Geography of Littland: Difference between revisions
(Creation) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
==Political geography== | ==Political geography== | ||
{{Main|Administrative divisions of Littland}} | {{Main|Administrative divisions of Littland}} | ||
{| style="background:none;" | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%;" | |||
|- | |||
! [[Administrative divisions of Littland#Counties|County]] !! [[List of cities in Littland|Capital city]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Kaslund Municipality]]|| [[Kaslund]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Aadal County]]|| [[Aadal]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Aalhavn County]]|| [[Aalhavn]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Tronmark County]]|| [[Aakirkeby]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Klinstrup County]]|| [[Klinstrup]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Fangel County]]|| [[Fangel]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Tystrup County]]|| [[Hjermitslev]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Halling County]]|| [[Halling]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Varborg County]]|| [[Stenmose]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Rødholm County]]|| [[Alestrup]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Solbjerg County]]|| [[Gistrup]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Tirslund County]]|| [[Tirslund]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Klarskov County]]|| [[Klarskov]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Guldberg County]]|| [[Lerte]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Sønderland County]]|| [[Frankerup]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Malskland|Malskland County]]|| [[Karlino]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Regions== | ==Regions== | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 2 November 2022
 | |
| Continent | Argis |
|---|---|
| Region | Central Argis |
| Area | |
| • Total | 198,000 km2 (76,000 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 1,836 km (1,141 mi) |
| Borders | 4,296 km (2,669 mi) |
| Highest point | Sol Mountain, 2,026 m (6,646 ft) |
| Lowest point | Nørrehuse, 3.8 m (12.4 ft) |
| Longest river | Arup River, 940.4 km (584.3 mi) |
| Climate | Temperate climate |
| Terrain | Lowlands, heathland, hills, mountains, forests |
| Natural resources | coal, copper, iron, natural gas, limestone, timber, arable land |
Topography
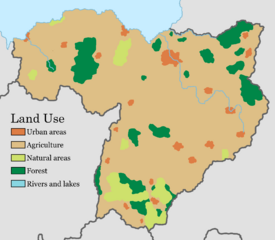
Land use
Biodiversity
Climate
Littland has a temperate climate. The southern mountain ranges are dominated by a climate climate area, the central and northern part of Littland experience a temperate climate year-round. Warm summers and chilly winters are characteristic of the Littish climate. The warmest part of Littland is the Aalhavn region while the coldest is the Malskland due to its elevation. Due to climate change, winters are becoming dryer and snow is rarer and rarer in the northern part of the country. Many plants and flora call Littland home and grow naturally. The most wide-spread type of tree in Littland are conifers such as spruce and pine.
| Climate data for Littland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.9 (30.4) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
2.7 (36.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.4 (72.3) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
9.6 (49.3) |
4.1 (39.4) |
1.0 (33.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
5.6 (42.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
3.0 (37.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49 (1.9) |
39 (1.5) |
35 (1.4) |
34 (1.3) |
42 (1.7) |
70 (2.8) |
67 (2.6) |
81 (3.2) |
58 (2.3) |
72 (2.8) |
61 (2.4) |
53 (2.1) |
661 (26) |
| Source: Littisk Meteorologisk Institut | |||||||||||||
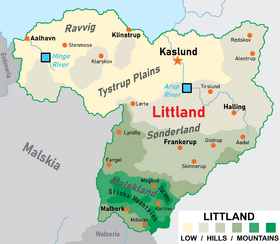
Political geography
RegionsHistorically Littland has been divided into many regions, culturally, politically, linguistically and economically. While these regions no longer exist de jure, they are still identifiable in the modern Littland.
Some regions still in use today, in the form of counties are Aadal, Tronmark and Sønderland. |