are also the cities with the highest tourist flow in Ionio. As for airlines, the most widely used is [[Ionian Airlines]] and its competitor [[Sila Airways]], which handle both passenger and cargo traffic | |||
===Water=== | ===Water=== | ||
[[File:Lanterna di Genova 27-09-2011.JPG|300px|thumb|right|The old lighthouse in Taranto harbor]] | |||
The first ports are of the cities of [[Taranto]], [[Sibari]] and [[Rossano]] that were founded by Aromans settlers who arrived in the 700s. From that time the ports came to assume a key role for fast communications along the Ionian coast and the rest of the world. During the 1800s things changed with the introduction of railroads, which became the main transportation system for moving goods and people within the Ionian and into the mainland, but ports continued to assume a key role with the glubal trade. | |||
Ionian ports have undergone upgrades and extensions to accommodate the ever-increasing traffic of cargo ships. Same with cruise traffic where modern cruise docks have been installed in port cities. In total Ionio has 5 main seaports followed by 6 secondary seaports. Both ports are equipped with cruise docks. The busiest port in Ionio remains the Port of Traanto | |||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| Line 323: | Line 556: | ||
During the colonial period, castles and palaces were built. Many Mantellan architects such as [[Luigi Cannavaro]] came to Ionio to teach their styles to local architects. These cultural exchanges made it possible to create original styles in Ionio where pre-colonial elements were mixed with the elements of the various [[Europa (continent)|Europa]]n architectural styles. | During the colonial period, castles and palaces were built. Many Mantellan architects such as [[Luigi Cannavaro]] came to Ionio to teach their styles to local architects. These cultural exchanges made it possible to create original styles in Ionio where pre-colonial elements were mixed with the elements of the various [[Europa (continent)|Europa]]n architectural styles. | ||
During the XXX the first skyscrapers were built and after the XXX {{wp|Art Deco|Art Deco}} spread. At the same time, {{wp|Futurism|Futurism Architecture}} which ended at the end of XXX | During the XXX the first skyscrapers were built and after the XXX {{wp|Art Deco|Art Deco}} spread. At the same time, {{wp|Futurism|Futurism Architecture}} which ended at the end of XXX. It resumed with other types of style such as {{wp|Googie architecture}}, {{wp|New Formalism (architecture)|New Formalism}}, {{wp|Mid-century modern|Mid-century modern architecture}}, {{wp|High-tech architecture}} and {{wp|Neo-futurism}}. | ||
===Visual Art and Literature=== | ===Visual Art and Literature=== | ||
| Line 335: | Line 568: | ||
===Newspapers and Television=== | ===Newspapers and Television=== | ||
[[File:Fox Plaza HD.jpg|thumb|left|The headquarters of Wolf Broadcasting Company|220px]] | |||
Newspapers were the primary source of news in Ionio. During the second half of the nineteenth century many newspapers were born but with the introduction of radio, television and the internet the number of newspapers decreased. Today the most important newspapers are [[Libero Quotidiano]] and the [[Corriere di San Foca]]. Then there are several newspapers spread throughout the national territory and there are small newspapers that are spread only within the states. | |||
With the development of the radio began the rapid diffusion of radio stations that had a local diffusion. But already in this began to form the first degrees of society in the field of telecommunications, but the real explosion occurs around 1950 with the rapid spread of television. | |||
With the rapid spread of television brought a period called occupation of the ether, a phenomenon that led to the birth of large media corporations. The first television and radio company was [[Ionio Broadcasting Corporation]], followed by [[Mediaset Communication ]], [[Tropea Broadcasting System]] and finally [[Wolf Broadcasting Company]] which are considered the largest television broadcasters in Ionio. Transmission companies were created at the local level but occupied frequencies in a savage way causing regulation by the state. In 1974 [[Ionio Broadcasting Corporation]] was taken over by [[Fininvest]] and consequently passed into the management of the young [[John Colucci]]. After a period of adjustment with the laws on the regulation of the sector began the golden age of Ionian television that lasted throughout the 80s. | |||
During the 90s there was the period of television trash and rivalry between [[Ionian Broadcasting Corporation]] and [[Mediaset Communication]] and the revival [[Wolf Broadcasting Company]]. With the advent of the Internet, companies had to adapt to new needs and in 20XX the transition to digital television broadcasting was completed. With the purchase by the Colucci family of the telecommunications company [[Telecom]] the largest telecommunications conglomerate was created with the merger between [[Ionio Broadcasting Corporation]] and Telecom forming the new company [[IonioCast]] causing another war between the major companies and triggering a series of interventions to regulate the internet service and the rapid spread of streaming services. | |||
===Music=== | ===Music=== | ||
| Line 341: | Line 582: | ||
[[File:Giorgio Moroder Melt! 2015 02 (cropped).jpg|300px|thumb|right|[[Antonio Moroder]] pioneer of {{wp|Italo disco|Ionio Disco}} and {{wp|electronic dance music|electronic dance music}}, is known as the "Father of Disco"]] | [[File:Giorgio Moroder Melt! 2015 02 (cropped).jpg|300px|thumb|right|[[Antonio Moroder]] pioneer of {{wp|Italo disco|Ionio Disco}} and {{wp|electronic dance music|electronic dance music}}, is known as the "Father of Disco"]] | ||
From {{wp|folk music|folk music}} to {{wp|Classical music|Classical music}}, music is an intrinsic part of Ionian culture. Thanks to the Mantellan settlers, Europan musical instruments were imported and local musical artists managed to create music by combining local elements with Europan elements. Since in [[Mantella]] is the birthplace of {{wp|Italian opera|Mantellan Opera}} has also spread in Ionio with the formation of internationally renowned musicians. | From {{wp|folk music|folk music}} to {{wp|Classical music|Classical music}}, music is an intrinsic part of Ionian culture. Thanks to the Mantellan settlers, Europan musical instruments were imported, and local musical artists managed to create music by combining local elements with Europan elements. Since in [[Mantella]] is the birthplace of {{wp|Italian opera|Mantellan Opera}} has also spread in Ionio with the formation of internationally renowned musicians. | ||
The Ionian music scene changed rapidly with the introduction of new musical styles such as {{wp|jazz|jazz}}, {{wp|progressive rock|progressive rock}} and other musical genres of new conception. | The Ionian music scene changed rapidly with the introduction of new musical styles such as {{wp|jazz|jazz}}, {{wp|progressive rock|progressive rock}} and other musical genres of new conception. | ||
Ionio contributed to the development of {{wp|disco|disco}} and {{wp|electronic music|electronic music}}, with [[Ionio disco]], known for its futuristic sound and prominent use of synthesisers and {{wp|drum machines|drum machines}}, being one of the earliest electronic dance genres. By the latter half of the 1990s, a subgenre of [[Ionio Dance]] emerged. Taking influences from Ionio disco and [[Ionio House]], Ionio dance generally included | Ionio contributed to the development of {{wp|disco|disco}} and {{wp|electronic music|electronic music}}, with [[Ionio disco]], known for its futuristic sound and prominent use of synthesisers and {{wp|drum machines|drum machines}}, being one of the earliest electronic dance genres. By the latter half of the 1990s, a subgenre of [[Ionio Dance]] emerged. Taking influences from Ionio disco and [[Ionio House]], Ionio dance generally included synthesiser riffs, a melodic sound, and the usage of vocoders. Since 2010 the {{wp|Synthwave|Synthwave}} genre is spreading which is a musical genre based mainly on music associated with the soundtracks of action, science fiction and horror films of the 80s. Other influences are drawn from the art and video games of the decade. Synthwave musicians often espouse nostalgia for the culture of the 80s and attempt to capture the atmosphere of the era and celebrate it. | ||
Today, Ionian pop music is represented annually with the [[Sibari Music Festival]] and [[EurthVision Song Competition]]. Many singers like [[Lucia Ramos]], [[Ettore Capone]] are world-famous singers. | Today, Ionian pop music is represented annually with the [[Sibari Music Festival]] and [[EurthVision Song Competition]]. Many singers like [[Lucia Ramos]], [[Ettore Capone]] are world-famous singers. | ||
| Line 365: | Line 606: | ||
===Football=== | ===Football=== | ||
[[File:Patriots-Steelers 2005.jpg|250px|thumb|left|A Calcio a Griglia match in Ionio]] | |||
[[File:The Stadio Olimpico di Roma before the match AS Roma vs HJK Helsinki (2022).jpg|250px|thumb|right|A Calcio match in Ionio]] | |||
Football is the most practiced sport in Ionio. Although there are several variations of football, the two most practiced sports of football are {{wp| Association football| Football}} and the {{wp| Gridiron football|Calcio a Griglia}} | |||
Calcio is regulated by the [[Ionian Football Federation]] which operates the Ionian football system where the top league is the [[Serie A]]. In addition to the Serie A is made the [[Ionian Cup]] which is an annual competition that decrees the champion of Ionian Calcio. [[Ionian Football Federation]] is a member of [[UENA Football]] and [[AMFC]] | |||
Calcio a Griglia is run by [[Ionian Federation of Gridiron Football]]. In total there are only two professional leagues. The first concerns the football played by university teams while the most important league is [[Ionio Football League | IFL]] which manages the only top professional league. To avoid conflicts of the two sports it was established that during the autumn winter Calcio a Griglia would be practiced while during the spring and summer Calcio is practiced. | |||
All Ionian universities came together to form [[National University Athletic Association]] (NUAA) which runs all university sports competitions including Football and Calcio a Griglia. On the evening of the first day of the New Year, the [[New Year Buwl]] is held, which is a friendly game of the winner of the [[Ionio Buwl]] of the IFL with the winner of the [[Sun Buwl]] of the NUAA. | |||
===Motoring=== | ===Motoring=== | ||
[[File:Green flag at Daytona.JPG|250px|thumb|left|An Ionian Stock Car Race]] | |||
Motorsports are the second most followed in Ionio. The [[Ionica Stock Cup]] series is the Stock Car Racing championship run by the [[Jonica Stock Car Auto Racing Association]]. | |||
Very important is the Automobile Club Ionica that manages all the car and motorcycle races. [[Ionica Grand Prix]] is the highest moment of the motoring season in which there is the [[KAP World Grand Prix]] race and many ionian go to see it to cheer the [[Scuderia Tommaso]]. Also important is the [[Ionica Motorcycle Grand Prix]] where the Ionian team [[Lorenzo Corse]] participates. Very impressive are the Motorcycle Chariot Race which are the modern version of the Chariot Race inherited from the Aroman empire. | |||
===Other sports=== | ===Other sports=== | ||
Basketball, volleyball and cycling are the other most followed sports although they are followed in a minor way | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:47, 17 February 2024
Federal Republic of Ionio Repubblica federale di Ionio | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Libertà e Giustizia Freedom and Justice | |
 | |
| Capital | San Foca |
| Largest | Taranto |
| Official languages | Cristinese |
| Recognised regional languages | Mantellan |
| Religion (2022) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic |
• President | John Colucci |
• Vice President | Alberto Salvini |
• Speaker of the Senate | Elisabetta De Gregori |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Formation | |
| Area | |
• | 314,212 km2 (121,318 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | 30,768,932 |
• Density | 97.9/km2 (253.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | 546,730,395,348 |
• Per capita | 17,769 |
| Currency | Auro (𐠓) (IOL) |
| Time zone | UTC -05:00 |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy AD |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +69 |
| ISO 3166 code | ION |
| Internet TLD | .ni |
Ionio ([ˈjɔːnjo]] (![]() listen italian) ), officially the Federal Republic of Ionio (Cristinese: Repubblica federale di Ionio), is a sovereign state in Aurelia on Eurth. Ionio bordered to the nord by Advocatius and to the east by Heartfilia
listen italian) ), officially the Federal Republic of Ionio (Cristinese: Repubblica federale di Ionio), is a sovereign state in Aurelia on Eurth. Ionio bordered to the nord by Advocatius and to the east by Heartfilia
Geography and environment
Geography and Climate
TBA
Geology and Symsymic Risk
TBA
History
Pre-colonial history

Little is known about the prehistoric Ionio. Some archaeological finds have shown human presence about 40,000 years BCE. It is assumed that these humans were hunter-gatherers and lived in small communities.
Archaeological experts have found remains of the Tengrol Empire. Although the Tengrol Empire collapsed about 200 CE as the people of this empire were nomads, but it is assumed that there are perhaps more causes that led to the collapse of this empire. The presence of the Tengrol people continues today in Ionio where a small minority of the descendants of the Tengrol people live.
Colonial period

In 700 Aroman colonists (specifically, Arakhóran) arrived from the Aurelian Empire which in the present day corresponds to Kirvina. They founded the coastal trading cities of Sibarha (Σιβαρά), Tarassa (Ταραccα), and Miróia (Μιρόια). They maintained a presence as part of the Aurelian Empire's eastern provinces. With the presence of the Aroman settlers were imported knowledge of mathematics, metalworking, architecture, science along with the breeding of cattle, pigs, horses and different plants for agriculture.
By 1200s CE, their influence began to recede, and they were conquered by local tribes. These tribes founded the Kingdom of Ionio, a ‘melting pot’ state on their former location. With the formation of this kingdom begins a slow process of integration between the tribal cultures and the culture of the colonies of the Aurelian Empire. The period of maximum expansion of the kingdom dates back to about 1323 - 1443 where this kingdom had an intense economic and social activity.
The duration of this reign lasted until 1500, when Ionio went through a period of rapid economic decline. Because of its mostly isolationist policy, this led to a collapse of civilization. The remaining city-states were weak and constantly at war with each other. These continuous struggles have provoked a weakening of the various city states becoming prey for future colonizers.
In 1518 the first settlers from Gotneska arrived and founded the city of Torre dell' Orso and began to establish a colonial empire north of Ionio. In the city lies the tomb of the explorer James Clarke who died after discovering Ionio. During colonization, goutian culture such as rugby was imported, which would later evolve into Calcio a Griglia.
In 1520 came the explorer mantellan Marco Caboto who landed on the coasts of Ionian but which were uninhabited. When he returned to his homeland I indicated the presence of uninhabited lands that can be colonized. Then an expedition for the colonization of these new lands started and on July 4, 1520 the first settlers arrived and the mantellan colonization of Ionio begins.
The exploration began and the settlers met the indigenous peoples and the various city states that were at war with each other. Mantellan's army took advantage of this situation to gain as much ground as possible. The war with the local population took place until 1550 but in 1540 the expansionist aims of mantle were concentrated in the north of the Ionian and declared war on the colonial empire of Gotneska which lasted until 1550 with the peace treaty that sanctioned the victory of Mantella but had to respect the colonies of Gotneska that were present in the North Ionio.
During this period the colonizers imposed the culture and religion of Mantellan. This process encountered many obstacles but during the seventeenth century the Cristinese language became the language that everyone spoke and the official religion was Christian Apostolic. The times of the various earlier cultures were converted into basilicas and churches. This process was sped up as the mantellan government sent experts in culture, architecture, scientists to Ionium to educate people about the new culture. The cities underwent a process of restructuring by adding Renaissance and Baroque elements. Although this process characterized the main culture of Ionian, the management of the colony by Mantellan and the various policies adopted by the various governors was increasing the discontent of the population.
During the eighteenth century the ideas of the Enlightenment arrived in Ionio and began to spread quickly among the high local population. The philosophy of the Enlightenment is considered the catalyst of the Ionian War of Independence as the population was unhappy with the new taxes that the governor Antonio De Santis had applied.
Revolution
Throughout the eighteenth century there was a popular discontent that involved all the beginnings of the population. The ideas of the Enlightenment had introduced new liberal and democratic concepts. With the outbreak of the Heartfilian Revolutionary War the Ionian populations saw an opportunity to declare independence and on July 10, 1760 Ionian Declaration of Independence was signed, starting war with the Mantellan forces.
Mantellan's forces tried to control the situation but the revolutionaries had more local experience than Mantellan's army. The revolutionaries were aided by the Wampanoag Empire and Exarchate of Kirvina which led to a quick resolution of the conflict. In December 10 of 1764 there was the battle of Taranto which determined the defeat of the Mantellan army and the liberation of Ionian from the colonial period.
December 13, 1764 is signed the Treaty of Rossano which sanctioned the end of the dominion of Mantellan as well as compensation for damages. In this period a provisional government was established which had the task of writing the new constitution and the formation of the new government.
The formation of the constitution turned out to be complicated as the monarchists wanted to restore the monarchy of the Ionian kingdom while the republicans wanted a republic. After a long debate, a compromise was reached that is indicated in Article 4 allowing the states to adopt their form of government and forming the Kingdom of Sila while the other states adopted republican forms.
On March 4, the birth of the Federal Republic of Ionio is proclaimed and March 10 the first elections are called in which the first Mario Bertinotti is elected as the first president, who was the general who led the revolutionaries to victory. Also in this period the San Foca Federal District was founded and the foundation of the city of San Foca then followed by the foundation of the coastal city of Torre Canne.
The age of reform and growth
With the Mario Bertinotti government began an intense phase of social but also economic reforms as well as a political transformation of Ionio that are guided on the ideas of the Enlightenment. Among the social reforms that Mario Bertinotti introduced was the free market concept and education reform that anadava to reduce the role of religion and put more emphasis on the sciences. At the same time they began a plan to rebuild merchant ports that had been partially destroyed by the War of Independence, and with the reforms on free allowed a reconstruction of ports and cities.
In 1765 with the government-sponsored banking reform allowed the birth of the Banca Ionica founded by Antonio Colucci which then spawned a dynasty of entrepreneurs contemporarily there was the agraia reform that allowed the emancipation of peasants and consequently allowed economic development.In later times the first Ionian univerist institutions were founded as well as the first theater companies. New newspapers sprung up during this period and with a vibrant economy and culture allowed the foundations of Ionian post First Aurelian War to be laid.
This period of great change saw the birth of the Conservative party, which defended traditional values, but in the elections of 1769 Mario Bertinotti's Democratic party won the election and continued the process of reforms that shaped modern Ionian society. As time went on, new technologies were introduced from the old world that allowed for an improvement in agricultural and manufacturing production, which in the late eighteenth century was also coming into being thanks to the freedom that the state guaranteed, making in the eyes of the Ionians their nation into a beacon of freedom on the Aurelian continent.
The period from 1800 until 1810 is considered the period of crisis that then led to the outbreak of the First Aurelian War that was initiated by Kirvina. During this period the state faced several challenges including the modernization of the army and naval as well as a turbulent period that led in 1804 to the victory of Luca Bellini of the Pan Aurelian party That involved Ionio in joining the Kirvina coalition.
First Aurelian War
TBA
Industrialisation
TBA
The Roaring Years and Great Depression
TBA
Second Aurelia War
TBA
After the War and Economic Boom
TBA
The Years of Lead (1969 - 1979)
TBA
Economic and cultural revival
TBA
- 90s Tangentopoli (Political corruption scandal)
21st century
WIP
- Ionian Lira (I₤) (1764 - 1999)
- 8 September 2022 Ionio announces its position on the Zaxari v Côte de Fourrure Conflict crisis. The government of John Colucci announces sanctions against Côte de Fourrure and help with his neighbor friend Zaxar
- Shfakien War
Politics
Government
Ionio is a federal republic of 6 states and federal district. It is a federal republic and a representative democracy "in which majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law." In the Ionian federalist system, citizens are subjected to three levels of government: federal, state, and local. The government is regulated by a system of checks and balances defined by the Ionian Constitution, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. The Constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The Constitution has been amended 28 times; the first ten amendments (Bill of Rights) and the Fourteenth Amendment form the central basis of Ioninan' individual rights. All laws and governmental procedures are subject to judicial review, and any law can be voided if the courts determine that it violates the Constitution. Constitutional Court of Ionio is the only top-level juridical body that has power to revise laws that are passed by states and the federal government. It is also responsible for settling conflicts of attribution between the powers of the federal government and the states and between the states themselves as well as judging the accusations brought against the president and verifying the admissibility of referendums.
The federal government comprises three branches, all physically headquartered in San Foca:
- Legislative The bicameral Congress, made up of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies, makes federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment, by which it can remove sitting members of the federal government.
- Executive The president is the commander-in-chief of the military, can veto legislative bills before they become law (subject to congressional override), and appoints the members of the Cabinet (subject to Senate approval) and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies.
- Judicial The Supreme Court of Cassation is the highest court in Ionio for both criminal and civil appeal cases. Where a law now has an unclear interpretation, judges may request verification by the Constitutional Court of Ionio for appropriate verification of laws.
The lower house, the Chamber of Deputies, has 300 voting members, each representing a congressional district for a five-year term. House seats are apportioned among the states by population. Each state then draws single-member districts to conform with the census apportionment.
The upper house, the Senate, has 100 members with each state having two senators, elected at large to five-year terms. The Senate is unique among upper houses in being the most prestigious and powerful portion of the country's bicameral system; political scientists have frequently labeled it the "most powerful upper house" of any government.

The president serves a five-year term and may be elected to the office no more than twice. The president is elected by direct vote taking into account the percentage of the votes that political parties and coalitions take. Constitutional Court of Ionio consists of fifteen judges, whose election is up to different bodies: five are chosen by Parliament, five by the President of the Republic and five by three colleges of which the most important magistrates are part. Their term of office is 6 years.
Article 4 of the Ionian Constitution describes the formation of states and their forms of government that must be democratic and respect the current 28 amendments. Article 4 is remembered as the law of compromise between monarchists and republicans after the war of independence and to avoid a civil war that would last for many years. With this article was formed the state Kingdom of Sila which represents the heir to the ancient Kingdom of Ionium. Although members of the House of Cosenza have limited powers only within the Kingdom of Sila as the government is a constitutional monarchy, in the eyes of the federal government they are regarded as ordinary people although they are addressed in the formal style.
Law and criminal justice
The Ionian judicial system is based on Aroman law modified by the Napoleonic code(?) and later statutes. The Supreme Court of Cassation is the highest court in Ionio for both criminal and civil appeal cases. The Constitutional Court of Ionio (Corte Costituzionale) rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and is a post XXXX innovation. Since their appearance in the beginning of the 20th century, Ionian organised crime and criminal organisations have infiltrated the social and economic life of many regions which would later expand into some foreign countries including XXXX.
Law enforcement
Law enforcement in Ionio is provided by multiple police forces, five of which are national agencies. The Polizia di Stato (State Police) is the civil national police of Ionio. The Carabinieri is the common name for the Arma dei Carabinieri, a Gendarmerie-like military corps with police duties. They also serve as the military police for the Ionian armed forces. The Carabinieri are considered as federal police and since XXXX also includes the Polizia Autostradale that is responsible for controlling and intervening in the highway network of Ionio.
The Guardia di Finanza, (Anglish: Financial Guard) is a corps under the authority of the Minister of Economy and Finance, with a role as police force. The Corps is in charge of financial, economic, judiciary and public safety. The Polizia Penitenziaria (Prison Guards, literally Penitentiary Police) operate the Ionian prison system and handle the transportation of inmates.
Foreign relations
TBA
Military
TBA
Administrative divisions
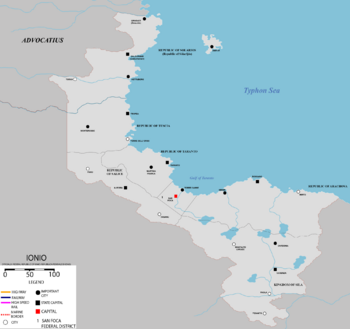
The Federal Republic of Ionio is divided into 6 states and a federal district
| Name | Capital | Population | Flag | Coat of Arms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Foca Federal District | San Foca | |||
| Republic of Taranto | Taranto | |||
| Republic of Arachova | Rossano | |||
| Republic of Salice | Salice | |||
| Kingdom of Sila | Cosenza | |||
| Republic of Tropea | Tropea | |||
| Republic of Solarios | Galdurmar |
Demographics
TBA
Largest cities
TBA
Immigration
TBA
Languages
TBA
Religion
TBA
Education
TBA
Health
TBA
Holidays
TBA
Economy
TBA
Agriculture
According to the last national agricultural census, there were 1.6 million farms in 2018 (−32.4% since 2010) covering 12.7 million hectares (63% of which are located in Northern Ionio). The vast majority (99%) are family-operated and small, averaging only 8 hectares in size. Of the total surface area in agricultural use (forestry excluded), grain fields take up 31%, olive tree orchards 8.2%, vineyards 5.4%, citrus orchards 3.8%, sugar beets 1.7%, and horticulture 2.4%. The remainder is primarily dedicated to pastures (25.9%) and feed grains (11.6%).
Ionio is the world's top wine producer, and one of the leading in olive oil, fruits (apples, olives, grapes, oranges, lemons, pears, apricots, hazelnuts, peaches, cherries, plums, strawberries and Kiwifruit), and vegetables (especially artichokes and tomatoes). The most famous Ionian wines are probably the Monterossoo and the Leccese Barolo. Other famous wines are Sibari, Brindisi, Brunello di Montalto, Frascati, Montepulciano di Taranto, Morellino di Martina Franca, and the sparkling wines Aurora and Fasano. Quality goods in which Ionio specialises, particularly the already mentioned wines and regional cheeses, are often protected under the quality assurance labels DOC/DOP. This is considered important in order to avoid confusion with low-quality mass-produced ersatz products.
Mineral resources

Mining activities in the Ionian are diverse but depend on location. The Sila mountain range contains coal deposits that were exploited during the industrial revolution for coal production, and iron ore gaiciments are present to a small extent.
The main element of mining activity is quartz and silica. Important gaiciments of pure quartzite and are used to produce silica and then used in the production of microchips and solar panels while low-grade quartzite is used in the construction industry.
There are small deposits of minerals such as copper, zinc, graphite and are recorded considerable presence of lead indicating the possibility of presence of uranium and thorium.
In addition to the presence of minerals, the production of marble is also notable, with Lumi Marble being cosdierated of a valuable variety and thus used throughout the world for the construction of buildings and in sculpture.
Oil industry and chemical industry
The oil industry is highly developed, even though Ionio has very few oil fields. Most oil is imported from countries such as Fulgistan and TBA . Most refineries are located in coastal areas. The most famous is the Taranto refinery that manages to process more than 540,000 barrels per day.
In the state of Tropea and Salice, there are few oil and natural gas deposits that are mined by the Hydraulic fracturing.
Industry
The industrial sector is very popular especially the metal industries, nuclear industry, war industry, shipbuilding and railway car. Since 1980 onwards is spreading the high technological industry (chips, computers and mobile phones). Widespread in the railway industry, oil refining and natural gas. In the nations has spread the processing of agricultural products.
Ionio has an important manufacturing industry that is more concentrated in the north of the country. Thanks to the available resources, steel industries have developed that are mostly concentrated in Taranto. In Taranto there is the largest foundry in Ionio and therefore a fundamental hub in the industries that need iron and steel. Going down to the south and north, the model of small and medium-sized family-run industries prevails and in this case they produce textile material and luxury goods.
In this sector is also considered the sector that is called The Ionian Style – especially in industrial design, furniture, cars – is characterized by the mixture of imagination and design rigor and is characterized by the use of materials considered waste, but at the same time innovative. Museums and awards are dedicated to Sicilian design, represented by companies, specialization schools and artists such as Gio Pontile, Enrico Sottsass and Bruno Mulinari, such as the Compasso d'Oro Award, the oldest and most prestigious design award in the world. The Fiorenza Fair, the largest South American exhibition center, annually hosts numerous international design exhibitions.
Advanced and diversified, the Ioninan industry is particularly developed in the sectors of shipbuilding, household appliances, chemical, pharmaceutical, metallurgical, agri-food and defense. In the automotive sector, which together with petrochemical and steel was the basis of the country's post-war industrialization.
High-tech industry
With technological development and scientific research investment, it has enabled the development of the computer industry as well as the photovoltaic industry. Over the years the Ionian computer industry has developed intensively allowing the creation of large companies such as Blume Technology Corporation and Nakatomi Corportarion that produce not only microprocessors but also technological consumer goods.
In addition to companies that produce hardware there are also companies that produce software such as Devotion that produce video games. Thanks to the university system, new software houses are continuously being born that continue to innovate the technological sector of Ionio.
In addition to computer companies there are also pharmaceutical industries such as Schiroli Farmaceutici that produce pharmaceuticals as well as investing in the search for new medicines. In Ionio there are also companies that allow treatment using phage therapy with a collaboration with the universities of Ionio under a strict control of the Ministry of Health.
The military industry is being driven by Ionian Military Industries, Alenia Defense and Betona companies, which are investing in the development of modern weapons as well as modern security systems.
Banking
Ionio's banking sector is highly developed. The first banks were founded soon after the creation of Ionian due to the reforms that were undertaken.
The city of San Foca is home to Ionio Stock Exchange a major financial center for stock trading while in the city of Taranto there is Ionio Mercantile Exchange which manages commodity futures exchange. The Ionio Stock Exchange is divided into two fundamental units. Ionio Industrial Average which deals with traditional industries and Automated Quotations Ionio Industrial Average where high-tech and next-generation industries are listed.
Over the years, some States of Ionio have adopted tax relief laws that allow the registration of Offshore company.
Tourism
Tourism is considered the key sector of Ionian economy. Thanks to an efficient transportation infrastructure, they allow for a constant handling of tourists throughout the year favored by the Mediterranean and sub-tropical climate.
In Ionio there are many companies operating for the industrial sector especially the cruise company TSC Cruises.
In Ionio there are also companies related to fun and amusement parks. The most famous company is Belmont Park which runs amusement parks and water parks, followed by Sette Bnadiere and Federico Fazzellini.
In the republic of Tropea and the Republic of Solarios there is special interest in gambling tourism.
The summer season is the most important because it manages a large amount of tourists who come from all over the world. During the winter season, winter tourism is widespread in the states of Sila and Arachova, although beach resorts in northern Ionio prevail because of its warm climate. The city Camigliatello Silano is famous for its ski slopes and various winter sports and for its policy against light pollution that allowed it to attract turisit to see Milky Way at night
Thanks to the spectacular landscape many tourists come every year who visit Ionio and the number of tourists grows every year so much that there have been investment plans for the enhancement of infrastructure to manage the large amount of tourists. People mainly visit Ionio for its rich culture, cuisine, history, fashion, architecture and art although there is also tourism related to gambling.
Energy sector
Due to the deposits present and the import of coal, oil, and natural gas, it has enabled Ionian to produce electricity. But the primary ecological energy source remains hydropower because of the sila mountain range and its rivers. Geotemical and wind power have also enabled environmentally friendly development of energy production, but the primary contributing factor is solar panels, which have saved pollution from power plants
Garbage collection also makes it possible to participate in electricity production with incinerators present in all states also due to the widespread diferentiated collection throughout the nation.
Insert nuclear section
Ionio invests in the search for alternative energy sources including the production of Biofuels as well as solutions for storing and reusing carbon dioxide
Infrastructure
Highway and Road

The Ionian road network is very large and extensive, and its first construction riasle in the period when Aroman settlers founded the first towns. Things changed dramatically with the industrial revolution and the introduction of the first automobiles in 1910 until the first modern road network was built in 1916.
This changed in 1956 when the volume of automobiles increased and plans began for the first national highway network, which was achieved in 1960 with the development of the Ionian Interstate. Until 1995, the interstate was state-owned with fuel tax funding but with computerization, the state-owned Interstate Ionica Corporation was created to manage the highway network and its construction and made the entire highway network tolled by adopting the Open road tolling system, consequently eliminating the fuel tax that was used to fund the highway.
In addition to the highway there are national roads and local roads which are state-run but with delegation to the relevant administrations. There is a network of local and national and international bus transportation but they are reduced due to the strong competition of railways especially in national and international connections while at the local level they work very well as some bus companies are run by the railway companies.
Rail
Railway development dates back to the XXXX just after the First Aurelian War. In this period the first railway companies were born and in comity with the industrial revolution also began the rapid railway development of Ionio. In 1893, the Ionian federal government had to intervene to improve the railway situation, and eventually a law was passed that sanctioned the acquisition Rail infrastructure from private railway companies and the establishment of the state-owned Rete Ferroviaria Ionica company, which operates Rail infrastructure and asset management related to railways.
This thing marks a profound change in railroad management but allowed for an increase in research and development by the railroad companies that turned first into the development of the Streamliner steam locomotives and finally in 1939 came the development of the progenitor of modern high-speed trains with ETV 0 that managed to reach 200 km/h using the 3KV DC electric transmission method. With this breakthrough came the electrification of the national railway until 1964 where they experimented with 25KV AC electric traction with ETV 100 that touched the maximum speed of 220 km/H
The synergy between universities, private companies and public companies made it possible to develop the first Ionian high-speed railway in 1984 connecting San Foca with Taranto. The success of this venture made it possible to create the current rail network by improving the method of rail transportation and creating the backbone of the modern Ionian railway network.
At present, the Ionian railway network is extensive especially in the south central part of the nation including the high-speed railway that connects the main cities.The rail tracks and infrastructure are managed by Rete Ferroviaria Ionica which is a state-owned corporation and acts as an impartial gidget in disputes between private railroad companies while ensuring the free railroad market.
There are a total of 5 private ferroviaire companies that are the result of various mergers of old railway companies. The most important company is Ferrovia Ionica followed by Nuovo Trasporto Ferroviario and Solarios Railroad Corporation. Then there is Avanti Sila, Ionita which are smaller railroad companies that focus heavily on regional services although they have expressed interest in domestic and international services. In recent years, the first experiments for high-speed rail transport for light freight have begun, finding great success.
Air

Air transportation became widespread in the 1950s and 1960s with the introduction of the first jet planes. Because of its artistic beauty and its central location in mainland Aurelia allowed Ionian to become a center of air transportation but things changed as early as 1964 with the introduction of the first high-speed trains and the gradual improvement of the railroad caused a collapse in domestic demand forcing Ionian air companies to focus more on the international market.
Currently, the busiest airport in Ionian is San Foca International Airport followed by Rossano International Airport and Tropea International Airport which are also the cities with the highest tourist flow in Ionio. As for airlines, the most widely used is Ionian Airlines and its competitor Sila Airways, which handle both passenger and cargo traffic
Water
The first ports are of the cities of Taranto, Sibari and Rossano that were founded by Aromans settlers who arrived in the 700s. From that time the ports came to assume a key role for fast communications along the Ionian coast and the rest of the world. During the 1800s things changed with the introduction of railroads, which became the main transportation system for moving goods and people within the Ionian and into the mainland, but ports continued to assume a key role with the glubal trade.
Ionian ports have undergone upgrades and extensions to accommodate the ever-increasing traffic of cargo ships. Same with cruise traffic where modern cruise docks have been installed in port cities. In total Ionio has 5 main seaports followed by 6 secondary seaports. Both ports are equipped with cruise docks. The busiest port in Ionio remains the Port of Traanto
Culture
Architecture
Ionio had a development with different styles of architecture. The first cities founded by settlers were based on Renaissance architecture but over time there have been different styles of construction.
During the colonial period, castles and palaces were built. Many Mantellan architects such as Luigi Cannavaro came to Ionio to teach their styles to local architects. These cultural exchanges made it possible to create original styles in Ionio where pre-colonial elements were mixed with the elements of the various Europan architectural styles.
During the XXX the first skyscrapers were built and after the XXX Art Deco spread. At the same time, Futurism Architecture which ended at the end of XXX. It resumed with other types of style such as Googie architecture, New Formalism, Mid-century modern architecture, High-tech architecture and Neo-futurism.
Visual Art and Literature
Visual art and pre-colonial literature was saved and is still available today. With the arrival of the Mantellan settlers, there was a radical change. Mantellan artists came to Ionio to teach local artists and there was a mixing with indigenous culture with Europan culture, creating numerous works of art. During the period of the war of independence, the visual art and literature were used as propaganda messages and to inspire nationalist poems.
When Ionio was hit by the industrial revolution, the style of Verismo where many novels were made. Also, the genre of Adventure. When the Futurism movement exploded, many writers and painters became interested in this movement. The Futurist movement together with the Art Deco movement heavily influenced the Ionian culture that still persists today, although only a few key concepts are used and readapted to the modern context. In modern times there is no one genre but more subgenres that it is difficult to understand a dominant genre.
Newspapers and Television
Newspapers were the primary source of news in Ionio. During the second half of the nineteenth century many newspapers were born but with the introduction of radio, television and the internet the number of newspapers decreased. Today the most important newspapers are Libero Quotidiano and the Corriere di San Foca. Then there are several newspapers spread throughout the national territory and there are small newspapers that are spread only within the states.
With the development of the radio began the rapid diffusion of radio stations that had a local diffusion. But already in this began to form the first degrees of society in the field of telecommunications, but the real explosion occurs around 1950 with the rapid spread of television.
With the rapid spread of television brought a period called occupation of the ether, a phenomenon that led to the birth of large media corporations. The first television and radio company was Ionio Broadcasting Corporation, followed by Mediaset Communication , Tropea Broadcasting System and finally Wolf Broadcasting Company which are considered the largest television broadcasters in Ionio. Transmission companies were created at the local level but occupied frequencies in a savage way causing regulation by the state. In 1974 Ionio Broadcasting Corporation was taken over by Fininvest and consequently passed into the management of the young John Colucci. After a period of adjustment with the laws on the regulation of the sector began the golden age of Ionian television that lasted throughout the 80s.
During the 90s there was the period of television trash and rivalry between Ionian Broadcasting Corporation and Mediaset Communication and the revival Wolf Broadcasting Company. With the advent of the Internet, companies had to adapt to new needs and in 20XX the transition to digital television broadcasting was completed. With the purchase by the Colucci family of the telecommunications company Telecom the largest telecommunications conglomerate was created with the merger between Ionio Broadcasting Corporation and Telecom forming the new company IonioCast causing another war between the major companies and triggering a series of interventions to regulate the internet service and the rapid spread of streaming services.
Music

From folk music to Classical music, music is an intrinsic part of Ionian culture. Thanks to the Mantellan settlers, Europan musical instruments were imported, and local musical artists managed to create music by combining local elements with Europan elements. Since in Mantella is the birthplace of Mantellan Opera has also spread in Ionio with the formation of internationally renowned musicians.
The Ionian music scene changed rapidly with the introduction of new musical styles such as jazz, progressive rock and other musical genres of new conception.
Ionio contributed to the development of disco and electronic music, with Ionio disco, known for its futuristic sound and prominent use of synthesisers and drum machines, being one of the earliest electronic dance genres. By the latter half of the 1990s, a subgenre of Ionio Dance emerged. Taking influences from Ionio disco and Ionio House, Ionio dance generally included synthesiser riffs, a melodic sound, and the usage of vocoders. Since 2010 the Synthwave genre is spreading which is a musical genre based mainly on music associated with the soundtracks of action, science fiction and horror films of the 80s. Other influences are drawn from the art and video games of the decade. Synthwave musicians often espouse nostalgia for the culture of the 80s and attempt to capture the atmosphere of the era and celebrate it.
Today, Ionian pop music is represented annually with the Sibari Music Festival and EurthVision Song Competition. Many singers like Lucia Ramos, Ettore Capone are world-famous singers.
Cinema
With the spread of cinema in the world also in Ionio important films were made that have made the history of cinema. At the beginning the films were made with an experimental scenography but after the XXXX there was the real diffusion of cinema thanks to world-famous directors such as Federico Rimbaldi and Massimo Leone, who made various masterpieces of cinema neorealism.
During the 60s the genre Spaghetti Western both dramatic and comic while producing genre films Poliziotteschi where police and crime violence were exalted. The comedy spread but reached its peak during the 80s where the genre Sexy comedy all'ionica dominated.
Between the 80s and 90s the genre spreads was Slasher while in recent times there is no dominant genre, but many films of different genres are produced.
In addition to the important film production companies, independent production companies are founded in recent years that are able to generate films of excellent quality. The most influential studios of Ionio is that of Rossano, while the Tropea Film Studio is famous for action scenes and genres such as Crime drama and Gangster film.
Sport
Football
Football is the most practiced sport in Ionio. Although there are several variations of football, the two most practiced sports of football are Football and the Calcio a Griglia
Calcio is regulated by the Ionian Football Federation which operates the Ionian football system where the top league is the Serie A. In addition to the Serie A is made the Ionian Cup which is an annual competition that decrees the champion of Ionian Calcio. Ionian Football Federation is a member of UENA Football and AMFC
Calcio a Griglia is run by Ionian Federation of Gridiron Football. In total there are only two professional leagues. The first concerns the football played by university teams while the most important league is IFL which manages the only top professional league. To avoid conflicts of the two sports it was established that during the autumn winter Calcio a Griglia would be practiced while during the spring and summer Calcio is practiced.
All Ionian universities came together to form National University Athletic Association (NUAA) which runs all university sports competitions including Football and Calcio a Griglia. On the evening of the first day of the New Year, the New Year Buwl is held, which is a friendly game of the winner of the Ionio Buwl of the IFL with the winner of the Sun Buwl of the NUAA.
Motoring
Motorsports are the second most followed in Ionio. The Ionica Stock Cup series is the Stock Car Racing championship run by the Jonica Stock Car Auto Racing Association.
Very important is the Automobile Club Ionica that manages all the car and motorcycle races. Ionica Grand Prix is the highest moment of the motoring season in which there is the KAP World Grand Prix race and many ionian go to see it to cheer the Scuderia Tommaso. Also important is the Ionica Motorcycle Grand Prix where the Ionian team Lorenzo Corse participates. Very impressive are the Motorcycle Chariot Race which are the modern version of the Chariot Race inherited from the Aroman empire.
Other sports
Basketball, volleyball and cycling are the other most followed sports although they are followed in a minor way