Florentia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
Florentia has an area of 325 747 km2 and a population of 26 223 000 inhabitants (2020). Its capital city is [[Montcharmin]] but its biggest city is [[Belleville]]. While most of the country is very flat, dominated by forests, grasslands and bayous supplied by an important and complex system of natural waterways, the northern part of the country has hills and small plateaus where can be found the source of the two main rivers of the country, the [[Saint-Elme river|Saint-Elme]] and the [[Borria river|Borria]]. Because of the arid North of the [[Cashari Island]], Northern Florentia occasionally suffers from small sandstorms, while Southern Florentia occasionally suffers from hurricanes. | Florentia has an area of 325 747 km2 and a population of 26 223 000 inhabitants (2020). Its capital city is [[Montcharmin]] but its biggest city is [[Belleville]]. While most of the country is very flat, dominated by forests, grasslands and bayous supplied by an important and complex system of natural waterways, the northern part of the country has hills and small plateaus where can be found the source of the two main rivers of the country, the [[Saint-Elme river|Saint-Elme]] and the [[Borria river|Borria]]. Because of the arid North of the [[Cashari Island]], Northern Florentia occasionally suffers from small sandstorms, while Southern Florentia occasionally suffers from hurricanes. | ||
| Line 158: | Line 152: | ||
Florentia has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa), with long, hot, humid summers and short, mild winters. The subtropical characteristics of the country are due to its low latitude, low lying topography, and the combined influences of the [[Cashari Sea]] and its waterways system. | Florentia has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa), with long, hot, humid summers and short, mild winters. The subtropical characteristics of the country are due to its low latitude, low lying topography, and the combined influences of the [[Cashari Sea]] and its waterways system. | ||
Rain is frequent throughout the year, although from April to September is slightly wetter than the rest of the year, which is the country's wet season. There is a dip in precipitation in October. In summer, thunderstorms build during the heat of the day and bring intense but brief, tropical downpours. In winter, rainfall is more frontal and less intense. | |||
Summers in southern Florentia have high temperatures from June through September averaging 32°C or more, and overnight lows averaging above 21°C. At times, temperatures in the 32–37°C, combined with dew points in the 24–26°C, create sensible temperatures over 49°C). The humid, thick, jungle-like heat in southern Florentia is a famous subject of countless stories and movies. | |||
Temperatures are generally warm in the winter in the southern part of the country, with highs around [[Belleville]], [[Mouvant]], the rest of southern Florentia and the [[Cashari Sea]], averaging 19°C. The northern part of the country is mildly cool in the winter, with highs averaging 15°C. The overnight lows in the winter average well above freezing throughout the country, with 8 °C the average near the Sea and an average low of 3 °C in the winter in the northern part of the country. | |||
{| class="toc sortable" style="text-align: center; font-size: smaller;" | |||
|+ Average temperatures in Louisiana (°F/°C) | |||
|- | |||
! || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Jan{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Feb{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Mar{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Apr{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}May{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Jun{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Jul{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Aug{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Sept{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Oct{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Nov{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Dec{{spaces|2}} || data-sort-type="number" | {{spaces|2}}Annual{{spaces|2}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Shreveport, Louisiana|Shreveport]]<ref name="Shreveport">{{cite web | |||
|url = https://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=shv | |||
|title = NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data | |||
|publisher = National Weather Service Forecast Office, Shreveport, LA, [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] | |||
|access-date = February 21, 2012 | |||
|archive-date = June 27, 2015 | |||
|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150627103535/http://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=shv | |||
|url-status = live | |||
}}</ref> | |||
| {{cvt|47.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|50.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|58.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|65.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|73.4|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|80.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|83.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|83.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|77.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|66.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|56.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|48.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|65.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Monroe, Louisiana|Monroe]]<ref name="Shreveport"/><!--Shreveport Regional Airport--> | |||
| {{cvt|46.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|50.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|57.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|65.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|73.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|80.4|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|76.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|66.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|56.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|48.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|65.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Alexandria, Louisiana|Alexandria]]<ref name="Shreveport" /> | |||
| {{cvt|48.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|52.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|59.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|66.4|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|74.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|80.7|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|83.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|83.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|78.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|58.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|50.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|66.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Lake Charles, Louisiana|Lake Charles]]<ref name="Lake Charles">{{cite web | |||
|url = http://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=lch | |||
|title = NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data | |||
|publisher = National Weather Service Forecast Office, Lake Charles, LA, [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] | |||
|access-date = February 21, 2012 | |||
|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160822005550/http://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=lch | |||
|archive-date = August 22, 2016 | |||
|url-status = live | |||
}}</ref><!--Lake Charles Regional Airport--> | |||
| {{cvt|51.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|55.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|61.4|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|75.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|81.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|83.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|78.7|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|70.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|61.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|53.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Lafayette, Louisiana|Lafayette]]<ref name="Lake Charles" /><!--Lafayette Regional Airport--> | |||
| {{cvt|51.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|55.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|61.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|75.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|81.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.8|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|78.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|69.7|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|61.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|53.7|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[Baton Rouge, Louisiana|Baton Rouge]]<ref name="Baton Rouge">{{cite web | |||
|url = http://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=lch | |||
|title = NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data | |||
|publisher = National Weather Service Forecast Office, New Orleans/Baton Rouge, LA, [[National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration]] | |||
|access-date = February 21, 2012 | |||
|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160822005550/http://w2.weather.gov/climate/xmacis.php?wfo=lch | |||
|archive-date = August 22, 2016 | |||
|url-status = live | |||
}}</ref><!--Baton Rouge area--> | |||
| {{cvt|51.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|54.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|61.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|67.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|75.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|80.7|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|78.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|60.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|52.9|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|68.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|- | |||
! [[New Orleans]]<ref name="Baton Rouge" /><!--New Orleans Audubon--> | |||
| {{cvt|54.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|57.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|63.6|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|70.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|77.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|82.4|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|84.0|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|84.1|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|80.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|72.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|63.5|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|56.2|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} || {{cvt|70.3|F|C|abbr=values|disp=x|/}} | |||
|} | |||
===Flora and fauna=== | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 19:51, 11 August 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Confederate States of Florentia Etats Confédérés de Florentie (Lysian) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Pour l'Empereur et la Liberté !" "For the Emperor and Liberty" | |
| Anthem: "La Marche des Gens de Cœur" "Dans les bayous de Bayave" (unofficial, popular) | |
 Map of Florentia | |
| Capital | Montcharmin |
| Largest | Belleville |
| Official languages | Lysian |
| Recognised national languages | Florentian creole |
| Recognised regional languages | Stillian |
| Ethnic groups (2022) | Lysian (69,4%) Natives (17,3%) Esonian (6,9%) Stillian (4,8%) |
| Religion (2022) | Orthodox (70%) Animism (16,7%) Agnostic (6%) Tocalic (4%) Other (3,3%) |
| Demonym(s) | Florentian |
| Government | Confederation of autonomous states within a Parliamentary Monarchy |
• Emperor | Ambroise IV |
• Confederal Chancellor | Hugo Lysandre Dellague |
| Legislature | Confederal Senate |
| Independance [from Lysia] in 1789 | |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 26 223 000 |
| Currency | Imperial Franc (IF) |
Florentia, officially the Confederate States of Florentia, is a develloping country on Eurth, located in Eastern Alharu, on the Cashari Island. It has a population of approximatly 25 323 000 inhabitants and has a size of 325 747 km2. The political capital city is Montcharmin, while the economic capital city is Belleville.
Florentia is a confederal parliamentary monarchy, ruled by an Emperor and a Senate. A former Lysian colony, Florentia broke free in 1789. After an era of glory because of its high value agricultural products, Florentia slowly began to lose power and influence because of its outdated means of production (mainly the use of slavery). The head of state is Emperor Ambroise IV, while the head of the legislature, appointed by the Emperor among the 12 Senators, is the Confederal Chancellor Hugo Lysandre Dellague.
The Florentian economy is mainly based on high-quality agricultural exports, the main ones being cotton, tobacco and sugar cane. There is also a develloping mining sector in the northern states and small industries centered around tobacco products and textile. Tourism also holds an important place. Because of the presence of both de jure and de facto slavery in 8 of the 12 states, Florentia is subject to economic sanctions from numerous countries.
Etymology
Florentia has been named by the founders of Port-Rouge - the first lysian settlement on the Cashari Island - to honor the Lysian sailor Florent Bouvier who explored the Saint-Elme river and its delta.
Geography
Florentia has an area of 325 747 km2 and a population of 26 223 000 inhabitants (2020). Its capital city is Montcharmin but its biggest city is Belleville. While most of the country is very flat, dominated by forests, grasslands and bayous supplied by an important and complex system of natural waterways, the northern part of the country has hills and small plateaus where can be found the source of the two main rivers of the country, the Saint-Elme and the Borria. Because of the arid North of the Cashari Island, Northern Florentia occasionally suffers from small sandstorms, while Southern Florentia occasionally suffers from hurricanes.
Rivers, lakes and reservoirs
Florentia has thousands of small rivers and creeks, creating a complex system of natural and navigable waterways in all the country. The country also has numerous bayous along the Saint-Elme river, the Borria river and the coast. Those water ressources provide recreation, civil and freight transporation, fishing, hunting, crop irrigation and water for human consumption, and millions of Florentians are reliant on it.
Climate
Florentia has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa), with long, hot, humid summers and short, mild winters. The subtropical characteristics of the country are due to its low latitude, low lying topography, and the combined influences of the Cashari Sea and its waterways system.
Rain is frequent throughout the year, although from April to September is slightly wetter than the rest of the year, which is the country's wet season. There is a dip in precipitation in October. In summer, thunderstorms build during the heat of the day and bring intense but brief, tropical downpours. In winter, rainfall is more frontal and less intense.
Summers in southern Florentia have high temperatures from June through September averaging 32°C or more, and overnight lows averaging above 21°C. At times, temperatures in the 32–37°C, combined with dew points in the 24–26°C, create sensible temperatures over 49°C). The humid, thick, jungle-like heat in southern Florentia is a famous subject of countless stories and movies.
Temperatures are generally warm in the winter in the southern part of the country, with highs around Belleville, Mouvant, the rest of southern Florentia and the Cashari Sea, averaging 19°C. The northern part of the country is mildly cool in the winter, with highs averaging 15°C. The overnight lows in the winter average well above freezing throughout the country, with 8 °C the average near the Sea and an average low of 3 °C in the winter in the northern part of the country.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sept | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shreveport[1] | 47.0/8.3 | 50.8/10.4 | 58.1/14.5 | 65.5/18.6 | 73.4/23.0 | 80.0/26.7 | 83.2/28.4 | 83.3/28.5 | 77.1/25.1 | 66.6/19.2 | 56.6/13.7 | 48.3/9.1 | 65.9/18.8 |
| Monroe[1] | 46.3/7.9 | 50.3/10.2 | 57.8/14.3 | 65.6/18.7 | 73.9/23.3 | 80.4/26.9 | 82.8/28.2 | 82.5/28.1 | 76.5/24.7 | 66.0/18.9 | 56.3/13.5 | 48.0/8.9 | 65.5/18.6 |
| Alexandria[1] | 48.5/9.2 | 52.1/11.2 | 59.3/15.2 | 66.4/19.1 | 74.5/23.6 | 80.7/27.1 | 83.2/28.4 | 83.2/28.4 | 78.0/25.6 | 68.0/20.0 | 58.6/14.8 | 50.2/10.1 | 66.9/19.4 |
| Lake Charles[2] | 51.8/11.0 | 55.0/12.8 | 61.4/16.3 | 68.1/20.1 | 75.6/24.2 | 81.1/27.3 | 82.9/28.3 | 83.0/28.3 | 78.7/25.9 | 70.1/21.2 | 61.1/16.2 | 53.8/12.1 | 68.6/20.3 |
| Lafayette[2] | 51.8/11.0 | 55.2/12.9 | 61.5/16.4 | 68.3/20.2 | 75.9/24.4 | 81.0/27.2 | 82.8/28.2 | 82.9/28.3 | 78.5/25.8 | 69.7/20.9 | 61.0/16.1 | 53.7/12.1 | 68.5/20.3 |
| Baton Rouge[3] | 51.3/10.7 | 54.6/12.6 | 61.1/16.2 | 67.6/19.8 | 75.2/24.0 | 80.7/27.1 | 82.5/28.1 | 82.5/28.1 | 78.1/25.6 | 68.9/20.5 | 60.0/15.6 | 52.9/11.6 | 68.0/20.0 |
| New Orleans[3] | 54.3/12.4 | 57.6/14.2 | 63.6/17.6 | 70.1/21.2 | 77.5/25.3 | 82.4/28.0 | 84.0/28.9 | 84.1/28.9 | 80.2/26.8 | 72.2/22.3 | 63.5/17.5 | 56.2/13.4 | 70.3/21.3 |
Flora and fauna
History
(WIP.)
- Lysian explorers found Port-Rouge along the Saint-Elme river, the 28 of May, 1587. Beginning of the Lysian colonization of actual Florentia. Natives are enslaved by setlers
- Lysia being a republic and Florentian being mostly monarchists, tensions grows. Lysia take some decision which would the straw that breaks the camel's back, and Florentia declare independance.
- War of independance (WIP).
- Election of the Emperor of Florentia : the second son of the King of Louvier is elected. The Emperor holds most of the power and the states have a little autonomy.
- 1850's-1860s : the imperial family die in a tragic incident and the Florentian crown goes to the King of Louvier. Thus, Florentia and Louvier become a personnal union.
- The Louvian King, pressured by natives, try to outlaw Florentian slavery. Nine of the twelve states secede from the Empire : beginning of the Florentian cival war with the slave states opposing Louvier and the anti-slavery states. The slave states win and abdicate the Louvian King from the throne of Florentia, installing his second son. The victorious states write the "Confederal Act", lightening a lot the power of the Emperor is very lightened while giving huge autonomy to the states.
- 1887 : Drafting of the "Charter of the Master and the Slave", guaranteeing the first rights to slaves and greatly limiting the punishments given by the masters. The charter is signed by five of the states.
- 2019 : One of the most severe states with regard to slaves undergoes a major slave revolt. The slaves managed to organise themselves and control part of the state, with no advances on either side. (WIP)
- 2022 : Florentia and the revolt sign an armistice, but are technicly still at war with each other. (WIP)
Politics
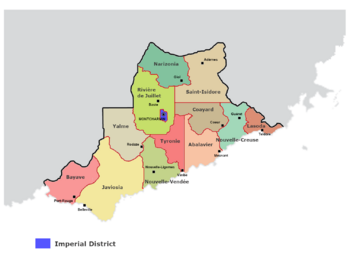
The Confederate States of Florentia are divided in 12 states which have an important autonomy.
List of the Florentian states
| # | Name | Type of regime | State capital | Population | Leading political party | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Javiosia | Kingdom (constitutional monarchy) | Belleville | 9 103 000 | Constitutionalist Union | |
| 2 | Lasoda | Duchy (semi-constitutional monarchy) | Teldore | 1 539 000 | Coalition (Constitutionalist Union, Legitimist Stillian Party) | 
|
| 3 | Nouvelle-Vendée | Kingdom (semi-constitutional monarchy) | Nouvelle-Ligomes | 820 000 | New-Vendean Party | |
| 4 | Abalavier | Kingdom (absolute monarchy) | Mouvant | 1 507 000 | N/A | |
| 5 | Bayave | Marquisate (semi-constitutional monarchy) | Port-Rouge | 915 000 | Popular Party | 
|
| 6 | Nouvelle-Creuse | Kingdom (semi-constitutional monarchy) | Guéret | 1 338 000 | Legitimist Party of Nouvelle-Creuse | 
|
| 7 | Rivière de Juillet | Kingdom (constitutional monarchy) | Baste | 3 498 000 | Constitutionalist Union | 
|
| 8 | Yalme | Duchy (constitutional monarchy) | Rodaze | 1 180 000 | National Liberal Party of Yalme | 
|
| 9 | Tyronie | Kingdom (constitutional monarchy under a military junta) | Vimbe | 602 000 | N/A | 
|
| 10 | Narizonia | Republic (Unitary and presidential republic, authoritarian democracy) | Giol | 2 293 000 | Free Lysian Action | |
| 11 | Saint-Isidore | Republic (Federal and parliamentary republic, full democracy) | Adèrnes | 1 722 000 | Republican Party | |
| 12 | Coayard | Republic (Unitary and semi-presidential republic, full democracy) | Coeur | 806 000 | Liberty Union | 
|
Central government
The executive power is hold by the Emperor, although it is very small. Most of the power comes from the legislative one, incarned by Confederal Senate. It is composed of twelve senators, one per state. Senators are elected every two years, without limit to the number of terms, by the citizens of their respective states. Each senator has one vote, except the Confederal Chancelor, named by the Emperor, which has two votes.
States government
(WIP.)
Economy
(WIP. Employment. Exports. Energy. Transport. Media. Currency.)
The Florentian currency is the Imperial Franc, or "Franc Impérial" in Lysian.
Agriculture
- Huge export-based agriculture economy
- One of the main exporter of tobacco, cotton
- Also produces some maize, wheat, soybean
- Use of slavery
Mining
- Important sulphur and magnesium ressources. Few natural gaz
- Exploitation of sand (one of the main exporter) and controversy over the progressive destruction of beaches
Industry
- Industry (textile, cigares) in Javiosie
- Developping industry in a few other states
Tourism
- Important tourism, despite a boycott due to the use of slaves
- Renown to be a "return to the past"
- Famous steam boats cruise on the Saint-Elme river
Demographics
(WIP. Ethnic groups. Language. Religion. Health. Education.)
Cultures
(WIP. Literature. Visual arts. Music. Cuisine. Sport.)
- Culture : Louisianian creole, natives
Traditionnalism
- Stuck in the past, glorification of the "good old time" in the late XIXth, start of the XXth.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data". National Weather Service Forecast Office, Shreveport, LA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on June 27, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data". National Weather Service Forecast Office, Lake Charles, LA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on August 22, 2016. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "NowData—NOAA Online Weather Data". National Weather Service Forecast Office, New Orleans/Baton Rouge, LA, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on August 22, 2016. Retrieved February 21, 2012.

