Batsweda: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Batsweda''', officially the '''Republic of Batsweda''', is a country on the southeastern coast of [[Europa (continent)|Azania]] on [[Eurth]]. Bordered by [[Yien]] to its south and the [[Konstantinopoli Sea]] to the east, | '''Batsweda''' ({{wp|Arabic|Sahrabic}}: البهودة, ''āl-Bahūda''), officially the '''Republic of Batsweda''' ({{wp|Arabic|Sahrabic}}: جمهورية البهودة, ''Ǧumhūriyat āl-Bahūda''), is a country on the southeastern coast of [[Europa (continent)|Azania]] on [[Eurth]]. Bordered by [[Yien]] to its south and the [[Konstantinopoli Sea]] to the east, | ||
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
The [[Anglish language|Anglish]] name for the state, ''Batsweda'', comes from the {{wp|Bassa langauge|Banno}} endonym for the region, ''Ɓɛ́xwáɖá'', meaning "the pepper forest" or "the pepper bush" (''ɓɛ́-nì xwáɖá''), referring to the region's heavily forested environment and its notable cultivation of peppers and other spices. This name was first seen in the 16th century Sahrabic tome ''A Guide to the Southern Lands of Azania'', in mentioning the [[Batsweda Empire]]. The [[Sahrabic language|Sahrabic]] name for the country, ''āl-Bahūda'' (البهودة), was also first mentioned within this work. | The [[Anglish language|Anglish]] name for the state, ''Batsweda'', comes from the {{wp|Bassa langauge|Banno}} endonym for the region, ''Ɓɛ́xwáɖá'', meaning "the pepper forest" or "the pepper bush" (''ɓɛ́-nì xwáɖá''), referring to the region's heavily forested environment and its notable cultivation of peppers and other spices. This name was first seen in the 16th century Sahrabic tome ''A Guide to the Southern Lands of Azania'', in mentioning the [[Batsweda Empire]]. The [[Sahrabic language|Sahrabic]] name for the country, ''āl-Bahūda'' (البهودة), was also first mentioned within this work. | ||
Revision as of 07:10, 23 September 2024
Republic of Batsweda | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "O, Dawn of Liberty" | |
 Location of Batsweda (dark green) | |
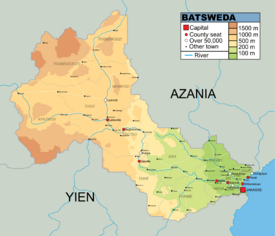 Map of Batsweda | |
| Capital and largest city | Jakasse |
| Official languages | Anglish, Sahrabic |
| Recognised national languages | Banno, Latso, Mi, Nitnide |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | 34.3% Banno 22.8% Latso 19.9% Nitnide 14.5% Mi 6.4% Sahrab 2.1% Other |
| Religion (2020) | 51.9% Salam 38.1% Christianity 5.2% Traditional faiths 3.3% no religion 1.5% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Batswedan |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary directorial republic under a military junta |
| Dialla Sacko (interim) John Obuor (interim) | |
| Samuel Nyantah (interim) | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Independence from the Pepper Coast Company | |
• Conquest of the Tsweda river basin | c. 1500 |
• Siege of Jakasse | 12 May 1811 |
• Independence declared | 11 November 1960 |
• Joined the Assembled Nations | 1 January 1961 |
• End of the First Batsweda Civil War | 12 February 1969 |
| 27 September 2002 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 33,550 km2 (12,950 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 14.2 |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 1,214,380 |
• Density | 36.2/km2 (93.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $4.062 billion |
• Per capita | $3,345 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $1.475 billion |
• Per capita | $1,215 |
| Gini (2024) | medium |
| Currency | Batswedan gerah (₲) (BDG) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (Central Europan Time) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +360 |
| ISO 3166 code | BD |
| Internet TLD | .bd |
Batsweda (Sahrabic: البهودة, āl-Bahūda), officially the Republic of Batsweda (Sahrabic: جمهورية البهودة, Ǧumhūriyat āl-Bahūda), is a country on the southeastern coast of Azania on Eurth. Bordered by Yien to its south and the Konstantinopoli Sea to the east,
Etymology
The Anglish name for the state, Batsweda, comes from the Banno endonym for the region, Ɓɛ́xwáɖá, meaning "the pepper forest" or "the pepper bush" (ɓɛ́-nì xwáɖá), referring to the region's heavily forested environment and its notable cultivation of peppers and other spices. This name was first seen in the 16th century Sahrabic tome A Guide to the Southern Lands of Azania, in mentioning the Batsweda Empire. The Sahrabic name for the country, āl-Bahūda (البهودة), was also first mentioned within this work.
The Pepper Coast, an alternative name used by Anglish speakers for the region since the mid-17th century, was popularized by the Pepper Coast Company after its colonization of modern-day Batsweda's coast in the early 19th century. This name soon became the official name of the territory, and remained so until 1960, when the Batswedan War of Independence ended in decolonization, with the newly independent government officially renaming the state Batsweda in its first constitution.
Geography
Climate
Ecology
History
Antiquity
- By 750 BCE, the earliest signs of human habitation in modern-day Batsweda are seen.
- The Banno people enter the region around 500 BCE, forming sedetary communities based on farming and livestock.
- The fortified settlement of Old Jakasse is founded in the 2nd century BCE, and power in centralized into a local semi-urbanized kingdom.
Kingdom of Jakasse
- By the 1st century BCE, the Kingdom of Jakasse expands throughout the Tsweda river basin, forming an economy based on the exportation of spices, dyes, and gold to the rest of Azania and Europa, especially the Aroman Empire.
- The Latso and Mi peoples settle in the kingdom by the 2nd century CE, employed and metalworkers and pastoralists in the state's northern periphery.
- Pushed on its southern border by the expanding Sarafid Empire, the Kingdom of Jakasse is invaded and conquered by the Sarafids in 416 CE, bringing the region under the influence of its southern neighbour.
Middle Ages
- Under Sarafid rule, the region of modern-day Batsweda is positioned as a periphery province of the empire, with Old Jakasse entering into a period of economic decline. By the 700s CE however, Old Jakasse re-establishes itself as a major trading port.
- In 756 CE, with the collapse of the Sarafid Empire, various fortified settlements and tribes within the Tsweda river basin assert their independence. These small city-states, chief among them Old Jakasse, Sena, and Kpaba, emerge as notable centres of trade, namely around the exchange of gold and spices.
- By 1100, Sahrabic merchants and scholars position themselves within the gold trade, founded the Old Jakasse Madrassa and, by the 1300s, successfully convertimg the Batswaden coast to Salam, with Old Jakasse becoming a notable centre of Sahrab-Banno cultural exchange and learning.
- In 1225, Old Jakasse is besieged and the Bastwedan coast annexed by Yien. Around the same time, the Latso people in the region's north unite into the Latso Kingdom in 1229.
- Between 1505 and 1517, with the growing frequency of Orinese attacks on Yien, an emboldened Banno Salamic merchant class in Old Jakasse successfully rebel against the central authority, with the revolt extending to the rest of the Tsweda river basin. In 1517, Koseda I declares himself Kã́á ("king") of the Batsweda Empire, a large multi-ethnic entity focused on the production and exportation of gold and spices.

