Caerlannach: Difference between revisions
4leafclovrs (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
4leafclovrs (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
| established_event1 = Proclamation | | established_event1 = Proclamation | ||
| established_date1 = 12 December 1972 | | established_date1 = 12 December 1972 | ||
| established_event2 = Free State | | established_event2 = [[Caerlanni Free State|Free State]] | ||
| established_date2 = 19 February 1976 | | established_date2 = 19 February 1976 | ||
| established_event3 = [[Deconstructional Period (Caerlannach)|Deconstruction]] | | established_event3 = [[Deconstructional Period (Caerlannach)|Deconstruction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:23, 20 November 2024
Autonomous Tribes of Caerlannach Treibheanna Uathrialacha na Caerlannaí | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Anthem: Iomann an Phobail (Mealliagian) "The People's Hymn" | |
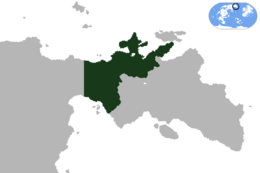 Location of Caerlannach in Eastern Argis (dark green) | |
| Location | Eastern Argis |
| Capital and largest city | Dúnradh (de jure) |
| Official languages | Caerlanni Mealliagian |
| Demonym(s) | Caerlanni |
| Government | Decentralized confederation of autonomous tribes |
| Council of the High Tribes | |
• High Chief | Sionnach |
| Legislature | Lower Council of the Tribesa |
| Independence from Gotneska | |
• Proclamation | 12 December 1972 |
| 19 February 1976 | |
| 1977-1998 | |
• Establishment | February 2, 1998 |
| Area | |
• Total | 448,200 km2 (173,100 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 3.1% |
| Population | |
• January 2024 estimate | |
• 2022 census | 14,551,761 |
• Density | 32.5/km2 (84.2/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $174.24 billion |
• Per capita | $12,000 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $109.14 billion |
• Per capita | $7,500 |
| Currency | Local currencies Gotaish Dollarb |
| |
Caerlannach (Caerlanni Mealliagian: Caerlannaí, pronounced [ˈkaɾlaːnəx]), officially the Autonomous Tribes of Caerlannach (Caerlanni Mealliagian: Treibheanna Uathrialacha na Caerlannaí[a]), is a semi-nomadic confederation of tribes located in the north of Argis on Eurth, with a population of about 15 million. Its de jure capital and largest city is Dúnradh, which is located in the southern portion of the nation. Caerlannach maintains a unique form of governance under the High Chief (Ardri Cennasaí) and the Comhairle na dTreibheanna Ard (Council of the High Tribes), a council of tribal leaders representing each of the seven autonomous tribes. Caerlanni Mealliagian is the official language, and Caerlannach's tribal society is marked by its high reverence for the land and heritage.
The landscape of Caerlannach is predominantly rugged and mountainous, with fertile lowlands along the its narrow coastlines in the north, lush valleys, and thick forests in the south. The region's geological activity includes coastal cliffs, heaths, and a few volcanic zones. Much of the country experiences a temperate oceanic climate with mild, wet winters and cool, breezy summers.
Historical records and oral histories suggest Caerlannach's original tribes settled in the region as early as the 1st century AD. These tribes were organized around clan loyalties and followed spiritual practices, Paganism in particular, closely tied to nature, under the guidance of druids and pagan priests. In the late 7th century to early 9th century AD, Caerlannach was divided into many petty kingships vying for dominance and the title of High King of Caerlannach. Following the 10th century Gotneska invasion, Gotneska claimed sovereignty. A war for independence in the 1970s led by Ronan Luathach was followed by the establishment of the Caerlanni Free State. After a series of initiatives for decentralization, establishment of temporary communes, self-defense networks, and a manifesto, the Autonomous Tribes of Caerlannach was established 1998. As of now, the political entity is still slowly integrating with the wurld through Chonnachta tribe and the Council of the High Tribes.
Caerlannach is known for its close-knit tribal society and a political structure that prioritizes cooperation among tribes. The Council of the High Tribes, comprised of elected representatives from each tribe, oversees the legislative process. It operates under a “non-hierarchical” ethos, with the High Chief as a unifying figurehead who represents the collective identity of Caerlannach on the wurld stage.
Most of Caerlannach's tribes still live forager style of living, relying mostly on bartering with other tribes, especially the Chonnachta, where a coupon- and stamp-based system is used for trading necessary goods.
Today, Caerlannach is recognized throughout the wurld for its commitment to traditional ecological knowledge, sustainable land practices, and the preservation of its traditions and customs. It has one of the highest rates of biodiversity protection and is celebrated for its progressive environmental initiatives. Although the entity maintains a minimalist approach to state governance, its citizens enjoy universal access to basic services through tribal councils, funded and managed by community-based Chonnachta tribe. The entity also has the epithet "Eurth's Conservation" for the entity's strong nature conservation and heavy anti-poaching efforts.
Etymology
The name Caerlannach is derived from a combination of Ruainic and early Mealliagic linguistic roots. The prefix "Caer-" is a term for "fort" or "fortified place," often associated with ancient settlements or defensive strongholds. "Lannach" originates from the Mealliagic "lann", meaning "enclosure" or "land," thus signifying a "fortified land" or "protected territory." This etymology embodies the historical and cultural significance tribal autonomy that defines Caerlannach’s heritage, particularly in the context of its rugged landscape and strong tribal traditions.
Politics
High Chief
(Oileán Fionnghlas Castle)
The political system of Caerlannach is structured as a decentralized anarchist confederation, characterized by a shared governance model among its seven autonomous tribes. The head of state is the Ardri Cennasaí (High Chief), a primarily symbolic figure chosen to represent the unity of the tribes on the international stage. Executive authority rests with the Comhairle na dTreibheanna Ard (Council of the High Tribes), which functions as the collective head of government and is responsible for national policy. Legislative functions are formally assigned to the Comhairle Íochtarach na dTreibheanna (Lower Council of the Tribes), though this body serves mainly ceremonial purposes.
The current High Chief, Sionnach, is the first to hold the title, having assumed the position following the establishment of the Autonomous Tribes. His role is largely ceremonial, intended to symbolize unity across the tribes rather than exercise direct executive power. High Chief Sionnach fulfills duties in diplomacy and presides over significant national events, serving as a respected spokesperson for Caerlannach’s collective identity. He also acts as an advisor to the Council of the High Tribes and represents Caerlannach on the international stage, though he holds no decision-making authority within the government.
The Council of the High Tribes is Caerlannach’s primary executive body, composed of representatives from each tribe, chosen according to each tribe's own customs. This Council functions as a collective head of government, overseeing national affairs, including economic strategy, defense, and inter-tribal relations. Its decentralized structure reflects Caerlannach’s commitment to an anarchist model that emphasizes consensus and cooperation rather than centralized control. This cooperative approach is designed to respect tribal autonomy while facilitating coordination on issues affecting the confederation as a whole.
The Lower Council of the Tribes, which serves as Caerlannach’s legislative body, comprises 35 members, with each tribe contributing five representatives. Its role, however, is largely ceremonial, as the Council of the High Tribes delegates most legislative powers. The Lower Council serves to promote inter-tribal communication, support cultural initiatives, and reinforce the ceremonial aspects of tribal governance. By maintaining a presence in Caerlannach’s political structure, the Lower Council reinforces the confederation’s values of mutual respect and tribal representation.
Caerlannach’s diplomatic relations reflect its emphasis on selective engagement with the international community. It maintains a close alliance with Gotneska. Additionally, the nation is currently under the oversight of an Assembled Nations peacekeeping mission, designed to ensure stability within the autonomous tribal regions. Most of Caerlannach’s foreign diplomatic affairs are managed by the Chonnachta tribe, which has developed a specialized role in international relations. This arrangement allows Caerlannach to uphold its traditional decentralized governance model while engaging in essential international diplomacy.
Local government
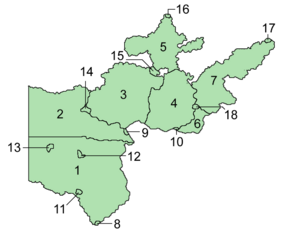
The local government structure of Caerlannach evolved significantly with the formation of the Autonomous Tribes in 1998. Seven primary territories were initially established, their boundaries drawn according to natural geographical features and traditional migration patterns of each tribe. This structure allowed for regional governance that mirrored long-standing tribal affiliations and maintained ecological alignment with the land. In 2005, the High Council of the Tribes signed an agreement with Gotneska to establish three Cathair Shaor (Free Cities) along their shared border, aiming to streamline cross-border travel and trade for both nations. A further expansion of the local government framework took place in 2010 when the High Council authorized the formation of eight Áitreabh Buain (Permanent Settlements) throughout Caerlannach, including Dúnradh, the capital. These settlements were intended to foster inter-tribal trade, stable agricultural production, and serve as more accessible hubs for longer-term residency.
The local government structure assigns distinct responsibilities to each type of region. The seven territories are directly governed and maintained by the tribes, which exercise control over resources, governance, and societal functions within their respective lands. The free cities operate as the primary entry points for foreigners seeking to enter Caerlannach, serving as hubs for immigration paperwork, customs, and limited commerce. These free cities are the only regions outside of Dúnradh where official entry documentation for Caerlannach is processed. The eight permanent settlements are overseen by sub-tribes from the territories in which they reside, tasked with ensuring stable food supplies through agriculture and livestock management, supporting local trade, and providing temporary accommodations for travelers and residents. The settlements aim to enhance local resource sustainability and foster inter-tribal cooperation by supporting a more fixed population, balancing Caerlannach’s otherwise nomadic tribal lifestyle with key areas for community gathering and commerce.
|
Foreign relations
The foreign relations of Caerlannach are administered by the External Affairs Collective (Cnuasach Gnóthaí Eachtracha), an institution overseen by the High Council and facilitated by the High Chief as the de facto foreign minister. Caerlannach is a full member of the AN and maintains diplomatic ties with various countries, particularly those in the region of Argis, with whom it shares historical and cultural affinities. Its international presence is relatively limited, reflecting its focus on regional cooperation and a cautious approach to global engagement.
Caerlannach emphasizes neutrality in international politics, drawing from its historical experience as a protectorate and its subsequent fight for independence.
References
Footnotes
- ↑ Treibheanna Uathrialacha Caerlannach is also used in some documents.
Bibliography
- Brannagh, Chonnachta (2003). Caerlannach: Roots and Revolution. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. ISBN 978-0-8612-3541-8.
- Caomhanach, Luathach (2014). The Spiritual and Political Life of Caerlannach. Senex Media. p. 210. ISBN 978-0-9573-6208-5.
- D’Arcy, Chonnachta (2010). Nature and Nomads: Ecology and Society in Caerlannach. University of Sitia Press. ISBN 978-1-8454-8364-2.
- Gallagher, Uí Caerlann (2008). Reviving the Old Gods: Paganism and Druidry in Caerlannach. Senex Media. p. 195. ISBN 978-0-7562-6410-3.
- Hennessy, Colm (2011). The Autonomous Tribes of Caerlannach: From Revolution to Self-Governance. Dúnradh: Argis University Press. p. 276. ISBN 978-0-9217-5142-7.
- Mac Seáin, Orlaith; Fitzgibbon, Chonnachta (2005). Caerlannach’s Coastal and Mountain Heritage: Geology and Landscape. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. p. 314. ISBN 978-0-7125-9823-1.
- Ní Dhónaill, Chonnachta; de Brún, Fiachra (2009). The Tribal Economics of Caerlannach. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. ISBN 978-1-9013-6814-0.
- Ó Ceallaigh, Uí Caerlann (2012). Living Legends: Oral Histories of the Caerlannach Tribes. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-0-8714-9327-6.
- O’Sullivan, Uí Caerlann (2018). Environmental Guardianship in the Caerlannach Tribes. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. ISBN 978-1-5094-7563-5.
- Walsh (2007). Tribal Unity and Caerlannach Governance: A Decentralized Nation. Dúnradh: Northern Lights Press. p. 223. ISBN 978-0-8764-3391-0.