Geography of Littland: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| km area = 198,000 | | km area = 198,000 | ||
| miles area = auto | | miles area = auto | ||
| km coastline = | | km coastline = 885 | ||
| borders = | | borders = 2,198 km (1,366 mi) | ||
| highest point = [[Sol Mountain]],<br/>2,026 m (6,646 ft) | | highest point = [[Sol Mountain]],<br/>2,026 m (6,646 ft) | ||
| lowest point = [[Nørrehuse]],<br/>3.8 m (12.4 ft) | | lowest point = [[Nørrehuse]],<br/>3.8 m (12.4 ft) | ||
| longest river = [[Arup River]],<br/> | | longest river = [[Arup River]],<br/>513.4 km (319 mi) | ||
| climate = {{wpl|temperate climate|Temperate climate}} | | climate = {{wpl|temperate climate|Temperate climate}} | ||
| terrain = Lowlands, heathland, hills, mountains, forests | | terrain = Lowlands, heathland, hills, mountains, forests | ||
| natural resources = coal, copper, iron, natural gas, limestone, timber, arable land | | natural resources = coal, copper, iron, natural gas, limestone, timber, arable land | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''[[Littland]]''' is a county located in [[Argis|Central Argis]]. It stretches from the [[Glinka Mountains]] in the south, to the [[Amber Lake]] in the north and covers an area of 198,000 square kilometers. | |||
==Topography== | ==Topography== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
==Land use== | ==Land use== | ||
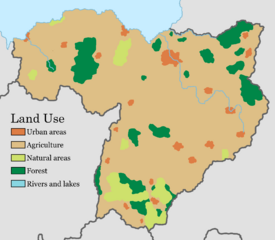
[[File:LandUsageMap.png|left|thumb|275px|Map over land usage in Littland]] | [[File:LandUsageMap.png|left|thumb|275px|Map over land usage in Littland]] | ||
A vast majority of Littland is used for agriculture. | |||
Littland used to be covered by 70% forest yet this has been in decline every since the 1500s. | |||
Urbanization has expanded cities and almost 13 million Litts live in urban areas. | |||
National parks preserve some more diverse areas, such as heathland and wetlands. | |||
==Biodiversity== | ==Biodiversity== | ||
| Line 79: | Line 87: | ||
==Political geography== | ==Political geography== | ||
{{Main|Administrative divisions of Littland}} | {{Main|Administrative divisions of Littland}} | ||
Littlands current 16 counties (''amter'') were created following the County Reform of 2004, which also granted autonomy to the [[Malskland]] region which has a considerable majority of the countrys Malskic population. Every county has a county mayor (''amtsborgmester'') and a county council (''amtsråd'') which are elected in local elections. The Malskland county council, called the [[Malskland Assembly]] is unique both in the powers it has and having 100 seats rather than the standard 45 seats county councils have. Each county is further divided into 253 municipalities (''kommuner''), lead by a mayor (''borgmester'') and municipal council (''kommunalråd''). | |||
{| style="width:98%; background:none;" | {| style="width:98%; background:none;" | ||
| Line 118: | Line 126: | ||
| [[Sønderland County]]|| [[Frankerup]] | | [[Sønderland County]]|| [[Frankerup]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Malskland|Malskland County]]|| [[Karlino]] | | [[Malskland|Malskland Autonomous County]]|| [[Karlino]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 01:01, 5 November 2022
 | |
| Continent | Argis |
|---|---|
| Region | Central Argis |
| Area | |
| • Total | 198,000 km2 (76,000 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 885 km (550 mi) |
| Borders | 2,198 km (1,366 mi) |
| Highest point | Sol Mountain, 2,026 m (6,646 ft) |
| Lowest point | Nørrehuse, 3.8 m (12.4 ft) |
| Longest river | Arup River, 513.4 km (319 mi) |
| Climate | Temperate climate |
| Terrain | Lowlands, heathland, hills, mountains, forests |
| Natural resources | coal, copper, iron, natural gas, limestone, timber, arable land |
Littland is a county located in Central Argis. It stretches from the Glinka Mountains in the south, to the Amber Lake in the north and covers an area of 198,000 square kilometers.
Topography
Land use
A vast majority of Littland is used for agriculture.
Littland used to be covered by 70% forest yet this has been in decline every since the 1500s.
Urbanization has expanded cities and almost 13 million Litts live in urban areas.
National parks preserve some more diverse areas, such as heathland and wetlands.
Biodiversity
Climate
Littland has a temperate climate. The southern mountain ranges are dominated by a climate climate area, the central and northern part of Littland experience a temperate climate year-round. Warm summers and chilly winters are characteristic of the Littish climate. The warmest part of Littland is the Aalhavn region while the coldest is the Malskland due to its elevation. Due to climate change, winters are becoming dryer and snow is rarer and rarer in the northern part of the country. Many plants and flora call Littland home and grow naturally. The most wide-spread type of tree in Littland are conifers such as spruce and pine.
| Climate data for Littland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.9 (30.4) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
2.7 (36.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.4 (72.3) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
9.6 (49.3) |
4.1 (39.4) |
1.0 (33.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
5.6 (42.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
3.0 (37.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49 (1.9) |
39 (1.5) |
35 (1.4) |
34 (1.3) |
42 (1.7) |
70 (2.8) |
67 (2.6) |
81 (3.2) |
58 (2.3) |
72 (2.8) |
61 (2.4) |
53 (2.1) |
661 (26) |
| Source: Littisk Meteorologisk Institut | |||||||||||||
Political geography
Littlands current 16 counties (amter) were created following the County Reform of 2004, which also granted autonomy to the Malskland region which has a considerable majority of the countrys Malskic population. Every county has a county mayor (amtsborgmester) and a county council (amtsråd) which are elected in local elections. The Malskland county council, called the Malskland Assembly is unique both in the powers it has and having 100 seats rather than the standard 45 seats county councils have. Each county is further divided into 253 municipalities (kommuner), lead by a mayor (borgmester) and municipal council (kommunalråd).
RegionsHistorically Littland has been divided into many regions, culturally, politically, linguistically and economically. While these regions no longer exist de jure, they are still identifiable in the modern Littland.
Some regions still in use today, in the form of counties are Aadal, Tronmark and Sønderland. |