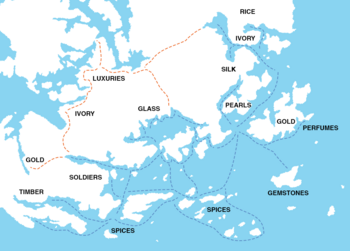
Pearl Road
The Pearl Road or Pearl Route refers to an ancient maritime trade network that connected several important parts of southern Europa on Eurth. This long-distance network enabled much greater economic interaction between peoples from Azania, Amutia and the Orient. As a side effect these increased exchanges led to a more unified, shared culture among these nation states.
Evolution
The Pearl Road was established in the 2nd Century CE. Evidence of these movements can be seen in shipwrecks recovered in the Rivdon Bay and Rosario Sea, which contained trade items from faraway regions. It wasn't exactly one single unified trade network, but rather a patchwork of overlapping local trade networks. Nations and city-states along the Pearl Road centred their economies on both sea and land. The trade route included crossing several bodies of waters skirting the Oriental Ocean and Adlantic Ocean, but not yet into the open ocean. The Pearly gates was an informal name for the strait between Tamurin and Orioni, a term later repurposed by some early Christians. By the 9th century Ayubi became one of the final links in the Pearl Road.
Routes
Clockwise from east to west, this maritime trade route connected:
- Jasmine Sea trade by the Shakyan principalities.
- Paraia Sea trade by the Three Kingdoms of Jaihu, Koku and Ide Jima.
- Oriental states such as Tamarini and Orioni.
- Overlap with local the Miirosi maritime trade.
- The Meteorolan archipelago.
- Ancient Hakenian naval trade network around the Memopotamian peninsula.
- Intra-Azanian trade.